Abstract
Coal mine underground reservoirs play a significant role in energy utilization while also contributing to energy security. Prolonged immersion in mine water reduces the long-term strength of coal, subsequently leading to continuous creep damage in coal pillars. This manifests as the propagation of damage, ultimately resulting in instability, which affects their load-bearing capacity and impermeability. A multi-faceted approach involving laboratory experiments, similar model tests, and numerical simulations was employed to investigate the mechanical properties of water-immersed coal and the continuous creep damage process in coal pillars. Key findings reveal that water immersion significantly diminishes the long-term strength of coal; for example, initial instantaneous strain rose from 0.16% (non-immersed) to 0.25% (8-week immersion), with final creep strain reaching 1.15% versus 0.78%, respectively. The combined modeling methods effectively replicated the creep damage process, demonstrating that when concentrated stress exceeds the reduced long-term strength of coal, damage propagates toward the center of the pillar, forming continuous creep damage extending approximately 3.8 m within 7 years. This study contributes to our understanding of the creep damage mechanism in coal pillars and supports the long-term stability evaluation of CMURs.
1. Introduction
Underground coal mine reservoirs (CMURs) employ strip coal pillars and artificial dams to create isolated reservoirs designed for the collection, filtration, purification, and qualitative utilization of mining water, as well as the storage of saline water [1]. CMURs play a critical role in enhancing energy utilization through effective water resource management and the repurposing of goaf areas, while also bolstering energy security by ensuring the stability and impermeability of coal pillars. This technology is instrumental in promoting sustainable, efficient, and safe advancements in the coal energy industry. However, the inherent creep behavior of coal presents a substantial challenge to the long-term safety of CMUR, potentially causing creep-induced damage that undermines the overburden pressure-bearing capacity and anti-seepage performance of the reservoirs [2,3].
In contrast to conventional coal pillars in mining operations, CMUR coal pillars are subjected to both overburden pressure and water–rock interactions, often involving exposure to high-salinity mine water [4,5]. Studies by Li et al. [6], Chen et al. [7], and Danesh et al. [8] have demonstrated that water significantly reduces the long-term strength of coal through mechanisms such as wetting-induced softening, mineral dissolution, and microcrack lubrication, thereby accelerating creep damage and enhancing permeability. In CMUR, creep deformation can damage a specific width of a coal pillar, triggering stress redistribution that initiating further creep damage in adjacent areas, leading to the progressive failure of the pillar structure. Such continuous damage processes in coal pillars have been documented by Zhang et al. [9], Wu et al. [10], and Qu et al. [11]. Consequently, elucidating the mechanisms of continuous damage in coal pillars is critical for ensuring the long-term safety and stability of CMUR operations.
Extensive research has explored the creep behavior of coal, yielding significant advancements in understanding the mechanisms and theoretical models of coal under diverse conditions, including damage states, pore pressure, water immersion, and temperature. Experimental studies on coal samples have elucidated the influence of the degree of damage on the mechanical properties and creep deformation, leading to the development of creep-damage constitutive models to investigate creep mechanisms in coal pillars [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Regarding pore pressure, investigations into the creep behavior of coal-rock systems under varying pore pressures have analyzed creep damage states and the impact of creep on permeability through experimental and theoretical approaches [8,18,19,20,21]. Creep tests on water-immersed coal samples have enabled the formulation of creep models to quantify the effects of water content on permeability, creep behavior, and the degradation mechanisms of coal-pillar dams [7,22,23,24,25,26]. Additionally, temperature-dependent creep models have been developed to assess creep deformation under thermal effects [27,28,29,30]. These studies highlight the pivotal role of understanding the intricate creep processes and damage performance of coal dams in CMURs for advancing engineering applications.
The integration of similarity models and numerical simulations provides an effective approach for studying the continuous creep damage of coal pillars, though research on this specific process remains limited. Experimental and numerical simulations encounter significant challenges in capturing time-dependent damage propagation, requiring advanced techniques in material similarity and numerical integration [31,32]. Specifically, similarity model studies must maintain time-scale similarity relationships to ensure that experimental outcomes accurately replicate creep damage under time-varying conditions [33]. Meanwhile, numerical modeling demands robust methods to effectively simulate the progressive nature of creep damage [34]. Notably, similarity-based creep simulations have been successfully applied in other fields, and numerical simulations of continuous damage processes have been conducted in various engineering projects [35,36]. Numerical models offer advantages in time efficiency and provide detailed data for mechanistic analysis, though laboratory-derived parameters and simplified mechanical assumptions may lead to deviations from actual conditions. These successful applications offer valuable reference methodologies for investigating the continuous creep damage of coal pillars, paving the way for significant breakthroughs in understanding creep processes in coal pillars.
Motivated by these challenges, this study conducted laboratory experiments to examine the mechanical properties of water-immersed coal. Additionally, a similarity-based simulation test, combined with numerical modeling, was performed to investigate the continuous creep damage of coal pillars. A comparative analysis of the similarity test and numerical model was conducted, focusing on the damage process and stress evolution. Through a comprehensive analysis of damage progression, stress dynamics, and theoretical insights, this study elucidates the characteristics and underlying mechanisms of continuous creep damage in coal pillars, offering critical insights for enhancing the engineering maintenance and long-term stability of CMUR.
2. Research Methodology
In order to investigate the continuous creep damage of a coal pillar in the CMUR, this paper conducted a set of creep experiments of water-immersed coal samples to obtain their creep performance. Then a similarity model of a generalized strip coal pillar was conducted, aiming to assess the behavior of creep damage. Additionally, associated with the creep experiment of coal samples and our previous creep model, a numerical model of the similarity experiment was utilized to analyze the mechanism of such damage evolution. Details of the creep experiments, similarity modeling, and numerical modeling are introduced as follows.
2.1. Creep Experiments of Water-Immersed Coal
2.1.1. Experiment Materials and Apparatus
The tested coal samples, drilled from Rencheng coal mine of Shandong province, were made into cylinder-shaped ones with a diameter of 50 mm and a height of 100 mm, as displayed in Figure 1a. In order to investigate the creep behavior of water-immersed coal samples, as illustrated in Figure 1b, the vacuum defoamer bucket producted by OTS of China was applied to make coal samples saturated within 8 h. All the immersed coal samples were placed on the platform (Figure 1c) of the MTS815-Flex Test GT rock mechanic testing system (Figure 1d) of the Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development of China, Beijing, China. This system is capable of conducting long-term creep tests for rock materials with a loading capability of axial load up to 4600 kN; the displacement data and loading force can be recorded automatically by the system.
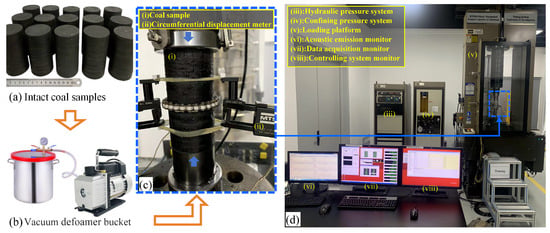
Figure 1.
Tested coal samples and the involved testing system of creep experiments.
2.1.2. Creep Experiment Procedure
A large number of studies revealed that the influence of water immersion on the mechanical properties of coal has a limited time. As suggested by the experiments of Li et al. [37], Ai et al. [38], and Song et al. [39], the effect of water on the coal structure and mechanical properties takes place within approximately 4 weeks. Therefore, immersed coal samples of 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks were tested to assess their creep performance.
Multistage creep experiments with uniaxial compression were implemented in this study. Prior to the creep experiments, the uniaxial compression strengths of the involved coal samples were tested, suggesting an average value of about 16.09 MPa. In the multistage creep experiments, each load increment of stress level is defined as 20 % of the uniaxial compression strength, and the creep duration of each stage is 48 h.
