Real-Time Gas Emission Modeling for the Heading Face of Roadway in Single and Medium-Thickness Coal Seam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of Gas Emission Prediction Models for Excavation Faces
2.1. Influencing Factors of Gas Emission at Excavation Faces
2.1.1. Gas Content, Pressure, Seepage Velocity, and Diffusion Rate in Coal Seams
2.1.2. Geological Structures, Excavation Techniques, and Coal Seam Occurrence
- -
- Degree of coal/rock fragmentation;
- -
- Volume of material dislodged.
2.2. Prerequisites
- (1)
- The height of the excavation roadway is assumed to be equal to the coal seam thickness, the surface of the roadway’s face is entirely composed of coal for a thick seam, simplifying gas flow into the roadway to one-dimensional flow.
- (2)
- The test mine’s heading roadway has a rectangular profile, with the coal seam thickness equal to the roadway height. The seam exhibits stable conditions, and no roof or floor coal remains at the heading face.
- (3)
- The complete excavation cycle is defined as cutting completion →, auxiliary operations → cutting initiation, → cutting completion.
- (4)
- Within each cutting cycle, the advance rate remains uniform. Concurrently, cut coal produced during cutting is continuously loaded onto conveyors and transported out of the working face.
2.3. Foundation Model Construction
x2 = l1 + l2
xi = l1 + l2 + ... + li
xn = l1 + l2 + ... + ln−1 + ln = l
t2 = (th,1 + tr,1) + (th,2 + tr,2)
...
ti = (th,1 + tr,1) + (th,2 + tr,2) + ... + (th,i + tr,i)
tn = (th,1 + tr,1) + (th,2 + tr,2) + ... + (t′h,n + t′r,n)
τn−2 = (t′h,n + t′r,n) + (th,n−1 + tr,n−1)
...
τ1 = (t′h,n + t′r,n) + (th,n−1 + tr,n−1) + ... + (th,2 + tr,2)
τ0 = (t′h,n + t′r,n) + (th,n−1 + tr,n−1) + ... + (th,2 + tr,2) + (th,1 + tr,1)
- (1)
- τ is a dependent variable derived inversely from position x for a given excavation state (current or historical). Thus, for the current excavation state tn = τ0, where n denotes the ongoing cycle index, and 0 represents the excavation face position.
- (2)
- During excavation progression, any spatiotemporal position must be defined by (x,t), as expressed in Equation (8).
- (3)
- Assuming a constant advance rate, the exposure time τ(x) at different positions x under current excavation conditions is given by Equation (9).
3. Gas Emission Prediction Model for Excavation Faces
3.1. Coal Wall Gas Emission Model
3.2. Heading Face Gas Emission Model
3.2.1. Fundamental Assumptions
- (1)
- Per Figure 1, the heading face (region B/B′) exhibits irregular geometry during operation. While gas flows radially from this zone into the roadway, modeling radial flow would result in double counting of sidewall gas emissions, compromising accuracy. Thus, only unidirectional flow from the heading face zone (Segment Sf in Figure 1) is considered modeled via 1D flow theory.
- (2)
- At each cutting cycle initiation, the following apply:
- -
- Coal wall gas content ahead of the heading face equals undisturbed in situ gas content (unless modified by regional outburst elimination or pre-drainage).
- -
- This content remains constant until cutting begins.
- -
- The gas content in dislodged coal equals the residual content after gas desorption from the previous cutting cycle.
- (3)
- During halting periods between cycles, gas desorption reduces coal mass gas content. We assume the following:
- -
- Gas content variation is confined within the current cycle’s advance length.
- -
- Total gas emission cannot exceed the total gas content of dislodged coal during the cycle.
