Abstract
Blending kaolin is an effective method to alleviate fouling and slagging during the combustion of Zhundong coal. The influence of blending kaolin with varying particle sizes on the adsorption behavior of alkali metal sodium and the ash fusion characteristics was studied using sodium capture experiments and ash fusion temperature tests. The results indicate that kaolin particle size is a critical factor influencing sodium retention. As the particle size decreases, the sodium retention rate increases accordingly. In the absence of kaolin, the sodium retention rate was only 28.03%. However, when 75–100 µm particles of kaolin were added, the retention rate increased to 43.49%. Further reducing the particle size to 20–63 µm resulted in an additional increase of 10.51%. Additionally, decreasing the kaolin particle size contributed to the noticeable increase in ash fusion temperatures. After 75–100 µm kaolin was blended, the DT and FT of the ash were 1137 °C and 1161 °C, respectively. With 20–63 µm kaolin, the DT increased by 42 °C, and the FT increased by 36 °C. This trend is attributed to the enhanced decomposition and transformation of sulfates in the ash, which promotes the formation of high-melting-point feldspar minerals such as anorthite and gehlenite. These findings provide important data support for understanding the influence of kaolin particle size on the ash fusion behavior during the combustion of Zhundong coal.
1. Introduction
Coal resources are the foundation of global energy supply and remain dominant in the energy structure [1,2]. Despite global decarbonization and the shift toward oil and gas, coal continues to serve as a strategic bridge fuel for energy security, particularly in developing and energy-intensive economies. The Zhundong (ZD) coalfield located in the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang is China’s largest fully explored coalfield, with reserves of 390 billion tons [3]. ZD coal exhibits high volatility, medium-high moisture, and low ash content [4,5] with a notably high alkali metal content that lowers ash fusion temperature and promotes slagging and fouling in boilers [6,7].
Scholars [8,9] have conducted extensive research on coal rich in alkali and alkaline earth metal (AAEM) elements. They found that under the same conditions that ZD coal exhibited a greater tendency for deposition than bituminous coal or even biomass, confirming that the high alkali metal content in the fuel leads to a lower ash fusion temperature. As an efficient adsorbent, kaolin can remove harmful substances such as alkali metals, heavy metals, and fine particulate matter produced during the combustion of ZD coal [10]. Kaolin possesses a typical layered crystal structure, with each layer consisting of an Al-O octahedral layer and a Si-O tetrahedral layer, which are tightly connected by hydrogen bonds [11]. This unique layered crystal structure endows kaolin with exceptional adsorption properties and excellent stability. At low temperatures, kaolinite gradually transforms into amorphous metakaolin through dehydroxylation, which is one of its primary products during high-temperature decomposition [12]. Due to the loss of hydroxyl groups, metakaolin exhibits an unsaturated coordination state. Meanwhile, as the temperature rises, gaseous metals diffuse to the surface of kaolin, and they are adsorbed and simultaneously undergo chemical reactions, generating sodium aluminosilicates (nepheline and albite) [13]. With the temperature rising above 1100 °C, metakaolin converts into crystalline mullite, a mineral with a relatively weak adsorption capacity [14]. The efficiency of kaolin in capturing gaseous alkali metals in boilers is primarily related to the thermal decomposition and transformation behavior of kaolin.
The fusion characteristics of coal ash are generally regarded as the key parameters for evaluating the caking and fouling of ash in boilers. Vassilev et al. [15] demonstrated that an increase in the content of alkaline metals such as Ca, Na, and Fe in coal will lead to a significant decrease in the ash fusion temperature, while an increase in the content of Si and Al has the opposite effect. Zhu et al. [16] found that when the ratio of base to acid was higher than 0.4, this type of additive tended to lower the fusion temperature of the ash. The Si- and Al-based minerals react with gaseous Na to convert the alkali metals in the coal into a solid state, thereby achieving the regulation of the coal ash fusion temperature [17,18]. The research on kaolin additives has shown that their influence on the fusion temperature of ash is closely related to the blending ratio [7]. With a kaolin blending ratio below 3%, the ash fusion temperature decreases significantly; at ratios exceeding 6%, the temperature rises rapidly [19,20]. At low blending ratios of kaolin, its components of Si and Al tend to participate in the formation of low-temperature eutectic mixtures and low-temperature co-crystals, which promotes the release of Ca and Na [21]. At present, most studies have focused on the influence of the proportion of kaolin addition of the transformation of coal ash minerals and the fusion temperature of the ash. However, the grindability of kaolin and coal is inconsistent. After blended and ground, the particle size distribution of kaolin is unclear, and the effects of different particle sizes of kaolin on the transformation of coal ash minerals and the ash fusion temperature are also unknown. Therefore, it is more important to study the influence of kaolin particle size on the adsorption and ash fusion characteristics of alkali during the combustion of ZD coal.