2.2. Similarity Model Test of a Coal Pillar
2.2.1. Generalized Similarity Model
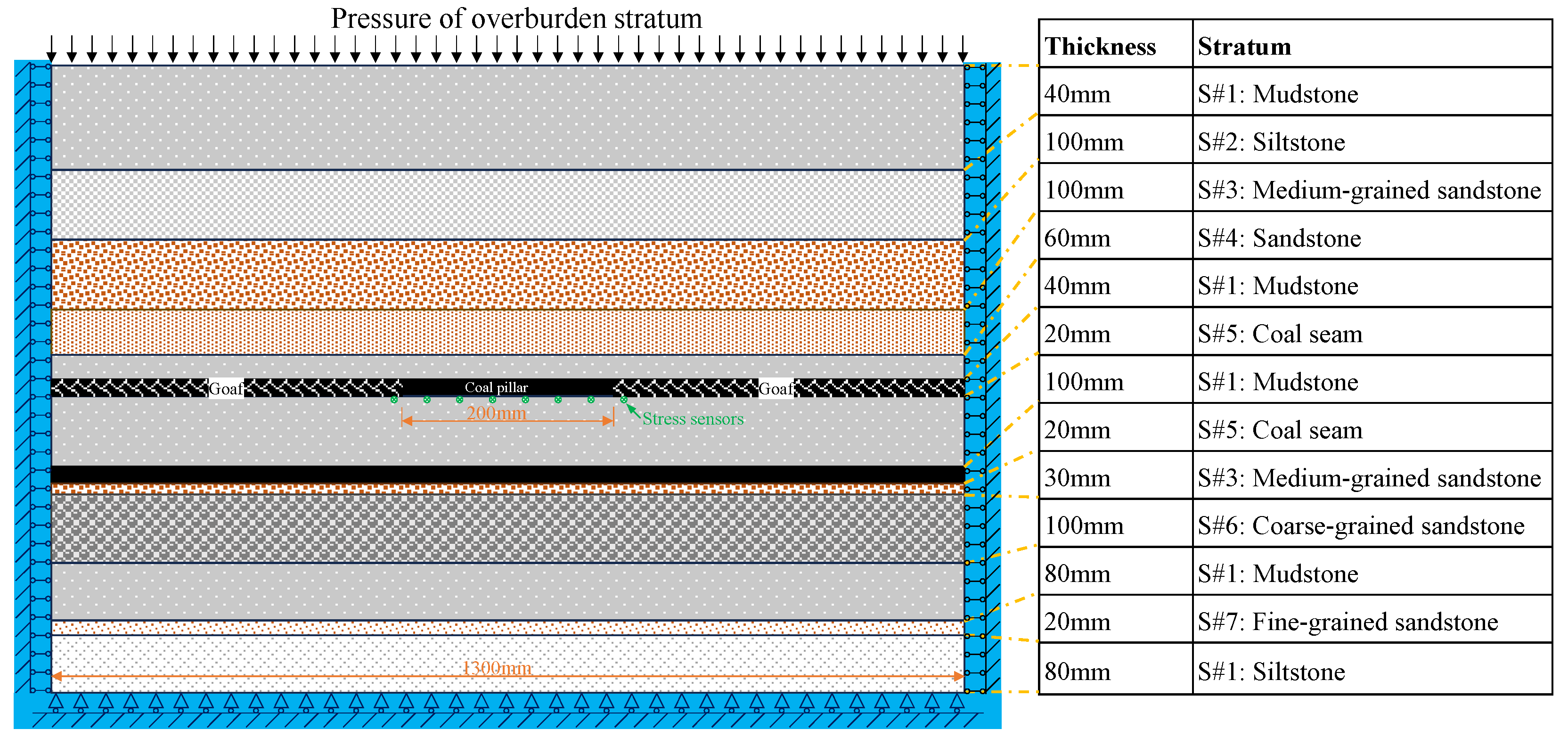
Since the coal pillars in the CMUR are stripped ones, crossing to the axial direction of the coal pillar, the stress and strain status of coal pillars can be generalized as a 2D model [40,41]. The geological conditions of the studied model are referenced as those of a coal mine in China [42]. The similarity ratio in geometry is set at 1:200 in this study, as plotted in Figure 2, and the generalized model for the similarity model experiment has 7 kinds of rock layers according to the experiment platform, namely, mudstone (), siltstone (), medium-grained sandstone (), sandstone (), coal seam (), coarse-grained sandstone (), and fine-grained sandstone (). Since the dimensions available for the similarity model on the platform are 1300 mm × 900 mm × 100 mm, the studied coal pillar is made in the middle area of the model with a length of 200 mm (40 m in the prototype) and a thickness of 20 mm (4 m in the prototype). The mining goaves beside the coal pillar were excavated during the experiment. The displacements of the model were measured by the digital image correlation (DIC) method, and the stress along the bottom surface of the tested coal pillar was detected by the stress sensors. The overburden pressure is simulated by iron blocks with an average pressure of 8.5 MPa in the prototype, corresponding to a depth of 525 m buried coal seam.
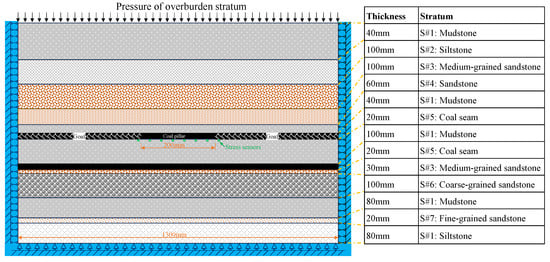
Figure 2.
Generalized model of a coal pillar for the similarity model experiment.
2.2.2. Similarity Ratio and Materials
Corresponding to the prototype, the laboratory model should satisfy the similitude of geometry and statics, but also the similarity in terms of time-dependent properties. In the view of geometric and static similitude, take the length (L), mass (M), and time (T) as the fundamental dimensions, in which the similarity proportions of length and density of the test model to prototype are defined by 1:200 and 1:1.5. Since the similarity ratio of gravity acceleration is naturally 1:1, that of time is . In terns of the time-dependent properties of similar materials, when the Maxwell creep model is applied in the similarity law and considering the viscoelastic-plastic behavior of the coal pillar, the viscosity and creep strength of materials should match the similitude relation [43,44]. According to the similarity law and dimension analysis, the alternatively involved physical quantities and similarity proportion are listed in Table 1. Following the suggestions of Li et al. [42], the physical and mechanical parameters of the coal-measure stratum are listed in Table 2.

Table 1.
Similarity proportion of the physical quantities.

Table 2.
Mechanical parameters of the coal measure stratum.
As suggested by Gong et al. [45] and Yang et al. [46], the compounds of sand, lime, and gypsum were utilized as the basic materials for the Similitude materials of rock layers. The elastic modulus reflects the stiffness of materials in the elastic stage and is a critical parameter for both geometric and mechanical similarity in physical modeling. Compressive strength characterizes a material’s resistance to failure, which is essential for assessing the long-term stability of coal pillars under sustained loads [47]. According to the similarity ratio of the elastic modulus and compressive strength, the similar materials of these 7 types of stratum were determined by orthogonal tests. Specifically, according to the orthogonal regression analysis with different proportions of mixtures, the gravimetric proportions of sand to lime to gypsum for stratum to are determined as 5:0.6:0.4; 7:0.5:0.5; 6:0.2:0.8; 3:0.5:0.5; 9:0.8:0.2; 7:0.5:0.5; and 4:0.2:0.8, respectively.
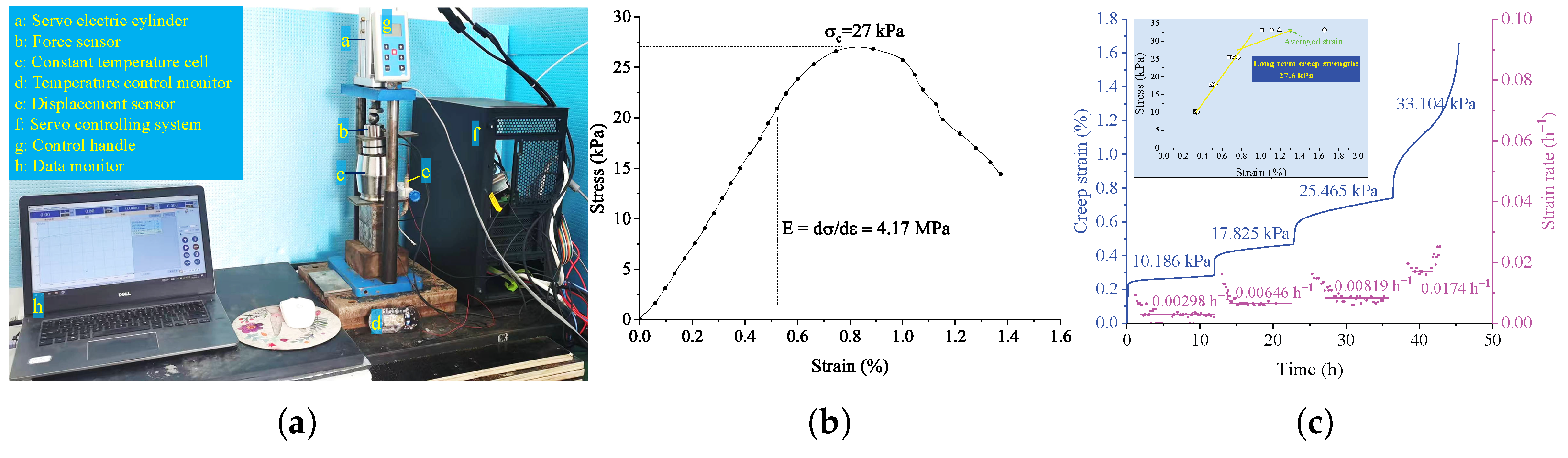
For similar materials of a coal pillar, the mixtures of sand, paraffin powder, gypsum, and lime were utilized with a gravimetric proportion of 7:0.4:0.6:0.2 according to laboratory tests at about 40 C, as displayed in Figure 3a. The measured uniaxial strength and elastic modulus in Figure 3b are 27 kPa and 4.17 MPa, respectively. The creep strain of similar materials for coal pillars is plotted in Figure 3c. The similarity of similar materials is analyzed and compared to the data of water-immersed coal in Section 3.
