Modelling of Selected Algorithms for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Photovoltaic Panels
Abstract
1. Introduction
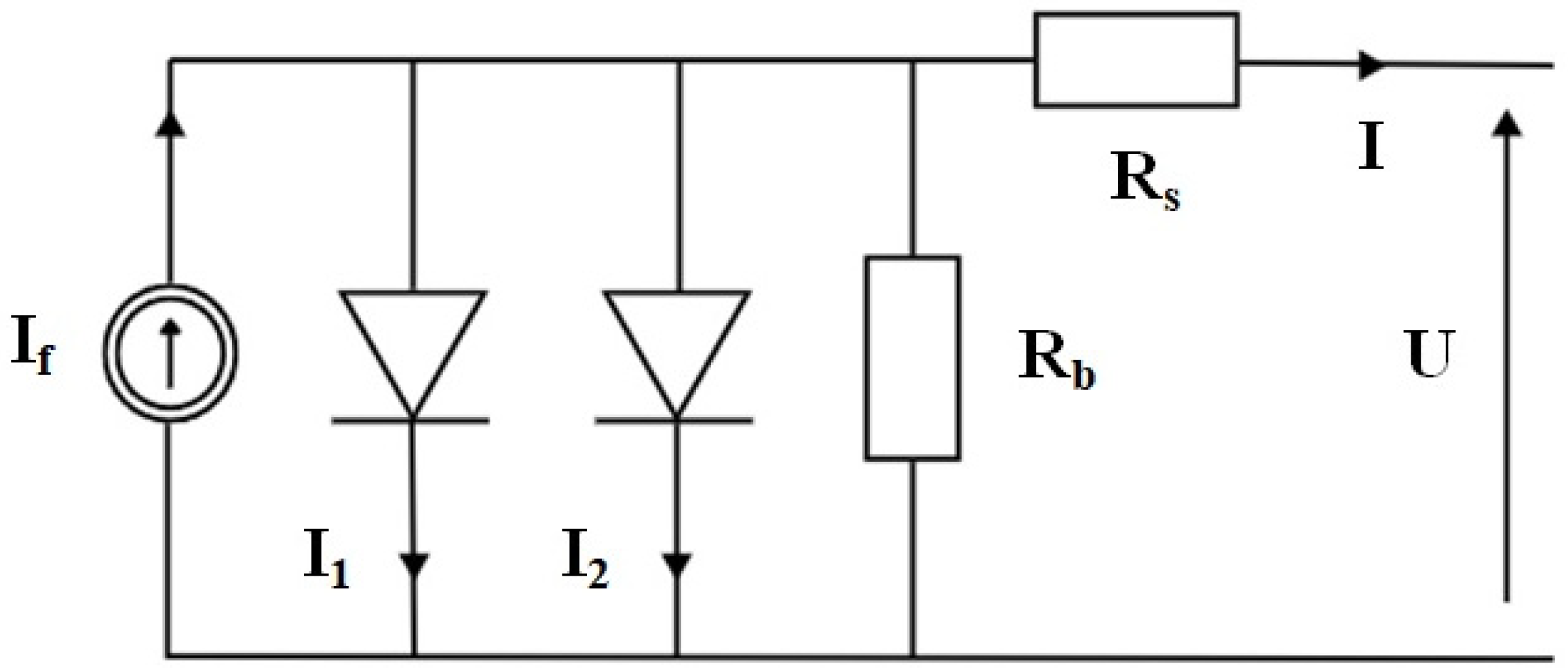
1.1. Electrical Diagram and Mathematical Model of a Photovoltaic Cell
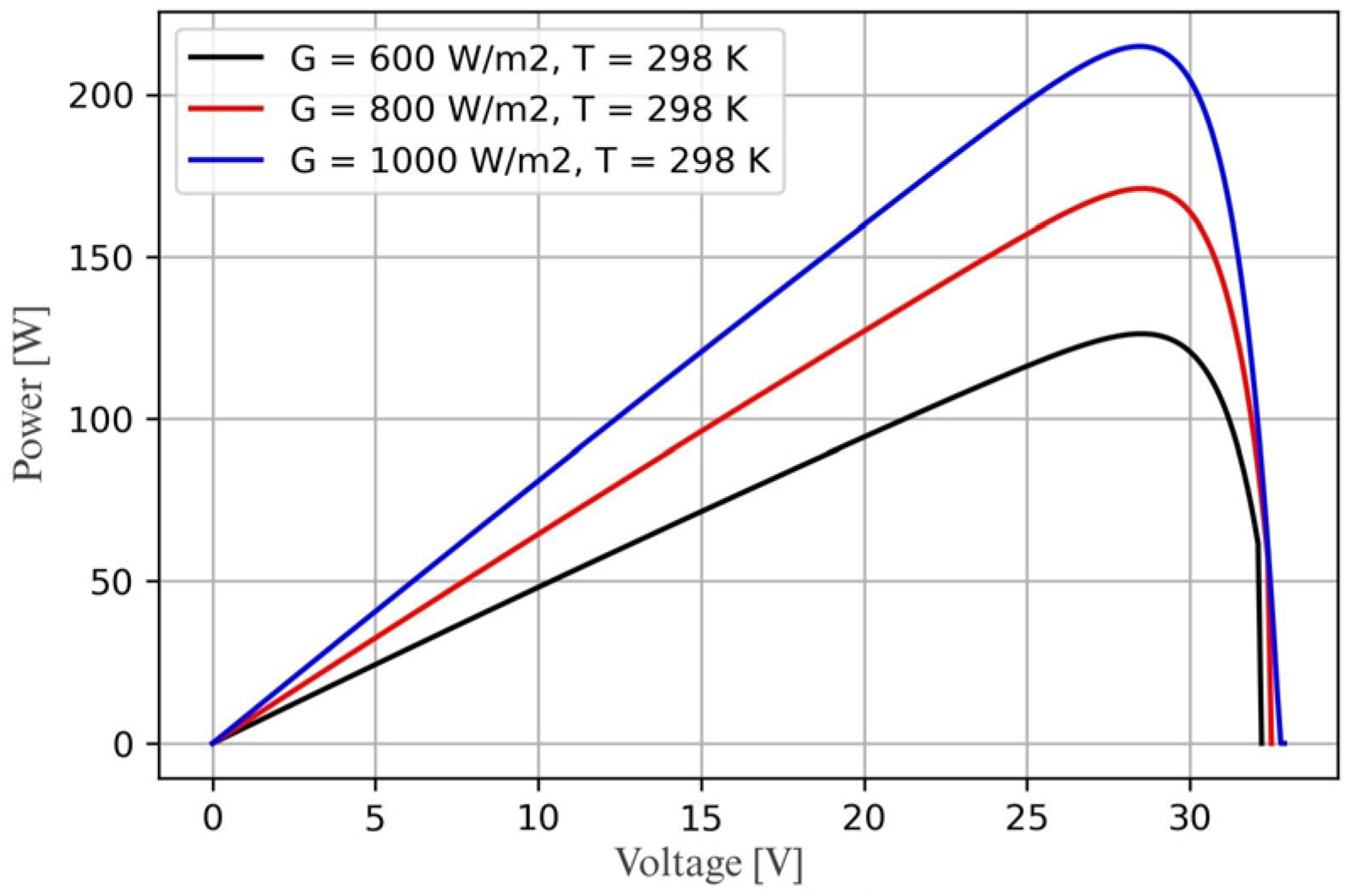
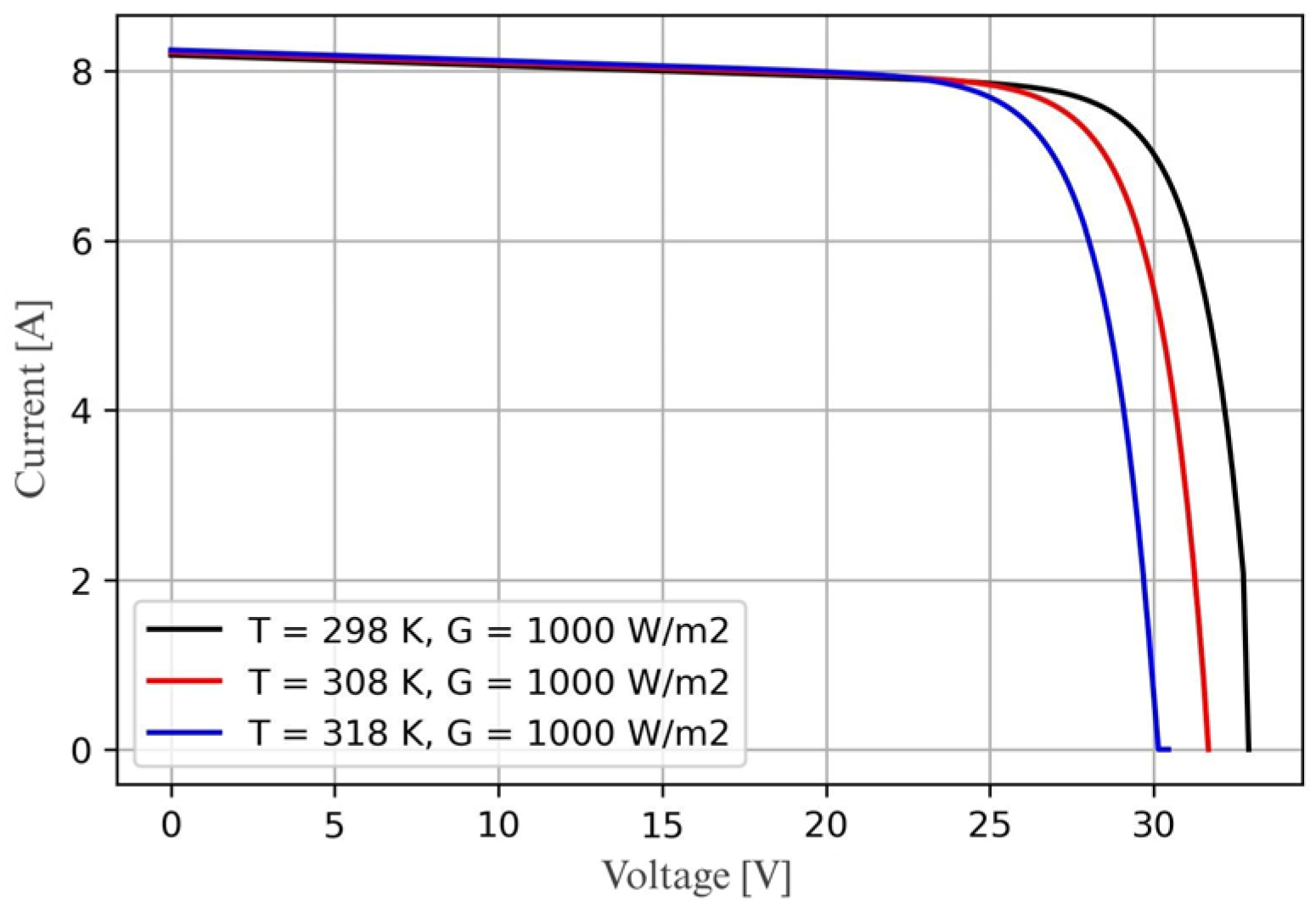
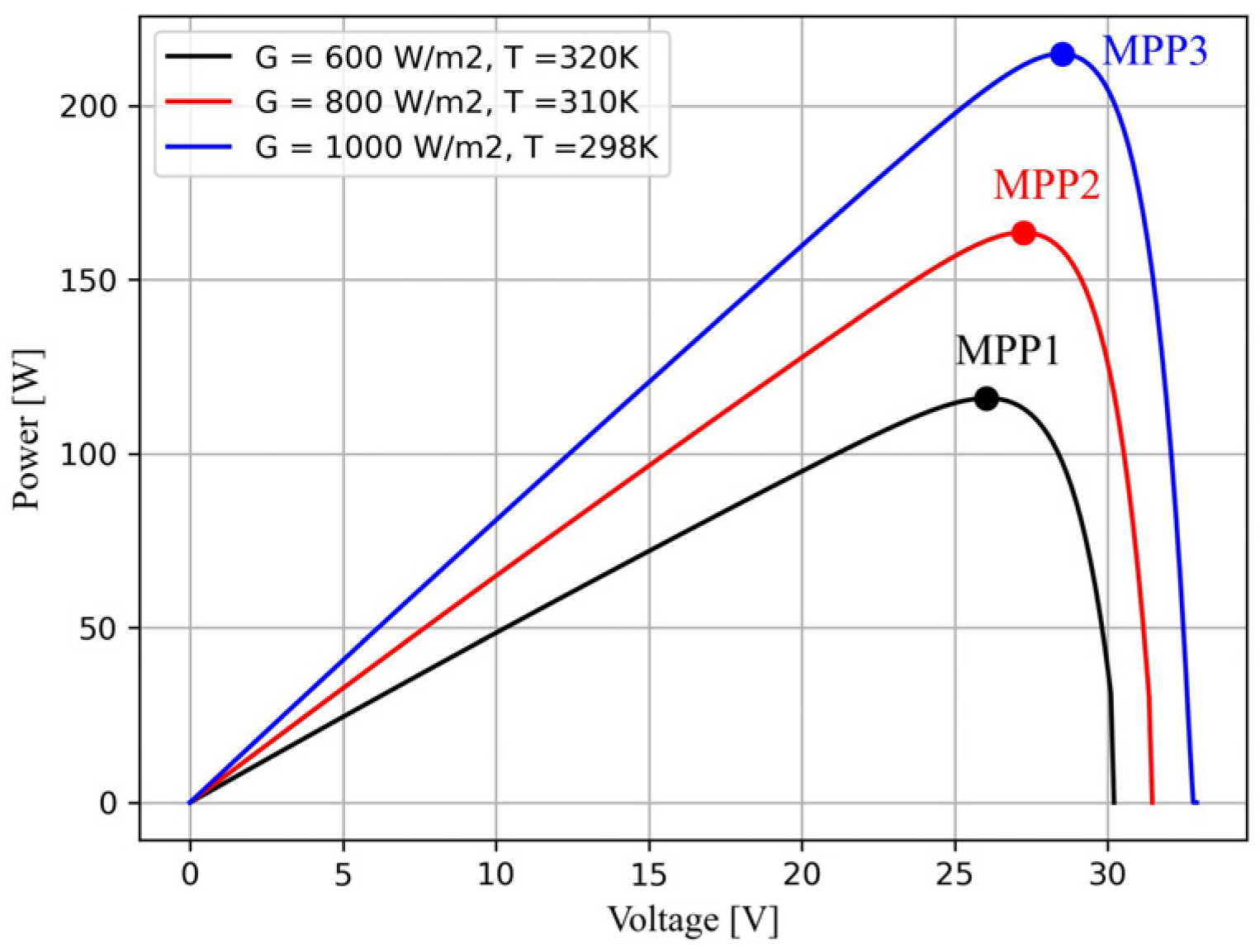
1.2. Photovoltaic Panel Performance Characteristics
1.3. Maximum Power Point Tracking of Photovoltaic Panels
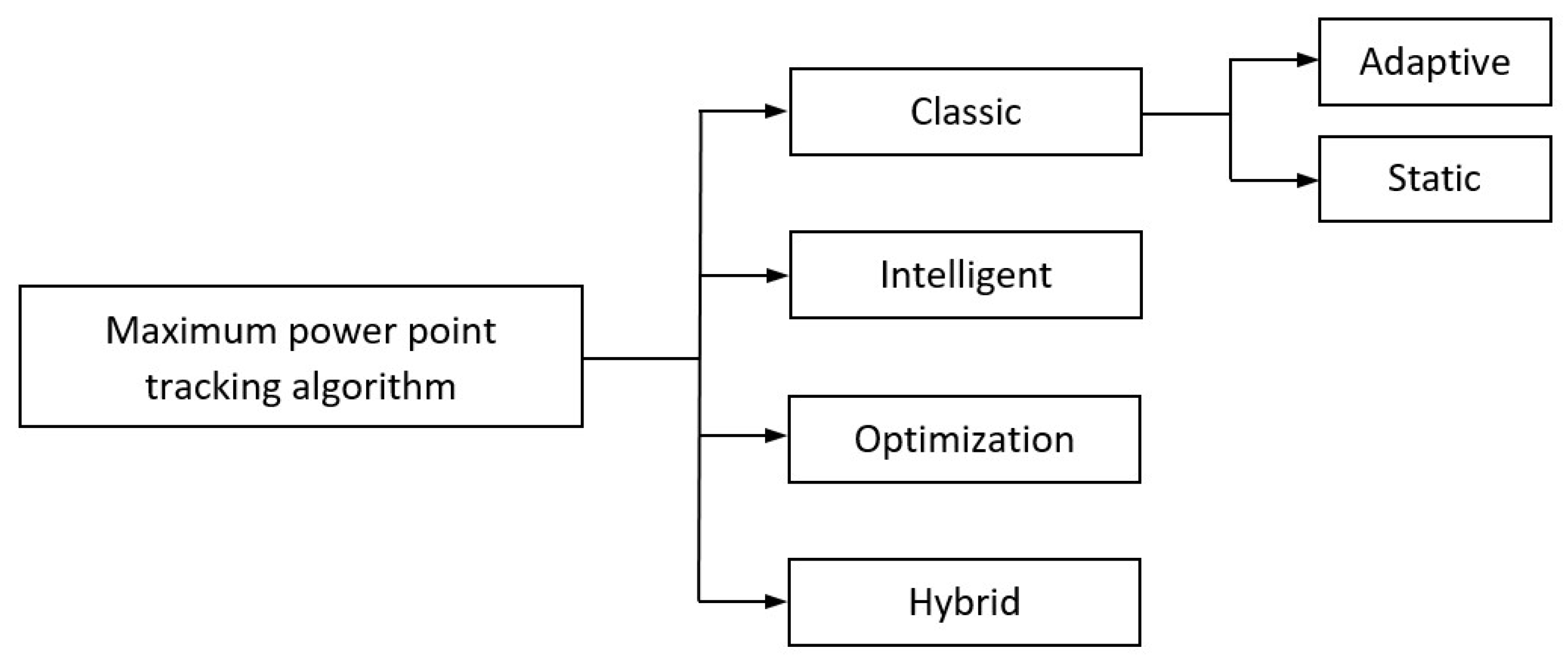
1.4. Classification of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Classical Algorithms
2.1.1. Methods Based on Open-Circuit Voltage Measurement
2.1.2. Table Lookup Method
2.1.3. Curve Fitting Method
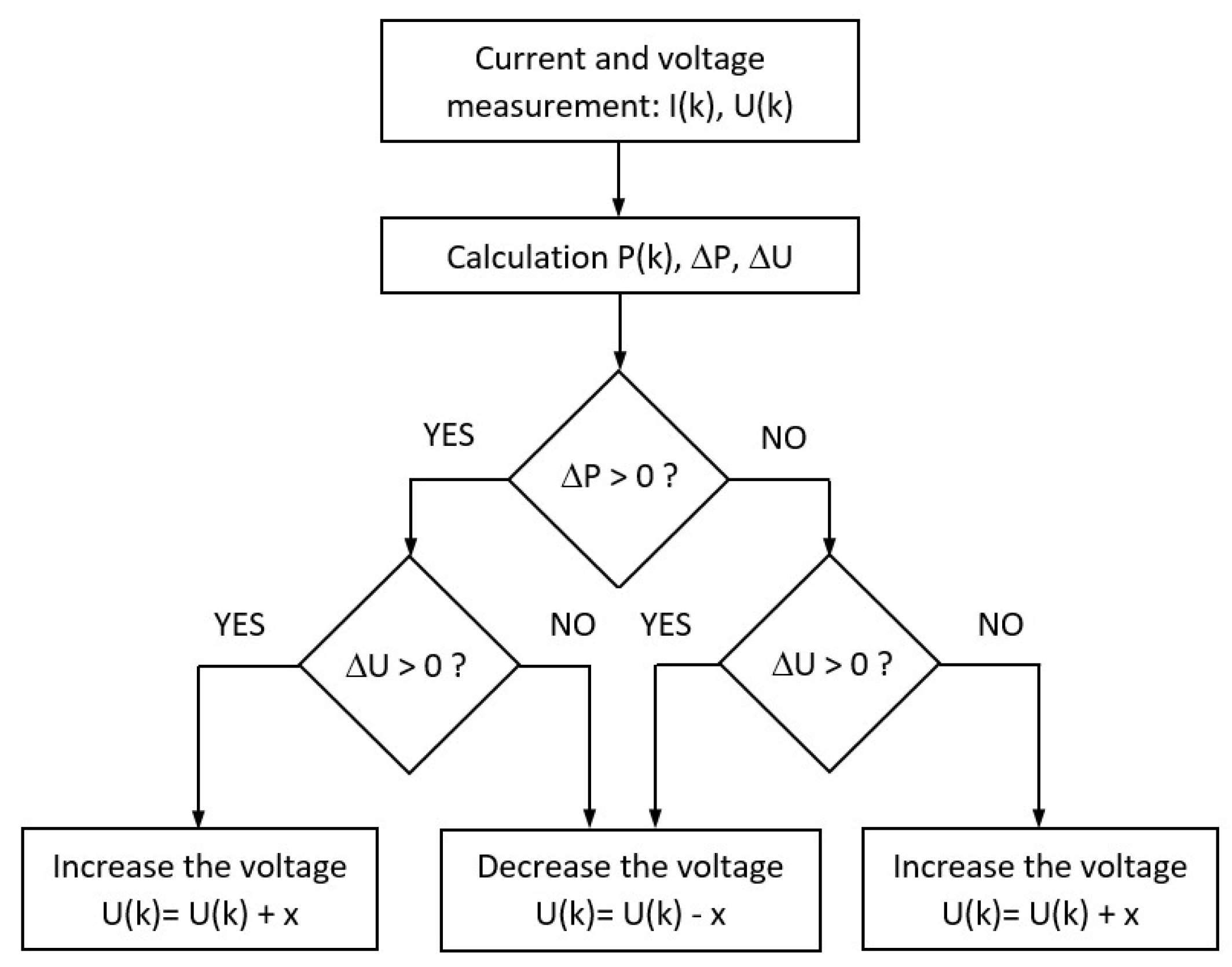
2.1.4. Perturb and Observe Algorithm (P&O Algorithm)
2.1.5. Method of Incremental Conductance
2.2. Optimisation Algorithms
2.2.1. PSO Algorithm
2.2.2. The Grey Wolf Optimisation (GWO) Algorithm
2.3. Intelligent Algorithms
2.3.1. An Algorithm Employing Fuzzy Logic
2.3.2. Algorithms Using Artificial Intelligence
2.4. Hybrid Algorithms
3. Results and Discussion—Simulation and Comparative Analysis of Selected Algorithms
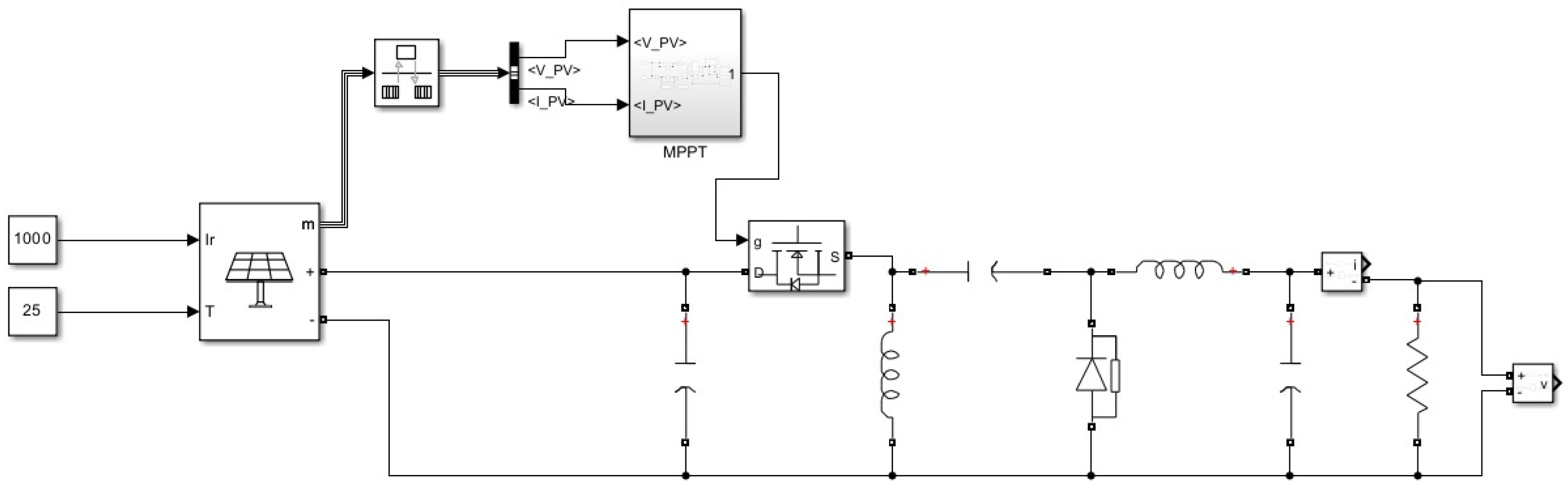
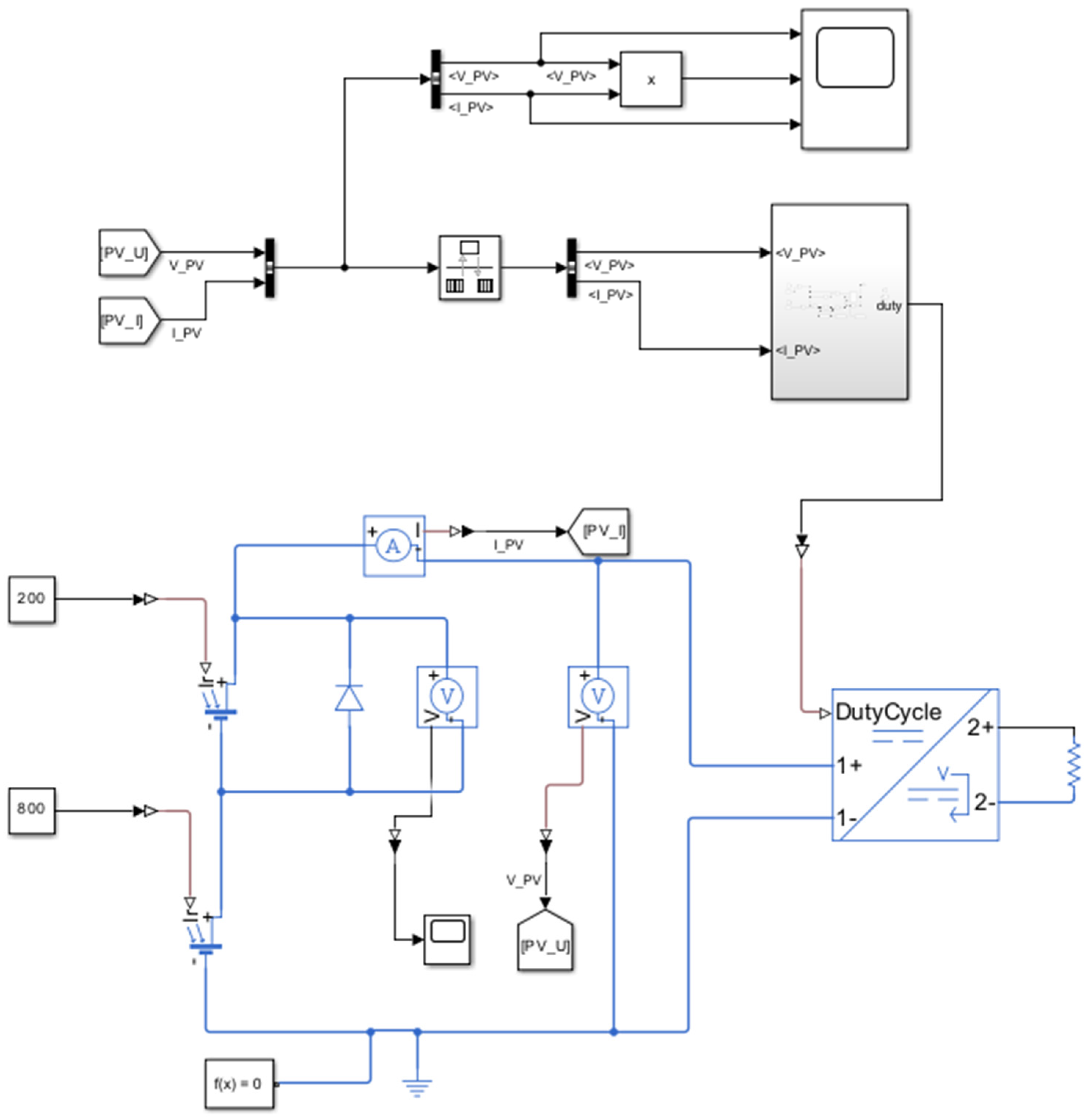
3.1. Diagram of the System Used in the Simulation
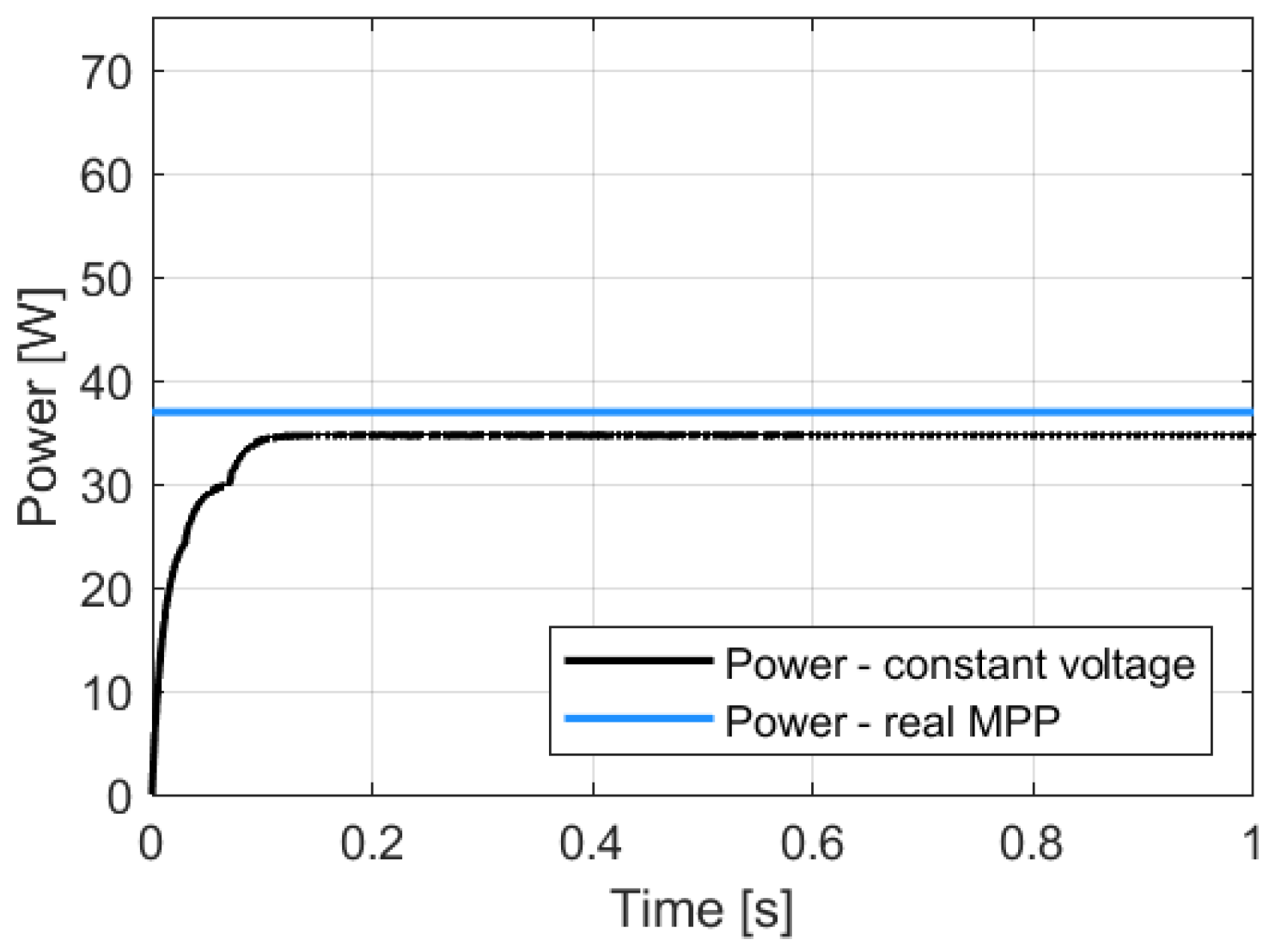
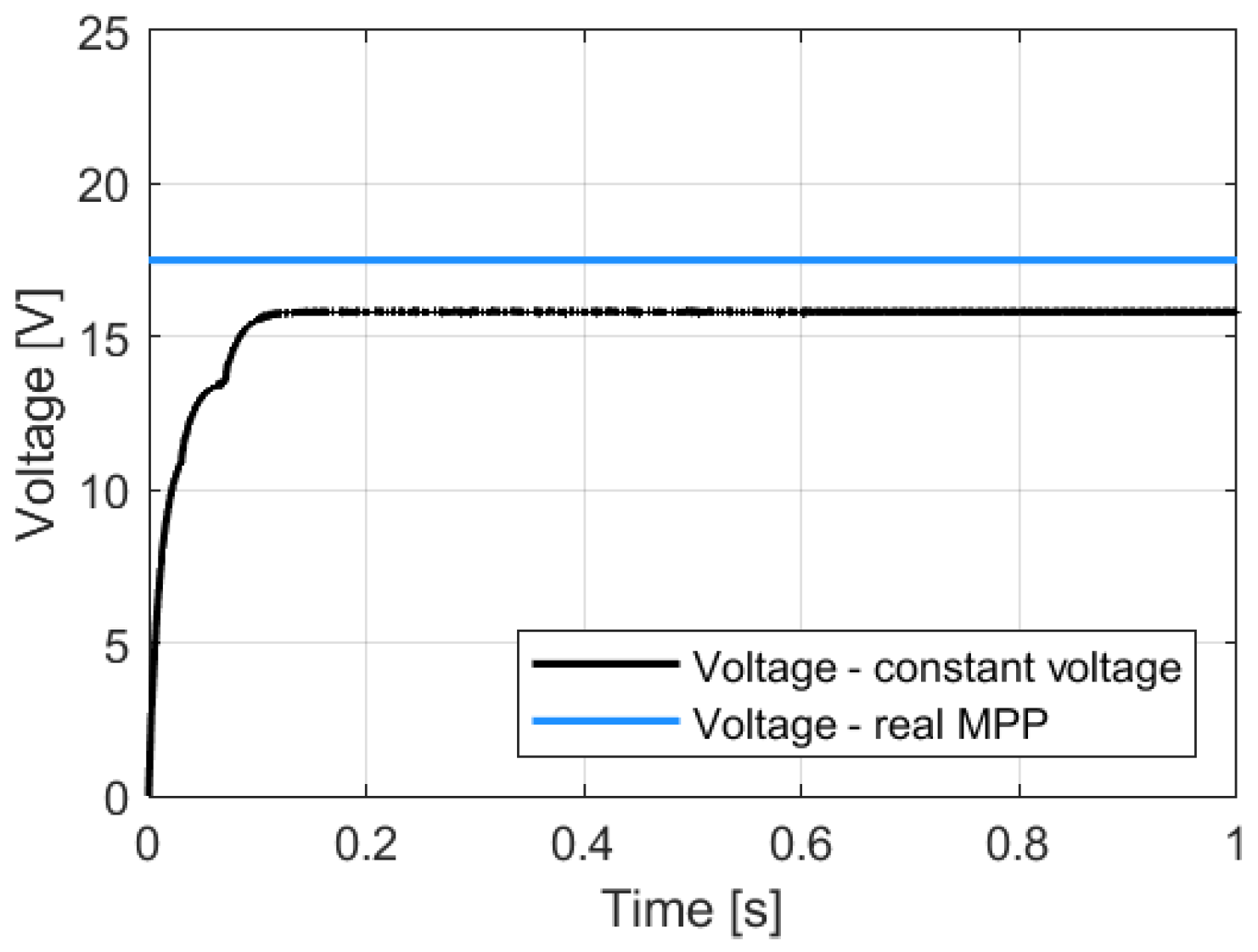
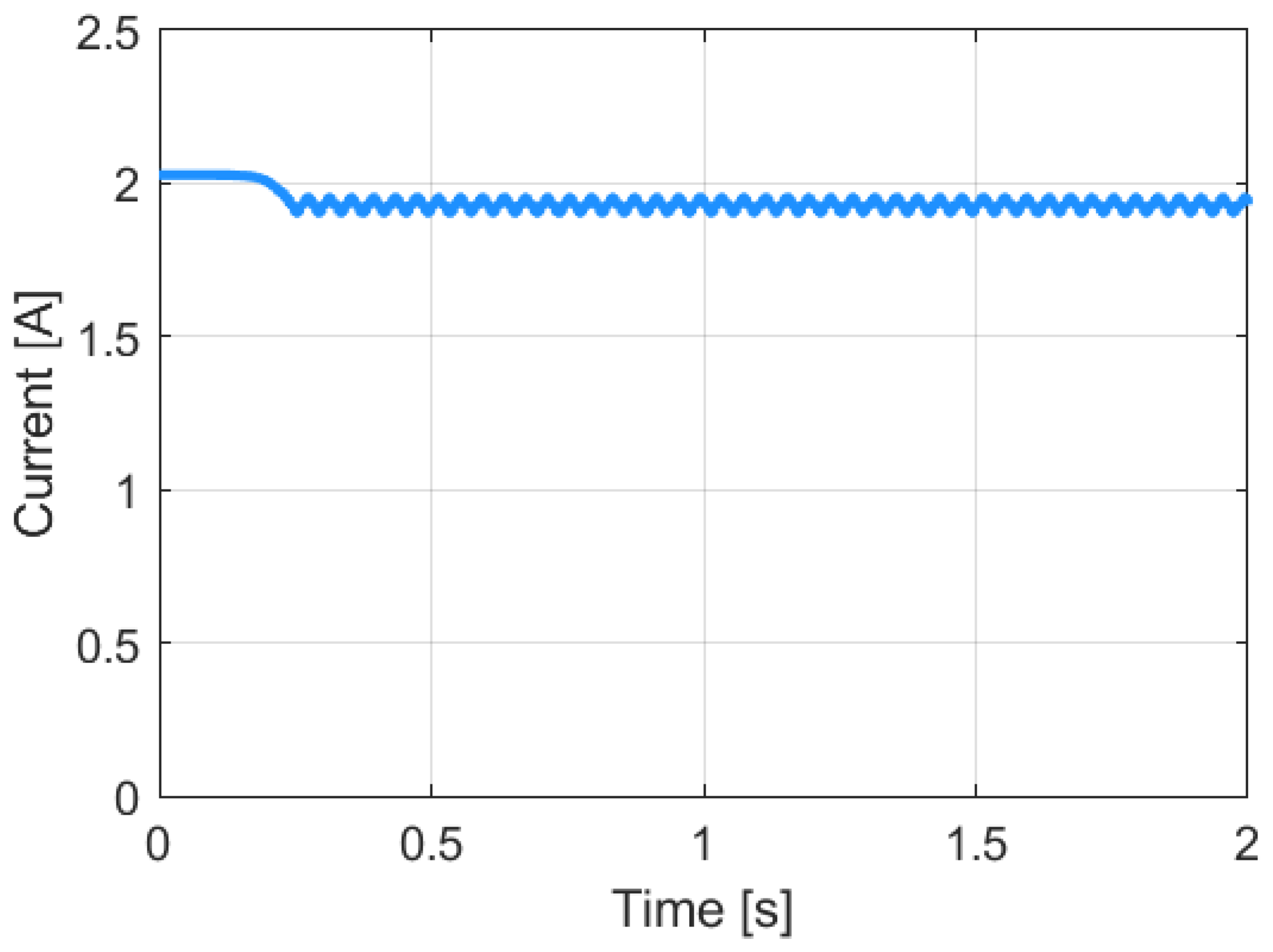
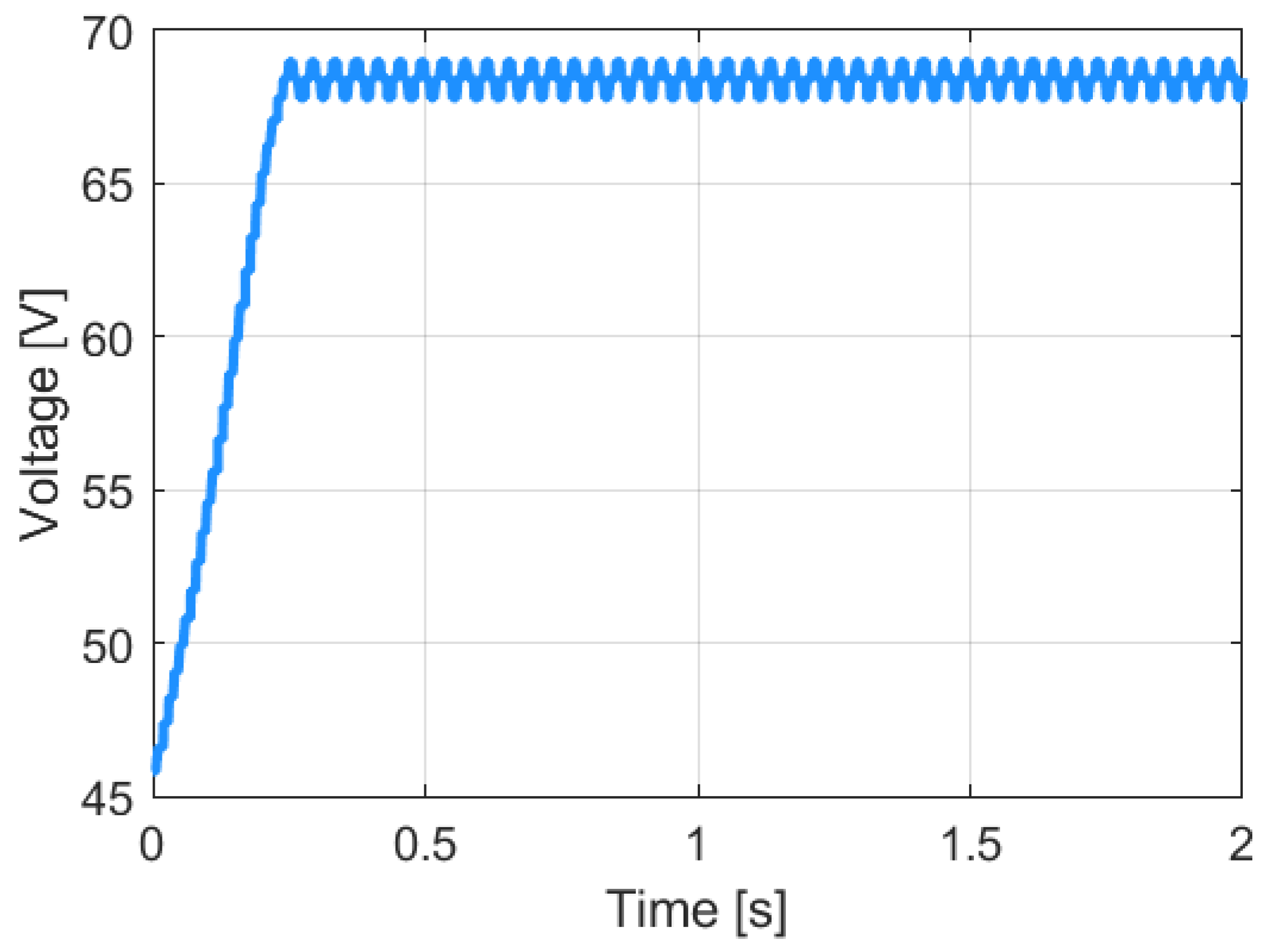
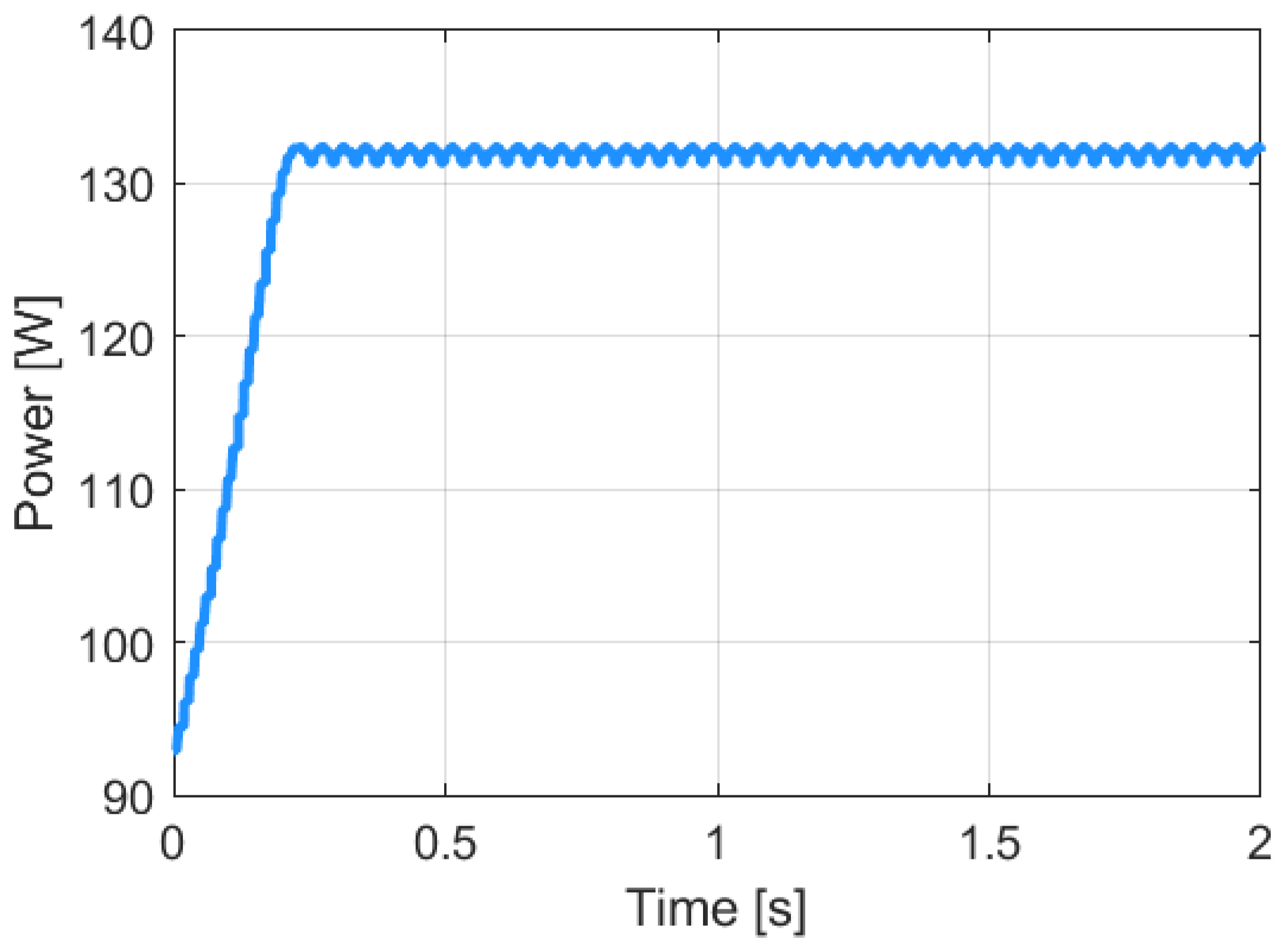
3.2. Simulation of the Operation of the Constant Voltage Algorithm
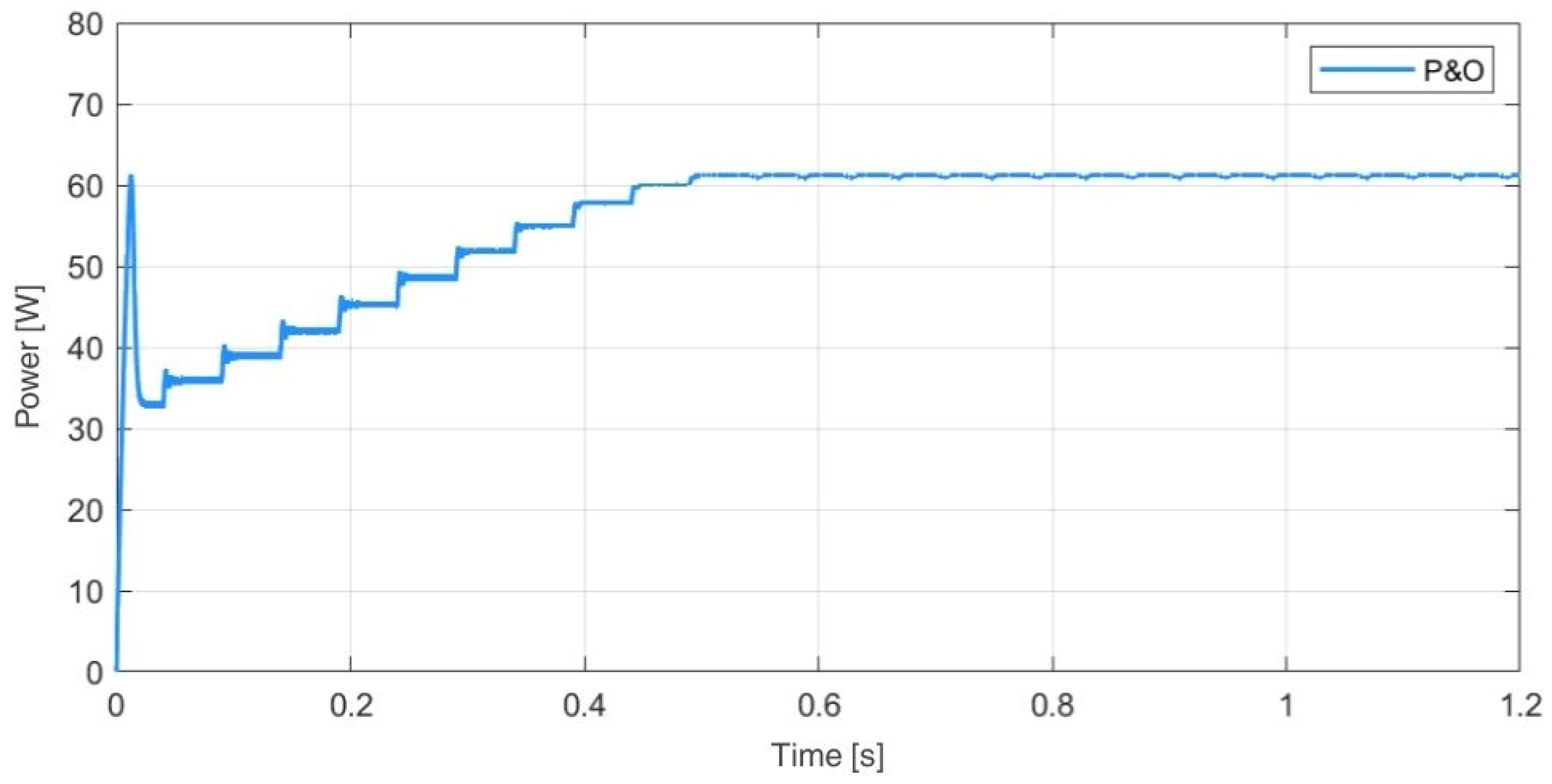
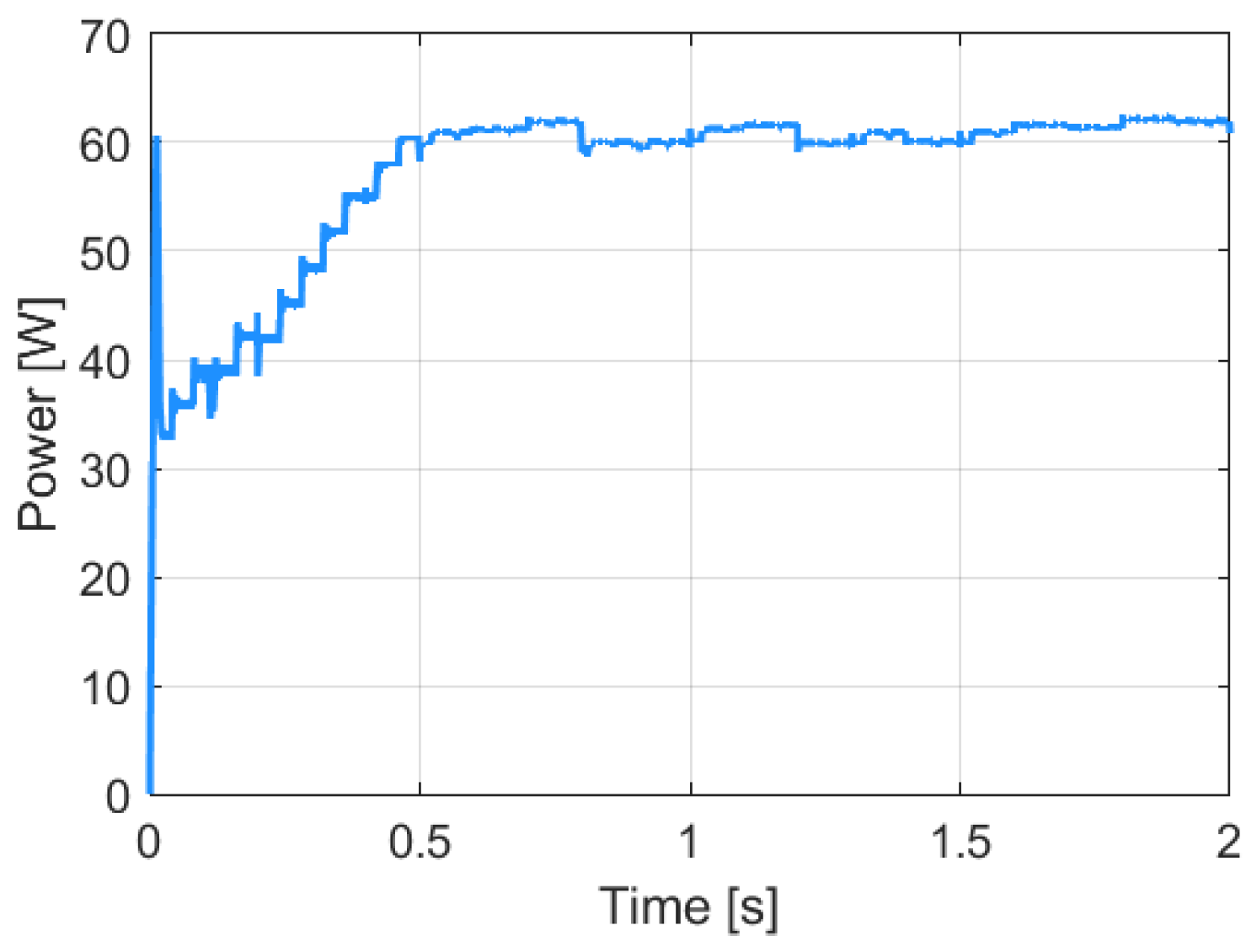
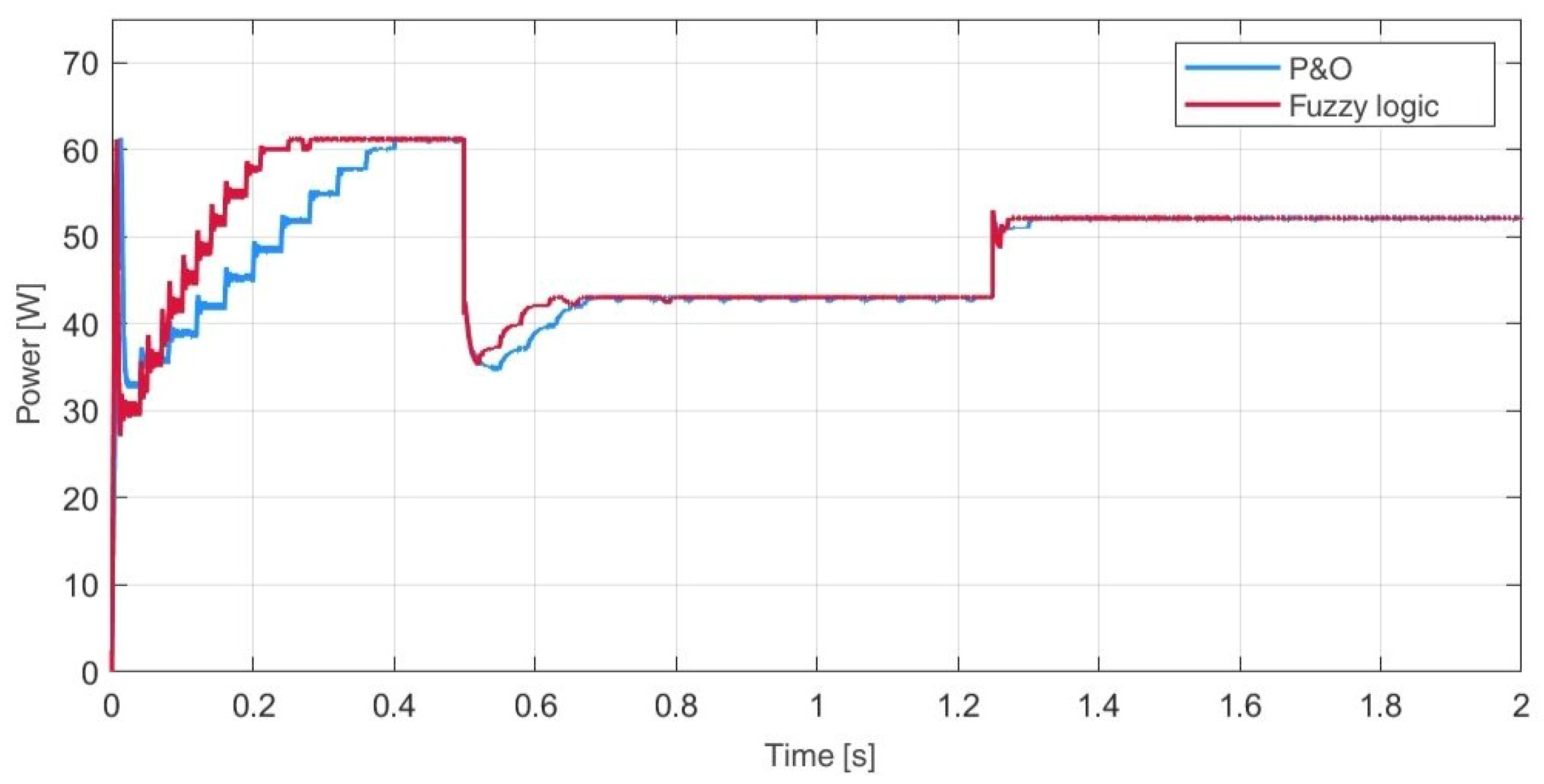
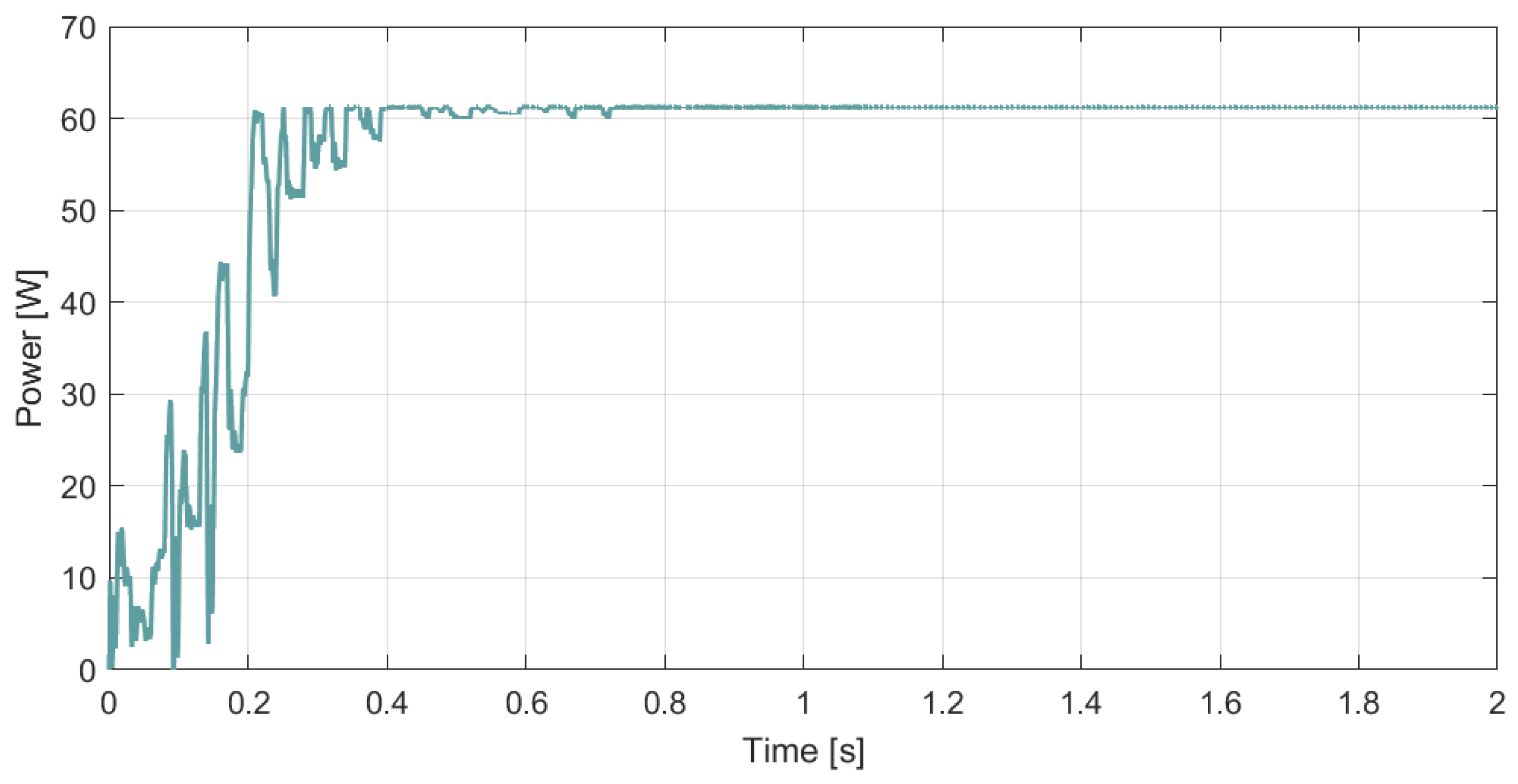
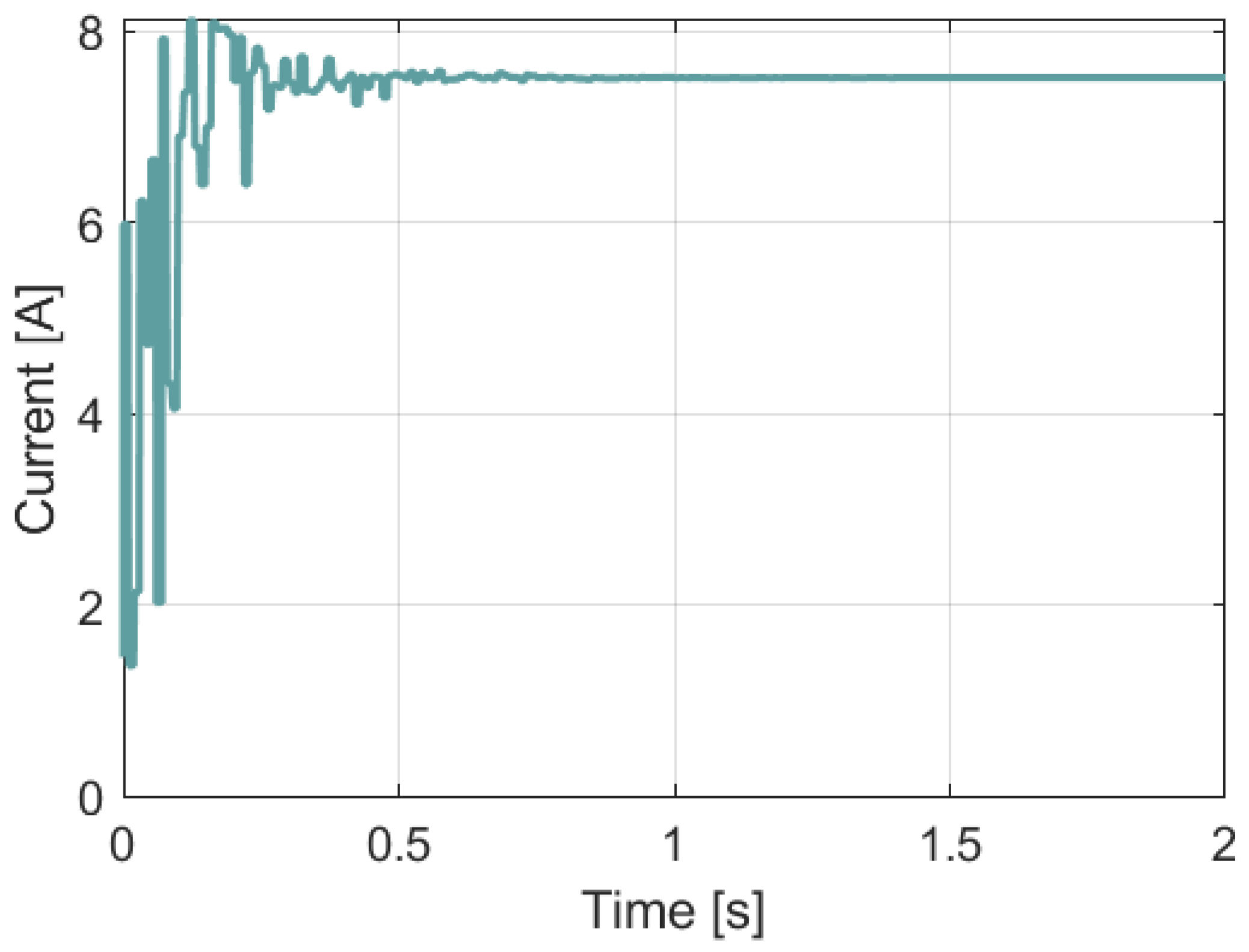
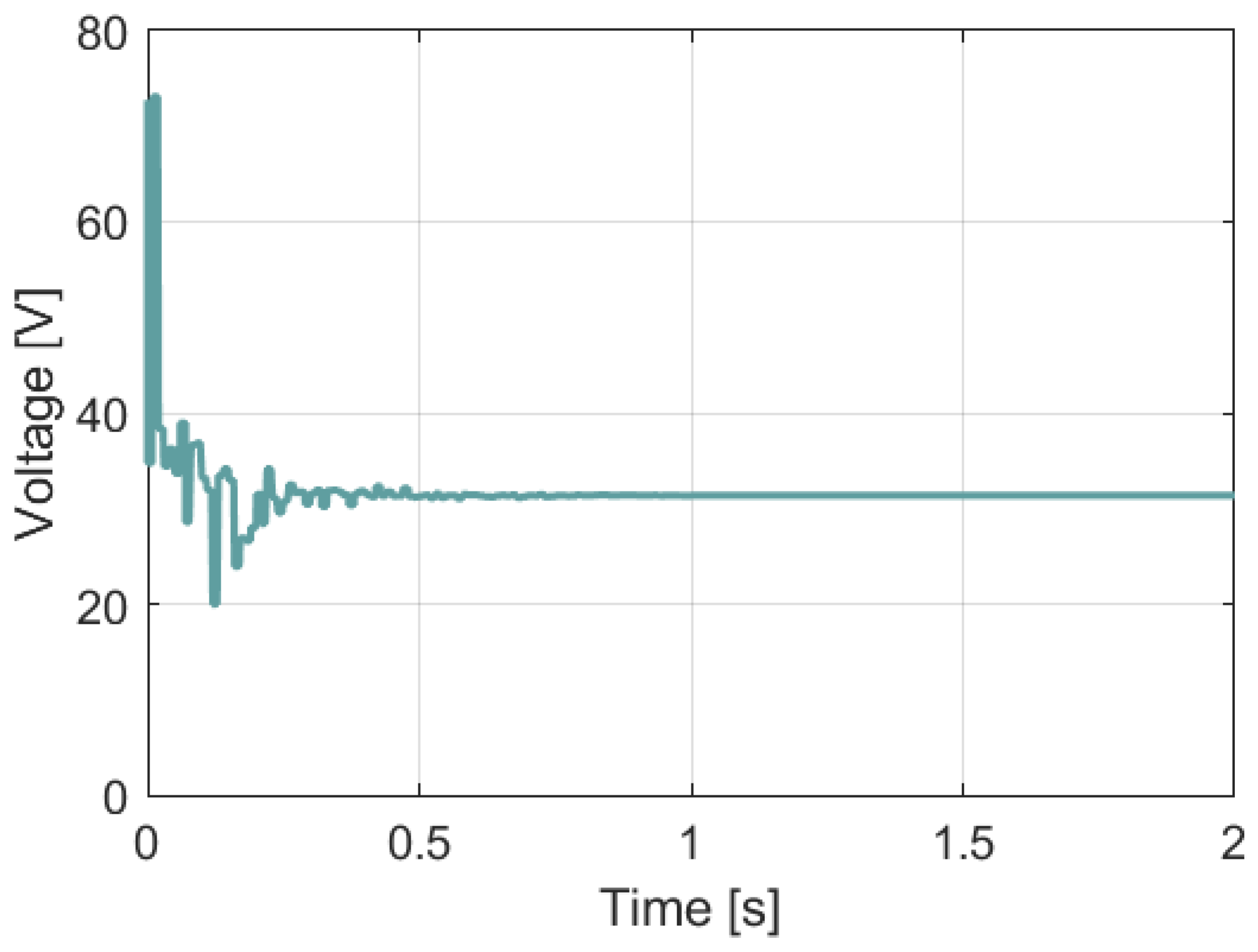
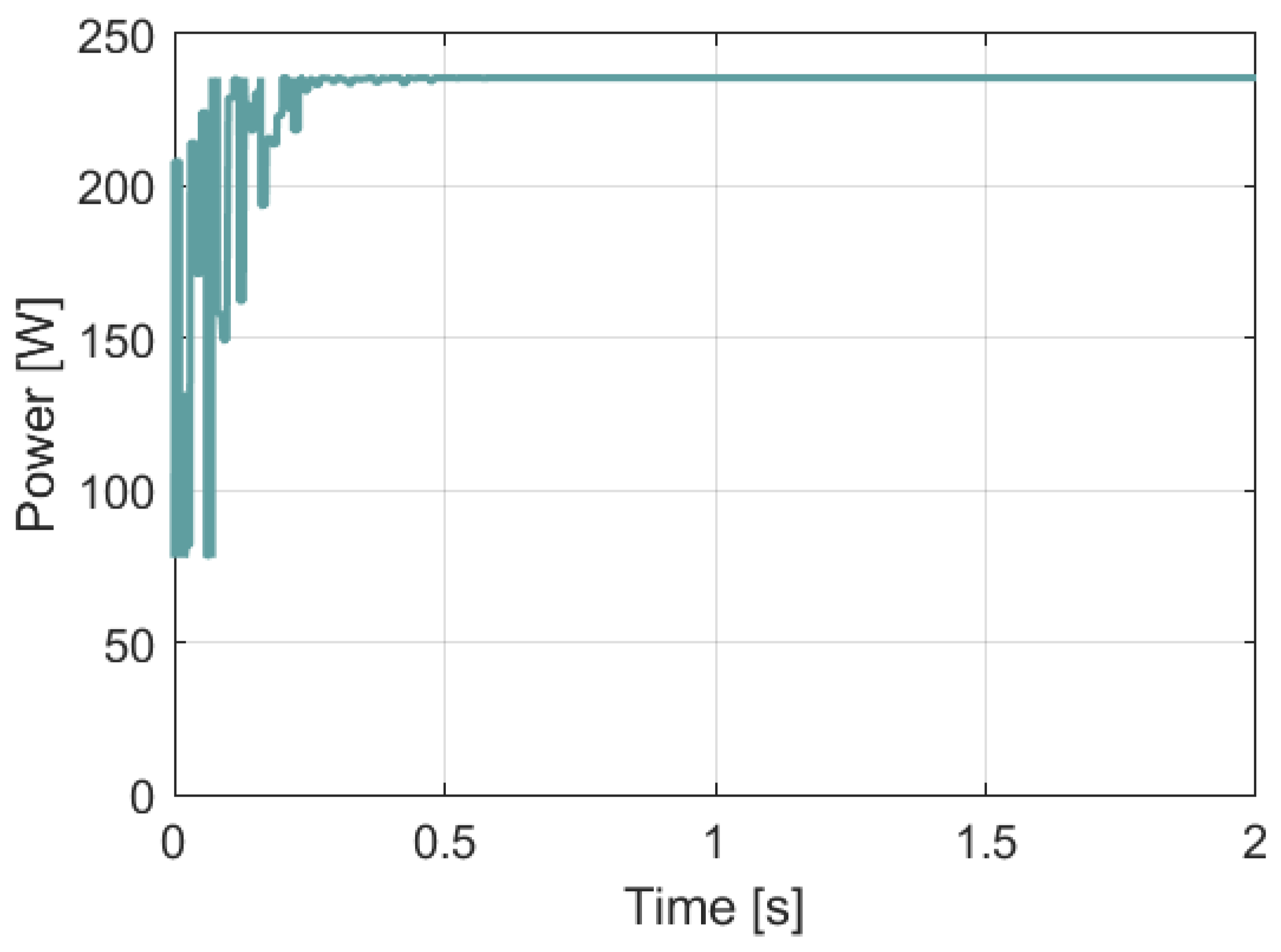
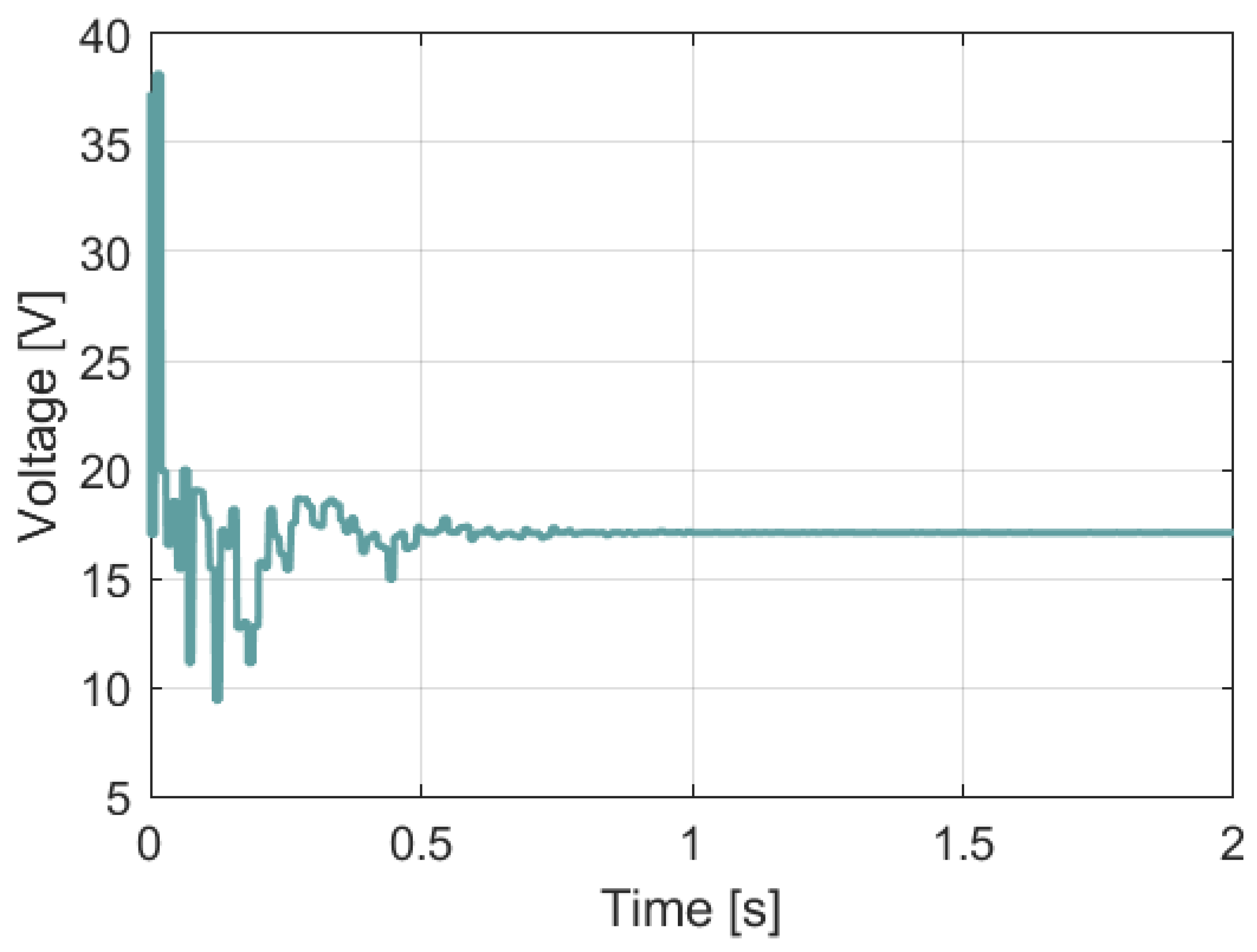
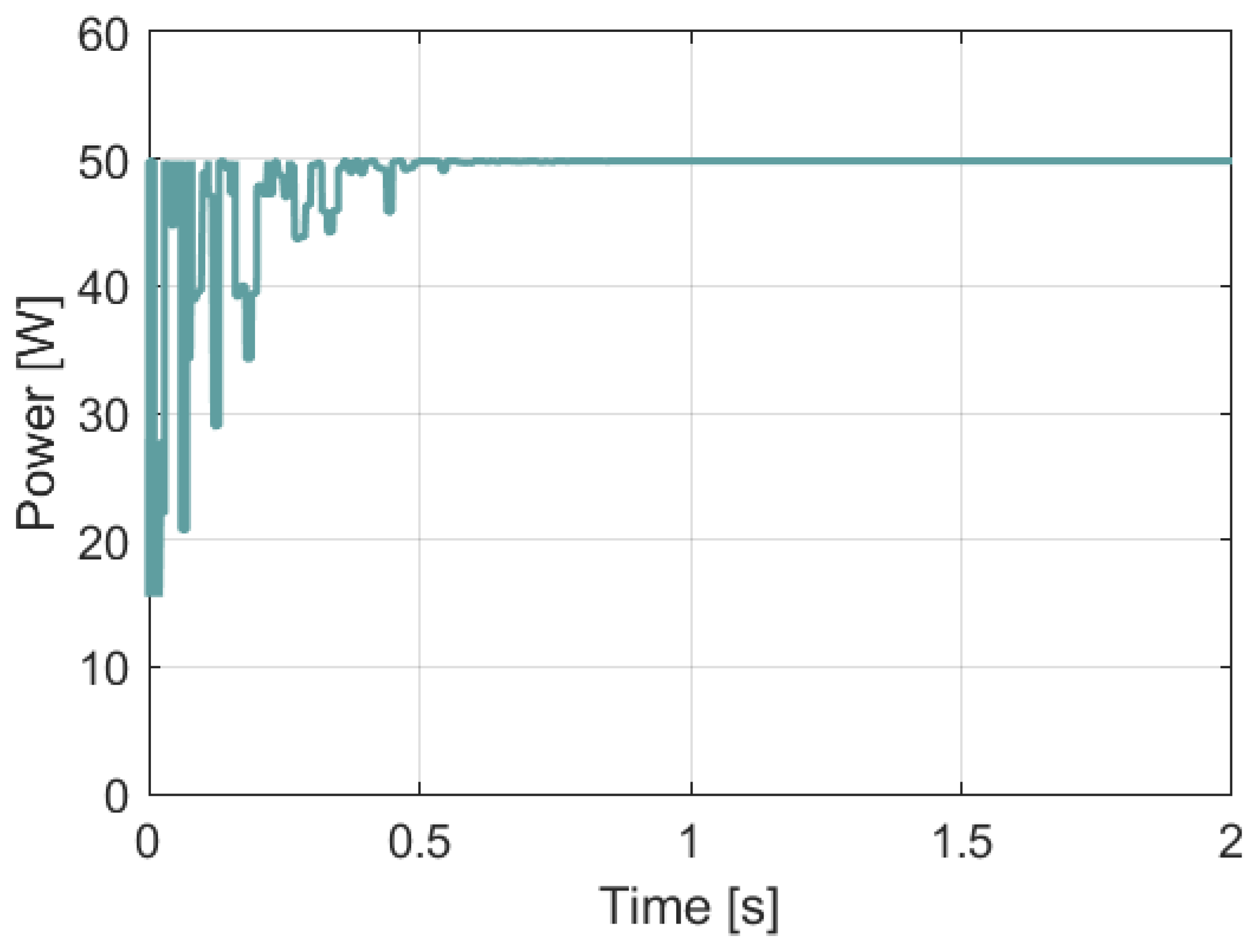
3.3. Simulation of the Perturb and Observe MPPT Algorithm (P&O)
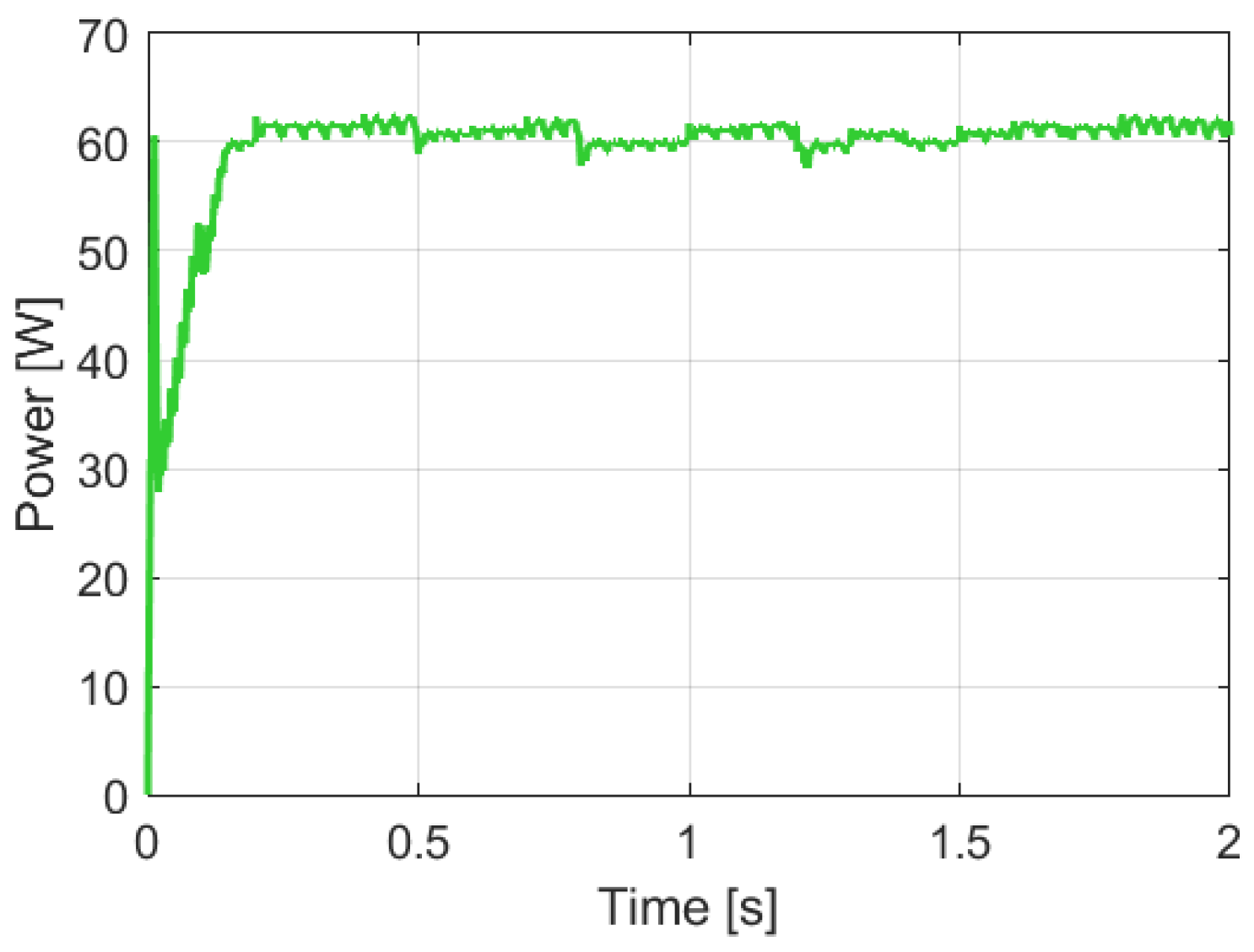
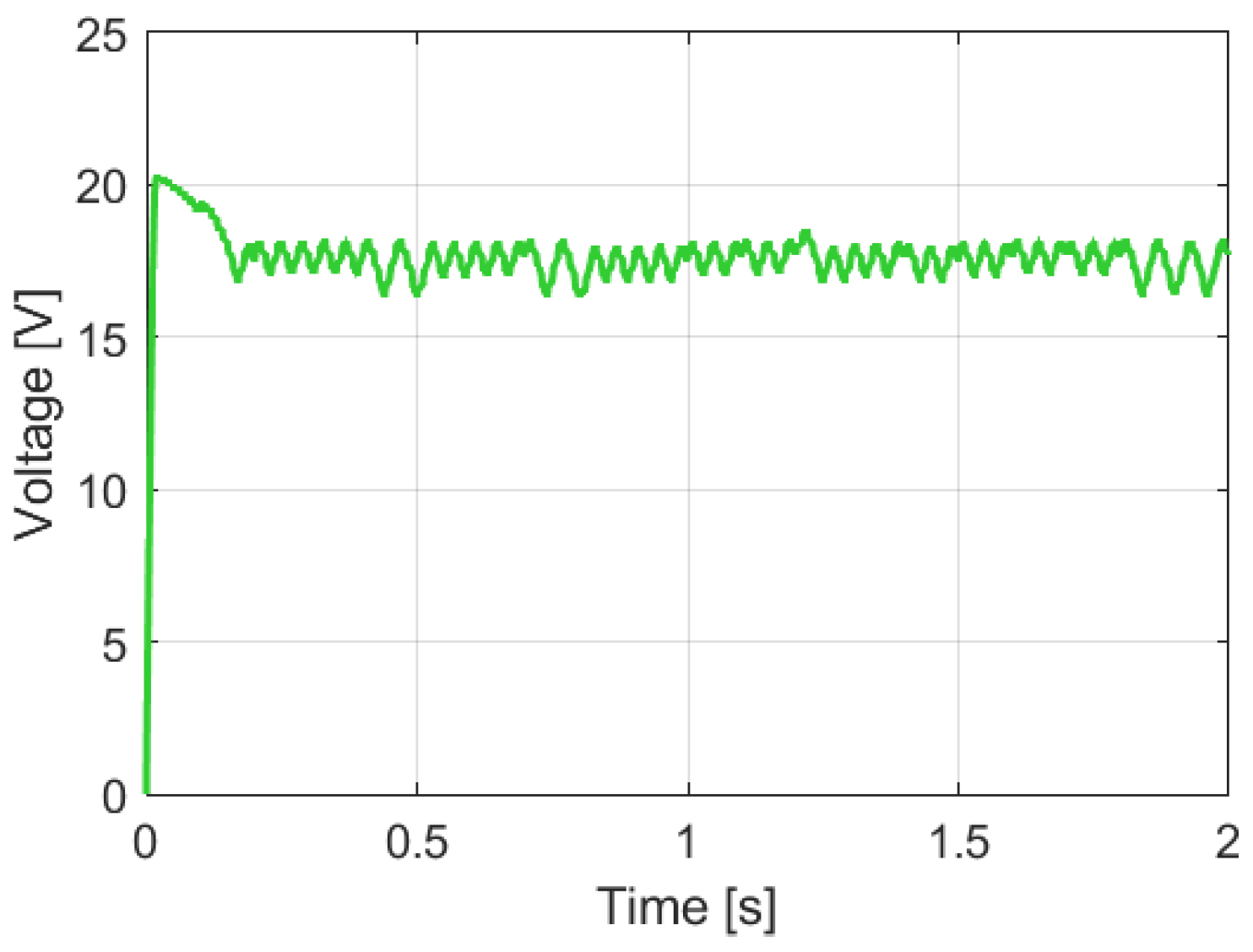
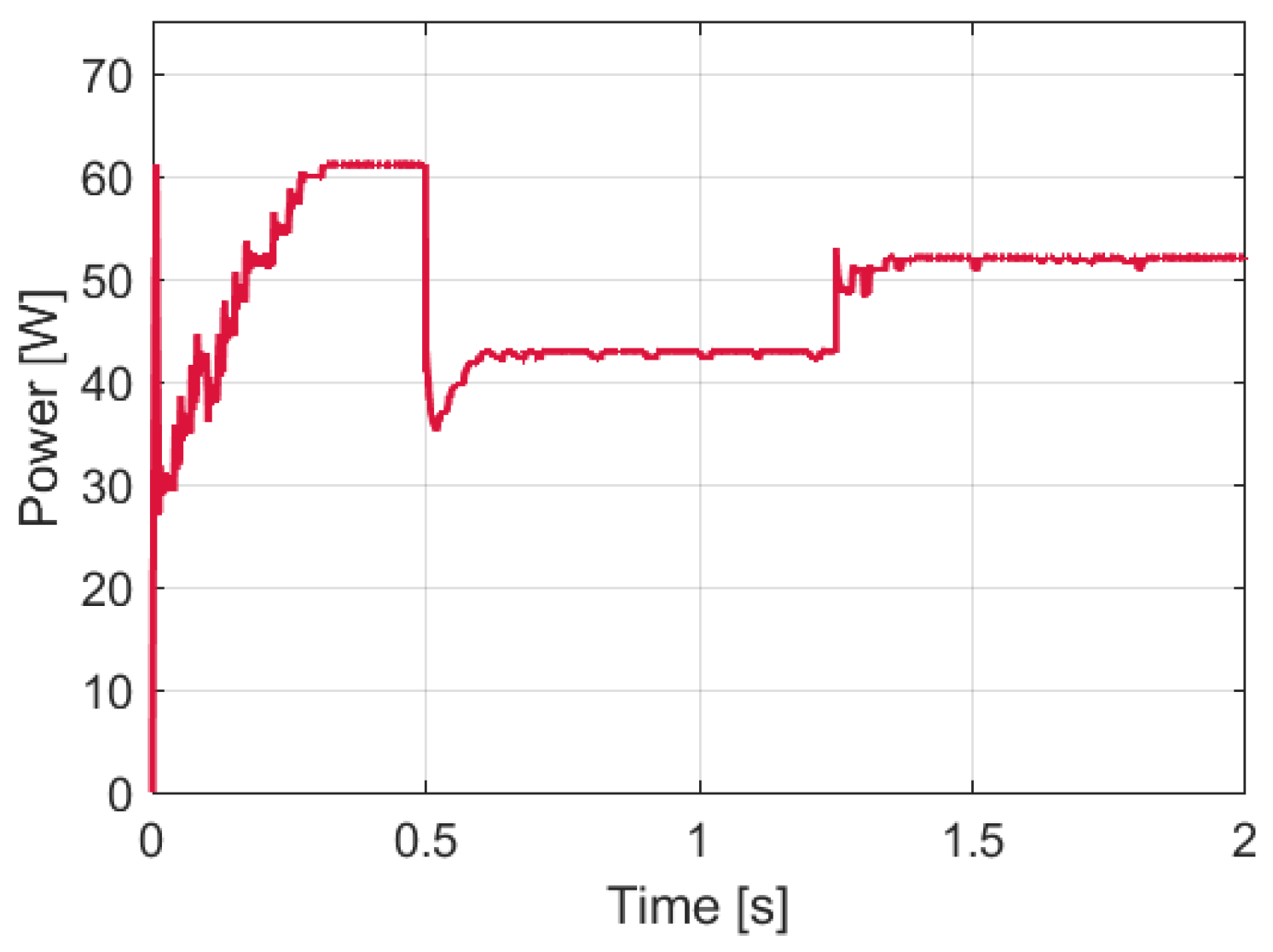