Generally speaking, particles with smaller diameters have larger surface areas, more surface-active sites, and stronger adsorption capabilities [22,23]. To investigate the effect of kaolin particle size on the adsorption of alkali metal sodium in ZD coal and its ash fusion characteristics, X-ray diffraction (XRD) was utilized to analyze mineral transformations, scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy dispersive X-ray (SEM-EDS) analysis was conducted on the microscopic morphology and elemental distribution of the ash sample, ash fusion temperatures were measured using an ash fusion point analyzer, and sodium retention rates were determined using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). These findings provide valuable data to mitigate slagging and fouling issues during ZD coal combustion.
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Raw Material Preparation
In this study, ZD coal was selected as the experimental raw coal, and the kaolin was used as the blending additive. First, according to the Chinese standards GB/T 212-2008 [24] and GB/T 30733-2014 [25], the proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of raw coal were conducted, and the content of fixed carbon and oxygen were calculated by differences. And the results are shown in Table 1. Meanwhile, following the Chinese standard GB/T 219-2008 [26], the ash fusion temperatures of the coal ash were tested. The ash fusion characteristics are evaluated using four characteristic temperatures: deformation temperature (DT), softening temperature (ST), hemisphere temperature (HT), and flow temperature (FT). The data on the ash fusion temperatures of the raw coal are shown in Table 2. Furthermore, the ash composition was analyzed under the standard of GB/T 1574-2007 [27]. The analysis results are presented in Table 3, and the proximate and ultimate analysis shows the raw coal has a moisture content of 25.40% and ash content of 9.67%. The deformation temperature of the raw coal is 1149 °C, and the flow temperature is 1193 °C, indicating a relatively low ash fusion temperature. Na2O accounts for 3.2% of the raw coal ash composition. In contrast, the Na2O content in the blended kaolin is only 1.11%, while the Al2O3 content is 22.99%. The SiO2 content is as high as 68.17%, so it is classified as a high-silica and -aluminum mineral.

Table 1.
Proximate and ultimate analyses of raw coal (wt.%).

Table 2.
ZD coal ash fusion temperature.

Table 3.
Chemical composition of ZD coal ash and kaolin (wt.%).
Kaolin contains no calorific value, and adding it to coal may reduce the boiler’s combustion efficiency. In addition, a low blending ratio may lead to an insignificant effect on the ash fusion temperature. Therefore, to increase the ash fusion temperature and minimize the impact of kaolin content on load, kaolin with different particle sizes was blended with ZD coal at a 2% ratio to analyze the influence of particle size on sodium capture and ash fusion characteristics. The particle size of kaolin at 75–100 µm, 63–75 µm, and 20–63 µm were uniformly blended with the raw coal. The mixed samples were labeled as C-K1, C-K2, and C-K3, respectively.
2.2. Sodium Adsorption Characteristic Experiment
A fixed-bed combustion system was employed for the experiment involving kaolin blending to retain sodium, as shown in Figure 1. The system consists of an air supply unit, a heating unit, and a gas-washing unit. The air supply unit is composed of an air compressor and a mass flow meter. The heating unit utilizes a TL1500-1500 dual-zone tubular furnace. The gas-washing unit employs dilute nitric acid and low-concentration sodium hydroxide solutions to absorb the flue gas generated during the reaction.
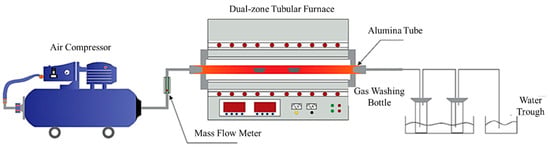
Figure 1.