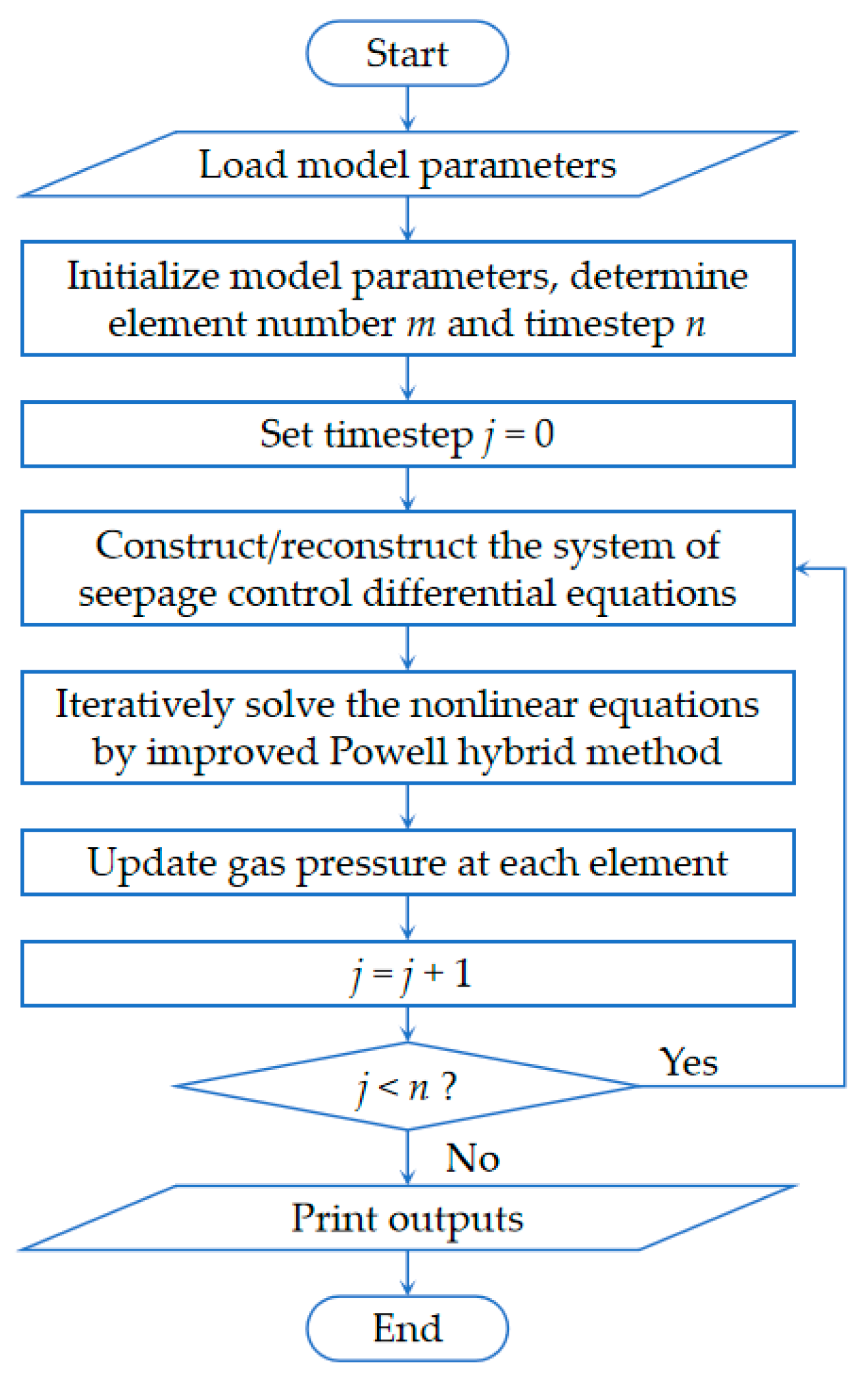
3.2.2. Numerical Solution of Gas Seepage
3.2.3. Gas Emission During Cutting Halts
3.2.4. Gas Emission During Cutting Operations
- (1)
- The gas content distribution profile ahead of the coal wall is known.
- (2)
- Gas is immediately released from coal upon fragmentation.
4. Field Validation
4.1. Numerical Solution of Gas Emission Model
- -
- Ventilation method: forced auxiliary ventilation;
- -
- Tunnel cross-section shape: rectangular;
- -
- Tunnel width: 6 m, tunnel height: 3.7 m, cross-sectional area: 22.2 m2;
- -
- Air velocity: 0.41 m/s;
- -
- Airflow rate: 9.1 m3/s;
- -
- : 1.5 × 10−4 m/s;
- -
- Xr: 3.76 m3/m3;
- -
- Coal seam gas pressure = 0.32 MPa;
- -
- Constant atmospheric pressure at the exposed surface: 101,325 Pa;
- -
- Constant gas pressure at reservoir boundary: 0.32 MPa.