3.4. Simulation of the Performance of a Fuzzy Logic-Based Algorithm
3.5. Simulation of the PSO Algorithm Operation
3.6. Simulation of the Hybrid PSO + P&O Algorithm Operation
3.7. Comparison of Selected Qualitative Parameters
- Stabilisation time 98–100% [s]—the time required for the algorithm to reach and remain within 98% of the maximum power point.
- Rise time 10–90% [s]—the time taken for the algorithm to increase from 10% to 90% of the maximum power point.
- Accuracy [%]—the extent to which the maximum power point identified by the algorithm corresponds to the actual maximum power point.
- Energy loss [%]—the relative energy loss during the simulation before the MPPT algorithm stabilises at the maximum power point (including any oscillations).
- Standard deviation (from 98%) [%]—the standard deviation calculated from the moment the algorithm stabilises between 98% and 100% of the MPP.
- Standard deviation (entire window [%]—the standard deviation calculated over the entire time window, i.e., for the full duration of the simulation).
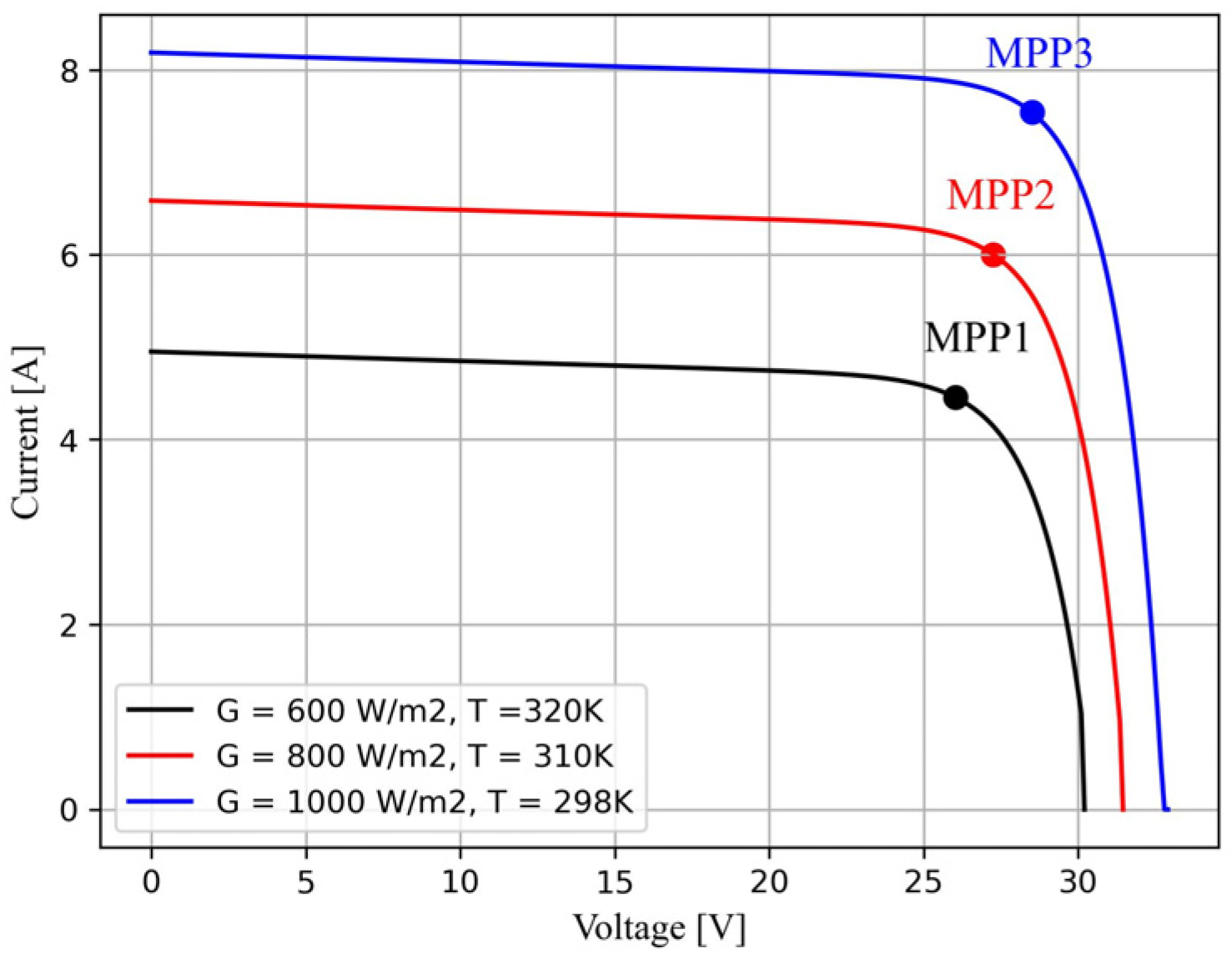
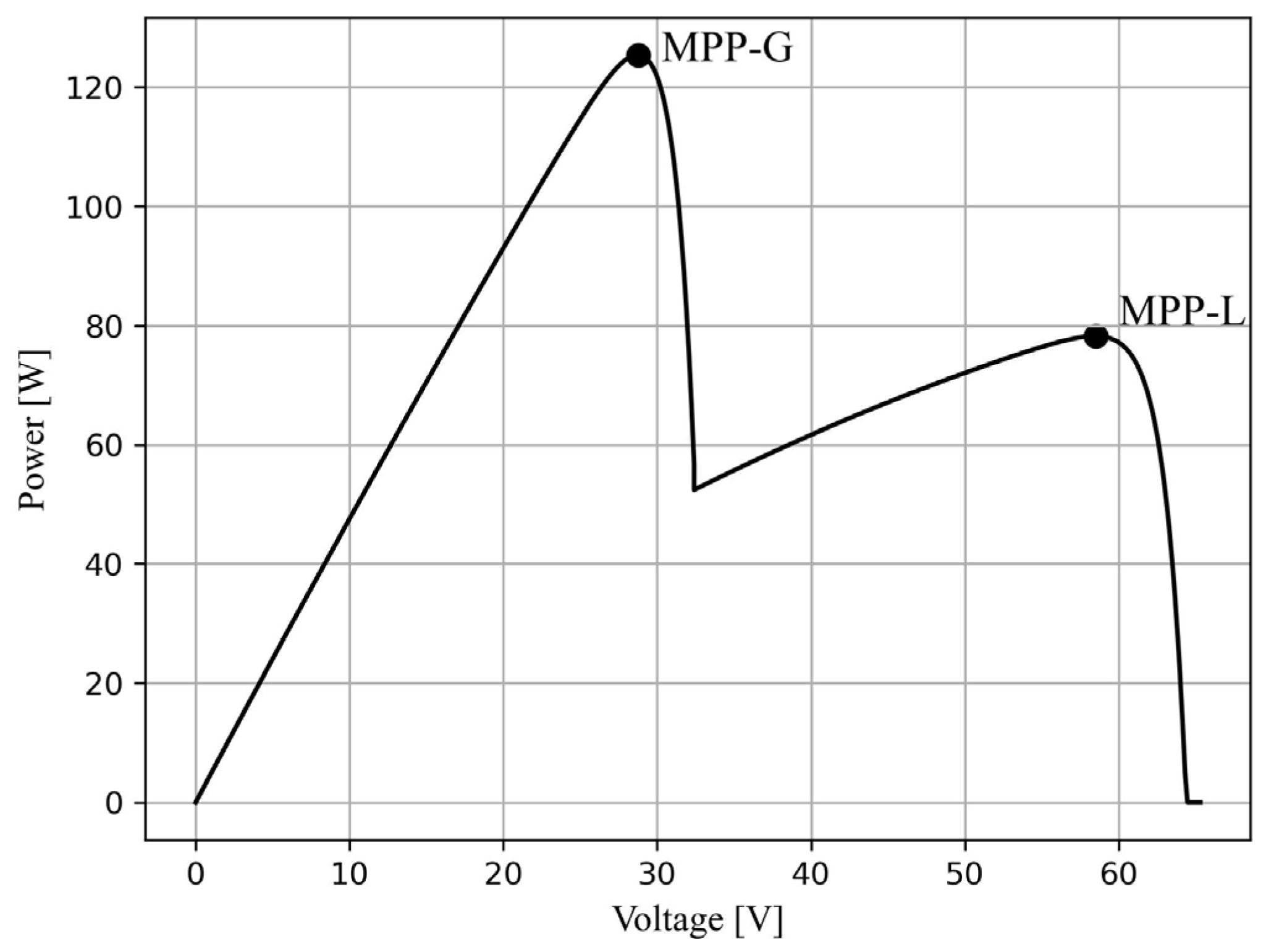
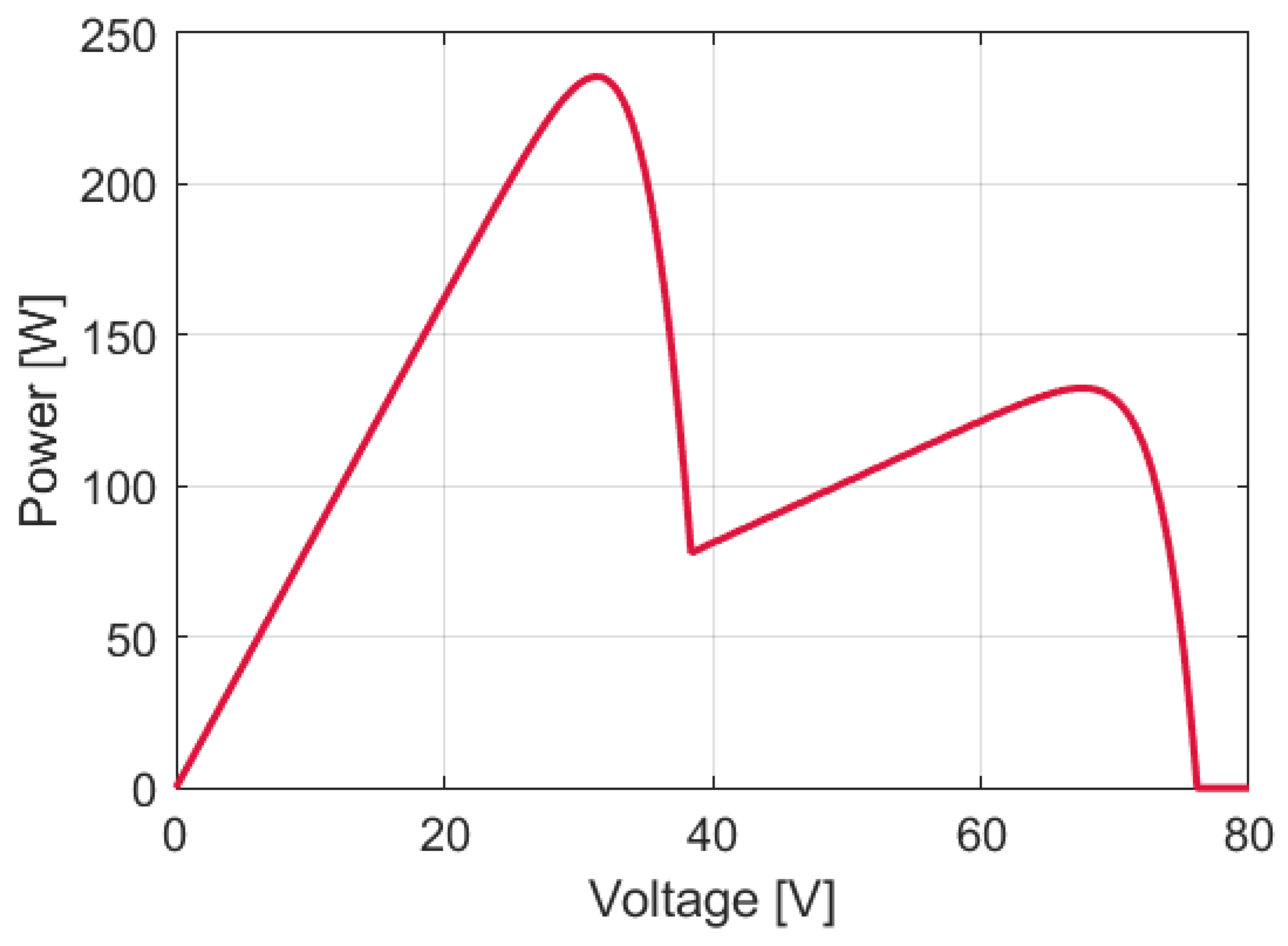
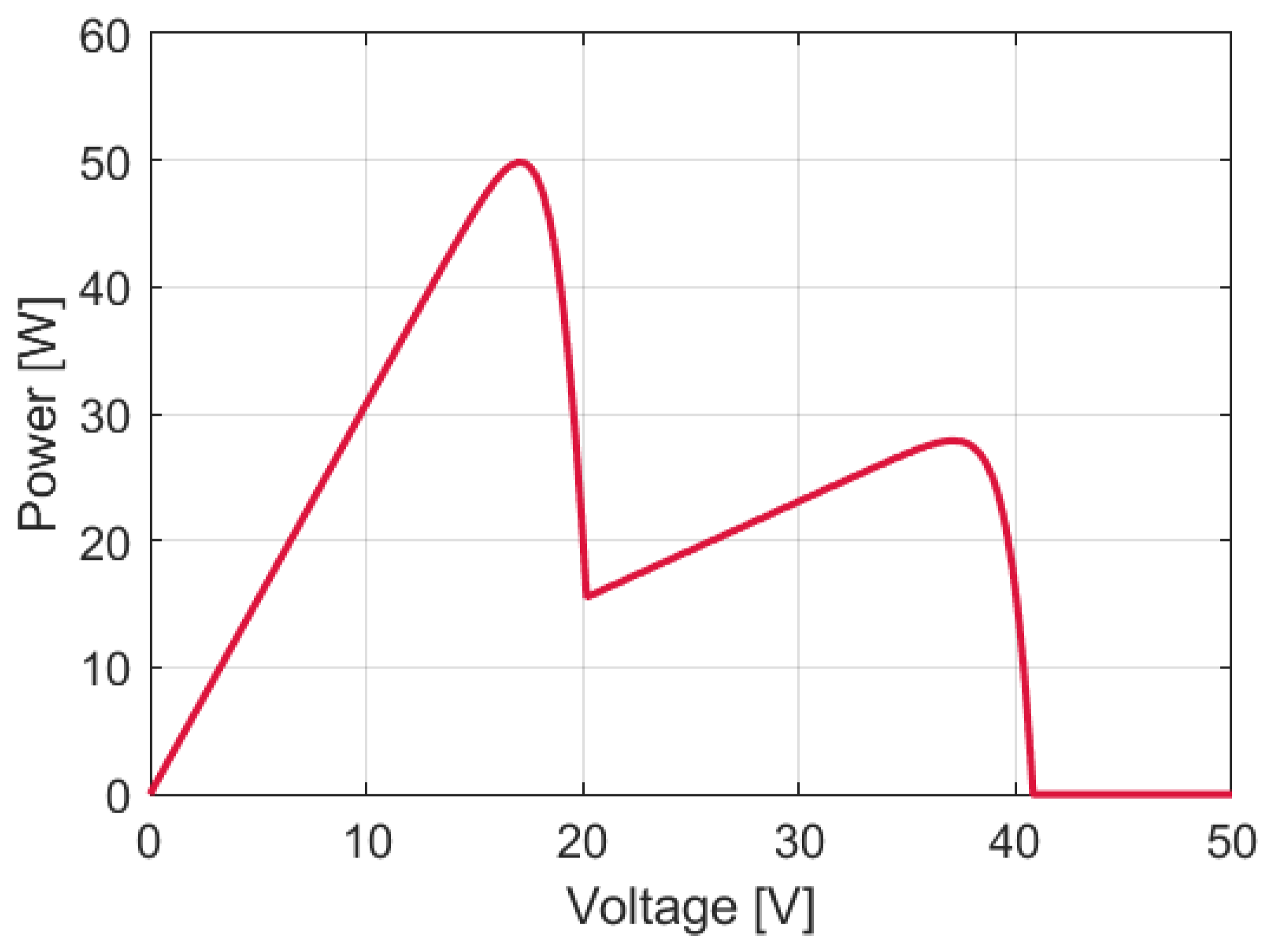
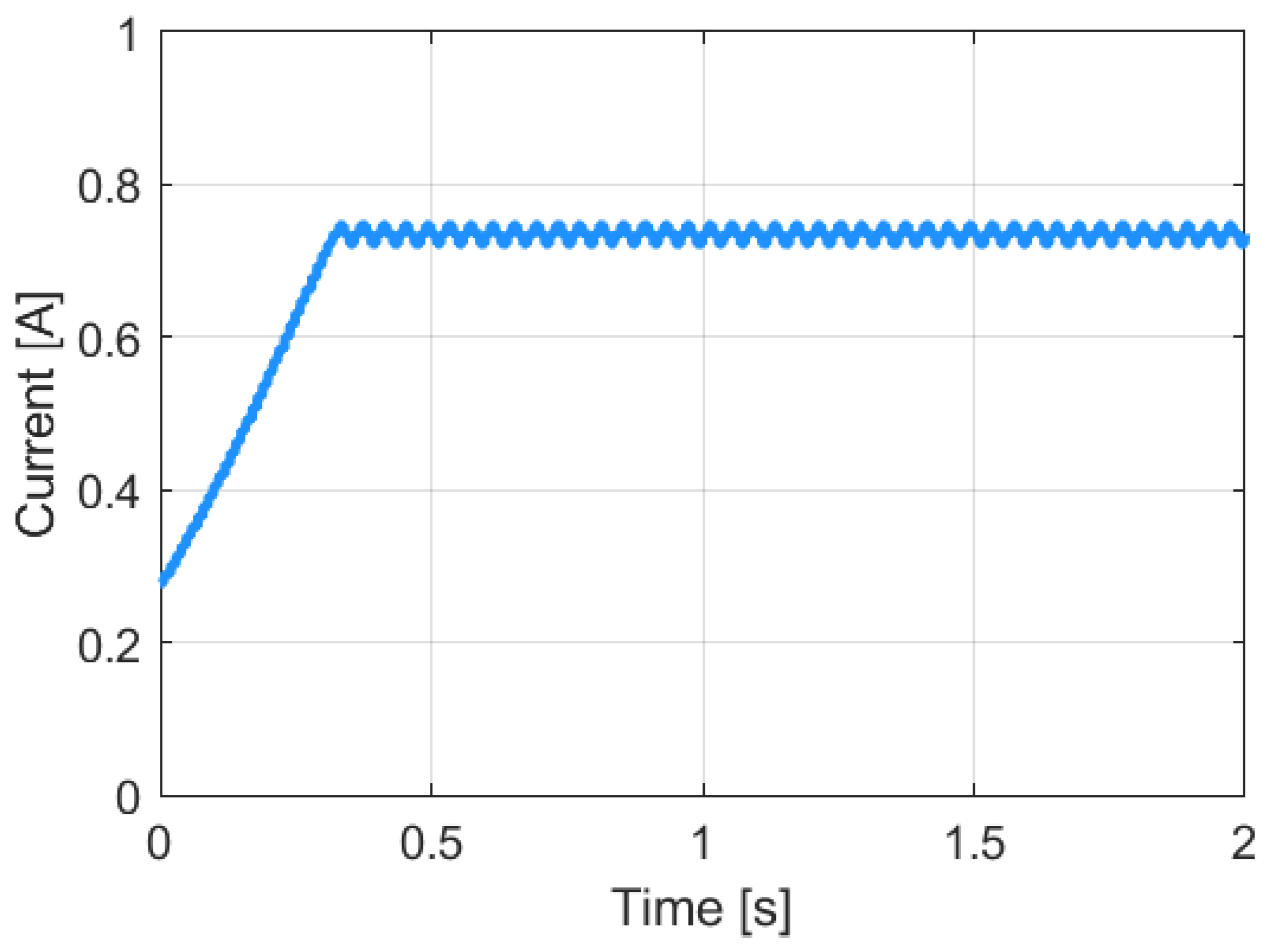
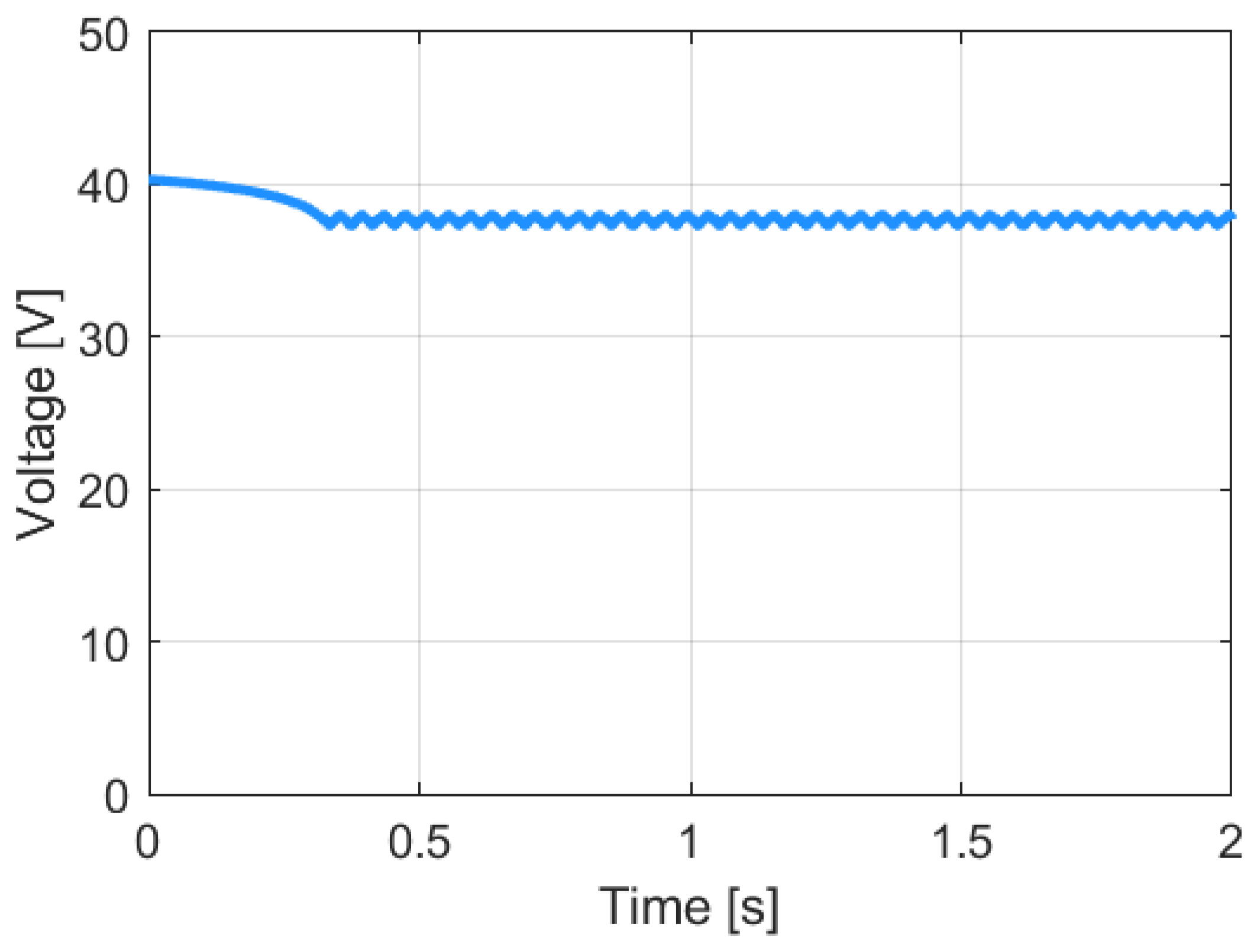
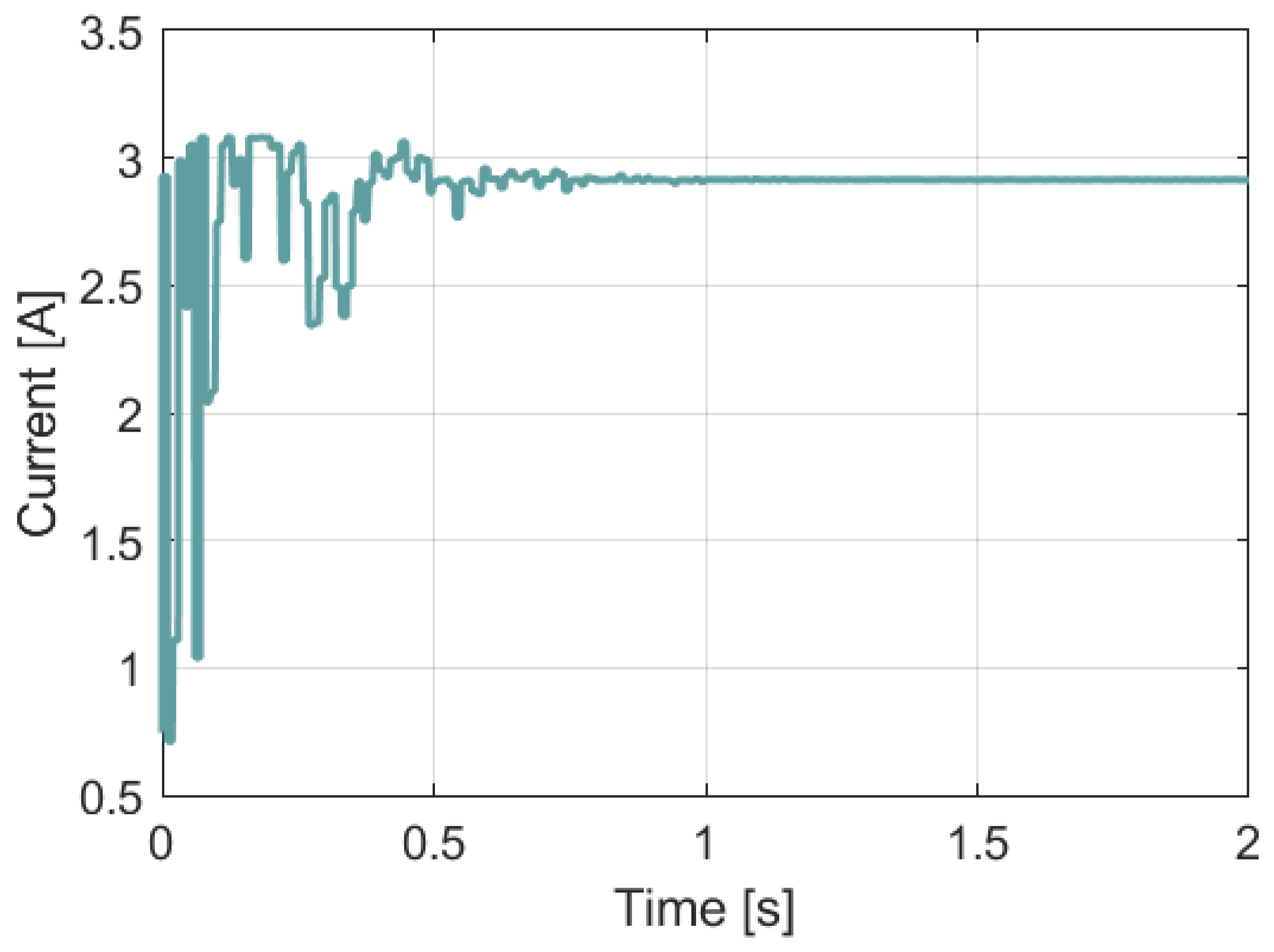
3.8. Simulation of the Application of Selected Algorithms in the Situation of Partial Shading of the PV Installation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Instytut Energetyki Odnawialnej. Rynek Fotowoltaiki w Polsce 2024. Warszawa. Available online: https://ieo.pl/raport-rynek-fotowoltaiki-w-polsce-2024pv-2024 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Macías, J.; Herrero, R.; José, L.S.; Núñez, R.; Antón, I. On the validation of a modelling tool for Vehicle Integrated PhotoVoltaics: Reflected irradiance in urban environments. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2024, 277, 113060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez-Garcia, A.; Voarino, P.; Raccurt, O. Environments, needs and opportunities for future space photovoltaic power generation: A review. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.U.I.; Meyer, E.L. Perovskite-based solar cells in photovoltaics for commercial scalability: Current progress, challenges, mitigations and future prospectus. Sol. Energy 2025, 286, 113172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzębska, G. Energia ze Źródeł Odnawialnych i jej Wykorzystanie; Wydawnictwa Komunikacji i Łączności: Warsaw, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hanzelka, Z.; Piątek, K. Instalacje Fotowoltaiczne w Systemie Elektroenergetycznym: Jakość Dostaw Energii Elektrycznej, Warunki Techniczne Przyłączenia Instalacji PV; Hanzelka, Z., Piątek, K., Eds.; PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2024; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkiewicz, P. Energetyka Solarna w Badaniach Naukowych; Kwiatkiewicz, P., Ed.; Fundacja na rzecz Czystej Energii: Poznań, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tytko, R. Fotowoltaika: Podręcznik dla Studentów, Uczniów, Instalatorów, Inwestorów; Wydawnictwo i Drukarnia Towarzystwa Słowaków w Polsce: Kraków, Poland, 2020; Volume IV. [Google Scholar]
- Abidi, H.; Sidhom, L.; Chihi, I. Systematic Literature Review and Benchmarking for Photovoltaic MPPT Techniques. Energies 2023, 16, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzmiel, G. Układy śledzące punkt maksymalnej mocy w inwerterach stosowanych w instalacjach fotowoltaicznych. Electr. Eng. 2016, 87, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, A.; Rodziewicz, T.; Wacławek, M. Algorytmy śledzenia punktu mocy maksymalnej (MPPT) w systemach fotowoltaicznych. Proc. ECOpole 2012, 6, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Chen, G.J.; Liu, C.L.; Su, C.Y. Comprehensive review on fast maximum power point tracking algorithms for solar power generation systems. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrouche, B.; Guessoum, A.; Belhamel, M. A simple behavioural model for solar module electric characteristics based on the first order system step response for MPPT study and comparison. Appl. Energy 2012, 91, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KYOCERA. Specifications for the KC200GT Multicrystalline Photovoltaic Module. 