Abstract
The co-firing of coal and refuse-derived fuel (RDF) from municipal solid waste recycling is gaining support in countries in which energy production is based on solid fuels. It is the result of the rising priority given to renewable energy sources, the circular economy, and effective waste management through sorting, recycling, and thermal conversion. Despite the increasing efficiency of recycling and the ever-lower quantities of waste delivered to waste dumps, the problem of the residual fraction remains unsolved. The portion of mixed municipal waste that cannot be recycled exhibits a high energy value. For this reason, it should be neither stored nor burnt in household boiler rooms, as doing so would constitute an environmental hazard. However, the waste can be used as an additive to fine coal in power boilers, provided that they are equipped with flue gas monitoring and purification systems. Tests involving proportionally prepared compositions of fine coal and refuse-derived fuel burnt in a laboratory boiler revealed a major variability in the flue gas parameters (physicochemical), depending on the applied proportions of the individual components. For instance, when burning a composition of 50% fine coal and 50% refuse-derived fuel, a reduction in CO2 emissions by about 12% was noted compared with that when burning fine coal exclusively. Furthermore, when burning refuse-derived fuel, an addition of 20% fine coal is enough to produce a 2.8% reduction in CO emission. Meanwhile, a composition of 80% fine coal and 20% refuse-derived fuel would reduce the emissions by 393 ppm. During the measurements, it was also noted that most of the measured parameters indicated a decrease in individual gas contents relative to the emissions obtained when burning fine coal or refuse-derived fuel exclusively. These relationships can be applied to prepare fuel compositions based on refuse-derived fuel and fine coal, depending on the power and flue gas purification capabilities of individual cogeneration systems.
1. Introduction
Waste generation is an inherent process that accompanies living organisms from unicellular life forms to humans. As an important biological process in the geological history of Earth, it produced oxygen as a waste form and contributed to the development of the atmospheric composition that enabled the growth of life as we know it today [1]. Currently, following the progress of civilisation, the problem of waste has become so broad that the assimilation and storage processes previously employed by nature with success now prove insufficient [2]. The rate of technological advancement and urban growth, driven by a constant increase in consumption, leads to the global production of municipal waste at a level of billions of tons per year [3]. It should be noted that, according to data from the Central Statistical Office (GUS), 14.2 million tons of municipal waste were collected in Poland in 2024. The environmental interference of human-made waste, such as nano- and microplastics, petroleum products, and industrial and hazardous waste, can reverse the trend of life support and growth in its current form. Storing such waste, as well as bio-waste from municipal sources and urban greenspace maintenance, results in excess greenhouse gas emissions, which can even begin processes leading to another mass extinction by accelerating the greenhouse effect [4,5]. The rising awareness of the hazards related to the vast quantities of waste produced at each step of humanity’s existence necessitates a change in the approach to waste management and production. New technologies for biodegradable packaging production are gradually being introduced, while products of everyday use are planned with the aim of being repurposed or material recycled. Nevertheless, the current level of global recycling, at about 20%, is strongly unsatisfactory, while the thermal conversion of waste encounters social protests against incineration plant construction [6,7]. Another issue in material recycling from waste is the availability of technology and the different technological advancements of individual countries burdened with waste problems. Low-income countries often struggle with a lack of access to modern technologies applied in recycling due to high investment costs, while certain materials require very specific and expensive recycling methods. Therefore, countries with higher technological advancement that possess more efficient and less power-consuming recycling methods exhibit higher recycling levels and better quality of the obtained recycled material. Regardless, even in such countries, municipal waste recycling processes cannot encompass all fractions. After separating paper, metals, plastics, and glass, the residual municipal solid waste (RMSW) is characterised by a complex and heterogeneous composition that encompasses, e.g., organic fractions, textiles, composites, and fine irrecoverable waste in the form of various types of plastics [8]. The quantity of the generated waste and residual fraction remains significant and requires developing effective and environmentally acceptable methods for its management [9]. Thermal waste conversion methods, such as waste-to-energy combustion, are applied over a longer perspective as an alternative to residual waste storage, making it possible to reduce the waste volume while producing heat and power [10]. However, burning pure residual waste can generate numerous technical difficulties. These arise from variable fraction compositions, high moisture content, differences in boiler designs, and potential increased pollutant emissions if the flue gas purification systems are not adapted to such an unstable fuel. One solution for stabilising the composition of residual waste intended for energy conversion can be its co-firing with fine coal, which to a degree also constitutes a waste fraction as a by-product of hard coal mining and processing [11]. The co-firing of RMSW with conventional fuels such as coal, biomass, or natural gas can offer a multitude of benefits, including improving the combustion process stability, increasing energy efficiency, and reducing pollutant emissions. Properly prepared fuel compositions enable the use of existing power infrastructure for co-firing residual material with fine coal, which will contribute to the partial replacement of fossil fuels and a potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions in the power sector [12,13,14].