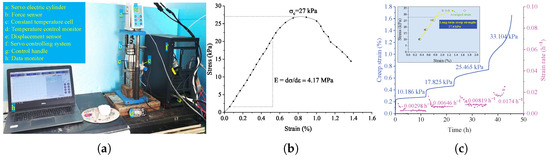
Figure 3.
Laboratory tests for similar materials. (a) Test equipment, (b) uniaxial compression curve, and (c) creep strain curve.
2.2.3. Model Test Procedure
The physical model of Figure 2 was excavated to form the goafs beside the coal pillar at one time. Then the fine copper tube (0.8 mm in diameter) was heated and kept at a constant temperature of about 40 C. Considering the effect of water immersion on the coal pillar, which is very fast, and for the sake of accelerating the experiment process, the temperature was raised to 60 C. This physical model experiment lasted about 1 month, and the coal pillar failed. The temperature in the experiment is around the phase transition temperature of paraffin powder. In such a case, the materials may have a certain degree of thermal expansion, while such thermal strain is very small; therefore, the influence of temperature is limited to the mechanical distribution of the similar model.
2.3. Numerical Modeling of a Coal Pillar
2.3.1. Numerical Model Setup
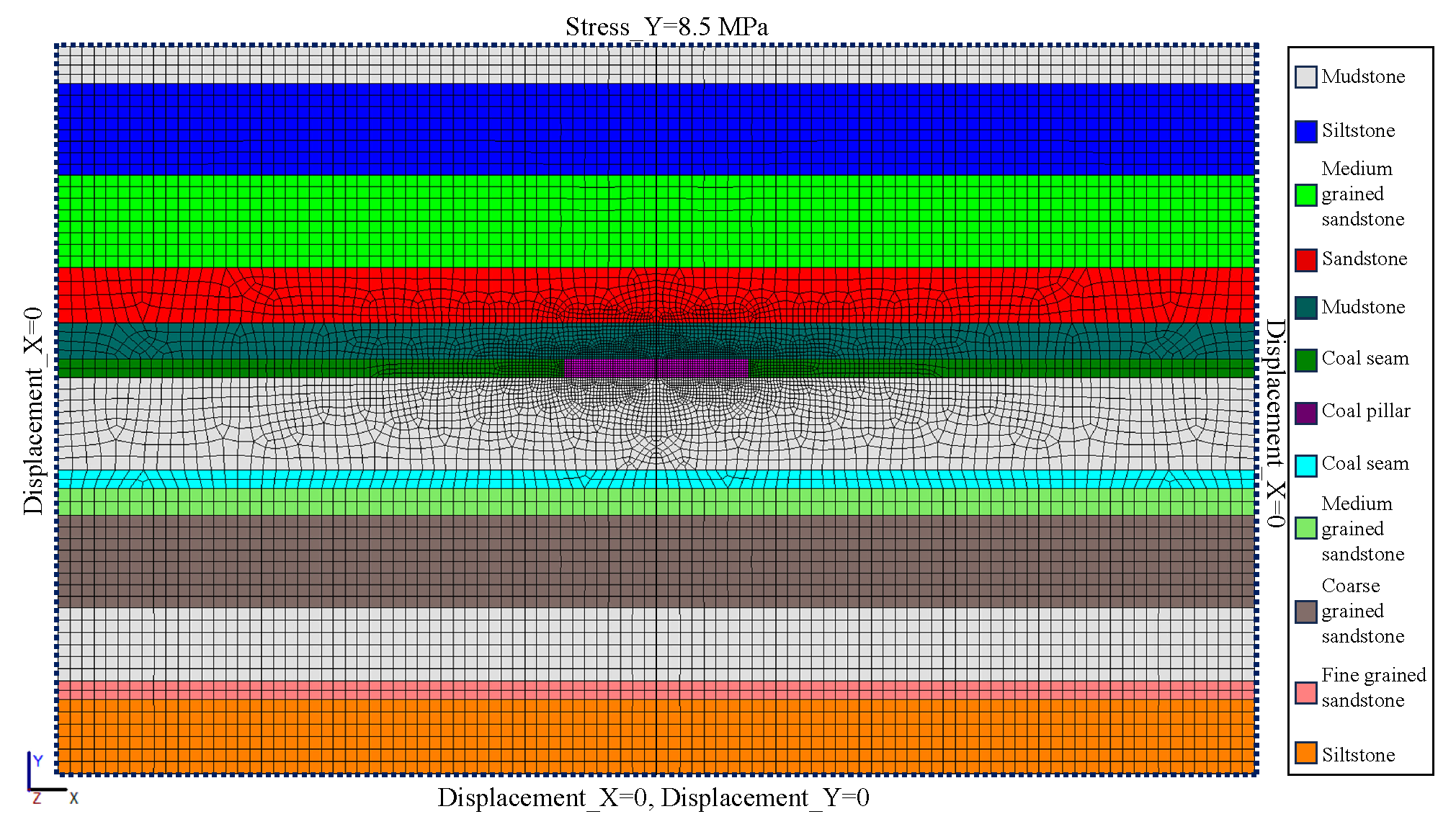
The prototype model of Figure 2 was numerically modeled by multi-physical software, namely, OpenGeoSys 5.8. This software is an open source platform allowing one to insert the computation model into the code source in the C++ program [48]. The numerical model is displayed in Figure 4, in which 12,214 quad elements are adopted in the modeling. The sizes of the element of the coal pillar are 0.5 m × 0.5 m, and the maximum dimension of the element in this model is limited to 2 m.
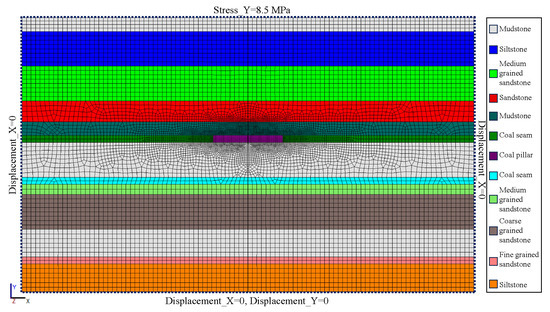
Figure 4.
Numerical model of a coal pillar in CMUR.
2.3.2. Boundary Conditions
The boundary conditions of the numerical model are the same as the physical model, as shown in Figure 4. Specifically, the left and right sides were fixed in normal displacement, and the bottom side was fixed in both the vertical and lateral displacement; the top side of the model was loaded with a constant pressure of 8.5 MPa.
2.4. Parameters Assign
The parameters in Table 2 are used in the numerical modeling for calculating the elastoplastic status of the model. Additionally, for the coal pillar, the creep parameters for a modified Maxwell model, which considered the plastic deformation of materials, were identified from the creep data of water-immersed coal samples. The consideration of choosing this mode is the similarity relationship on the viscosity of similar materials and the coal sample, which is based on the modified Maxwell model, and the implementation of numerical integration available in OpenGeoSys software. The governing equation for the creep deformation of coal pillar can be expressed by
in which , , , and represent the total strain, elastic strain, viscoelastic strain, and viscoplastic strain, respectively. , , , , K, G, and f mean the volumetric stress, derivative stress, viscosity for viscoelastic deformation, viscosity for viscoplastic deformation, bulk modulus, shear modulus, and yield potential, respectively. is the Macaulay bracket which includes the cases of when and when . According to the creep strain of the coal samples immersed for 8 weeks, the creep parameters of coal are determined by Equation (1) as GPa, GPa, Pa·h, and Pa·h. The Drucker–Prager criteria are applied as the yield potential; thus, the cohesion and friction of the coal seam in Table 2 was used in the modeling.