2025. Available online: https://www.energymatters.com.au/images/kyocera/KC200GT.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Rybak, T.; Mołczan, A.; Jarmuła, S.; Lichoń, M.; Majewska, S.; Michalski, M. Badanie wpływu zabrudzenia paneli fotowoltaicznych trawą na ich sprawność. Instal 2024, 463, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Rahmani, R.; Yusof, R.; Renani, E.T. Analytical Modeling of Partially Shaded Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2013, 6, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, J.C.; Tan, R.H.G.; Mok, V.H.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Tan, C. Impact of Partial Shading on the P-V Characteristics and the Maximum Power of a Photovoltaic String. Energies 2018, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystkowiak, M.; Gwóźdź, M. Przekształtnik energoelektroniczny dla elektrowni fotowoltaicznej współpracującej z siecią energetyczną. Pr. Nauk. Inst. Masz. Napędów Pomiarów Elektr. Politech. Wrocławskiej 2015, 71, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Consoli, A.; Cacciato, M.; Crisafulli, V. Power converters for photovoltaic generation systems in smart grid applications. Eletrônica Potência 2009, 14, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbytskyi, I.; Lukianov, M.; Nassereddine, K.; Pakhaliuk, B.; Husev, O.; Strzelecki, R.M. Power Converter Solutions for Industrial PV Applications—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, H.R.; Prasetya, A.; Zainal, Y.B.; Hidayat, M.R.; Taryana, E.; Megiyanto, G. Comparison Model of Buck-boost and Zeta Converter Circuit using MPPT Control Incremental Conductance Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application (ICSEEA), Tangerang, Indonesia, 18–20 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, M.; Mendoza, E.Y.; Flores, J.L. Passivity Based-Control of Output Voltage Regulation with MPPT for Photovoltaic Panel Using two SEPIC Converters. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Autumn Meeting on Power, Electronics and Computing (ROPEC), Ixtapa, Mexico, 4–6 November 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yaich, M.; Dhieb, Y.; Bouzguenda, M.; Ghariani, M. Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm of MPPT Controller for PV system application. E3S Web Conf. 2022, 336, 00036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, E.; Gokkus, G.; Gorgun, A. Design and implementation of a PI-MPPT based Buck-Boost converter. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Bucharest, Romania, 25–27 June 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. SG-23–SG-28. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Liu, X.; Lee, K.Y. Maximum Power Point Tracking and Voltage Regulation of Two-Stage Grid-Tied PV System Based on Model Predictive Control. Energies 2020, 13, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Xu, R.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Z. Integration of MPPT algorithms with spacecraft applications: Review, classification and future development outlook. Energy 2024, 308, 132927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.B.; Zhao, D.; Rehman, A.U.; Ouahada, K.; Hamam, H. An adapted model predictive control MPPT for validation of optimum GMPP tracking under partial shading conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, S.; e Silva, R.N.A.L. Hybrid MPPT Technique PSO-P&O Applied to Photovoltaic Systems Under Uniform and Partial Shading Conditions. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2021, 19, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizon, N. Global Maximum Power Point Tracking (GMPPT) of Photovoltaic array using the Extremum Seeking Control (ESC): A review and a new GMPPT ESC scheme. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, I.U.V.; Haidi, J.; Putra, R.F.A.; Silalahi, L.M. Comparison of MPPT Optimization Methods for P&O and PSO Solar Panels to Overcome Partial Shading. Int. J. Electron. Telecommun. 2024, 70, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltawil, M.A.; Zhao, Z. MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, V.R.; Bhukya, M.N. A simple and efficient MPPT scheme for PV module using 2-Dimensional Lookup Table. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Conference at Illinois (PECI), Urbana, IL, USA, 19–20 February 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, S.; Ramesh Babu, N. Maximum power point tracking algorithms for photovoltaic system—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzelis, E.; Kampitsis, G.; Papathanassiou, S. A MPPT algorithm for partial shading conditions employing curve fitting. In Proceedings of the 32th EU PVSEC, Munich, Germany, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirateruna, E.S.; Afroni, M.J.; Ayu, A.F. Implementation of PSO algorithm on MPPT PV System using Arduino Uno under PSC. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Robot. 2023, 5, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamuk, N. Performance Analysis of Different Optimization Algorithms for MPPT Control Techniques under Complex Partial Shading Conditions in PV Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, K.; Sefa, I.; Altin, N. Grey Wolf Optimization Based MPPT Algorithm for Solar PV System with SEPIC Converter. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Power Electronics and their Applications (ICPEA), Elazig, Turkey, 25–27 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Barambones, O.; Bencherif, A.; Rahmani, A. A New MPPT-Based Extended Grey Wolf Optimizer for Stand-Alone PV System: A Performance Evaluation versus Four Smart MPPT Techniques in Diverse Scenarios. Inventions 2023, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.M.; Addoweesh, K.E.; Mashaly, H.M. A fuzzy logic control method for MPPT of PV systems. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 874–880. [Google Scholar]
- Baramadeh, M.Y.; Abouelela, M.A.A.; Alghuwainem, S.M. Maximum Power Point Tracker Controller Using Fuzzy Logic Control with Battery Load for Photovoltaics Systems. Smart Grid Renew. Energy 2021, 12, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.; Ishaq, M.; Tchier, F.; Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, Z. Fuzzy-based maximum power point tracking (MPPT) control system for photovoltaic power generation system. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, R.; Chowdhury, S.S.; Abedin, F.; Rahman, K.M. Implementation of MPPT Technique of Solar Module with Supervised Machine Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.00728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareswaran, K.; Vignesh Kumar, V.; Palani, S. Application of a combined particle swarm optimization and perturb and observe method for MPPT in PV systems under partial shading conditions. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, J.S.; Gnanavadivel, J.; Kumar, N.S.; Veni, K.K. Design and Simulation of Fuzzybased DC-DC Interleaved Zeta Converter for Photovoltaic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 11–12 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 704–709. [Google Scholar]
- Seguel, J.L.; Seleme, S.I.; Morais, L.M.F. Comparative Study of Buck-Boost, SEPIC, Cuk and Zeta DC-DC Converters Using Different MPPT Methods for Photovoltaic Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, K.; Arif, M.S.B.; Masud, M.I.; Ahmad, M.F.; Alqarni, M. Optimal Selection of Extensively Used Non-Isolated DC–DC Converters for Solar PV Applications: A Review. Energies 2025, 18, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.-K.; Wei, Y.-C.; Chen, B.-C. A Study on the Fuzzy-Logic-Based Solar Power MPPT Algorithms Using Different Fuzzy Input Variables. Algorithms 2015, 8, 100–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.; Nfah, E.M.; de Dieu Nguimfack Ndongmo, J.; Alombah, N.H. An Enhanced P&O MPPT Algorithm for PV Systems with Fast Dynamic and Steady-State Response under Real Irradiance and Temperature Conditions. Int. J. Photoenergy 2022, 2022, 6009632. [Google Scholar]





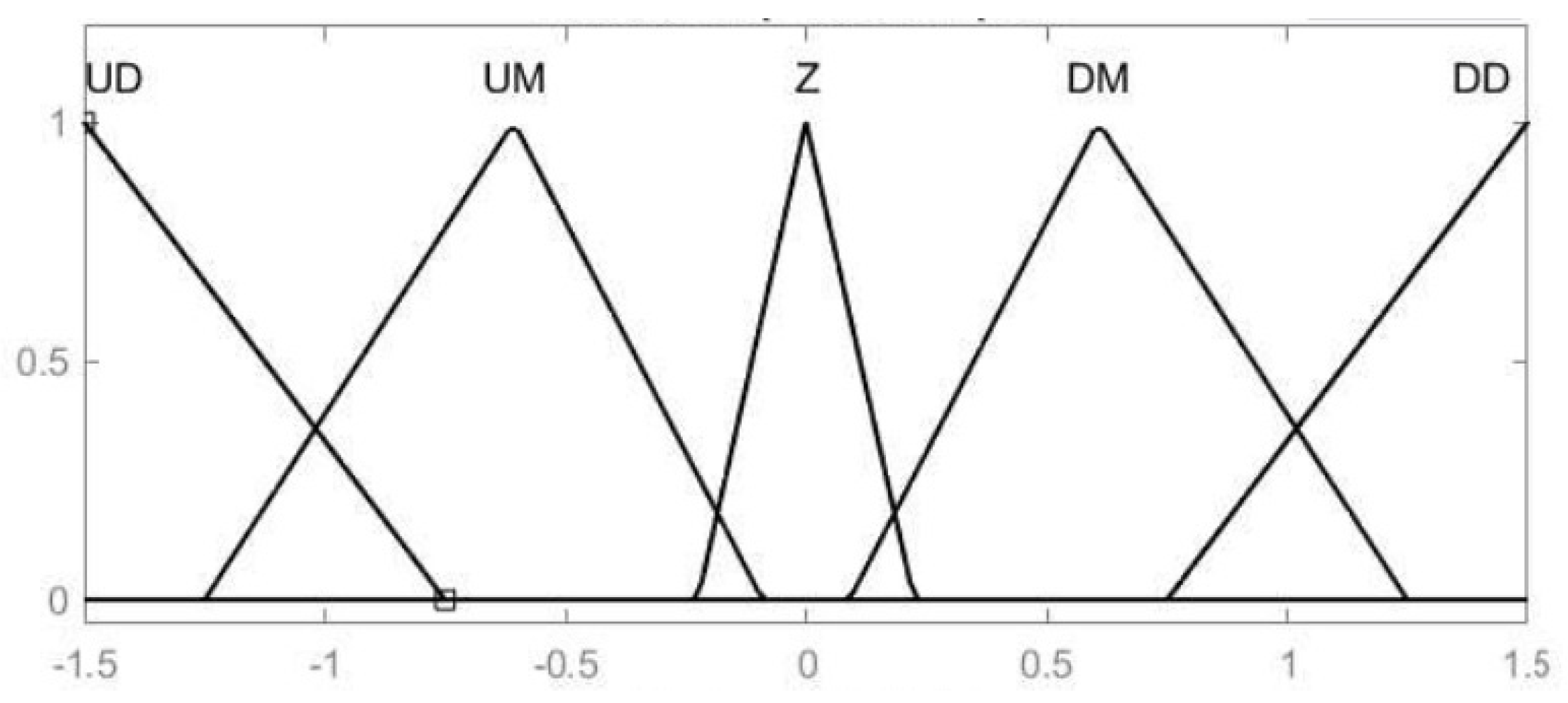

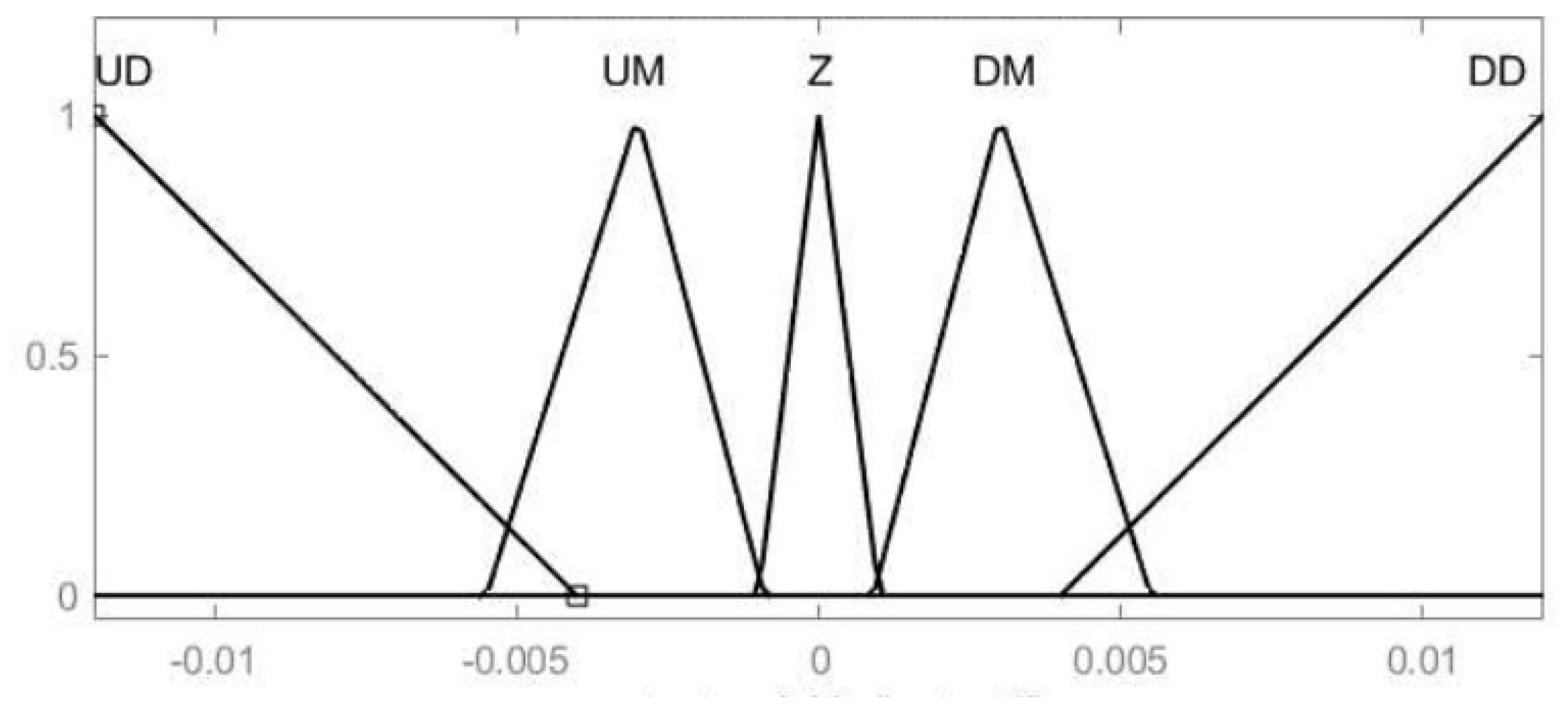



| Set of Rules | E | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UD | UM | Z | DM | DD | ||
| ∆E | UD | Z | DD | DM | Z | UD |
| UM | DD | DM | Z | Z | UD | |
| Z | DD | DM | Z | UM | UD | |
| DM | DD | Z | Z | UM | UD | |
| DD | DD | Z | UM | UD | Z | |
| w | velocity change weight | 0.4 |
| c1 | local factor | 0.75 |
| c2 | global coefficient | 1.6 |
| r1, r2 | random coefficients | 0–1 |
| Selected Algorithm | P&O (x = 0.0025) | P&O (x = 0.01) | FLC | PSO | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stabilisation time 98–100% [s] | 0.445 | 0.13 | 0.215 | 0.392 | 0.245 |