2. Materials and Methods
For use in this experiment, 50 kg of fine coal was purchased from a fossil fuel distributor from southern Poland. It was characterised by technical parameters typical of fuels used in low-power boilers, the type most commonly installed in households. Following a physicochemical analysis performed in a certified laboratory, the coal in the product named “fine coal” was classified as 32.1 as per standard PN-G-97002:2018-11 [15]. Furthermore, 50 kg of residual waste generated during the recycling of commingled municipal waste was obtained from a producer from western Poland. The waste was offered as refuse-derived fuel (RDF), whose primary recipients are cement plants.
The fuels were individually subjected to physicochemical analysis in order to determine their parameters, including total humidity (PN-ISO 589:2006 [16]), combustion heat, and calorific value, as well as ash (PN-ISO 1928:2020-05 [17]), sulphur (PN-G-04584:2001 [18]), total carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen (PN-G-04571:1998 [19]), chlorine (PN-ISO 587:2000 [20]), and mercury contents (PN-ISO 15237:2007 [21]). To confirm the percentage contribution of the primary components in the obtained residual waste, an analysis for the presence of organic and inorganic components was performed as per standard ISO 21644:2021-07 [22]. Additionally, an optical analysis was conducted for a more accurate determination of the percentage contribution of individual solid components, with a composition identification of thermally unconverted (woody biomass, non-woody biomass, cellulose, bark) and converted (charcoal, biocoal) organic matter, mineral matter (sand, quartz, stone dust, ceramics, glass, metal, rust, ash, slag), and petroleum products (plastics, rubber, paint, grease, glue, polymer resin, tar). The applied petrographic analysis consisted of an optical assessment of preparations based on the tested material in reflected light using oil immersion as per the methodology developed for charcoal, coal, and biomass briquettes, as well as pellets formed from organic and inorganic waste [23,24]. The analysis consisted of identifying the individual components or their groups on the polished surface of the microsection in 500 to 1000 points determined through the intersection of the crosswire in the microscope ocular. An ocular magnification of 10× and objective magnification of 50× were applied. Before the analysis began, the microsection was fixed on a microscopic slide on plasticine, after which it was levelled using a mini-press and placed in the grip of an object stage-mounted on a microscope frame. After a solid component was identified, it was registered in dedicated petrographic analysis software using a keyboard or other instrument, and the image in the field of view was always moved automatically by the same distance. If the crosswire intersection in the ocular fell on the binding resin, the identification was not registered, and the image was only moved to continue the observation. The analysis enables component identification and the qualitative and quantitative determination of individual waste component contents, encompassing both compact and loose solids.
Seven samples with a weight of 5 kg each were prepared from both fuels, intended for the analysis of flue gas generated following their combustion in an experimental boiler with a power of 25 kW. The first sample consisted of 100% fine coal. The second sample was prepared with a weight ratio of 20% fine coal to 80% refuse-derived fuel through the precise mixing of both fuels in a rotary drum. Then, samples 3 to 6 were also mixed, according to the following proportions of fine coal to refuse-derived fuel, respectively: sample 3 consisted of 40% and 60%; sample 4, 50% and 50%; sample 5, 60% and 40%; and sample 6, 80% and 20%. Finally, sample 7 contained 100% refuse-derived fuel. Thus, the prepared samples were subjected to thermal conversion in a stoker-fired laboratory boiler designed for solid fuel combustion under controlled conditions [25] (Figure 1). The samples were burnt under identical conditions, one after another, at an airflow rate of 0.8 m3/min and an average fuel transfer velocity on the conveyor belt of 83 mm/min.

Figure 1.
Measurement stand with integrated experimental stoker-fired boiler: (a) laboratory boiler; (b) measurement stand; (c) fuel feeder.
The gas component emissions were measured using VARIO luxx MRU [26] and Testo 330 [27] stack gas emission analysers for extended industrial combustion measurements, which enable the measurement of O2, CO2, CO, NO, NOx, and SO2 emissions as well as flue gas temperature and furnace temperature. Additionally, the Gasmet Gt 5000 Terra analyser was used to measure the following chemical compounds in the flue gas: N2O, NH3, CH4, HCOH, and TOC. During the combustion of individual samples, dust was also collected on filter paper using an isokinetic particle sampling probe. The content of toxic elements that accompany emissions (arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, mercury, and lead) in the collected dust was determined using a Vanta XRF spectrometer.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Parameter Determination
The physicochemical parameters of the fine coal (sample 1) and separately tested residual waste (sample 7), obtained via analyses, are presented in Table 1A. Moreover, Table 1B presents the physicochemical analysis results for the individual compositions of fine coal (C) and residual waste (R). The analysed sample series encompassed fine coal (C) and residual waste (R) compositions in variable weight ratios, i.e., sample 2 (20% C: 80% R), sample 3 (40% C: 60% R), sample 4 (50% C: 50% R), sample 5 (60% C: 40% R), and sample 6 (80% C: 20% R).

