Time Delay Stability Analysis and Control Strategy of Wind Farm for Active Grid Frequency Support
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SFR Model Considering Time Delay
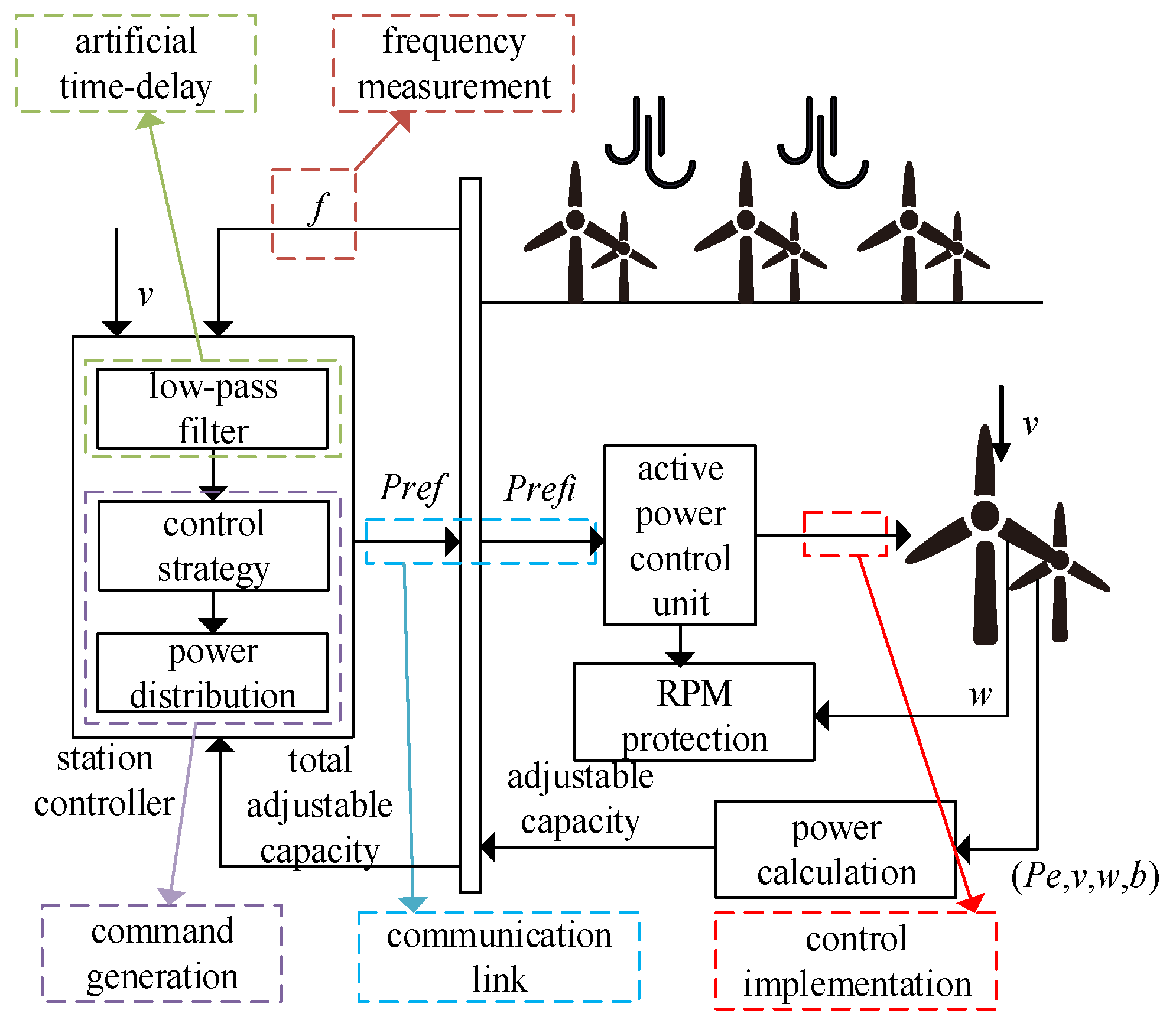
2.1. The Causes of Time Delay
- Frequency measurement: When WTs apply FM through rotor kinetic energy control, they take the frequency signal as input to change their output electric power. The frequency measurement requires 5–10 power frequency cycles to ensure accuracy.
- Artificial time delay: When WTs apply FM through virtual inertia control or comprehensive inertia control, the input signals include the differential of the frequency. Since the ideal differential signal cannot be realized, a low-pass filter is generally introduced to prevent the sensitive false triggering of FM due to noise or incorrect command generation. The low-pass filter produces a certain time delay.
- Generation of command signal: After the substation controller collects the frequency deviation signal and the differential signal, it takes a certain amount of time to generate the power command signal according to the established algorithm.
- Communication link: It takes a certain amount of time for the frequency signal measured at the point of connection of the wind farm to the grid to be transmitted to the substation controller and for the control signal to be sent to the rotor-side converter of the WT.
- Control implementation: After the WT receives the control signal, it takes a certain amount of time to respond to the given input control signal.