3. Experiment Result Analysis
3.1. Creep Behavior of Water-Immersed Coal
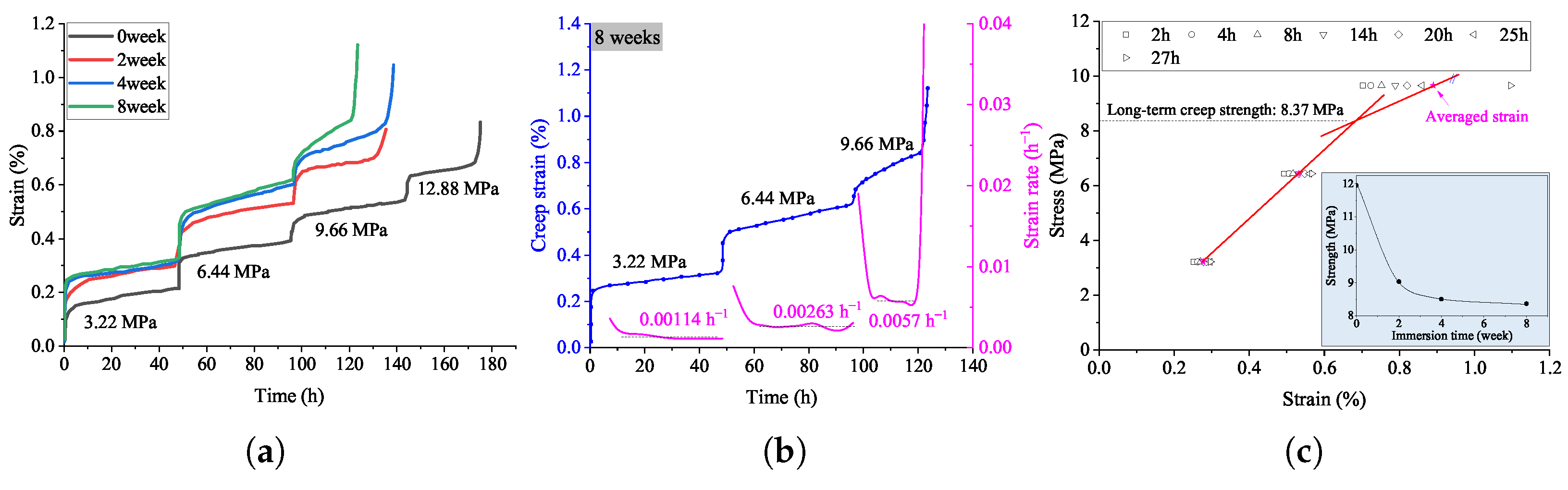
The measured creep strain of coal samples immersed from 0 to 8 weeks are plotted in Figure 5a. One can see that prolonged water immersion significantly influences the creep behavior of coal samples. The initial instantaneous strain exhibits a clear upward trend with increasing immersion time, rising from approximately 0.16% for non-immersed (0-week) samples to about 0.25% for 8-week-immersed samples, indicating that water softens the coal structure and enhances its initial deformation capacity. This is because of the water–rock interaction, exhibiting mineral dissolution, pore volume increase, structure softening, etc. [29,49]. In addition, at the lower stress condition, the creep behavior of coal after 2 weeks’ immersion is similar, and the coal samples failed at the third creep stage, which means water immersion decreased the strength of coal. In detail, at the first and second creep stage of the coal immersed for 4 and 8 weeks, their strains are very close to each other. As pointed out by Huang et al. [50], the structure changes induced by water immersion were complemented after about 2 weeks, and in the third stage, the strain of 8-week-immersed coal increased quickly with time, exhibiting fast creep damage under such creep stress, which was maybe caused by different consequences of the structure changes in different coal samples. Notably, the 8-week-immersed samples attain a final strain of approximately 1.15%, substantially higher than the 0.78% observed in non-immersed samples, underscoring the significant reduction in creep strength due to prolonged water immersion. These findings highlight the critical role of water immersion in accelerating creep deformation and weakening the long-term mechanical stability of coal. In the case of CMURs, once water gets into the coal pillar through the damaged fracture, the intact coal will be weakened in stiffness and strength, and consequently, new creep damage occurs and propagates forwards.
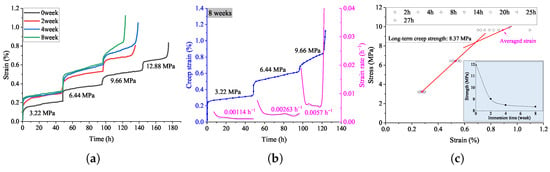
Figure 5.
Laboratory experiment results of (a) the creep strain curves of coal samples immersed at various times, (b) the strain rate, and (c) the isochronous curves of the sample immersed for 8 weeks.
Considering the effect of water immersion on coal materials is short in time. The physical model test and numerical modeling are based on the performance of coal immersed for 8 weeks. Its creep strain is displayed in Figure 5b, compared to the data of similar materials, as shown in Figure 3c, and the tendency of creep strain curves are shown to be close to each other, exhibiting the strain rate was increased about 2-fold in the next stage. As per Xia et al. [51], the softening effect of water to coal increases the viscosity of coal and increases the boundary lubrication of solid grain, thereby promoting the creep strain rate and reducing the strength of coal. According to the creep strain, the long-term strength of the coal and similar materials can be obtained by the isochronous curves [52], as shown in Figure 3c and Figure 5b. It is notable that the long term strength of coal decreases with immersion time, exhibiting an exponential deduction tendency, and the long term creep strength of the coal sample immersed for 8 weeks and the similar material are approximately 8.37 MPa and 27.6 kPa, the similar ratio of which is about 303:1, which matches well the similar ratio of strength in Table 2. Therefore, the materials for the physical model satisfy the similitude relations to the prototype coal pillar.
3.2. Evolution of Creep Damage in a Coal Pillar
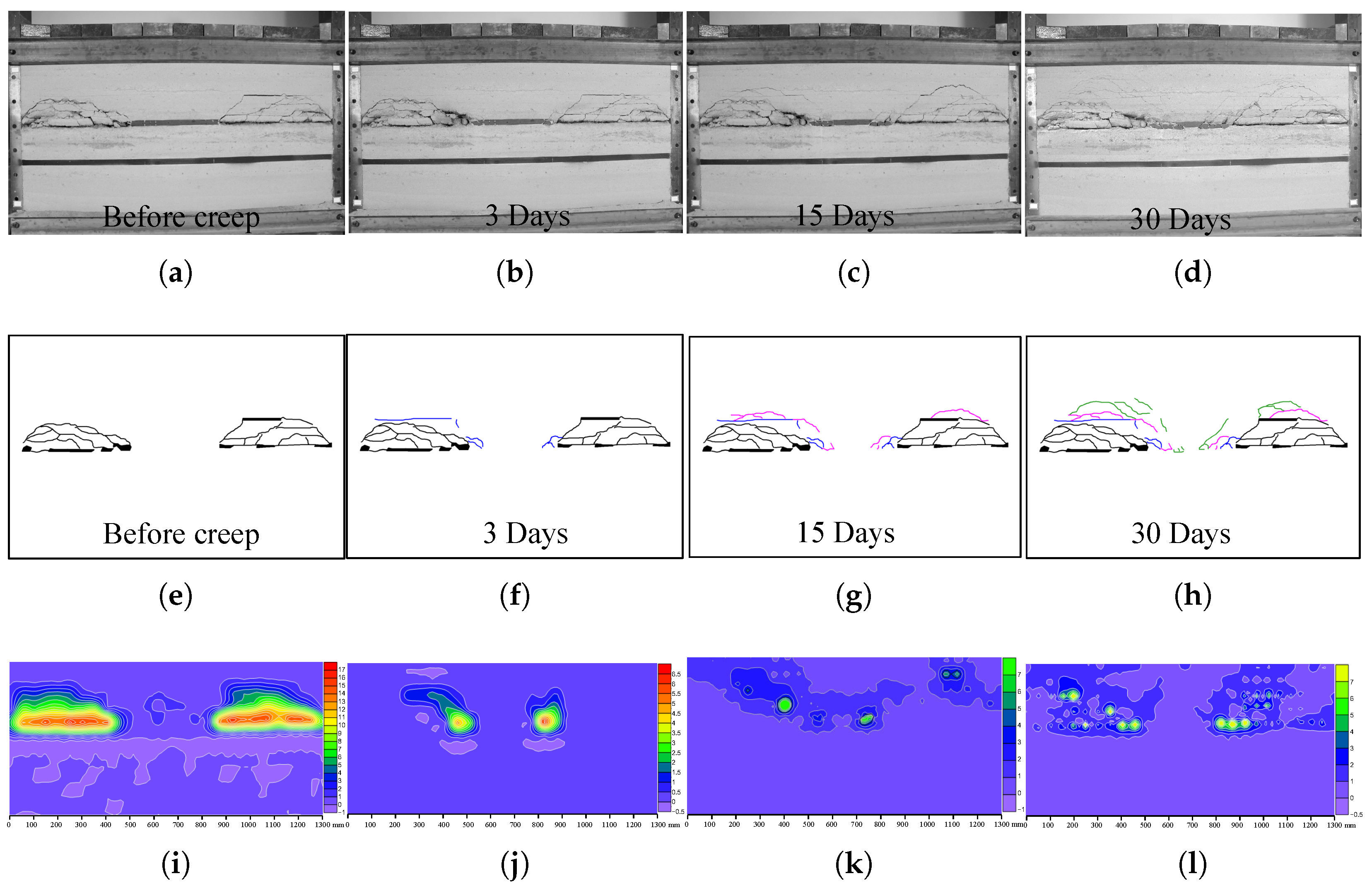
Th0e physical model shows the processes of damage in a coal pillar and rock layers, as displayed in Figure 6. In this figure, Figure 6a to Figure 6d are the field pictures of the physical model after excavation and creep of 3 days, 15 days, and 30 days, respectively. In order to better analyze the evolution of the creep damage of the studied coal pillar and overburden rock layers, Figure 6e to Figure 6h and Figure 6I to Figure 6l give the characterized fractures and displacement corresponding to Figure 6a to Figure 6d.
