Experimental Study on Co-Firing of Coal and Biomass in Industrial-Scale Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Systems and Methods
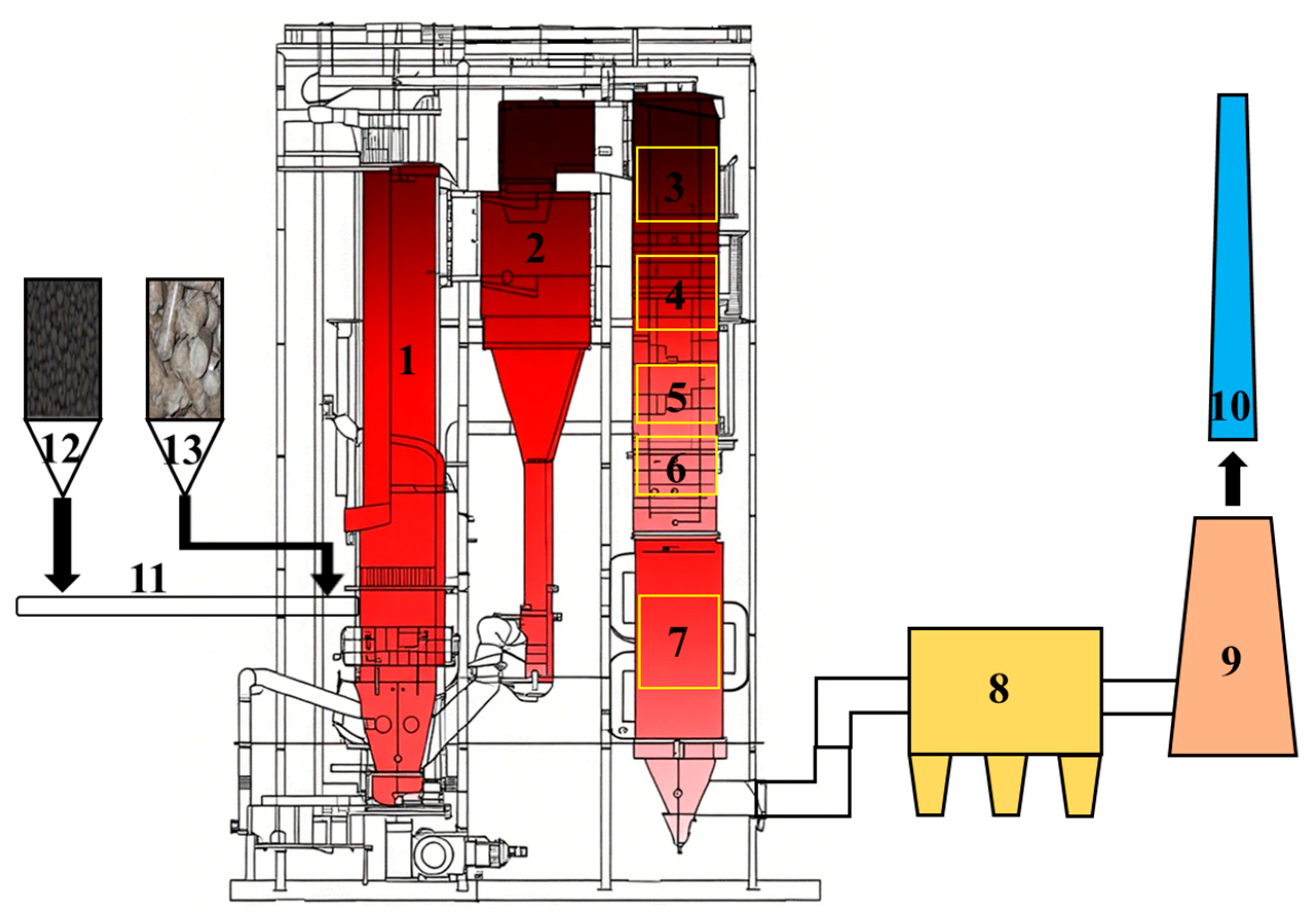
2.2.1. Boiler System
2.2.2. Feeding System
2.2.3. Experimental Design
2.2.4. Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Impact of Low-Ratio Co-Firing (≤10 wt%)
3.2. The Impact of High-Ratio Co-Firing (20 wt%)
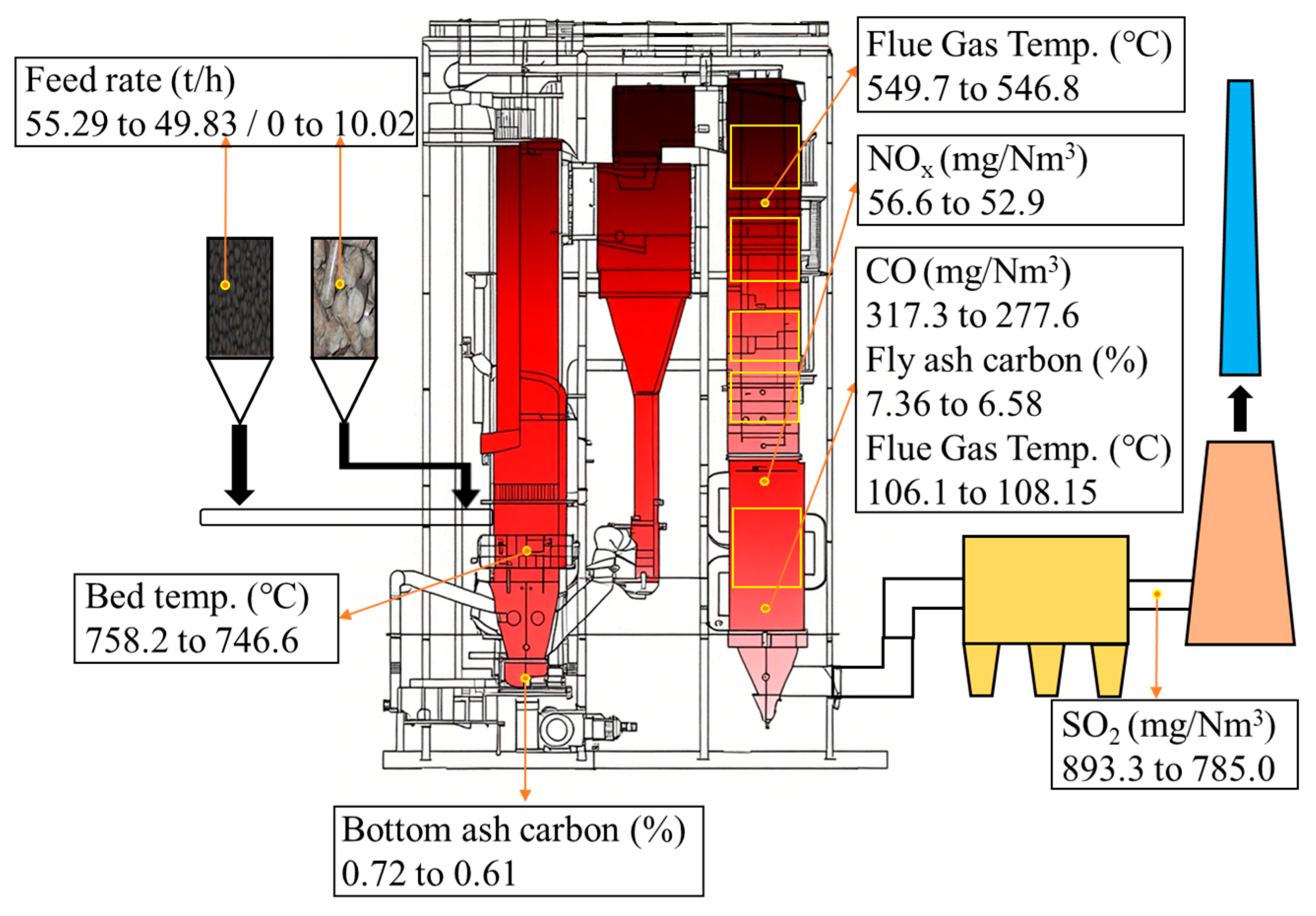
3.2.1. The Impact of Boiler Operating Parameters
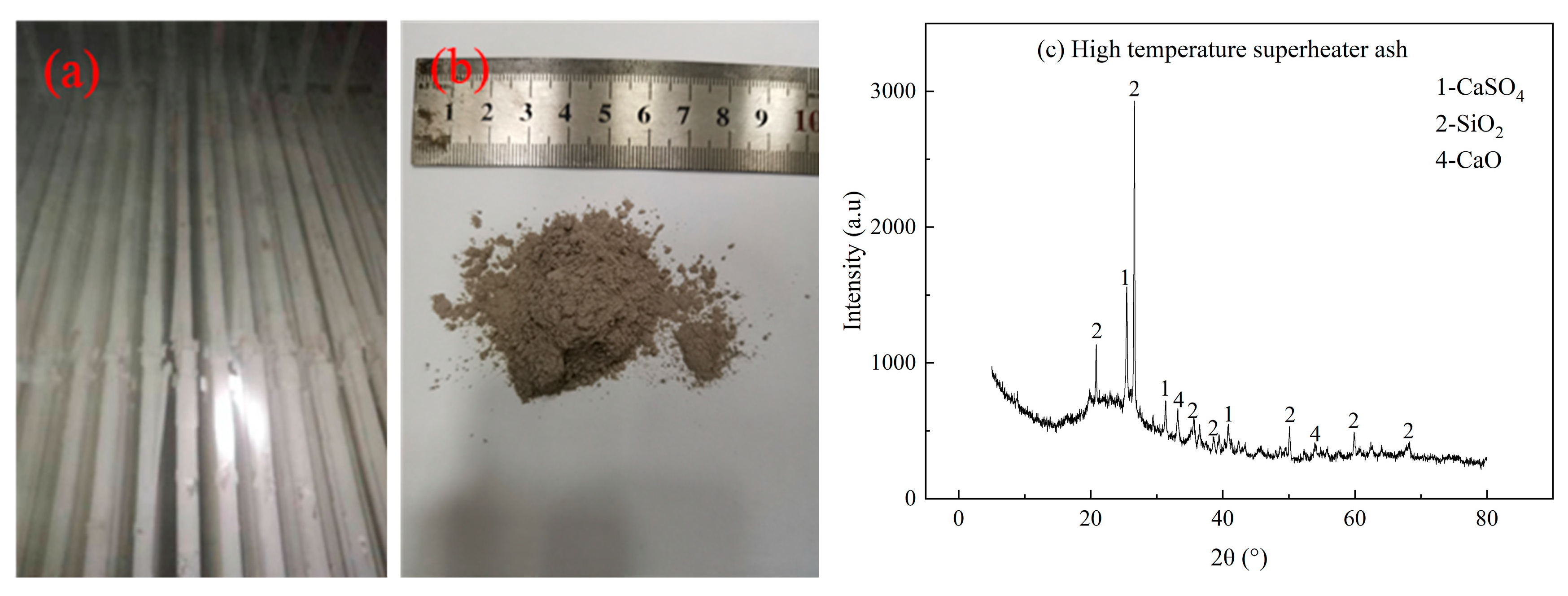
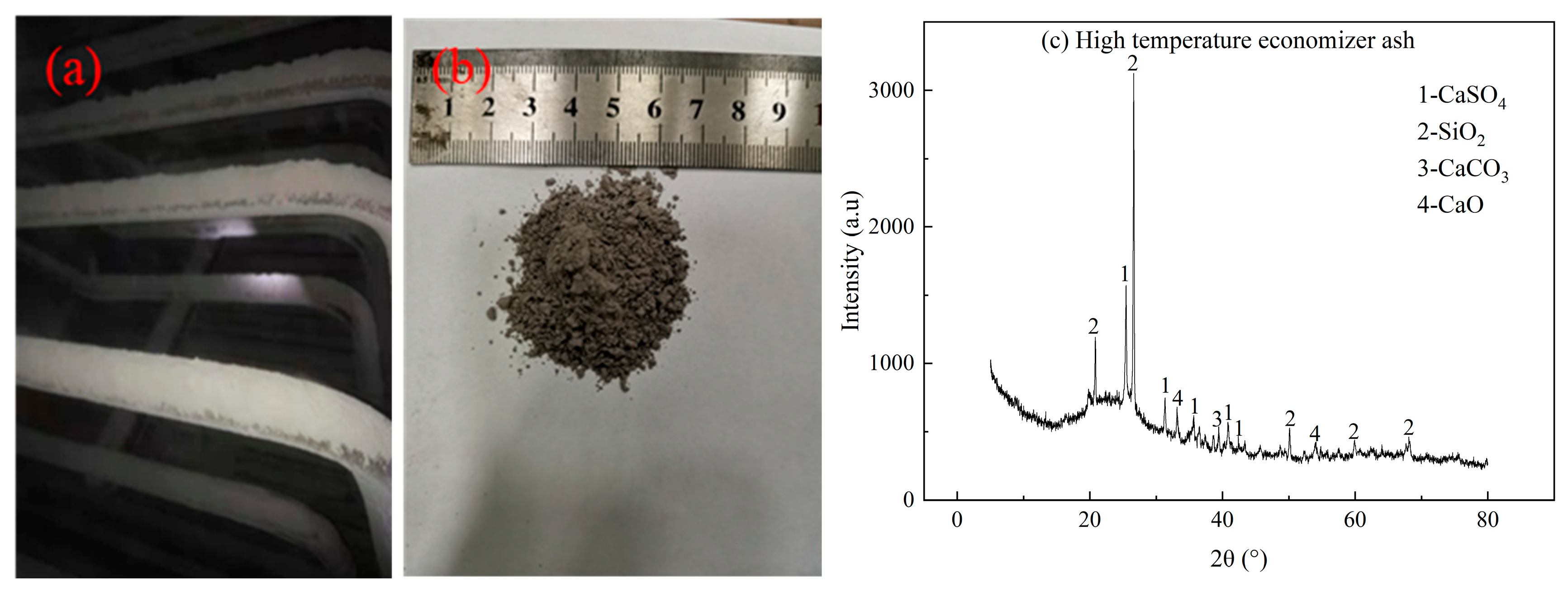
3.2.2. The Effect of the Heating Surface
3.2.3. Carbon Reduction and Technical Economic Indicators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFB | Circulating Fluidized Bed |
| PC | Pulverized Coal |
| wt% | Weight Percent (mass fraction) |
| LHV | Low Heat Value |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| XRF | X-Ray Fluorescence |
| ECR | Economic Continuous Rating |
| BMCR | Boiler Maximum Continuous Rating |
| APH | Air Preheater |
| SCR | Selective Catalytic Reduction |
| CNY | Chinese Yuan |
| DT | Deformation Temperature |
| ST | Softening Temperature |
| HT | Hemisphere Temperature |
| FT | Flow Temperature |
References
- Peng, B.; Zhao, Y.; Elahi, E.; Wan, A. Can third-party market cooperation solve the dilemma of emissions reduction? A case study of energy investment project conflict analysis in the context of carbon neutrality. Energy 2023, 264, 126280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkuah, M.; Alessa, N. Renewable Energy and Carbon Intensity: Global Evidence from 184 Countries (2000–2020). Energies 2025, 18, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, K.; Yin, X.; Mangla, S.K. The effect of carbon tariffs and the associated coping strategies: A global supply chain perspective. Omega 2024, 122, 102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, M. Mitigating CO2 emission in pulverized coal-fired power plant via co-firing ammonia: A simulation study of flue gas streams and exergy efficiency. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 256, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Lv, C.; Yao, L. Social welfare and equality equilibrium based carbon tax subsidy incentive approach for biomass-coal co-firing towards carbon emissions. Energy 2024, 291, 130282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cai, C.; Ge, T.; Zhang, M. Effect of Potassium on the Co-Combustion Process of Coal Slime and Corn Stover. Energies 2024, 17, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Lee, Y. Life Cycle Assessment of Torrefied Residual Biomass Co-Firing in Coal-Fired Power Plants: Aspects of Carbon Dioxide Emission. Energies 2024, 17, 6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; May, J.; Ströhle, J.; Epple, B. Flexibility of CFB Combustion: An Investigation of Co-Combustion with Biomass and RDF at Part Load in Pilot Scale. Energies 2020, 13, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Park, K.; Lee, G.-H.; Lee, J.-M.; Hwang, J. Optimal blending ratio of Elga caking coal in Samcheok circulating fluidized bed boilers: Experimental and practical insights. Fuel 2025, 386, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-j.; Yang, X.-m.; Zhang, L.; Ding, T.-l.; Song, W.-l.; Lin, W.-g. Emissions of SO2, NO and N2O in a circulating fluidized bed combustor during co-firing coal and biomass. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kim, R.-G.; Li, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Jeon, C.-h.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Ash thermomechanical properties and combustion characteristics during Co-combustion of anthracite and biomass for CFB combustors. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 198, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unchaisri, T.; Fukuda, S. Investigation of ash formation and deposit characteristics in CFB co-combustion of coal with various biomass fuels. J. Energy Inst. 2022, 105, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywanski, J.; Rajczyk, R.; Bednarek, M.; Wesolowska, M.; Nowak, W. Gas emissions from a large scale circulating fluidized bed boilers burning lignite and biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 116, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A. Simulation of co-firing coal and biomass in circulating fluidized beds. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 65, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.-P.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chien, W.-C.; Lee, H.-T.; Huang, C.C. Emissions during co-firing of RDF-5 with bituminous coal, paper sludge and waste tires in a commercial circulating fluidized bed co-generation boiler. Fuel 2008, 87, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Jin, Y.; Wang, M.; Feng, H.; Yin, J. Influence of papermaking biomass co-firing on operation energy efficiency and gas emission stability of a coal-fired thermal power plant: A case study. Energy 2025, 327, 136484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, K. Migration Behaviors of As, Se and Pb in Ultra-Low-Emission Coal-Fired Units and Effect of Co-Firing Sewage Sludge in CFB Boilers. Energies 2022, 15, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzelepi, V.; Zeneli, M.; Kourkoumpas, D.-S.; Karampinis, E.; Gypakis, A.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Grammelis, P. Biomass Availability in Europe as an Alternative Fuel for Full Conversion of Lignite Power Plants: A Critical Review. Energies 2020, 13, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Liu, Y. Optimizing sustainable biomass–coal co-firing power plant location problem under ambiguous supply. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 182, 109401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Safferman, S.I.; Saffron, C.M. Development and application of a decision support tool for biomass co-firing in existing coal-fired power plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, J. Co-firing in coal power plants and its impact on biomass feedstock availability. Energy Policy 2013, 60, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Liu, L.-C.; Kang, J.-N.; Peng, S.; Mi, Z.; Liao, H.; Wei, Y.-M. Economic feasibility assessment of coal-biomass co-firing power generation technology. Energy 2024, 296, 131092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ghamari, M.; Ratner, A. Numerical modeling of co-firing a light density biomass, oat (Avena sativa) hulls, and chunk coal in fluidized bed boiler. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 56, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J. Experimental study on industrial-scale CFB biomass gasification. Renew. Energy 2020, 158, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Peng, Z.; Gao, H.; Gong, X. Performance analysis of a novel biomass gasification system coupled to a coal-fired power plant based on heat and water recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 299, 117822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, C. NO emission during the co-combustion of biomass and coal at high temperature: An experimental and numerical study. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 115, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgurén, T.; Andersson, K.; Fry, A.; Eddings, E.G. NO formation during co-combustion of coal with two thermally treated biomasses. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 235, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Mikulčić, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, H. Numerical study of biomass Co-firing under Oxy-MILD mode. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 2566–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Dai, G.; Heberlein, S.; Chan, W.P.; Wang, X.; Tan, H.; Lisak, G. Assessing the effect of size and shape factors on the devolatilization of biomass particles by coupling a rapid-solving thermal-thick model. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 183, 106835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
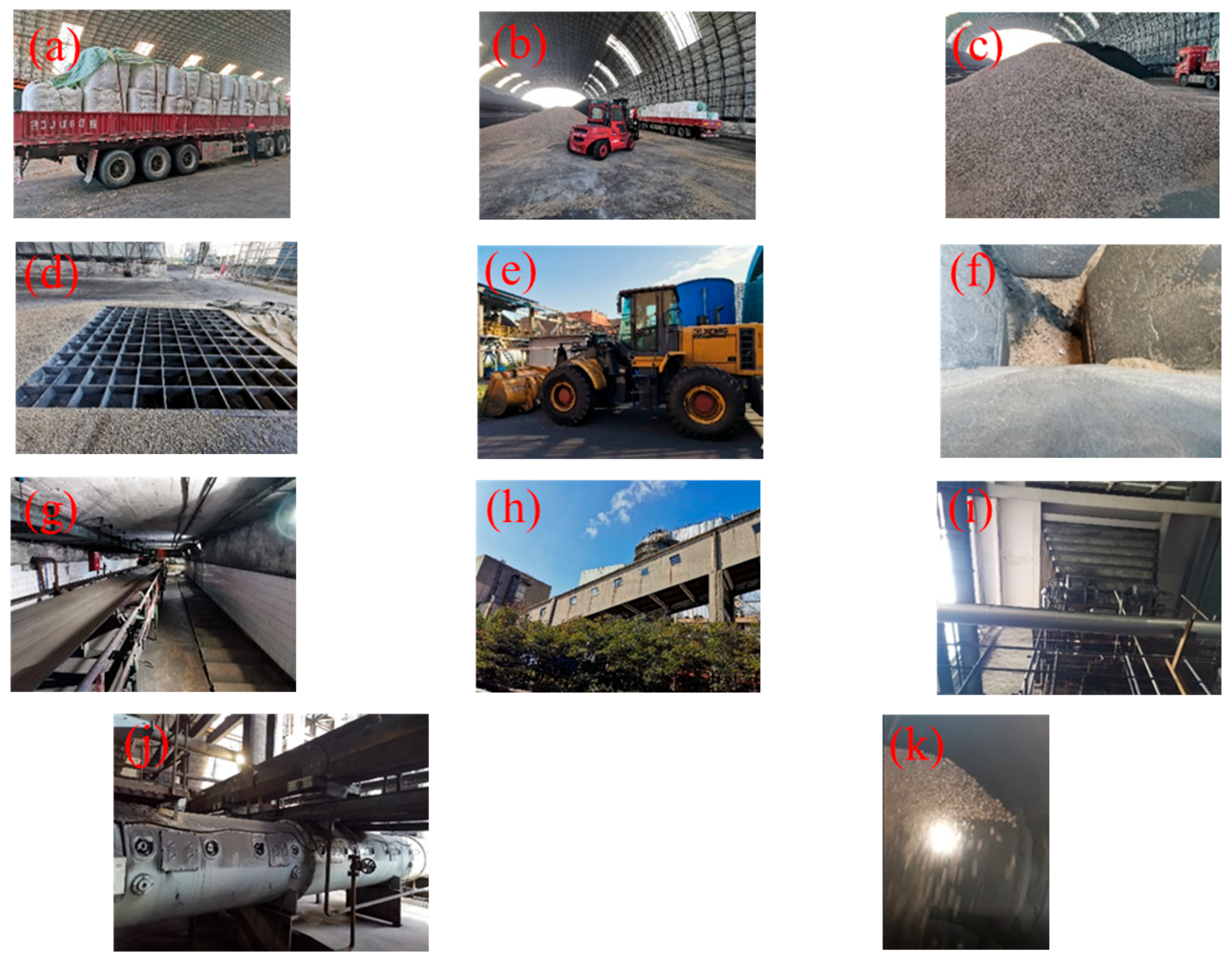


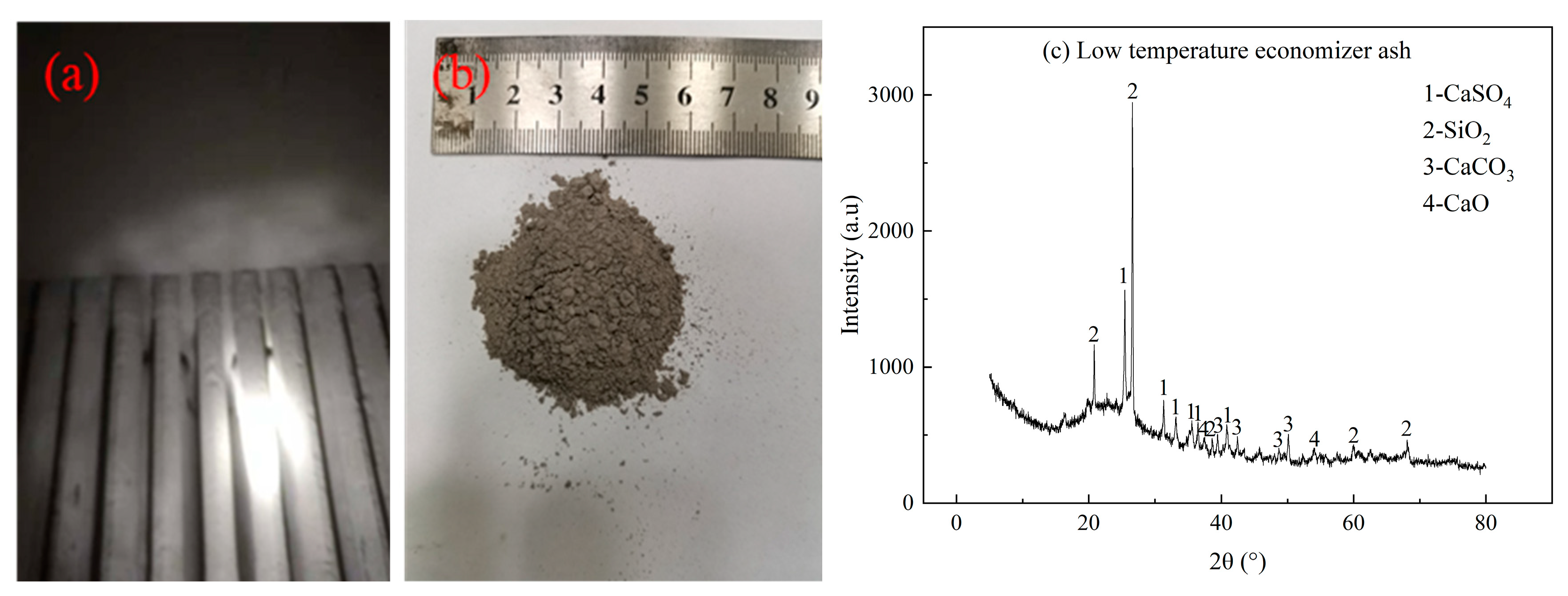
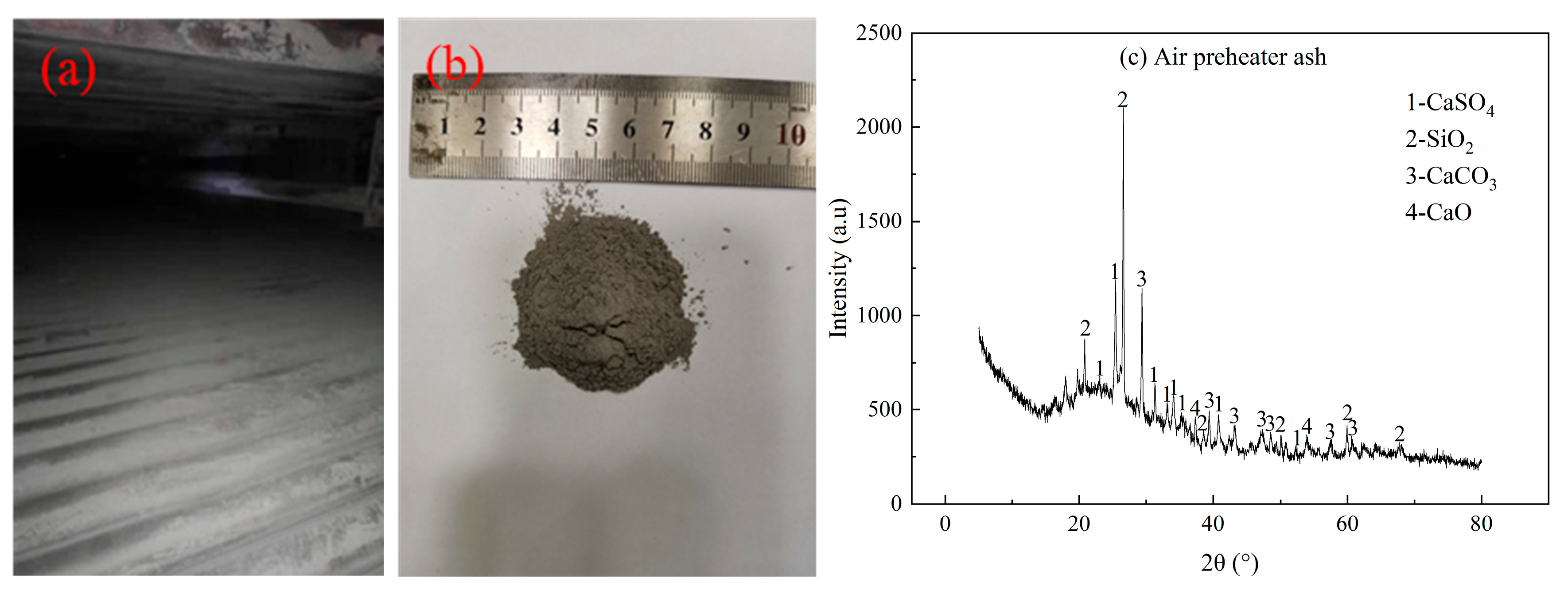

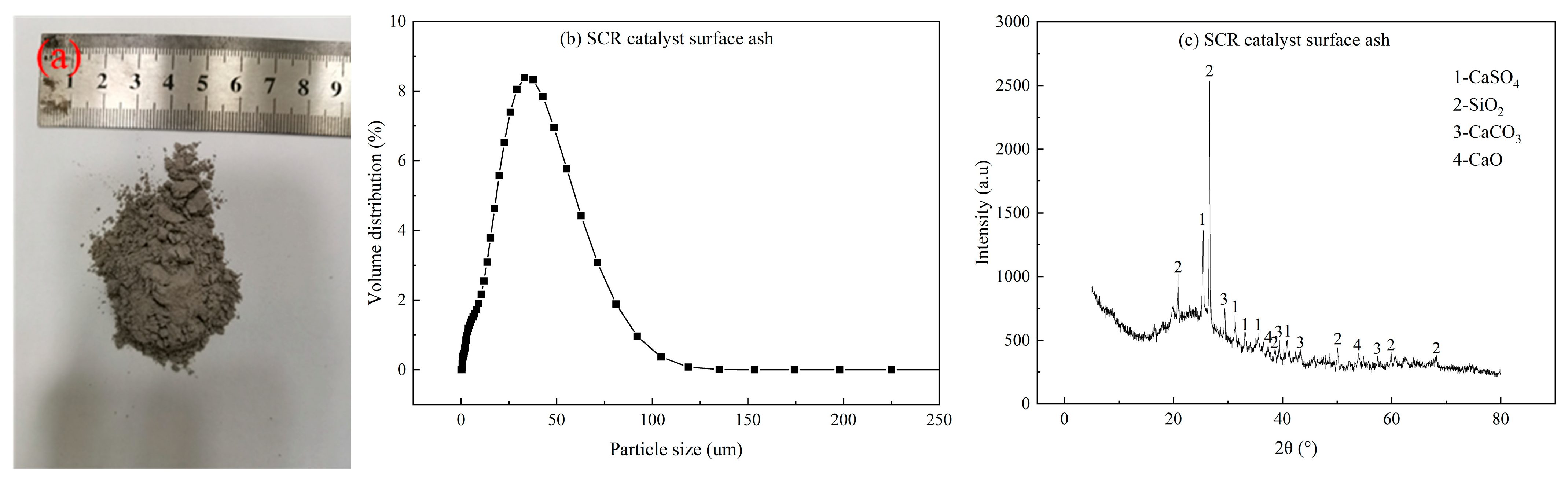

| Calorific Value | Ash Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Qar.net (MJ/kg) | 15.94 | SiO2 (%) | 31.87 |
| Proximate analysis | Al2O3 (%) | 4.89 | |
| Mar (%) | 7.40 | Fe2O3 (%) | 3.60 |
| Aar (%) | 6.39 | CaO (%) | 25.42 |
| FCar (%) | 15.7 | MgO (%) | 5.98 |
| Var (%) | 70.51 | K2O (%) | 5.47 |
| Elemental analysis | Na2O (%) | 2.66 | |
| Car (%) | 42.16 | TiO2 (%) | 0.74 |
| Har (%) | 4.63 | SO3 (%) | 8.70 |
| Oar (%) | 37.01 | P2O5 (%) | 10.17 |
| Nar (%) | 2.27 | ||
| Sar (%) | 0.14 | ||
| Ash fusion temperature | |||
| DT (°C) | ST (°C) | HT (°C) | FT (°C) |
| 1150 | 1201 | 1210 | 1218 |
| As (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Pt (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) | Ni (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.27 | 0.96 | 26.35 | 9.86 | 44.55 | 0.42 | 4.68 | 163.16 |
| Parameter | Unit | Design Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rated evaporation capacity (ECR) | t/h | 571 |
| Maximum evaporation (BMCR) | t/h | 620 |
| Steam drum operating pressure | MPa | 10.84 |
| Steam drum design pressure | MPa | 11.50 |
| Main steam pressure | MPa | 9.81 |
| Main steam temperature | °C | 540 |
| Feedwater temperature | °C | 223 (BMCR) |
| 215 (ECR) | ||