- -
- Coal adsorption constants:
- -
- a = 22.35 m3/t;
- -
- b = 0.78 × 10−6 Pa−1;
- -
- Porosity φ = 0.067;
- -
- Permeability K = 1.45 × 10−16 m2;
- -
- Apparent density Pc = 1270 kg/m−3.
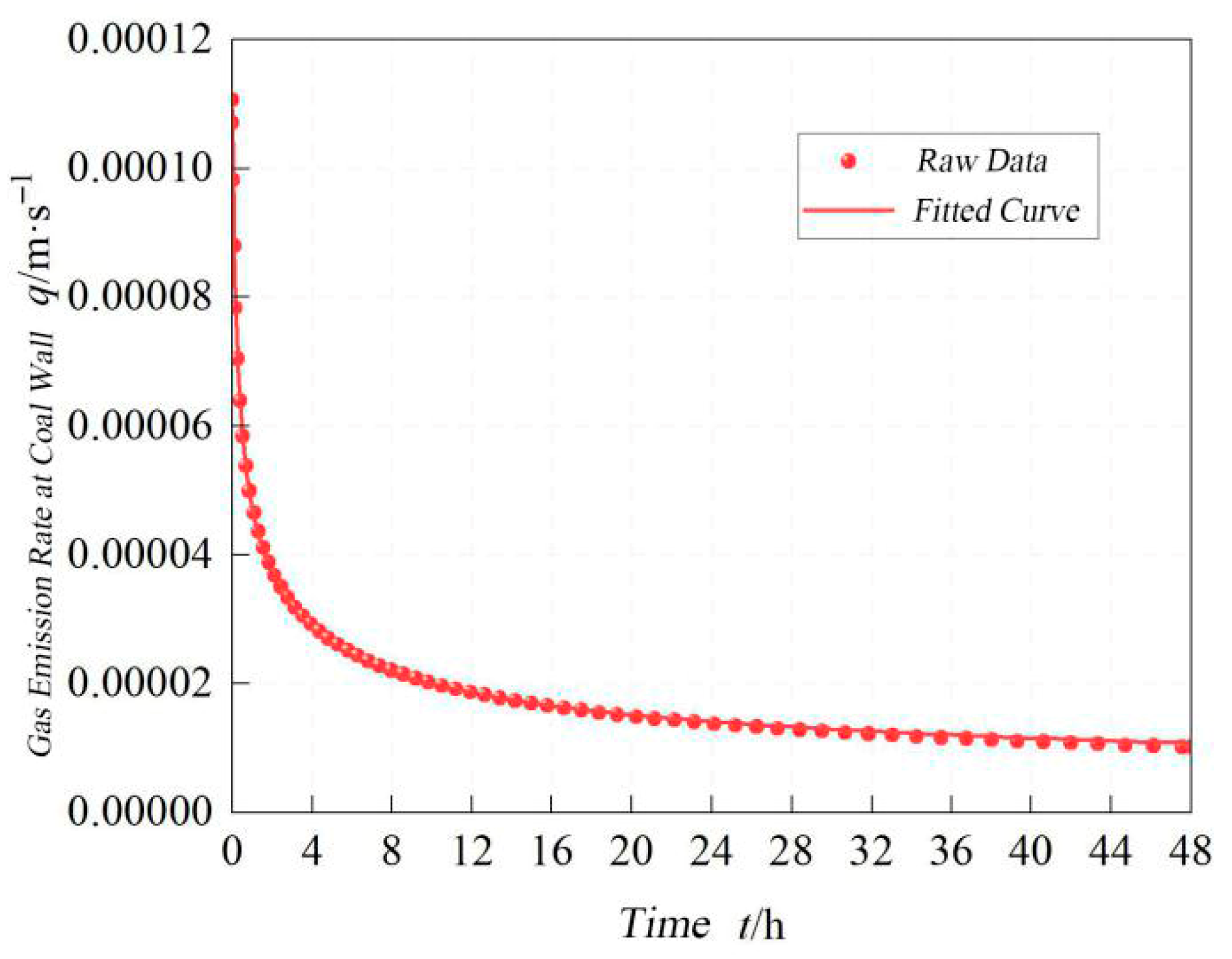
(183151.788 + t)0.224/(t + 300.639)0.166