Sodium retention experiment of the dual-temperature zone tubular furnace.
During the experiment, 4 g of the coal sample was weighed and placed in an alumina crucible. The sample was then heated from room temperature in the tubular furnace, with the airflow rate maintained at 0.2 L/min. The target temperatures were set at 900 °C, 1000 °C, 1100 °C, and 1200 °C, respectively. Below 900 °C, the heating rate was controlled at 10 °C/min, while above 900 °C, it was adjusted to 5 °C/min. After reaching each target temperature, calcination was continued for an additional hour to ensure the completion of the reaction.
2.3. Calculation of Sodium Retention Rate
To investigate the sodium capture performance of kaolin with different particle sizes in raw coal at various temperatures, the chemical extraction method was employed to measure the sodium content in coal ash [28]. The capture performance of sodium in coal ash is represented by the sodium retention rate η, and the calculation formula is shown in Equation (1).
MNa,H(d,T) represents the sodium content (wt.%) of the coal ash obtained after adding kaolin with particle size d at temperature T. In contrast, MNa,D represents the sodium content (wt.%) in the raw ZD coal.
2.4. Experimental Methods
The ash fusion temperatures were tested using an ash fusion point instrument (YHHR-4000, Changzhou Aeolian Technology Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China). Coal ash was shaped into triangular cones (height of 20 mm, bottom edge length of 7 mm) using 10% dextrin as a binder. Ash fusion behavior was examined in an ash fusion temperature analyzer under atmosphere condition. The room temperature was raised to 900 °C, with a heating rate of 15 °C/min. After reaching 900 °C, the heating rate decreased to 5 °C/min. Four characteristic temperatures of ash samples were determined by comparing the real-time shape of each triangular cones with the shape described in Chinese standard (GB/219–2008). The final result AFT values represent the average of three parallel measurements. The coal ash was digested using a microwave digestion system (Multiwire PRO, Anton Paar GmbH, Graz, Austria) with a mixture of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. The digestion was followed by multiple acid evaporation treatments, and the sample was diluted to 50 mL with deionized water. The sodium content was tested using ICP-OES (AAA7900, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) under the following conditions: RF power of 1550 W, plasma gas flow rate of 15.0 L/min, carrier gas flow rate of 1.05 L/min, and sampling depth of 8.0 mm. The mineral composition in coal ash was analyzed by comparing with the standard cards in the Jade 6.5 software package using XRD (SmartLab 9 kW, Rigaku Corporation, Akishima, Japan). During the XRD data collection, Cu Kα radiation with a wavelength of 0.154 nm was employed under operating conditions of 40 kV and 30 mA. The diffraction patterns were recorded with a step size of 0.02°, a scanning speed of 2°/min, and a 2θ range of 3°–30°. SEM-EDS (Phenom Pure, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bleiswijk, The Netherlands) was used to analyze the microscopic morphology and elemental distribution of coal ash under different reaction conditions, with spectral acquisition conducted using the Phenom ProSuite system. The measurements were performed with an energy resolution of 129 eV (Mn Kα, nominal value) and a spatial resolution of approximately 2 μm at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Coal Ash and Variation in the Ash Formation Rate
Figure 2 illustrates the macroscopic morphology of coal ash under different reaction conditions. At 900 °C, the coal ash appears predominantly grayish white, with the surface exhibiting a distinctly loose texture. When the temperature exceeds 1000 °C, the coal ash without kaolin addition turns reddish brown. Although the ash samples remain relatively loose, noticeable agglomeration is observed. Although the blended samples with added kaolin also showed signs of agglomeration, the extent of molten agglomeration decreased significantly with decreasing kaolin particle size, and the overall ash yield was also noticeably reduced.
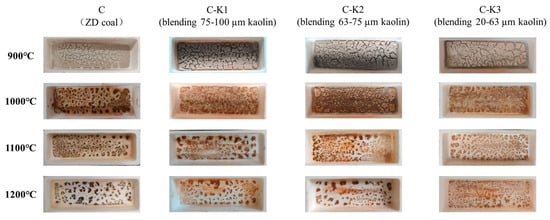
Figure 2.
Macroscopic morphology of coal ash.