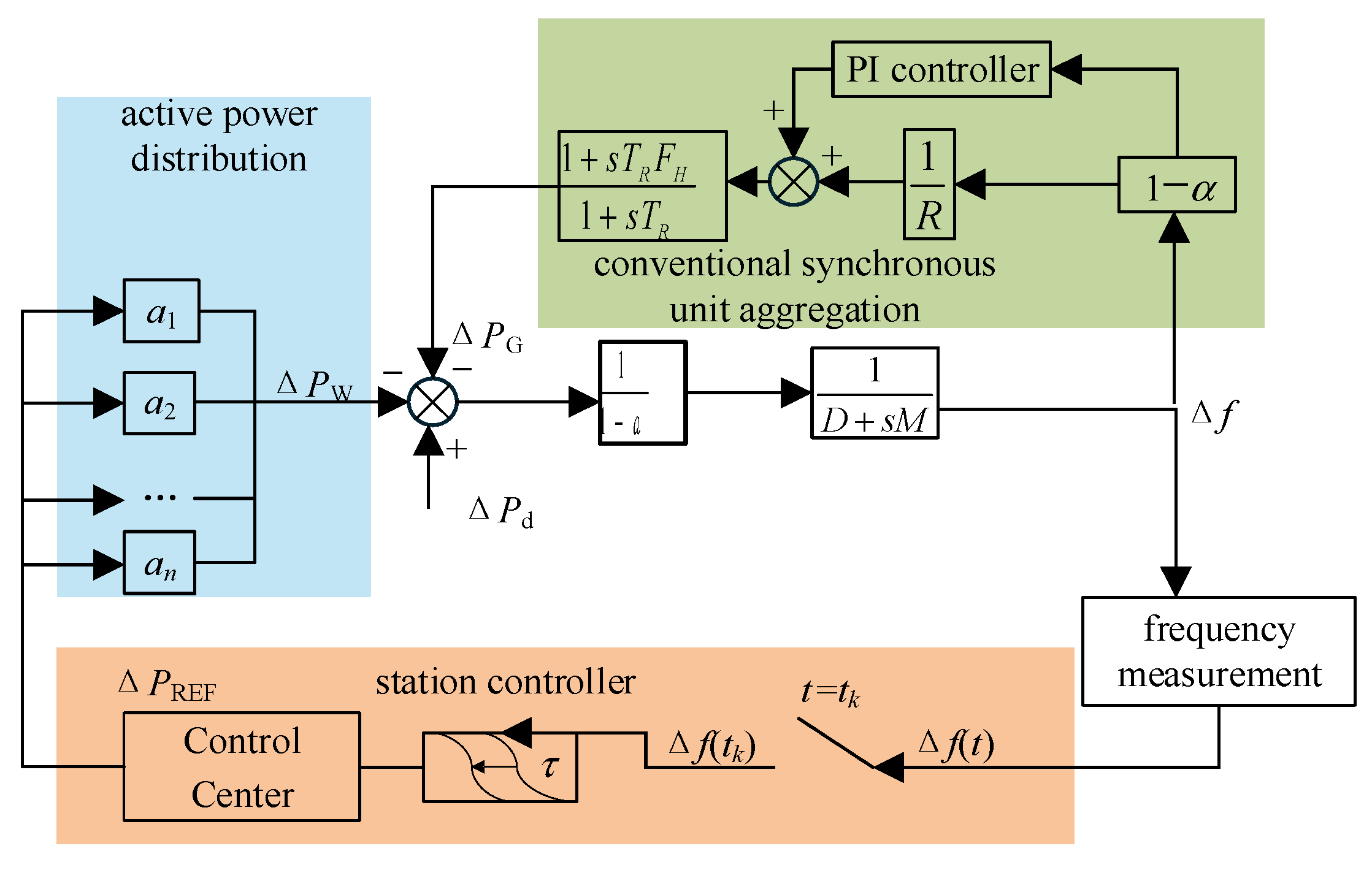
2.2. System Frequency Control Framework
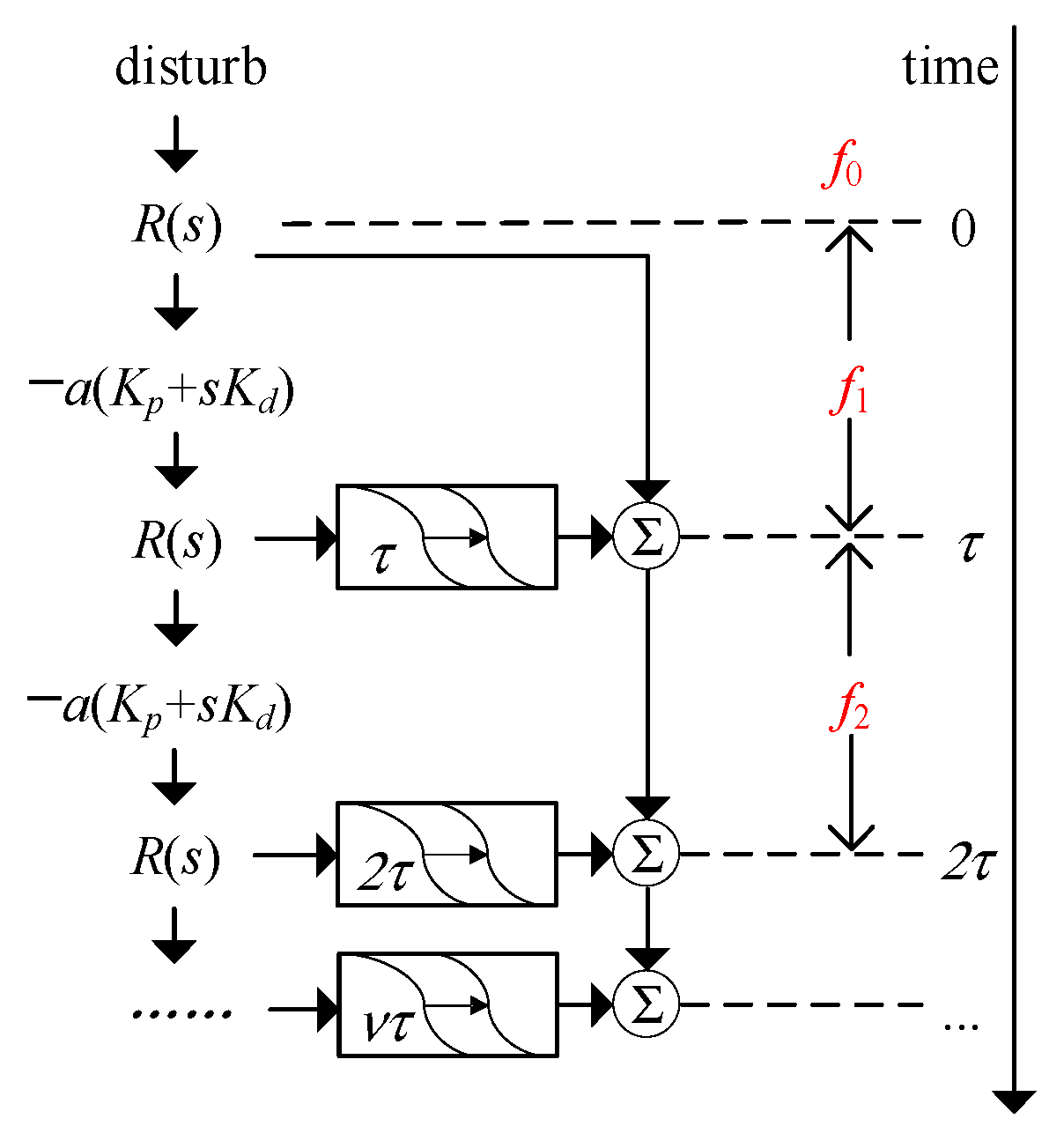
3. Stability Criteria of WT Frequency Regulation with Time Delay
3.1. Time Delay Stability of Droop Control
3.2. Time Delay Stability of Comprehensive Inertia Control