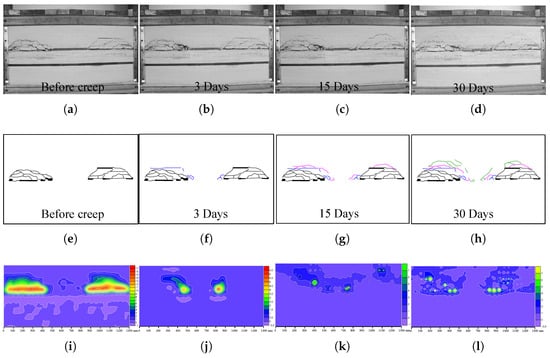
Figure 6.
Result of the physical model in terms of (a–d) field pictures, (e–h) characters of fracture evolution, and (i–l) displacement increment measured by digital image correlation before creep and with creep of 3 days, 15 days, and 30 days, respectively.
Obviously, fractures propagated gradually during the creep of a coal pillar. In more detail, Figure 6a,e, typical mining-induced fracture appeared over both the left and right goaves, correspondingly, and a large displacement was observed in the fractured areas (please see Figure 6i). When the model was subjected to the creep experiment, creep damage was observed in the coal pillar, leading to fracture propagation in the overburden rock layers, specifically, on the third day, and new fractures appeared above the side wall of the coal pillar. In addition, the damaged coal pillar parts were extruded forward to the mined goaf (see Figure 6b). On the 15th day, as shown in Figure 6c,g, new creep failure occurred in the coal pillar, fracture in the overburden rock layer interacted (please see the red line in Figure 6g with slight deformation (as shown in Figure 6k). With the creep damage of the coal pillar moving forward to the center part and the time reaching 30 days, damaged fractures occurred in the roof and the height of fractures was increased, which led to rock movement at both the roof above the coal pillar and the rock layers above fracture zones (see Figure 6h,l). As a whole, the creep damage in the coal pillar shows a continuous and steep propagation, and as a consequence, overburden rock layers moved and fracture propagated towards the center part of the coal pillar.
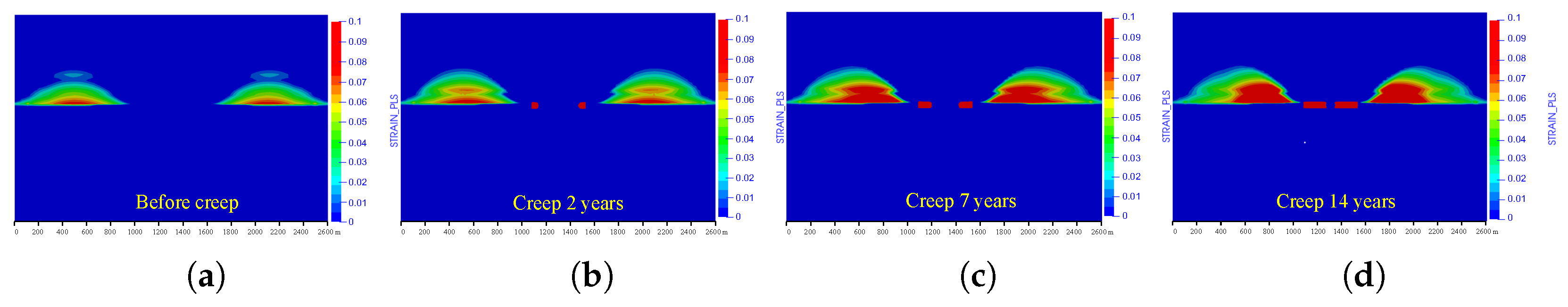
The numerical modeling work calculated the whole process of the coal excavation and creep deformation of the coal pillar, and the plastic strain within 14 years is illustrated in Figure 7. Figure 7a to Figure 7d suggest that the coal pillar was damaged and concentrated on the left and right sides of the coal pillar. As the creep period increased, the degree of damage steadily increased, and the damage range gradually broadened. Meanwhile, the damaged area in the roof was extended toward the middle part of the model, and these areas were expanded in both vertical and lateral directions. A comparison in Figure 7a to Figure 7d and Figure 6e to Figure 6h suggests a good match in the evolution of damaged zones.
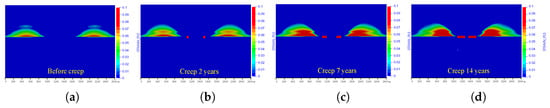
Figure 7.
Numerical modeling results of the plastic strain (a–d) before creep and creep of 2 years, 7 years, and 14 years, respectively.
Obviously, both the physical and numerical models suggest the coal pillar will be damaged continuously during the creep process, thereby leading to crack propagation in the roof layers. In addition, the numerical modeling has a good capacity of recovering the evolution of creep damage in both the coal pillar and overburden rock layers, which is proper for the analysis of the mechanism of creep damage in the coal pillar.
4. Mechanism of Creep Damage in a Coal Pillar
4.1. Stress Evolution in the Coal Pillar
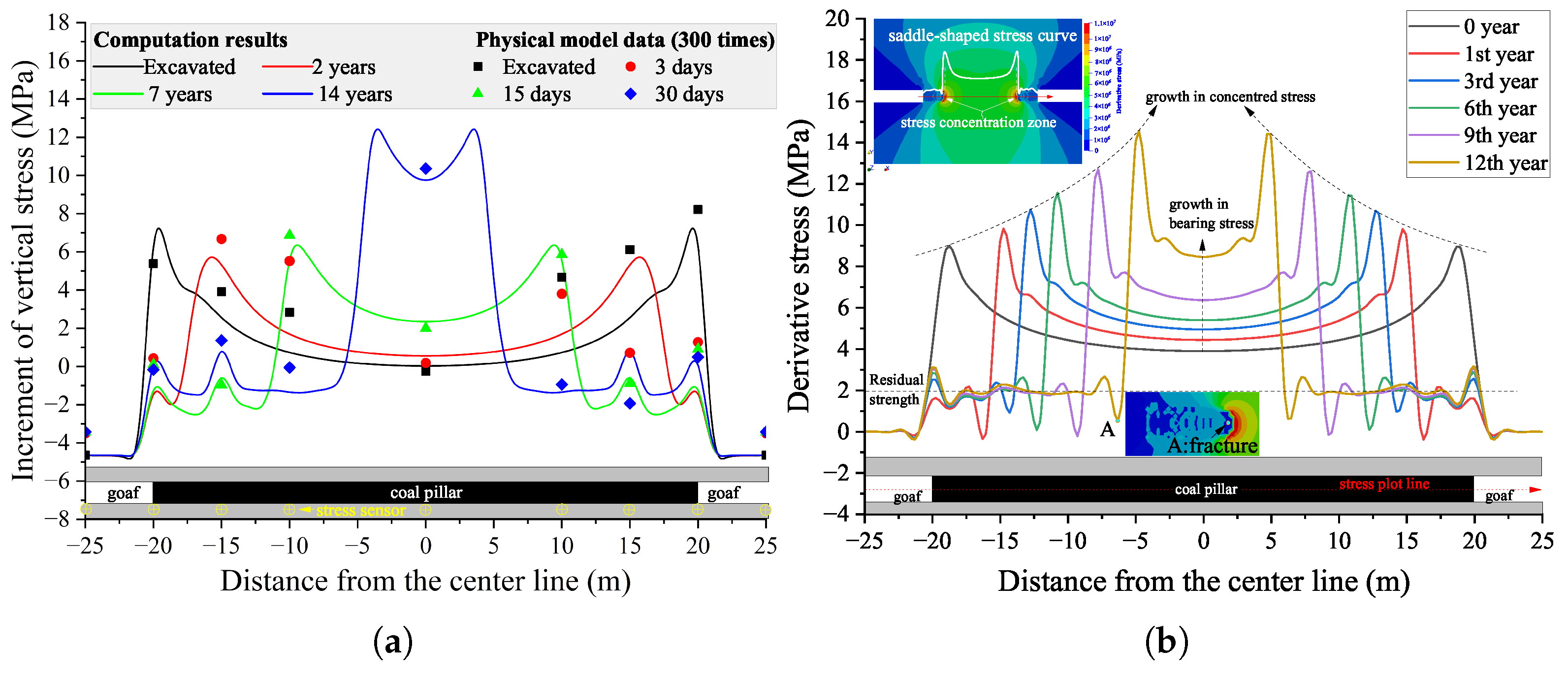
The above analysis of the damage process of a coal pillar and the overburden rock layers shows continuous damage evolution, which will lead to stress redistribution in the coal pillar, thereby inducing the status of creep loading in a coal pillar. The increment of vertical stress in the similar model (amplified according to the similitude ratio of stress) and the numerical one are compared in Figure 8a, despite some measured stress in the physical model failed to show the maximum stress point, such as the measurements on the right side of the physical model on the third day. Some difference exists between the measured data and calculated ones; the stress ranges along the coal pillar of the numerical model are close to those of the similar model. Therefore, numerical modeling can recover the stress status in the prototype of a similar model.