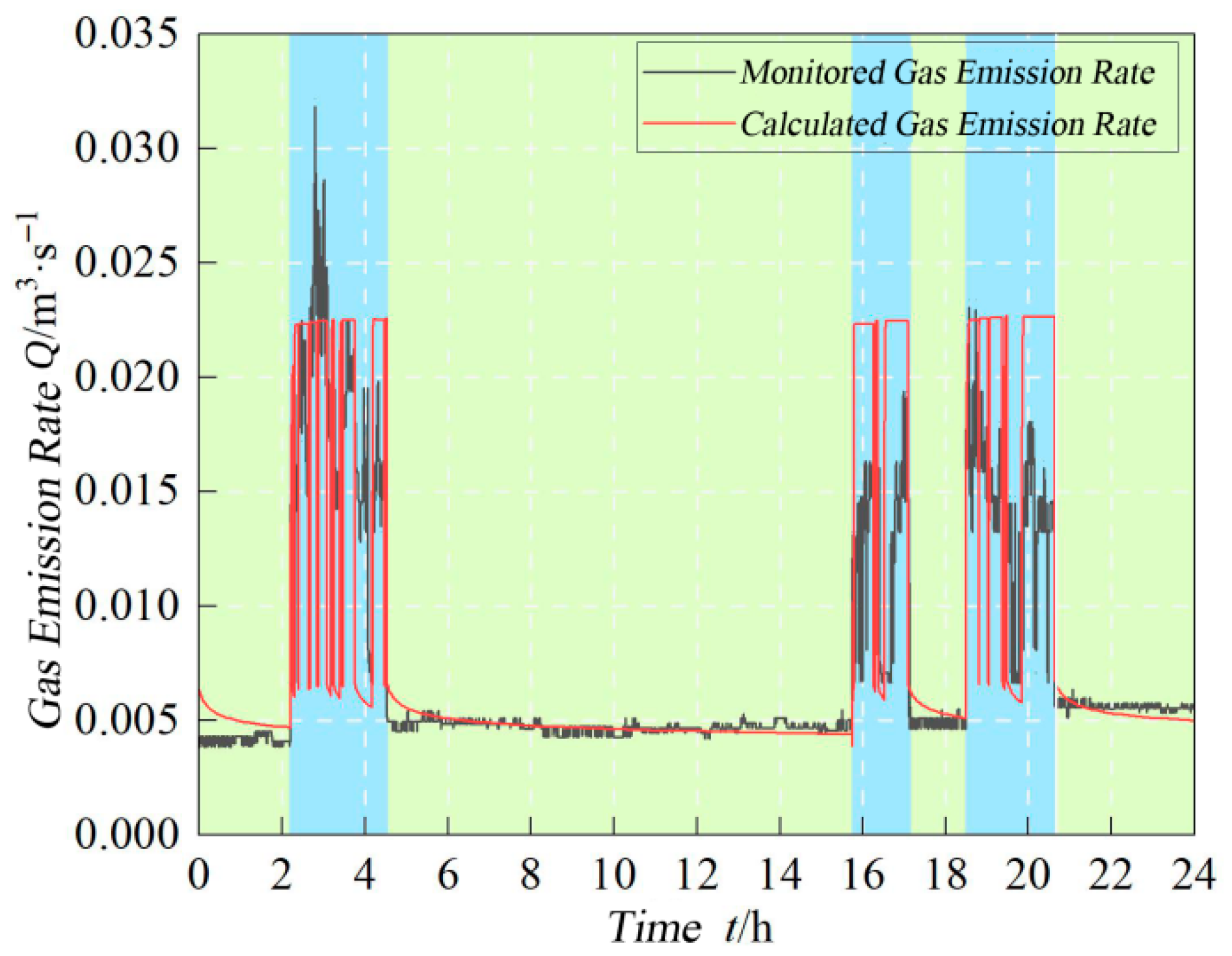
4.2. Field Validation
- -
- Green zones: Roadway halting periods;
- -
- Blue zones: Active production periods;
- -
- Black curve: Field monitoring data;
- -
- Red curve: Model-predicted emission rate.
