Research on the Law of Top Coal Movement and Influence Factors of Coal Caving Ratio for Fully Mechanized Top Coal Caving Working Face
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Top Coal Dispersoid Media Flow Law and Mobility Evaluation
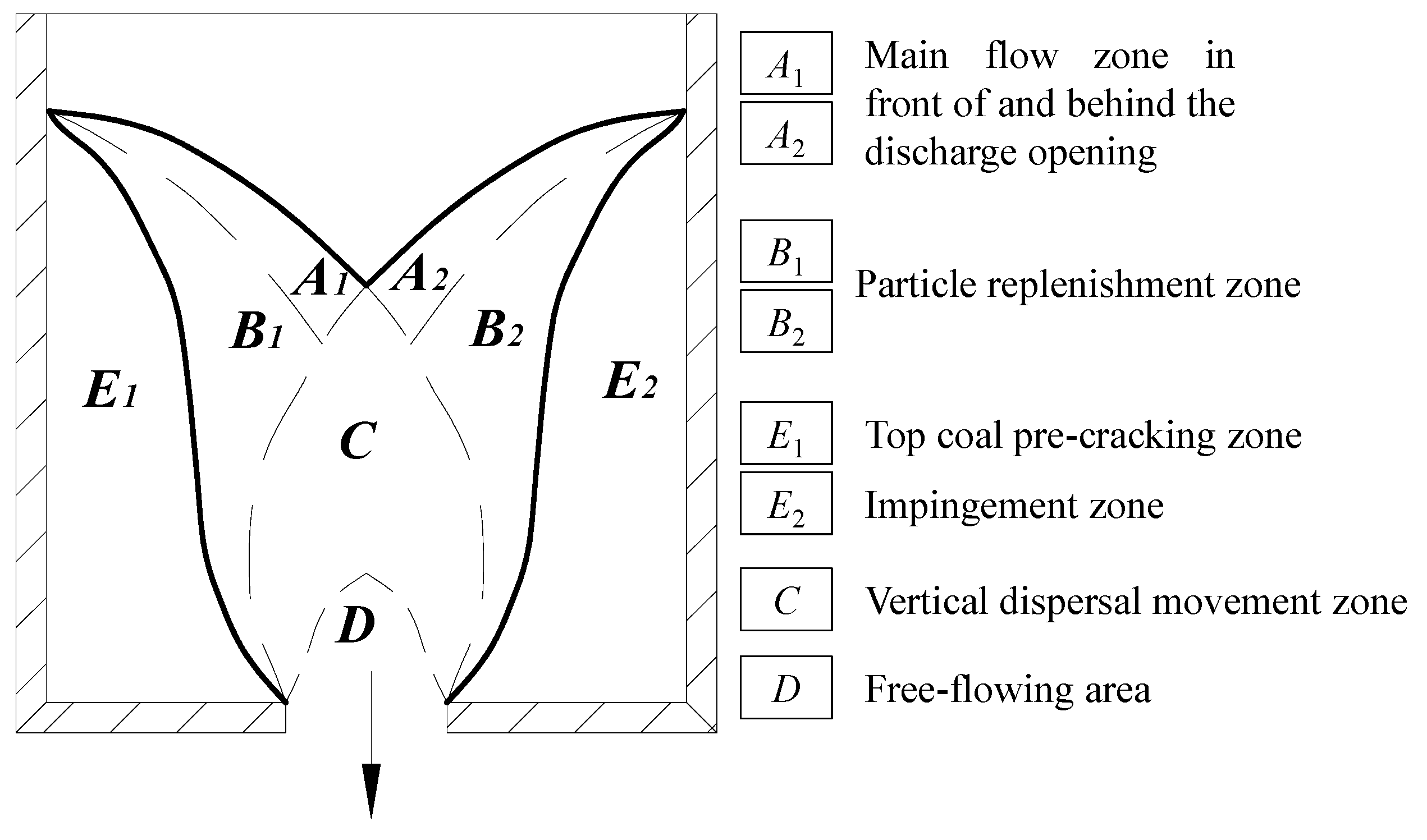
2.1. Top Coal Dispersoid Flow Characteristics and Types of Top Coal Arching
2.2. Flow Model of Top Coal Dispersoid