| Economizer outlet water temp. | °C | 310 |
| Primary air outlet temp. (APH) | °C | 285 |
| Secondary air outlet temp. (APH) | °C | 280 |
| Flue gas temperature | °C | 135 |
| Boiler efficiency | % | 92.36 |
| Dust concentration (APH outlet) | g/Nm3 | 31.35 |
| Flue gas flow (APH outlet) | Nm3/h | 537,899 |
| SO2 emission concentration (APH outlet) | mg/Nm3 | 400 |
| NOx emission concentration (APH outlet) | mg/Nm3 | 150 |
| Ca/S molar ratio (at 90% desulfurization) | / | 2.8 |
| Bottom ash to fly ash ratio | / | 40%:60% |
| Parameter | Baseline Case (70% Coal + 30% Petroleum Coke) | Co-Firing Case (5 wt% Biomass) | Co-Firing Case (7 wt% Biomass) | Co-Firing Case (10 wt% Biomass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual blending ratio | 0% | 4.85% | 6.73% | 9.40% |
| Boiler load (%) | 370 | 370 | 370 | 370 |
| Biomass fuel feed rate (t/h) | 0 | 2.53 | 3.56 | 5.0 |
| Total fuel feed rate (t/h) | 51.75 | 52.1 | 52.9 | 53.2 |
| Average bed temperature (°C) | 865.5 | 868.2 | 873.3 | 875.6 |
| Attemperating water flow (t/h) | 5.38/0.19/0.43 | 5.0/0.12/0.17 | 4.49/0.13/0.43 | 5.52/0.4/0.63 |
| SCR inlet NOx (mg/Nm3) | 53.1/25.6 | 53.7/20.1 | 52.2/19.7 | 33.2/17.8 |
| High-temp. superheater outlet gas temp. (°C) | 519.1/515.1 | 516.3/513.7 | 518.0/514.3 | 522.8/520.0 |
| High-temp economizer outlet gas temp. (°C) | 345.2/347.5 | 344.7/347.1 | 345.0/346.1 | 345.8/348.3 |
| Exhaust gas temperature (°C) | 99.3/114.7 | 97.7/113.5 | 99.7/115.4 | 100.5/116.6 |
| Primary air plenum pressure (kPa) | 13.89 | 13.78 | 13.01 | 13.21 |
| Absorption tower inlet/outlet SO2 (mg/Nm3) | 2776.6/4.96 | 2727.7/4.85 | 2864.3/5.5 | 2729.5/5.38 |
| Fabric filter differential pressure (Pa) | 593/989.6 | 599.2/965.5 | 600.6/965.8 | 597.8/988 |
| Absorption tower inlet/outlet dust (mg/Nm3) | 1.71/0.29 | 1.46/0.29 | 1.77/0.29 | 1.67/0.292 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | SO3 | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-temp. superheater ash | 30.86 | 25.05 | 3.97 | 15.42 | 2.92 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 9.12 | 9.62 |