Figure 3 shows the microscopic morphology of coal ash after the co-combustion of ZD coal with different kaolin samples at 900 °C and 1100 °C. At 900 °C, a small number of large particles are observed in the coal ash blended with 75–100 µm kaolin, with particle diameters around 30 µm. In contrast, when blended with 20–63 µm kaolin, no large particles are present, and the ash consists of uniformly small particles.
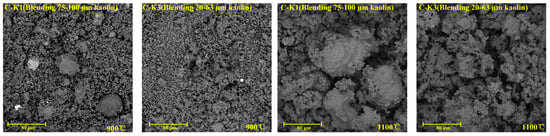
Figure 3.
Microscopic morphology of coal ash.
At 1100 °C, the morphology of the coal ash undergoes significant changes. For ash blended with 75–100 µm kaolin, the surface displays large particles exceeding 80 µm in diameter. Additionally, adhesion is observed both among small particles and between small and large particles, which may be attributed to sintering phenomena occurring at elevated temperatures. In contrast, for ash blended with 20–63 µm kaolin, no obvious large particles are observed on the surface; however, the adhesion between particles is more pronounced, suggesting that the smaller particles undergo fusion, resulting in more extensive bonding [29].
Figure 4 presents the ash formation rate for kaolin blending with varying particle sizes. It can be seen that at the same combustion temperature, the ash formation rate is negatively correlated with the particle size of the added kaolin, indicating that a decrease in particle size leads to an increase in the ash formation rate. This may be attributed to the fact that kaolin with smaller particle sizes has a larger specific surface area, which offers more active adsorption sites, thereby enhancing its ability to adsorb gaseous substances and increasing the ash formation rate.
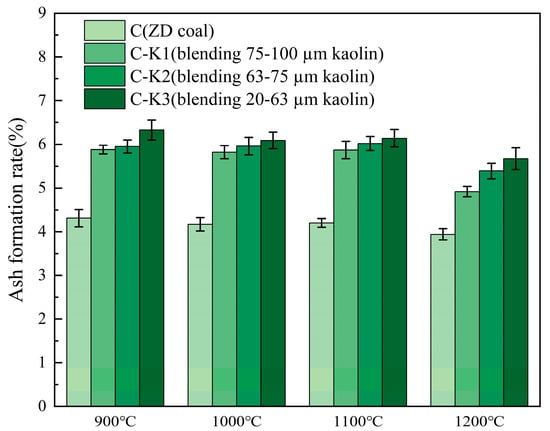
Figure 4.
Ash formation rate after blending different particle sizes of kaolin.
However, as the combustion temperature increases, the ash formation rates of all samples show a significant decreasing trend. This can be explained by the fact that chemical reactions between minerals in the coal ash become more complete at higher temperatures. Additionally, elevated temperatures promote the release of gaseous species, resulting in a reduced ash formation rate as the combustion temperature rises.
3.2. Transformation Process of Coal Ash Minerals
Figure 5 shows the mineral composition of coal ash under different conditions. The chemical reaction equations for the minerals in coal ash are provided in Table 4. Table 5 lists the main minerals and their chemical formulas.
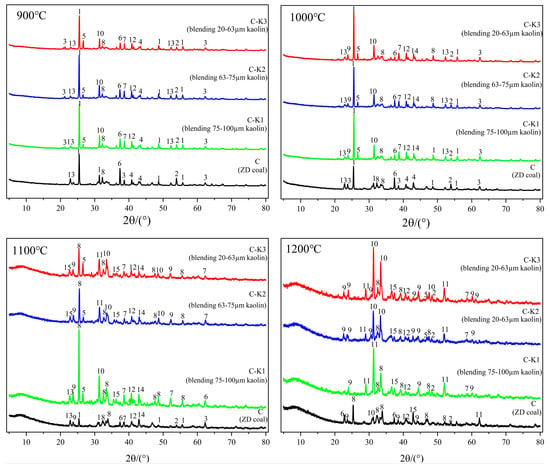
Figure 5.
Composition of coal ash minerals with different particle sizes of kaolin additives.

Table 4.
Major mineral-forming reactions in coal ash.

Table 5.
Main minerals in coal ash.