- (1)
- Emission rates decrease gradually yet remain relatively stable;
- (2)
- Model predictions align well with monitoring trends;
- (3)
- Field data shows greater volatility due to uneven gas release patterns and ventilation inhomogeneities.
- -
- Drastic emission surges occur due to massive fragmented coal generation and large-scale fresh coal wall exposure;
- -
- While model predictions match overall emission trends, localized deviations exist because:
- (1)
- The model assumes uniform advance rates, whereas actual cutting speeds vary;
- (2)
- Resulting fluctuations in coal fragmentation degrees;
- (3)
- Dynamic changes in the fresh wall exposure area.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- By comprehensively accounting for gas emission patterns and influencing factors at excavation faces, we developed a gas emission calculation model based on excavation procedures. This model establishes mathematical relationships for coal wall exposure times at different positions and implements distinct calculation methods for gas emission rates from both freshly exposed coal walls and newly dislodged coal.
- (2)
- Excavation procedures significantly alter the dynamics of roadway gas emissions. Specifically, the following conditions apply:
- -
- Coal fragmentation generates newly dislodged coal and fresh coal walls, representing the primary cause of emission rate surges.
- -
- During non-excavation periods, emission rates are governed predominantly by exposed coal seam thickness and exposed wall length.
- (3)
- Through numerical analysis of a unidirectional flow model simulating sudden coal wall exposure, we established that:
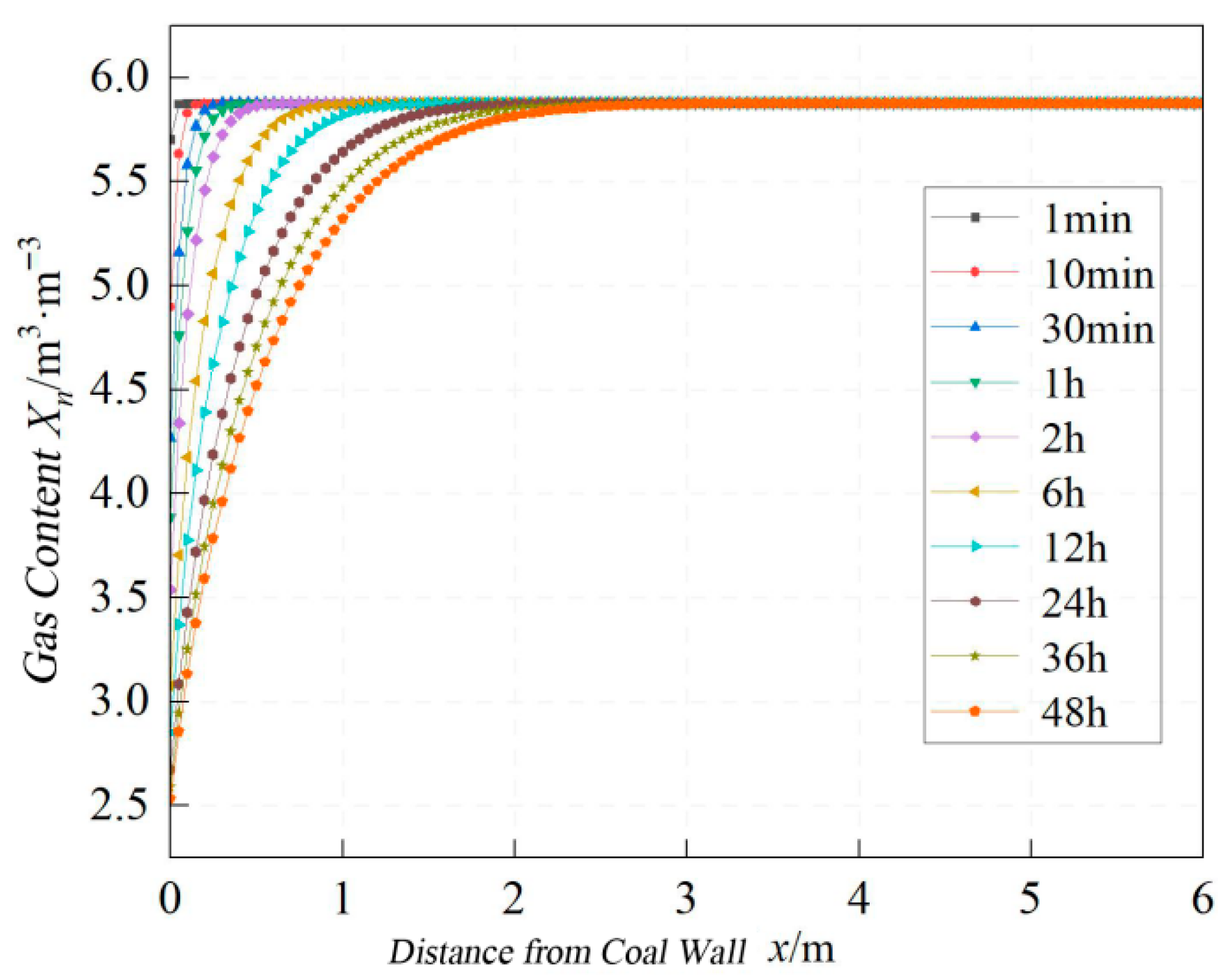
- -
- Gas content within coal exhibits an arctangent functional relationship with distance from the coal wall across varying exposure times.
- -
- A comprehensive fitted equation was derived for gas content calculation at arbitrary spatiotemporal positions (x,t).
- -
- The coal wall gas emission rate follows a power function decay over time.
- (4)
- For an actual excavation roadway in the experimental mine, we implemented the developed real-time gas emission mathematical model through Python programming, calculating theoretical emission rates. Field validation confirmed substantial agreement in trend prediction between monitoring system measurements and model-calculated emission rates. The Python-based implementation provides mines with a practical tool for dynamic outburst risk assessment during excavation cycles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Coal Mine Safety Administration. Detailed Rules for the Prevention and Control of Coal and Gas Outbursts: Document No. 28 (2019) Issued by the Department of Technology and Equipment; National Coal Mine Safety Administration: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- AQ 1018-2006; Methodology for Prediction of Gas Emission in Underground Mines. China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Zhou, S.; Sun, J. Theory of gas flow in coal seam and its application. J. China Coal Soc. 1965, 2, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S. Mechanism of gas flow in coal seams. J. China Coal Soc. 1990, 15, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Song, H.; Li, X. Dimensionless analysis on gas emission law around tunneling face. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 882–887. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wei, J.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y. Coalbed gas seepage law and permeability calculation method based on Klinkenberg effect. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 22, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J. Numerical value analysis of coal bed methane influentequation. Coal Sci. Technol. 2001, 29, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Hu, C.; Xiong, Z. Gas flowing model of mining face and solve it using COMSOL. J. China Coal Soc. 2012, 37, 967–971. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P. Study of flow in gas flow fields of coal seams. J. China Coal Soc. 1987, 12, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Duan, W. Error analysis of borehole gas flow model and its application. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2021, 38, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Numerical calculation and field application of gas emission from coal wall in dynamic mining face. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X. Equation of gas flow in seams with boreholes and its application. J. China Coal Soc. 1988, 13, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Li, C.; Ye, Q.; Li, Z.; Hao, M.; Wei, S. Modeling of gas emission in coal mine excavation workface: A new insight into the prediction model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 100137–100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Hao, M.; Qiao, Z.; Guo, J. Model development and analysis of dynamic gas emission from tunneling face zone. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 10378–10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, R. Study on the Long-Distance Gas Pre-Drainage Technology in the Heading Face by Directional Long Borehole. Energies 2022, 15, 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Peng, Y.; Song, D. Risk Prediction of Coal and Gas Outburst Based on Abnormal Gas Concentration in Blasting Driving Face. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 3917846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Kang, X.; Tang, M.; Hu, J. Study on Prediction of Outburst Risk of Excavation Face by Initial Gas Emission. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 4866805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, C.; Shu, L.; Pan, Z.; Yuan, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q. A Novel In-Seam Borehole Discontinuous Hydraulic Flushing Technology in the Driving Face of Soft Coal Seams: Enhanced Gas Extraction Mechanism and Field Application. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 885–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, E.; Li, Z.; Qin, B. Risk assessment of coal and gas outburst in driving face based on finite interval cloud model. Nat. Hazards 2021, 110, 1969–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y. OpenFOAM solver of the methane behaviour near the coal mine tunnelling face and its application. J. Geophys. Eng. 2021, 18, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Fan, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Ye, X. Temperature variations of coal in the heading face measured using a thermo-hydro-mechanical model considering desorptional heat. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 181, 115969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Ren, J.; Wang, C. Analysis of the Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Gas Explosion in Heading Face. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 8871865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Li, Z. Study on Dynamic Prediction Model of Gas Emission in Tunneling Working Face. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2020, 194, 506–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ai, D. Study of gas emission law at the heading face in a coal-mine tunnel based on the Lattice Boltzmann method. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhai, M.; Li, Y.; Gong, B.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Roadway portal and self-moving hydraulic support for rockburst prevention in coal mine and its application. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D. Investigations on the mechanism of the microstructural evolution of different coal ranks under liquid nitrogen cold soaking. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2025, 47, 2596–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, B. Enhanced permeability mechanism in coal seams through liquid nitrogen immersion: Multi-scale pore structure analysis. J. Cent. South Univ. 2025, 32, 2732–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Experimental study of effect of liquid nitrogen cold soaking on coal pore structure and fractal characteristics. Energy 2023, 275, 127470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Zhu, N.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S. Experimental study on compressive behavior and failure characteristics of imitation steel fiber concrete under uniaxial load imitation steel ffber concrete under uniaxial load. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 399, 132599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, A.E. Coal Mine Methane Emission; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Barrer, R.M. Diffusion in and Through Solids; Cambridge University Press: Oxford, UK, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, P.; Brown, H.; Nemcik, J.; Ting, R. Spatial context in the calculation of gas emissions for underground coal mines. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, T.; Kumpulainen, P.; Majanne, Y.; Häyrinen, A. Model based NOx emission monitoring in natural gas fired hot water boilers. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Hou, S. Dynamic distribution of gas pressure and emission around a diving roadway. J. China Coal Soc. 2007, 32, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H. Study and application of a continuous inversion model of coal seam gas pressure in front area of heading face. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Q. A Gas Pressure Prediction Model of the Excavation Face Based on Gas Emission. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y. Application of Directional Long Borehole Technology in Working Face of Thick Coal Seam Along Top Driving. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 474, 042035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Qin, Z.; Fan, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y. Gas Outburst Warning Method in Driving Faces: Enhanced Methodology through Optuna Optimization, Adaptive Normalization, and Transformer Framework. Sensors 2024, 24, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Han, Y. Research on the law of gas diffusion from drill cuttings. J. China Coal Soc. 2013, 38, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; An, F.; Su, W.; Jia, H.; Chen, X. Direct determination of the diffusion coefficient variation of coal based on Fick’s law and model establishment. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Gong, X.; Wu, G. Solving of coal seam gas seepage based on Crank-Nicolson difference method. Min. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 51, 28–35. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, P.; Gong, X.; Jin, H.; Ma, X. Real-Time Gas Emission Modeling for the Heading Face of Roadway in Single and Medium-Thickness Coal Seam. Energies 2025, 18, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174592
Yang P, Gong X, Jin H, Ma X. Real-Time Gas Emission Modeling for the Heading Face of Roadway in Single and Medium-Thickness Coal Seam. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174592
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Peng, Xuanping Gong, Hongwei Jin, and Xingying Ma. 2025. "Real-Time Gas Emission Modeling for the Heading Face of Roadway in Single and Medium-Thickness Coal Seam" Energies 18, no. 17: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174592
APA StyleYang, P., Gong, X., Jin, H., & Ma, X. (2025). Real-Time Gas Emission Modeling for the Heading Face of Roadway in Single and Medium-Thickness Coal Seam. Energies, 18(17), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174592