4. Analysis of Time Delay Stability and Control Strategies
4.1. PI Controller Design for Dynamic Performance Enhancement
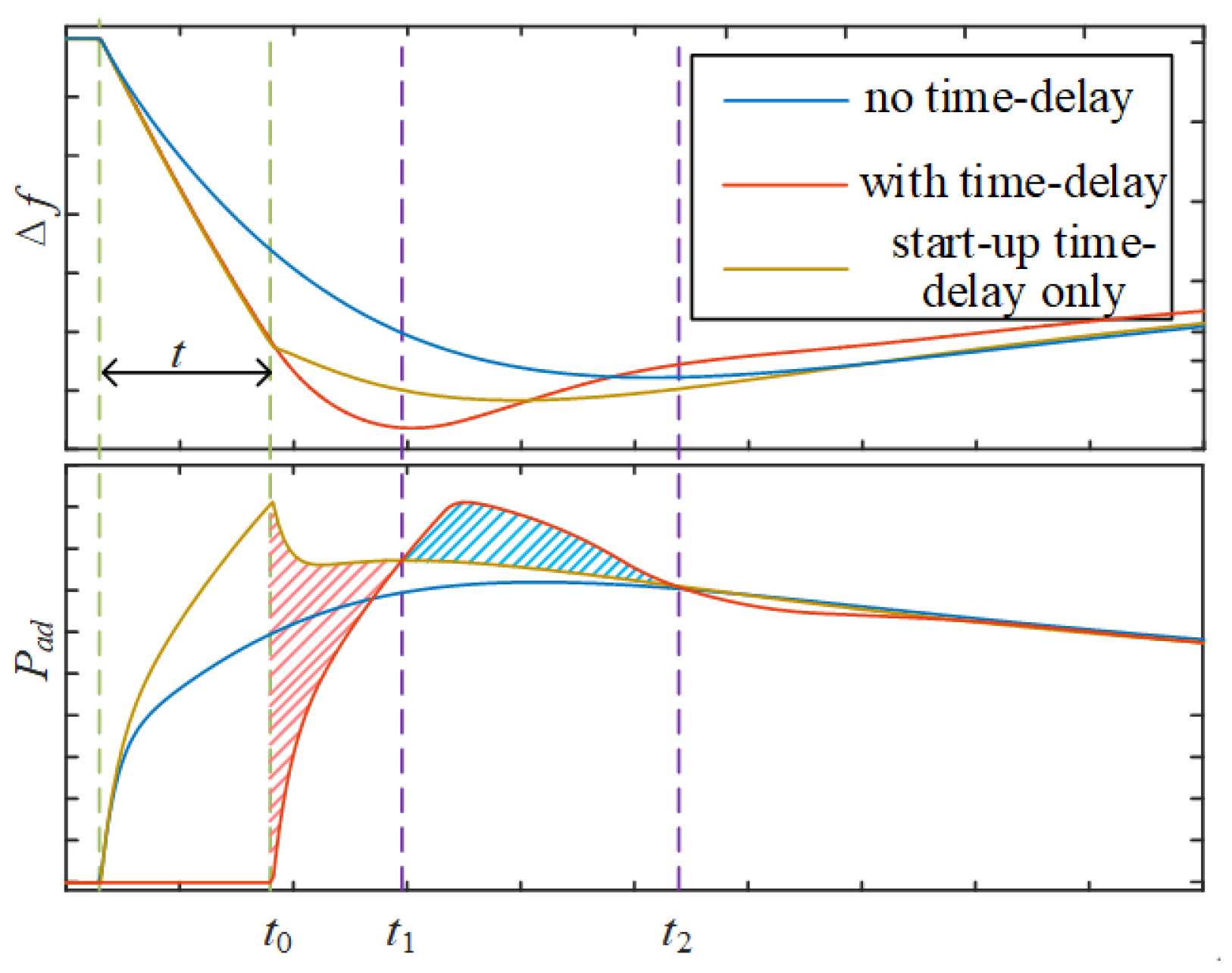
4.2. Additional Control for Time Delay Compensation of Wind Turbines