| Rise time 10–90% [s] | 0.29 | 0.101 | 0.182 | 0.34 | 0.153 |
| Accuracy [%] | 98.9–99.9 | 98.2–99.8 | 99.90 | 99.90 | 99.90 |
| Energy Loss [%] | 4.74 | 2.26 | 3.47 | 7.96 | 5.12 |
| Standard Deviation (from 98%) [%] | 0.25 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.44 |
| Standard Deviation (entire window) [%] | 11.39 | 8.34 | 7.85 | 22.13 | 17 |
| Constant Voltage | P&O | FLC | PSO | PSO + P&O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm Group Features | Classic | Classic | Smart | Optimisation | Hybrid |
| Measurement | Voc (V) | V, I | V, I | V, I, items, ratings | V, I, time items, ratings |
| Dynamics | Medium | Low | High | Low | Medium |
| Accuracy | Low | Medium | High | Extremely high | Extremely high |
| Oscillation | Small | Average | Low | Low | Low |
| Complexity level | Low | Low | Very high | Medium | High |
| Partial Shading Tolerance | None | Low | Medium | High | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trzmiel, G.; Jajczyk, J.; Szulta, J.; Chamier-Gliszczynski, N.; Woźniak, W. Modelling of Selected Algorithms for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Photovoltaic Panels. Energies 2025, 18, 5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195223
Trzmiel G, Jajczyk J, Szulta J, Chamier-Gliszczynski N, Woźniak W. Modelling of Selected Algorithms for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Photovoltaic Panels. Energies. 2025; 18(19):5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195223
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrzmiel, Grzegorz, Jarosław Jajczyk, Jan Szulta, Norbert Chamier-Gliszczynski, and Waldemar Woźniak. 2025. "Modelling of Selected Algorithms for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Photovoltaic Panels" Energies 18, no. 19: 5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195223
APA StyleTrzmiel, G., Jajczyk, J., Szulta, J., Chamier-Gliszczynski, N., & Woźniak, W. (2025). Modelling of Selected Algorithms for Maximum Power Point Tracking in Photovoltaic Panels. Energies, 18(19), 5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18195223









