Abstract
The pursuit of sustainable and environmentally benign energy storage solutions has propelled significant interest in organic batteries, which utilize redox-active organic compounds as electrode materials. A pivotal component in determining their electrochemical performance, safety, and long-term stability is the electrolyte. Polymer-based electrolytes (PBEs) have emerged as promising candidates owing to their intrinsic advantages, such as enhanced thermal stability, mechanical integrity, and the mitigation of leakage and flammability risks associated with conventional liquid electrolytes. Unlike previous reviews that broadly cover solid electrolytes, this review specifically focuses on the unique developments of polymer-based electrolytes tailored for organic batteries over the past few years. This review presents a comprehensive overview of the recent progress in PBEs specifically designed for organic battery systems. It systematically examines various categories, including solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs), valued for their structural simplicity and stability; gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs), noted for their high ionic conductivity and processability; and polymer-inorganic composite electrolytes, which synergistically integrate the mechanical flexibility of polymers with the ionic conductivity of inorganic fillers. Additionally, the review delves into the latest advancements in ionogels and poly(ionic liquid) electrolytes, highlighting their potential to overcome existing limitations and enable next-generation battery performance. The article concludes with a critical discussion on prevailing challenges and prospective research directions, emphasizing the importance of advanced material design, interfacial engineering, and sustainable synthesis approaches to facilitate the practical realization of high-performance organic batteries.
1. Introduction
The demand for sustainable, high-performance energy storage technologies has intensified with the rapid advancement of electric mobility, wearable electronics, and grid-scale renewable integration [1,2]. Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have long dominated this landscape, owing to their high energy density, elevated operating voltages, and excellent cycling stability [3,4]. However, their practical energy density and cost are insufficient to meet the rapidly growing market demand. The energy density of LIBs falls short of the 500 Wh kg−1 cell-level target and USD 100 kWh−1 pack-level cost benchmark proposed by the U.S. DOE’s Battery500 Consortium for long-range electric vehicles and affordable grid storage [5,6]. This gap arises largely from constraints in electrode capacity and reliance on scarce transition metals such as cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which, despite offering higher specific capacity, are limited by global reserves, uneven geographical distribution, and high extraction costs [7,8,9]. Although recycling technologies have been developed to recover these critical elements, current methods are energy-intensive, economically burdensome, and environmentally unsustainable [10].
Conversely, cathode chemistries based on abundant elements, such as LiFePO4, offer superior safety, excellent cycle life, and material availability. However, their lower operating voltage and modest theoretical capacity (~170 mAh g−1) limit the gravimetric energy density to ~90–120 Wh kg−1 for standard LiFePO4 and up to 160–180 Wh kg−1 for advanced formulations [11,12]. While these chemistries circumvent critical metal scarcity, they are still insufficient to meet the 500 Wh kg−1 target. These combined limitations have thus spurred interest in alternative, earth-abundant, low-cost, and environmentally benign battery chemistries.
In recent years, organic batteries employing redox-active organic compounds as electrodes have gained traction as promising candidates for next-generation energy storage. Organic electrodes offer several advantages over their inorganic counterparts, including facile synthesis, structural tunability, compatibility with various charge carriers, and the use of lightweight, naturally abundant elements (C, H, N, O, and S) [13]. Many of these materials can be derived from biomass or synthesized under mild conditions, and their molecular structures are highly customizable to achieve high capacity. Their universal conversion-based redox mechanisms also enable applicability across a wide range of metal-ion systems (e.g., Na+, K+, Zn2+, Mg2+), broadening their functional scope [13,14,15].
Despite these advantages, one of the major challenges limiting the practical deployment of organic batteries is the dissolution of active organic materials in conventional liquid electrolytes, which leads to capacity fading and performance degradation. Strategies such as molecular polymerization, structural modifications, and physical immobilization have been explored to mitigate dissolution, though often at the cost of reduced practical capacity [16]. As such, the development of optimized electrolyte systems has become critical, not only to stabilize the organic electrode–electrolyte interface but also to unlock the full electrochemical potential of organic materials.
Among the various electrolyte systems studied, ranging from aqueous and organic liquid electrolytes to inorganic solids, polymer-based electrolytes (PBEs) have emerged as particularly promising [13,17]. PBEs combine features of both liquid and solid systems, offering higher safety than flammable liquid electrolytes, greater mechanical flexibility than rigid inorganic solids, and the ability to suppress dissolution of organic electrodes. Although PBEs generally exhibit lower thermal stability than inorganic solids, their reduced flammability provides a notable safety advantage over conventional liquid electrolytes. Additionally, the tunable polymer matrices allow optimization of ionic conductivity, interfacial compatibility, and mechanical properties for specific organic battery systems. PBEs can be broadly categorized based on material composition into solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs), gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs), polymer–inorganic composite electrolytes, and ionogel/poly(ionic liquid) electrolytes [13]. These categories also correlate with their physical states: all-solid systems (SPEs and some composites) provide high thermal stability and safety with moderate conductivity, semi-solid systems (GPEs and certain ionogels) enhance ionic transport while maintaining structural integrity, and quasi-solid systems (immobilized liquids in polymer networks) combine improved conductivity with mechanical robustness [18,19]. By integrating these composition- and state-based perspectives, PBEs offer versatile solutions for flexible, high-energy-density, and all-solid-state organic battery systems.
This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advancements in polymer-based electrolytes (PBEs) for organic batteries, which face unique challenges in safety, electrode compatibility, and ionic transport compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. While several reviews have summarized polymer electrolytes in general, interface between Li anode and solid-state electrolytes, or for traditional lithium-ion systems, this work specifically focuses on PBEs for organic batteries, integrating material composition, structural features, ion transport mechanisms, and electrochemical behaviors [20,21,22]. PBEs are categorized into four classes: solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs), gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs), polymer–inorganic composite electrolytes, and ionogels/poly(ionic liquid) electrolytes. The review also addresses current challenges, such as limited ambient-temperature conductivity and interfacial stability, and highlights future directions in material innovation, interface engineering, and scalable fabrication strategies. This focused discussion aims to support the rational design of polymer-based electrolytes and facilitate the development of safe, efficient, and sustainable organic energy storage technologies.
2. Polymer-Based Electrolytes
Polymer-based electrolytes have garnered significant interest due to their inherent advantages such as mechanical flexibility, low density, ease of processing into various forms, and strong interfacial compatibility with electrode surfaces [23]. An ideal polymer electrolyte should not only offer ionic conductivity comparable to that of liquid electrolytes but also demonstrate a high ion transference number, minimal interfacial resistance, robust thermal and electrochemical stability, a wide electrochemical window, and adequate mechanical strength [24]. For organic batteries, solid or quasi-solid polymer electrolytes are particularly beneficial as they help suppress the dissolution and shuttle effects associated with organic active materials [13,23]. Structures and names of polymer matrices in the electrolytes are listed in Figure 1.
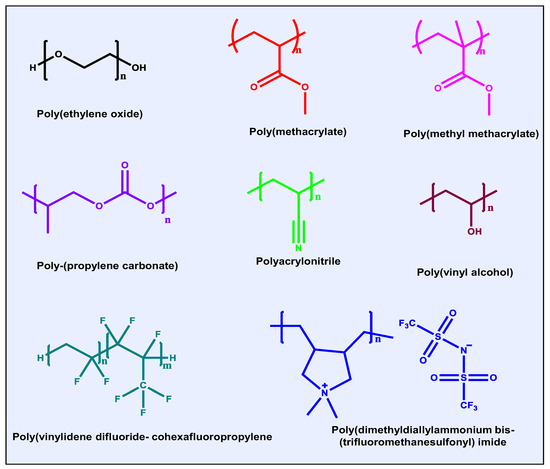
Figure 1.
Structures and names of polymer matrices in electrolytes.
