Study on Partial Discharge Characteristics of Mixed Metal Particles Under Combined Power Frequency and Switching Impulse Voltage
Abstract
1. Introduction
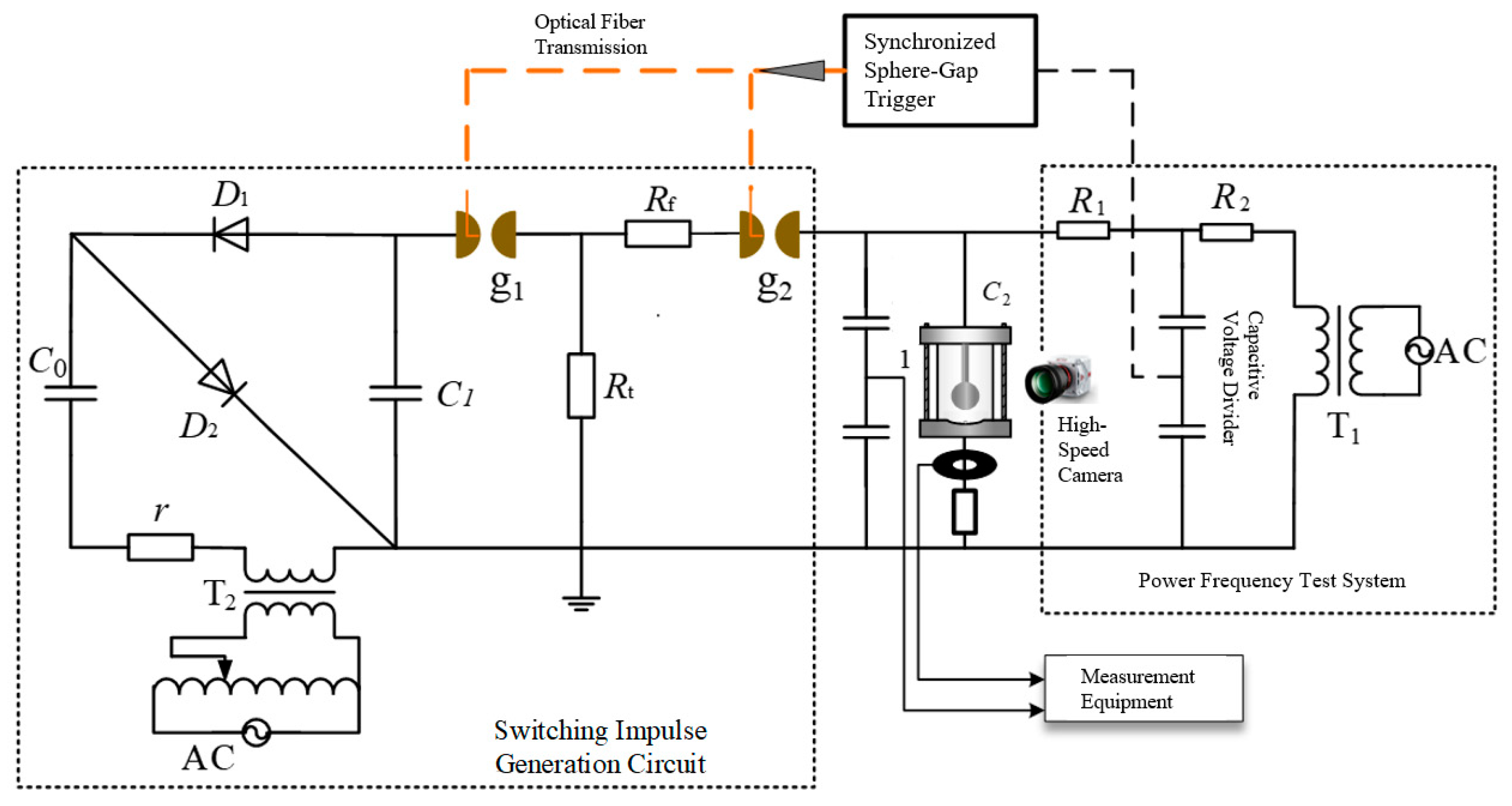
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. AC-Switching Impulse Combined Voltage Test System
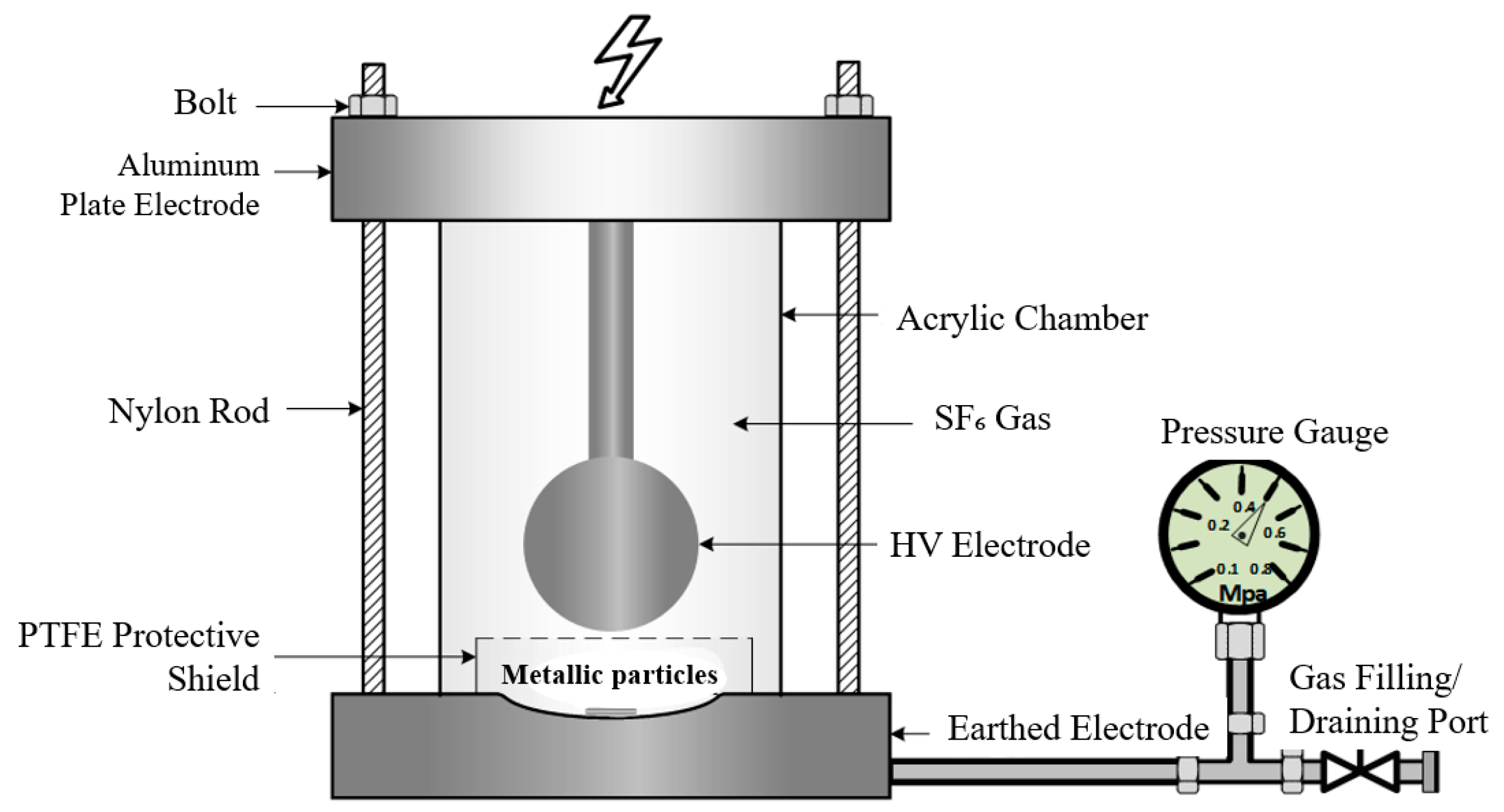
