Waste to Energy: Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Microalgal Biomass and Bakery Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates and Their Preparation
2.2. Equipment and Digester Configuration
2.3. Anaerobic Digestion Methodology
2.4. Analytical Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
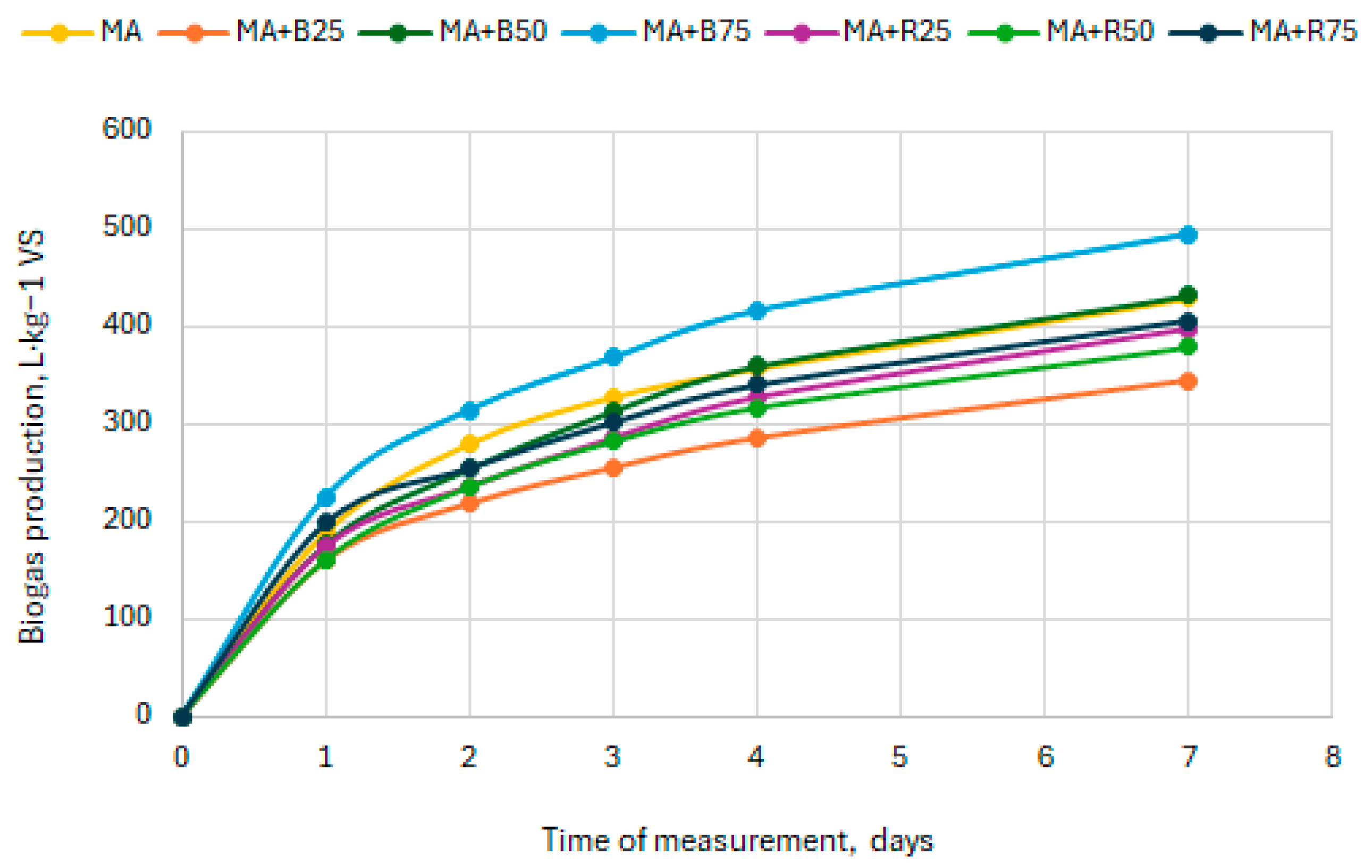
3.1. Biogas Production from Bakery Waste
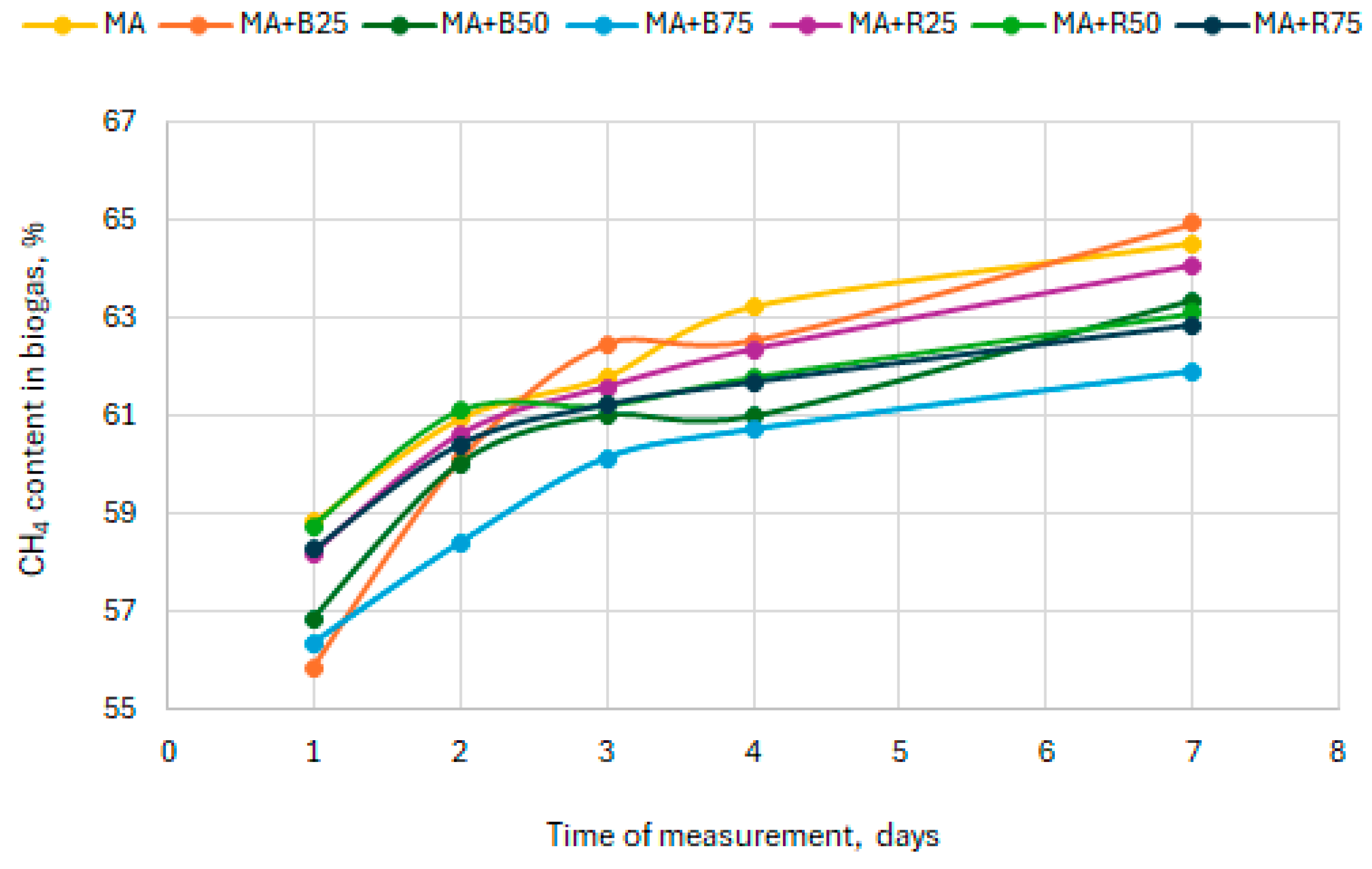
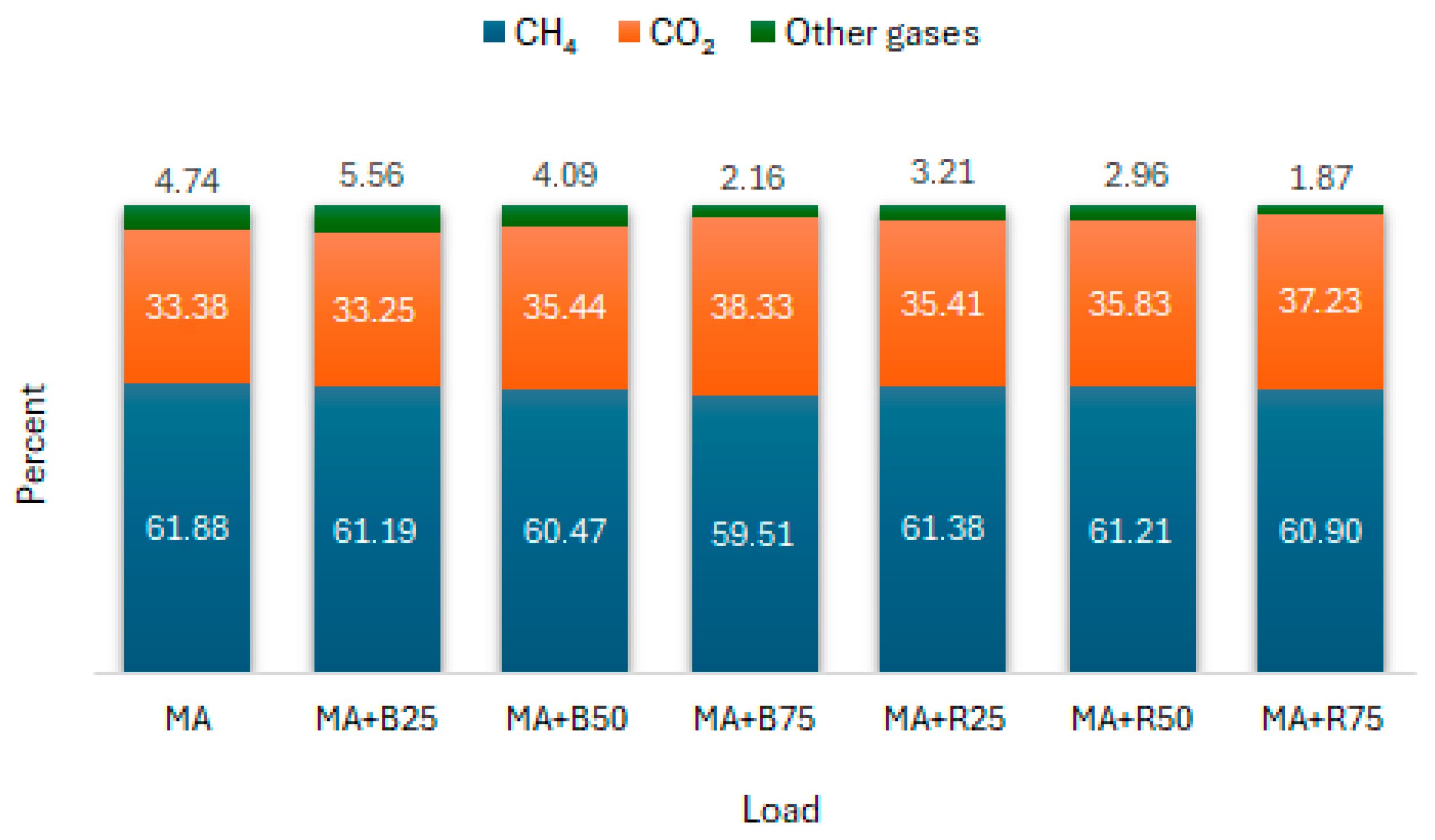
3.2. Methane Content in Biogas
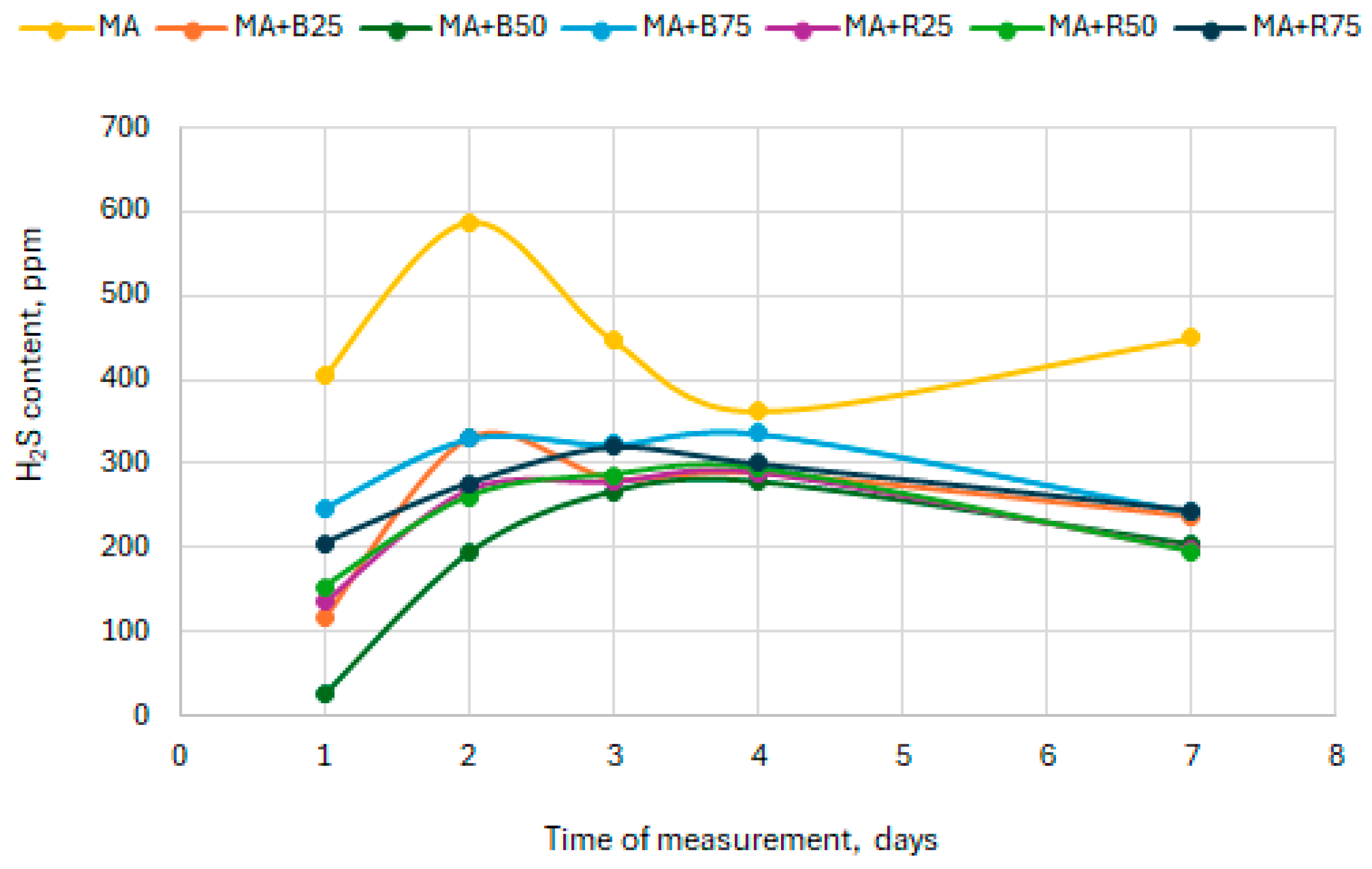
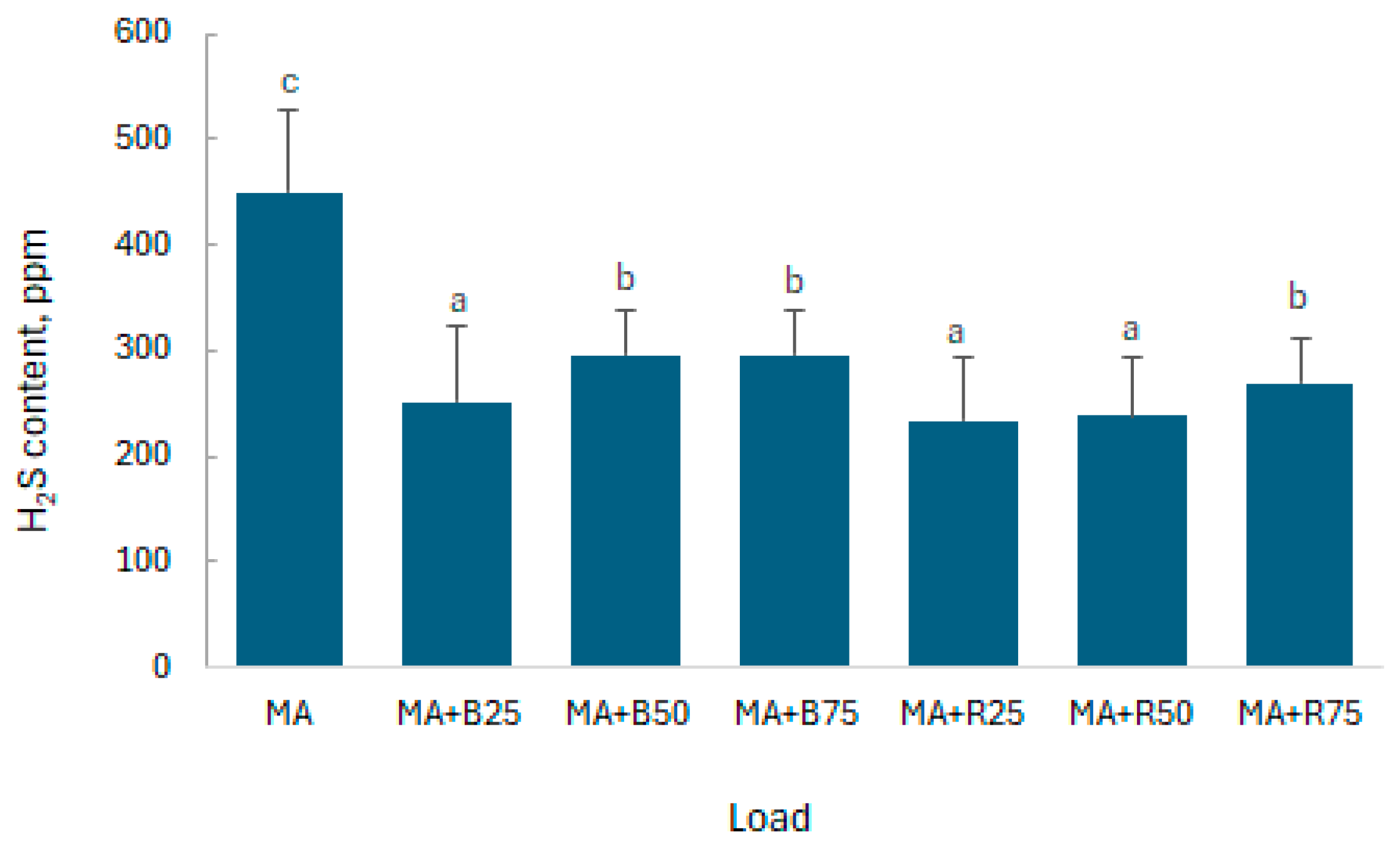
3.3. Hydrogen Sulphide Content in Biogas
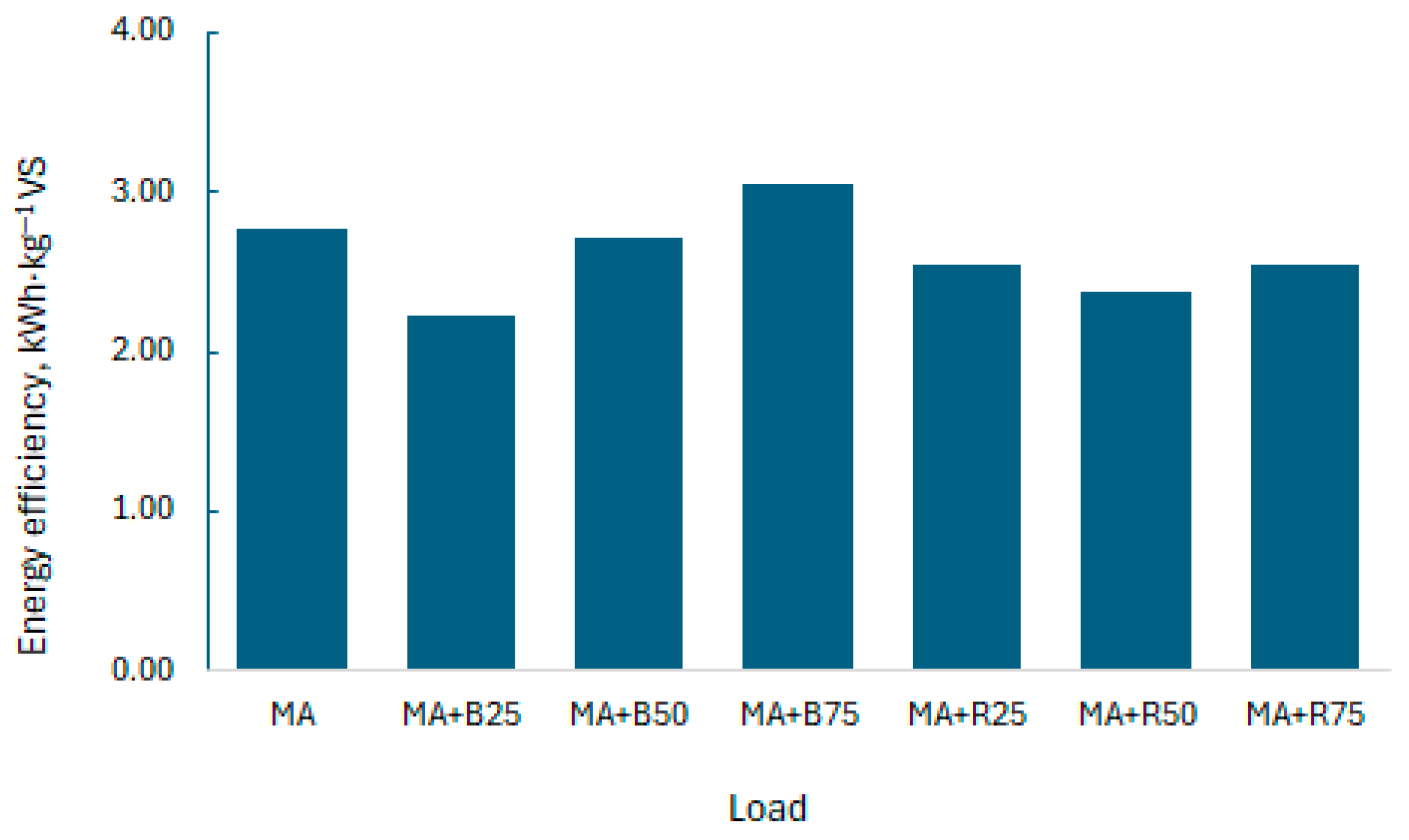
3.4. Energy Efficiency for the Anaerobic Digestion Process
3.5. Potential CO2 Emissions Avoided Compared to Fossil Fuels
3.6. Operational Conditions of Anaerobic Digestion (pH, Temperature, ORP)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EF | Emission Factors |
| HHV | Higher Heating Value |
| LHV | Lower Heating Value |
| OLR | Organic Loading Rate |
| ORP | Oxidation-Reduction Potential |
| TS | Total Solids |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
References
- Jamil, F.; Inayat, A.; Hussain, M.; Akhter, P.; Abideen, Z.; Ghenai, C.; Shanableh, A.; Abdellatief, T.M.M. Valorization of Waste Biomass to Biofuels for Power Production and Transportation in Optimized Way: A Comprehensive Review. Processes 2022, 10, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.C.; Sinha, S.; Bhatnagar, P.; Nath, Y.; Negi, B.; Kumar, V.; Gururani, P. A Concise Review on Waste Biomass Valorization through Thermochemical Conversion. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2024, 6, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignogna, D.; Szabó, M.; Ceci, P.; Avino, P. Biomass Energy and Biofuels: Perspective, Potentials, and Challenges in the Energy Transition. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.J.P.; Mishra, R.K.; Chinnam, S.; Binnal, P.; Dwivedi, N. A Comprehensive Study on Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Solid Waste: A Review on Configurations, Operating Parameters, Techno-Economic Analysis and Current Trends. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. The Promotion of Anaerobic Digestion Technology Upgrades in Waste Stream Treatment Plants for Circular Economy in the Context of “Dual Carbon”: Global Status, Development Trend, and Future Challenges. Water 2024, 16, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerström, A.; Al Seadi, T.; Rasi, S.; Briseid, T. The Role of Anaerobic Digestion and Biogas in the Circular Economy; IEA Bioenergy Task 37; Report No. 2018:8; Murphy, J.D., Ed.; IEA Bioenergy: Cork, Ireland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kupryaniuk, K.; Witaszek, K.; Vaskina, I.; Filipek-Kaźmierczak, S.; Kupryaniuk, J.; Sołowiej, P.; Dach, J. The Effect of Corn Ensiling Methods on Digestibility and Biogas Yield. Energies 2025, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuksa, P.; Hakl, J.; Míchal, P.; Hrevušová, Z.; Šantrůček, J.; Tlustoš, P. Effect of silage maize plant density and plant parts on biogas production and composition. Biomass Bioenerg. 