Table 1.
Physicochemical parameters of fine coal and residual waste, as well as individual fine coal and residual waste compositions.
The conducted total humidity analysis revealed that the lowest value was characteristic of fine coal, at a level of 6.48%, while the residual waste exhibited the highest, at a level of 15.16%. In the case of the fine coal and residual waste compositions, the highest moisture content was found in sample 2, at a level of 15.07%, and the lowest in sample 6, with a value of 12.10%. The measurements indicated that residual waste was the dominant factor influencing the moisture level in the samples, as its moisture content was more than twice that of the coal fines. In all the analysed compositions, regardless of proportions, the moisture content remained at a level not exceeding 16%. As per standard PN-EN ISO 21640:2021-10 [28], from the perspective of moisture content (15–20%), these compositions can be permitted for combustion in installations adapted to this kind of fuel. The ash content in the tested fine coal, residual waste, and their compositions ranged within 13.5% to 15.97% [29,30]. This was most likely related to the minor difference in ash content between the two components, amounting to 1.82% [31,32]. The sulphur content in the coal sample was determined at 1.15%, which constituted a value six times greater than in the waste sample. The high sulphur content in the coal [33] resulted in a higher sulphur content in the compositions, which increased together with greater quantities of coal relative to waste. As per the measurements, the next parameter, i.e., the coal combustion heat, was 9% higher than the waste combustion heat. In contrast, the calorific value of coal was greater by 27% than that of the waste. These differences probably result from aspects such as the higher moisture content and major organic fraction content in the waste. The calorific value of the tested residual fraction sample was 18.55 MJ/kg, which is within the range of values given in the literature, from 12 to 24 MJ/kg [34,35]. In the case of the analysed fuel compositions, the lowest combustion heat and calorific value were noted for the composition of 20% coal and 80% waste. Their levels were 23,375 kJ/kg and 18,682 kJ/kg, respectively. Meanwhile, the highest values were obtained for the composition at a ratio of 80% coal and 20% waste, in which the combustion heat and calorific value were 24,764 kJ/kg and 20,890 kJ/kg, respectively. The fine coal was also characterised by a total carbon content higher by over 14% than that in the waste. Moreover, the hydrogen content in the residual waste was determined at a level 74% higher than in the coal, which was similar for nitrogen at 48% and chlorine at 170%. Mercury content analysis in the residual waste revealed it to be 90% lower than in the fine coal, which corresponded to greater mercury contamination of the composition samples (2–6), together with the increase in coal content. Regarding mercury, nitrogen, and chlorine, which are elements with a negative effect on flue gas quality during combustion, preparing fuel compositions from residual waste and fine coal should factor in the ratios of these elements between the precursors. Chlorine content is typically related to a major proportion of petrochemical (PVC) and biodegradable components in residual waste [36,37]. The remaining chemical analyses for determining the volatile matter content, vitrinite reflectance, and caking power were performed exclusively for fine coal in order to classify it as per standard PN-G-97002:2018-11.
3.2. Characteristics of Solid Components in the Residual Waste
The determined percentage contributions of individual solid components in the refuse-derived fuel are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Petrographic and chemical analysis results for residual waste.
The residual waste composition was determined via optical analysis by distinguishing three basic groups of solid components: organic matter, inorganic matter, and petroleum products. A comparative analysis was performed as well using methodology compliant with ISO 21644:2021-07 to determine the percentage content of organic and inorganic matter. The determination of solid components, particularly the ratio of the biodegradable fraction to the non-biodegradable, as well as the percentage contribution of ballast (inorganic matter such as sand, quartz, ceramics, glass, metals, rust, ash, and slag), has major significance when selecting the optimal method of energy repurposing for waste [38,39]. It can also facilitate the selection of the appropriate percentage distribution when preparing compositions with coal, e.g., to reduce chlorine or nitrogen content in the prepared fuel by decreasing or increasing the individual component quantities (the coal-to-residual waste ratio). An analysis of the residual waste sample revealed its composition to include 56% organic material, 32% petroleum products, and 12% inorganic residues, including both natural components (sand) and post-industrial materials, as well as fragments of everyday use products (Figure 2).