2.2. Metallic Particle Defect Model
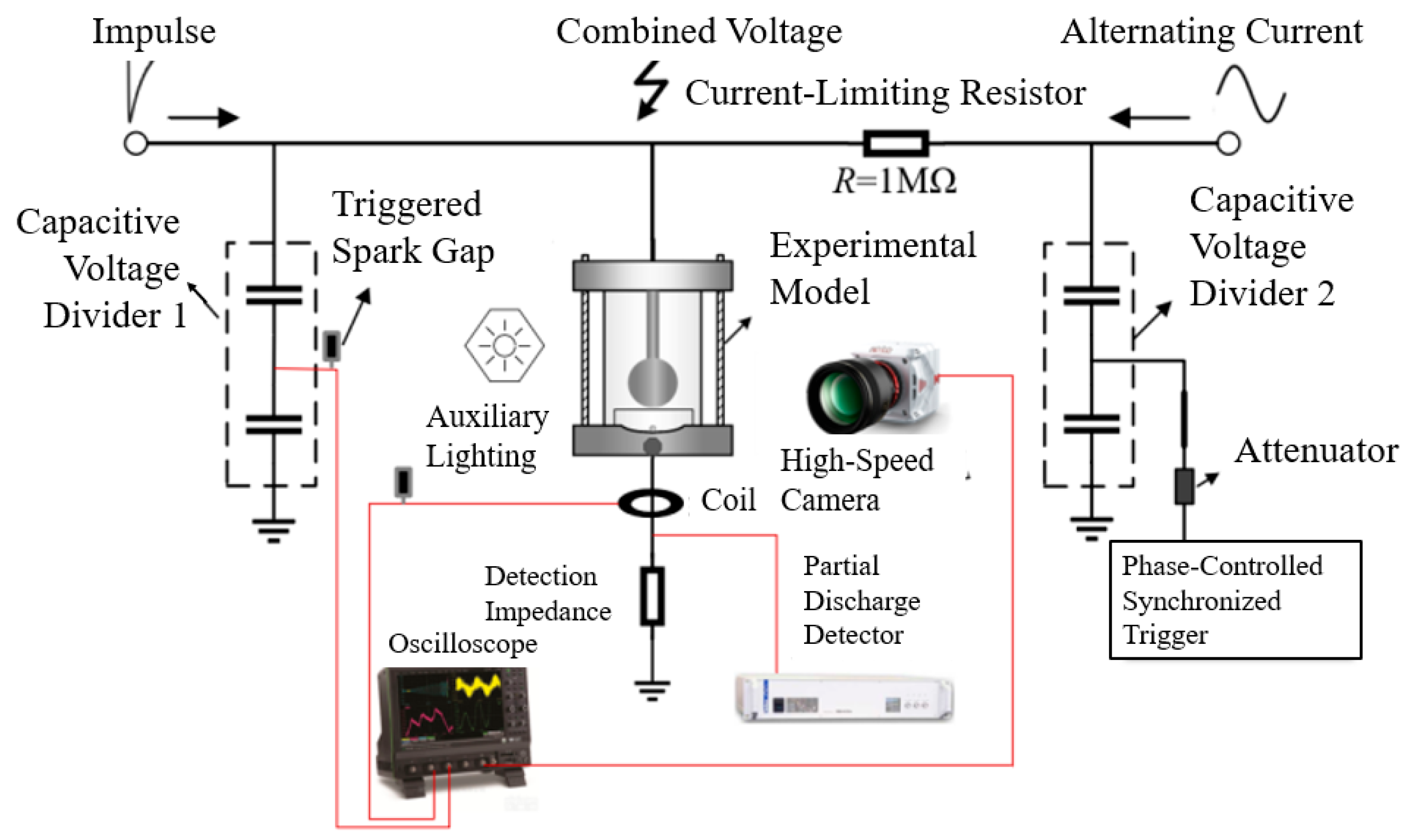
2.3. Correlative Analysis System for Partial Discharge Detection and Motion Capture
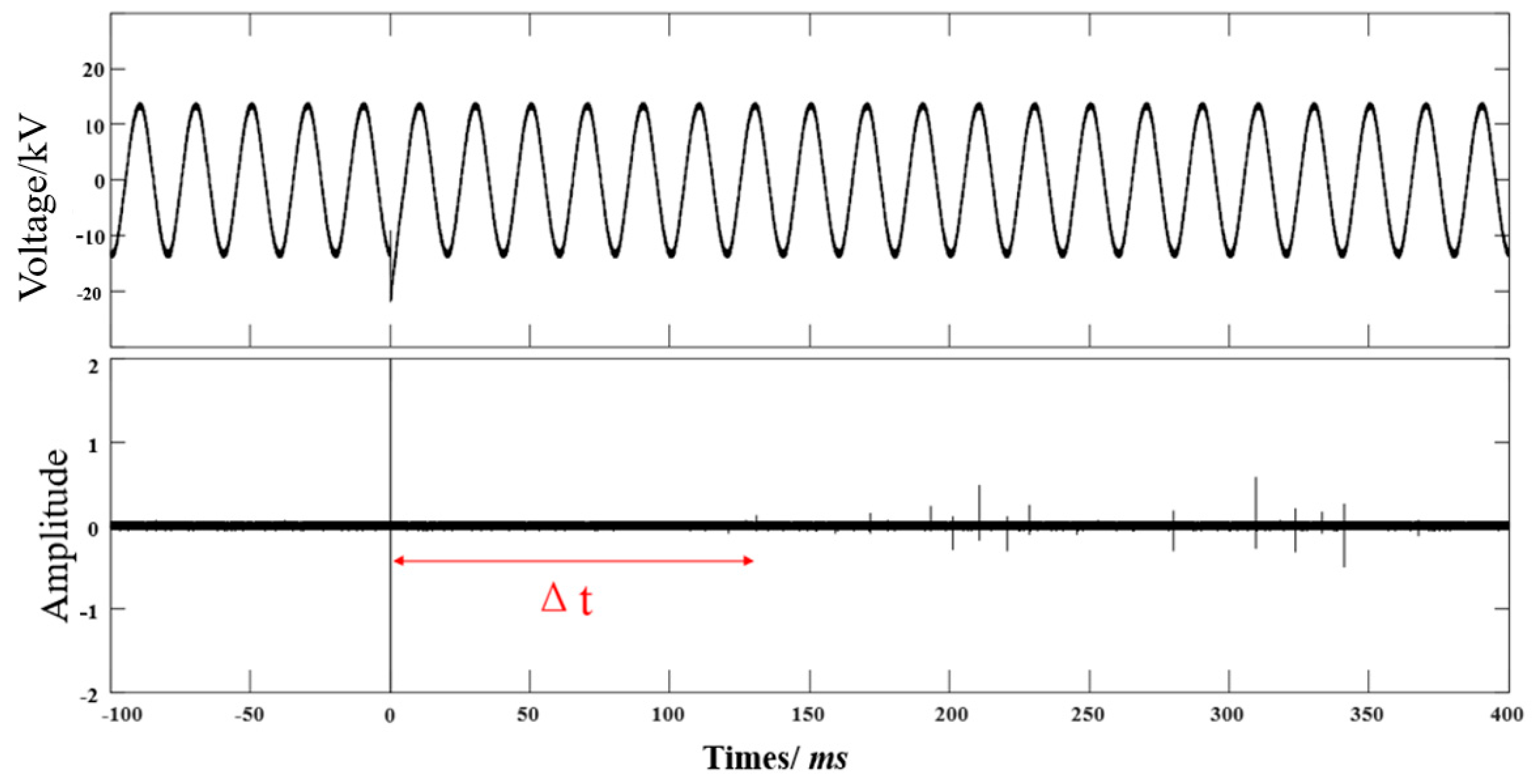
2.4. Experimental Methodology
3. Partial Discharge Characteristics of Single-Type Metallic Particles Under Combined Voltage
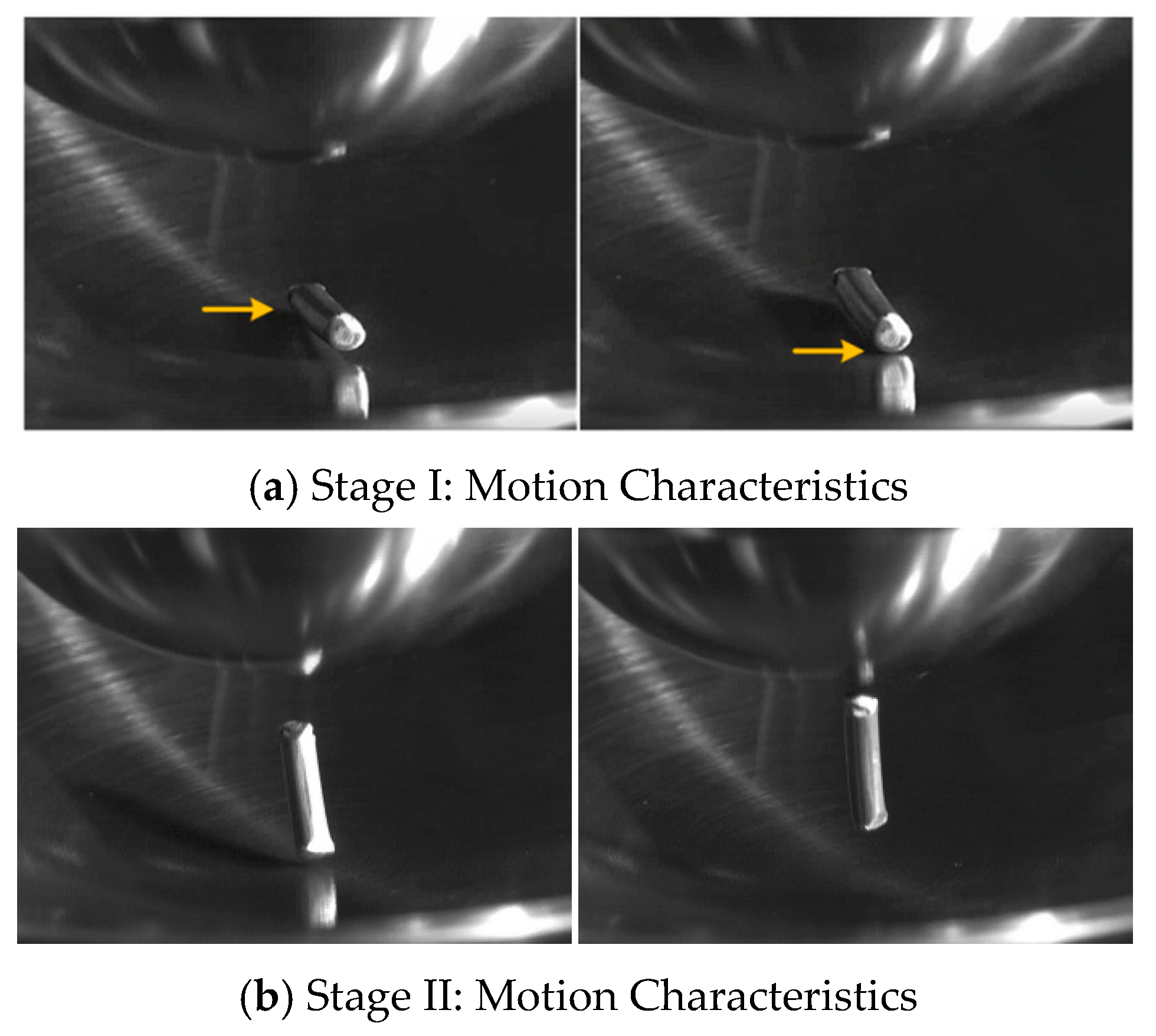