2.2.1. Top Coal Flow Without Support Influence
2.2.2. Top Coal Flow Considering Bracket Influence
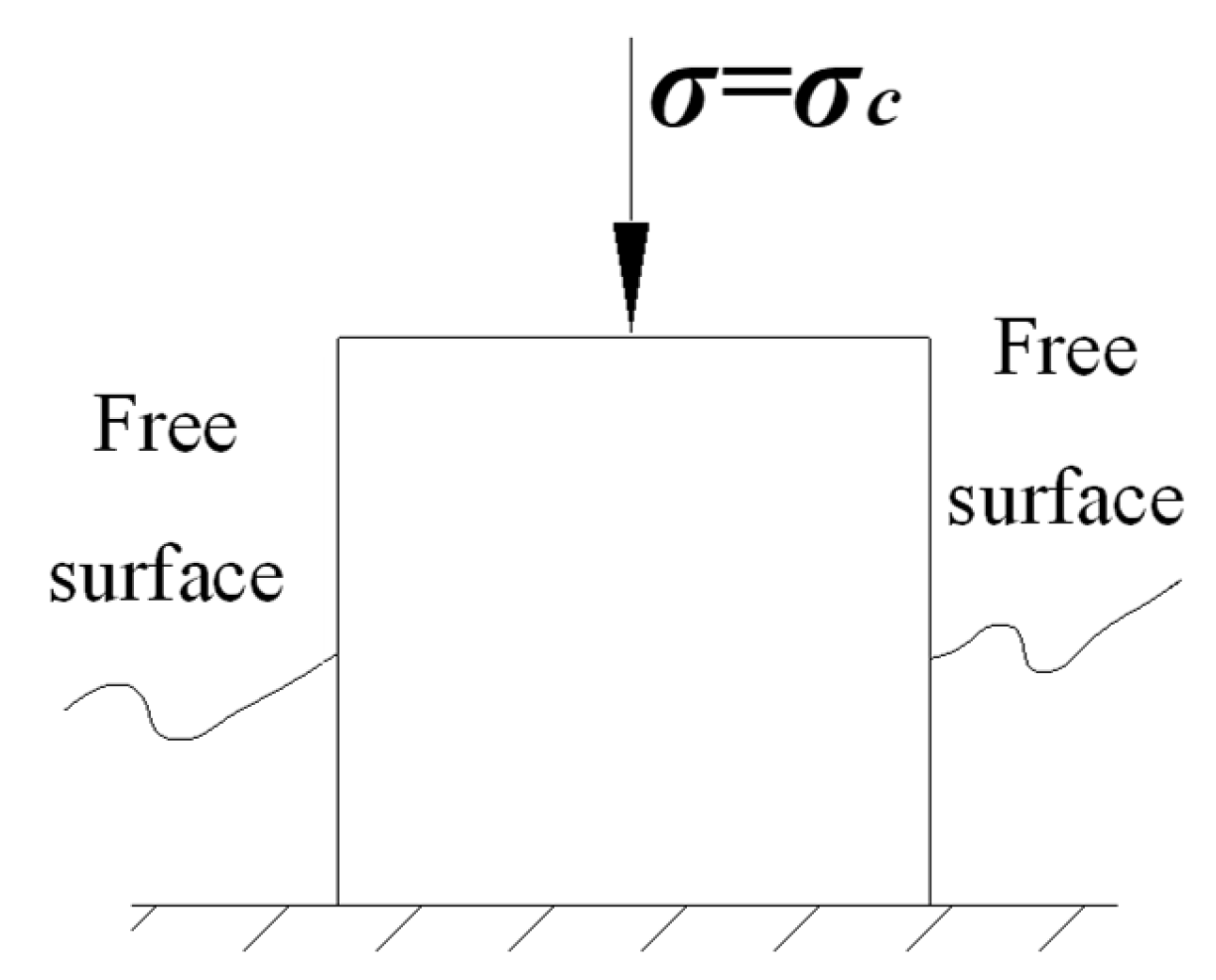
2.3. Mobility Analysis of Top Coal Dispersoid
3. Analysis of the Influence of Lumpiness on the Caving Rate of Top Coal and Arch Formation
3.1. Influence of Lumpiness on Top Coal Caving Rate
3.2. Judgment of Arch Formation of Top Coal Dispersoid
