Pattern-Aware BiLSTM Framework for Imputation of Missing Data in Solar Photovoltaic Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. The Proposed PA-BiLSTM Method
3.1. Normalization Solar Generation Data
3.2. Feature Embedding
3.2.1. Region Embedding
3.2.2. Time Embedding
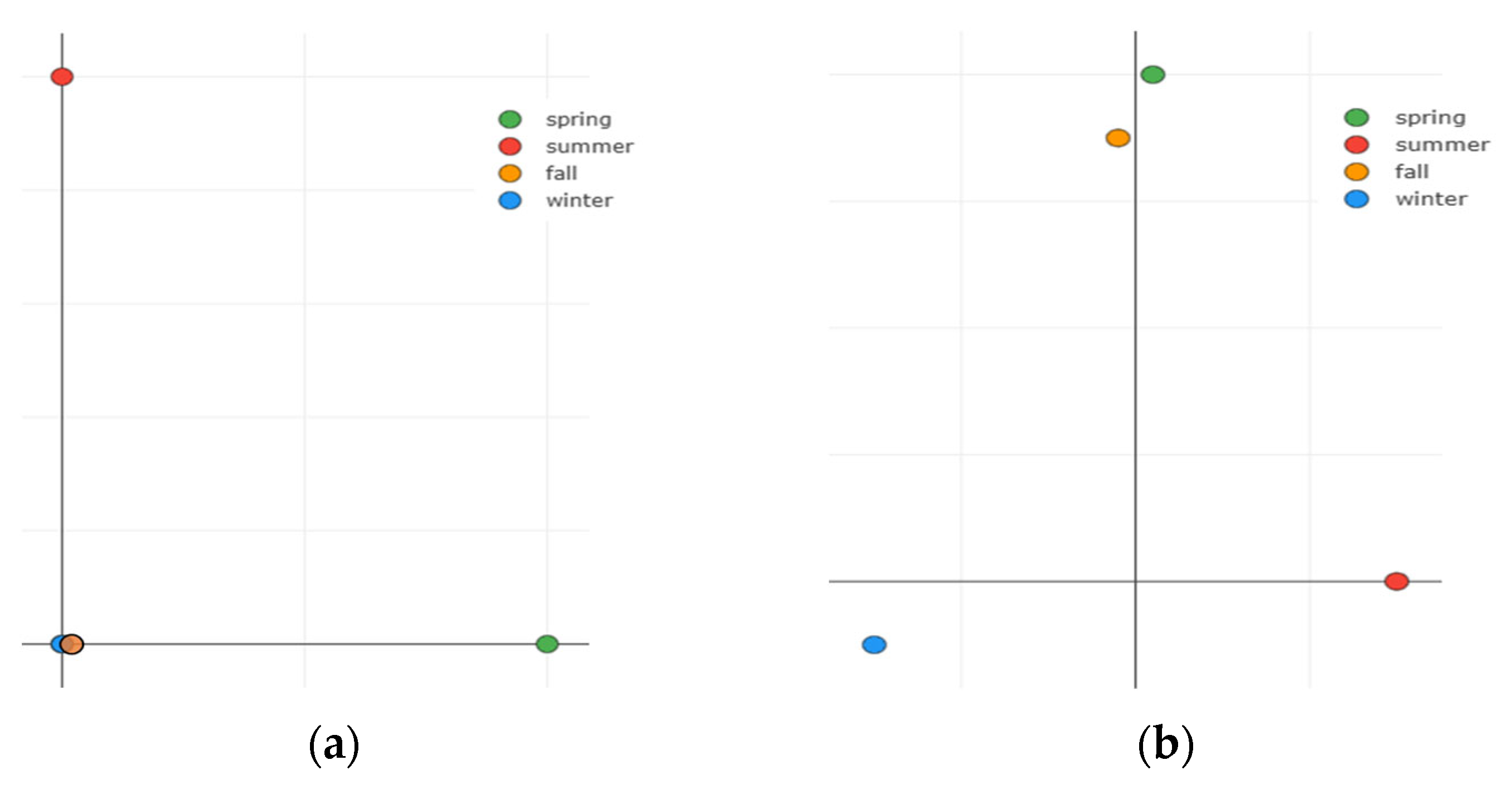
3.2.3. PCA-Based Seasonal Embedding
- (10 features) Hourly mean generation profiles for the 10 h period from 08:00 to 17:00.
- Overall mean and standard deviation, as defined in Equations (4) and (5).
- The maximum value shown in Equation (6) and the 25th and 75th percentiles shown in Equations (7) and (8) to describe the range and spread.
- The skewness and kurtosis of the distribution, as shown in Equations (9) and (10).
- The proportion of high-generation (>0.8) and low-generation (<0.1) intervals, calculated according to Equations (11) and (12).
