Enhanced Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure: Effects of Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio and Magnetite-Mediated Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Substrate, Inoculum, and Magnetite
2.2. Biochemical Methane Potential Test
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
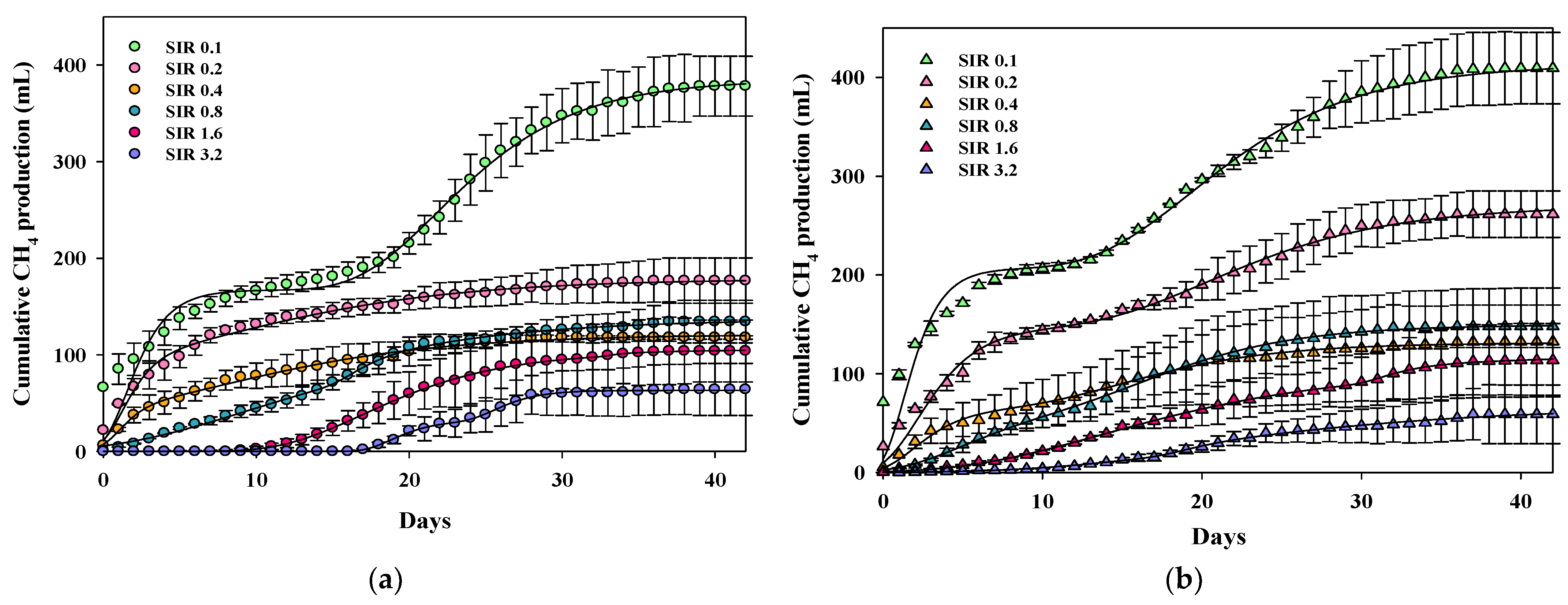
3.1. Effects of Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio and Magnetite Addition on Methane Production
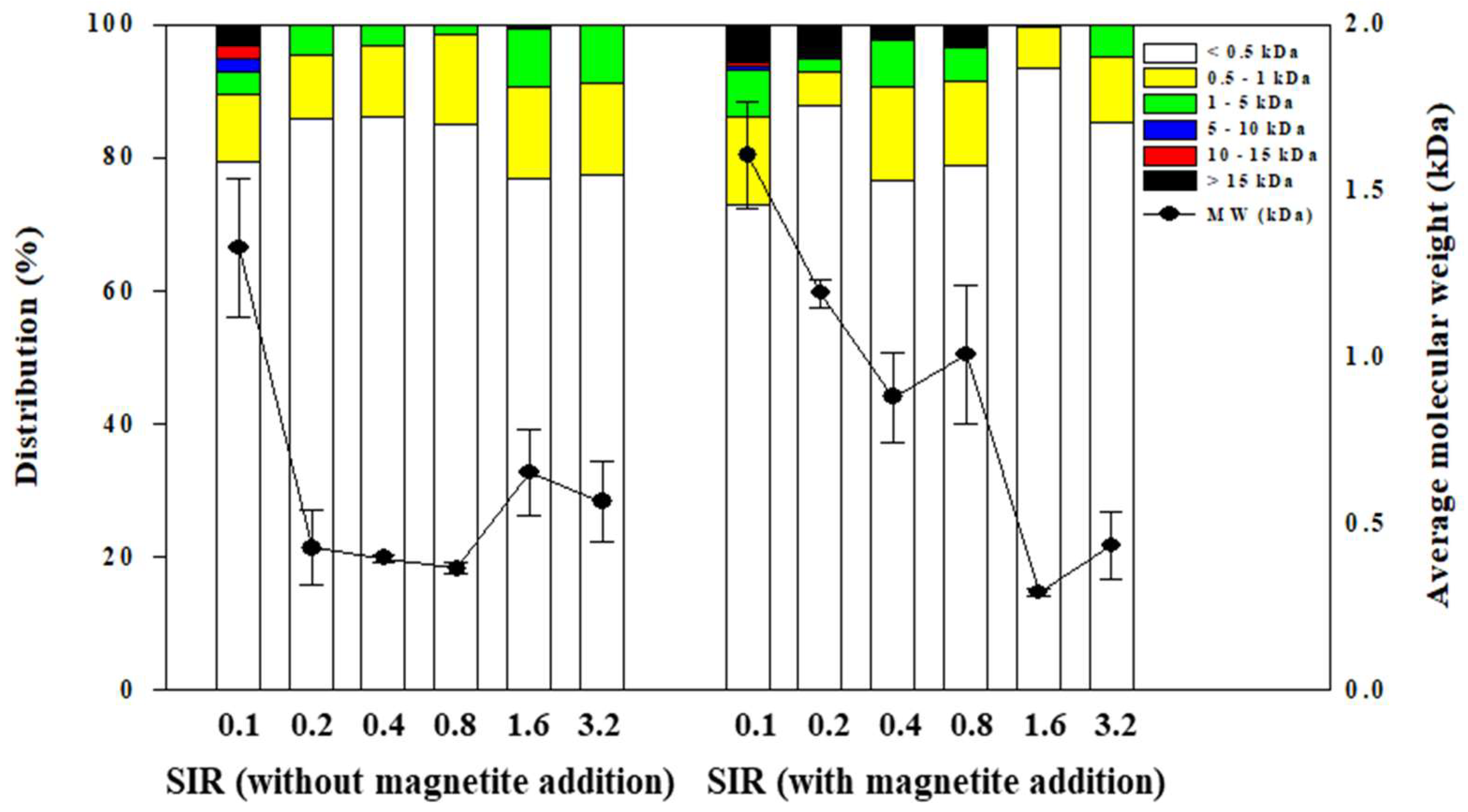
3.2. Effects of SIR and Magnetite Addition on Organic Acid Accumulation and MW Distribution
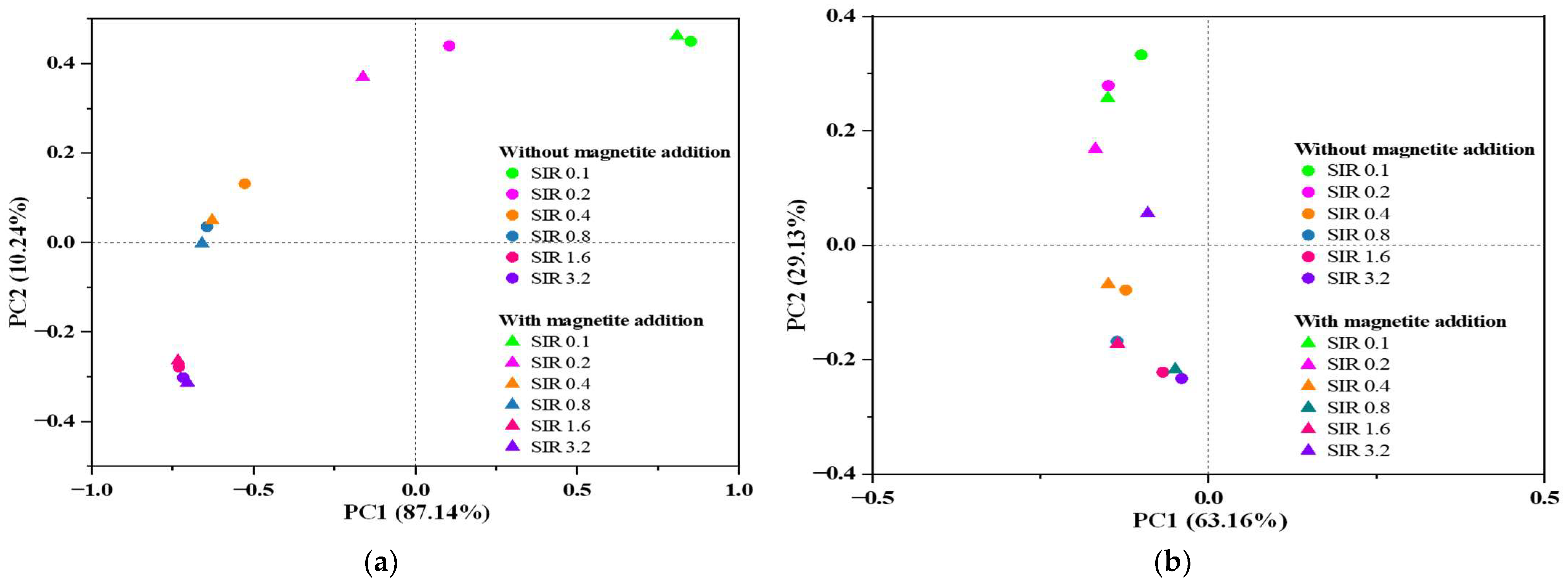
3.3. Microbial Community Dynamics
3.3.1. Alpha and Beta Diversity and Community-Level Shifts
3.3.2. Comparative Analysis of Dominant Microbial Taxa Under Different SIR and Magnetite Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, H.; Li, D.; Stanislaus, M.S.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, X.; Yang, Y. Development of a bio-zeolite fixed-bed bioreactor for mitigating ammonia inhibition of anaerobic digestion with extremely high ammonium concentration livestock waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelme-Ayala, P.; El-Din, M.G.; Smith, R.; Code, K.R.; Leonard, J. Advanced treatment of liquid swine manure using physico-chemical treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.S.; Parajuli, R.; Scott, E.; Canter, T.; Lim, T.T.; Popp, J.; Thoma, G. Dairy and swine manure management–Challenges and perspectives for sustainable treatment technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilajeliu-Pons, A.; Puig, S.; Pous, N.; Salcedo-Dávila, I.; Bañeras, L.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. Microbiome characterization of MFCs used for the treatment of swine manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 288, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batstone, D.J.; Rodríguez, J. Modelling anaerobic digestion processes. In Anaerobic Biotechnology: Environmental Protection and Resource Recovery; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015; pp. 133–160. [Google Scholar]
- Bartocci, P.; Massoli, S.; Zampilli, M.; Liberti, F.; Yunjun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhou, H.; Gul, E.; Bidini, G. Substrate Characterization in the Anaerobic Digestion Process. In Bioenergy Research: Basic and Advanced Concepts; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 307–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Peng, Y.; Yang, P.; Peng, X. Anaerobic digestion: A review on process monitoring. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y. Comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestions of thermal hydrolysis pretreated swine manure: Process performance, microbial communities and energy balance. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Huang, W.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z. Effects of different alkalis on hydrolysis of swine manure during dry anaerobic digestion and resultant nutrients availability. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, V.; Fernández, M.; Santalla, E. The effect of substrate/inoculum ratio on the kinetics of methane production in swine wastewater anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 21308–21317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Nakamoto, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Utsumi, M.; Sugiura, N. Influence of substrate-to-inoculum ratio on the batch anaerobic digestion of bean curd refuse-okara under mesophilic conditions. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, T.; Chang, J.; Tang, Q.; Luo, T.; Cui, Z. Effect of substrate to inoculum ratio on biogas production and microbial community during hemi-solid-state batch anaerobic co-digestion of rape straw and dairy manure. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 884–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, P.; Ahmed, B.; Tiwari, S.B.; Aryal, N.; Khursheed, A.; Kazmi, A.A.; Tyagi, V.K. Conductive material engineered direct interspecies electron transfer (DIET) in anaerobic digestion: Mechanism and application. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Im, S.; Song, Y.-C.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, D.-H. Enhanced anaerobic digestion by stimulating DIET reaction. Processes 2020, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajay, C.; Mohan, S.; Dinesha, P.; Rosen, M.A. Review of impact of nanoparticle additives on anaerobic digestion and methane generation. Fuel 2020, 277, 118234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Jung, S.P.; Kim, S.-H. Enhancing anaerobic digestion for rural wastewater treatment with granular activated carbon (GAC) supplementation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Brown, R.C.; Wen, Z. Biochar as an additive in anaerobic digestion of municipal sludge: Biochar properties and their effects on the digestion performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6391–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Lu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. The