2020, 140, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, S.; Xin, F.; Zhou, J.; Jia, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M.; Dong, W. Biomethane Production from Lignocellulose: Biomass Recalcitrance and Its Impacts on Anaerobic Digestion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusweireh, R.S.; Rajamohan, N.; Sonne, C.; Vasseghian, Y. Algae biogas production focusing on operating conditions and conversion mechanisms—A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, L.; Alcázar-Ortega, M.; Benreguieg, A. A Perspective on Biogas Production from Algae Biomass: A Promising Third-Generation Biofuel for the Sustainable Development. In Biogas in the 21st Century—Developments and Perspectives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambusiti, C.; Bellucci, M.; Zabaniotou, A.; Beneduce, L.; Monlau, F. Algae as promising feedstocks for fermentative biohydrogen production according to a biorefinery approach: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, R. Fast-growing phototrophic microorganisms and the productivity of phototrophic cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 2261–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H. Advancements and Prospects in Algal Biofuel Production: A Comprehensive Review. Phycology 2024, 4, 548–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes de Souza, M.; Meers, E.; Mangini, S. The potential of microalgae for carbon capture and sequestration. EFB Bioecon. J. 2024, 4, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrot-Paw, M.; Koniuszy, A.; Gałczyńska, M.; Zając, G.; Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J. Production of Microalgal Biomass Using Aquaculture Wastewater as Growth Medium. Water 2020, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.R.; Deprá, M.C.; de Menezes, C.R.; Zepka, L.Q.; Jacob-Lopes, E. Microalgae Cultivation in Wastewater: How Realistic Is This Approach for Value-Added Product Production? Processes 2025, 13, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Ansari, F.A.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F. Unlocking the potential of microalgae: Cultivation in algae recycled effluent with domestic wastewater for enhancing biomass, bioenergy production and CO2 sequestration. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, I.; Pandey, S.; Vinayagam, R.; Priyadarshini, R.; Shanmugam, S.; Sankaran, V. A Recent Update on Enhancing Lipid and Carbohydrate Accumulation for Sustainable Biofuel Production in Microalgal Biomass. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hosano, N.; Hosano, H. Recovering Microalgal Bioresources: A Review of Cell Disruption Methods and Extraction Technologies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, S.; Serlini, N.; Esteves, S.M.; Miros, S.; Halim, R. Cell Walls of Lipid-Rich Microalgae: A Comprehensive Review on Characterisation, Ultrastructure, and Enzymatic Disruption. Fermentation 2024, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Zieliński, M.; Bartkowska, I. Co-Fermentation of Microalgae Biomass and Miscanthus × giganteus Silage—Assessment of the Substrate, Biogas Production and Digestate Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Padrino, S.; Brito, A.; Díaz, L. Biogas production from anaerobic digestion of solid microalgae residues generated on different processes of microalgae-to-biofuel production. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 4659–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Process performance and methane production optimizing of anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure and corn straw. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milledge, J.J.; Nielsen, B.V.; Maneein, S.; Harvey, P.J. A Brief Review of Anaerobic Digestion of Algae for Bioenergy. Energies 2019, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, A.; Osman, A.I.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Alajeeli, N.; Al-Hinai, M.; Rooney, D.W. Techno-economic evaluation of biogas production from food waste via anaerobic digestion. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupančič, M.; Možic, V.; Može, M.; Cimerman, F.; Golobič, I. Current Status and Review of Waste-to-Biogas Conversion for Selected European Countries and Worldwide. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Ali, A.; Alam, M.Z.; Mohamed Abdoul-latif, F.; Jami, M.S.; Gamiye Bouh, I.; Adebayo Bello, I.; Ainane, T. Production of Biogas from Food Waste Using the Anaerobic Digestion Process with Biofilm-Based Pretreatment. Processes 2023, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.B.H.; Makkawi, Y.T. A review of post-consumption food waste management and its potentials for biofuel production. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7756–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohamadsadeghi, S.; Karimi, K.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M. Biogas production from food wastes: A review on recent developments and future perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmee, S.K. Liquid Biofuels from Food Waste: Current Trends, Prospect and Limitation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unis, R.; Gnaim, R.; Kashyap, M.; Shamis, O.; Gnayem, N.; Gozin, M.; Liberzon, A.; Gnaim, J.; Golberg, A. Bioconversion of Bread Waste into High-Quality Proteins and Biopolymers by Fermentation of Archaea Haloferax mediterranei. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1491333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; He, W.; Cheng, Q. Review in anaerobic digestion of food waste. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.; Liang, T.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qi, C. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Microalgae at Variable Mixing Ratios: Enhanced Performance, Kinetic Analysis, and Microbial Community Dynamics Investigation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovskis, V.; Plume, I. Biogas Potential from Damaged Bread. In Proceedings of the 16th International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 24–26 May 2017; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Lansing, S. Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production from Co-Digestion of Gummy Waste with a Food Waste, Grease Waste, and Dairy Manure Mixture. Energies 2019, 12, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrot-Paw, M.; Koniuszy, A.; Ratomski, P.; Sąsiadek, M.; Gawlik, A. Biogas production from Arthrospira platensis biomass. Energies 2023, 16, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFRA. UK Government GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting: Methodology Paper for Emission Factors; Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA). 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/government-conversion-factors-for-company-reporting (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Mussgnug, J.H.; Klassen, V.; Schlüter, A.; Kruse, O. Microalgae as substrates for fermentative biogas production in a combined biorefinery concept. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.D.; Drosg, B.; Allen, E.; Jerney, J.; Xia, A.; Herrmann, C. A perspective on Algal Biogas; IEA Bioenergy Task 37 Technical Brochure 2015; Report No. 2015:8; International Energy Agency Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Mörtelmaier, C.; Winter, J.; Gallert, C. Co-digestion of wheat and rye bread suspensions with source-sorted municipal biowaste. Waste Manag. 2015, 40, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbry-Muzyka, A.; Madi, H.; Rüsch-Pfund, F.; Gandiglio, M.; Biollaz, S. Biogas composition from agricultural sources and organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermoso, F.G.; Bartacek, J.; Jansen, S.; Lens, P.N.L. Screening of Biomethane Production Potential from Dominant Microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 51, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Carmona, M.; Tapia-Rodríguez, A.; Morales, M.; Celis, L.B.; Alatriste-Mondragón, F.; Razo-Flores, E. Methane Production from Thermally Pretreated Scenedesmus obtusiusculus Biomass in Semi-Batch Reactors at Low Reaction Times. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 136, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.P.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.J. Comparative Testing of Energy Yields from Micro-Algal Biomass Cultures Processed via Anaerobic Digestion. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, R.; Arumugam, M. Selective degradation of the recalcitrant cell wall of Scenedesmus quadricauda CASA CC202. Planta 2017, 246, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.L.; Soares, J.; Vieira, B.B.; Batista-Silva, W.; Martins, M.A. Extraction of proteins from the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus BR003 followed by lipid extraction of the wet deproteinized biomass using hexane and ethyl acetate. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sialve, B.; Bernet, N.; Bernard, O. Anaerobic digestion of microalgae as a necessary step to make microalgal biodiesel sustainable. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, R.; Raposo, S.; Morais, E.G.; Rodrigues, B.; Afonso, V.; Gonçalves, P.; Marques, J.; Cerqueira, P.R.; Varela, J.; Teixeira, M.R.; et al. Biogas Production from Microalgal Biomass Produced in the Tertiary Treatment of Urban Wastewater: Assessment of Seasonal Variations. Energies 2022, 15, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.K. Gas Utilization from Sewage Waste. CiteSeerX Technical Report. 2002, pp. 1–20. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?doi=c7f9c446794ed90fc5b02c6366130e583de5cea3 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Kisielewska, M.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M. Comparison of biogas production from anaerobic digestion of microalgae species belonging to various taxonomic groups. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2020, 46, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, R.; Galway, B.; Bustamante, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Biomethane potential evaluation of co-digestion of sewage sludge and organic wastes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, B.; Tsapekos, P.; Alfaro, N.; Díaz, I.; Fdz-Polanco, M.; Rafiee, S.; Angelidaki, I. A review on prospects and challenges of biological H2S removal from biogas with focus on biotrickling filtration and microaerobic desulfurization. Biofuel Res. J. 2017, 4, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Wang, Q.; Ngo, H.H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Nghiem, L.D. Hydrogen sulphide management in anaerobic digestion: A critical review on input control, process regulation, and post-treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y. A Review on Sulfur Transformation during Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Solid Waste: Mechanisms, Influencing Factors and Resource Recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, N.; Boivin, S. A Review of Biogas Purification Processes. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2009, 3, 42–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckebosch, E.; Drouillon, M.; Vervaeren, H. Techniques for Transformation of Biogas to Biomethane. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milledge, J.J.; Heaven, S. Energy Balance of Biogas Production from Microalgae: Effect of Harvesting Method, Multiple Raceways, Scale of Plant and Combined Heat and Power Generation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.C.; Bassin, I.D.; Cammarota, M.C. Microalgae and Cyanobacteria Biomass Pretreatment Methods: A Comparative Analysis of Chemical and Thermochemical Pretreatment Methods Aimed at Methane