These electrolytes are typically composed of an organic polymer matrix doped with lithium or other metal salts and may also incorporate plasticizers or solvents such as propylene carbonate (PC), ethylene carbonate (EC), 1,3-dioxolane (DOL), dimethoxyethane (DME), or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Furthermore, the incorporation of inorganic fillers—both passive (e.g., SiO2, Al2O3), which are non-conductive and primarily enhance mechanical strength and reduce polymer crystallinity to promote ion mobility, and active (e.g., Li7La3Zr2O12, Li0.33La0.557TiO3), which are lithium-ion-conducting ceramics—can significantly influence the electrolyte’s properties. The role of active fillers, however, remains under debate: while several studies report that they can directly participate in Li-ion transport by forming continuous conductive pathways within the polymer matrix [25,26], others suggest their primary function is to suppress polymer crystallinity and improve interfacial conduction rather than provide bulk ion-conducting channels [27]. Thus, the contribution of ceramic fillers to ionic conductivity is likely situation-dependent, influenced by filler type, morphology, dispersion, and polymer–filler interactions [28]. In recent years, ionogel-based systems and poly(ionic liquid) (PIL) electrolytes have also emerged as attractive alternatives, offering enhanced conductivity and electrochemical stability [13,29].
Based on solvent content, polymer electrolytes are broadly classified into two categories: solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) and gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs). SPEs, being solvent-free, are effective in preventing the dissolution of organic redox-active compounds. However, conventional SPEs often suffer from low ionic conductivity (in the range of 10−8 to 10−5 S cm−1 at room temperature) and limited interfacial contact with electrodes. To overcome these limitations, SPEs incorporating with covalent organic frameworks (COFs) as fillers have recently been explored. The ordered pore structures and high surface area of COFs facilitate ion transport and improve interfacial compatibility, thereby enhancing ionic conductivity and enabling better performance even at sub-ambient temperatures. For instance, Zhang et al. incorporated TpPa-SO3Li into a PVDF matrix, where the COF filler provided rapid Li+ transport pathways and strong polymer compatibility. This design achieved an impressive ionic conductivity of 1.93 mS cm−1 at 30 °C with a transference number of 0.44, while also delivering excellent cycling stability, as evidenced by lithium-symmetric cells operating for over 2500 h and LiFePO4/Li batteries retaining 93.8% capacity after 300 cycles at 0.5 C [30].
On the other hand, GPEs have attracted wide attention as they combine the high ionic conductivity of liquid electrolytes with the mechanical integrity of solids. Substituting liquid electrolytes with GPEs in organic batteries can enhance electrochemical performance while reducing leakage risks. However, the presence of substantial solvent content in GPEs can still lead to the undesirable dissolution of organic materials. To overcome this, the development of advanced quasi-solid-state or all-solid-state composite electrolytes, especially those incorporating inorganic components or designed using PILs, has become a key area of ongoing research.
2.1. Solid Polymer Electrolytes
Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs), typically composed of a polymer matrix such as polyethylene oxide (PEO), poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP), or polyacrylonitrile (PAN) blended with lithium salts without the use of organic solvents, have emerged as promising alternatives to liquid electrolytes for solid-state batteries. Their intrinsic advantages, such as lightweight design, mechanical flexibility, and enhanced safety due to the absence of flammable solvents, make them attractive candidates for next-generation energy storage systems. However, their practical application remains constrained by low ionic conductivity at ambient temperature and suboptimal interfacial compatibility with electrodes. These deficiencies often necessitate elevated operating temperatures, which compromise safety and long-term stability.
To address these limitations, several strategies have been investigated to improve the ion transport capabilities and interfacial properties of SPEs. One widely studied approach involves the incorporation of molecular plastic crystals, particularly succinonitrile (SN), as solid plasticizers [31]. Owing to its high polarity and diffusivity, SN effectively dissolves lithium salts and facilitates ion mobility; however, due to its weak mechanical integrity, it is commonly integrated into a polymer matrix. Several studies have demonstrated that SN enhances ionic conductivity by suppressing polymer crystallinity and providing fast ion transport channels. For instance, Fan et al. reported the role of SN as a versatile additive for polymer electrolytes, improving both conductivity and electrochemical stability [32]. More recently, Kim et al. demonstrated all-solid-state lithium–organic batteries using solid-state single-ion electrolytes. These electrolytes were prepared by hybridizing SN with x-PS@PSTFSI−Li+ nanoparticles, hereafter referred to as single-ion NP electrolytes, achieving high ionic conductivity (0.2 × 10−3 S cm−1 to 1.0 × 10−3 S cm−1), a lithium transference number of 0.99, and excellent mechanical stability (>10 MPa) over a wide temperature range (room temperature to 90 °C) [33].
In parallel, polymer engineering techniques, including copolymerization, crosslinking, and polymer blending, have been widely employed to enhance thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and ionic transference in solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) [22,34]. Among polymer hosts, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) is extensively used due to its strong lithium salt solvation via ether oxygen atoms [35]; however, its high crystallinity at room temperature restricts ionic conductivity. To overcome this limitation, strategies such as polymer blending and crosslinking have been applied using PEO, its derivatives (e.g., PEG, functionalized PEG), and other polymers [36], effectively disrupting crystalline domains to increase the amorphous fraction and improve ionic transport [37]. Blending PEO with polymers such as poly(acrylonitrile) (PAN), poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF), poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) has demonstrated improved ionic conductivity, mechanical stability, and electrochemical performance [38,39]. Additionally, combining hyperbranched polymers with linear PEO enhances ionic conductivity and reduces interfacial resistance by further increasing the amorphous character [40]. Crosslinking further suppresses polymer crystallinity and cold crystallization, boosting room-temperature ionic conductivity. Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) allows facile UV or thermal crosslinking to form mechanically robust matrices [41], while functionalized PEG systems—such as PEG-grafted polymers or PEG-functionalized covalent organic frameworks (COFs)—enhance ion transport, salt dissociation, and electrochemical stability, often restricting anion movement in single-ion conductors. Beyond PEG and PEO, polycarbonates such as poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) offer superior mechanical strength and higher Li-ion transference, overcoming the semi-crystalline limitations of PEG-based systems and providing a pathway toward next-generation lithium batteries [42].
Recent advancements have also introduced novel structural platforms such as covalent organic frameworks (COFs). Unlike conventional linear polymers, COFs provide rigid, porous architectures that maintain ion transport even at sub-zero temperatures. A hydrazone-linked COF-based SPE achieved an ionic conductivity of 10−5 S cm−1 at −40 °C and exhibited excellent capacity retention in lithium-organic batteries. These findings underscore COFs’ potential to suppress active material dissolution and ensure long-term electrochemical stability [29].
A particularly promising development was reported by Zhao et al., who designed a biphasic solid polymer electrolyte (FPEC) by blending PVDF-HFP with poly(ethylene carbonate) complexed with LiTFSI (PECLi). In this system, PVDF-HFP offers mechanical support and a porous scaffold, while the high lithium salt concentration in PECLi forms a polymer-in-salt domain that drives ion transport. This dual-phase configuration enables two synergistic lithium-ion conduction pathways—through the PECLi phase and via interfacial interactions with PVDF-HFP—resulting in improved conductivity (1.08 × 10−4 S/cm at 30 °C), an extended electrochemical window (~4.5 V), and strong dendrite suppression. When applied in LiFePO4/Li cells, the FPEC facilitated enhanced rate performance and stable cycling, attributed to the formation of a robust electrode–electrolyte interface and a well-integrated conductive network [43]. Although commonly referred to as a solid polymer electrolyte, the FPEC developed by Zhao et al. is better described as a biphasic polymer-in-salt/porous polymer hybrid with solid-like characteristics, rather than a traditional SPE.
