NVH Optimization of Motor Based on Distributed Mathematical Model Under PWM Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Distributed Flux Method
2.1. Motor Model and Control Model
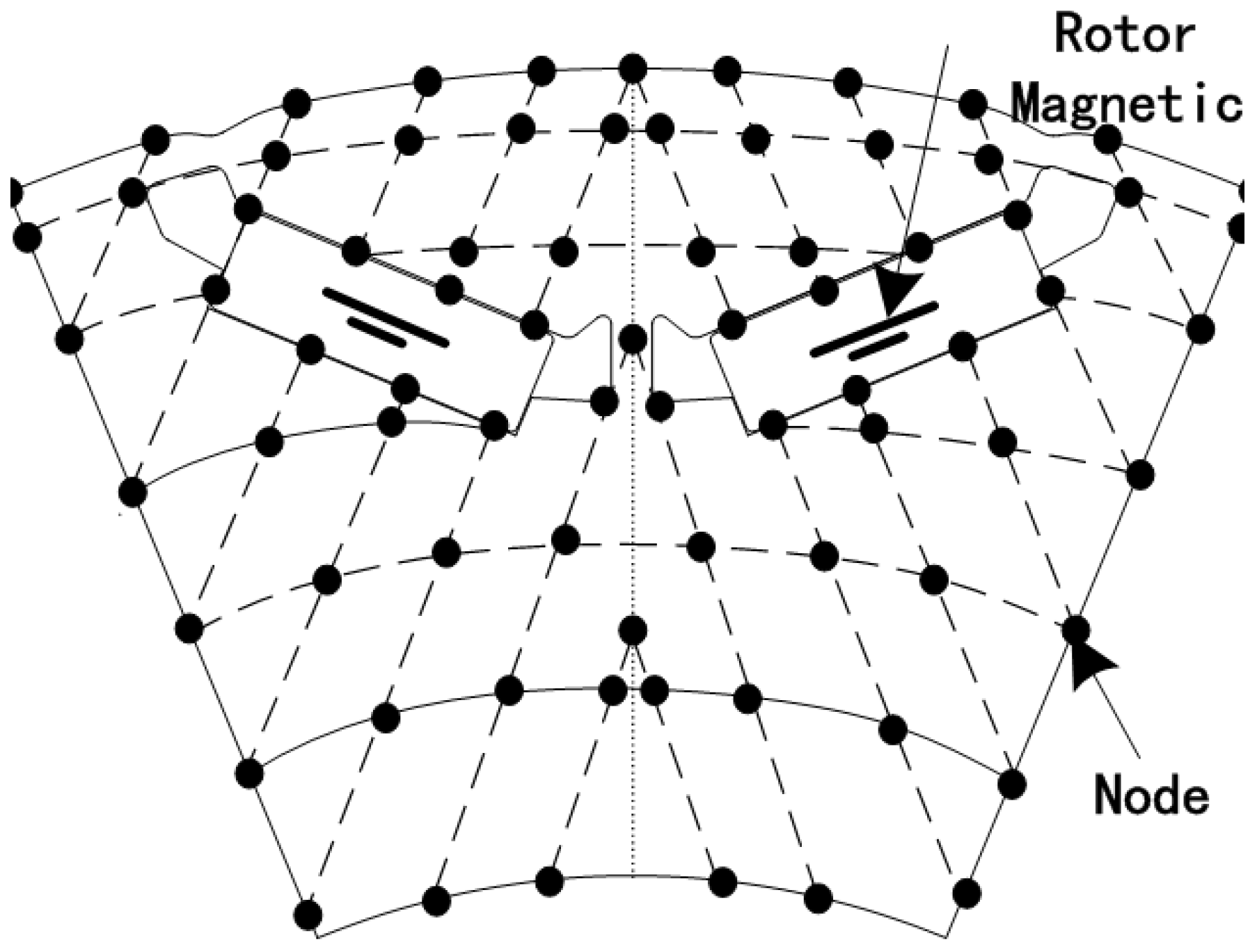
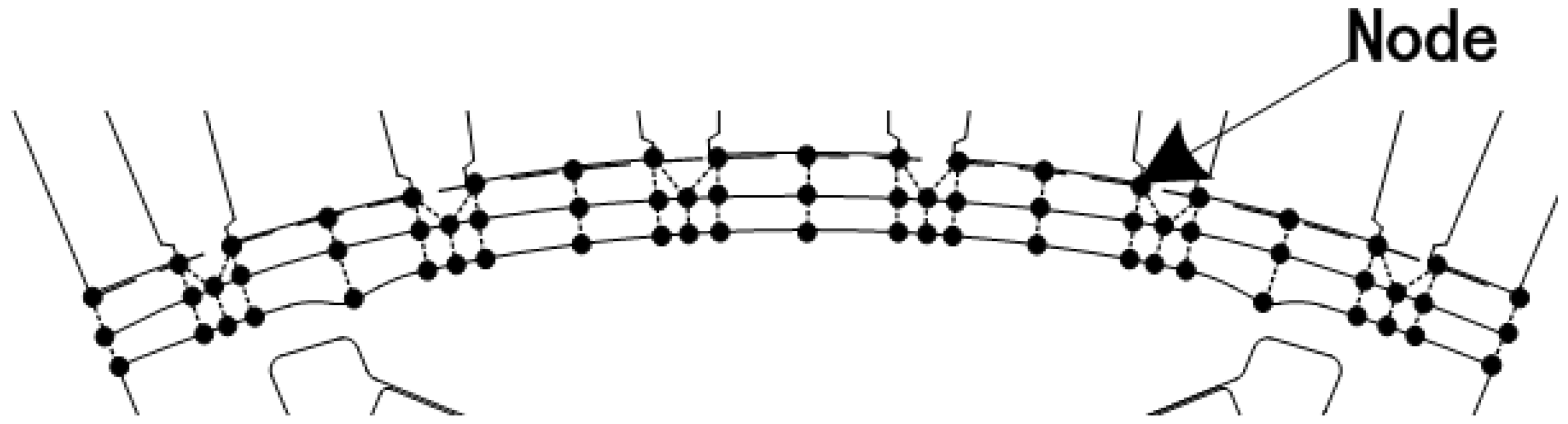
2.2. Distributed Nodes
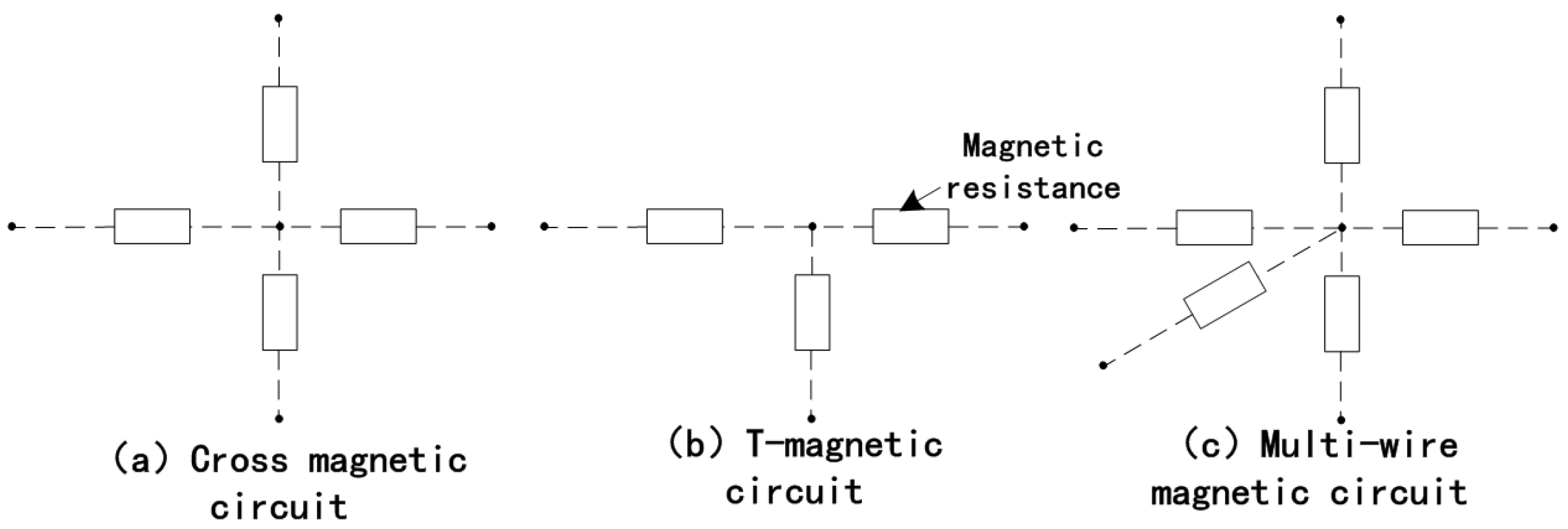
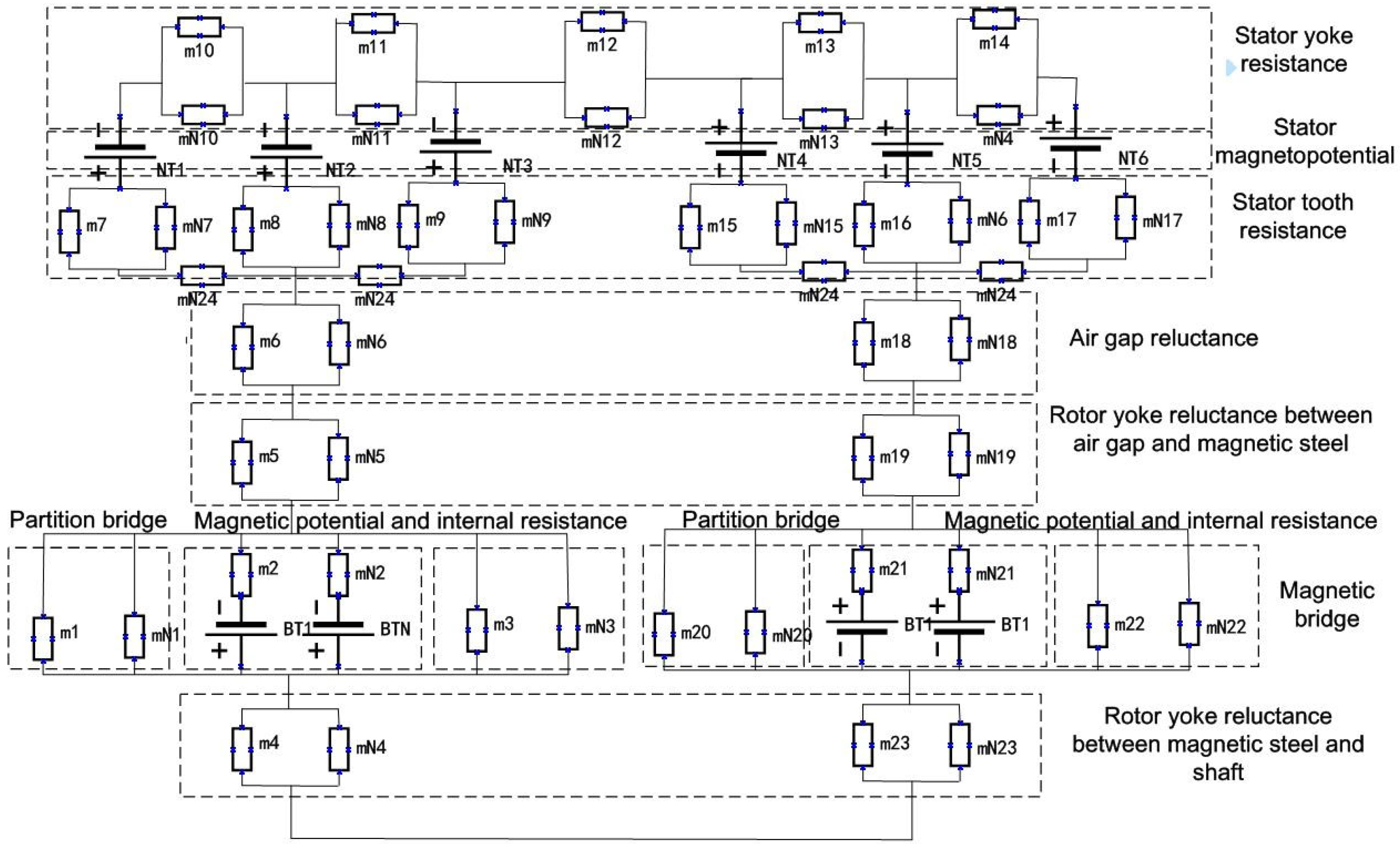
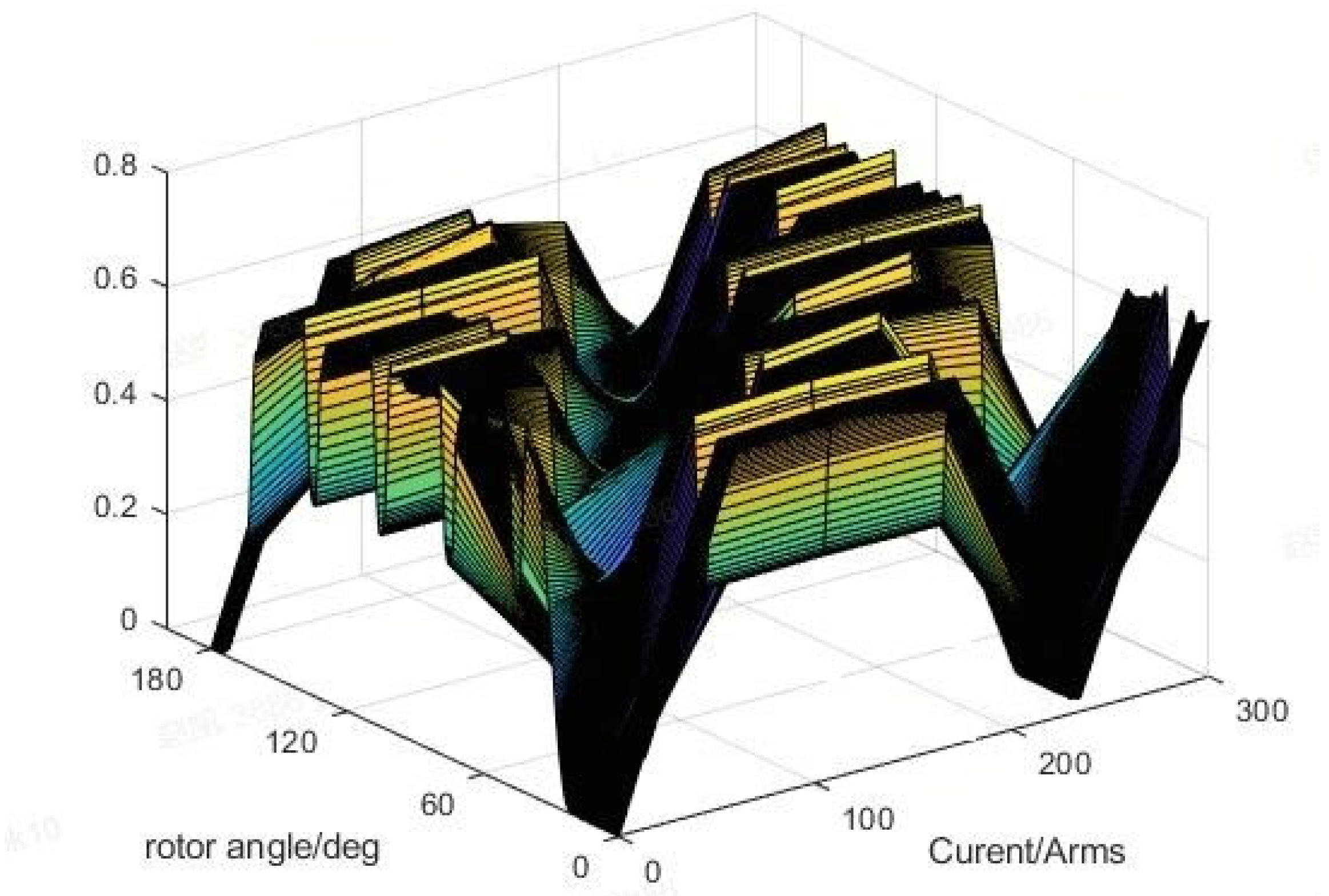
2.3. Distributed Flux Density
2.4. Distributed Electromagnetic Force Waves
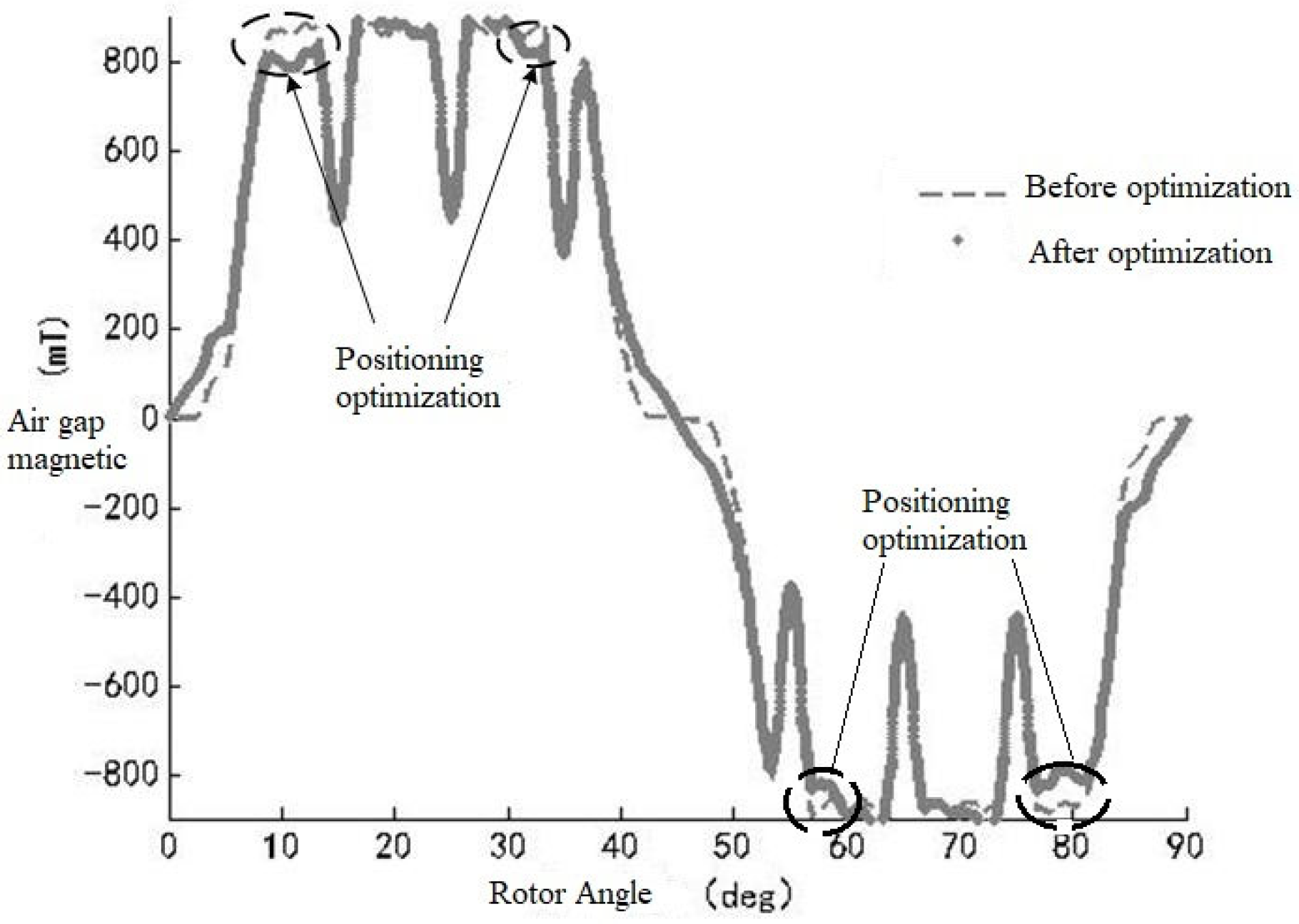
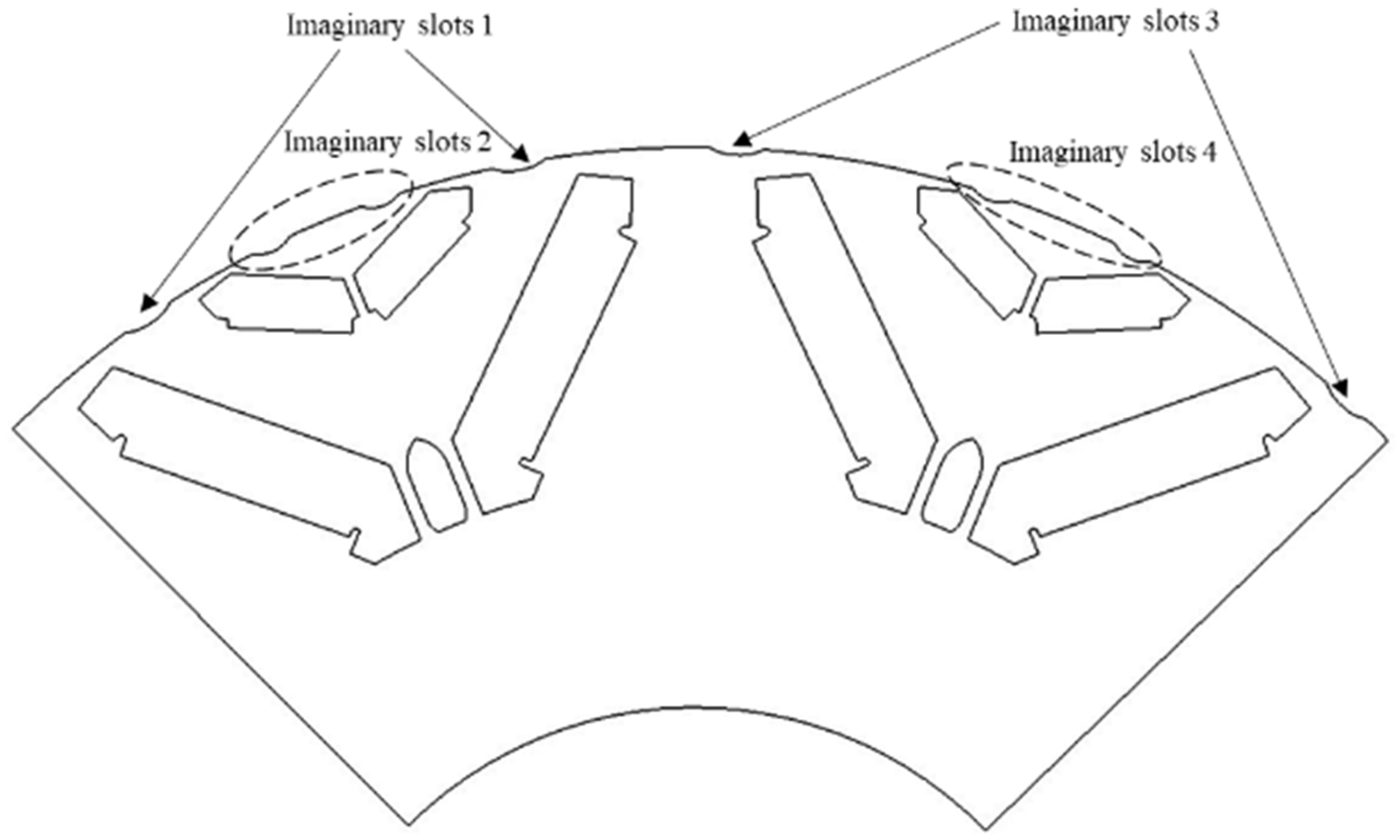
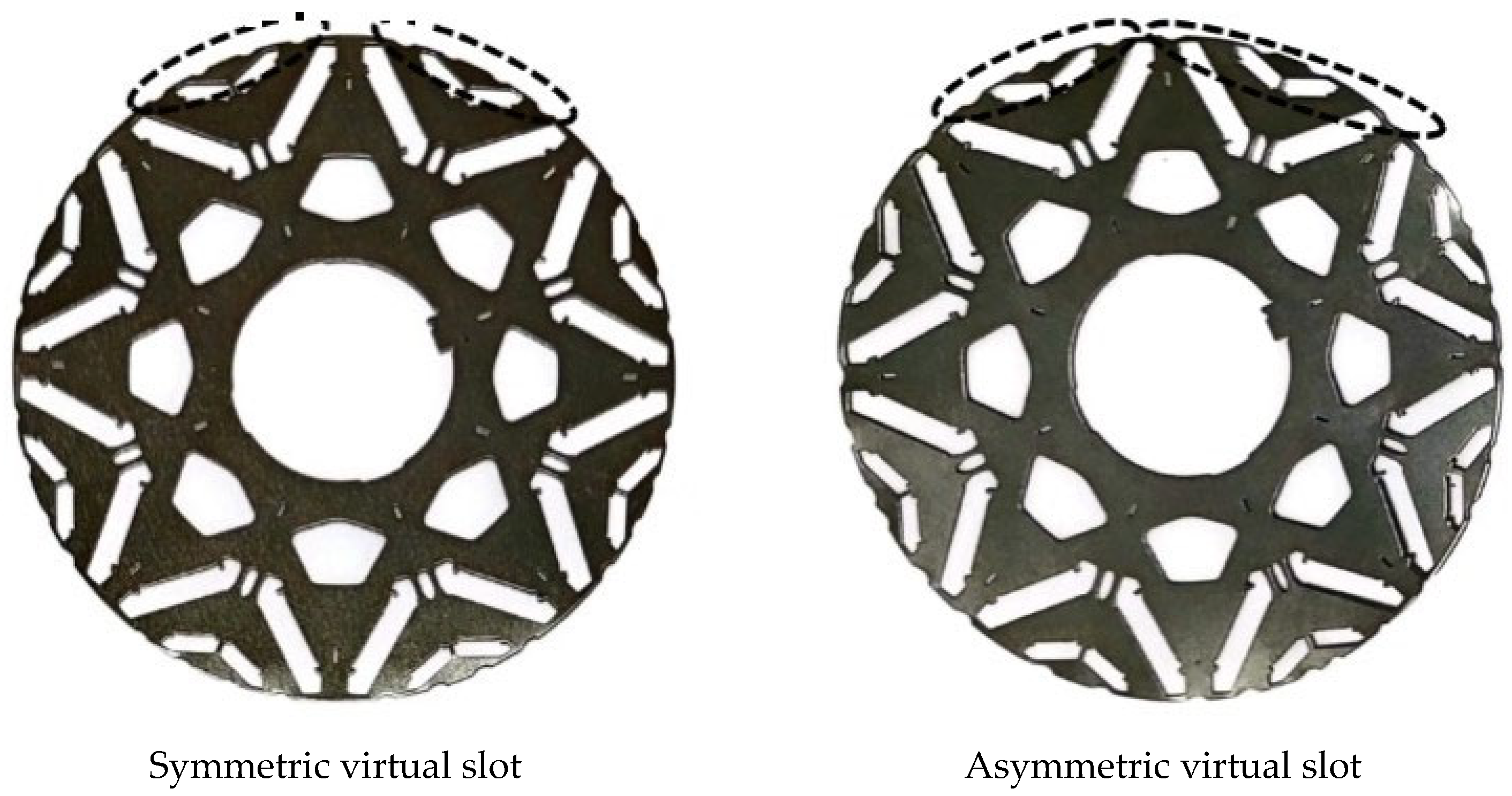
2.5. NVH Optimization
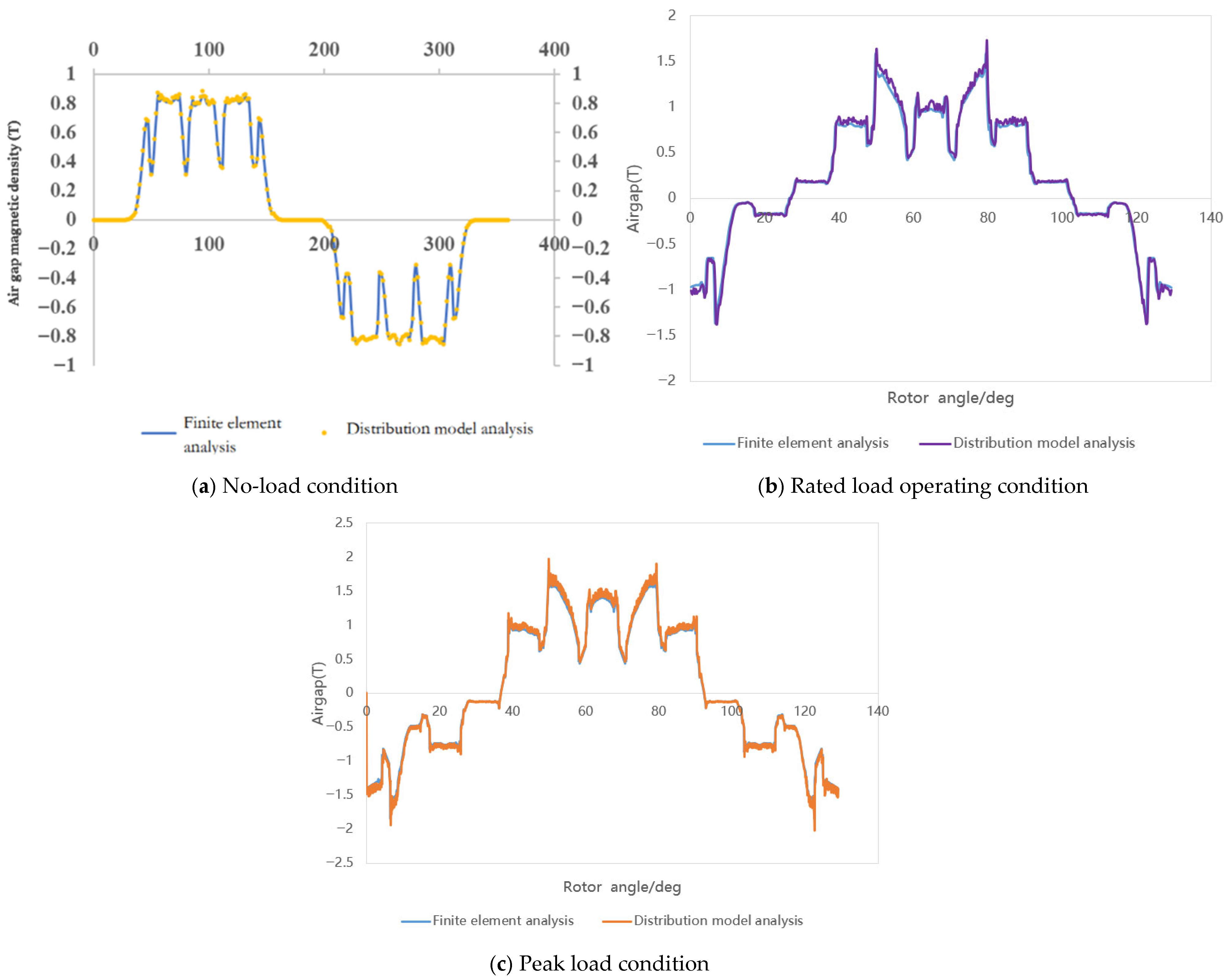
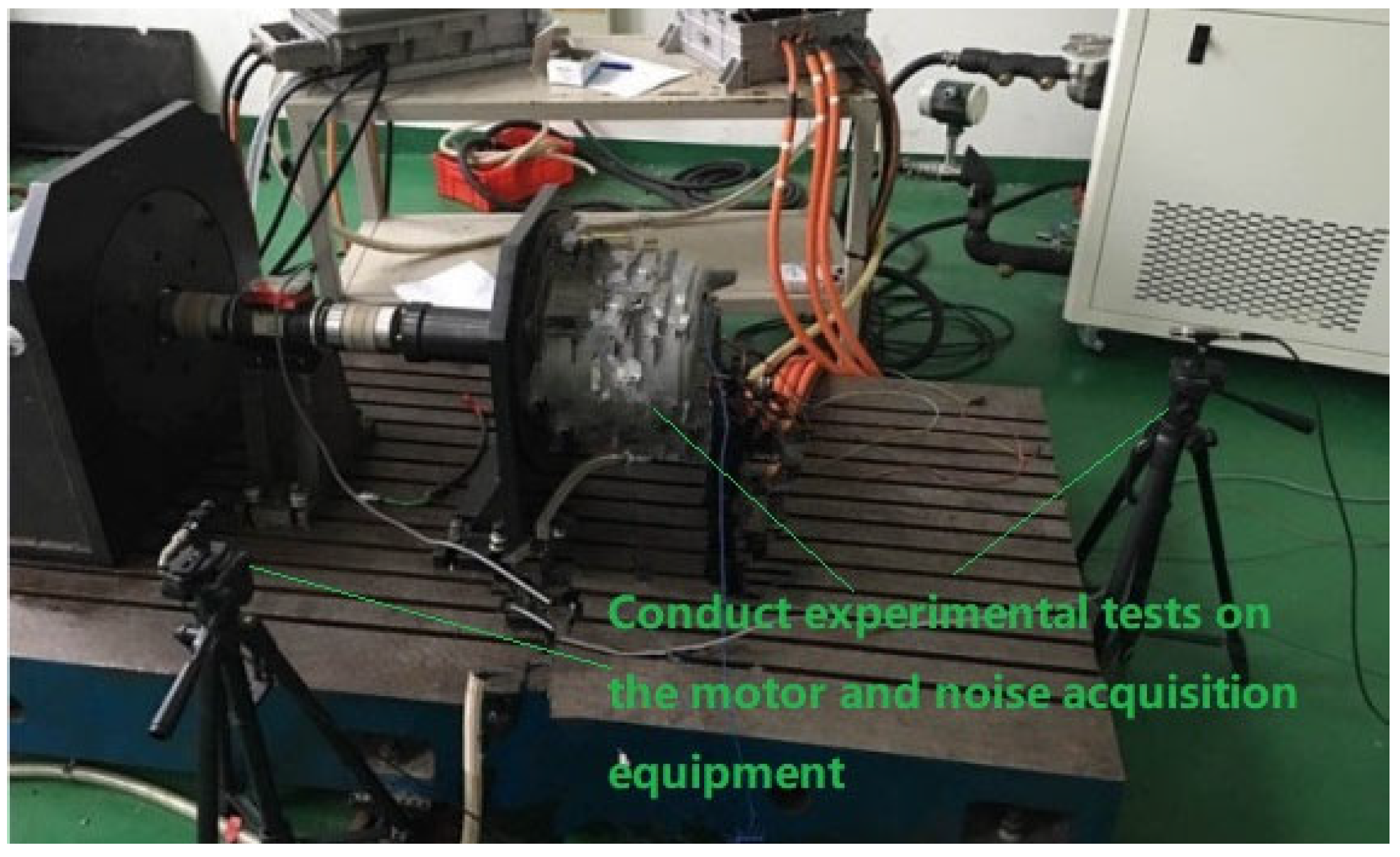
3. Experimental Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NVH | Noise, vibration and harshness |
| PWM | Pulse width modulation |
References
- Du, J.; Ouyang, M.; Wu, X.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Song, Z. Technological direction prediction for battery electric bus under influence of China’s new subsidy scheme. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bai, F.; Sun, J. Multi-objective optimization algorithm for optimizing NVH performance of electric vehicle permanent agnet synchronous motors. J. Power Electron. 