Production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Montero, R.; Vassalle, L.; Passos, F.; Ortiz, A.; García-Galán, M.J.; García, J.; Ferrer, I. Scaling-Up the Anaerobic Digestion of Pretreated Microalgal Biomass within a Water Resource Recovery Facility. Energies 2020, 13, 5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Świca, I.; Zieliński, M. Ultrasonic Disintegration to Improve Anaerobic Digestion of Microalgae with Hard Cell Walls—Scenedesmus sp. and Pinnularia sp. Plants 2023, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, A.; Shayegan, J. Effects of temperature and mixing modes on the performance of municipal solid waste anaerobic slurry digester. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuli, A.; Khadka, A.; Sapkota, L.; Ghimire, A. Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time and Organic-Loading Rate on Two-Staged, Semi-Continuous Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste during Start-Up. Fermentation 2022, 8, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-S.; Dong, J.-J.; Yu, J.-H.; Yin, H.; Hu, S.-M.; Huang, S.-X.; Yuan, X.-Z. Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time on Anaerobic Digestion of Wheat Straw in Semicontinuous Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactors. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2457805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, A.; Harun, R.; Idrus, S. Performance Monitoring of Anaerobic Digestion at Various Organic Loading Rates of Commercial Malaysian Food Waste. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 775676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Barreiro-Vescovo, S.; de Godos, I.; Fernández, M.; Arbib, Z.; Ballesteros, M. Biochemical Methane Potential of Microalgae Biomass Using Different Microbial Inocula. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S.E.; Bucuricova, L.; Ferreira, J.A.; Souza Filho, P.F.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Zamani, A. Valorization of Bread Waste to a Fiber- and Protein-Rich Fungal Biomass. Fermentation 2021, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ryu, J.; Lee, S.R. Influence of carbon type and carbon to nitrogen ratio on the biochemical methane potential, ph, and ammonia nitrogen in anaerobic digestion. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianides, D.; Bagaki, D.A.; Timmers, R.A.; Zrimec, M.B.; Theodoropoulou, A.; Angelidaki, I.; Kougias, P.; Zampieri, G.; Kamergi, N.; Napoli, A.; et al. Biogenic CO2 Emissions in the EU Biofuel and Bioenergy Sector: Mapping Sources, Regional Trends, and Pathways for Capture and Utilisation. Energies 2025, 18, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, V.; Petracchini, F.; Segreto, M.; Tomassetti, L.; Naja, N.; Cecinato, A. Environmental impact of biogas: A short review of current knowledge. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2018, 53, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.; Borja, R.; Weiland, P.; Travieso, L.; Colmenarejo, M.F. Effect of substrate concentration and temperature on the anaerobic digestion of piggery waste in a UASB reactor. Biotechnol. Lett. 2000, 22, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Kulupa, T.; Kubiak, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Pilarski, K.; Niewiadomska, A. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste—A Short Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelenda, A.M.; Baltrusaitis, J. Design of Conventional Batch Distillation of Anaerobic Digestate to Isolate Ammonium Bicarbonate Considering Non-Ideal Mixture Behavior. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2025, 19, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, J.; Ding, H.H.; Chang, S. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Assay Method for Anaerobic Digestion Research. Water 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.A.; Mehta, C.M.; Batstone, D.J. Influence of low pH on continuous anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2017, 113, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, C.; Song, L.; Zhang, J. Anaerobic digestion of food waste and its microbial consortia: A historical review and future perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.R.; Landis, A.E.; Rittmann, B.E.; Young, M.N.; Parameswaran, P. Enhancing Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste through Biochemical Methane Potential Assays at Different Substrate: Inoculum Ratios. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongvichiankul, C.; Deebao, J.; Khongnakorn, W. Relationship between pH, Oxidation Reduction Potential (ORP) and biogas production in mesophilic screw anaerobic digester. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Duarte, M.S.; Magalhães, C.P.; Pereira, M.A.; Cavaleiro, A.J. Micro-Aeration for Improving Anaerobic Treatment and Biogas Production from Organic Pollutants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 109, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Wu, Z.; Shrestha, S.; Lee, P.-H.; Raskin, L.; Khanal, S.K. Intermittent Micro-Aeration: New Strategy to Control Volatile Fatty Acid Accumulation in High Organic Loading Anaerobic Digestion. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
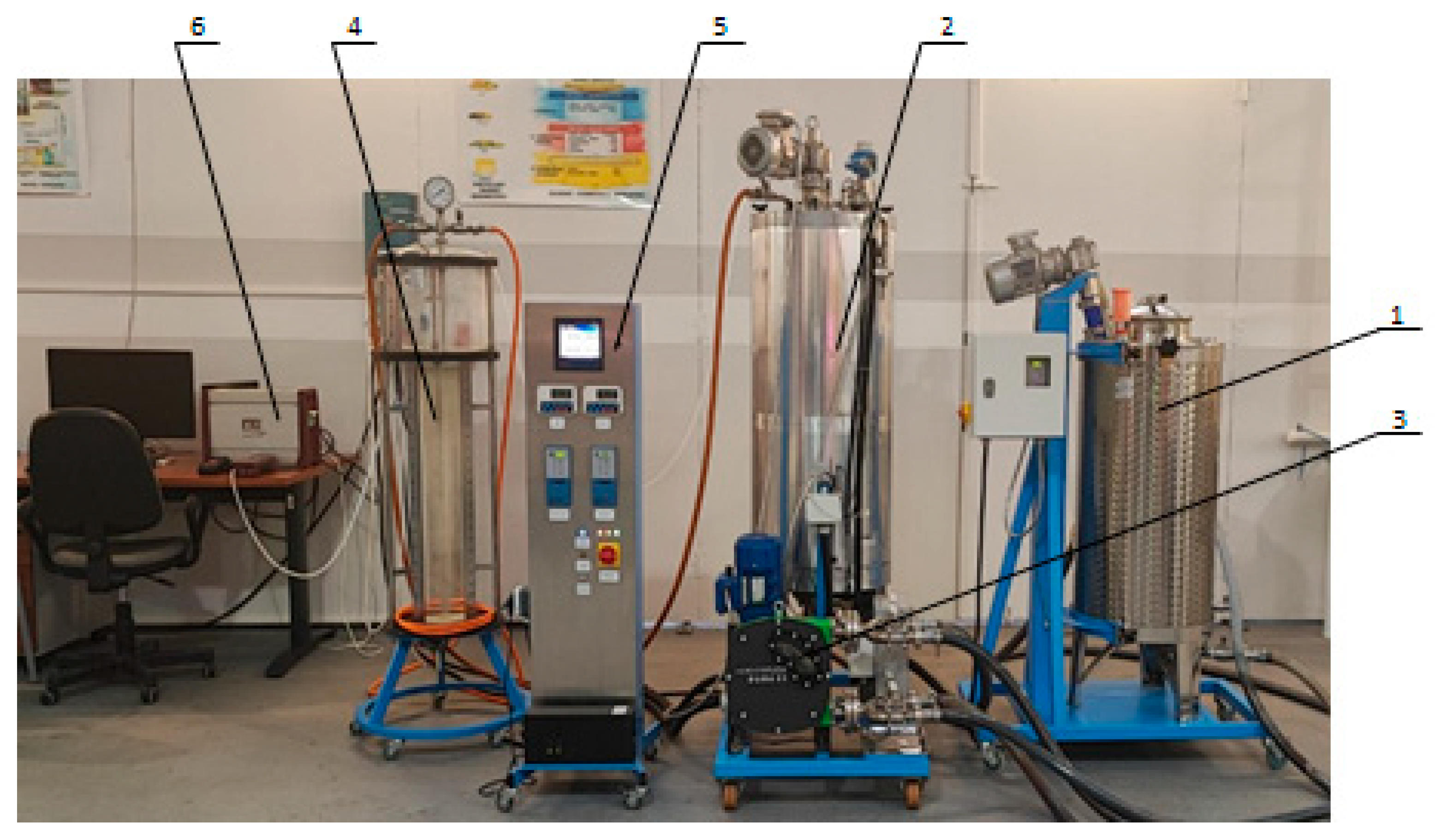



| Parameters | Unit | Method/Instrument | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biogas volume | L | Gas meter | Continuous |
| pH | - | Probe integrated with the digester control and measurement system | Continuous |
| Temperature | °C | Probe integrated with the digester control and measurement system | Continuous |
| Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) | mV | Probe integrated with the digester control and measurement system | Continuous |
| Methane (CH4), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Oxygen (O2), Nitrogen (N2) | % (v/v) | Biogas analyser (OPTIMA MRU) | On measurement days (1, 2, 3, 4, 7) |
| Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) | ppm | Biogas analyser (OPTIMA MRU) | On measurement days (1, 2, 3, 4, 7) |