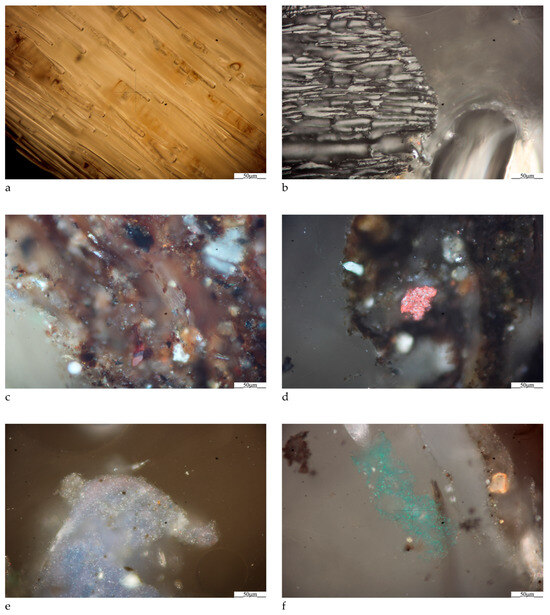

Figure 2.
Photomicrographs with examples of organic matter—biomass (a) end charcoal (b), inorganic matter—ash (c) end rust (d), petroleum products—plastic (e,f).
3.3. Emission Characteristics During the Combustion of the Tested Samples
The measurement results from the combustion of individual samples are provided in Table 3.

Table 3.
Combustion parameter analysis for fine coal and residual waste samples and their compositions.
A significant difference in the flue gas temperature was noted during the combustion of sample 1 (100% coal) and sample 7 (100% residual waste). The flue gas temperature for coal was over twice as high as that for the residual waste. In contrast, the observable flue gas temperature increase, together with the greater contribution of coal in the composition with waste, is non-uniform (Figure 3a) relative to the composition proportions; however, this is significant given that the flue gas temperatures for samples 2 and 6 differed by 121 °C. The furnace temperature for the individual samples also exhibited certain variability and increased together with the greater coal content in the composition, stabilising for the sample with a 50%/50% coal-to-waste ratio (Figure 3b). A higher carbon content likely contributed to stabilising the combustion process. Carbon burns uniformly and predictably and possesses a higher calorific value, resulting in an elevated temperature within the combustion chamber, while waste materials exhibit variable composition and moisture levels that can lead to temperature fluctuations [40]. A major difference in the furnace temperatures was also found for samples 1 and 7, where it was 74.8 °C higher for sample 1 than for sample 7. The increase in flue gas and furnace temperatures can be associated with the greater moisture content in the waste relative to the humidity of coal. The sample humidity decreased as more coal was added to the compositions. This led to better combustion conditions, which could be observed in the temperature increase for both the furnace and the flue gas as well as reduced oxide emissions [41]. The lowest carbon dioxide emission, at a level of 14,040 ppm, was noted during the combustion of sample 7, while the highest emission of 18,134 ppm was observed for sample 1. In the case of the compositions, the lowest carbon dioxide emission at a level of 16,026 ppm was found for the composition containing 50% coal and 50% waste (Figure 3c). Carbon monoxide emissions were lowest during the combustion of fine coal without additions, and they oscillated at a level of 811 ppm, whereas during the combustion of only the residual waste, they reached a level of 1708 ppm (Figure 3d). Coal burned more efficiently, emitting less CO due to its relatively uniform chemical composition and physical properties. In contrast, waste incineration resulted in higher CO emissions because of its varied composition [42]. According to standard PN-EN 303-5+A1:2023-05 [43], in the case of combustion in household boilers, the emission should range between 436 ppm CO (for boilers with automatic stoking) and 611 ppm CO (for boilers with manual stoking). However, burning waste in household installations is prohibited by law, and as this study demonstrated, the emissions from waste combustion exceed those found for coal by a factor of two. In this study, neither the tested fine coal nor the waste fulfilled the CO emission standards for household installations; however, the goal of the study was not to analyse this characteristic but to determine the variability in the emissions of carbon monoxide and other measured gases at various proportions of coal and residual waste. This study demonstrates that adding coal to waste reduces the CO emissions. The CO emission decreased from 1708 ppm to 1315 ppm for the composition of 80% coal and 20% waste. Meanwhile, in the case of the 50% coal and 50% waste composition, the emission reduction was about 150 ppm relative to that when burning just the waste. The nitrogen oxide emissions exhibit a clear falling tendency for the 80% coal and 20% waste composition, relative both to burning coal or waste exclusively. Moreover, in the case of NO, it is a marked difference from 5 ppm for coal to 15 ppm for waste (Figure 3e). Co-firing fine coal with the residual waste provided negative results in this test, as an unfavourable influence on the NOx emissions was observed. Both the 20% coal and 80% waste composition and the 80% coal and 20% waste composition increased the NOx emission compared with that when burning coal or waste exclusively (Figure 3f). This phenomenon has also been documented by other researchers; it shows a correlation with the biomass fraction present in the waste stream [44,45]. The lowest sulphur dioxide emission was recorded when burning the composition containing 40% coal and 60% waste, and it was 235 ppm lower relative to burning just coal while decreasing by 12 ppm compared with that when burning residual waste exclusively (Figure 3h). The methane measured in the flue gas reached the highest level of 65.9 ppm when burning the residual waste, and it decreased by 50 ppm for the composition containing 80% fine coal and 20% waste, which was nevertheless higher by 14 ppm than the CH4 emission when burning just coal (Figure 3i). For all samples, a NH3 emission was only noted during the combustion of the residual waste [46]. Burning waste exclusively also exhibited higher HCHO content in the flue gas than that when burning just coal, and a rising tendency for this compound also occurred as the contribution of waste in the composition increased. The value recorded for the total organic carbon (TOC) in the flue gas for the composition containing 80% coal and 20% waste was slightly lower (by 0.4 ppm) than that when burning just waste (Figure 3j). However, as the waste content in the composition increased, the TOC level rose successively, reaching 8.2 ppm for the 20% coal and 80% waste composition. Additionally, the level of this emission increased by 19.96 ppm compared with that when burning just coal; thus, there was an over twofold increase for the composition containing the lowest waste proportion (20%).