At temperature stages of 900 °C and 1000 °C, the mineral composition of coal ash from raw coal combustion primarily consists of anhydrite (CaSO4), quartz (SiO2), and sulfates, with only trace amounts of silicate minerals. Upon kaolin addition, the diffraction peaks of certain sulfates in the coal ash transform into those of nepheline (NaAlSiO4) and gehlenite (Ca2Al2SiO7), as described by the reactions in Equations (2)–(5). At 1000 °C, compared to raw coal without kaolin, the diffraction peak intensity of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) significantly decreases after kaolin addition, while the diffraction peak of albite (NaAlSi3O8) intensifies with decreasing kaolin particle size. This is attributed to the high content of silico-aluminous oxides in kaolin, which adsorb sodium in the coal ash to form albite, as shown in Equation (6). As kaolin particle size decreases, the NaAlSi3O8 diffraction peak becomes more pronounced, indicating that smaller kaolin particles enhance the reaction between sodium and aluminosilicates. The formation of spinel (MgAl2O4) in coal ash after kaolin blending is likely due to the increased Al2O3 content from kaolin, which reacts with periclase (MgO) to form MgAl2O4, as described in Equation (7). Furthermore, blending with kaolin of 20–63 µm particle size significantly enhances the diffraction peak intensity of calcium silicate (Ca2SiO4). Smaller kaolin particle sizes are more conducive to reacting with silicon dioxide to form silicates, as shown in Equation (8) [30].
At 1100 °C, the sulfate content in raw coal decreases significantly, with elements such as Na, Ca, and Mg predominantly present as silicates. The addition of kaolin markedly enhances the intensity of the Ca2SiO4 diffraction peak, while the sulfate diffraction peak disappears, attributed to the decomposition of calcium sulfate [31]. Additionally, as kaolin particle size decreases, Fe2O3, MgO, and SiO2 react to form iron magnesium olivine (Mg1.86Fe0.14SiO4), as described by Equation (9). Concurrently, the increased diffraction peak intensity of sodium-containing minerals, such as nepheline, suggests that smaller kaolin particle sizes enhance surface active sites [32], thereby improving the sodium capture efficiency of kaolin.
At the high-temperature condition of 1200 °C, sodium in raw coal predominantly exists as sodium silicate and albite, while calcium primarily occurs as calcium silicate, with a minor fraction as aluminosilicate. Upon kaolin addition, the diffraction peaks of albite and anorthite significantly increase, as described by the reaction in Equation (10). This is likely due to the reaction of Al2O3 in kaolin with sodium silicate and calcium silicate, leading to the formation of feldspar-like minerals [33]. Furthermore, as the particle size of blended kaolin decreases, the diffraction peaks of silicate minerals in coal ash largely disappear, while those of high-melting-point minerals, such as anorthite, gehlenite, and albite, are significantly enhanced. This suggests that smaller kaolin particle sizes promote the transformation of low-melting-point silicate minerals into high-melting-point feldspar group minerals.
Figure 6 shows the distribution of elements on the surface of coal ash with different particle sizes of kaolin blended at 1000 °C. In the case of blending 75–100 µm kaolin, there are large particles larger than 80 µm, with loose surfaces and numerous small pores. The surface of the large particles is mainly composed of Si and Al, along with some sodium and a small amount of calcium. It is speculated that the main component is a sodium-calcium-containing aluminosilicate. The particles around the large particles are distributed relatively evenly. The main elements are Ca, S, and O. Based on XRD analysis, the main mineral is calcium sulfate. As the particle size of blended kaolin is reduced to 20–63 µm, the particle sizes of the surface particles of the ash sample become uniform. By comparing C-K1 with C-K3, it was found that after adding large-sized kaolin, the surface Na content of the ash sample was lower than that of the small-sized one. The smaller the particle size is, the higher the content of adsorbed alkali metal Na.
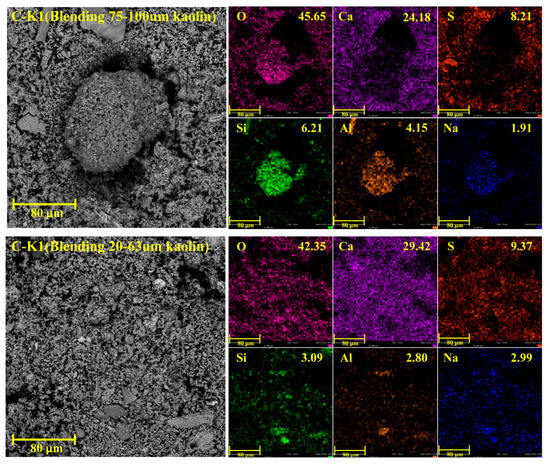
Figure 6.