3.3. Proposed Pattern-Aware Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (PA-BiLSTM)
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Data Description
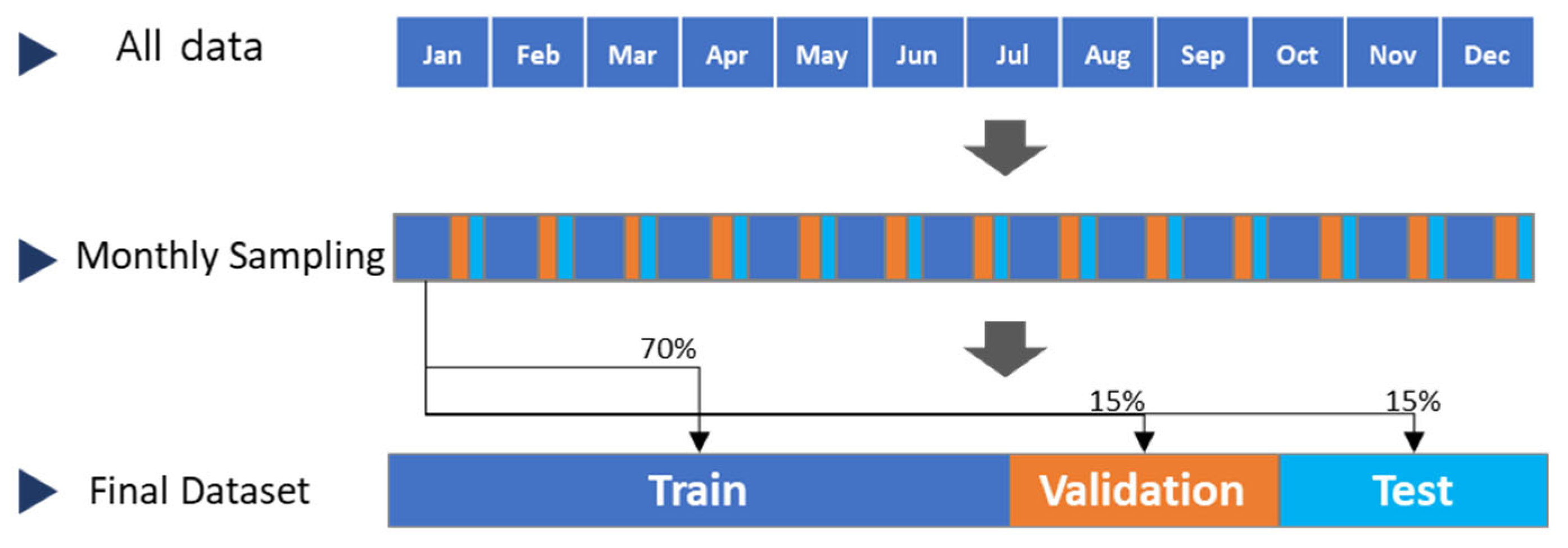
4.2. Missing Pattern Simulation and Experimental Setup
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
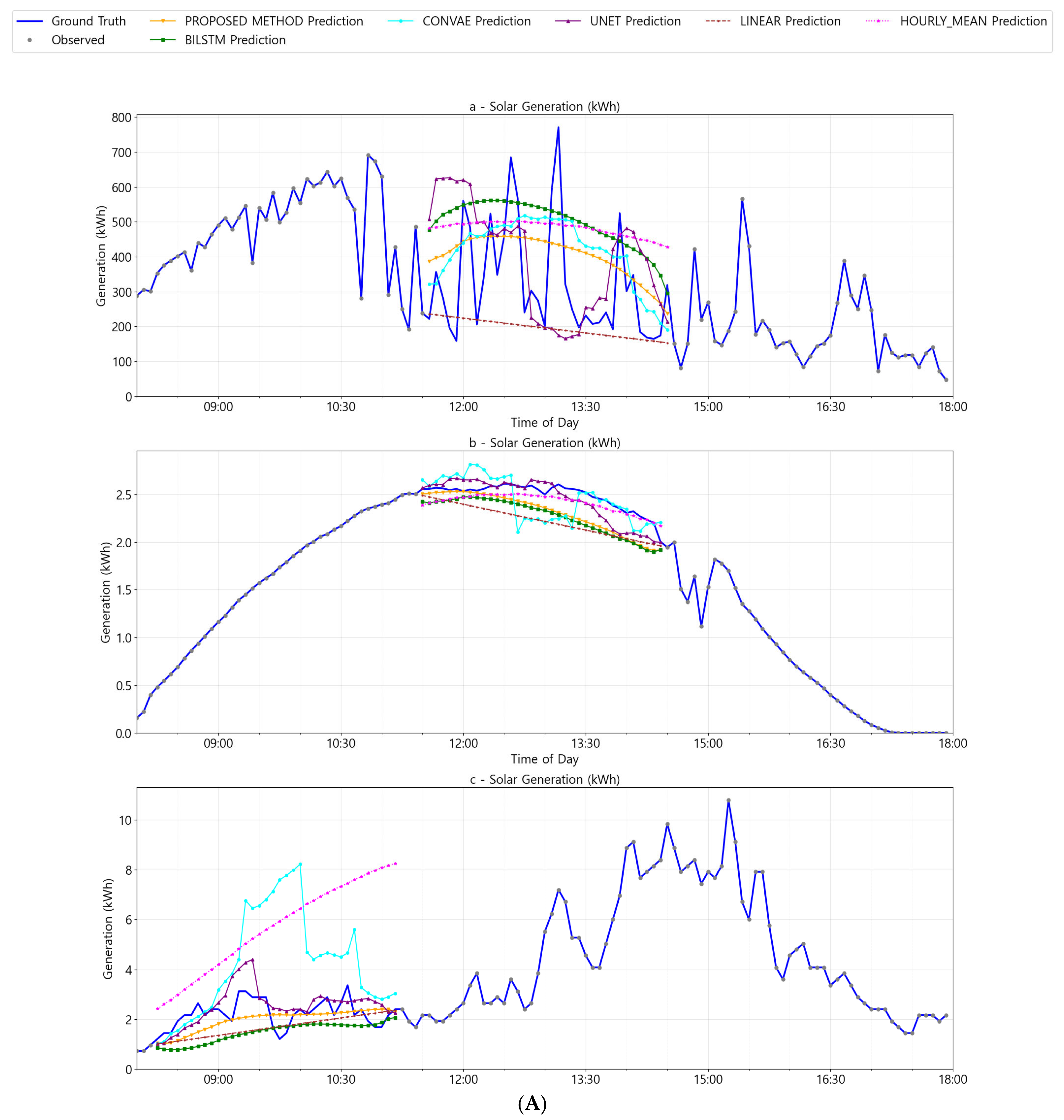
4.4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ember. Global Electricity Review 2025. Available online: https://ember-energy.org/latest-insights/global-electricity-review-2025/ (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- RE100. 2024 RE100: Annual Disclosure Report. Available online: https://www.there100.org/our-work/publications/2024-re100-annual-disclosure-report (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Yonhap News Agency. S. Korea Launches Task Force to Create RE100 Industrial Complex. Available online: https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20250716002900320 (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Lee, D.; Kim, D.; Joo, S.-K. Interval-Stochastic Programming for Integrated Generation, Transmission, and Energy Storage System (ESS) Planning Considering Uncertainty in Renewable Energy Sources. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 30834–30844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Joo, S.-K. Transmission Pricing Incorporating the Impact of System Fault and Renewable Energy Uncertainty on the Transmission Margin. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 103779–103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Joo, S.-K. Economic Analysis of Large-Scale Renewable Energy (RE) Source Investment Incorporating Power System Transmission Costs. Energies 2023, 16, 7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Lee, J. Investment Decision for Long-Term Battery Energy Storage System Using Least Squares Monte Carlo. Energies 2024, 17, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. Missing-Data Tolerant Hybrid Learning Method for Solar Power Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-Paz-Centeno, I.; García-Ordaz, M.T.; García-Olalla, Ó.; Alaiz-Moretón, H. Imputation of missing measurements in PV production data within constrained environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 217, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chew, B.S.H.; Ding, H.; Zhao, G. An Integrated Missing-Data Tolerant Model for Probabilistic PV Power Generation Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 4447–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.; Falcão, B.; Mohamed, M.A.; Annuk, A.; Marinho, M. Employing machine learning for advanced gap imputation in solar power generation databases. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Srinivasan, D. SolarGAN: Multivariate solar data imputation using generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xuan, L.; Gong, D.; Xie, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, D. A WGAN-GP Approach for Data Imputation in Photovoltaic Power Prediction. Energies 2025, 18, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, H. Denoising autoencoder-based missing value imputation for smart meters. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 40656–40666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Ku, T.-Y.; Park, W.-K. Denoising Masked Autoencoder-Based Missing Imputation within Constrained Environments for Electric Load Data. Energies 2023, 16, 7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, T.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z. Small Sample Data Augmentation Method for Photovoltaic Power Generation Based on Improved Variational Auto-encoder. In Proceedings of the 2024 36th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2024; pp. 1047–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Jiang, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Zhai, C. A Bi-directional Missing Data Imputation Scheme Based on LSTM and Transfer Learning for Building Energy Data. Energy Build. 2020, 211, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Li, Y. BRITS: Bidirectional Recurrent Imputation for Time Series. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Purushotham, S.; Cho, K.; Sontag, D. Recurrent Neural Networks for Multivariate Time Series with Missing Values. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H. A Novel GAN Architecture Reconstructed Using Bi-LSTM and Style Transfer for PV Temporal Dynamics Simulation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 2826–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Wi, Y.-M. Impact of Revised Time of Use Tariff on Variable Renewable Energy Curtailment on Jeju Island. Electronics 2021, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Jordon, J.; van der Schaar, M. GAIN: Missing Data Imputation using Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; Volume 80, pp. 5689–5698. [Google Scholar]
- Denhard, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Habte, A.; Sengupta, M. Evaluation of Time-Series Gap-Filling Methods for Solar Irradiance Applications; No. NREL/TP-5D00-79987; National Renewable Energy Lab.(NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]






| Region | Number of Solar Generators |
|---|---|
| Gyeonggi-do | 1 |
| Gyeongsangnam-do | 9 |
| Gyeongsangbuk-do | 4 |
| Daejeon | 2 |
| Busan | 2 |
| Sejong | 3 |
| Incheon | 4 |
| Jeollanam-do | 15 |
| Jeollabuk-do | 4 |
| Chungcheongnam-do | 4 |
| Chungcheongbuk-do | 2 |
| Hour | Model | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LI | 0.00793 | - | - | - | - |