5. Case Study
5.1. Time Delay Effects on System Frequency Stability in Droop Control
5.2. Time Delay Effects on System Frequency Stability in Comprehensive Inertia Control
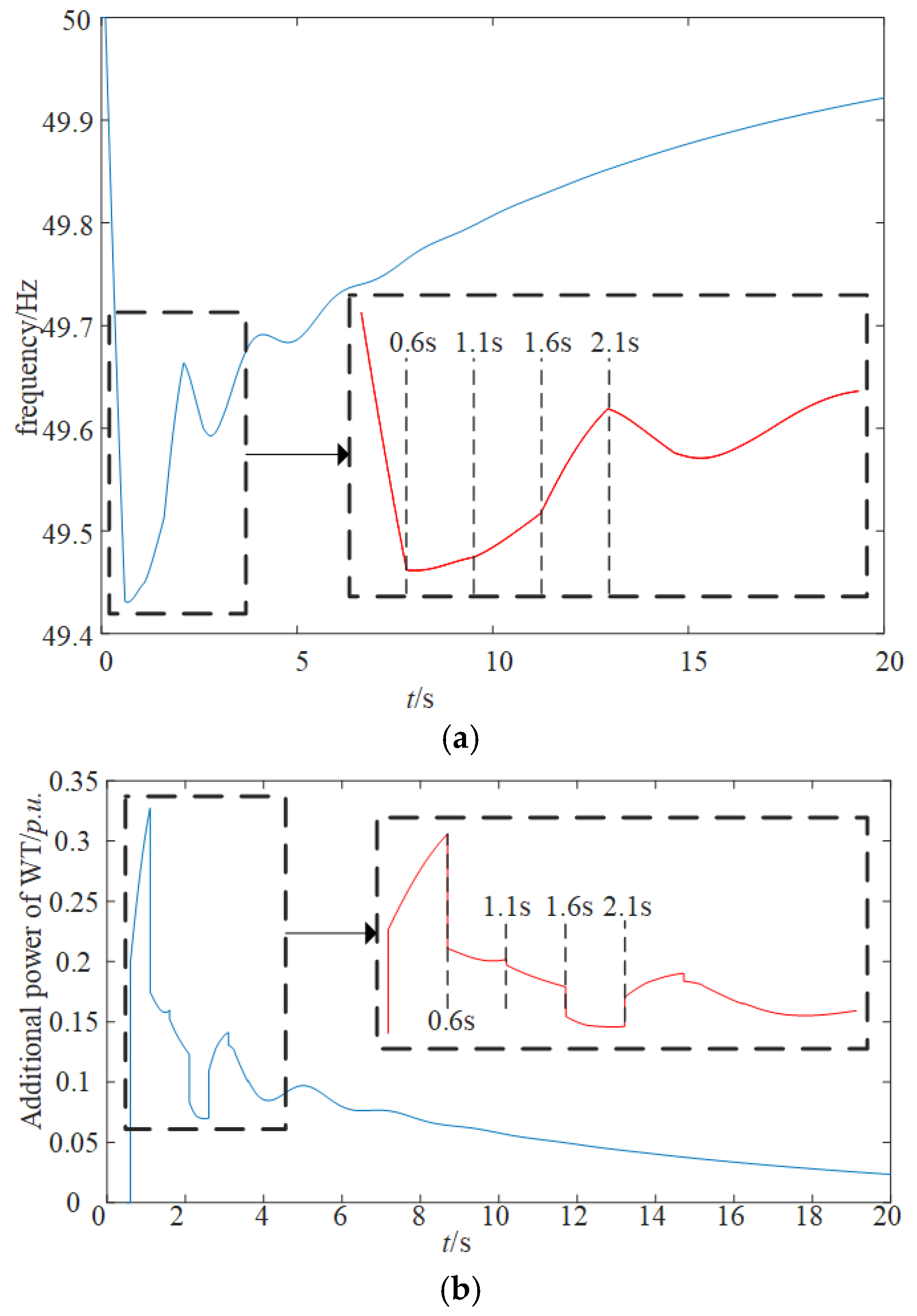
5.3. Enhancement Strategies for System Frequency Time Delay Stability
