Peer-to-Peer Distributed Algorithms for Wide-Area Monitoring and Control in Power Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The definition of a peer-to-peer distributed algorithm for the determination of the total inertia for wide-area monitoring in power systems;
- The definition of a peer-to-peer distributed algorithm for the determination of the average frequency for wide-area control in power systems;
- Demonstration of the two proposed distributed algorithms in a real-world power system, referring to the case of the large-scale interconnected European system.
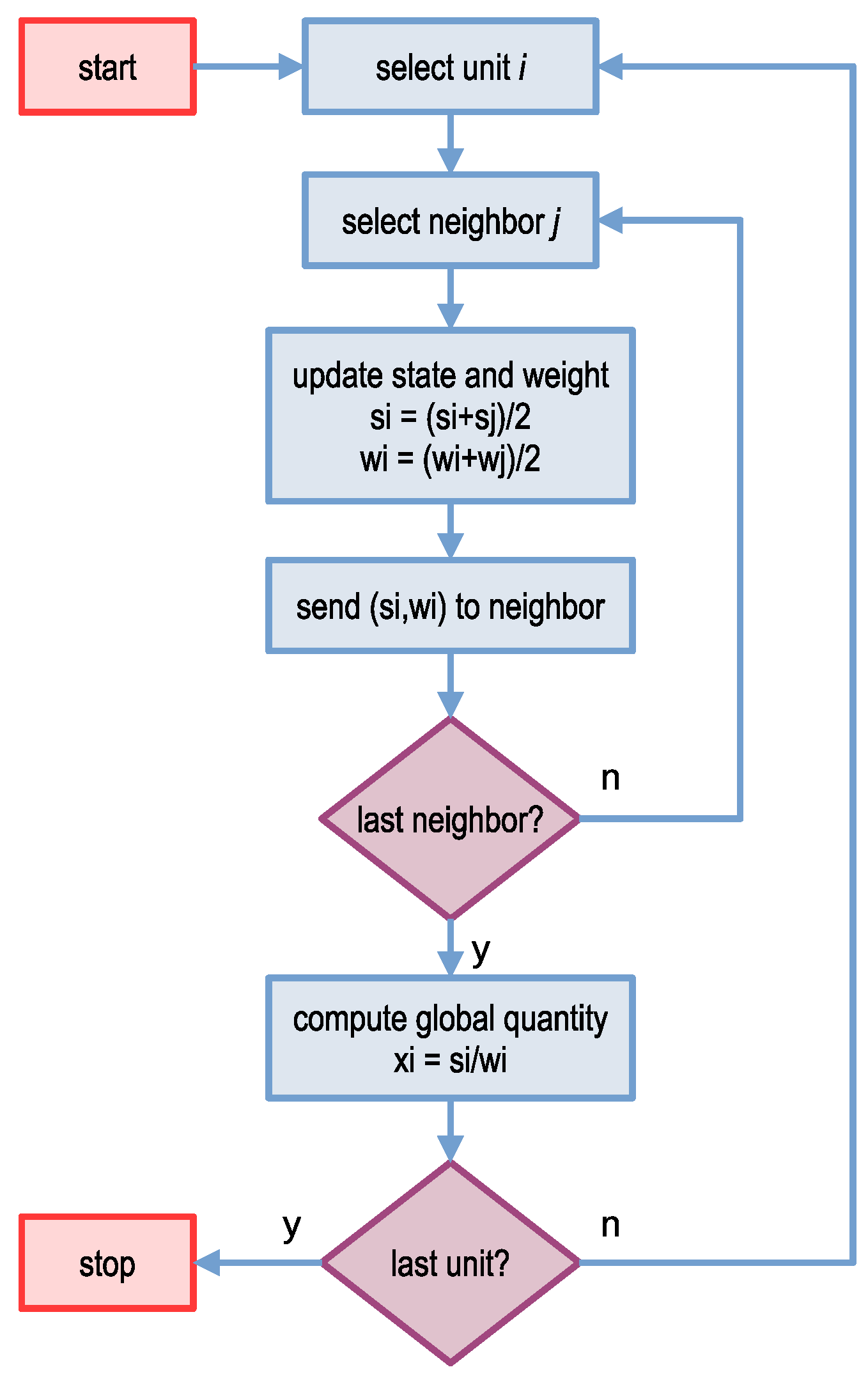
2. The Proposed Peer-to-Peer Algorithms
2.1. Algorithm #1: Total Inertia
| Algorithm 1 Algorithm #1 for determination of the total inertia |
|
2.2. Algorithm #2: Average Frequency
| Algorithm 2 Algorithm #2 for determination of the average frequency |
|
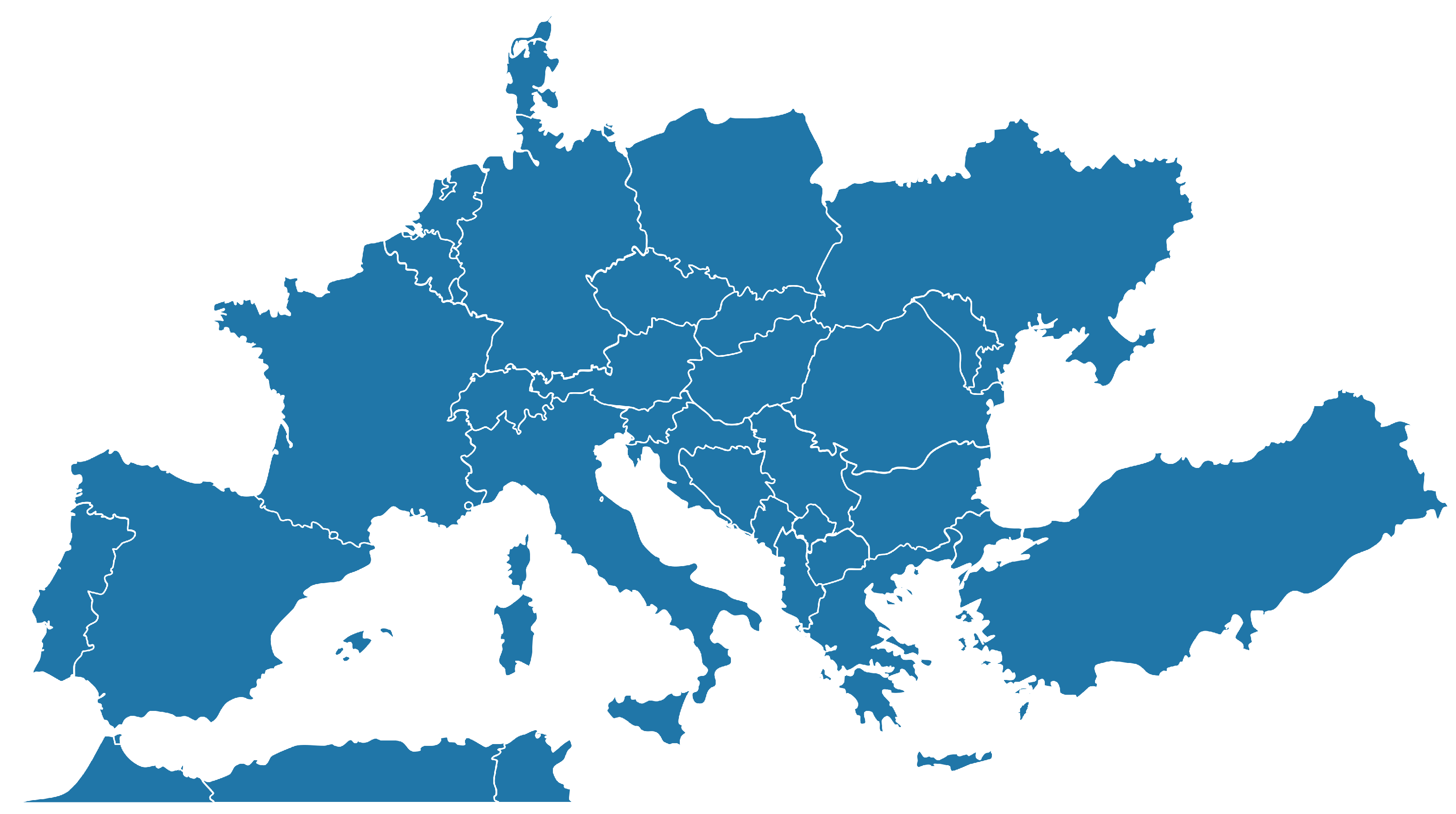
3. The Application Case
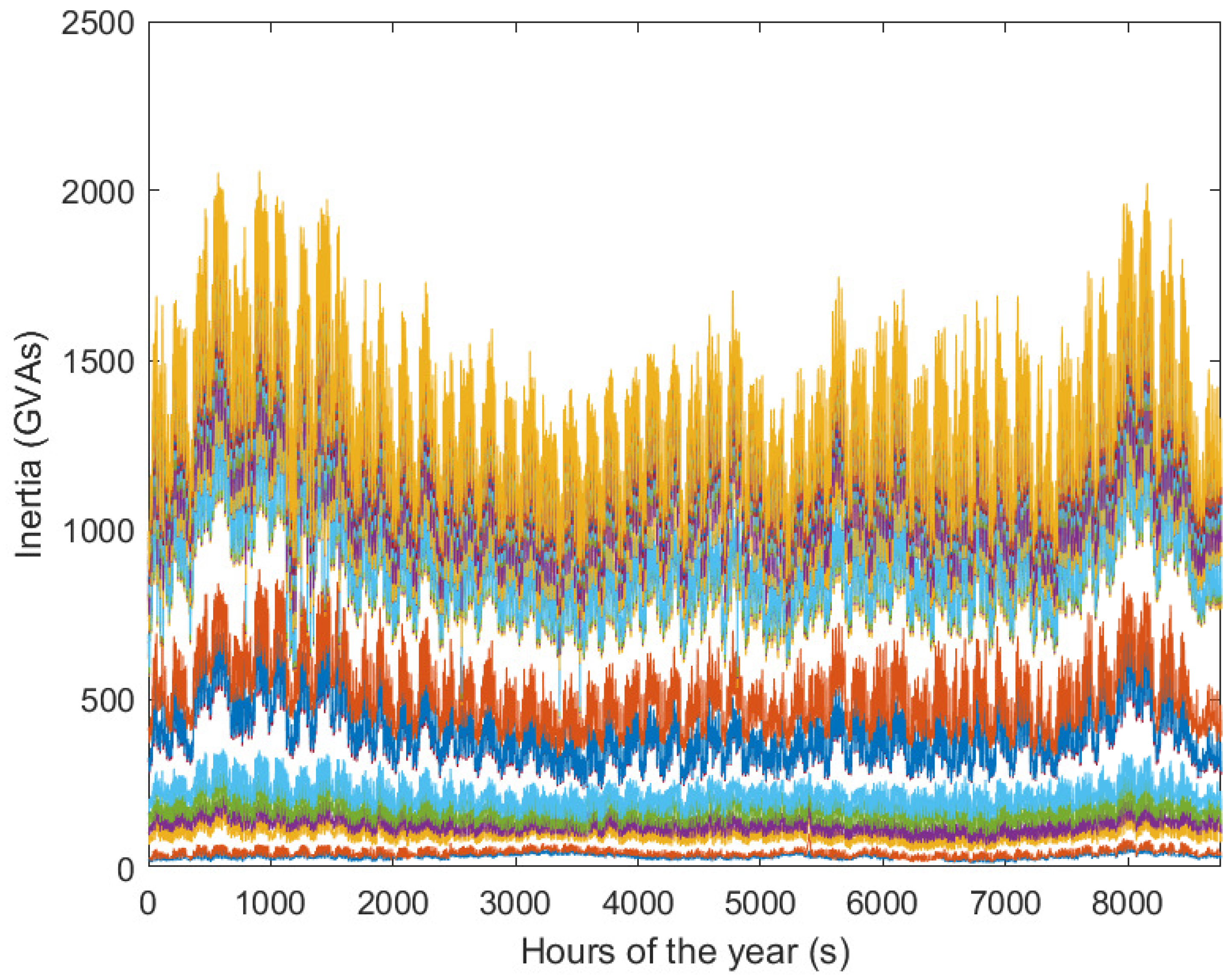
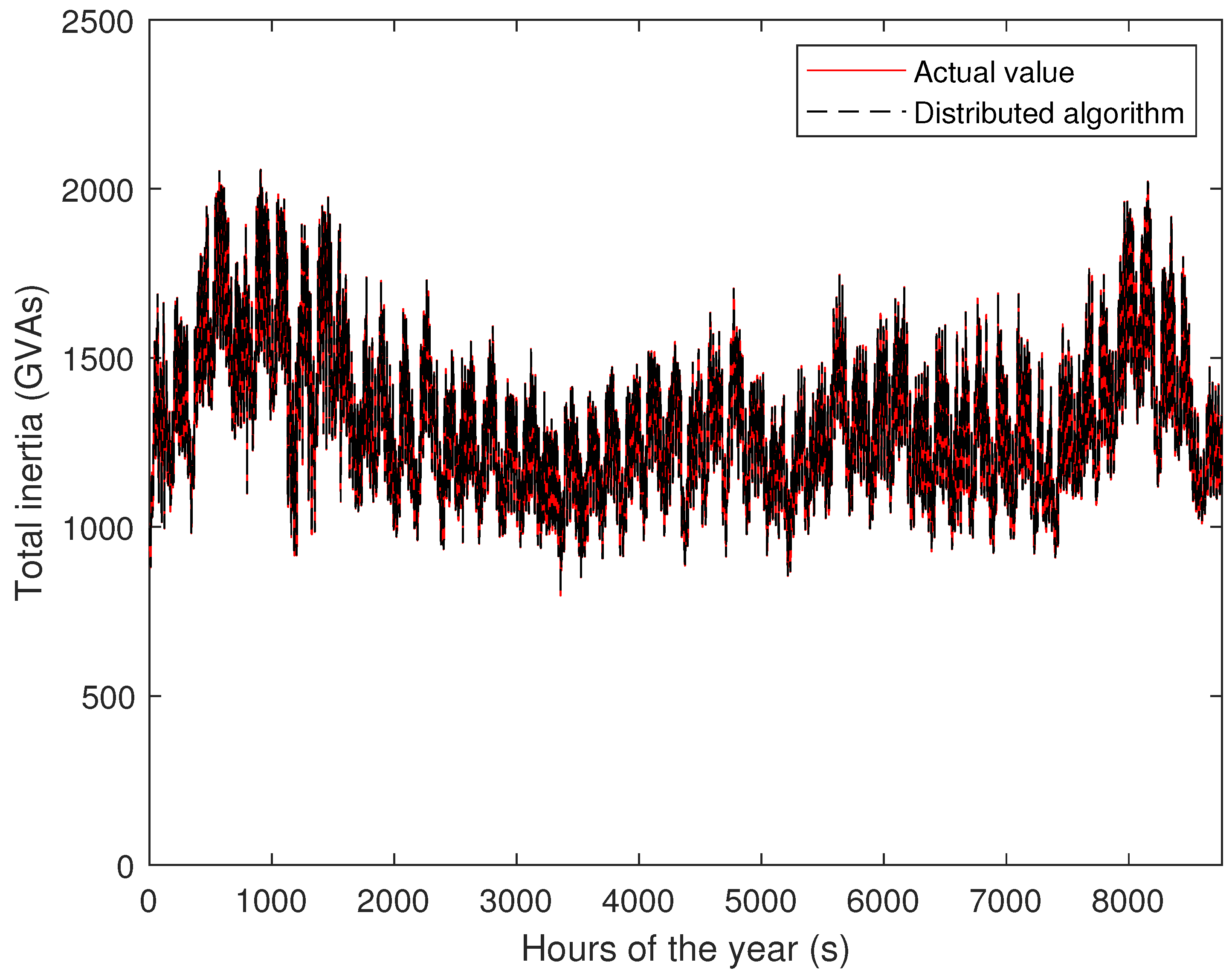
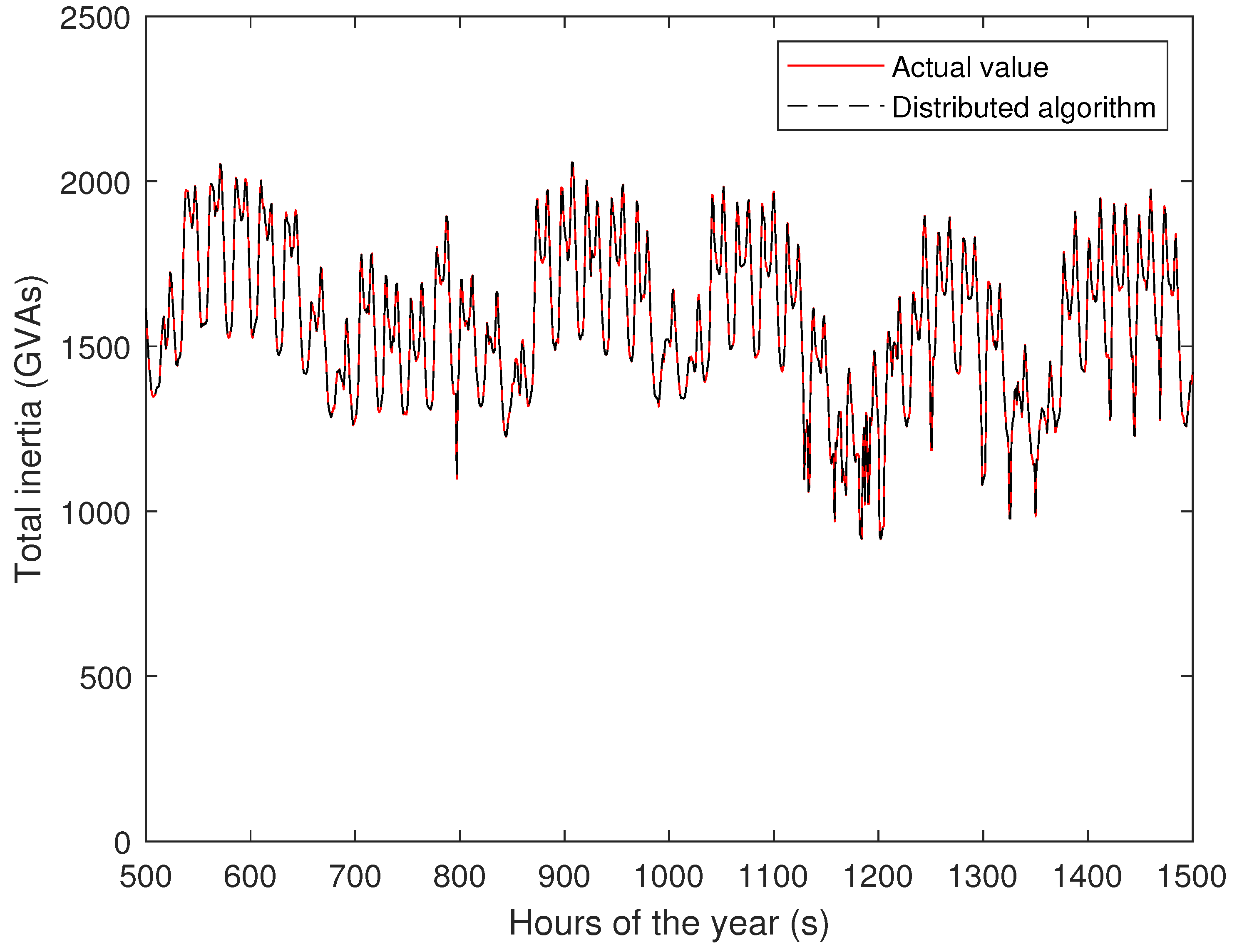
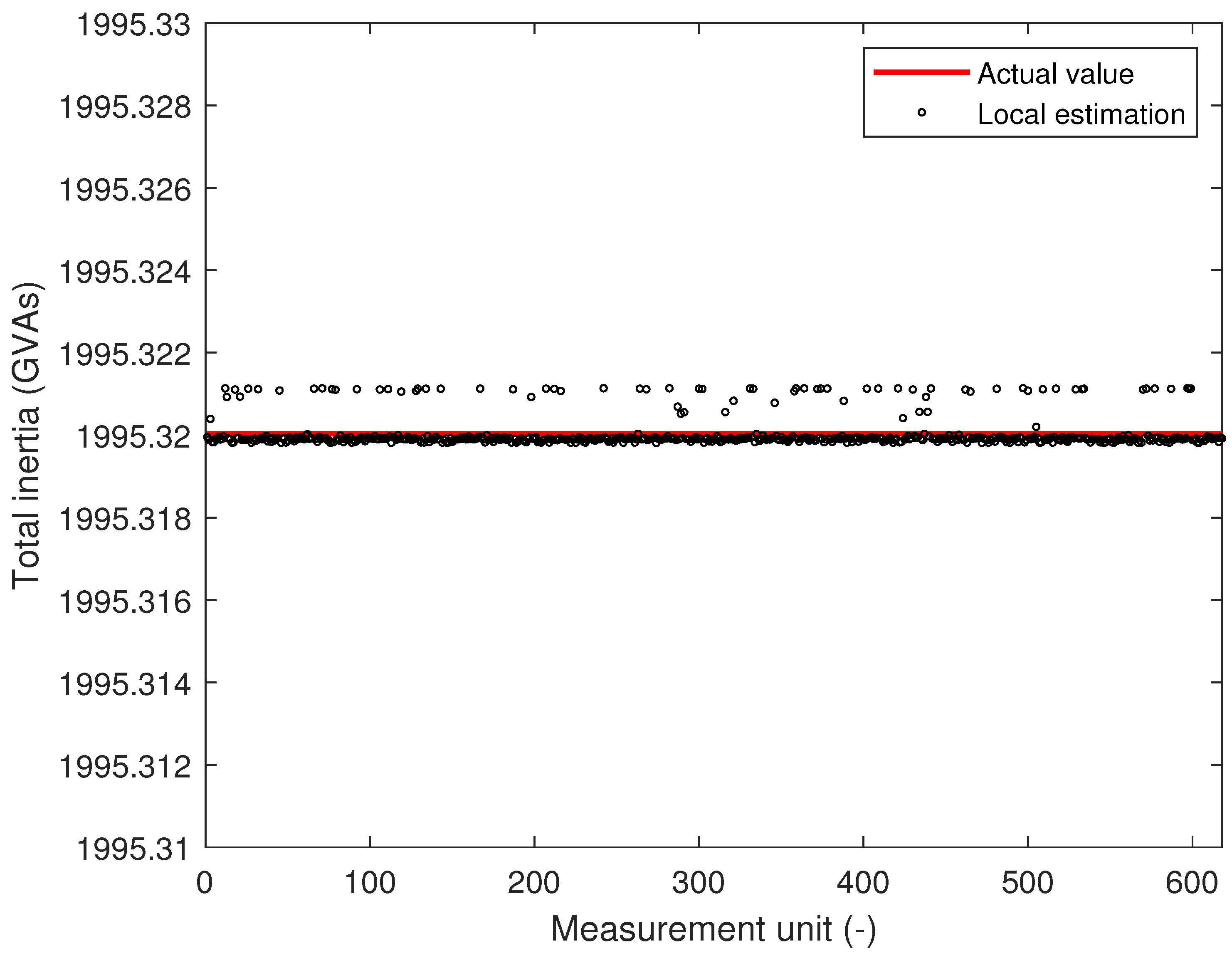
3.1. Application #1: Total Inertia
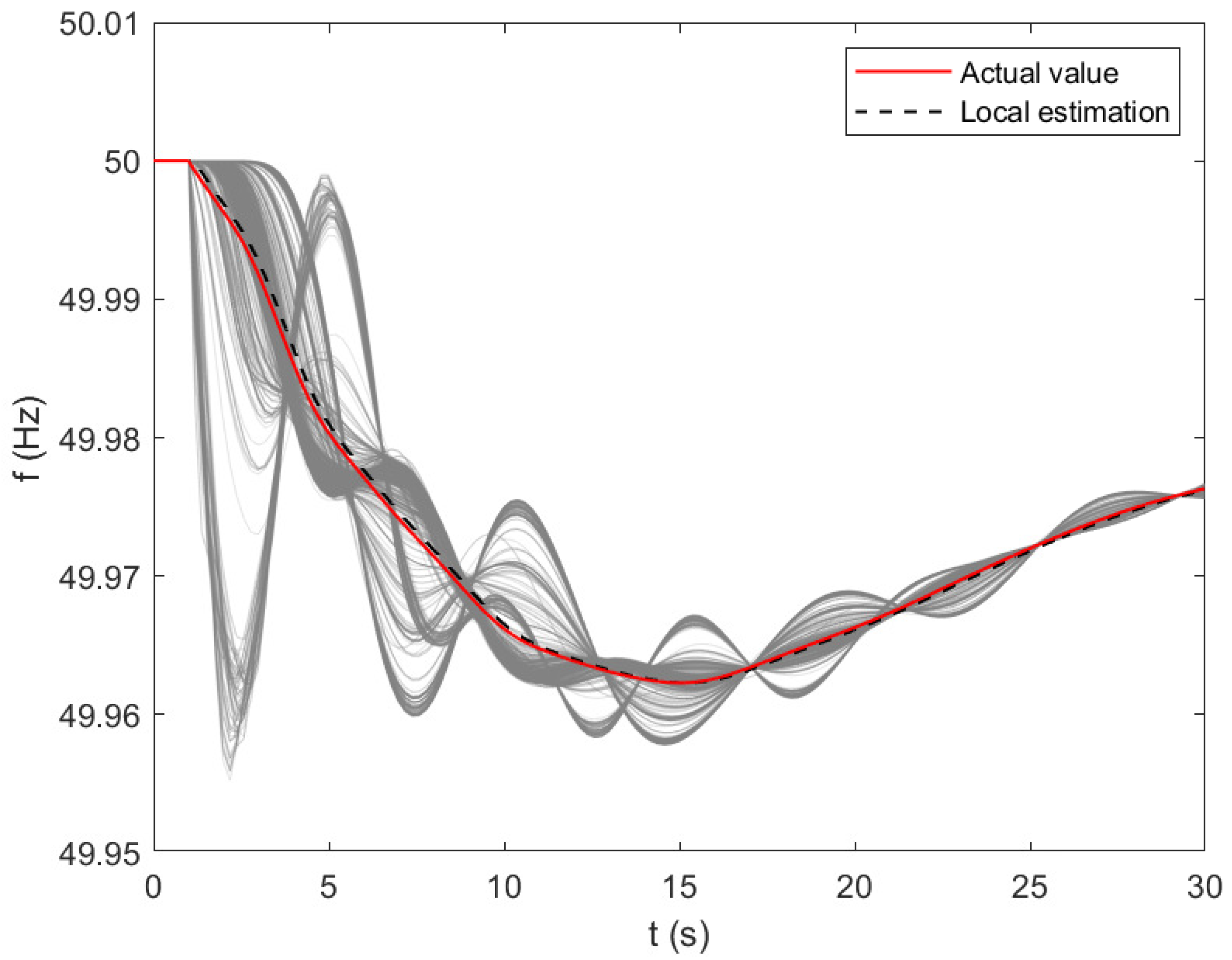
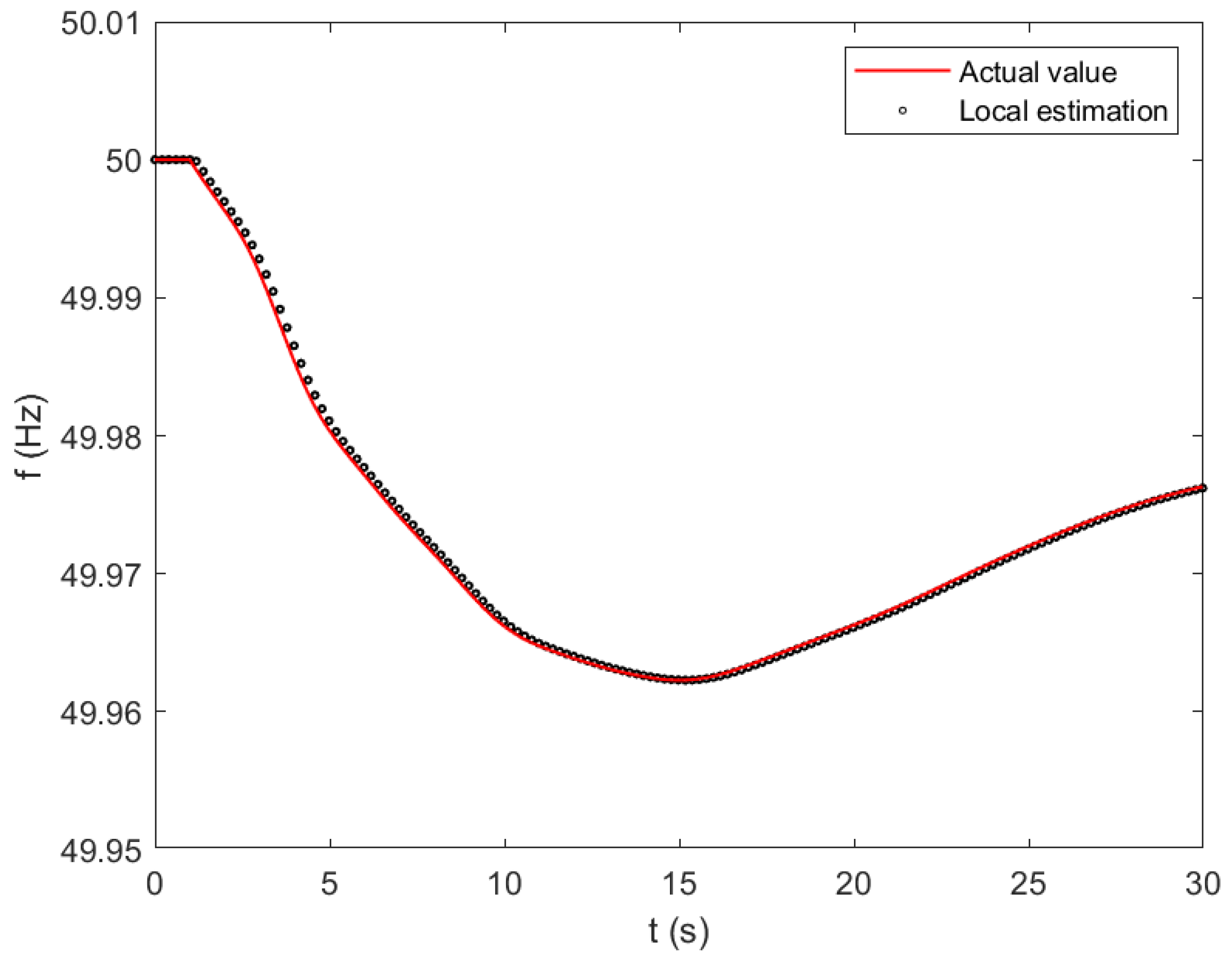
3.2. Application #2: Average Frequency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers; Now Foundations and Trends: Hanover, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Fax, J.A.; Murray, R.M. Consensus and Cooperation in Networked Multi-Agent Systems. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tse, D. Geometry of feasible injection region of power networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 49th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, IL, USA, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengelkamp, E.; Notheisen, B.; Beer, C.; Dauer, D.; Weinhardt, C. A blockchain-based smart grid: Towards sustainable local energy markets. Comput. Sci.—Res. Dev. 2018, 33, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.; Cherukuri, S.H.C.; Pindoriya, N.M. Peer-to-peer energy trading in smart grid: Frameworks, implementation methodologies, and demonstration projects. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Callaway, D.S.; Hiskens, I.A. Decentralized Charging Control of Large Populations of Plug-in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson-Porco, J.W.; Dörfler, F.; Bullo, F. Synchronization and power sharing for droop-controlled inverters in islanded microgrids. Automatica 2013, 49, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostinia, M.; Beheshti, M.T.H.; Alavi, S.A.; Guerrero, J.M. Distributed control strategy for DC microgrids based on average consensus and fractional-order local controllers. IET Smart Grid 2021, 4, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dragičević, T.; Rodriguez, J. A Unified Distributed Cooperative Control of DC Microgrids Using Consensus Protocol. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Xu, Y.; Lu, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, T. Event-Triggered Control for Consensus of Multiagent Systems With Fixed/Switching Topologies. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Sun, S. Event self-triggered leader-following consensus of multi-agent systems with general dynamics. IET Control Theory Appl. 2020, 14, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Xie, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, B. Distributed Event-triggered Consensus Control for Heterogeneous Multi-agent Systems under Fixed and Switching Topologies. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trip, S.; De Persis, C. Frequency Regulation in Power Grids by Optimal Load and Generation Control. In Smart Grids from a Global Perspective: Bridging Old and New Energy Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, M.; Dimarogonas, D.V.; Sandberg, H.; Johansson, K.H. Distributed Control of Networked Dynamical Systems: Static Feedback, Integral Action and Consensus. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 1750–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M. Reinforcement Learning Meets the Power Grid: A Contemporary Survey with Emphasis on Safety and Multi-agent Challenges. Found. Trends Electr. Energy Syst. 2025, 8, 169–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Luna, E.; Marlés-Sáenz, E.; Candelo-Becerra, J. A comprehensive review of distributed control techniques for the operation of modern electrical distribution networks. Math. Model. Eng. Probl. 2023, 10, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Zhenghong, T.; Wenxin, L. Online multi-agent deep reinforcement learning platform for distributed real-time dynamic control of power systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Yan, D.; Qian, G.; Li, J.; Shi, X.; Xu, J.; Wei, M.; Ji, H.; Yu, H. Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Distributed Voltage Control of Flexible Distribution Networks with Soft Open Points. Energies 2024, 17, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z. A Distributed Event-Triggered Fixed-Time Secondary Control for DC Microgrids Without Continuous Signal Transmission. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 5123–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.J.; Naeini, M. Multi-Area Distributed State Estimation in Smart Grids Using Data-Driven Kalman Filters. Energies 2022, 15, 7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotti, D.; Bizzarri, F.; Brambilla, A.; Giudice, D.d.; Grillo, S.; Linaro, D.; Ledesma, P.; Amaris, H. Inertia Estimation of a Power System Area Based on Iterative Equation Error System Identification. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 6469–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bof, N.; Carli, R.; Schenato, L. Average Consensus with Asynchronous Updates and Unreliable Communication. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Guo, H.; Liu, D.; Chang, Y.; Wan, H. Performance optimization of a thermoelectric generator for automotive application using an improved whale optimization algorithm. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 5528–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, H.; Wei, R.; Li, Z. A Distributed Market-Aided Restoration Approach of Multi-Energy Distribution Systems Considering Comprehensive Uncertainties from Typhoon Disaster. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Scaglione, A. Robust Decentralized State Estimation and Tracking for Power Systems via Network Gossiping. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, G.; Dai, R.; Wang, Z. Graph Computing based Distributed State Estimation with PMUs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.09477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekatos, V.; Giannakis, G.B. Distributed Robust Power System State Estimation. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1204.0991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parede, V.T.; Aoki, A.R.; Teixeira, M.D.; Fernandes, T.S.P.; Barreto, N.E.M.; Grando, F.L.; da Silva, V.A.; Guerra, F.A.; Ramos, M.P.; da Costa, C.H.; et al. Electrical Event Detection and Monitoring Data Storage from Wide Area Measurement System. Energies 2023, 16, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Ashton, P.M.; Li, M.; Pisica, I.; Taylor, G.; Rawn, B.; Ding, Y. A Data Driven Approach to Robust Event Detection in Smart Grids Based on Random Matrix Theory and Kalman Filtering. Energies 2021, 14, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnoo, M.A.; Anwar, A.; Haque, M.E.; Mahmood, A.N. Decentralized Federated Anomaly Detection in Smart Grids: A P2P Gossip Approach. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2407.15879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musca, R.; Riva Sanseverino, E. Metodo per L’interazione tra Elementi di Misura nei Sistemi Elettrici di Potenza. Italian 102025000010371, 8 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kempe, D.; Dobra, A.; Gehrke, J. Gossip-based computation of aggregate information. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Cambridge, MA, USA, 11–14 October 2003; pp. 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liao, X.; Huang, T. Average consensus in sensor networks via broadcast multi-gossip algorithms. Neurocomputing 2013, 117, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimakis, A.G.; Sarwate, A.D.; Wainwright, M.J. Geographic Gossip: Efficient Averaging for Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 56, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyeres, M.; Kenyeres, J.; Skorpil, V. The analysis of the push-sum protocol in various distributed systems. Eur. Sci. J. 2016, 12, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, M.J.; Marzullo, K. Directional Gossip: Gossip in a Wide Area Network. In Proceedings of the Third European Dependable Computing Conference EDCC-3, Prague, Czech Republic, 15–17 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaeinia, P.; Gharesifard, B.; Linder, T.; Touri, B. Push-Sum on Random Graphs: Almost Sure Convergence and Convergence Rate. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsianos, K.I.; Rabbat, M.G. Distributed consensus and optimization under communication delays. In Proceedings of the 2011 49th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, IL, USA, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsianos, K.I.; Rabbat, M.G. The Impact of Communication Delays on Distributed Consensus Algorithms. arXiv 2012. arXiv:1207.5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, A.M.; del Giudice, D.; Linaro, D.; Bizzarri, F. Electric power-system’s global-inertia estimation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 160, 110135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, K.; Jain, S.K.; Padhy, P.K. Inertia estimation in modern power system: A comprehensive review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 211, 108222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, J.; Aristidou, P.; Ortega, R. Online Estimation of Power System Inertia Using Dynamic Regressor Extension and Mixing. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4993–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musca, R.; Riva Sanseverino, E.; Zizzo, G.; Giannuzzi, G.; Pisani, C. Wide-Synchronization Control for Power Systems with Grid-Forming Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 4998–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, M.G.; Musca, R. A novel wide-area control for general application to inverter-based resources in power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 160, 110086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musca, R.; Riva Sanseverino, E.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C. Wide-Area Damping Control for Clustered Microgrids. Energies 2025, 18, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENTSO-E SPD (System Protection & Dynamics) Subgroup. Dynamic Model of Continental Europe V2. Available online: https://eepublicdownloads.blob.core.windows.net/public-cdn-container/clean-documents/SOC%20documents/CE_Dynamic_Model_v2_user_s_manual.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Semerow, A.; Höhn, S.; Luther, M.; Sattinger, W.; Abildgaard, H.; Garcia, A.D.; Giannuzzi, G.M. Dynamic Study Model for the Interconnected Power System of Continental Europe in Different Simulation Tools. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Busarello, L.; Musca, R. Impact of high share of converter-interfaced generation on electromechanical oscillations in Continental Europe power system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 3918–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENTSO-E. Inertia and Rate of Change of Frequency (RoCoF), Brussels. Available online: https://www.entsoe.eu/Documents/SOC%20documents/Inertia%20and%20RoCoF_v17_clean.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- ENTSO-E. Transparency Platform. Available online: https://transparency.entsoe.eu/ (accessed on 24 July 2025).