4. Discussion of Measures and Practices for Preventing Arching of Dispersoid Medium of Top Coal
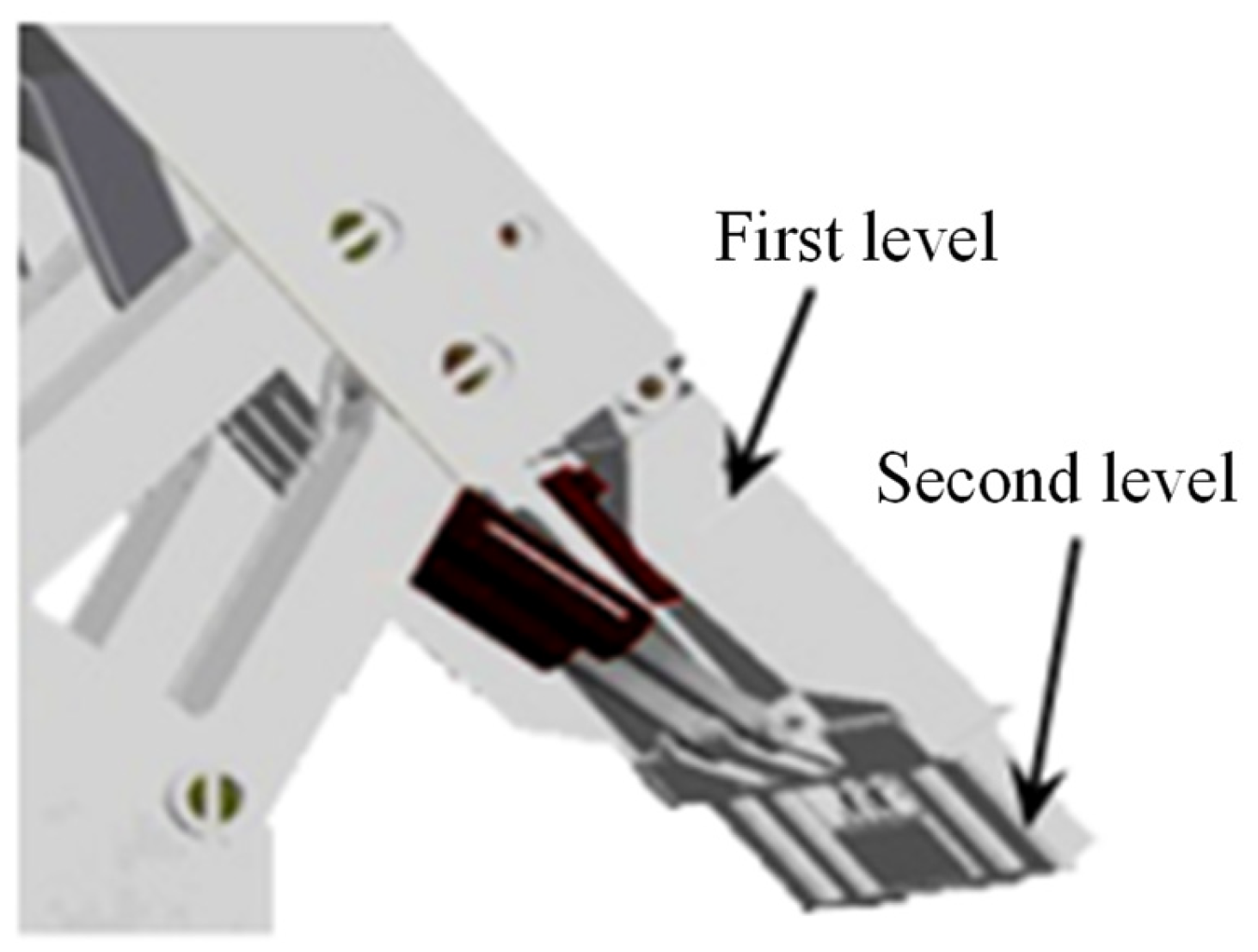
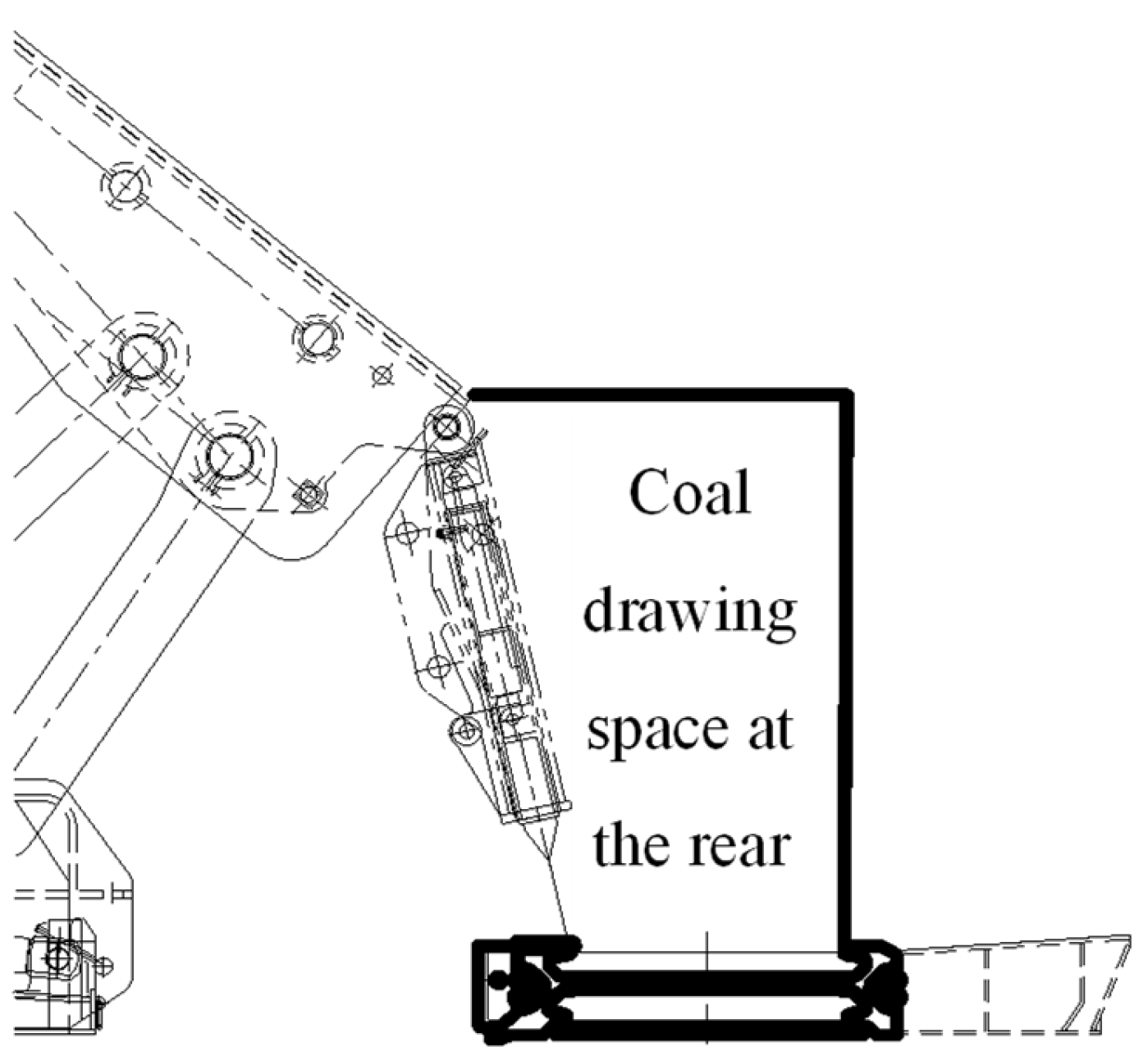
4.1. Extra-Large-Height Fully Mechanized Top Coal Caving
4.2. Pre-Rupturing Top Coal by Multiple Alternating Loads
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Coal gangue arching is an important influencing factor on poor top coal mobility and low top coal recovery rate. Using dispersoid mechanics theory can provide the influencing factors of the top coal body sliding surface resistance and reduction measures; that is, increase the height of coal cutting to reduce the thickness of the top coal, and design hydraulic support for large-height top coal caving to improve the mobility of the top coal.