| HA | 0.03370 | - | - | - | - | |
| BiLSTM | 0.00743 | 0.00786 | 0.00746 | 0.00765 | 0.00750 | |
| ConvAE | 0.00861 | 0.00855 | 0.00829 | 0.00842 | 0.00911 | |
| Unet | 0.00856 | 0.00847 | 0.00821 | 0.00831 | 0.00857 | |
| PA-BiLSTM (proposed) | 0.00720 | 0.00723 | 0.00744 | 0.00742 | 0.00725 | |
| Hour | Model | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| 2 | LI | 0.01172 | - | - | - | - |
| HA | 0.03657 | - | - | - | - | |
| BiLSTM | 0.01001 | 0.01013 | 0.01013 | 0.00990 | 0.0102 | |
| ConvAE | 0.01515 | 0.01502 | 0.01482 | 0.01528 | 0.0152 | |
| Unet | 0.01151 | 0.01155 | 0.01118 | 0.01105 | 0.0116 | |
| PA-BiLSTM (proposed) | 0.01010 | 0.00984 | 0.00996 | 0.00977 | 0.0098 | |
| Hour | Model | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| 3 | LI | 0.01613 | - | - | - | - |
| HA | 0.03808 | - | - | - | - | |
| BiLSTM | 0.01397 | 0.0136 | 0.01328 | 0.0136 | 0.0136 | |
| ConvAE | 0.02275 | 0.0232 | 0.02303 | 0.0230 | 0.0226 | |
| Unet | 0.01518 | 0.0054 | 0.01526 | 0.0155 | 0.0162 | |
| PA-BiLSTM (proposed) | 0.01313 | 0.0133 | 0.01334 | 0.0131 | 0.0131 | |
| Hour | Model | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
| 4 | LI | 0.02147 | - | - | - | - |
| HA | 0.03892 | - | - | - | - | |
| BiLSTM | 0.01605 | 0.0166 | 0.01591 | 0.0163 | 0.0162 | |
| ConvAE | 0.02600 | 0.0271 | 0.02684 | 0.0265 | 0.0255 | |
| Unet | 0.01952 | 0.0199 | 0.01954 | 0.0197 | 0.0196 | |
| PA-BiLSTM (proposed) | 0.01579 | 0.0154 | 0.01675 | 0.0152 | 0.0157 |
| Model | 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MAE | MAE | MAE | |||||
| BiLSTM | 0.0166 | 0.98 | 0.0341 | 0.89 | 0.068 | 0.61 | 0.102 | 0.28 |
| ConvAE | 0.0256 | 0.96 | 0.0421 | 0.88 | 0.059 | 0.77 | 0.076 | 0.66 |
| Unet | 0.0155 | 0.97 | 0.0361 | 0.86 | 0.058 | 0.71 | 0.080 | 0.55 |
| PA-BiLSTM (proposed) | 0.0123 | 0.98 | 0.0259 | 0.93 | 0.0474 | 0.81 | 0.070 | 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, M.; Joo, S.-K. Pattern-Aware BiLSTM Framework for Imputation of Missing Data in Solar Photovoltaic Generation. Energies 2025, 18, 4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174734
Jang M, Joo S-K. Pattern-Aware BiLSTM Framework for Imputation of Missing Data in Solar Photovoltaic Generation. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174734
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Minseok, and Sung-Kwan Joo. 2025. "Pattern-Aware BiLSTM Framework for Imputation of Missing Data in Solar Photovoltaic Generation" Energies 18, no. 17: 4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174734
APA StyleJang, M., & Joo, S.-K. (2025). Pattern-Aware BiLSTM Framework for Imputation of Missing Data in Solar Photovoltaic Generation. Energies, 18(17), 4734. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174734