2022, 22, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpinel, A.; Bouvet, P.; Dupont, J.B. NVH multiobjective and robust optimization of electric motor design, including power losses. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings, INTER-NOISE24, Nantes, France, 25–29 August 2024; Volume 270, pp. 7073–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, P.; Cao, C.; Hu, D.; Yan, X.; Song, Z. Acoustic simulation of the electric vehicle motor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2095, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, A.; Choi, S. Active current harmonic suppression for torque ripple minimization at open phase faults in a five-phase PMa-SynRM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Bang, T.K.; Jo, S.T.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, J.Y. A study on the shaft stability and prediction of electromagnetic and NVH characteristics of permanent magnet synchronous machine according to the different pole/slot combination. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 025121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Meng, D.; Su, H. Simulation, verification and optimization design of electromagnetic vibration and noise of permanent magnet synchronous motor for vehicle. Energies 2022, 15, 5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.F.; Liu, H.J.; Bu, B.B.; Zhang, Z.Y. Rapid calculation and optimization of vibration and noise of permanent-magnet synchronous motors for EVs based on equivalent structural network. Machines 2022, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.Z.; Wang, X.F.; Xiong, F.; Ye, C.Y. Reduction of torque ripple in a wound-rotor brushless doubly-fed machine by using the tooth notching. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaee, S.; Budgett, D.M.; Taberner, A.J.; Nielsen, P.M.F. Hyperelastic constitutive model parameters identification using optical-based techniques and hybrid optimisation. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2023, 20, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Huo, S.; Wang, G.; Sun, C.; Li, Z. A Node-Based Smoothed Finite Element Method (NS-FEM) for free and forced vibration analysis of Three-Dimensional (3D) structures. Int. J. Comput. Methods 2024, 22, 2342010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.B.; Kim, C.H.; Cha, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, S.Y. A novel method for establishing an efficiency map of IPMSMs for EV propulsion based on the finite-element method and a neural network. Electronics 2021, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soresini, F.; Barri, D.; Ballo, F.; Gobbi, M.; Mastinu, G. Noise and vibration modeling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A review. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 8728–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotma, L.; Purnama, H.; Purnomo, E.D.; Arifin; Nasril; Azka, M.; Sulistiyo, W.; Perkasa, M.; Marpaung, F.; Nugroho, E.A. Materials selection for low-cost manufacturing of electric motorcycle platform by using Finite Element Method (FEM) evaluation and Digital Logic Method (DLM). AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 3069, 020030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Design of a distributed hybrid model predictive controller based on long short-term memory networks model for hub-motor electric vehicle with air suspension. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Belahcen, A. Research on the performances and parameters of interior PMSM used for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3533–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Qu, R.H.; Ye, D.L.; Lu, H.X.; Sun, J.B.; Ge, M.; Xu, H.W. Electromagnetie force and vibration analysis of permanent-magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 4246–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Chu, Q.; Li, C.; Meng, T. Research on influence of motor parameters on the Negative-Salient Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2022, 6, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Ren, J.; Xing, Z.; Gu, X. Analysis of permanent magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motor based on equivalent reluctance network model. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2022, 6, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.D.; Zhang, G.Y.; He, Z.C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Gao, H. Motor magnetic field analysis using the alpha Finite Element Method (αFEM). Int. J. Comput. Methods 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levent, A.H.; Lordoglu, A.; Aydeniz, M.G. Design and optimization of permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Izmir, Turkey, 20–23 October 2020; pp. 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre-Daniel, P.; Yin, X.; Fang, Y.T. Slotted Permanent-Magnet Machines: General analytical model of magnetic fields, torque, eddy currents, and Permanent-Magnet power losses including the diffusion effect. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; An, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, S.; Yin, X.; Lu, H. 3-D analytical model and direct measurement method of Ultra-Thin Open-Circuit Air-Gap field of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor with multi-segmented skew poles and multi-layered flat wire windings for electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Dai, S.; Wu, S.; Tang, R. Performance comparison between an amorphous metal PMSM and a silicon steel PMSM. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.L.; Kim, D.W.; Song, J.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Design of 100 kW propulsion motor for electric conversion vehicle based on vehicle driving performance simulation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Busan, Republic of Korea, 1–4 June 2016; pp. 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdyck, D.; Belmans, R.J.M. An acoustic model for a permanent magnet machine: Modal shapes and magnetic forces. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1994, 30, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Zhao, W.L. Research on weakening measure of radial electromagnetic force waves in permanent magnet synchronous motors by inserting auxiliary slots. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
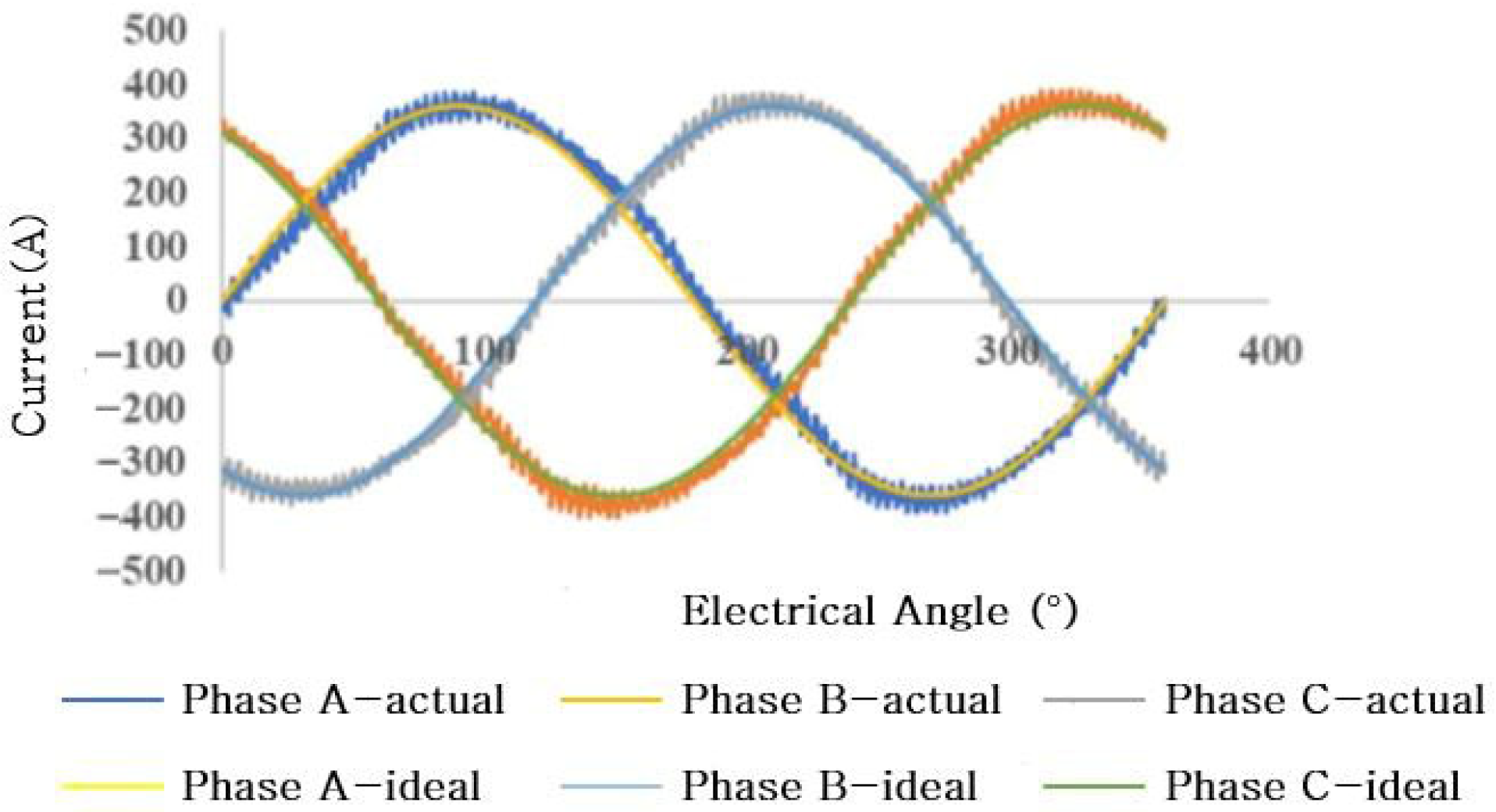
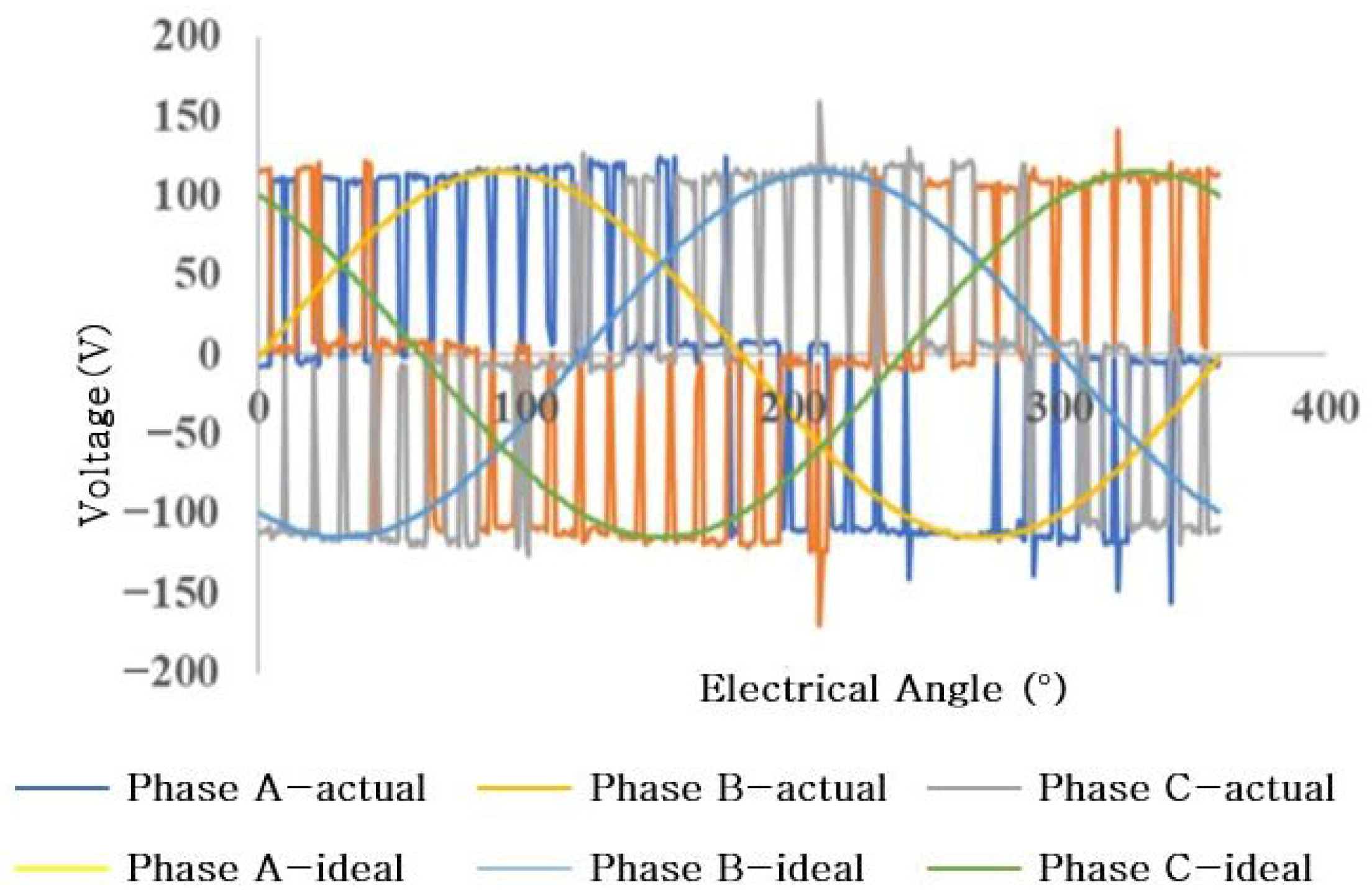
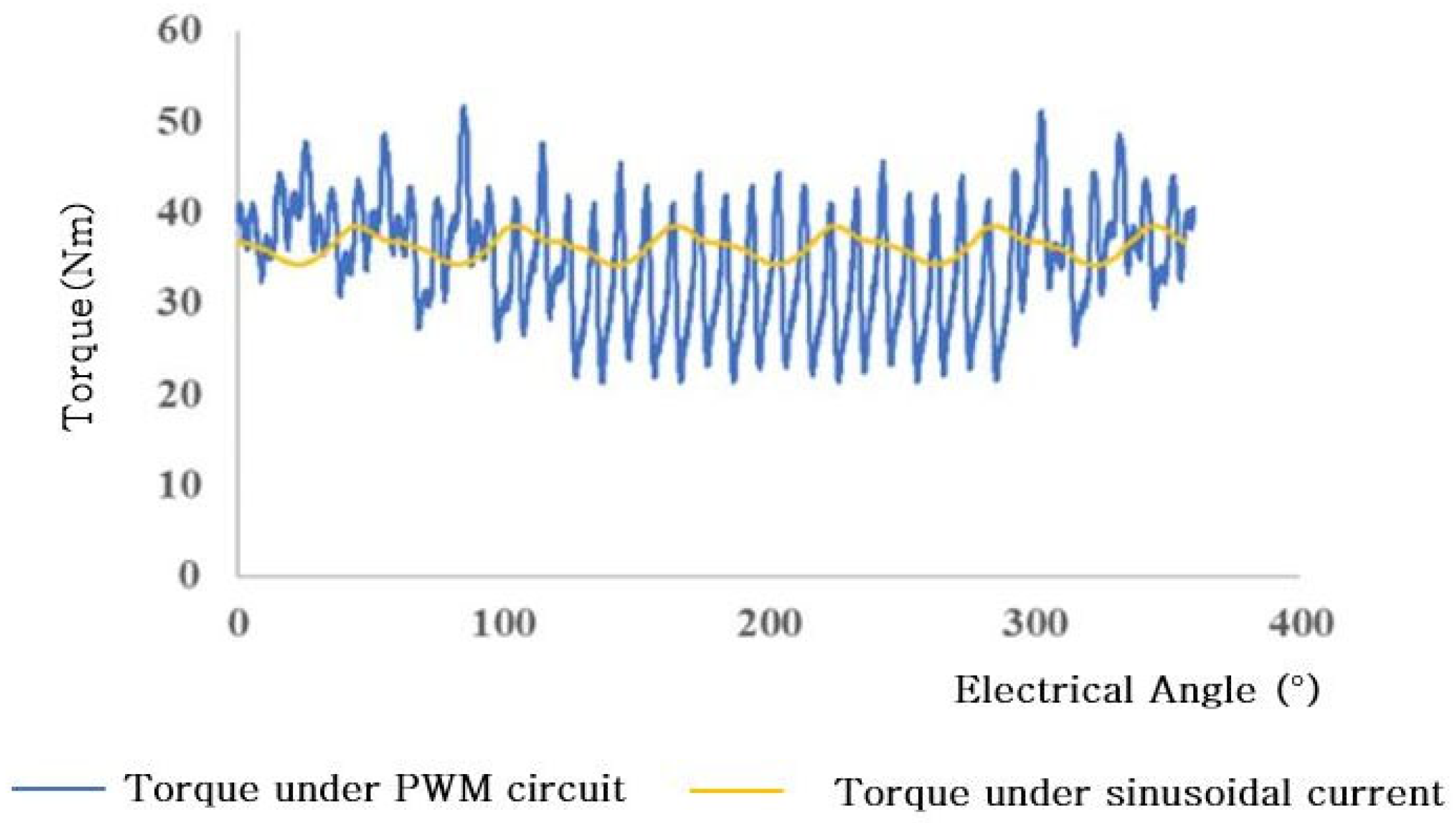
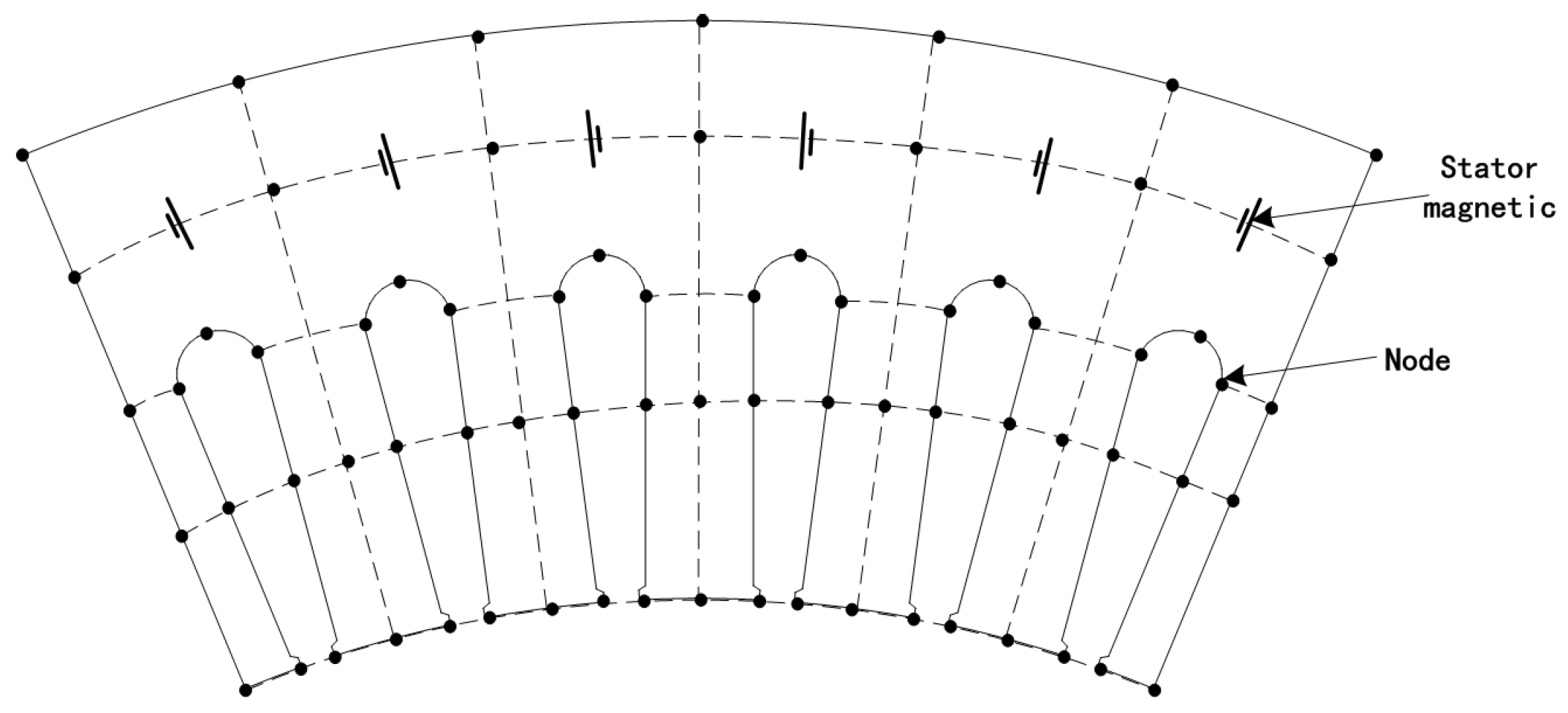



| Technical Indicators | Match Results |
|---|---|
| Maximum Torque (Nm) | 100 |
| Rated Torque (Nm) | 50 |
| Peak Power (kW) | 30 |
| Rated Power (kW) | 15 |
| Maximum Speed (rpm) | 10,000 |
| Rated Speed (rpm) | 3000 |
| Time of Simulation (s) | Time of Distributed Model (s) | The Amplitude Deviation of the Two Methods (T) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No load | 180 | 10 | 0.04 |