| Horizontal flue ash | 38.47 | 30.92 | 4.26 | 4.09 | 2.60 | 1.86 | 0.25 | 3.20 | 11.93 |
| Designed fuel ash | 48.97 | 34.87 | 7.19 | 2.46 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 0.22 | 1.93 | 2.90 |
| Car % | Har % | Oar % | Nar % | Sar % | Mar % | Aar % | Var % | FCar % | Qnet,ar(kJ/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 52.33 | 4.11 | 9.26 | 0.94 | 1.85 | 4.30 | 27.20 | 25.20 | 43.30 | 20,360.00 |
| Mixed fuel | 49.76 | 4.13 | 13.75 | 1.15 | 1.54 | 6.39 | 23.27 | 32.37 | 37.97 | 19,619.84 |
| Baseline Case (100% Coal) | Co-Firing Case (20 wt% Biomass) | |
|---|---|---|
| Actual blending ratio | 0 | 16.74% |
| Boiler load (t/h) | 432.24 | 418.19 |
| Steam temperature (°C) | 540 | 540 |
| Steam pressure (MPa) | 9.8 | 9.8 |
| Biomass fuel feed rate (t/h) | 0 | 10.02 |
| Total fuel feed rate (t/h) | 55.29 | 59.85 |
| Average bed temperature (°C) | 758.2 | 746.6 |
| Attemperating water flow (t/h) | 1.19/0.00/0.00 | 1.09/0.00/0.00 |
| SCR inlet NOx (mg/Nm3) | 56.6 | 52.9 |
| High temp. superheater outlet gas temp. (°C) | 536.4/563.0 | 531.2/562.3 |
| Exhaust gas temperature (°C) | 98.0/114.2 | 99.9/116.4 |
| Primary air plenum pressure(kPa) | 14.96/14.72/8.27 | 14.90/14.71/8.02 |
| Absorption tower inlet/outlet SO2 (mg/Nm3) | 893.3/1.7 | 785.0/1.3 |
| Bottom ash flow rate (t/h) | 5.04 | 4.16 |
| Fly ash carbon content (%) | 7.36 | 6.58 |
| Bottom ash carbon content (%) | 0.72 | 0.61 |
| Actual wet flue gas flow rate (Nm3/kg) | 6.94 | 6.78 |
| Exhaust gas heat loss (q2, %) | 5.18 | 5.21 |
| Gas incomplete combustion loss (q3, %) | 0.09 | 0.07 |
| Solid incomplete combustion loss (q4, %) | 2.43 | 2.00 |
| Radiation loss (q5, %) | 0.69 | 0.71 |