- (2)
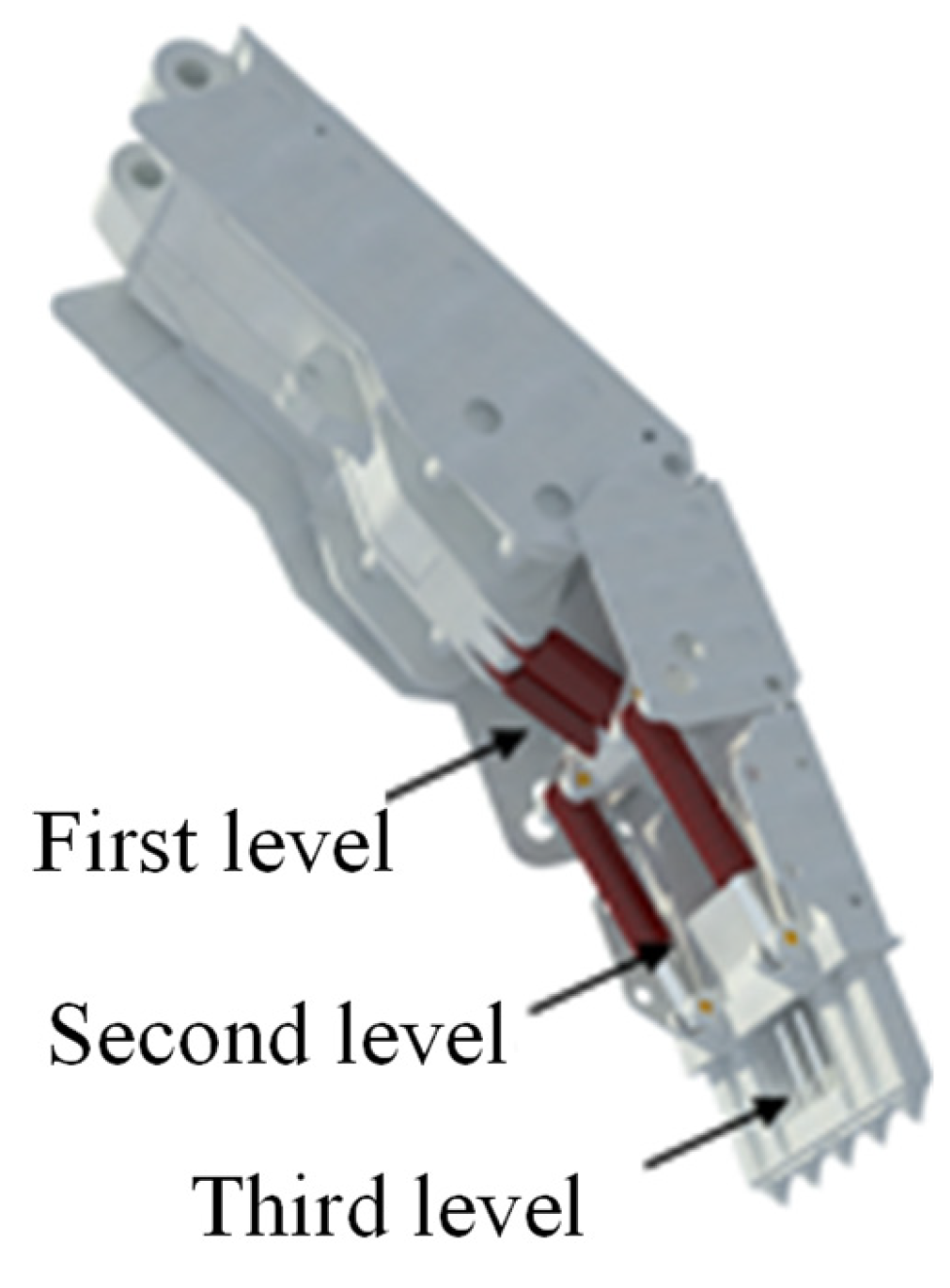
- The formula for calculating the arching rate of top coal is given; the larger the top coal lump size is, the lower the top coal caving rate is. Combined with the analysis of the balance mechanics of the coal caving arch, the critical coal caving opening size is obtained, and the design adopts a three-stage coal caving device to increase the size of the coal caving opening and reduce the arching rate of the top coal.