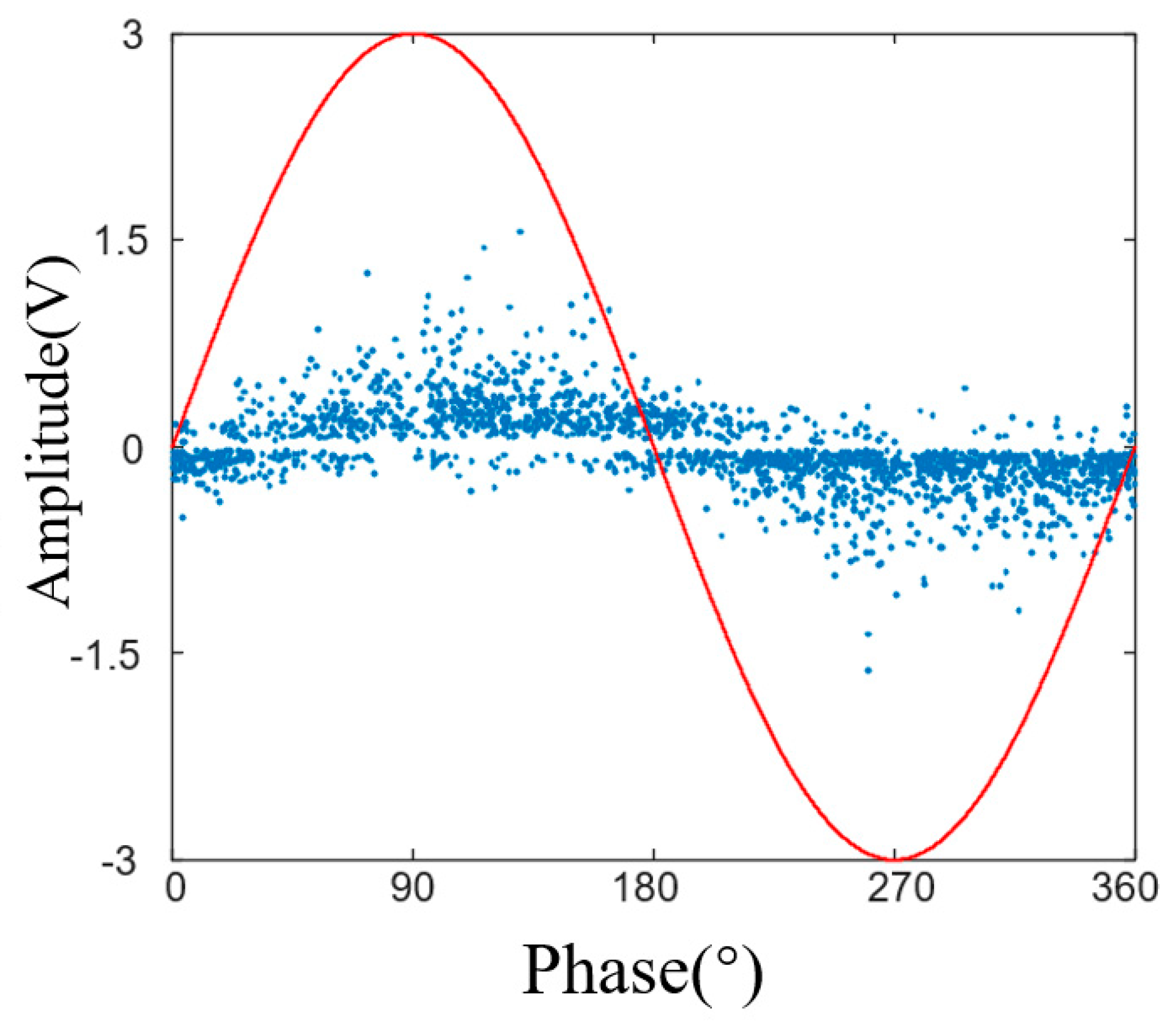
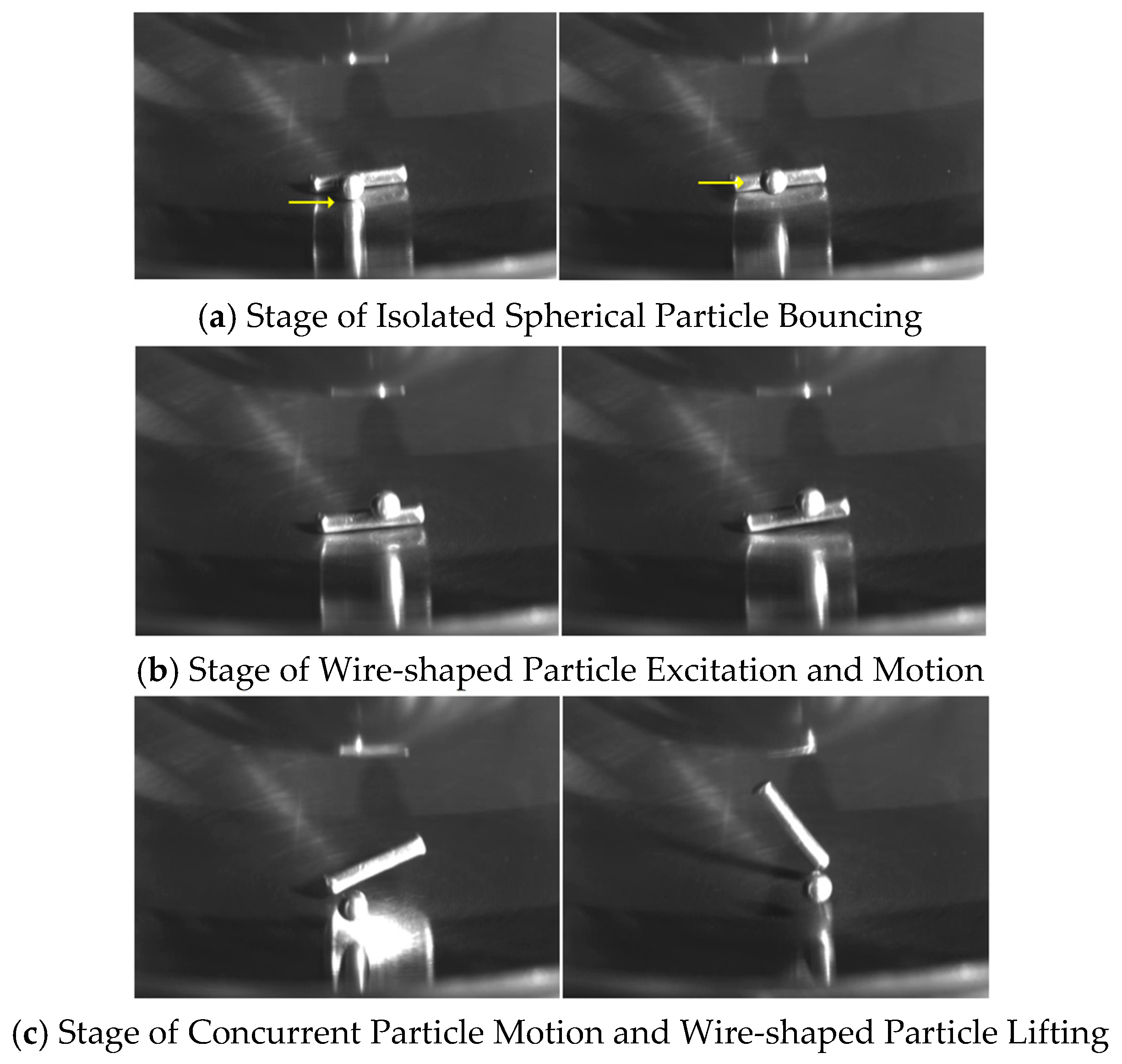
3.1. Partial Discharge Characteristics of a Single Wire-Shaped Particle
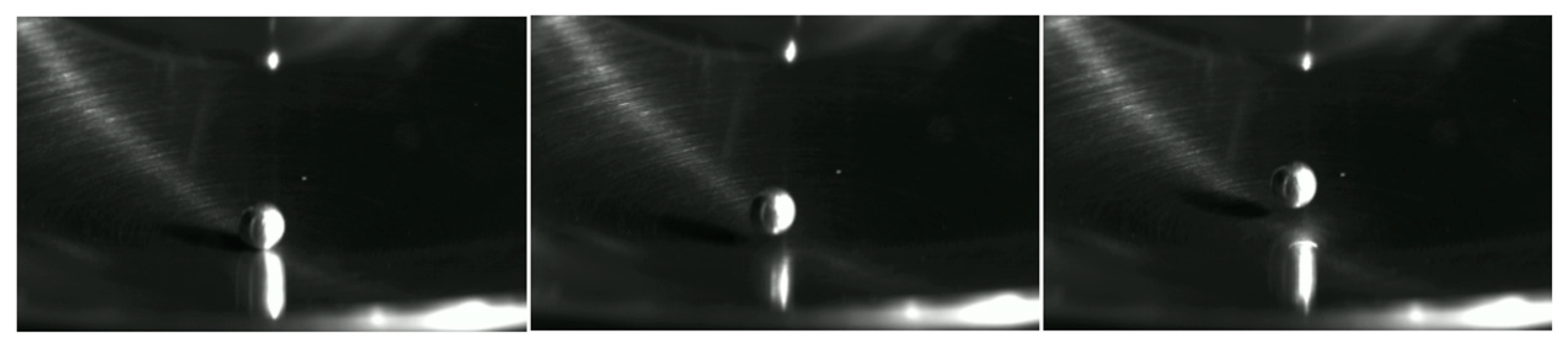
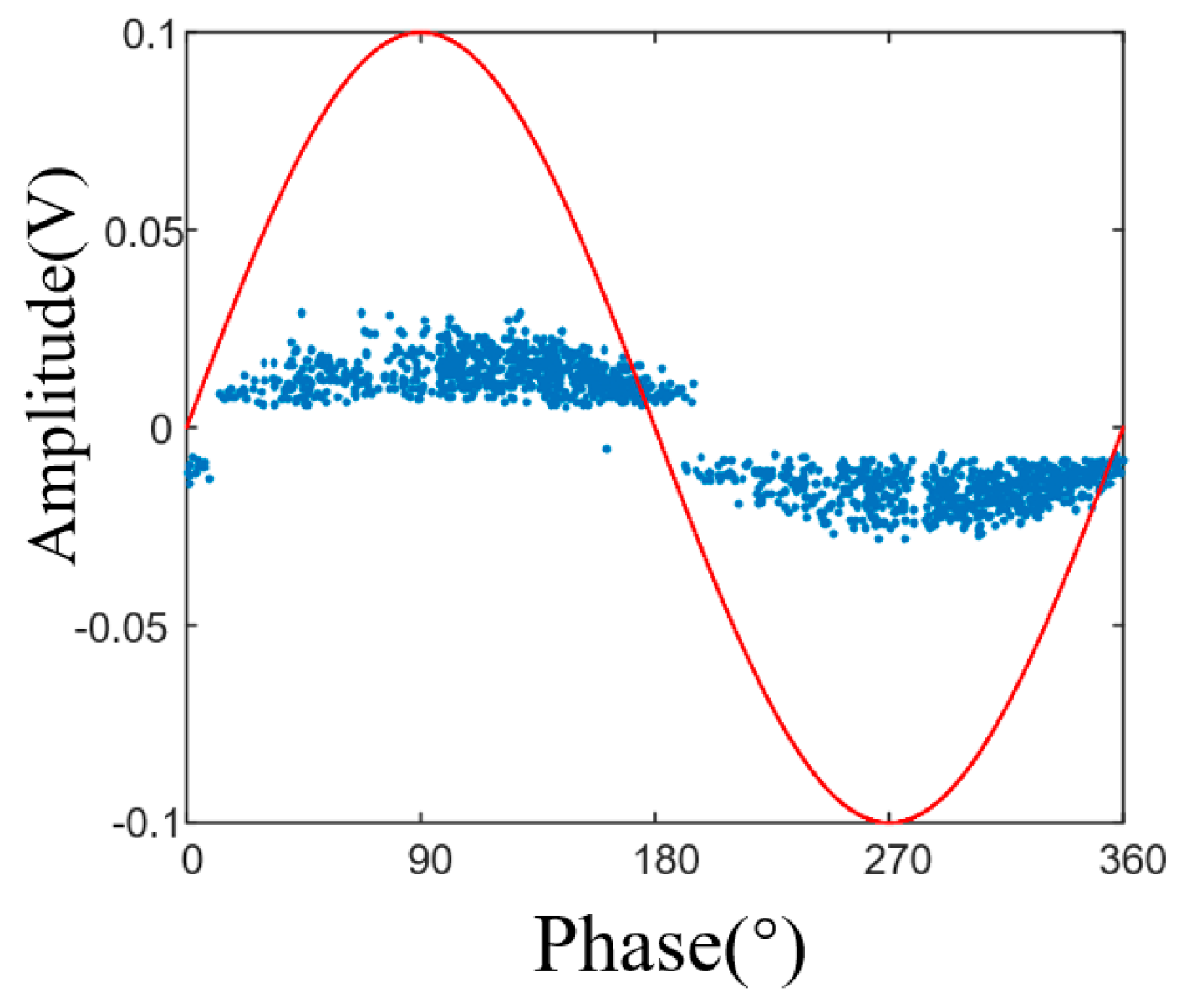
3.2. Partial Discharge Characteristics of a Single Spherical Metallic Particle
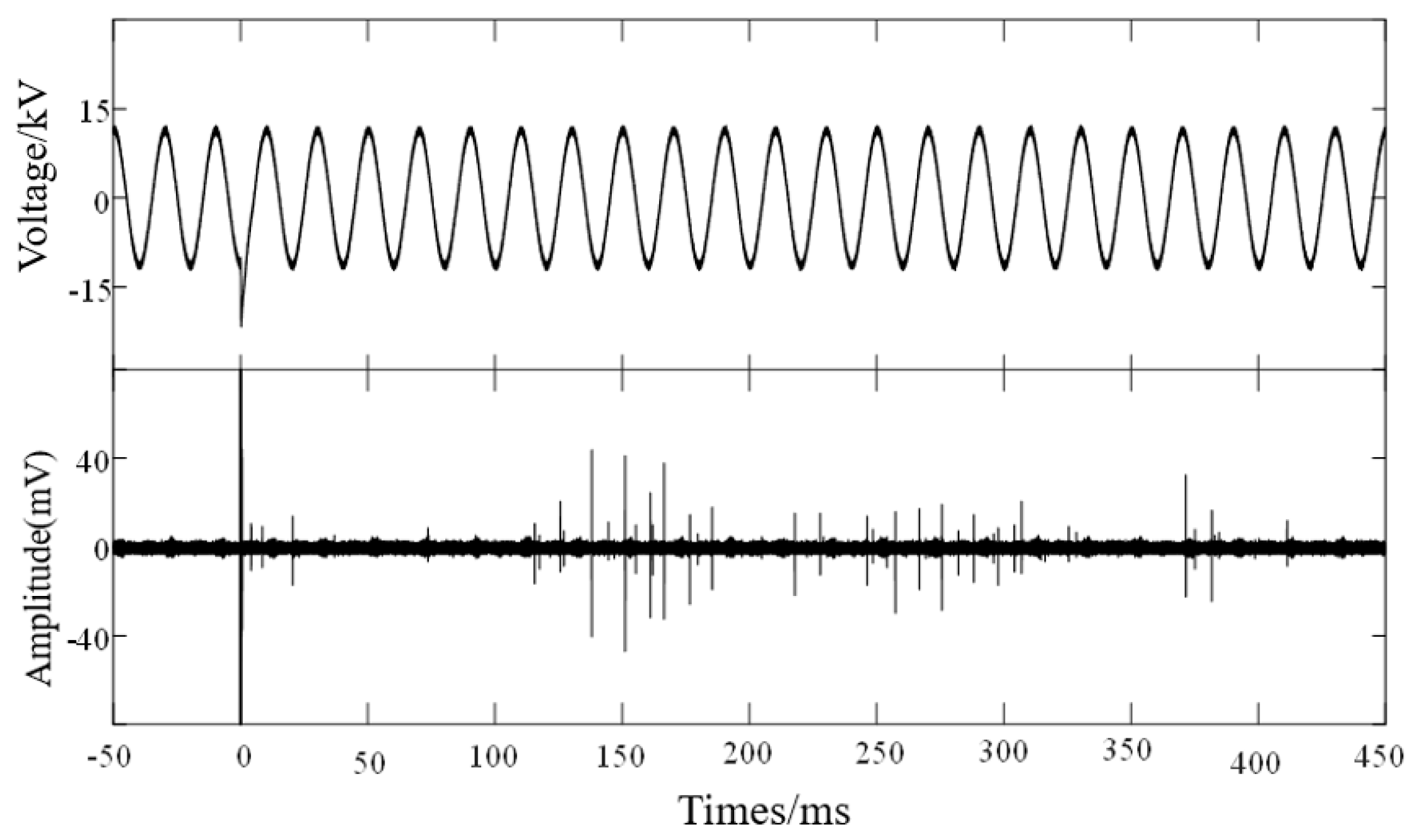
4. Partial Discharge Characteristics of Mixed Metal Particles Under Combined Voltage
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The switching impulse voltage can excite latent metallic particle motion under AC voltage and induce partial discharge. Wire-shaped particles exhibit a significant discharge initiation delay under the combined voltage; however, once they enter the vertical jumping stage, the discharge intensity increases rapidly and is often accompanied by large-magnitude discrete discharges. Spherical particles, in contrast, can be excited within the first AC cycle after the impulse without delay, but due to a weaker electric field distortion, their subsequent discharge amplitude is limited, without intense large-magnitude pulses.
- (2)
- Hybrid particles exhibit a staged evolution characteristic under the combined voltage: initially, the spherical particle jumps and triggers low-amplitude discharges; subsequently, collisions from the spherical particle excite the wire-shaped particle into “seesaw-like” and vertical motion, leading to a significant increase in discharge amplitude. Ultimately, a more dispersed PRPD pattern accompanied by numerous large-amplitude pulses is observed, demonstrating the typical characteristic of “spherical particles lead initiation, wire-shaped particles dominate discharge”, maintaining a more intense discharge state under the subsequent AC voltage.