| Ash/Slag sensible heat loss (q6, %) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Boiler efficiency (%) | 91.60 | 92.01 |
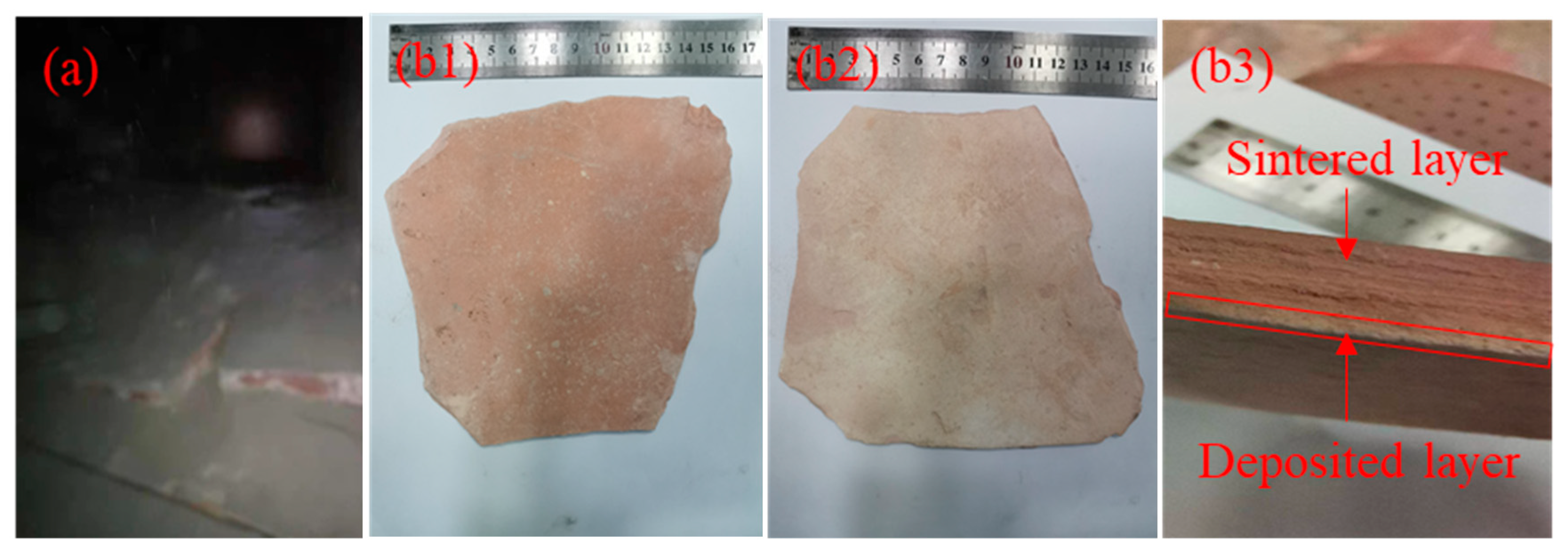
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | K2O | SO3 | MgO | P2O5 | Na2O | BaO | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sintered layer | 37.4 | 32.3 | 2.36 | 2.22 | 2.07 | 0.902 | 0.580 | 0.401 | 0.343 | 0.124 | 0.081 | 21.22 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | ZrO2 | BaO | MgO | P2O5 | SO3 | Others | |
| Deposited layer | 31.9 | 28.6 | 3.67 | 2.96 | 2.51 | 0.665 | 0.648 | 0.478 | 0.367 | 0.276 | 0.213 | 27.71 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | SO3 | P2O5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline case (100% coal) | 37.4 | 31.1 | 1.65 | 2.46 | 2.9 | 0.29 | 0.56 | 1.73 | 0.18 |
| Co-firing case (20 wt% biomass) | 39.0 | 30.6 | 1.73 | 2.93 | 3.76 | 0.51 | 0.69 | 2.18 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yu, C. Experimental Study on Co-Firing of Coal and Biomass in Industrial-Scale Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers. Energies 2025, 18, 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143832
Zhang H, Yu C. Experimental Study on Co-Firing of Coal and Biomass in Industrial-Scale Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers. Energies. 2025; 18(14):3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143832
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoteng, and Chunjiang Yu. 2025. "Experimental Study on Co-Firing of Coal and Biomass in Industrial-Scale Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers" Energies 18, no. 14: 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143832
APA StyleZhang, H., & Yu, C. (2025). Experimental Study on Co-Firing of Coal and Biomass in Industrial-Scale Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers. Energies, 18(14), 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143832