Distribution of elements on the surface of coal ash at 1000 °C.
3.3. Analysis of Coal Ash Fusion Characteristics
Table 6 shows the fusion temperatures of coal ash blended with kaolin at different particle sizes. It can be seen that after blending with 75–100 µm kaolin, the fusion temperature of the coal ash is significantly lower than that of the raw coal, with a DT of 1137 °C and FT of 1161 °C. This is consistent with the XRD results at 1200 °C, where the diffraction peak of Ca2SiO4 in the ash blended with 75–100 µm kaolin is significantly weakened, while the diffraction peak of Ca2Al2SiO7 is noticeably enhanced. Since the fusion temperature of Ca2Al2SiO7 is lower than that of Ca2SiO4 [34], the addition of 2% 75–100 µm kaolin leads to a decrease in ash fusion temperature.

Table 6.
The ash fusion temperature of coal ash and its main minerals.
As the kaolin particle size decreases, the fusion temperature of coal ash gradually increases. Specifically, with the addition of 20–63 µm kaolin, the deformation temperature of the ash increases by 42 °C, and the flow temperature rises by 36 °C. Referring to Table 6, at 1200 °C and with kaolin particle size reduced to 20–63 µm, the diffraction peak of Ca2Al2SiO7 becomes stronger, while that of CaAl2Si2O8 weakens. Since Ca2Al2SiO7 has a higher fusion temperature than CaAl2Si2O8, the formation of more high-fusion-point gehlenite is promoted by smaller kaolin particles. This is considered the main reason for the increase in ash fusion temperature when finer kaolin is blended [35]. Table 6 shows that the DT and HT of the kaolin samples with small particles are significantly higher than those of the samples with large particles. It confirms that an increase in the content of Ca2Al2SiO7 directly leads to a higher fusion temperature of the coal ash.
3.4. Sodium Retention Rate Analysis
Figure 7 shows the influence of blending kaolin with different particle sizes at 1100 °C on the sodium retention rate of ZD coal. The sodium retention rate of coal ash without kaolin addition is only 28.03%. After adding kaolin with a particle size of 75–100 µm, the sodium retention rate increases to 43.49%, which is 15.46% higher than that of the sample without kaolin. When the particle size of kaolin is further reduced to 20–63 µm, the sodium retention rate reaches 54%, an increase of 10.51% compared to the 75–100 µm kaolin-blended sample. As the particle size of kaolin decreases, the rate of increase in sodium retention gradually declines, and the increment in sodium retention rate weakens from 8.47% to 2.04%. This may be attributed to the progressive saturation of surface active sites as the kaolin particle size decreases, which limits the availability of new reactive sites [32].
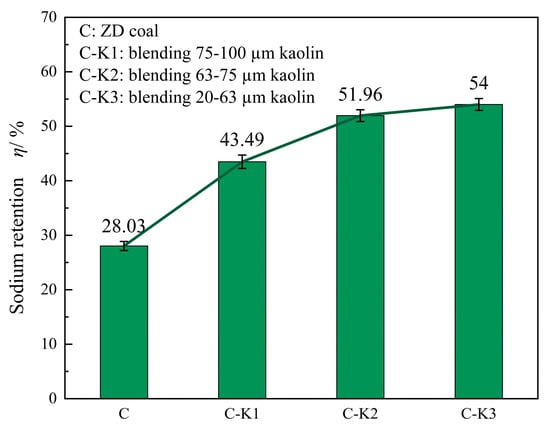
Figure 7.
Sodium retention rate under different blending particle sizes at 1100 °C.
4. Conclusions
This study investigates the effects of kaolin with various particle sizes on the sodium adsorption behavior and ash fusion characteristics of ZD coal under combustion temperatures ranging from 900 °C to 1200 °C, with a fixed kaolin blending ratio of 2%. A detailed analysis was conducted on the mineral transformation processes in the coal ash and the evolution of ash fusion temperatures. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- As the particle size of the blended kaolin decreases, the molten agglomerated state in ZD coal ash transforms into a compact sintered particle structure, and the ash yield gradually increases.
