Bayesian-Spatial Optimization of Emergency EV Dispatch Under Multi-Hazard Disruptions: A Behaviorally Informed Framework for Resilient Energy Support in Critical Grid Nodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling
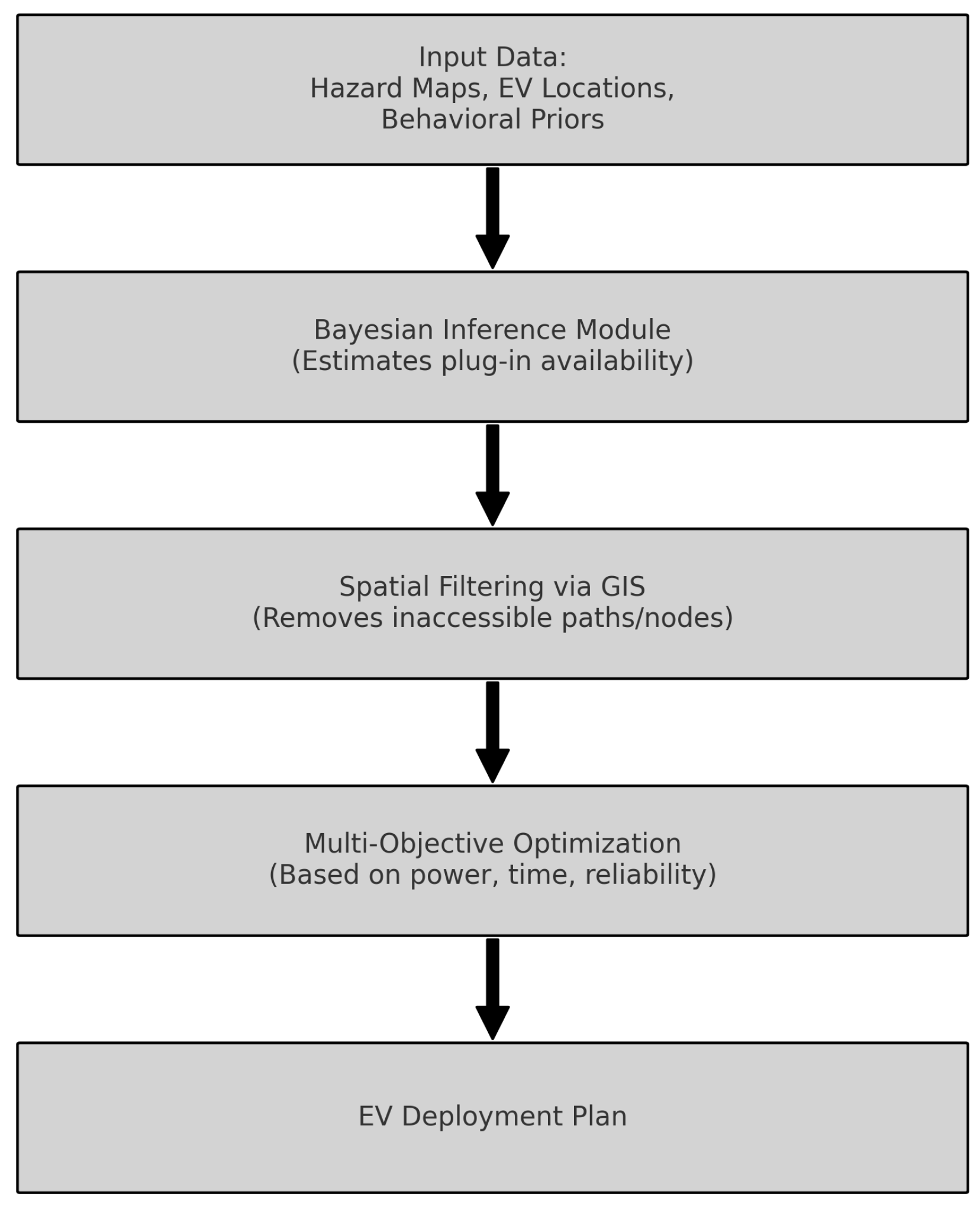
3. Method
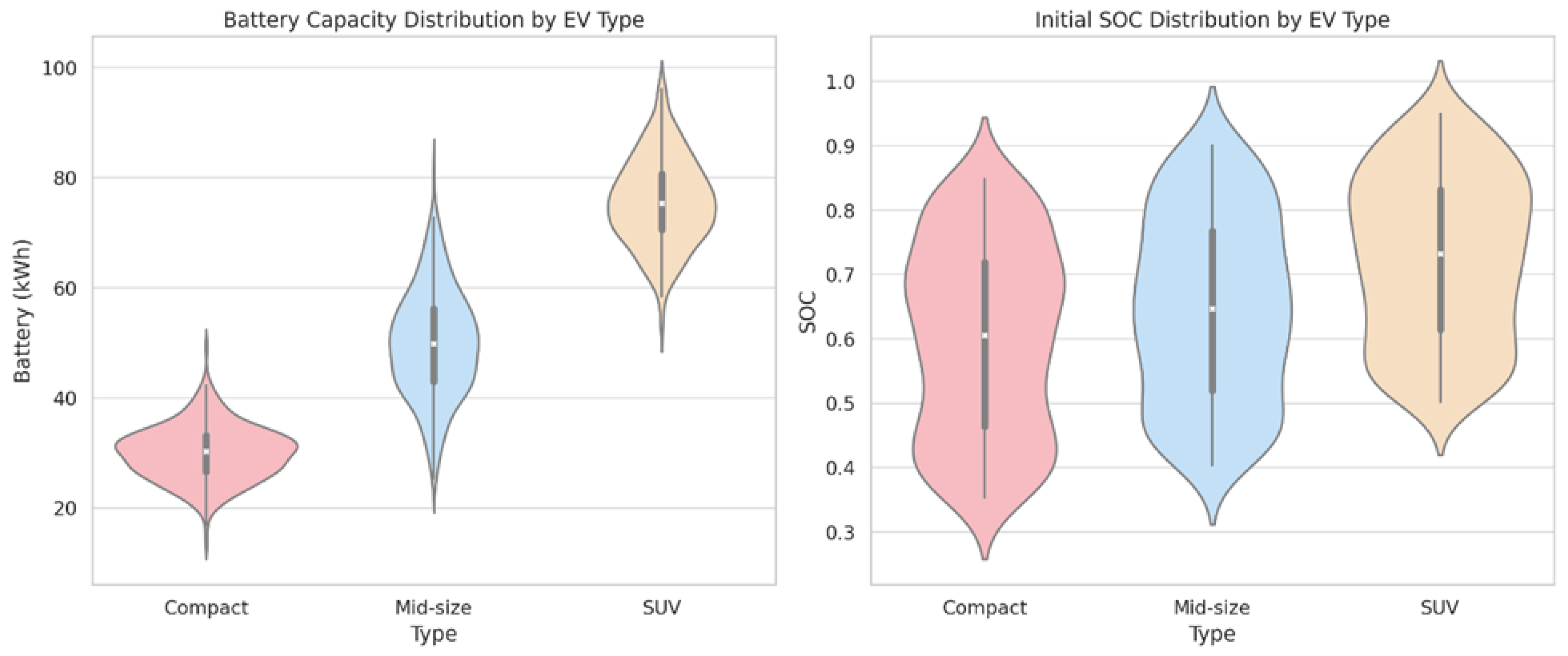
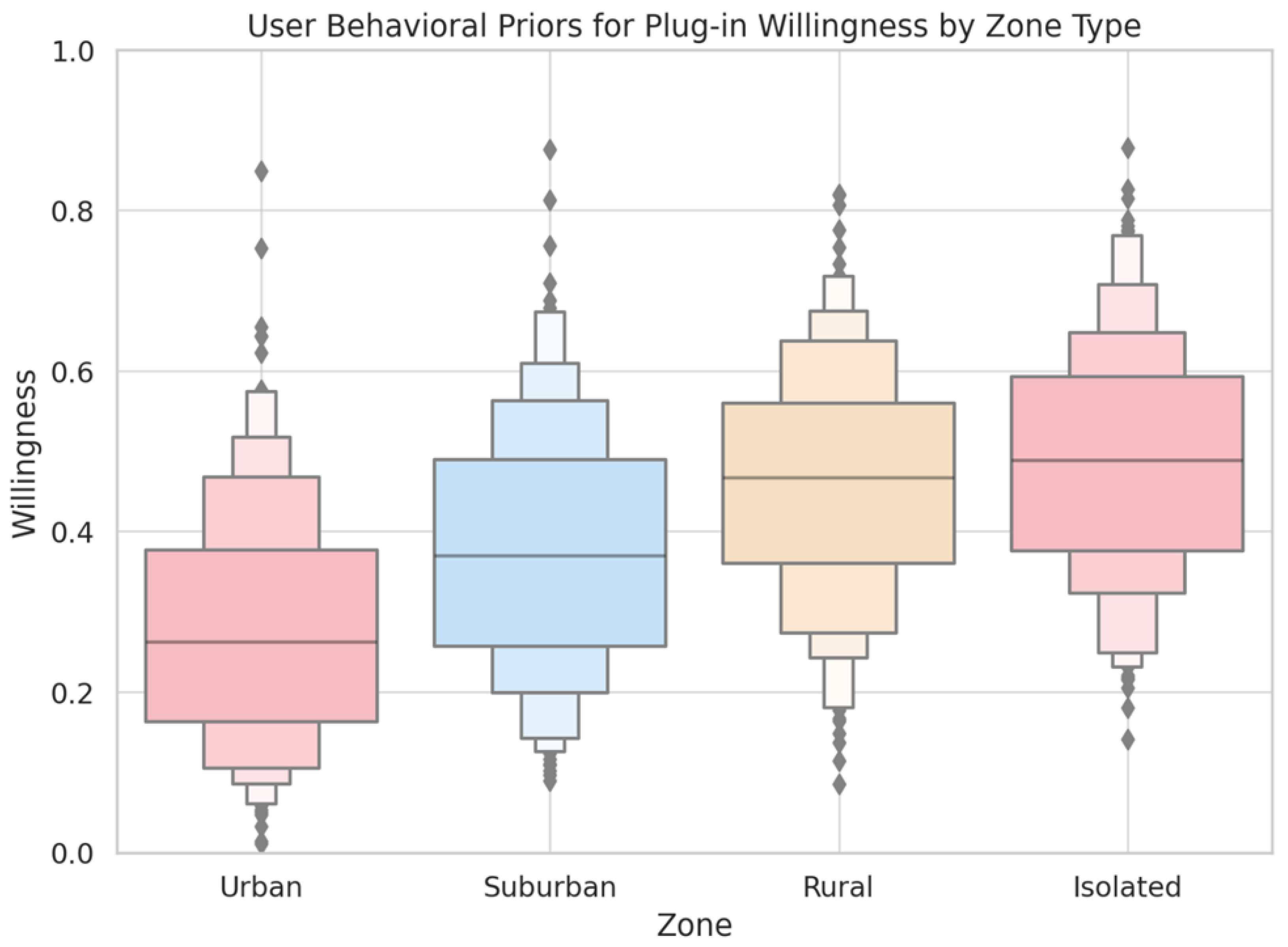
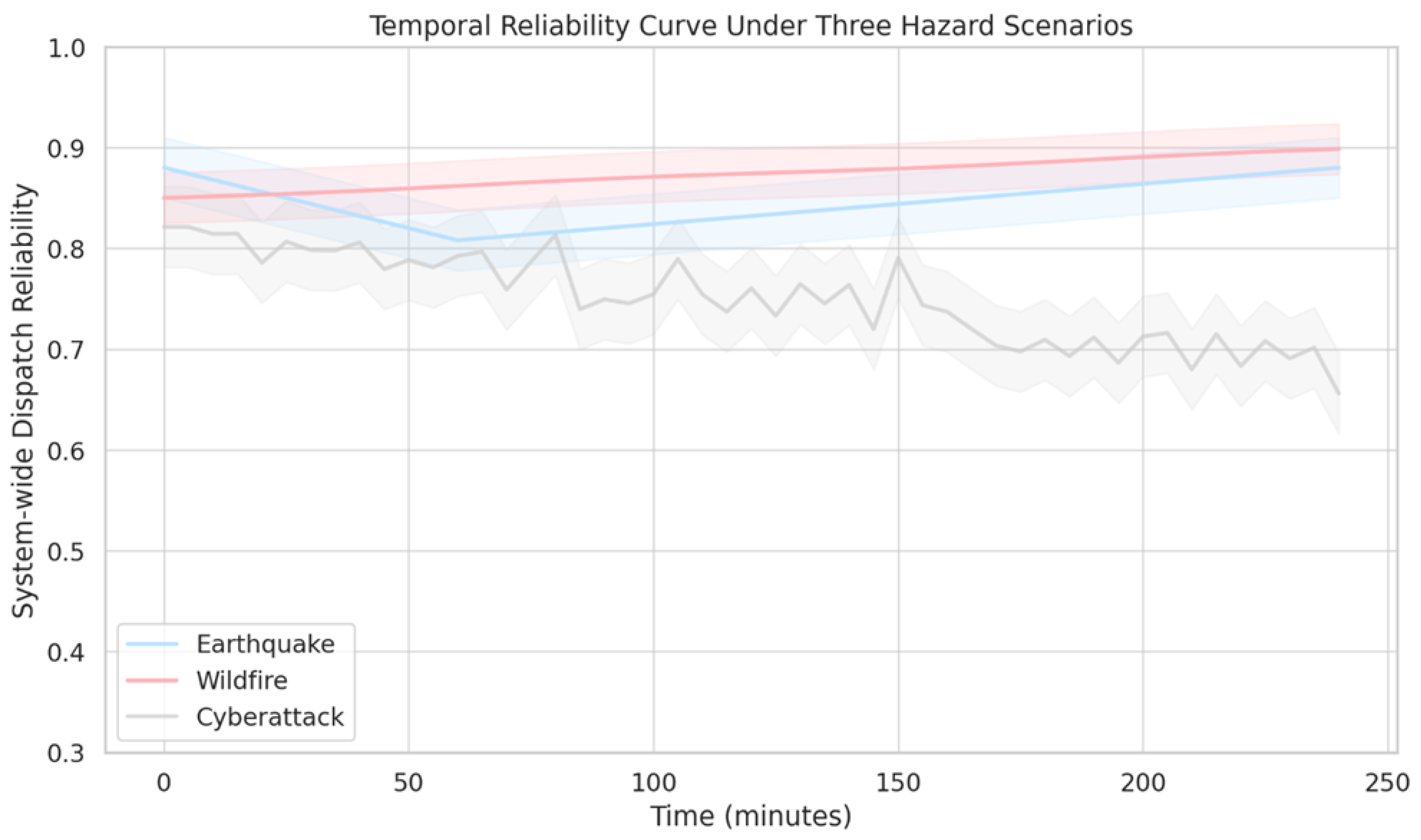
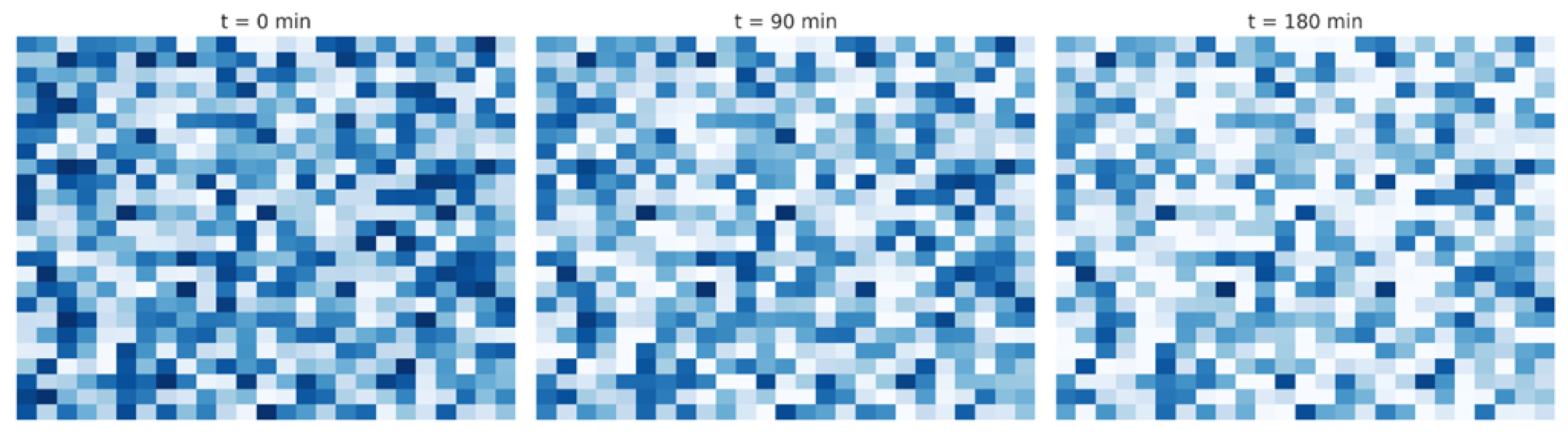
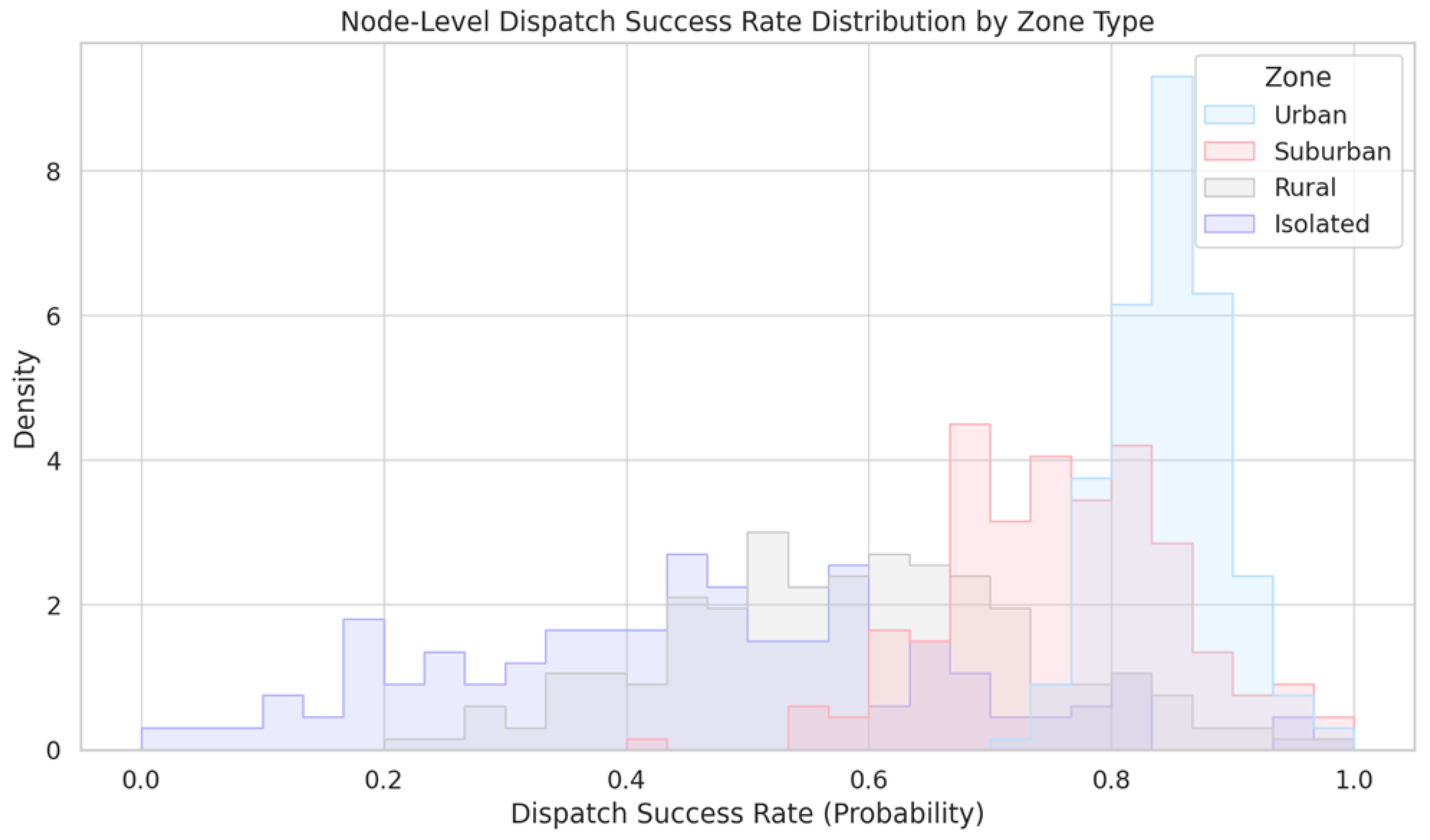
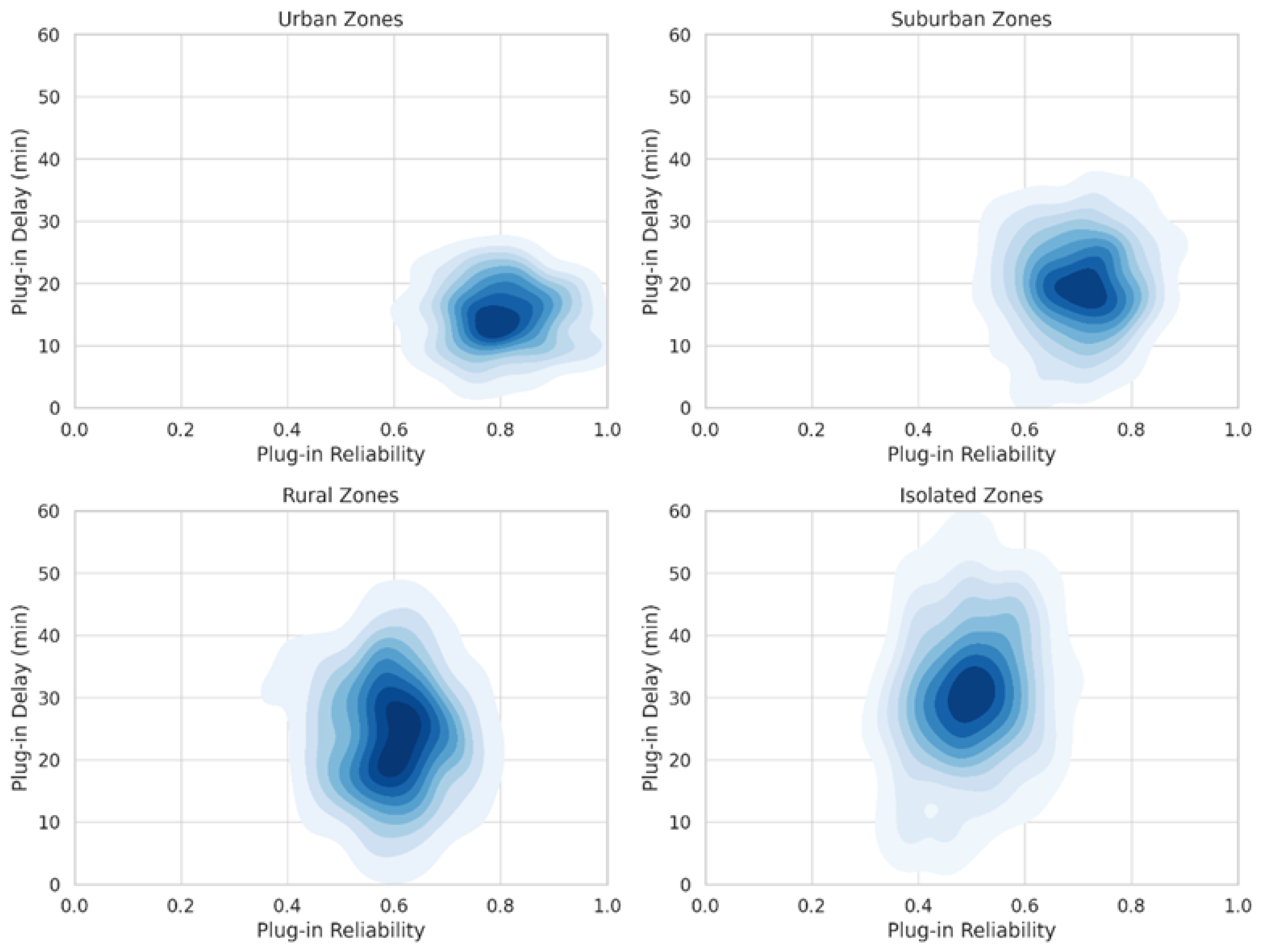
4. Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Explainable spatiotemporal multi-task learning for electric vehicle charging demand prediction. Appl. Energy 2025, 384, 125460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H. Hydrogen refueling of a fuel cell electric vehicle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 75, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasturk, U.; Schrotenboer, A.H.; Ursavas, E.; Roodbergen, K.J. Stochastic Cyclic Inventory Routing with Supply Uncertainty: A Case in Green-Hydrogen Logistics. Transp. Sci. 2024, 58, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hu, B. Frontiers in Operations: Battery as a Service: Flexible Electric Vehicle Battery Leasing. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2024, 26, 1189–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Xu, H.; Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Guo, C.; Chen, Z. Byzantine-Resilient Economical Operation Strategy Based on Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning for Multiple Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Considering Data Privacy. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Q. Electric Vehicles Management in Distribution Network: A Data-Efficient Bi-level Safe Deep Reinforcement Learning Method. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 40, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.P.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Fei, X.; Hu, Z.; Alhazmi, M.; Yan, X.; Wu, C.; Lu, S.; et al. Electric Vehicle Charging Planning: A Complex Systems Perspective. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.V.; Farhan, M.A.A. Optimal Simultaneous Allocation of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations and Capacitors in Radial Distribution Network Considering Reliability. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Control Strategies, Economic Benefits, and Challenges of Vehicle-to-Grid Applications: Recent Trends Research. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijon, J.; Döhler, J.S.; Hjalmarsson, J.; Brandell, D.; Castellucci, V.; Boström, C. An Analysis of Vehicle-to-Grid in Sweden Using MATLAB/Simulink. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, Y.; Burtch, G. Recharging Retail: Estimating Consumer Demand Spillovers from Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2024, 26, 797–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, S. Ensuring Sustainable Grid Stability through Effective EV Charging Management: A Time and Energy-Based Approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.R.; Haque, A.; Khan, M.A.; Kurukuru, V.S.; Mehfuz, S. On-Board Chargers for Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Performance and Efficiency Review. Energies 2024, 17, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, M.; Ali, M.H. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Driven Mitigation of Adverse Effects of Cyber-Attacks on Electric Vehicle Charging Station. Energies 2023, 16, 7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhao, A.P.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Fei, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiang, Y. Integrating solar-powered electric vehicles into sustainable energy systems. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2025, 2, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.; He, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, R.; Wang, Y.-X. Health-aware model predictive energy management for fuel cell electric vehicle based on hybrid modeling method. Energy 2023, 278, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C.; Han, W.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, T.; Jiang, C.Q. Automotive revolution and carbon neutrality. Front. Energy 2023, 17, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Mieth, R.; Konstantinou, C.; Karri, R.; Dvorkin, Y. Cyber Insurance Against Cyberattacks on Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoi, M.S.; Zhuang, S.; Munir, H.M.; Haris, M.; Hassan, M.; Usman, M.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Ro, J.-S. An in-depth analysis of electric vehicle charging station infrastructure, policy implications, and future trends. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11504–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhao, A.P.; Wang, Y.; Alhazmi, M. Hybrid energy storage for dairy farms: Enhancing energy efficiency and operational resilience. J. Energy Storage 2025, 114, 115811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.L.; Mandrioli, R.; Ricco, M.; Monteiro, V.; Monteiro, L.F.C.; Afonso, J.L.; Grandi, G. Electric Vehicles Charging Management System for Optimal Exploitation of Photovoltaic Energy Sources Considering Vehicle-to-Vehicle Mode. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 716389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Shahidehpour, M. Enhanced Coordinated Operations of Electric Power and Transportation Networks via EV Charging Services. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.P.; Alhazmi, M.; Huo, D.; Li, W. Psychological modeling for community energy systems. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Afifah, F.; Qi, J.; Baghali, S. A Stochastic Multi-Agent Optimization Framework for Interdependent Transportation and Power System Analyses. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, H.; Zhao, P. Energy management for hybrid energy storage system in electric vehicle: A cyber-physical system perspective. Energy 2021, 230, 120890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Tseng, C.L.; Wen, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Li, X. Scenario-Based Optimal Real-Time Charging Strategy of Electric Vehicles with Bayesian Long Short-Term Memory Networks. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ning, C.; Li, L.; Qiu, H.; Gu, W.; Dong, Z. Bayesian Nonparametric Two-Stage Distributionally Robust Unit Commitment Optimization: From Global Multimodality to Local Trimming-Wasserstein Ambiguity. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 6702–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Source | Description |
|---|---|
| California DMV Records | Electric vehicle (EV) registration data, including fleet size, model types, and distribution across Southern California counties. |
| OpenSHA | Seismic hazard data, including Peak Ground Acceleration (PGA) maps used to model earthquake-induced road and infrastructure damage. |
| MODIS and VIIRS | Wildfire data, including historical fire perimeters and propagation models used to simulate wildfire hazard zones. |
| U.S. DOE Alternative Fuel Data Center | Public EV charging station locations and operational data, including charger types (Level-2, Level-3) and fragility profiles for hazard analysis. |
| OpenStreetMap (OSM) | Road network topology data, used to model vehicle routes and network connectivity in the context of dynamic hazard scenarios. |
| NREL ResStock and ReEDS | Cyberattack scenario data, including grid topology and DER control systems, used for simulating cyberattack-induced infrastructure disruptions. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, S.; Li, X. Bayesian-Spatial Optimization of Emergency EV Dispatch Under Multi-Hazard Disruptions: A Behaviorally Informed Framework for Resilient Energy Support in Critical Grid Nodes. Energies 2025, 18, 4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174629
Chen X, Liu X, Yu X, Li Y, Luo S, Li X. Bayesian-Spatial Optimization of Emergency EV Dispatch Under Multi-Hazard Disruptions: A Behaviorally Informed Framework for Resilient Energy Support in Critical Grid Nodes. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174629
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xi, Xiulan Liu, Xijuan Yu, Yongda Li, Shanna Luo, and Xuebin Li. 2025. "Bayesian-Spatial Optimization of Emergency EV Dispatch Under Multi-Hazard Disruptions: A Behaviorally Informed Framework for Resilient Energy Support in Critical Grid Nodes" Energies 18, no. 17: 4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174629
APA StyleChen, X., Liu, X., Yu, X., Li, Y., Luo, S., & Li, X. (2025). Bayesian-Spatial Optimization of Emergency EV Dispatch Under Multi-Hazard Disruptions: A Behaviorally Informed Framework for Resilient Energy Support in Critical Grid Nodes. Energies, 18(17), 4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174629