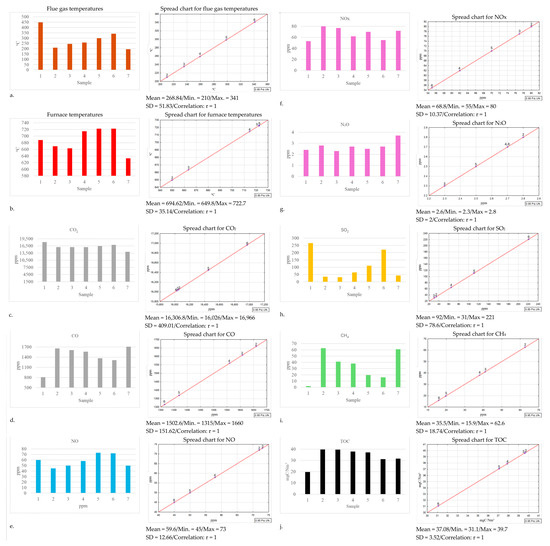
Figure 3.
Graphic representation of combustion parameter analysis for fine coal and residual waste samples and their compositions, with spread charts.
3.4. Spectrographic Analysis of Dust
Analysing the flue gas dust deposited on the filters for the presence of toxic elements revealed no major concentrations for either of the fuels, i.e., fine coal and residual waste, or their compositions. The concentrations of arsenic, chromium, and nickel were below the detection levels, which made their precise quantitative determination impossible. Cadmium was found at a relatively high level of 0.6 ppm in the residual waste combustion dust [47], but a further dust emission analysis revealed a considerable reduction in the content of this element, reaching zero, when burning the composition with a coal contribution of 60%. Note that the gradual cadmium concentration reduction in the dust was already observable in the composition with coal-to-waste proportions of 50%/50%. The cobalt concentration in the dust was at a similar level regardless of whether the combustion encompassed compositions of residual waste and coal or each fuel individually. This would entail that the cobalt in the dust originating from the combustion of coal and waste compositions does not accumulate in the dust nor does its concentration decrease relative to the burning of each fuel individually. The lowest copper, manganese, and molybdenum contents in the dust were found for coal and the highest for residual waste. As for the compositions from both fuels, increasing the coal proportion exhibited a marked influence on reducing the content of these elements in the combustion dust. Although mercury was detected in the fuel samples and compositions before burning, its presence was not found in the collected flue gas dust after sample combustion. The absence of this element in the dust could be related to the sensitivity of the apparatus or to other factors, leading to the lack of determinable mercury accumulation in dust [48,49]. In the case of the compositions and the residual waste, the mercury concentration in the dust could be affected by its low content in the residual waste as well as by the presence of chlorine [50,51]. The lead content in the tested dust was determined at a level of 12 ppm for coal and 8 ppm for the residual waste. A rising tendency was observed for the lead concentration in the dust together with the increase in coal content in the compositions, reaching 16 ppm for the composition containing 80% fine coal and 20% waste. At combustion temperatures of 500–1000 °C, lead may occur as oxides, which are readily adsorbed onto the surface of dust particles. However, this accumulation is not uniform, as part of the element can migrate to the bottom ash or fly ash [52]. The elemental concentration measurement results for the individual samples are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Elemental concentration measurement results for individual samples.