Another advancement involves the design of polymer-in-salt solid electrolytes (PISSEs), which address the low conductivity of conventional SPEs without relying on external fillers or solvents. Liu et al. developed a PVDF-HFP-based PISSE that achieved a room-temperature ionic conductivity of 1.24 × 10−4 S cm−1. PVDF- HFP serves as an excellent host for lithium salts due to its high fluorine content, hydrophobicity, porous structure, mechanical strength, and thermal stability, which together facilitate salt dissociation and form well-defined ionic channels for efficient lithium-ion transport [44]. The high dielectric constant of PVDF-HFP enhances ion dissociation, while its lamellar and amorphous domains provide continuous pathways for rapid Li+ conduction. Additionally, the mechanical robustness of PVDF-HFP helps suppress lithium dendrite growth during cycling, contributing to long-term stability [45,46]. A key innovation in this work was the full infiltration of the PISSE into a binder-free TiO2 nanoarray electrode, creating a 3D-integrated solid-state lithium battery (SSLB). This architecture enabled continuous ionic and electronic pathways, resulting in excellent capacity retention, rate capability, and mechanical flexibility. Notably, a two-cell pouch configuration delivered a stable output of 3.7 V under physical deformation, underscoring the feasibility of these systems for flexible and wearable electronics [47].
In another study [48], LMP testing cells adapted from Blue Solutions’ technology were evaluated, differing mainly in the TMQ-based positive electrode. Electrochemical tests at 100 °C using a dry PEO-based electrolyte revealed superior performance compared to traditional liquid electrolyte systems (Figure 2a–d). Unlike the low capacity (~110 mAh/g) and rapid degradation seen in carbonate electrolytes, LMP cells achieved ~92% of TMQ’s theoretical capacity and retained ~190 mAh/g after 20 cycles at 1 Li/30 min. The PEO membrane effectively slowed TMQ diffusion, with high coulombic efficiency (~100%) and good rate capability (70% capacity at 1 Li/12 min). Post-mortem analysis confirmed TMQ diffusion as the primary cause of capacity loss (30% after 15 cycles), indicated by the orange discoloration of the membrane. However, the Li interface remained morphologically intact, unlike in Li/S cells, which show severe Li2S deposition. The results suggest that TMQ is better retained within the PEO matrix, highlighting the promise of LMP technology for stable cycling with small organic molecules [48].
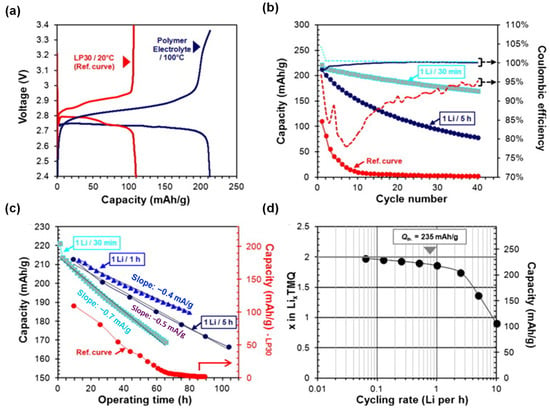
Figure 2.
(a) First-cycle voltage–capacity profile of LMP cells with TMQ at 1 Li/5 h (100 °C), compared to a reference cell with liquid electrolyte at 1 Li/10 h (20 °C), (b) Discharge capacities and coulombic efficiencies of LMP cells at different rates versus the liquid-electrolyte cell, (c) Discharge capacity versus operating time and, (d) Rate capability of an LMP cell tested between 3.2 and 2 V at 100 °C under sequential current densities of 1065, 532, 266, 107, 53.5, 26.75, 13.3, and 6.68 mA g−1. Reproduced with permission from Elsevier [48].
More recently, Zhang et al. introduced a locally high-concentration solid polymer electrolyte system termed “Li-polymer in F diluter” (LPIFD). This design integrates a polymer-in-salt matrix with an inert fluorinated polymer diluter to create a single-phase electrolyte with uniform ion conduction and robust mechanical properties. The fluorinated polymer not only enhances the mechanical strength but also facilitates the formation of a LiF-rich, organic-deficient solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), which effectively mitigates dendrite formation (Figure 3a–d). The distinctive Li–polymer compositions of the three LPIFDs lead to varied SEI chemistries. XPS depth profiling shows that PEO-LPIFD forms an inorganic-rich SEI with reduced carbon species (Figure 3e), while PMMA-LPIFD exhibits a higher organic-to-inorganic ratio (Figure 3f), attributed to the instability of ester groups with Li metal compared to polyether. In contrast, PTFEP-LPIFD generates a LiF-containing SEI, demonstrating the stabilizing role of fluorinated polymers (Figure 3g). These results confirm that LPIFDs favor the formation of robust, organic-deficient SEIs that suppress dendrite growth.
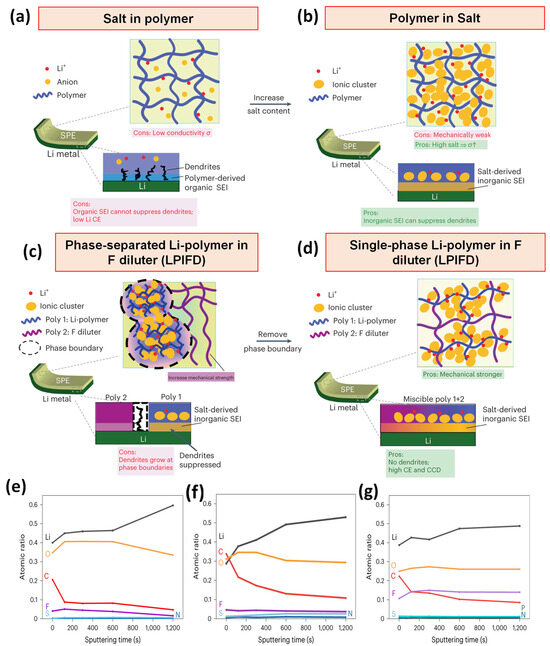
Figure 3.
Schematic of LPIFD SPE design: (a) Salt-in-polymer electrolyte, (b) Polymer-in-salt electrolyte, (c) Phase-separated LPIFD, (d) Single-phase LPIFD; SEI composition: atomic composition ratios at different sputtering times (0, 120, 300, 600, 1200 s) for (e) PEO-LPIFD, (f) PMMA-LPIFD, and (g) PTFEP-LPIFD (adapted from [49]).
Specifically, unlike the non-uniform SEI in PEO-LPIFD and the organic-rich SEI in PMMA-LPIFD, PTFEP-LPIFD exhibits an almost constant elemental ratio from surface to inner SEI (Figure 3c). Fewer C signals and stronger F signals indicate an organic-lean, fluorinated SEI with high inorganic content. A pronounced LiF peak, arising from the uniform distribution of PTFEP in PVDF-HFP, results in a homogeneous LiF-rich SEI that retains mechanical strength, minimizes interfacial stress, and effectively suppresses Li dendrite growth. The LPIFD system achieved a high ionic conductivity of 3.0 × 10−4 S cm−1, a coulombic efficiency of 99.1%, and supported a critical current density of 3.7 mA cm−2. Furthermore, it enabled the long-term cycling of high-voltage LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2||Li cells at 4.5 V for over 450 cycles, demonstrating its potential for high-energy lithium-metal battery applications [49].
Collectively, these innovations reflect a significant shift toward multifunctional solid polymer electrolyte systems that can simultaneously address ionic conductivity, mechanical robustness, and interfacial stability. The convergence of polymer–salt synergy, advanced architectures (e.g., COFs, 3D-infiltrated electrodes), and high-voltage-compatible chemistries is driving the development of next-generation SPEs. These efforts are crucial for advancing solid-state organic batteries that are not only high-performing but also intrinsically safe and suitable for flexible electronic applications.