| Rated load | 200 | 12 | 0.06 |
| Peak load | 200 | 12 | 0.1 |
| Order | Single Symmetrical Imaginary Slot | Combined Asymmetrical Imaginary Slots | Polar Groove Fit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The no-load air gap magnetically dense | 5/7 | 3.2%/2.2% | 1.6%/1.7% | 8P48 |
| 11/13 | 1.6%/1.5% | 0.5%/0.4% | 8P48 | |
| 15/17 | 1.0%/0.8% | 0.3%/0.4% | 8P48 | |
| 23/25 | 0.6%/0.4% | 0.8%/0.7% | 8P48 | |
| The 4500 rpm peak torque harmonic order | 24 | 3623 | 2971 | 8P48 |
| 48 | 2532 | 1899 | 8P48 | |
| 96 | 1219 | 1377 | 8P48 | |
| 40 | 823 | 428 | 8P48 | |
| 56 | 516 | 186 | 8P48 | |
| 64 | 423 | 110 | 8P48 | |
| 40 | 768 | 310 | 6P54 | |
| 56 | 588 | 130 | 6P54 | |
| 64 | 398 | 79 | 6P54 | |
| The 8500 rpm peak power harmonic order | 24 | 1545 | 1267 | 8P48 |
| 48 | 4531 | 3398 | 8P48 | |
| 96 | 825 | 932 | 8P48 | |
| 40 | 521 | 313 | 8P48 | |
| 56 | 362 | 188 | 8P48 | |
| 64 | 265 | 245 | 8P48 | |
| 40 | 550 | 232 | 6P54 | |
| 56 | 392 | 188 | 6P54 | |
| 64 | 314 | 187 | 6P54 |
| fr r Magnetic Flux Density Harmonic Order | fr = (μ +1) f | fr = (μ − 1) f | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (μ + v) p | (μ − v) p | ||
| fr | μ/v | μ/v | |
| 2f | 1/1 | 3/1 | |
| 4f | 3/−5 | 5/7 | |
| 8f | 7/−5 | 9/7 | |
| 10f (40th) | 9/−11 | 11/13 | |
| 14f (56th) | 13/−11 | 15/13 | |