Figure 4 illustrates the elemental concentration distributions of all samples in order to visualise the diversification of their contents in both the individual fuels and their compositions. In the analysed mixtures, a slight upward trend in the accumulation of arsenic, manganese, and molybdenum was observed, while the concentration of cobalt and chromium remained at a similar level across all samples. Conversely, nickel showed a lower concentration in samples with less of the residual fraction. Mercury was not detected in the dusts, whereas cadmium was noted in trace amounts in the tested samples. The concentrations of copper and lead were difficult to correlate with the dominant fraction in the mixtures, despite the large disparity in their content in the precursors. The probable cause of this phenomenon is the carriers of these elements in the waste [53,54]; however, additional research into the residual fraction is required to precisely determine the component responsible for their accumulation.
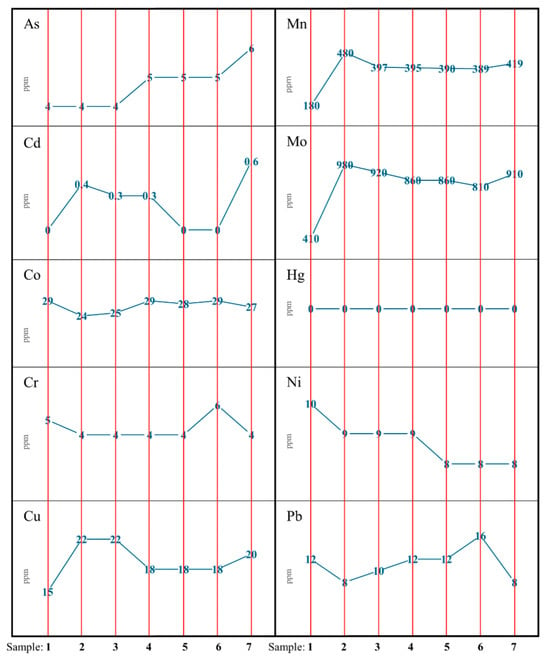
Figure 4.
Elemental concentration distributions in individual fuel samples (fine coal—sample 1; residual waste—sample 7) and their compositions (samples 2,3,4,5,6).
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
The results reveal significant challenges related to the co-firing of fine coal with the residual fraction after municipal waste recycling (refuse-derived fuel, RDF) for energy recovery. Through emission measurements, the fine coal and residual waste compositions exhibited carbon dioxide emission reduction within 6% to 12% compared with that when burning coal exclusively. This is a beneficial phenomenon resulting from the partial replacement of coal, a fossil fuel, with a fuel containing over 50% biomass. Emissions from biomass are considered neutral with regard to the CO2 balance; therefore, the increase in CO2 emissions by 12% to 17% during composition combustion relative to burning just the waste, as demonstrated in this study, has no significant impact on the environment in the total co-firing balance, unlike burning coal exclusively. Moreover, adding fine coal to residual waste results in a linear reduction in carbon monoxide emissions during combustion. This relationship was observed when the CO emission decreased within 3% to 23% as the coal content in the composition increased. Based on this study, the use of fuel compositions containing various proportions of fine coal and the residual fraction after municipal waste recycling reveals both positive and negative effects. The remaining parameters determined in the flue gas during the combustion of the tested fuels, such as NOx, SO2, CH4, and TOC, also exhibited rising or falling tendencies depending on the composition contents. The elemental concentrations in the dust collected from the flue gas were found to vary as well depending on the tested composition proportions, exhibiting certain rising or falling relationships. A more detailed analysis of these relationships requires using a higher-resolution apparatus; therefore, they are presented as preliminary trends in this work.