2.2. Gel Polymer Electrolytes
Gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs) represent a pivotal advancement in battery electrolyte design, offering a promising alternative to both liquid and solid polymer electrolytes. Positioned between the two, GPEs combine the fluid-like ionic conductivity of liquid electrolytes with the mechanical stability of solid polymer matrices. This hybrid nature makes them particularly advantageous for overcoming the limitations associated with solid polymer electrolytes, such as low room-temperature ionic conductivity and high interfacial resistance, and the solubility issues of organic active materials in liquid systems. Their integration into battery systems has been especially impactful in organic batteries, where electrolyte properties significantly affect performance and stability. Several studies have highlighted the superior electrochemical behavior achieved through GPE integration. For instance, a quasi-solid-state electrolyte system comprising poly(methacrylate) (PMA) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) in a DMSO–LiClO4 medium achieved an impressive ionic conductivity of 5.7 × 10−4 S cm−1. This formulation delivered an initial discharge capacity of 422 mAh g−1 and retained nearly 90% of its capacity over 100 cycles, markedly outperforming traditional liquid electrolyte systems [50]. In parallel, PVDF-HFP-based GPEs with porous architectures have demonstrated enhanced cycling and rate capabilities by improving electrolyte retention and restricting the migration of dissolved redox species, thus mitigating capacity fading [51].
Beyond conventional polymers, polyimide (PI) has garnered interest for its dual function as both an electrode host and GPE matrix. Electrospun PI membranes, characterized by their interconnected porous networks and superior solvent uptake, have proven effective in stabilizing organic battery systems, especially when used in combination with carbon nanotube (CNT)-modified electrodes [13,52]. In a more advanced approach, the in situ polymerization of 1,3-dioxolane (DOL), catalyzed by Nafion, resulted in a multifunctional GPE with molecular sieving and charge repulsion capabilities. This electrolyte design significantly enhanced interfacial contact, limited the shuttle of soluble intermediates, and enabled reliable performance across an extended temperature range (−70 to 100 °C) when used with organic electrodes such as TAQB and PTCDA [53].
In addition to suppressing the dissolution of active materials, GPEs have shown remarkable effectiveness in stabilizing alkali metal anodes. As depicted in Figure 4a, the incorporation of GPEs in lithium-ion batteries can suppress dendrite formation, preventing direct contact between lithium metal anodes and cathodes [54]. For example, replacing the organic-liquid electrolyte in a glass-fiber separator with a crosslinked PMMA-based polymer-gel electrolyte in potassium batteries enables dendrite-free K+ plating/stripping and stabilizes the electrode/electrolyte interface [55]. The chemical structure of the cross-linked PMMA in the polymer-gel electrolyte is shown in Figure 4b. The polymer matrix wets the potassium anode, while its crosslinked architecture with tunable pore sizes facilitates the formation of a stable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI), enhancing both safety and cycling stability [55]. These findings highlight the multifunctional role of GPEs in prolonging cycle life and improving overall electrochemical performance.
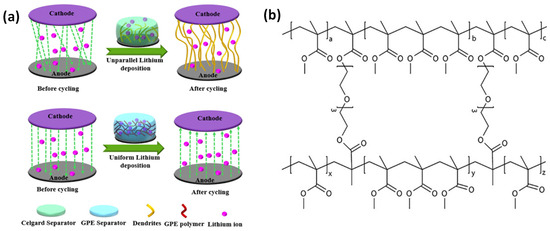
Figure 4.
(a) GPE application in lithium-ion battery to suppress dendrite formation from lithium metal anode to cathode (adapted from [54]), (b) Chemical structure of the cross-linked PMMA in the polymer-gel electrolyte (adapted from [55]).
The evolution of GPEs has also been marked by innovations aimed at scalability and practical deployment. One significant development is the design of a printable GPE based on methacrylate polymers incorporating ionic liquids. This system, compatible with UV-induced one-step polymerization, supports roll-to-roll fabrication and eliminates the need for post-treatment processes. The resulting GPE demonstrates ionic conductivities up to 10−4 S cm−1 at room temperature and offers robust mechanical properties suitable for acting as both electrolyte and separator.
For the first time, a printable GPE tailored for all-organic batteries was formulated using a mixture of methacrylate monomers, a cross-linking agent (TEG-DMA), a functional nanofiller, and an ionic liquid (IL), with photopolymerization initiated by camphorquinone. This viscous formulation can be cast directly onto battery electrodes and subsequently polymerized in situ via UV irradiation. In particular, composition 6 (volIL:volM 2:1, 10 mol% TEG-DMA) yielded free-standing GPEs that delivered stable cycling over 1000 cycles, achieving discharge capacities of 24 mAh g−1 at 0.1 C and 18 mAh g−1 at 5 C, along with high coulombic efficiency. Notably, when the GPE was polymerized directly on the cathode, enhanced electrode–electrolyte interface contact led to improved swelling and even higher capacities of 32 mAh g−1 at 0.1 C. Despite relatively lower ionic conductivity and higher ohmic drop, the system retained long-term cycling stability, maintaining 17 mAh g−1 at 1 C after 1000 cycles (Figure 5). These results highlight the promise of printable GPEs for high-performance, all-organic solid-state batteries [56]. The galvanostatic charge/discharge (GCD) profiles of coin cells with PTMA cathode, TCAQ anode, and GPE 6 as electrolyte and separator are presented in Figure 5.
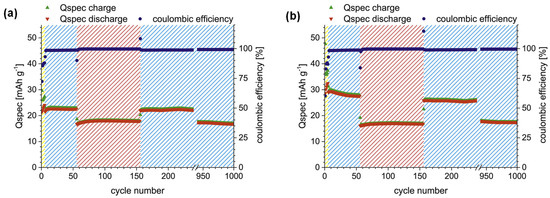
Figure 5.
GCD profile of coin cells; (a) free-standing (covered) GPE and (b) casted onto PTMA composite electrode (adapted from [56]).
Further advancing this field, smart GPEs tailored for sodium-ion batteries have been developed via in situ radical polymerization of cyanoethylurea- and isocyanate-functionalized methacrylates in conventional NaPF6-based carbonate electrolytes. These GPEs enhance thermal and chemical stability by forming resilient interfacial layers and undergoing secondary crosslinking reactions at elevated temperatures (above 120 °C). This adaptive behavior effectively suppresses unwanted ion transport and mitigates harmful electrode-electrolyte crosstalk. As a result, sodium-ion pouch cells incorporating this GPE exhibit superior safety and prolonged cycling, even at elevated temperatures around 50 °C [57].
Expanding the application landscape further, a bioinspired GPE designed for lithium metal batteries has been engineered for operation across a broad temperature range (–30 to 80 °C). Utilizing a branched polymer framework with side chains capable of double dipole interactions, this GPE regulates lithium-ion solvation by creating a weak coordination environment. This leads to rapid, uniform lithium deposition and enhances electrochemical performance under extreme conditions. Notably, the GPE achieves high ionic conductivity (1.03 × 10−4 S cm−1 at –40 °C) and a remarkable Li+ transference number of 0.83, enabling stable cycling with capacities exceeding 170 mAh g−1 at 80 °C while remaining effective at sub-zero temperatures [58].
In summary, recent innovations in gel polymer electrolyte design underscore a paradigm shift in battery development, one that prioritizes safety, scalability, and performance across diverse chemistries and environmental conditions. Whether through advanced polymer architectures, smart thermal reactivity, or printable formats, GPEs are redefining the operational boundaries of modern energy storage systems and positioning themselves as a central component in the next generation of flexible, high-energy, and durable batteries.