6. Conclusions
- (1)
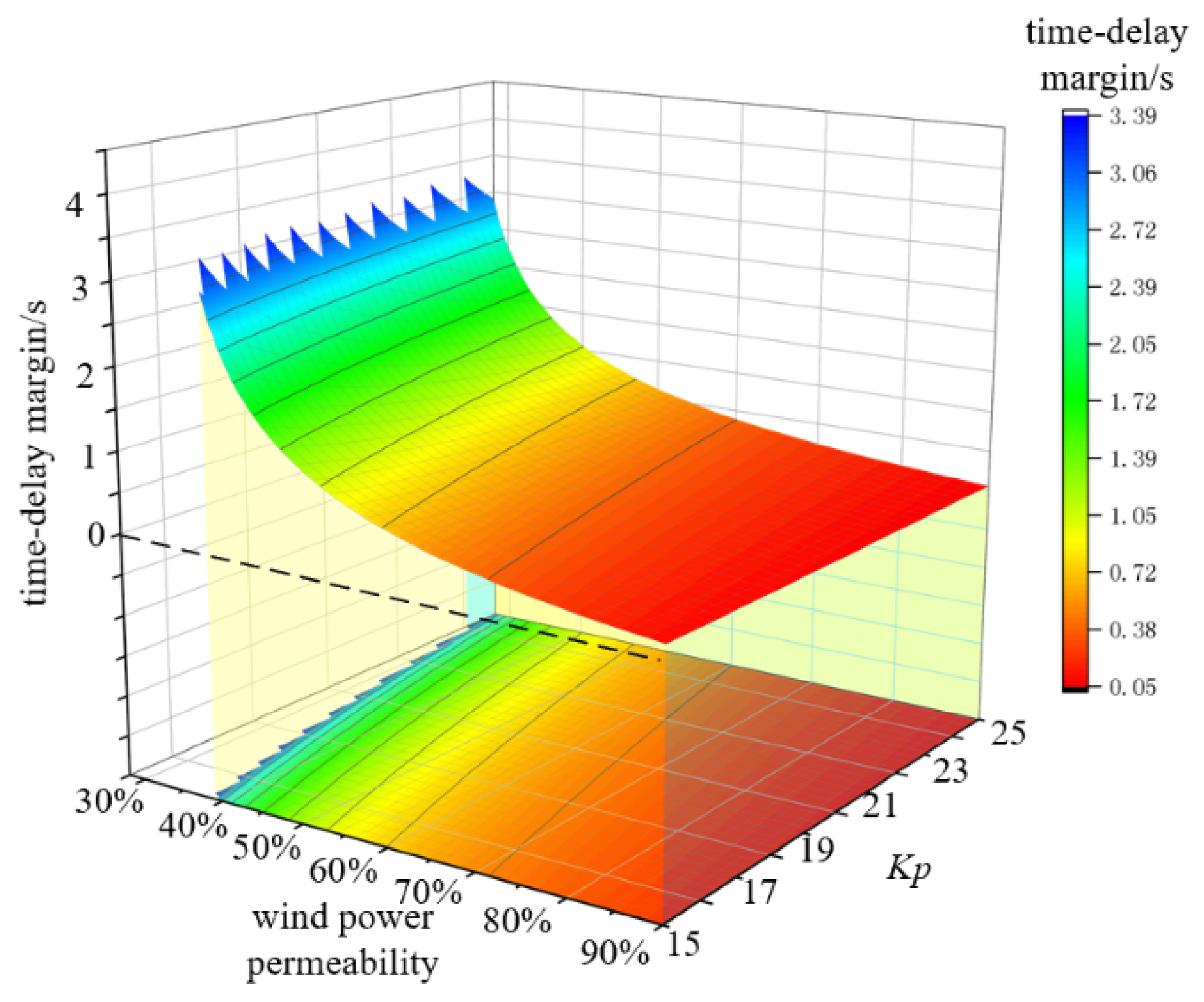
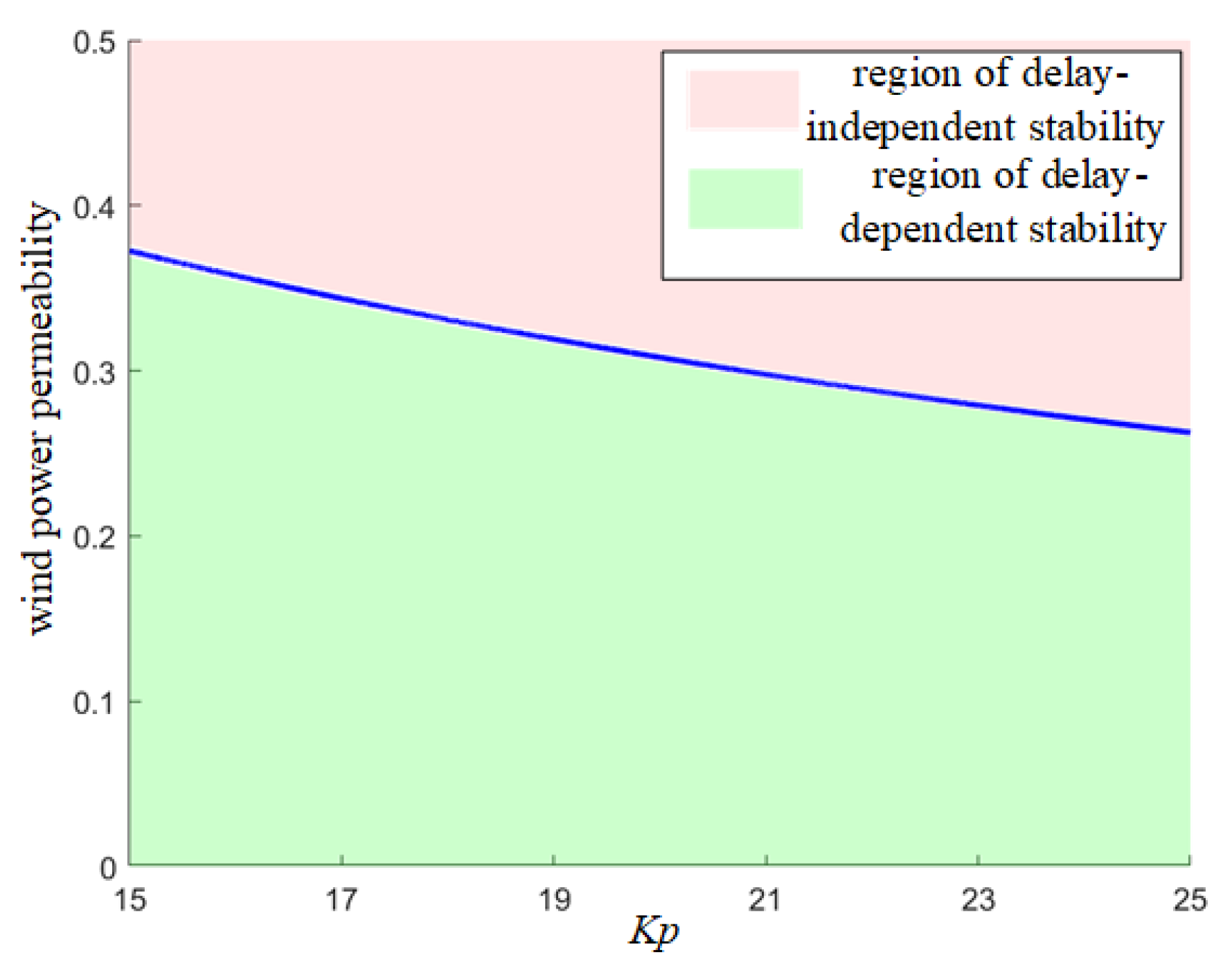
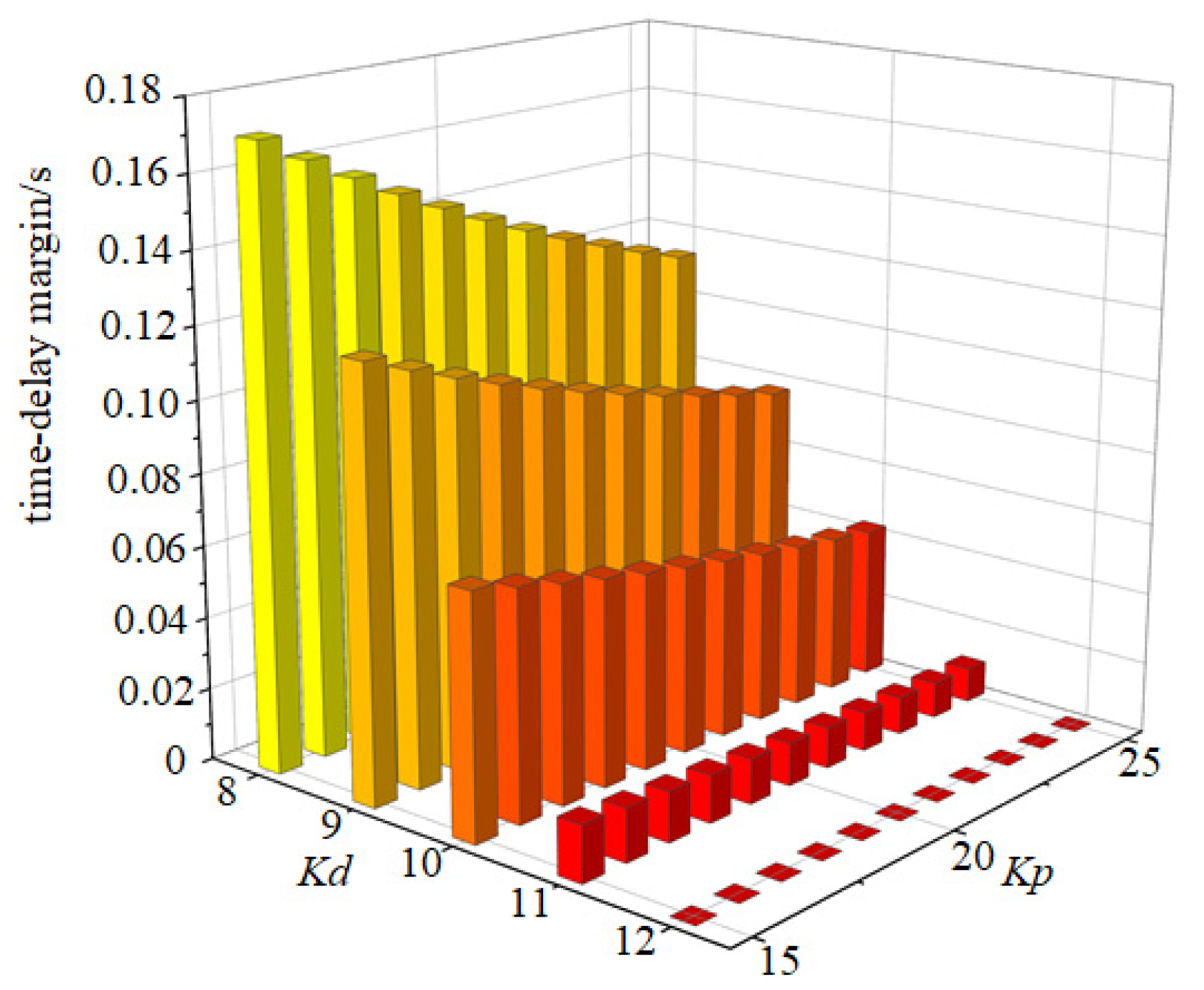
- Delay-independent stability boundaries exist for wind power penetration during system FM. These boundaries decrease with increasing wind turbine control parameters. Within the delay-dependent stability region, the system FM time delay margin decreases with larger control parameters, with virtual inertia control parameters exerting a more significant impact.