- (3)
- The oversize height comprehensive caving stent provides a new effective method for mining hard and 15~25 m extra-thick coal seams, and offers practical guidance for improving mining efficiency and recovery in similar thick seam conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ran, Q.C.; Liang, Y.P.; Zou, Q.L.; Ye, C.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Ma, T.F.; Wu, Z.P.; Zhang, B.C. Mechanical behavior and acoustic emission characteristics of initially damaged coal under triaxial cyclic loading and unloading. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Tian, S.X.; Jiang, Z.B.; Xie, H.G.; Ma, T.F.; Ran, Q.C. Effect of silica nanofluid on coal wettability and its stability characterization. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 022015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.B.; Chen, H.J.; Ye, C.F.; Feng, Z.C.; Ran, Q.C. Acoustic emission spatiotemporal evolution and multifractal spectrum of sandstone under the coupled effects of wet-dry cycles and cyclic loading. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 087107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.L.; Ma, T.F.; Liang, J.Y.; Xu, B.C.; Ran, Q.C. Mesomechanical weakening mechanism of coal modified by nanofluids with disparately sized SiO2 nanoparticles. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2025, 188, 106056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.C.; Liang, Y.P.; Zou, Q.L.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhan, J.F.; Chen, L.; Wu, Z.P.; Ma, T.F. Failure mechanisms of sandstone subjected to cyclic loading considering stress amplitude effects. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2025, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.F.; Yu, M.G.; Zheng, K.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.M. Influence of ignition positions on the flame behavior of non-uniform methane-air mixture explosions in vertically closed pipes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 196, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.C.; Li, J.X.; Zhu, Y.R.; Rudolph, V.; Chen, Z.W. Impact of gas adsorption on coal relative permeability: A laboratory study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2025, 194, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.F.; Zou, Q.L.; Wang, P.T.; Li, Q.S.; Fan, C.J.; Ran, Q.C.; Huo, Z.X.; Zhang, J.Y. Regulation mechanism of surfactant-SiO2 nanoparticle compound on the mechanical property and microstructure of coal: Effect of the type of surfactant. Powder Technol. 2025, 466, 121459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Wang, G.F.; Yang, Z.K.; Wu, S.L. Adaptability analysis and optimization study of four-leg shield caving support in ultra thick seam with high tough-ness and thinner immediate roof. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2018, 35, 1164–1169+1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.C.; Liang, Y.P.; Yang, Z.L.; Zou, Q.L.; Ye, C.F.; Tian, C.L.; Wu, Z.P.; Zhang, B.C.; Wang, W.Z. Deterioration mechanisms of coal mechanical properties under uniaxial multi-level cyclic loading considering initial damage effects. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2025, 186, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.J.; Tian, S.X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, T.F.; Ran, Q.C.; Luo, X.B. Research on the performance and application of nano-MgO modified ultrafine cement-based sealing materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.P.; Yang, Y.; Xin, G.Y.; Zou, Q.L.; Ran, Q.C.; Qin, D.K. Mechanical properties and crack propagation characteristics of mudstone under different loading frequencies. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 316, 110863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.M.; Wang, E.Y.; Feng, X.J.; Liu, S.X.; Chen, D. Disasters of gas-coal spontaneous combustion in goaf of steeply inclined extra-thick coal seams. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 16, 4141–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, E.L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Su, W.W.; Wang, L.; Ye, X.Y.; Wang, T.F. Gas transport behavior of tectonic and intact coal reservoirs during CO2-enhanced coalbed methane recovery. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 0281949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.C.; Chen, P.; Liang, Y.P.; Ye, C.F.; Zhang, B.C.; Wu, Z.P.; Ma, T.F.; Chen, Z.H. Hardening-damage evolutionary mechanism of sandstone under multi-level cyclic loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 307, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H. Study on factors affecting mine pressure of large mining height fully-mechanized mining and its adaptability. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Chen, D.Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.M.; Zhai, M.H.; Li, Y.Z.; Gong, B.; Sun, Z.G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.K. Roadway portal and self-moving hydraulic support for rockburst prevention in coal mine and its application. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, R.; Jiang, B.; Li, S.C.; He, M.C.; Sun, H.B.; Wang, L.; Qin, Q.; Yu, H.C.; Luan, Y.C. Study on failure mechanism of roadway with soft rock in deep coal mine and confined concrete support system. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 81, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.H.; Wang, G.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, H.L. Overlying strata fracture structure and stability control technology for ultra large mining height working face. Coal Sci. Technol. 2017, 45, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.H.; Chen, D.Y.; Li, X.L.; Li, H.H.; Liu, S.M.; Li, C.Q.; Zhang, J.W. Research on the technology of gob-side entry retaining by pouring support beside the roadway in “three soft” coal seam: A case study. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 017123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, X.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, X. Influence of loading and unloading of hydraulic support on the caving property of top coal. Steel Compos. Struct. 2023, 48, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Cheng, D.L.; Yang, Y.C.; Wei, W.J.; Li, Z.L.; Song, Z.Y. Numerical and theoretical investigations of the effect of the gangue-coal density ratio on the drawing mechanism in longwall top-coal caving. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.P.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.J.; Jiao, Y.Y.; Zhu, S.T.; Zhang, G.H. Mechanism of hydraulic fracturing for controlling strong mining-induced earthquakes induced by coal mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 181, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, R.X.; Li, G.H.; Sun, D.D.; Li, P. Development of gravity flow draw theory and determination of its parameters. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2023, 171, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.F.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, L.F.; Wang, H.X.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, L.W.; Wang, H. Investigation of ground subsidence response to an unconventional longwall panel layout. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.J.; Zhang, R.; Gao, M.Z.; Xie, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, A.L.; Wang, M.N.; Zhang, Z.T. Characterization of energy-driven damage mechanism and gas seepage in coal under mining-induced stress conditions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 181, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Canbulat, I.; Saydam, S.; Fan, G.; Zhang, D. Assessment of factors and mechanism contributing to groundwater depressurisation due to longwall mining. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.J.; Wang, J.C.; Li, J.L.; Wu, S.X.; Li, Z.X.; Liu, X.Y. The Size Distribution Characteristics and Spatial Motion Law of Granular Top-Coal in Longwall Top-Coal Caving (LTCC). Min. Metall. Explor. 2025, 42, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, D.; Wu, X.B.; Wu, Y.P.; Xie, P.S.; Yan, Z.Z.; Chen, S.M. Boundary quantitative characterization of the top-coal limit equilibrium zone in fully mechanized top-coal caving stope along the strike direction of working face. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, W.S.; Wang, C. Determination of working resistance of support parameter variation of large mining height support: The case of Caojiatan coal mine. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2024, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.T.; Chen, M.L.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.S.; Wang, C.H.; Azhar, N.; Oduro, N.B. Characterization of 10 nm-10 μm coal dust particles generated by simulated different cutting and drilling parameters: Mass concentration distribution, number concentration distribution, and fractal dimension. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.C.; Peng, Y.; Xia, B.W.; Fang, L.L. Material point method with a strain-softening model to simulate roof strata movement induced by progressive longwall mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2023, 170, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, C.H.; He, F.; Yang, Y. Numerical modelling of loose top coal and roof mass movement for a re-mined seam using the top coal caving method. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Zhang, J.W. BBR study of top-coal drawing law in long wall top-coal caving mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2015, 40, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M. Research on the law of top coal movement and coal-gangue interface evolution in fully mechanized caving face. China Coal 2015, 41, 63–66+77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.S.; Tu, S.H.; Wang, C. Numerical simulation on top-coal arching mechanism. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2014, 31, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Zhang, F.T.; Ji, M.; Gao, L.S.; Jin, Z.Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, L.P. Research on the reasonable coal caving technological parameters of extra-thick coal seam. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2012, 29, 809–814. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.P.; Rui, X.T.; Hong, J.; Rong, B.; Liu, Z.J. Dynamic simulation of granular system. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 2529–2532+2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Si, Y.L.; Shi, L. Numerical Simulation of the Effect of Particle Size on Coal Caving Ratio. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2011, 28, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.C.; Song, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Chen, Y. Theoretical model of drawing body in LTCC mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Liu, C.Y.; Wang, L.Q. Similar simulation research on arch mechanism of direct roof falling under fully mechanized top coal caving face. Coal Sci. Technol. 2007, 35, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Kuang, T.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.Y.; Quan, C.Y. Controlling mine pressure by subjecting high-level hard rock strata to ground fracturing. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 1336–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Yue, J.C.; Liu, C.; Feng, C.; Li, H.M. Study of automated top-coal caving in extra-thick coal seams using the continuum-discontinuum element method. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 122, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Bai, D.; Yu, B.; Tai, Y.; Meng, X.B.; Zhang, W.Y. Ground fracturing of multi-strata for strong ground pressure control in extra-thick coal seams with hard roofs: Numerical simulation and case study. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 303, 110129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.C.; Liang, Y.P.; Ye, C.F.; Ning, Y.H.; Ma, T.F.; Kong, F.J. Failure analysis of overlying strata during inclined coal seam mining: Insights from acoustic emission monitoring. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 181, 109915. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.P.; Zhu, S.C.; Ran, Q.C.; Zou, Q.L.; Ding, L.Q.; Yang, Y.; Ma, T.F. Characteristics of overburden fracture conductivity in the shallow buried close coal seam group and its effect on low-oxygen phenomena. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 047103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Ran, Q.C.; Liu, H.; Ning, Y.H.; Ma, T.F. Characteristics of stress-displacement-fracture multi-field evolution around gas extraction borehole. Energies 2023, 16, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Zou, Q.L.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhang, B.C.; Ran, Q.C.; Kong, F.J.; Li, Q.S.; Chen, Z.H. Gas drainage optimization via fracture network characterization in coal mining. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 077131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.F.; Xie, H.P.; Wu, F.; Hu, J.J.; Ren, L.; Li, C.B. Asymmetric failure mechanisms of anisotropic shale under direct shear. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 183, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Chen, L.G.; Wang, D.; Luan, H.J.; Zhang, G.C.; Dong, L.; Liang, B. Mechanical properties and acoustic emission characteristics of soft rock with different water contents under dynamic disturbance. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.Y.; Wang, W.; Li, G.C.; Zhao, G.M.; Liang, D.X.; Xu, J.H. Mechanical behaviour and acoustic emission characteristics of the reinforced soft muddy rock under various moisture content levels. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.C.; Zhao, W.T.; Liang, Y.P.; Ye, C.F.; Ning, Y.H. Deciphering confining pressure effects on coal failure mechanisms using acoustic emission approaches. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 327, 111589. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.Y.; Liang, Y.P.; Ran, Q.C. Mechanical response of mudstone based on acoustic emission fractal features. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Lei, S.; Guo, K.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. Research on the Law of Top Coal Movement and Influence Factors of Coal Caving Ratio for Fully Mechanized Top Coal Caving Working Face. Energies 2025, 18, 4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164312
Zhang J, Cheng Z, Lei S, Guo K, Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen J. Research on the Law of Top Coal Movement and Influence Factors of Coal Caving Ratio for Fully Mechanized Top Coal Caving Working Face. Energies. 2025; 18(16):4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164312
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinhu, Zhiheng Cheng, Sheng Lei, Kai Guo, Liang Chen, Zherui Zhang, and Jiahui Chen. 2025. "Research on the Law of Top Coal Movement and Influence Factors of Coal Caving Ratio for Fully Mechanized Top Coal Caving Working Face" Energies 18, no. 16: 4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164312
APA StyleZhang, J., Cheng, Z., Lei, S., Guo, K., Chen, L., Zhang, Z., & Chen, J. (2025). Research on the Law of Top Coal Movement and Influence Factors of Coal Caving Ratio for Fully Mechanized Top Coal Caving Working Face. Energies, 18(16), 4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164312