2.3. Polymer-Inorganic Composite Electrolytes
To enhance the ionic conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical strength of polymer electrolytes, inorganic fillers are often introduced into polymer matrices, forming composite electrolytes. These fillers are generally categorized as non-conductive passive fillers like TiO2, SiO2, and Al2O3 or ionically conductive active fillers. Passive fillers help reduce polymer crystallinity and promote salt dissociation by interacting with surface groups, thereby increasing free ion concentration. In contrast, active fillers such as Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO), Li0.33La0.557TiO3, Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3, and Li1.4Al0.4Ge1.6(PO4)3 contribute directly to ion conduction by forming continuous transport pathways [27]. The first polymer–ceramic composite electrolyte was reported in 1982, incorporating Al2O3 particles into a PEO matrix, which enhanced both mechanical properties and ionic conductivity [59]. Al2O3 reduced PEO crystallinity and lowered its glass transition temperature, increasing the mobility of polymer segments and facilitating Li+ transport [60]. Similar improvements were observed in PEO–PMMA–LiTFSI composites with Al2O3, while other materials such as SiO2, TiO2, Y2O3-stabilized ZrO2, and Mg2B2O5 nanowires have also been investigated as passive fillers [25,26]. Ferroelectric ceramics like BaTiO3, PbTiO3, and LiNbO3 enhance polymer electrolytes by reducing interfacial resistance and improving Li+ conductivity through spontaneous polarization [61]. More recently, LiAlO2 has emerged as a promising filler, where its chemical stability and ability to interact with polymer chains help suppress interfacial resistance while simultaneously contributing to enhanced ionic transport [62].
The first experimental evidence of lithium-ion transport mechanisms within polymer–ceramic composite electrolytes, particularly those based on LLZO and polyethylene oxide (PEO), was reported by Zheng et al. Using selective isotope labeling combined with high-resolution solid-state 6Li/7Li NMR, it was shown that Li+ ions preferentially diffuse through LLZO ceramic particles rather than the polymer phase or the LLZO–PEO interface during cycling in symmetric cells (Figure 6). As illustrated in Figure 6a,b, a symmetric 6Li/composite/6Li cell clearly revealed the preferential diffusion of Li+ through LLZO during cycling. The corresponding NMR spectra (Figure 6c,d) indicated that ~39% of Li+ exchange occurred within the LLZO phase, compared to only ~6% at interfacial sites and negligible contribution from the polymer host. This confirms that the LLZO ceramic phase serves as the dominant conduction pathway, provided that a percolation network of LLZO particles is established within the composite matrix [27]. This direct evidence highlights the critical role of active fillers in facilitating long-range ion transport and underscores the importance of microstructural engineering in designing high-performance solid polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state batteries.
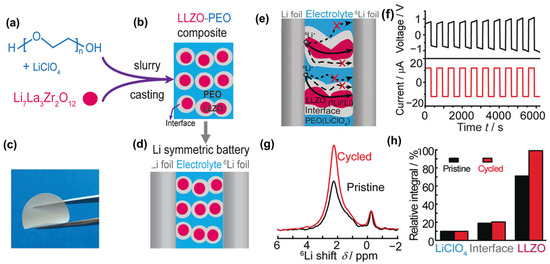
Figure 6.
LLZO–PEO composite electrolytes: (a,b) Synthesis, (c) flexible membrane, (d,e) Li+ transport pathways in symmetric 6Li/composite/6Li cell, (f) cycling profile, (g) 6Li NMR spectra before and after cycling, (h) quantitative Li+ distribution in LLZO, interface, and LiClO4 (adapted from [27]).
For instance, incorporating SiO2 into a PMA/PEG-based gel electrolyte significantly enhanced ionic conductivity and stability compared to TiO2, attributed to SiO2′s smaller size and higher surface activity [63]. This composite system demonstrated high capacity and retention in Li-organic batteries. Similarly, PEO/PEG electrolytes with γ-LiAlO2 suppressed the dissolution of anthraquinone (AQ) more effectively than liquid systems, though elevated temperatures still led to capacity fading due to polymer softening and increased solubility of active materials [64].
While blending inorganic fillers is straightforward, achieving uniform dispersion remains a challenge, as excessive filler content can lead to aggregation and hinder ion mobility. To address this, multilayered composite electrolytes have been developed. A notable example includes a structure integrating a PEO layer, a SiO2-ionic liquid (IL) quasi-solid layer, and an artificial SEI. This configuration enhances conductivity, minimizes active material dissolution, and maintains interfacial stability, achieving over 79% capacity retention after 100 cycles [65].
Another promising strategy involves embedding polymer and salts into 3D ion-conductive frameworks, such as electrospun LLTO, LLZO, or MOF@PAN networks. These structures not only provide mechanical robustness and flame resistance but also enable continuous ion transport. A recent MOF-integrated PEO electrolyte facilitated fast Li+ transport and reduced interfacial resistance, significantly improving the cycling stability of Li-IDAQ batteries by effectively limiting the shuttle of active materials [66,67,68,69].
In summary, polymer-inorganic composite electrolytes present a compelling solution for overcoming the limitations of conventional SPEs. By enhancing ion mobility and mechanical integrity while suppressing active material dissolution, these systems are key to advancing safe, efficient, and high-performance organic solid-state batteries, especially under ambient conditions.
2.4. Ionogel and Poly(ionic Liquid) Electrolytes
Ionogels and poly(ionic liquid) (PIL)-based electrolytes have garnered increasing attention for use in solid-state organic batteries due to their favorable attributes such as high salt solubility, broad electrochemical stability windows, and excellent thermal resistance. Typically, ionogels are synthesized by either dispersing ionic liquids (ILs) into polar polymer matrices or through in situ polymerization of monomers within ILs. In these systems, ILs simultaneously act as plasticizers and ion conductors, providing not only high ionic conductivity but also flame retardancy and the suppression of active material dissolution, critical parameters for enhancing both safety and cycling performance.
Recent advancements have introduced novel fabrication strategies. One such example involves ultraviolet (UV) curing of acrylate monomers in BMITFSI to create printable ionogel electrolytes that demonstrate robust mechanical integrity and effective ion transport. Furthermore, in situ polymerization directly on electrode surfaces has proven beneficial for improving electrode–electrolyte interfacial contact, subsequently enhancing initial discharge capacity. Nevertheless, a drawback in this approach is the potential presence of residual unpolymerized monomers, which may negatively affect capacity retention over extended cycling [70].
Ionogels are considered particularly promising for high-energy-density flexible solid-state capacitors (FSCs), given their high ionic conductivity and wide electrochemical operating window resulting from the immobilization of ILs within polymer networks [71]. However, the compatibility between ILs and conventional polymer matrices like polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) or polyacrylic acid (PAA) remains a limiting factor, often leading to suboptimal ion transport. To overcome this incompatibility, the integration of ILs directly into PILs has emerged as a compelling strategy for fabricating ionogels with improved homogeneity and performance [72].
Despite these advantages, PIL-based ionogels often suffer from inadequate mechanical strength. Their tensile strength and modulus are typically below 0.2 MPa and 0.1 MPa, respectively, insufficient for preventing short circuits and ensuring the reliability of flexible devices. In response, several strategies have been explored, such as introducing hyperbranched polymer architectures, utilizing hydrogen bonding interactions, and reinforcing with nanoparticles [73]. However, the development of ionogels that are simultaneously self-healing, mechanically robust, and highly conductive continues to pose a significant challenge.
In a notable study, Wu et al. incorporated a dynamic imidazole–zinc ion (Im–Zn2+) coordination motif into a PIL-based ionogel system. This design yielded a self-healing ionogel with impressive mechanical performance (tensile stress of 0.58 MPa and modulus of 3.0 MPa) and high ionic conductivity (0.36 mS/cm), making it suitable for FSC applications [74]. The Im–Zn2+ coordination is characterized by high directionality and tunable bonding strength—up to 350 kJ/mol, approaching that of conventional C–C covalent bonds, providing enhanced mechanical resilience [74]. The coordination occurs between Zn2+ ions and the lone-pair electrons (Nlpe) on the imidazole rings. This interaction was introduced into the PIL backbone through a one-step free radical copolymerization of 1-vinyl-3-ethylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (VmimBF4) and vinyl imidazole (VI), yielding a P(VI-co-VmimBF4) copolymer. The dynamic reversibility of the Im–Zn2+ coordination contributes to the material’s self-healing ability through topological rearrangements [74]. Moreover, the wide electrochemical window (up to 3.2 V) of the resulting ionogel enabled its integration with covalent organic framework/reduced graphene oxide (COF/rGO) electrodes, delivering a notable energy density of 46 Wh/kg, surpassing several previously reported systems [74].