| 16f (64th) | 15/−17 | 17/19 | |
| 20f | 19/−17 | 21/19 | |
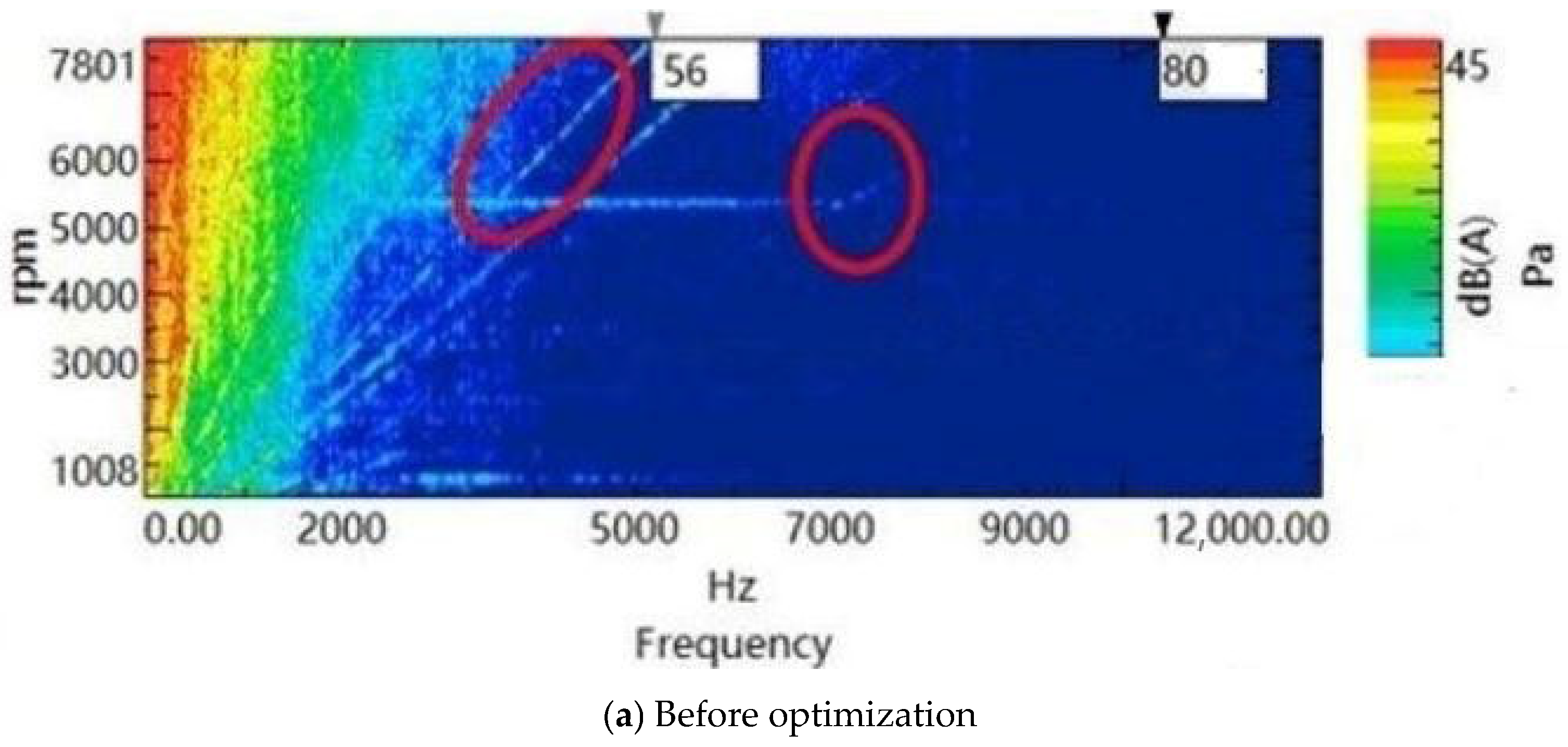
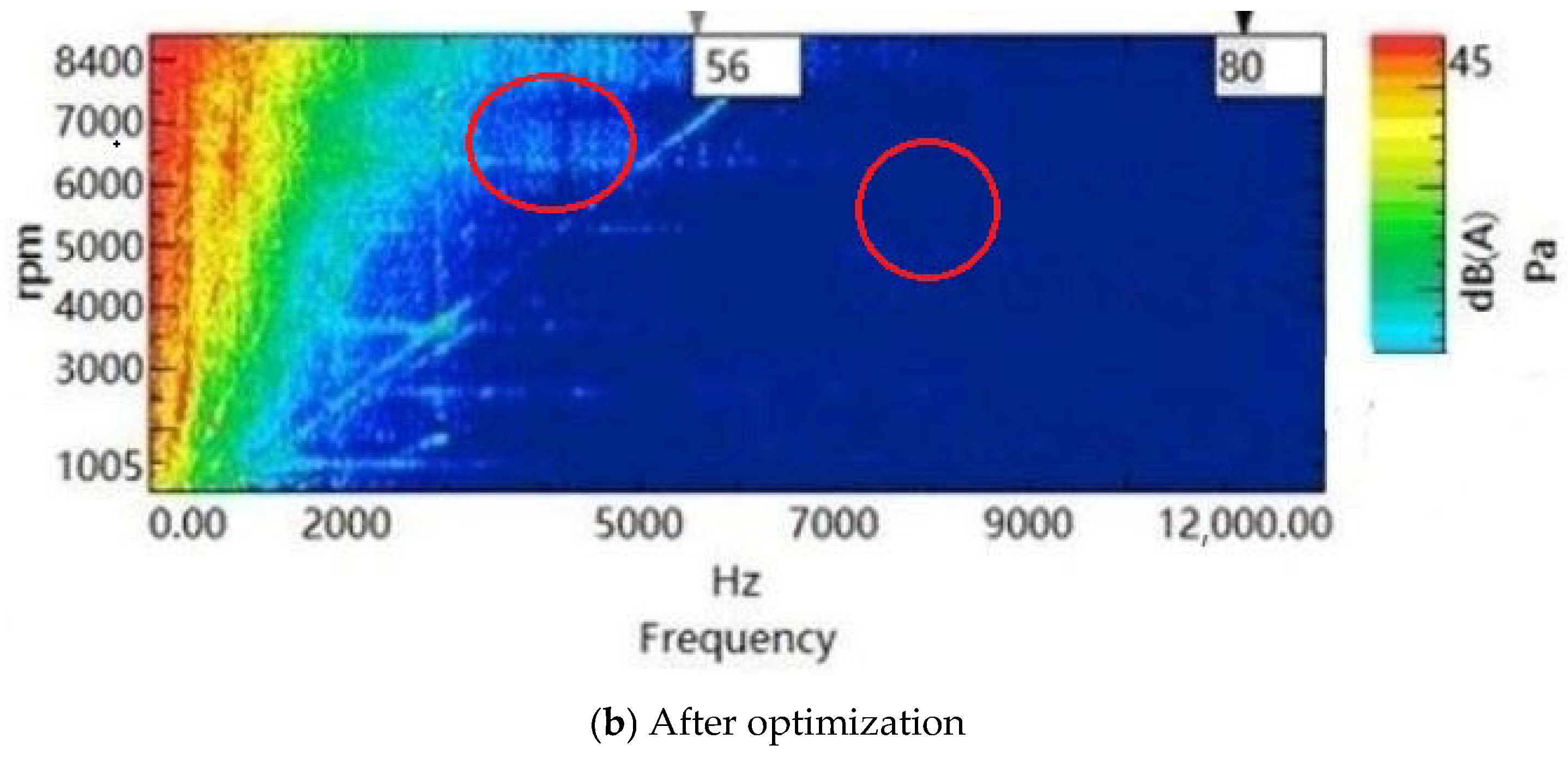
| Before Optimization (dB) | After Optimization (dB) | Reduce Value | Test Accuracy Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noise value | 50 | 40 | 10 dB | 2% |
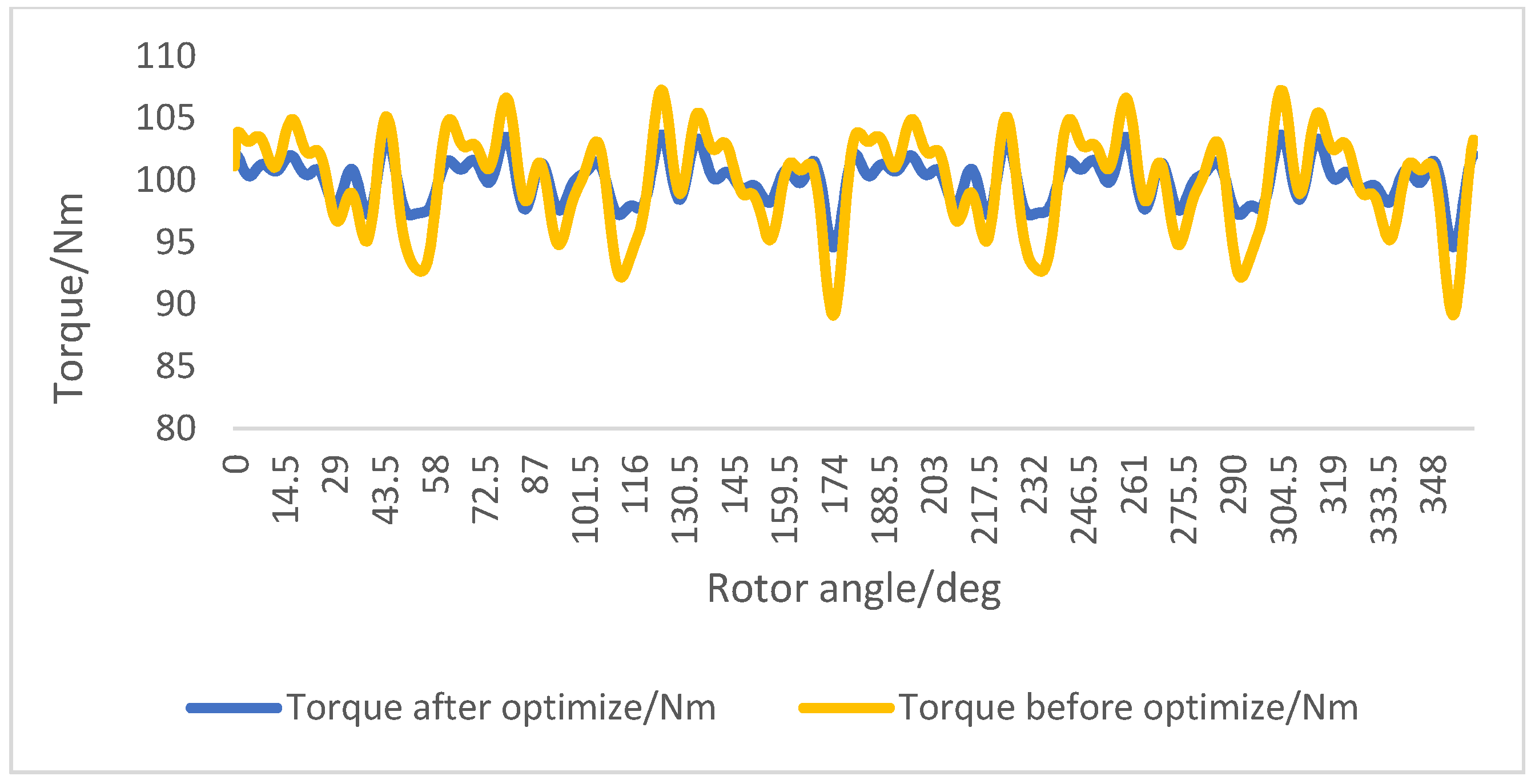
| Torque ripple | 10% | 5% | 5% | 2% |
| 8f | 7/−5 | 9/7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, K.; Jin, Z.; Luo, J. NVH Optimization of Motor Based on Distributed Mathematical Model Under PWM Control. Energies 2025, 18, 5395. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205395
Zhao K, Jin Z, Luo J. NVH Optimization of Motor Based on Distributed Mathematical Model Under PWM Control. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5395. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205395
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Kai, Zhihui Jin, and Jian Luo. 2025. "NVH Optimization of Motor Based on Distributed Mathematical Model Under PWM Control" Energies 18, no. 20: 5395. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205395
APA StyleZhao, K., Jin, Z., & Luo, J. (2025). NVH Optimization of Motor Based on Distributed Mathematical Model Under PWM Control. Energies, 18(20), 5395. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205395