The presented preliminary analyses make it possible to conclude that determining the potential for pollutant reduction in the flue gas is crucial for optimal fuel composition design. Therefore, this work provides a starting point for further research, opening perspectives for individual coal and waste co-firing process simulations. The use of modern technologies, process engineering, and AI in modelling such processes will enable precise combustion parameter adjustment in specific installations using appropriate fuel compositions, which may significantly contribute to a further reduction in pollutant emissions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.J. and P.R.; methodology, Z.J.; formal analysis, Z.J.; investigation, Z.J. and P.R.; resources, Z.J.; data curation, Z.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.J.; visualization, Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was conducted under Project #113320125-380, financed by the Polish Ministry of Education and Science. The project is co-financed by the Polish National Agency for Academic Exchange within the Polish Returns Programme (BPN/PPO/2021/1/00005/DEC/1), the National Science Centre, Poland (2022/01/1/ST10/00024), and by the funds granted under the Research Excellence Initiative of the University of Silesia in Katowice, Poland. Research activities are co-financed by the funds granted under the Research Excellence Initiative of the University of Silesia in Katowice.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lyons, T.; Reinhard, C.; Planavsky, N. The rise of oxygen in Earth’s early ocean and atmosphere. Nature 2014, 506, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosco, D.; De Molfetta, M.; Renzulli, P.; Notarnicola, B. Progress in monitoring methane emissions from landfills using drones: An overview of the last ten years. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Global Waste Management Outlook: Beyond an Age of Waste: Turning Rubbish into a Resource; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2024; COI: 20.500.12592/m905whx; Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/global-waste-management-outlook-2024 (accessed on 30 June 2025) (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Christensen, T.H.; Damgaard, A.; Bruun, H.H.; Jensen, L.S.; Jørgensen, P.; Gregersen, K.; Knox, K. Environmental assessment of solid waste management systems: A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2201–2219. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Global Waste Management Outlook 2024. Nairobi. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/44939/global_waste_management_outlook_2024.pdf?sequence=3 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Perceptional differences in the factors of local acceptance of waste incineration plant. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1067886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triassi, M.; De Simone, B.; Montuori, P.; Russo, I.; De Rosa, E.; Di Duca, F.; Crivaro, C.; Cerullo, V.; Pontillo, P.; Díez, S. Determination of Residual Municipal Solid Waste Composition from Rural and Urban Areas: A Step toward the Optimization of a Waste Management System for Efficient Material Recovery. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng-Chuen, C.; Bodirsky, B.; Krueger, T.; Mishra, A.; Popp, A. The world’s growing municipal solid waste: Trends and impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajczyńska, D.; Krzyżyńska, R.; Kulczycka, J.; Lewicka, E.; Mioduski, J.; Pokój, T. The characteristics of municipal solid waste in Poland and the possibilities of its energy recovery. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 896–906. [Google Scholar]
- Matli, C.; Challa, B.; Kadaverugu, R. Co-firing municipal solid waste with coal—A case study of Warangal City, India. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2019, 18, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Surroop, D.; Juggurnath, A. Investigating the energy potential from co-firing coal with municipal solid waste. Univ. Maurit. Res. J. 2011, 17, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Szykowska, K.; Walewska, A. The potential and prospects for the development of alternative fuel production. Contemp. Environ. Prot. Energy Probl. 2021, 177. Available online: https://scholar.googleusercontent.com/scholar?q=cache:or2RtWR7aAQJ:scholar.google.com/&hl=pl&as_sdt=0,5 (accessed on 30 June 2025).[Green Version]
- PN-G-97002:2018-11; Hard Coal—Classification—Types. WUG: Katowice, Poland, 2018.[Green Version]
- PN-ISO 589:2006; Hard coal—Determination of Total Moisture. WUG: Katowice, Poland, 2006.[Green Version]
- PN-ISO 1928:2020-05; Solid fuels—Determination of the Heat of Combustion by the Method of Combustion in a Calorimetric Bomb and Calculation of the Calorific Value. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.[Green Version]
- PN-G-04584:2001; Solid fuels—Determination of Total Sulfur and Ash Content Using Automatic Analyzers. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.[Green Version]
- PN-G-04571:1998; Solid fuels—Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen Content Using Automatic Analyzers—Macro Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.[Green Version]
- PN-ISO 587:2000; Solid Fuels—Determination of Chlorine Content Using Eschka’s Mixture. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.[Green Version]
- PN-ISO 15237:2007; Solid fuels—Determination of Total Mercury in Coal. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.[Green Version]
- ISO 21644:2021-07; Solid Recovered Fuels—Methods for Determining Biomass Content. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.[Green Version]
- Jelonek, I.; Jelonek, Z. Atlas: Microscopic Images of Solid Components Found in Pellet and Briquette Fuels Produced from Biomass; Ridero: Kraków, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-8221-585-4. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Jelonek, I.; Jelonek, Z. Photo Catalog for the Identification of Solid Contaminants in Charcoal and Charcoal Briquettes Using Optical Microscopy; Ridero: Kraków, Poland, 2019; ISBN 978-83-8155-888-4. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Rompalski, P.; Guzy-Proc, J. Stand for optimizing combustion process of solid fuels (biofuel, solid recovered fuel, energy mixtures, solid fuel granulates, coals). In Przegląd Górniczy; Stowarzyszenie Inżynierów i Techników Górnictwa ul.: Powstańców, oland, 2025; pp. 193–198. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- PN-EN ISO 21640:2021-10; Solid Secondary Fuels—Specifications and Classes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.[Green Version]