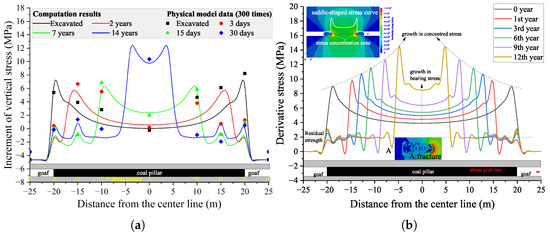
Figure 8.
Stress distribution in the coal pillar. (a) A comparison of the increment of vertical stress in the numerical model and the physical model; (b) evolution of the calculated derivative stress along the coal pillar.
The creep behavior is well known to the effect of derivative stress, as plotted in Figure 8b. The evolution of derivative stress along the coal pillar has a saddle-shaped curve; more specifically, the stress concentration zone at both sides of the coal pillar increase the stress, and then the middle part of the coal pillar has a stable bearing stress distribution. With the creep damage propagated toward the center part of the coal pillar, the concentrated stress moved correspondingly before the damaged edges. In addition, the maximum concentrated stress grew higher and higher; this is because the bearing stress in the elastic zone of the coal pillar was increased due to the shrinkage of elastic areas and the contraction of the damaged coal parts, which still have certain residual strength. Interestingly, as shown in Figure 8b, the fluctuation of the stress curves was observed before the concentrated stress area, which is induced by the fracture distribution in the damaged zone.
4.2. Theoretical Analysis of the Creep Damage of a Coal Pillar
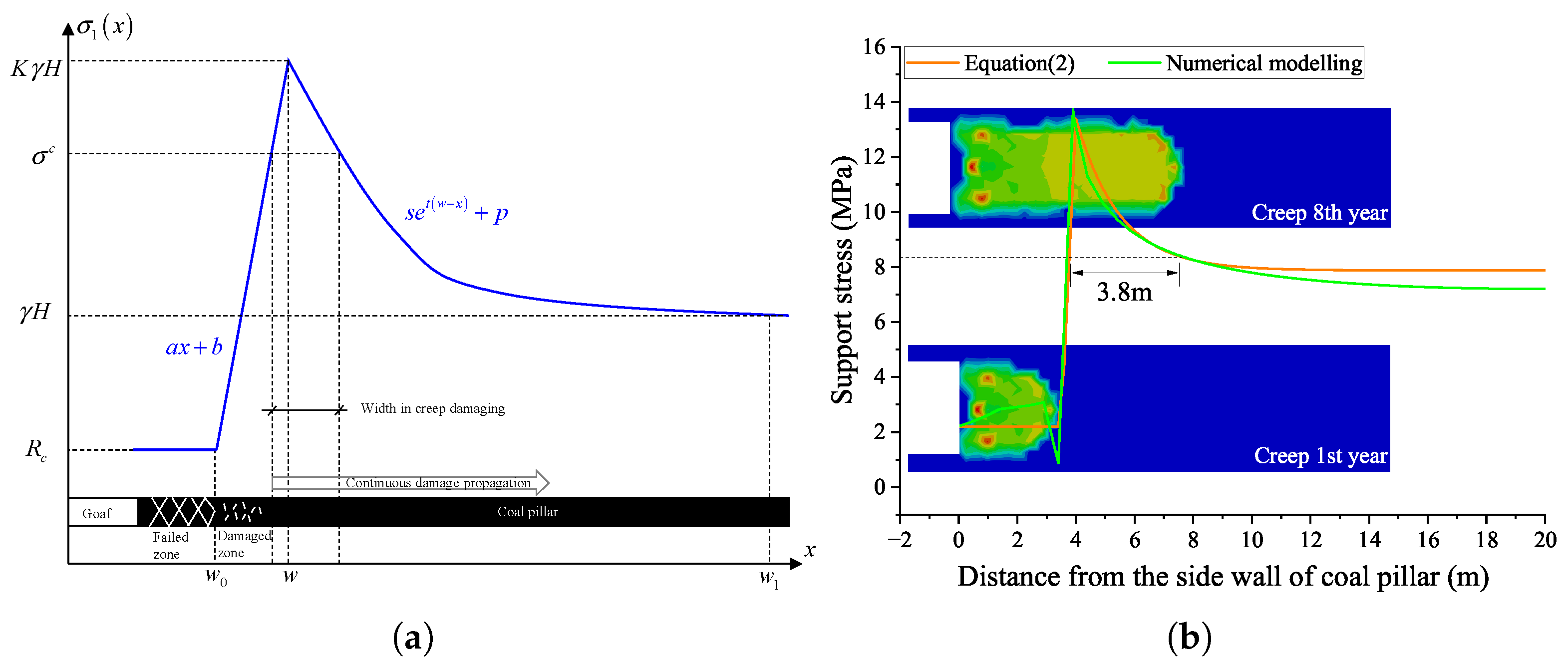
Both the similar model and numerical model suggest continuous creep damage in a coal pillar; the concentrated stress will still exist and move forward to the elastic area. Theoretically, for half of a coal pillar, the support stress distribution along the coal pillar has a formulation as shown in Figure 9a.
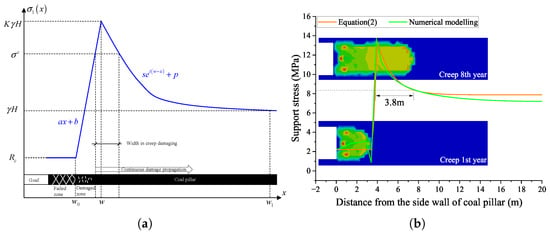
Figure 9.
Distribution of supporting stress as (a) a diagram and (b) a comparison between the data of numerical modeling along the coal pillar.
For an empirical expression of such a stress curve, the support stress inside and outside the plastic bearing zone is simplified into a mathematical model of linear increase and negative exponential decay, respectively, which is also called the mining support stress as defined by [53]
In which, x means the distance from the wall of the coal pillar (unit: m); w is the width of the plastic bearing zone of the coal body on one side of the goaf (unit: m); and a, b, s, m, and p are the parameters for the support stress model. According to the bearing characteristics of the surrounding rock on one side of the goaf, the model boundary conditions are
- When , the coal mass supporting stress is the peak stress , where K is the peak stress concentration coefficient.
- When , the coal mass supporting stress is the residual strength of the coal mass .
- When the distance x from the coal wall of the goaf approaches infinity, the supporting stress is the original rock stress .
Based on the above boundary conditions, the parameters of this model are solved as [54]
From Figure 9, one can find the width of a coal pillar in damaging process d, and according to Equations (2) and (3), this width can be determined by
In the studied case, let , MPa, = 17,500 N/m, m, MPa, m, and m. One can deduce the width of the coal pillar in the damaging process is about m, as shown in Figure 9b, and the calculated data according to Equation (2) is close to the result of numerical modeling, in terms of the support stress and the plastic strain areas. Therefore, the theoretical model is appropriate to describe the width of the coal pillar in the damaging process. It is reasonable to say that the concentrated stress over the creep strength drives the damage propagation in the coal pillar. From Figure 9, one can see that since water immersion decreases the creep strength of the coal pillar, the lower the creep strength , the wider the size of the coal pillar in the damaging process.