- (3)
- This study reveals the synergistic mechanism of power frequency voltage and switching impulse in triggering partial discharge: power frequency voltage (even if below the threshold) provides a “pre-excitation” field and charge preparation for discharge, while switching impulse plays a crucial “trigger” role by injecting high energy to drastically change the spatial charge distribution, thereby significantly reducing the threshold of subsequent power frequency discharge. Linear particles, due to their significant geometric asymmetry (tip effect), are the core cause of strong electric field distortion and delayed intense discharge. The study infers that an increase in the amplitude of the switching impulse accelerates this triggering process and shortens the discharge delay time. This mechanism indicates that in actual GIS operation, the risk of transient overvoltage “activating” latent metal particle defects is far more lethal than that of steady-state AC voltage itself.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.; Shao, M. Health Assessment Method for Gas-Insulated Switchgear Based on Fault Tree Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Power Science and Technology (ICPST), Kunming, China, 16–18 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Review on Mechanism and Suppression Strategies of Surface Flashover Induced by Metal Particles in DC GIS/GIL. High Volt. Eng. 2025, 51, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Review of Partial Discharge Detection Techniques for Electrical Equipment. High Volt. Eng. 2015, 41, 2583–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Du, B.; Xiao, M.; Liang, H.; Yao, H.; Zhang, W. Optimization of Permittivity Graded Spacer for Suppressing Metal Particles in AC-GIS. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 5th International Conference on Electrical Materials and Power Equipment (ICEMPE), Harbin, China, 3–6 August 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Li, C.; Pang, Z.; Ma, G.; Cui, X.; Zeng, Z.; Rong, Z. Moving behaviors and harmfulness analysis of multiple linear metal particles in GIS. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 3355–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Su, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, Q. Influence of metal particles with different morphologies on the electric field distribution and discharge characteristics of basin-type insulators in GIS. In Proceedings of the 2025 10th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE), Beijing, China, 15–19 April 2025; pp. 2737–2741. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Luo, L. Digital Deduction Method for Metal Particle Size in Gas Insulated Metal-enclosed Switchgear. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z. Flying Motion and Discharge Characteristics of Linear Particle Swarm and Cooperative Suppression Methods. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, W.; Luo, Y.; Ma, P.; Qi, L. Research on Surface Discharge and Electric Field Characteristics of GIS Basin Insulator under Different Metal Particle Defects. Insul. Mater. 2023, 56, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, H.; Jiang, P.; Wu, M.; Niu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q. Multi-Particle-in-Series Phenomenon and Discharge Properties Induced by Multiple Free Particles in GIS. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2023, 38, 4039–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Niu, B.; Zhang, T.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W. Study on the Motion Process of Foreign Metal Particles in GIS under High Voltage. High Volt. Appar. 2021, 57, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H. Motion Behavior and Discharge Characteristics of Metal Particles in GIS Under AC Operating Voltage. Ph.D. Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Motion of Free Metal Particles in GIS under Impact Vibration Excitation and Characteristics of Induced Gap Breakdown. High Volt. Eng. 2024, 50, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Hou, J.C.; Wang, H.T.; Han, X.T.; Li, J.H. Study on Motion Behavior and Partial Discharge Characteristics of Metal Particles in SF6 Gas under Electro-Mechanical Combined Action. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2023, 57, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Niu, B.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, C.; Li, J. Movement Behavior and Discharge Characteristics of Submillimeter Metal Particles Under AC Voltages Superimposed Mechanical Vibration. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2024, 32, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Bai, T.; Shi, T.; Wu, X.; Han, X.; Liu, W. Initial Characteristics of Submillimeter Metal Particles in GIS under Impact Vibration. Energies 2024, 17, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Han, W.; Fan, Z.; Sun, J.; Qin, W.; Liao, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, G. Acoustic Emission and Propagation Characteristics of Metal Particles in GIS. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2025, 32, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Partial Discharge and Motion Characteristics of Linear Metal Particles in SF6 under AC Superimposed Lightning Impulse Voltage. High Volt. Eng. 2024, 50, 5406–5414. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Gao, K.; Ren, M.; Huang, H.; Jin, L. Electric field analysis of different forms of metal particle adhesion defects in 110 kV GIS. J. Electr. Eng. 2024, 19, 316–324. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Ma, Y.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Han, X.; Yang, X. Study on Partial Discharge Characteristics of Mixed Metal Particles Under Combined Power Frequency and Switching Impulse Voltage. Energies 2025, 18, 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215650
Ren J, Ma Y, Qu Q, Wang Z, Wang Y, Wang L, Han X, Yang X. Study on Partial Discharge Characteristics of Mixed Metal Particles Under Combined Power Frequency and Switching Impulse Voltage. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215650
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jiyun, Yongfu Ma, Quanlei Qu, Zile Wang, Yuang Wang, Lili Wang, Xutao Han, and Xiaojie Yang. 2025. "Study on Partial Discharge Characteristics of Mixed Metal Particles Under Combined Power Frequency and Switching Impulse Voltage" Energies 18, no. 21: 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215650
APA StyleRen, J., Ma, Y., Qu, Q., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, L., Han, X., & Yang, X. (2025). Study on Partial Discharge Characteristics of Mixed Metal Particles Under Combined Power Frequency and Switching Impulse Voltage. Energies, 18(21), 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215650