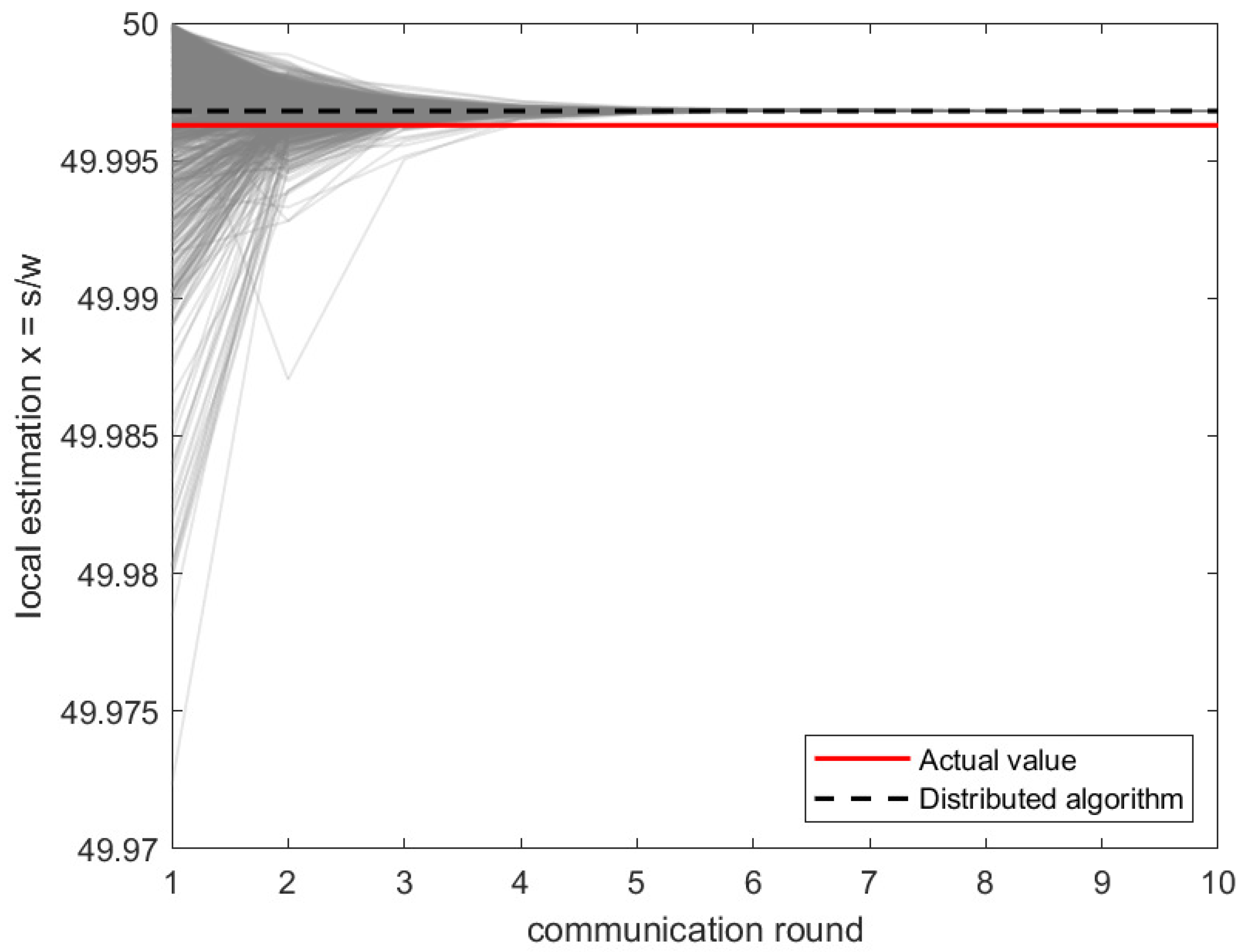
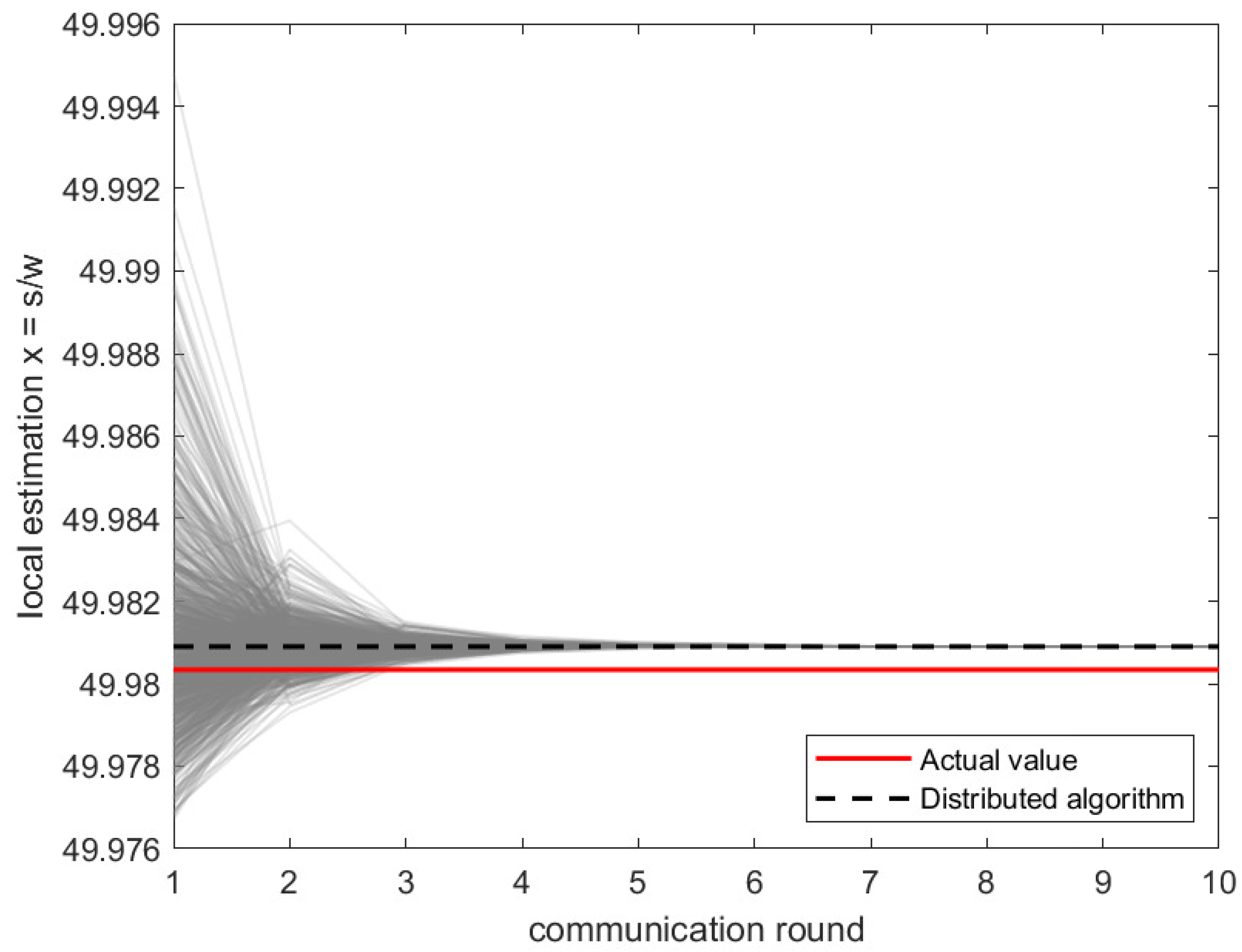
| Global Quantity | Application |
|---|---|
| Online inertia level monitoring | |
| Total inertia | Security-constrained dispatch and reserve sizing |
| Definition of advanced optimal inertia control | |
| Extended event classification | |
| Enhanced situational awareness and grid stability monitoring | |
| Average frequency | Identification and damping of inter-area oscillations |
| Enhanced detection of islanding and system separation | |
| Definition of advanced wide-area control schemes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musca, R.; Riva Sanseverino, E. Peer-to-Peer Distributed Algorithms for Wide-Area Monitoring and Control in Power Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18153972
Musca R, Riva Sanseverino E. Peer-to-Peer Distributed Algorithms for Wide-Area Monitoring and Control in Power Systems. Energies. 2025; 18(15):3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18153972
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusca, Rossano, and Eleonora Riva Sanseverino. 2025. "Peer-to-Peer Distributed Algorithms for Wide-Area Monitoring and Control in Power Systems" Energies 18, no. 15: 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18153972
APA StyleMusca, R., & Riva Sanseverino, E. (2025). Peer-to-Peer Distributed Algorithms for Wide-Area Monitoring and Control in Power Systems. Energies, 18(15), 3972. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18153972