interactive effects of ammonia and carbon nanotube on anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wei, L.; Liu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Dang, Y.; Sun, D.; Holmes, D.E. Magnetite enhances anaerobic digestion and methanogenesis of fresh leachate from a municipal solid waste incineration plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Jung, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. A long-term study on the effect of magnetite supplementation in continuous anaerobic digestion of dairy effluent–magnetic separation and recycling of magnetite. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Tong, Y.W. Micro–nano magnetite-loaded biochar enhances interspecies electron transfer and viability of functional microorganisms in anaerobic digestion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar]
- González-Fernández, C.; García-Encina, P.A. Impact of substrate to inoculum ratio in anaerobic digestion of swine slurry. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Córdova, M.E.H.; e Silva, H.L.d.C.; Barros, R.M.; Lora, E.E.S.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; de Freitas, J.V.R.; Santos, A.H.M.; Pedreira, J.R.; Flauzino, B.K. Analysis of viable biogas production from anaerobic digestion of swine manure with the magnetite powder addition. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Watanabe, K. Methanogenesis facilitated by electric syntrophy via (semi) conductive iron-oxide minerals. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Fang, W.; Chang, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G. Improvement of direct interspecies electron transfer via adding conductive materials in anaerobic digestion: Mechanisms, performances, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 860749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, D.; Dai, L.; Dong, B.; Dai, X. Magnetite triggering enhanced direct interspecies electron transfer: A scavenger for the blockage of electron transfer in anaerobic digestion of high-solids sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7160–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Lee, B.; Jo, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Jun, H.-B. Control of accumulated volatile fatty acids by recycling nitrified effluent. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2018, 16, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, Y. Syntrophic propionate oxidation: One of the rate-limiting steps of organic matter decomposition in anoxic environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00384-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, J.; Tao, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, Y.; Duan, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, G. Emerging strategies for enhancing propionate conversion in anaerobic digestion: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Liu, Y. Performance and mechanism of conductive magnetite particle-enhanced excess sludge anaerobic digestion for biogas recovery. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35559–35566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yin, C.; Jin, J.; Wu, K.; Yu, Z.; Deng, C. Characteristics of different molecular weight EPS fractions from mixed culture dominated by AnAOB and their role in binding metal ions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5491–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Substrate | Inoculum | |
|---|---|---|
| TCOD (g/L) | 33.5 ± 0.2 | 68.7 ± 7.1 |
| SCOD (g/L) | 16.9 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| TS (g/L) | 21.7 ± 0.3 | 72.8 ± 0.2 |
| VS (g/L) | 13.7 ± 0.2 | 61.4 ± 0.1 |
| Alkalinity (g CaCO3/L) | 23.6 ± 0.5 | 7.4 ± 0.1 |
| pH | 8.0 ± 0.2 | 7.5 ± 0.1 |
| SIRs (g VS/gVS) | Substrate (g VS) | Inoculum (g VS) | Magnetite (mM Fe) | Working Volume (mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without magnetite addition | 0.1 | 0.65 | 6.50 | 20 | 165 |
| 0.2 | 0.65 | 3.25 | 20 | 165 | |
| 0.4 | 0.65 | 1.63 | 20 | 165 | |
| 0.8 | 0.65 | 0.81 | 20 | 165 | |
| 1.6 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 20 | 165 | |
| 3.2 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 20 | 165 | |
| With magnetite addition | 0.1 | 0.65 | 6.50 | 20 | 165 |
| 0.2 | 0.65 | 3.25 | 20 | 165 | |
| 0.4 | 0.65 | 1.63 | 20 | 165 | |
| 0.8 | 0.65 | 0.81 | 20 | 165 | |
| 1.6 | 0.65 | 0.41 | 20 | 165 | |
| 3.2 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 20 | 165 |
| SIRs | CH4 Yield (mL/g COD) | CH4 Production Rate (mL/day) | Lag Phase (Day) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without magnetite addition | 0.1 | 262 ± 10 | 77 ± 5 | - |
| 0.2 | 110 ± 7 | 94 ± 4 | - | |
| 0.4 | 77 ± 6 | 49 ± 1 | - | |
| 0.8 | 90 ± 7 | 40 ± 1 | 3.1 ± 0.3 | |
| 1.6 | 70 ± 10 | 43 ± 1 | 11.6 ± 0.1 | |
| 3.2 | 45 ± 9 | 35 ± 1 | 17.1 ± 0.2 | |
| With magnetite addition | 0.1 | 267 ± 16 | 106 ± 4 | - |
| 0.2 | 170 ± 14 | 75 ± 3 | - | |
| 0.4 | 89 ± 9 | 43 ± 2 | - | |
| 0.8 | 102 ± 12 | 45 ± 1 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | |
| 1.6 | 77 ± 9 | 26 ± 1 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | |
| 3.2 | 39 ± 6 | 17 ± 1 | 11.5 ± 0.3 |
| Bacteria | Archaea | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIRs | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | |
| Without magnetite addition | 0.1 | 2.41 | 0.85 | 87 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 48 |
| 0.2 | 2.29 | 0.81 | 88 | 0.93 | 0.54 | 52 | |
| 0.4 | 1.95 | 0.70 | 87 | 0.96 | 0.52 | 54 | |
| 0.8 | 1.80 | 0.67 | 88 | 1.08 | 0.55 | 47 | |
| 1.6 | 1.40 | 0.58 | 71 | 1.24 | 0.59 | 55 | |
| 3.2 | 1.36 | 0.56 | 64 | 1.22 | 0.58 | 47 | |
| With magnetite addition | 0.1 | 2.37 | 0.84 | 85 | 0.91 | 0.54 | 46 |
| 0.2 | 2.19 | 0.78 | 84 | 0.93 | 0.54 | 44 | |
| 0.4 | 1.72 | 0.65 | 74 | 0.98 | 0.53 | 51 | |
| 0.8 | 1.71 | 0.65 | 65 | 1.09 | 0.55 | 46 | |
| 1.6 | 1.40 | 0.58 | 52 | 1.20 | 0.58 | 45 | |
| 3.2 | 1.45 | 0.58 | 65 | 1.36 | 0.65 | 55 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Ahn, B.-K.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Khan, W.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Yun, Y.-M. Enhanced Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure: Effects of Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio and Magnetite-Mediated Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer. Energies 2025, 18, 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174692
Lee J-S, Kim T-H, Ahn B-K, Jeon Y-J, Ahn J-H, Khan W, Kang S, Kim J, Yun Y-M. Enhanced Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure: Effects of Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio and Magnetite-Mediated Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174692
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jung-Sup, Tae-Hoon Kim, Byung-Kyu Ahn, Yun-Ju Jeon, Ji-Hye Ahn, Waris Khan, Seoktae Kang, Junho Kim, and Yeo-Myeong Yun. 2025. "Enhanced Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure: Effects of Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio and Magnetite-Mediated Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer" Energies 18, no. 17: 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174692
APA StyleLee, J.-S., Kim, T.-H., Ahn, B.-K., Jeon, Y.-J., Ahn, J.-H., Khan, W., Kang, S., Kim, J., & Yun, Y.-M. (2025). Enhanced Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure: Effects of Substrate-to-Inoculum Ratio and Magnetite-Mediated Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer. Energies, 18(17), 4692. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174692