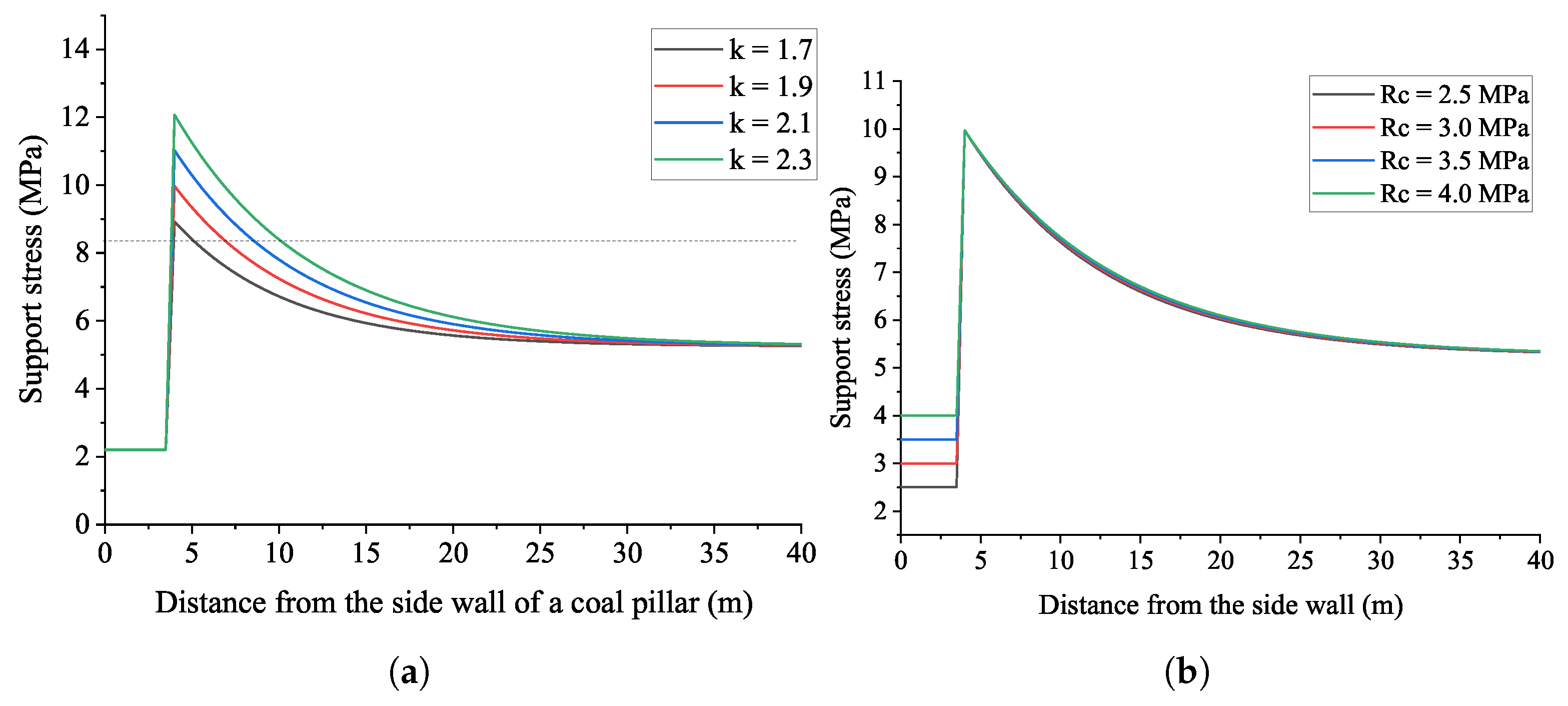
The influence of variable stress concentration coefficient and residual strength of coal on the support can be analyzed based on Figure 10.
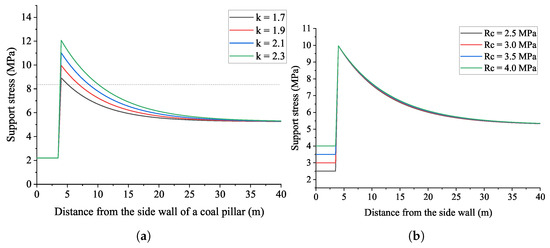
Figure 10.
Sensitive analysis on the parameters of (a) the stress concentration coefficient K and (b) the residual strength of coal .
In Figure 10a, one can see that the increased stress concentration coefficient enlarges the peak stress and slows the deduction of support stress after the peak value. In such a case, the width of the coal pillar within potential creep damage is increased; for instance, when , the width of the creep damage is about 2 m, and when , the value is promoted to about 7.5 m. The influence of residual strength on the support stress can be seen in Figure 10b. Obviously, the peak stress and the evolution of stress after peak stress are very limited. Therefore, the stress concentration coefficient is more sensitive to the support stress.
5. Discussion
In this study, experimental results from water-immersed coal samples indicate a significant reduction in creep strength. Theoretical analysis reveals that water immersion hastens coal pillar failure by inducing damage fractures ahead of the plastic zone, thereby increasing pillar permeability and exacerbating the water immersion effect.
Through the integration of similarity models and numerical simulations, it was observed that damage in the overlying rock layers forms water conduction channels. For instance, as the fracture propagation in Figure 6e to Figure 6h shows, wasted mine water is always stored in the mined goaf and the mining-induced fractures. When fractures through the coal pillar and laminated fractures were formed in the overburden rock layer, water channel may have occurred in the coal pillar and its overburden rocks. These channels are influenced by factors such as overburden pressure, water storage pressure, mining-induced stress, and the structural characteristics of the coal pillar [55]. Such channels significantly impair the anti-seepage performance of CMURs.
Furthermore, long-term exposure to concentrated saline water leads to the deterioration of coal pillars [56]. To address this, robust anti-seepage measures, including protective coatings, are crucial to isolate coal pillars from saline water contact. For corrosion channels formed within the coal pillar dam body due to prolonged immersion, grouting reinforcement is recommended to bolster the structural integrity of the coal pillar dam [57].
In summary, this study elucidates the significant reduction in the long-term strength of coal due to water immersion and the evolutionary law of creep damage in coal pillars. Specifically, the identified creep damage evolution can inform the development of stability assessment standards for CMUR coal pillars. Additionally, anti-seepage design can be optimized based on the fracture propagation process. Furthermore, the coal pillar width can be adjusted according to stress distribution changes to minimize the risk of concentrated stress exceeding critical limits.
6. Conclusions
This study investigates the creep damage behavior of coal pillars through laboratory experiments, similarity model testing, and numerical modeling, analyzing the damage process, stress evolution, and mechanisms of damage propagation. The findings yield the following conclusions:
- Water immersion significantly affects the long-term mechanical properties of coal, leading to material softening and a reduction in creep strength. Initial instantaneous strain increases with immersion time, from 0.16% for non-immersed samples to 0.25% for 8-week-immersed samples, with final strain reaching 1.15% in the latter, compared to 0.78% in the former.
- The combined approach of similarity modeling and numerical simulation effectively captures the creep damage processes in coal pillars. On day 3, new fractures formed above the coal pillar sidewall, with damaged sections extruding into the goaf. By day 15, further creep failure triggered overburden fracture interactions and slight deformation. By day 30, damage progressed to the pillar’s core, with creep-driven fractures continuously propagating centrally, accompanied by overburden rock movement.
- During the creep damage process, the trapezoidal stress distribution along a coal pillar undergoes significant changes, characterized by increasing concentrated and bearing stresses within the pillar.
- Redistributed concentrated stress, exceeding the long-term strength of coal, drives damage propagation toward the pillar’s center, resulting in continuous creep damage.