- (2)
- An accurate calculation method for system frequency responses considering time delays is proposed. This method ensures fixed system eigenvalues, avoiding infinite eigenvalues caused by exponential terms in time delays and errors from order-reduction approximations.
- (3)
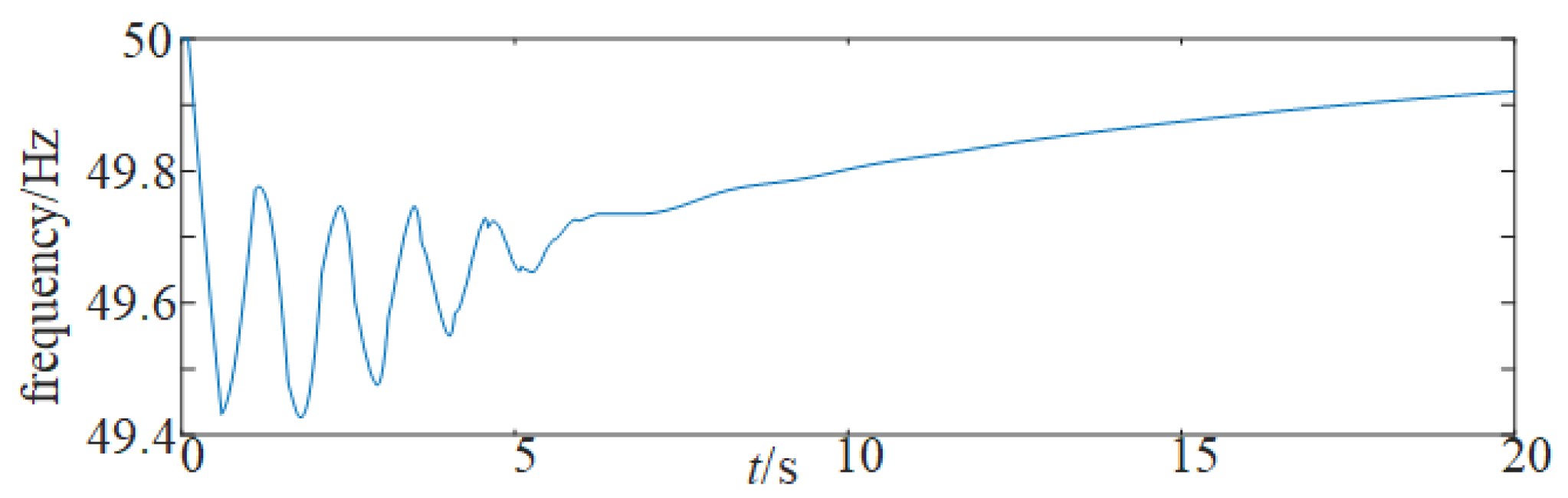
- Synchronous unit PI controller parameters designed via the LMI method significantly improve the system time delay margin. Time delay compensation applied to wind turbines during early FM events effectively suppresses severe frequency fluctuations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Yang, C.; Wei, W.; Zhao, B. Research on inertia system of frequency response for power system with high penetration electronics. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 5179–5192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Yao, W.; Zhao, H.; Ran, Y.; Xiao, B.; Wen, J. Dual-mode coordinated control strategy of photovoltaic stations for active grid voltage support. Power Syst. Technol. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Active frequency support strategy for new energy inverters based on virtual inertia fuzzy adaptive control. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2024, 52, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Min, Y. Power System Stability Analysis; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, B.; Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Wang, L. Primary frequency regulation model and aggregation of deloading wind turbinegenerators with pitch angle adjustment. Power Syst. Technol. 2023, 47, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Li, G. A Frequency Security Constrained Scheduling Approach Considering Wind Farm Providing Frequency Support and Reserve. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ding, Z. Fully-Distributed Deloading Operation of DFIG-Based Wind Farm for Load Sharing. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Li, Y.; Xiang, J. Coordinated Rotor Speed and Pitch Angle Control of Wind Turbines for Accurate and Efficient Frequency Response. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; De Haan, S.W.; Kling, W.L.; Ferreira, J.A. Wind turbines emulating inertia and supporting primary frequency control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; Pierik, J.; de Haan, S.W.H. Inertial response of variable speed wind turbines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2006, 76, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramtharan, G.; Ekanayake, J.B.; Jenkins, N. Frequency support from doubly fed induction generator wind turbines. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2007, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lin, W.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Yao, L.; Mao, B. Coordinated Frequency Control for Isolated Power Systems with High Penetration of DFIG-Based Wind Power. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 10, 1399–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, W.; Qi, H.; Shi, Z.; Geng, H. Coordinated Power Reserve Control of Wind Farm for Frequency Regulation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 55465–55473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, K.; Shao, C.; Lin, C.; Shahidehpour, M.; Tai, H.-M.; Hu, B.; Du, X. Integrated Assessment of the Reliability and Frequency Deviation Risks in Power Systems Considering the Frequency Regulation of DFIG-Based Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 2308–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Yan, G.-G.; Jin, Z.; Jin, E.; Zheng, T. Adaptive Frequency Droop Feedback Control-Based Power Tracking Operation of a DFIG for Temporary Frequency Regulation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 2682–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Dai, X. Stability and Stabilization of the Fractional-Order Power System with Time Delay. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 3446–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Cai, D.; Zhen, W.; Huang, Q. Delay-dependent stability control for power system with multiple time-delays. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 2316–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, R.; Wu, W.; Zou, Z. Analysis on characteristics of inertia and inertial response inpower system frequency dynamics. Proc. CSEE 2023, 43, 855–868. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Chen, L.; Min, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, F.; Jing, Z.; Song, X. Influence of Virtual Inertia Control Response Delay on Control Effect. Smart Power 2022, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Tian, Y.; Ding, L. Analytical solution for influential mechanism model of virtual inertia delay of wind power andits substitutability research. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2024, 48, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Su, J. Frequency response model and application of power system considering the frequency regulation delay of renewable energy station. Proc. CSEE 2024, 45, 4657–4669. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, D.; Zhang, X.; Ke, W.; Hu, B.; Nian, H. A Two-Stage Power Distribution Scheme of Multiple Wind Farms Participating in Primary Frequency Regulation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 5009–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Guo, F.; Nuno, E.; Cutululis, N.A. Frequency Stability of Power System with Large Share of Wind Power Under Storm Conditions. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 8, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, P.; Estevez, P.G.; Otero, A.; Galarza, C. Estimation of the Plant Controller Communication Time-Delay Considering PMSG-Based Wind Turbines. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.01751. [Google Scholar]
- O’Malley, M.; Holttinen, H.; Cutululis, N.; Vrana, T.K.; King, J.; Gevorgian, V.; Wang, X.; Rajaei-Najafabadi, F.; Hadjileonidas, A. Grand challenges of wind energy science—Meeting the needs and services of the power system. Wind Energy Sci. 2024, 9, 2087–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Kundur, P.; Balu, N.J.; Lauby, M.G. Power System Stability and Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Kharitonov, V.L.; Chen, J. Stability of Time-Delay Systems; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J. Stability Analysis and Application of Time-Delay Systems; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. Robust Control-Free Weight Matrix Method for Time-Delay Systems; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P. Stability Analysis and H_∞ Controller design for Linear Neutral Time-Delay systems. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Haerbin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]




| Method | Retarded Delay System (Droop Control) | Neutral Delay System (Integrated Inertia Control) | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency-domain method | √ | × | derivation complex for high-order models |
| Routh–Hurwitz stability criterion | √ | × | approximation introduces errors no exact delay margins |
| Nyquist stability criterion | √ | × | need approximation cannot directly compute delay margins |
| Lyapunov functionals | × | √ | conservative depends on functional construction not convenient for controller design |
| LMI | × | √ | conservative relies on numerical solvers, may be heavy for large-scale systems |
| Approximation + Root locus | √ | × | accuracy depends on order of approximation may miss high-frequency dynamics |
| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| f | System frequency |
| Δf | Frequency deviation |
| dΔf/dt | Rate of change of frequency |
| Pad | Additional power output of WT |
| PMPPT | Power output under maximum power point tracking |
| Pe | Electrical output power of WT |
| PREF | Reference active power of WT |
| ΔPW, ΔPW-i | Additional power injected by wind farm/WT i |
| ΔPG | Change in synchronous generator output power |
| ΔPL | Load disturbance power |
| Kp, Kp-i | Virtual inertia control parameters of wind farm/WT i |
| Kd, Kd-i | Droop control parameters of wind farm/WT i |
| τ | Time delay |
| τmax | Maximum permissible time delay |
| D | System damping coefficient |
| R | Primary frequency modulation droop coefficient |
| M | System inertia time constant |
| TR | Reheat time constant |
| FH | High-pressure cylinder power proportion |
| TG | Turbine governor time constant |
| TCH | High-pressure cylinder steam chamber volume time constant |
| α, αi | Wind power penetration level |
| n | Number of WTs |
| ΔPv | No practical significance, only convenient for calculation |
| ΔPm | No practical significance, only convenient for calculation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, X.; Yu, Q.; Liu, D.; Yuan, L.; Guo, M.; Li, X. Time Delay Stability Analysis and Control Strategy of Wind Farm for Active Grid Frequency Support. Energies 2025, 18, 4784. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174784
Yao X, Yu Q, Liu D, Yuan L, Guo M, Li X. Time Delay Stability Analysis and Control Strategy of Wind Farm for Active Grid Frequency Support. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4784. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174784
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Xin, Qingguang Yu, Ding Liu, Leidong Yuan, Min Guo, and Xiaoyu Li. 2025. "Time Delay Stability Analysis and Control Strategy of Wind Farm for Active Grid Frequency Support" Energies 18, no. 17: 4784. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174784
APA StyleYao, X., Yu, Q., Liu, D., Yuan, L., Guo, M., & Li, X. (2025). Time Delay Stability Analysis and Control Strategy of Wind Farm for Active Grid Frequency Support. Energies, 18(17), 4784. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174784