- (2)
- The addition of kaolin promotes the decomposition of low-melting-point sulfates in coal ash and facilitates their transformation into silicates and aluminosilicates. As the particle size of blended kaolin decreases, the diffraction intensities of sulfates in the ash decrease, while the silicates and aluminosilicates increase accordingly.
- (3)
- With decreasing kaolin particle size, the ash fusion temperature shows a gradual increase. Blending kaolin with a particle size of 75–100 µm into the ZD coal, its DT and FT were 1137 °C and 1161 °C. However, the particle size was reduced to 20–63 µm, its DT and FT were 42 °C and 36 °C higher, respectively, than those of the larger particle size kaolin. The particle size of kaolin decreases, and the high-melting-point silicates and aluminosilicates increase, thereby raising the ash fusion temperature.
- (4)
- A reduction in kaolin particle size significantly improves the sodium retention efficiency. Without kaolin addition, the sodium retention rate is only 28.03%, but it increases to 43.49% when 75–100 µm kaolin is blended. However, as the particle size decreases, the increase in sodium retention rate weakens from 8.47% to 2.04%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and B.W.; methodology, J.W.; software, J.W.; validation, J.W.; investigation, P.H., J.F., J.W. and B.J.; writing—original draft, J.F. and J.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W. and B.W.; resources, B.W., S.X. and Y.L. (Yin Liu); funding acquisition, Y.L. (Yifan Liang) and Y.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Science and Technology Project of State Grid Xinjiang Electric Power Research Institute (SGXJDK00NYJS2500042), Major Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (NO. 2024A01005-2), the Natural Science Foundation Project of the Autonomous Region: “Research on the Changes and Influences of Industrial Carbon Emission Efficiency in Xinjiang” (NO. 2022D01A285), Tianshan Talents Doctoral Recruitment Program (NO. 51052300571), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 22178298), and the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Tianshan Talents Innovation Project (NO. 2022TSYCCX0056).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to project data restriction.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xin, H.-H.; Wang, D.-M.; Dou, G.-L.; Qi, X.-Y.; Xu, T.; Qi, G.-S. The Infrared Characterization and Mechanism of Oxygen Adsorption in Coal. Spectrosc. Lett. 2014, 47, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, Z.; Weng, Q.; Che, D. Effect of ashing temperature on physical-chemical features of high-sodium ashes of Zhundong coals. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, X.; Querol, X.; Font, O.; Moreno, N.; Zhou, J. Environmental geochemistry of the feed coals and their combustion by-products from two coal-fired power plants in Xinjiang Province, Northwest China. Fuel 2012, 95, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, C.; Xu, H.; Ma, L.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Investigation on the influence of sulfur and chlorine on the initial deposition/fouling characteristics of a high-alkali coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 198, 106234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, G.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Shi, L.; Zhao, L.; Che, D. Simulation study on mineral transformation behaviors and ash fusion characteristics during high-alkali coal combustion under deep peaking conditions. Fuel 2025, 399, 135662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanmei, Y.; Hai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yuxin, W.; Qing, L. Effect of Si/Al/Na/Ca on Ash Fusion Characteristics of Zhundong Coal. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2018, 39, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Wang, H.F.; Li, X.; Wang, X.X.; Bie, N.X.; Yao, B.; Zhen, W.J.; Li, J.; Lou, C.; Yao, H.; et al. Investigation of Slagging Condition in a Zhundong Coal-Fired Boiler via In Situ Optical Measurement of Gaseous Sodium. Sensors 2024, 24, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Huang, Q.; Yao, Q. Fine particulate formation and ash deposition during pulverized coal combustion of high-sodium lignite in a down-fired furnace. Fuel 2015, 143, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ni, Y.; Yin, Q.; Wang, J.; Lv, L.; Cen, K.; Zhou, H. Research on element migration and ash deposition characteristics of high-alkali coal in horizontal liquid slagging cyclone furnace. Fuel 2022, 308, 121962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Cao, Z.; Di, H. Investigation on minerals migration during co-firing of different straw/coal blending ratios. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 74, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptáček, P.; Frajkorová, F.; Šoukal, F.; Opravil, T. Kinetics and mechanism of three stages of thermal transformation of kaolinite to metakaolinite. Powder Technol. 2014, 264, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwabe, P.O.; Wendt, J.O. Mechanisms governing trace sodium capture by kaolinite in a downflow combustor. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1996, 26, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, T.K.; Wendt, J.O.L. Mechanisms and Models Describing Sodium and Lead Scavenging by a Kaolinite Aerosol at High Temperatures. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgueras, M.B.; Díaz, R.M.; Xiberta, J.; García, M.P.; Pis, J.J. Influence of Sewage Sludge Addition on Coal Ash Fusion Temperatures. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Tu, H.; Bai, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation of slagging and fouling characteristics during Zhundong coal co-firing with a Si/Al dominated low rank coal. Fuel 2019, 254, 115730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Xing, H.; Wang, G.; Deng, H.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Yao, H. Correlations between the sodium adsorption capacity and the thermal behavior of modified kaolinite during the combustion of Zhundong coal. Fuel 2019, 237, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazidin, H.; Suyatno, S.; Prismantoko, A.; Karuana, F.; Sarjono; Prabowo; Setiyawan, A.; Darmawan, A.; Aziz, M.; Vuthaluru, H.; et al. Impact of additives in mitigating ash-related problems during co-combustion of solid recovered fuel and high-sulfur coal. Energy 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ji, J.; Wang, Q.; Fang, M. Ash deposition behavior of a high-alkali coal in circulating fluidized bed combustion at different bed temperatures and the effect of kaolin. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 33817–33827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Lou, C. Effect of Kaolin Addition on Combustion Behavior of Zhundong Coal Pellet Using Flame Emission Spectroscopy. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 197, 1809–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, D.; Yang, H.; Li, S. Understanding Ash Deposition for the Combustion of Zhundong Coal: Focusing on Different Additives Effects. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 7103–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengli, L.; Bo, J.; Guoxi, C.; Yu, S.; Zheng, T. Structural and evolutionary characteristics of pores-microfractures and their influence on coalbed methane exploitation in high-rank brittle tectonically deformed coals of the Yangquan mining area, northeastern Qinshui basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhsan, J.; Johnson, B.B.; Wells, J.D. A Comparative Study of the Adsorption of Transition Metals on Kaolinite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 217, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 212-2008; Proximate Analysis of Coal. National Standard PRC: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 30733-2014; Determination of Total Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen Content in Coal-Instrumental Method. National Standard PRC: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 219-2008; Determination of Fusibility of Coal Ash. National Standard PRC: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 1574-2007; Test Method for Analysis of Coal Ash. National Standard PRC: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, J.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Bai, Y. Transformation behavior of alkali metals in high-alkali coals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 169, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Wan, K.; He, Y.; Xia, J.; Cen, K. Inhibition of sodium release from Zhundong coal via the addition of mineral additives: A combination of online multi-point LIBS and offline experimental measurements. Fuel 2018, 212, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouia, F.; Belhouchet, H.; Sahnoune, F.; Bouzrara, F. Reaction sintering of kaolin-natural phosphate mixtures. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8064–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Tu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zeng, H.; Qiu, J. Decomposition and solid reactions of calcium sulfate doped with SiO2, Fe2O3 and Al2O3. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 113, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Tang, H.; Cai, T.; Chen, X.; Zan, H.; Ma, J.; Liang, C. Mechanism of kaolinite’s influence on sodium release characteristics of high-sodium coal under oxy-steam combustion conditions. Fuel 2021, 290, 119812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.-Q.; Wu, X.; De Girolamo, A.; Zhang, L. Inhibition of lignite ash slagging and fouling upon the use of a silica-based additive in an industrial pulverised coal-fired boiler. Part 1. Changes on the properties of ash deposits along the furnace. Fuel 2015, 139, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.-A.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Effect of CaO/Fe2O3 on ash fusibility during petroleum coke gasification and combustion. Fuel 2022, 331, 125667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, M.; Fan, H.; Fang, Y. Understanding Ash Fusion and Viscosity Variation from Coal Blending Based on Mineral Interaction. Energy Fuels 2017, 32, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).