This study primarily gives out the evolution law of creep damage in a coal pillar of a coal mine underground reservoir and the mechanism of the creep damage process. According to the outcome of this paper, the engineering measures and the assessment method according to the theory model of this paper are still needed for further study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Y. and H.Y.; Methodology, X.L.; Validation, S.Y. and X.G.; Formal analysis, Q.G.; Investigation, Z.C. and X.C.; Writing—original draft, X.L.; Writing—review and editing, Q.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Founding Committee (Grant No. 52274165), the Hebei Natural Science Founding Committee (Grant No. E2024508032), and the Project of Tianma Intelligent Control (Grant No. 2024-TM-014-J1).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data available are included in the present paper.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to Zhide Wu for their great help with the laboratory experiment, and additional thanks are given to Ze Li, Huan Yu and Tianzi Zhang for their help with the similar model experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Xueliang Li was employed by the company Beijing Tianma Intelligent Control Technology Co., Ltd. Author Xiangjun Cai was employed by the company Kailuan Energy Chemical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Bai, Q. Underground space utilization of coalmines in China: A review of underground water reservoir construction. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 107, 103657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J.; Liang, B. Study on the strength deterioration characteristic and damage model of coal pillar dams with repeated water immersion in underground reservoirs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Kou, M.; Li, M. A review of stability of dam structures in coal mine underground reservoirs. Water 2024, 16, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, G.; Zhang, H.; Qi, C.; Zhang, J. Failure analysis of coal pillars and overburden from underground water reservoir under the mining-water invasion coupling effect. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 151, 107406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Liu, W. Evaluation of long-term tightness of the coal pillar dam of underground reservoir and protection countermeasures. Energies 2023, 15, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, Q.; Li, X.; Zheng, C. Creep characteristics and long-term strength of underground water reservoirs’ coal pillar dam specimens under different osmotic pressures. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 141901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Xue, D.; Li, Z.; Ma, X. Creep behavior and permeability evolution of coal pillar dam for under-ground water reservoir. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.N.; Chen, Z.; Connell, L.D.; Kizil, M.S.; Pan, Z.; Aminossadati, S.M. Characterisation of creep in coal and its impact on permeability: An experimental study. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 173, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Han, P.; Bai, Q. Coal pillar failure analysis and instability evaluation methods: A short review and prospect. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.D.; Bai, J.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Yan, S.; Wu, S.X. Numerical study of failure mechanisms and control techniques for a gob-side yield pillar in the Sijiazhuang coal mine, China. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2019, 52, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yin, D. Experimental study on progressive failure characteristics of strip coal pillar models under different roof and floor conditions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, W. Microscopic Damage Mechanism of Coal Sample Under Uniaxial Compression Test Under Different Creep Pre-damage. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, J.; Spearing, A.; Chai, J.; Dong, C. Experimental study of the creep properties of coal considering initial damage. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 139, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, B.; Huang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y. The nonlinear creep behavior and creep damage constitutive model of coal rock. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, E.; Feng, X.; Wei, M.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, X. Triaxial creep damage–catastrophe instability characteristics and a nonlinear constitutive model of gas-bearing coal. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Xu, P.; Ranjith, P.G. Damage model of coal under creep and triaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 80, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zong, D.; Ma, L. Creep damage characteristics and constitutive model of pre-damage coal. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 158, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Zhou, H.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Pore-pressure and stress-coupled creep behavior in deep coal: Insights from real-time NMR analysis. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, S. Creep characteristics and creep model of coal based on pore water pressure. Processes 2023, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.N.; Chen, Z.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Kizil, M.S.; Pan, Z.; Connell, L.D. Impact of creep on the evolution of coal permeability and gas drainage performance. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Rong, T.; Wang, L. Effects of matrix-fracture interaction and creep deformation on permeability evolution of deep coal. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 127, 104236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, Y.; Rong, T.; Wang, L. Creep constitutive model and numerical realization of coal-rock combination deteriorated by immersion. Minerals 2022, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, D. Characterization of multi-step creep behavior and fractional derivative modeling for a water-saturated coal. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2024, 28, 2771–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, S.; Dang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J. Study on mechanical characteristics and energy accumulation and release law of coal samples with different saturation and creep damage. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2024, 44, 1477–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Zheng, C. Permeation–strain characteristics and damage constitutive model of coal samples under the coupling effect of seepage and creep. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 127, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Yang, G. Experimental study on creep characteristics of infiltrated coal-rock under load. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2023, 93, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Su, T.; Wei, Q.; Deng, T. A triaxial creep model for deep coal considering temperature effect based on frac-tional derivative. Acta Geotech. 2023, 17, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ju, Y.; Deng, T. On permeability evolution of coal induced by temperature, creep, and matrix–fracture interaction. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Hu, K.; Xie, S.; Jia, W.; Song, L. A Fractional Creep Model for Deep Coal Based on Conformable Derivative Con-sidering Thermo-Mechanical Damage. Processes 2024, 12, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, L. Fractional creep model of temperature-stress-time coupled damage for deep coal based on temperature-equivalent stress. Results Phys. 2022, 39, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yan, G.; Kong, S.; Bai, X.; Du, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Study on the Creep of Damage-Containing Anthracite: Theory and Experiment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, E.; Ding, Z. Research on the creep model of deep coal roadway and its numerical simulation re-production. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Li, C. Similar simulation test study on permeability evolution mechanism of fault sliding fracture zone. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wei, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Simulation analysis of the evolution law of creep rupture crack extension in X-fractured rock body. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Ch, J.G.; Senent, S.; Zeng, P.; Jimenez, R. DEM simulation of rock creep in tunnels using Rate Process Theory. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 142, 104559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhu, S.-F. Creep damage characterization of UNS N10003 alloy based on a numerical simulation using the Norton creep law and Kachanov–Rabotnov creep damage model. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2019, 30, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H. Experimental study of water storage soaking of coal mine underground reservoir to coal pillar dam body strength. Coal Min. Technol 2018, 23, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, T.; Wu, S.; Zhang, R.; Gao, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Z. Changes in the structure and mechanical properties of a typi-cal coal induced by water immersion. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 138, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhai, X.; Ma, T.; Wang, B.; Hao, L.; Zhou, Y. Effect of water immersion on pore structure of bituminous coal with different metamorphic degrees. Energy 2023, 274, 127449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Walton, G. Modeling the behavior of a coal pillar rib using bonded block models with emphasis on ground-support interaction. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 148, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, M.; Li, C. Optimization of staggered distance of coal pillars in multiseam mining: Theoretical analysis and numerical simulation. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, D.; Li, G.; Wei, S.; Wu, B. Feasibility Study on the Construction of Underground Reservoirs in Coal Goaf—A Case Study from Buertai Coal Mine, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, T.; Ran, J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H. Model test on creep deformation and failure characteristics of soft rock roadways. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 141, 106670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Gutierrez, M. Viscous-elastic-plastic response of tunnels in squeezing ground conditions: Analytical modeling and experimental validation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 146, 104888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.F.; Zhu, C.Y.; Zhu, G.W. Analysis of physical parameters of materials similar to coal and rock mass based on geophysical model construction of mines. Appl. Geophys. 2023, 20, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yue, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W. Experimental study on ratio optimization of similar materials for underground mining of Shendong coalfield: A case study of Shangwan coal mine. Processes 2023, 11, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, H.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chu, T. Study on the instability activation mechanism and defor-mation law of surrounding rock affected by water immersion in goafs. Water 2022, 14, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolditz, O.; Bauer, S.; Bilke, L.; Böttcher, N.; Delfs, J.O.; Fischer, T.; Zehner, B. OpenGeoSys: An open-source initiative for numerical simulation of thermo-hydro-mechanical/chemical (THM/C) processes in porous media. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Ma, J.; Hu, J. Microstructural Evolution and Damage Mechanism of Water-Immersed Coal Based on Physicochemical Effects of Inorganic Minerals. Materials 2024, 17, 5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. The influence of water immersion on the physical and chemical structure of coal. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2022, 194, 1136–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Research on damage mechanism and mechanical characteristics of coal rock under water immersion. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocente, J.C.; Paraskevopoulou, C.; Diederichs, M.S. Estimating the long-term strength and time-to-failure of brittle rocks from laboratory testing. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 147, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Tu, M.; Fu, B. Research on the redistribution law of lateral mining stress and the bearing characteristics of section coal pillar in extra-thick fully mechanized top-coal caving mining. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 4355977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.F.; Shen, W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.B.; Zhu, R.R. Study on Stress Weakening of Surrounding Rock in Lower Coal Roadway of Close Distance Coal Seam Based on Average Stress Concentration Difference. Coal Technol. 2023, 42, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Galav, A.; Singh, G.S.P.; Sharma, S.K. A numerical modeling approach for assessment of seepage characteristics and performance of protective water barrier pillars in underground coal mines. Sustainability 2022, 39, 2047–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Ji, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Yi, S.; Shi, X. Insight into the mechanical degradation of coal corroded by concentrated brine solution. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2024, 38, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhao, G.; Meng, X.; Cheng, X.; Gu, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhu, S. Development of cement-based grouting material for reinforcing narrow coal pillars and engineering applications. Processes 2022, 10, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).