PILs also offer other benefits, including improved mechanical formability, enhanced processability, and structural tunability. Although their intrinsic ionic conductivity is relatively lower than that of free ILs, performance can be substantially improved through the incorporation of conductive additives or additional ILs [75,76,77]. For instance, a composite consisting of polyDADMATFSI (poly(dimethyldiallylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide)) and EMIDCA (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide), reinforced with Zn(DCA)2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles, exhibited a remarkable ionic conductivity of 1.1 × 10−2 S/cm. Nonetheless, the associated Zn–PEDOT battery exhibited limitations such as low capacity and rapid capacity fade, indicating the need for further material and interface optimization. To explore the suitability of iongels as electrolytes in Zn batteries, Anastro et al. [78] investigated various optimized formulations. In their study, symmetrical coin cells utilizing (polyDADMATFSI)-based iongel (Figure 7a) demonstrated stable cyclability over 20 cycles at different current densities (0.01, 0.02, and 0.03 mA/cm2) at 50 °C. At the lowest current density of 0.01 mA/cm2, only a slight increase in polarization potential (<0.05 V) was observed, suggesting minimal solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation. At higher current densities (0.02 and 0.03 mA/cm2), initial slight decreases in potential were recorded, which subsequently stabilized within a range of 0.1–0.2 V after the initial cycles. The use of thinner membranes—compared to the current 250 μm thickness—may further reduce polarization effects. Overall, the iongel electrolyte exhibited promising electrochemical stability and potential for enhancing Zn battery performance. The configuration of the zinc symmetrical cell and its galvanostatic cycling behavior at different current densities with 30 min steps are illustrated in Figure 7b and 7c, respectively.
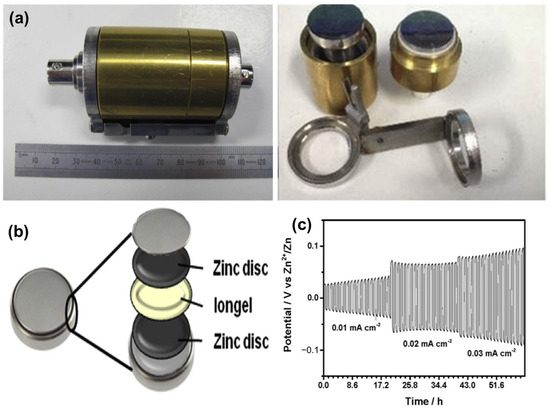
Figure 7.
(a) Air-tight barrel cell with stainless steel electrodes for conductivity measurement, (b) Scheme of a zinc symmetrical cell set up, (c) Galvanostatic cycling of the cell with ion gel as electrolyte at different current densities (adapted from [78]).
To further refine electrolyte–electrode integration, advanced techniques like layer-by-layer spray printing have been employed to embed conductive PILs within porous organic electrodes. This method significantly improves interfacial adhesion and reduces charge transfer resistance. However, it also promotes the dissolution of active electrode materials, which compromises Coulombic efficiency and accelerates capacity degradation over time [79]. While ionogels and PIL-based electrolytes show considerable potential for solid-state organic battery applications, their practical implementation remains in the developmental phase. Future research should prioritize the optimization of their chemical composition and structural design. Strategies such as incorporating rigid frameworks like metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) can enhance mechanical integrity, while precise modulation of IL content could help minimize issues related to electrode degradation. Such developments are crucial for realizing safer, more stable, and high-performing solid-state organic battery systems.
As evident from recent developments, polymer-based electrolytes encompassing both solid and gel variants are rapidly evolving as critical enablers of high-performance, safe, and flexible organic battery systems. Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) offer enhanced mechanical integrity and safety, while recent advances such as COF-based architectures, biphasic systems, and polymer-in-salt configurations have significantly improved ionic conductivity and interfacial stability. Gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs), on the other hand, bridge the gap between liquid-like conductivity and solid-like mechanical support, delivering superior electrochemical performance and long-term cycling stability. The integration of innovative materials, structural designs, and synergistic polymer–salt systems is accelerating the development of multifunctional electrolytes capable of addressing the unique challenges of organic batteries. For a clearer understanding and comparative evaluation of the diverse polymer electrolyte systems, their advantages and disadvantages are presented in Figure 8 below.
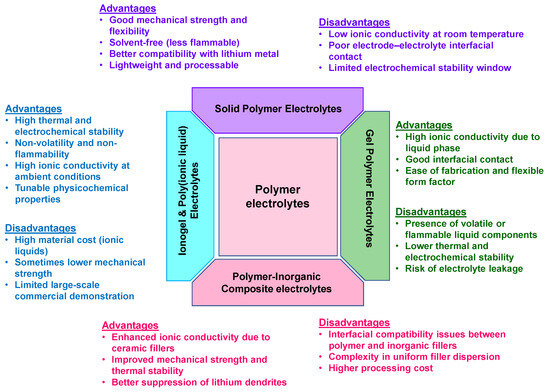
Figure 8.
Advantages and disadvantages of different polymer electrolyte systems.
3. Challenges and Prospects
Despite notable progress, the development of high-performance electrolytes for organic batteries remains in an early stage. Each electrolyte type, organic liquid, aqueous, inorganic solid, polymer-based, and composite, offers distinct advantages but also presents critical limitations. Therefore, tailoring electrolyte formulations to specific battery chemistries is essential to unlocking their full potential.
Liquid electrolytes are widely used due to their excellent ionic conductivity and compatibility with various organic electrodes. High-concentration electrolytes have shown promise in improving stability and broadening electrochemical windows, even under extreme conditions. However, issues such as high cost, viscosity, and poor wettability limit their scalability. Research is now focused on strategies like localized high-concentration electrolytes, deep eutectic systems, and cost-effective salts to improve performance while reducing economic and environmental impacts.
Solid-state electrolytes, including polymer-based and inorganic types, are gaining interest for their ability to suppress self-discharge and improve cycling stability. Yet, polymer electrolytes often suffer from low ionic conductivity at room temperature. While gel formulations or elevated operating temperatures can help, they may compromise the dissolution-inhibiting properties of the electrolyte. Quasi-solid and composite designs, particularly those combining polymers with inorganic fillers, are being explored to enhance conductivity and electrode compatibility.
Inorganic solid electrolytes, especially sulfide-based systems like Li3PS4 and Na3PS4, can effectively prevent the dissolution and shuttle of organic species. However, challenges persist due to poor interfacial contact, low electronic conductivity of organic materials, and the need for high electrolyte content within electrodes, which reduces energy density. The design of high-voltage-stable electrolytes (e.g., halides) and advanced interface engineering remains crucial for improving performance.
Plastic crystal and poly(ionic liquid) (PIL) electrolytes offer new directions for solid-state systems, though their interaction with metal anodes can lead to resistive interface formation. Additives like FEC may stabilize these systems but could negatively affect redox-active organics. Thus, fine-tuning electrolyte composition and interphase behavior is needed.