| Higher heating value (HHV), Lower heating value (LHV) | MJ/m3 | Calculated based on biogas composition | On measurement days (1, 2, 3, 4, 7) |
| Substrate | Load [%] | Avg. HHV [MJ/m3] | HHV Range [MJ/m3] | Avg. LHV [MJ/m3] | LHV Range [MJ/m3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| microalgae | 100 | 24.6 ± 0.9 | 23.4–25.7 | 22.2 ± 0.8 | 21.1–23.2 |
| bread | +25 | 22.2 ± 1.4 | 22.2–25.8 | 20.1 ± 1.2 | 20.1–23.3 |
| rolls | 23.2 ± 0.9 | 23.2–25.5 | 20.9 ± 0.8 | 20.9–23.0 | |
| bread | +50 | 22.1 ± 1.2 | 22.1–25.2 | 20.4 ± 0.8 | 20.4–22.7 |
| rolls | 23.4 ± 0.6 | 23.4–25.1 | 21.1 ± 0.6 | 21.1–22.6 | |
| bread | +75 | 22.4 ± 0.9 | 23.2–25.0 | 20.2 ± 0.8 | 20.2–22.2 |
| rolls | 23.2 ± 0.7 | 23.2–25.0 | 20.9 ± 0.6 | 20.9–22.6 |
| Substrate | Load [%] | Measurement [day] | pH | ORP [mV] | Load Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| microalgae | 100 | 1 | 7.07 | −308.6 | 36.87 |
| 2 | 7.07 | −320.5 | 36.87 | ||
| 3 | 7.07 | −278.1 | 36.98 | ||
| 4 | 7.07 | −312.6 | 36.98 | ||
| 7 | 7.08 | −322.7 | 36.87 | ||
| bread | +25 | 1 | 7.06 | −270.5 | 36.98 |
| 2 | 7.07 | −312.0 | 36.87 | ||
| 3 | 7.07 | −310.2 | 36.87 | ||
| 4 | 7.08 | −321.5 | 36.98 | ||
| 7 | 7.08 | −328.7 | 36.87 | ||
| rolls | 1 | 7.04 | −310.8 | 36.98 | |
| 2 | 7.05 | −309.6 | 36.98 | ||
| 3 | 7.05 | −308.7 | 36.87 | ||
| 4 | 7.06 | −309.7 | 36.87 | ||
| 7 | 7.06 | −307.8 | 36.87 | ||
| bread | +50 | 1 | 7.01 | −291.3 | 36.87 |
| 2 | 7.03 | −316.3 | 36.87 | ||
| 3 | 7.03 | −323.7 | 36.98 | ||
| 4 | 7.04 | −290.9 | 36.87 | ||
| 7 | 7.05 | −315.0 | 36.87 | ||
| rolls | 1 | 7.03 | −287.9 | 36.87 | |
| 2 | 7.04 | −302.2 | 36.98 | ||
| 3 | 7.05 | −289.6 | 36.87 | ||
| 4 | 7.07 | −273.0 | 36.98 | ||
| 7 | 7.07 | −285.3 | 36.87 | ||
| bread | +75 | 1 | 7.00 | −281.7 | 36.87 |
| 2 | 7.02 | −310.4 | 36.87 | ||
| 3 | 7.03 | −310.2 | 36.87 | ||
| 4 | 7.04 | −307.4 | 36.87 | ||
| 7 | 7.05 | −306.9 | 36.98 | ||
| rolls | 1 | 7.04 | −296.3 | 36.87 | |
| 2 | 7.05 | −301.9 | 36.87 | ||
| 3 | 7.05 | −294.3 | 36.98 | ||
| 4 | 7.06 | −311.2 | 36.98 | ||
| 7 | 7.06 | −302.5 | 36.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hawrot-Paw, M.; Tapczewski, J. Waste to Energy: Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Microalgal Biomass and Bakery Waste. Energies 2025, 18, 5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205516
Hawrot-Paw M, Tapczewski J. Waste to Energy: Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Microalgal Biomass and Bakery Waste. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205516
Chicago/Turabian StyleHawrot-Paw, Małgorzata, and Jacek Tapczewski. 2025. "Waste to Energy: Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Microalgal Biomass and Bakery Waste" Energies 18, no. 20: 5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205516
APA StyleHawrot-Paw, M., & Tapczewski, J. (2025). Waste to Energy: Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Microalgal Biomass and Bakery Waste. Energies, 18(20), 5516. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205516