- Kurose, R.; Ikeda, M.; Makino, H. Combustion characteristics of high ash coal in a pulverized coal combustion. Fuel 2001, 80, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VARIO Luxx MRU. Available online: https://www.mru.eu/en/products/detail/varioluxx/ (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Testo 330. Available online: https://www.testo.com/pl-PL/analizator-spalin-testo-330-2/p/0563-3372-75 (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Liang, W.; Ning, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, L.; Jiang, C.; Wang, G. Effect of Ash on Coal Combustion Performance and Kinetics Analysis. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2020, 194, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Yu, L.; Shi’en, H.; Yun, L.; Yanqing, N. Co-firing biomass with coal on ash deposition behavior at various temperatures in a Down-Fired furnace. Fuel 2024, 364, 131049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariana, H.; Prabowo; Edi, H.; Fairuz, K.; Arif, D.; Muhammad, A. A comprehensive evaluation of cofiring biomass with coal and slagging-fouling tendency in pulverized coal fired boilers. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokowska-Pawłowska, M. Variability of sulfur content and sulfide mineralization of coal petrographic components in selected coal seams Poruba (620) and Zaleskie beds (405). Czas. Syst. Wspomagania W Inżynierii Prod. 2017, 6, 101–110. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-eca99482-0b6d-4e48-b5e2-d1ed65685df3 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Maulidayanti, E.M.; Yuliani, M.; Robbani, M.H.; Wiharja, W.; Hambali, E.; Setyaningsih, D. Evaluasi Produksi Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) dari Sampah Perkotaan (Studi Kasus: RDF Plant di Kabupaten Cilacap). J. Teknol. Lingkung. 2024, 25, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Sharma, D.; Kumar, A.; Bansal, T.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, S.; Hussian, A.; Kamyab, H.; Haq, M. Utilization of refuse-derived fuel in industrial applications: Insights from Uttar Pradesh, India. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Effects of Moisture and Hydrogen Content on the Heating Value of Fuels. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2007, 29, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yijing, L.; Hua, Z.; Liming, S.; Pinjing, H. Occurrence of chlorine in municipal solid waste and its thermal transformation. CIESC J. 2021, 72, 4900–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rotter, S. Overview on the Chlorine Origin of MSW and Cl-Originated Corrosion During MSW & RDF Combustion Process. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2008; pp. 4255–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yue, C.; Ma, Y. Pollutant Emissions and Heavy Metal Migration in Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge and Coal. Energies 2024, 17, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisinella, V.; Götze, R.; Conradsen, K.; Damgaard, A.; Christensen, T.H.; Astrup, T.F. Importance of waste composition for Life Cycle Assessment of waste management solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Han, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Analysis and prediction of combustion characteristics of co-combustion of coal and biomass (straw, sludge and herb residue). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025, 150, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchapda, A.H.; Pisupati, S.V. A Review of Thermal Co-Conversion of Coal and Biomass/Waste. Energies 2014, 7, 1098–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, E.M.; Konieczny, T. Emissions from CO-Combustion of Coal and Municipal Solid Waste in domestic Central Heating Boiler. Inżynieria Ekol. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elyazeed, O.S.M.; Nofal, M.; Ibrahim, K.; Yang, J. Co-combustion of RDF and biomass mixture with bituminous coal: A case study of clinker production plant in Egypt. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN 303-5+A1:2023-05; Heating Boilers—Part 5: Heating Boilers Fired with Solid Fuels, with Manual and Automatic Fuel Charging, with a Nominal Output up to 500 kW—Terminology, Requirements, Testing and Marking. iTeh: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023.
- Dula, M.; Kraszkiewicz, A. Theory and Practice of Burning Solid Biofuels in Low-Power Heating Devices. Energies 2025, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatabø, G.; Cornelissen, G.; Carlsson, P.; Nilsen, P.; Tapasvi, D.; Bergland, W.; Sørmo, E. Industrially relevant pyrolysis of diverse contaminated organic wastes: Gas compositions and emissions to air. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, B.; Allen, G.; Marin, A.; Rector, L.; Ahmadi, M. Impacts of wood species and moisture content on emissions from residential wood heaters. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2022, 72, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 November 2010 on Industrial Emissions (Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32010L0075 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Lyu, Q.; Xin, F. Przegląd kontroli rtęci podczas współspalania węgla i biomasy w atmosferzeO2/CO2. Nauk. Stosow. 2024, 14, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, J.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, R.; Yue, T. Bibliometric analysis on mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants: A systematic review and future prospect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 19148–19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Dhyani, S.; Pujari, P.R. Coal-Fired Thermal Power Plants and Mercury Risks: Status and Impacts to Realize Minamata Convention Promises. Anthr. Sci. 2022, 1, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, F.; Lin, C.-J.; Zhang, L.; Hui, M.; Yang, M.; Su, H.; Hao, J. Mercury transformation and speciation in flue gases from anthropogenic emission sources: A critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2417–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R. Potential health impacts of burning coal beds and waste banks. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Kinoshita, S.; Takatsuki, H. The origin and behavior of lead, cadmium and antimony in MSW incinerator. Waste Manag. 1996, 16, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Shen, D.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Zhao, Y. Heavy metal source analysis in municipal solid waste (MSW): Case study on Cu and Zn. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).