Membranes also play a pivotal role but remain underexplored in organic battery research. Ion-selective membranes used in fuel cells and flow batteries offer insights into improving ion transport and selectivity. Innovations such as sulfonated polymers, restricted pore architectures, and inorganic fillers could be adapted to minimize shuttle effects and improve separator performance. However, cost and limited commercial availability remain barriers.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Organic batteries offer a promising and sustainable alternative to conventional lithium-ion systems. Advancing their practical utility requires a holistic approach that considers not only the ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability of electrolytes but also the interfacial compatibility with electrodes. Future research should focus on the following:
- Rational electrolyte design: Developing polymer and composite electrolytes with wide electrochemical windows, high ionic conductivity, and robust mechanical properties, while minimizing side reactions with organic electrodes.
- Interface engineering: Controlling SEI formation, optimizing electrode–electrolyte contact, and employing surface coatings or interlayers to stabilize interfaces and enhance long-term cycling.
- Integrated architectures: Designing fully infiltrated 3D electrode–electrolyte systems to maximize ion and electron transport and reduce interfacial impedance.
- Scalable and sustainable materials: Using cost-effective, environmentally friendly salts, polymers, and fillers suitable for large-scale applications.
- Advanced membranes and separators: Incorporating ion-selective or hybrid membranes to suppress shuttle effects and improve selectivity, enabling safer and higher-performing organic batteries.
By combining materials innovation, interface optimization, and structural engineering, the field of organic batteries can transition from laboratory demonstrations to commercially viable energy storage technologies, ultimately supporting sustainable and flexible energy solutions.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Research Council of Science and Technology (NST) through a grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (CRC23013-000), and the KIST Institutional Program (2E34042).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the institutional support provided by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Khan, M.K.; Raza, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Farooq, U.; Akram, M.U. Recent advancement in energy storage technologies and their applications. J. Energy Storage 2024, 92, 112112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmani, P.; Bahadur, J.; Tewari, C.; Gupta, D.K.; Kalita, U.; Jegadeesan, P.; Ravindran, T.R.; Alex, A.; Das, A.; Sahoo, N.; et al. Polyaniline modified waste-derived graphene/sulfur nanocomposite cathode for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, P.; Jalilian, M.; Amidi, A.M.; Zangeneh, M.R.; Riba, J.R. From Present Innovations to Future Potential: The Promising Journey of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Micromachines 2025, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.N.; Lee, Y.K.; Tewari, C.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.C. Simultaneous recycling and nitrogen doping in carbon fiber reinforced plastic using eco-friendly supercritical water treatment for Li-ion batteries anode application. Carbon 2024, 221, 118944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cai, X.; Cai, S.; Shao, Y.; Hu, C.; Lu, S.; Ding, S. High-energy lithium-ion batteries: Recent progress and a promising future in applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 6, e12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, H.; Cui, Y. Formulating energy density for designing practical lithium–sulfur batteries. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koech, A.K.; Mwandila, G.; Mulolani, F.; Mwaanga, P. Lithium-ion battery fundamentals and exploration of cathode materials: A review. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 50, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janek, J.; Zeier, W.G. A solid future for battery development. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, Z.; Cui, Y.; Dufek, E.J.; Goodenough, J.B.; Khalifah, P.; Li, Q.; Liaw, B.Y.; Liu, P.; Manthiram, A.; et al. Pathways forPractical High-Energy Long-Cycling Lithium Metal Batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Tewari, C.; Arya, T.; Kim, Y.N.; Pant, P.; Sati, S.; Dhali, S.; Negi, P.B.; Jung, Y.C.; Sahoo, N.G. Development of nitrogen and phosphorus dual-doped reduced graphene oxide from waste plastic for supercapacitor applications: Comparative electrochemical performance in different electrolytes. Next Energy 2025, 6, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J. Structure and performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials: A review. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redway, E.S.S. LiFePO4 Cell Energy Densities: Standard and Advanced Performance. Redway ESS Industry Analysis. 2025. Available online: https://www.redwayess.com/how-are-higher-energy-density-lifepo4-batteries-revolutionizing-energy-storage/?utm_source (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Li, M.; Hicks, R.P.; Chen, Z.; Luo, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y. Electrolytes in organic batteries. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 1712–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, C.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Ryu, S.; Jeong, H.S.; Jung, Y.C. Development of fluorescent epoxy composite with carbon-based nanomaterial additives derived from agricultural waste. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2024, 30, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, C.; SanthiBhushan, B.; Srivastava, A.; Sahoo, N.G. Metal doped graphene oxide derived from Quercus ilex fruits for selective and visual detection of iron (III) in water: Experiment and theory. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Yuan, S.; Ma, D.L.; Huang, X.L.; Meng, F.L.; Zhang, X.B. Tailored Aromatic Carbonyl Derivative Polyimides for High-Power and Long-Cycle Sodium-Organic Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazie, N.; Worku, D.; Gabbiye, N.; Alemayehu, A.; Getahun, Z.; Dagnew, M. Development of polymer blend electrolytes for battery systems: Recent progress, challenges, and future outlook. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2023, 12, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhong, C.; Liu, J.; Ding, J.; Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, J. Opportunities of flexible and portable electrochemical devices for energy storage: Expanding the spotlight onto semi-solid/solid electrolytes. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17155–17239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhu, X.; He, P.; Zhou, H. A stable quasi-solid electrolyte improves the safe operation of highly efficient lithium-metal pouch cells in harsh environments. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xiong, X.; Peng, J.; Wu, W.; Fan, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y. Tailored Engineering on the Interface Between Lithium Metal Anode and Solid-State Electrolytes. Energy Environ. Mater. 2025, 8, e12831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Z.; Wen, R. Recent Advances in In Situ Characterization of the Electrochemical Processes at the Alloy Anode-Electrolyte Interfaces. Langmuir 2025, 41, 6497–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, B.; Shamraiz, U.; Hu, M.; Xu, X.; Yu, B.; Jing, S.; Tao, Y.; Wang, J. Advances in Organic electrolytes for High-Performance zinc Batteries: Enhancing zinc anode Robustness and efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 515, 163617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Single-ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes: Design, preparation and application. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 1557–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Tang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Yan, X. Preparation and characterization of PEO-PMMA polymer composite electrolytes doped with nano-Al2O3. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Manthiram, A. A review of composite polymer-ceramic electrolytes for lithium batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 34, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Tang, M.; Hu, Y.Y. Lithium ion pathway within Li7La3Zr2O12-polyethylene oxide composite electrolytes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12538–12542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.Q.; Lv, F.; Xu, N.; Wu, M.T.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.P. Polyethylene oxide-based solid-state composite polymer electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 4581–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, Q.; Huang, W.; Xu, H.-S.; Wang, X.; Yu, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. Solution-Processable Covalent Organic Framework Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Li-Organic Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 3498–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, P.; Song, J.; Shi, C. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) as fast lithium-ion transport fillers for solid polymer electrolytes. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, L. An investigation of functionalized electrolyte using succinonitrile additive for high voltage lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 306, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.Z.; Hu, Y.S.; Bhattacharyya, A.J.; Maier, J. Succinonitrile as a versatile additive for polymer electrolytes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2800–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kang, H.; Kim, K.; Wang, R.Y.; Park, M.J. All-Solid-State Lithium–Organic Batteries Comprising Single-Ion Polymer Nanoparticle Electrolytes. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, D.; Rani, M.U. Optimization of polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries: Focus on enhancement strategies and film casting techniques. Ionics 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, Q.; Ma, W.; Yang, L. Polyethylene oxide-based composites as solid-state polymer electrolytes for lithium metal batteries: A mini review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Wen, K.; Guan, S.; Xue, C.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Nan, C.W. A cross-linked poly (ethylene oxide)-based electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries with long cycling stability. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 864478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.T.; Abdullah, O.G. Preparation and composition optimization of PEO: MC polymer blend films to enhance electrical conductivity. Polymers 2019, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.B.T.; Ding, L.; Pohle, B.; Schmeida, T.; Nguyen, H.B.A.; Mikhailova, D. Ternary PEO/PVDF-HFP-Based Polymer Electrolytes for Li-Ion Batteries. Batteries 2025, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, B.; Schmuck, M.; Kern, W. PEO based polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. In Proceedings of the 1st Joint Austrian & Slovenian Polymer Meeting ASPM, Graz, Austria, 26–28 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Prasannavenkadesan, V.; Katiyar, V.; Sudhakar, A.A. Polymer electrolytes: Evolution, challenges, and future directions for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Appl. Polym. 2025, 3, 499–531. [Google Scholar]
- Krutkramelis, K.; Xia, B.; Oakey, J. Monodisperse polyethylene glycol diacrylate hydrogel microsphere formation by oxygen-controlled photopolymerization in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandell, D.; Sun, B.; Mindemark, J. Functional Solid-State Polymer Electrolytes through Utilization of Polycarbonates. In Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts imlb2016; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2016; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Bai, Y.; An, M.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y. A rational design of solid polymer electrolyte with high salt concentration for lithium battery. J. Power Sources 2018, 407, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Singh, R.; Chand, P.; Kumar, M.; Singh, R.R.; Kumar, A. A review on polymer electrolyte materials in context to modifications in PVDF-HFP polymer host. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2025, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Das, M.; Raja, M.W. Role of LLZO active filler in PVDF-modified cellulosic paper matrix: A sustainable, thermally durable and high-performance separator for next generation lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2025, 654, 237838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.H.; Haleem, A.; Arwish, S.; Shah, A.; Hussain, H. PVDF-based solid polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: Strategies in composites, blends, dielectric engineering, and machine learning approaches. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 20629–20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yi, C.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Gui, Q.; Ba, D.; Li, Y.; Peng, D.; Liu, J. Designing polymer-in-salt electrolyte and fully infiltrated 3D electrode for integrated solid-state lithium batteries. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 13041–13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lécuyer, M.; Gaubicher, J.; Barrès, A.L.; Dolhem, F.; Deschamps, M.; Guyomard, D.; Poizot, P. A rechargeable lithium/quinone battery using a commercial polymer electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 55, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Koverga, V.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Bai, P.; Tan, S.; Dandu, N.K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Single-phase local-high-concentration solid polymer electrolytes for lithium-metal batteries. Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Cheruvally, G.; Choi, J.-W.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, D.S.; Song, C.E. Rechargeable Organic Radical Battery with Electrospun, Fibrous Membrane-Based Polymer Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; An, Y.; Dong, S.; Jiang, J.; Dou, H.; Zhang, X. Enhanced Cycle Performance of Polyimide Cathode Using a Quasi-Solid-State Electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 22294–22300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.-J.; Byeon, H.; Kim, J.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.-K. Binder-Free Organic Cathode Based on Nitroxide Radical Polymer-Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes and Gel Polymer Electrolyte for High-Performance Sodium Organic Polymer Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17980–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z.; Bai, P.; Su, H.; Xiong, P.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y. Soluble Organic Cathodes Enable Long Cycle Life, High Rate, and Wide-Temperature Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Islam, M.; Raut, B.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Nam, K.W. A comprehensive review of functional gel polymer electrolytes and applications in lithium-ion battery. Gels 2024, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Xue, L.; Xin, S.; Goodenough, J.B. A high-energy-density potassium battery with a polymer-gel electrolyte and a polyaniline cathode. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5547–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muench, S.; Burges, R.; Lex-Balducci, A.; Brendel, J.C.; Jäger, M.; Friebe, C.; Wild, A.; Schubert, U.S. Printable ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolytes for solid state all-organic batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 25, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Xu, G.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, T.; Huang, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, F.; Li, C.; et al. Smart gel polymer electrolytes enlightening high safety and long life sodium ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, W.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Kuang, X.; Yang, C.; Chen, S.; Han, X.; Quan, H.; et al. Bioinspired gel polymer electrolyte for wide temperature lithium metal battery. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, J.E.; Steele, B.C.H. Effects of inert fillers on the mechanical and electrochemical properties of lithium salt-poly (ethylene oxide) polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 1982, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambelli, C.C.; Bloise, A.C.; Rosario, A.V.; Pereira, E.C.; Magon, C.J.; Donoso, J.P. Characterisation of PEO–Al2O3 composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Takeda, Y.; Imanishi, N.; Yamamoto, O.; Sohn, H.J. Ferroelectric materials as a ceramic filler in solid composite polyethylene oxide-based electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbouazzaoui, K.; Mahun, A.; Shabikova, V.; Rubatat, L.; Edström, K.; Mindemark, J.; Brandell, D. Enabling High-Voltage Polymer-Based Solid-State Batteries Through Reinforcements with LiAlO2 Fillers. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2405249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hong, M.; Guo, D.; Shi, J.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J. All-Solid-State Lithium Organic Battery with Composite Polymer Electrolyte and Pillar [5] Quinone Cathode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16461–16464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. All-Solid-State Secondary Lithium Battery Using Solid Polymer Electrolyte and Anthraquinone Cathode. Solid State Ion. 2017, 300, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyu, Y.; Ganbe, Y.; Honma, I. Application of Quinonic Cathode Compounds for Quasi-Solid Lithium Batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 221, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Lin, Y.H.; Li, L.; Shen, Y.; Nan, C.W. Lithium-Salt-Rich PEO/Li0.3La0.557TiO3 Interpenetrating Composite Electrolyte with Three-Dimensional Ceramic Nano-Backbone for All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24791–24798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y.; Song, J.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Elastic and Well-Aligned Ceramic LLZO Nanofiber Based Electrolytes for Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Fan, L.Z. 3D Fiber-Network- Reinforced Bicontinuous Composite Solid Electrolyte for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 7069–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zou, H.; Chen, Y.; Kuang, W.; Ding, K.; Chen, L.; et al. A 3D Interconnected Metal- Organic Framework-Derived Solid-State Electrolyte for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Battery. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 47, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Thakur, A.; Thakur, R.C.; Kumar, A. A Review on Multifaceted Role of Ionic Liquids in Modern Energy Storage Systems: From Electrochemical Performance to Environmental Sustainability. Energy Fuels 2025, 39, 3703–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, T.; Douard, C.; Robert, K.; Asbani, B.; Lethien, C.; Brousse, T.; Le Bideau, J. Solid-state 3D micro-supercapacitors based on ionogel electrolyte: Influence of adding lithium and sodium salts to the ionic liquid. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 50, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, N.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Duan, W. Ionic liquid modified poly (vinyl alcohol) with improved thermal processability and excellent electrical conductivity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 5472–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, F.; Guan, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, J. Mechanically and environmentally stable triboelectric nanogenerator based on high-strength and anti-compression self-healing ionogel. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wen, L.; Li, X.; Feng, T.; Li, P.; Fang, Z.; Wu, M.; et al. Ionogel electrolyte with dynamic metal-ligand interactions enabled self-healable supercapacitor with high energy density. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 57, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Gong, Z.; Liu, C.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y. Design and fabrication of mechanically strong and self-healing rubbers via metal-ligand coordination bonds as dynamic crosslinks. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 207, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Zuo, J.L. Self-healing polymers based on coordination bonds. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1903762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Wu, D. Agar-based porous electrode and electrolyte for flexible symmetric supercapacitors with ultrahigh energy density. J. Power Sources 2021, 507, 230252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fdz De Anastro, A.; Casado, N.; Wang, X.; Rehmen, J.; Evans, D.; Mecerreyes, D.; Forsyth, M.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C. Poly(Ionic Liquid) Iongels for All-Solid Rechargeable Zinc/PEDOT Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 278, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.; Bu, J.; Quijano Velasco, P.; Roberts, M.R.; Grobert, N.; Grant, P.S. Single-Step Spray Printing of Symmetric All-Organic Solid-State Batteries Based on Porous Textile Dye Electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).