Research on the Characteristics of Electrolytes in Integrated Carbon Capture and Utilization Systems: The Key to Promoting the Development of Green and Low-Carbon Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electrolyte for Carbon Capture and Electrocatalytic Applications
- Expanding system compatibility with various electrode materials [7] and operational conditions.
2.1. Bicarbonate Electrolyte
2.2. Amine-Based Electrolytes
- 2345 cm−1: gaseous CO2 consumption (O=C=O asymmetric stretching, vas);
- 1675 cm−1: carboxyl group formation at the electrode interface (C=O stretching, v);
- 1607 cm−1: carboxylate ion generation (COO− asymmetric stretching, vas);
- 1604 cm−1: free amine regeneration (N-H in-plane bending, δ).
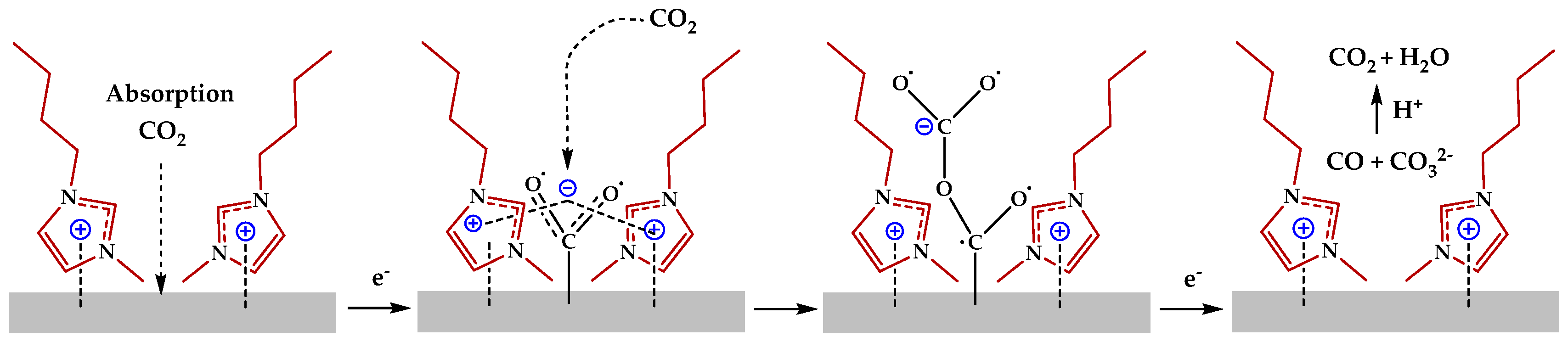
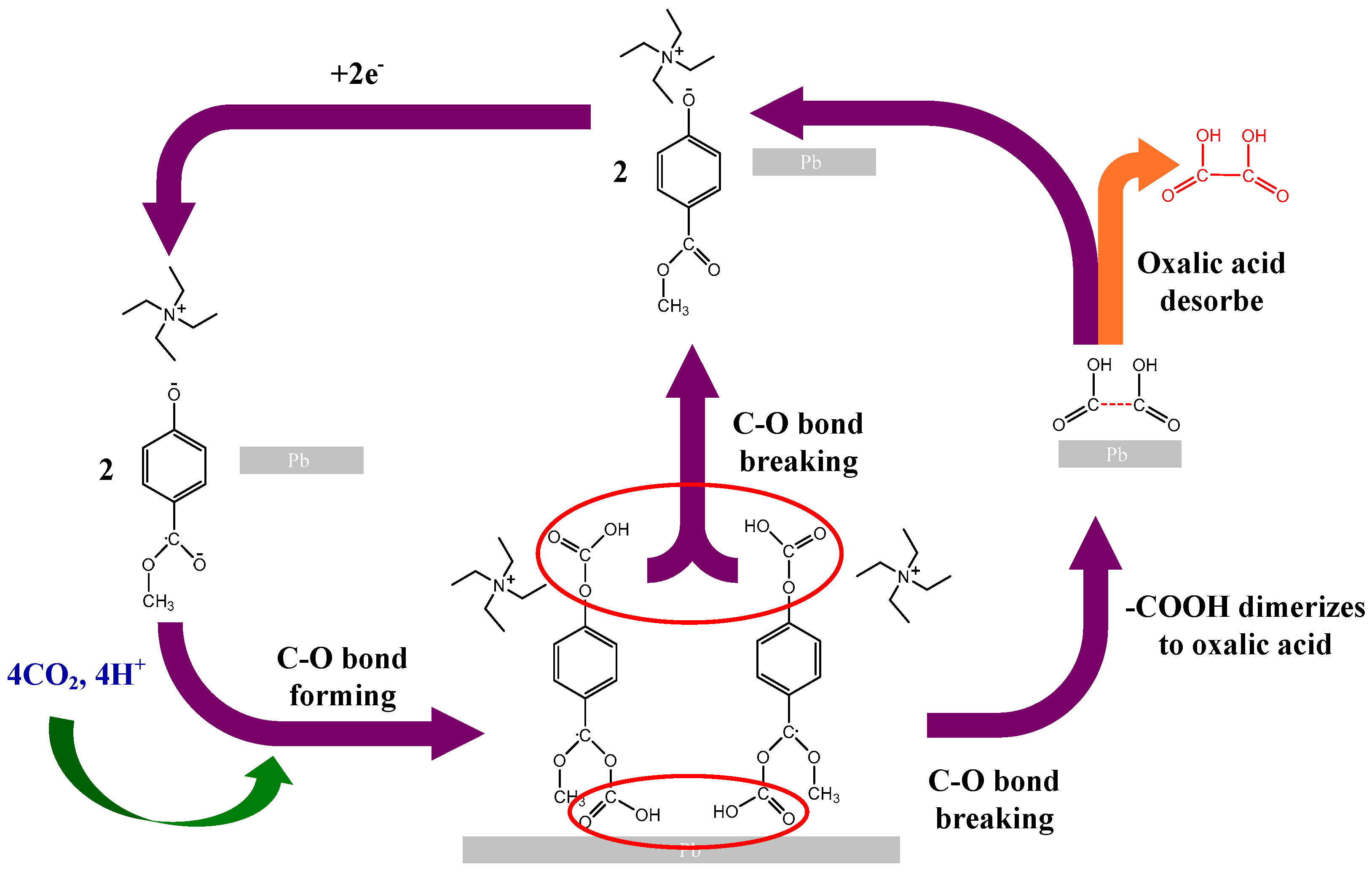
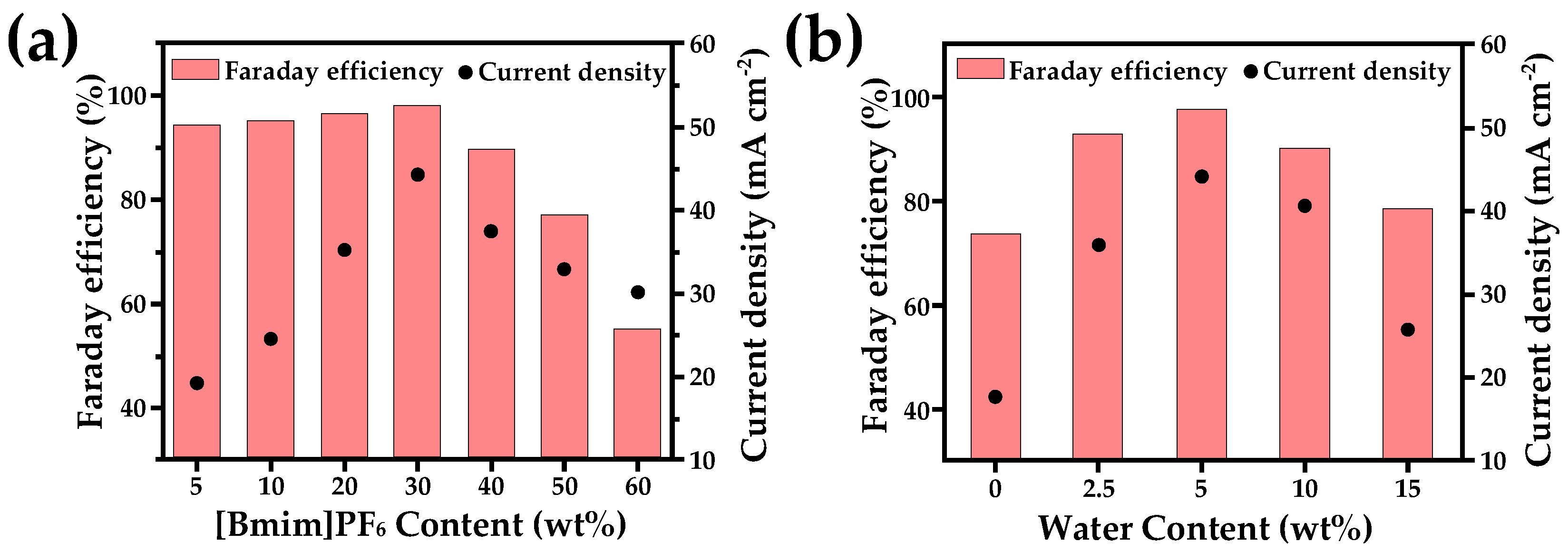
2.3. Ionic Liquid Electrolyte
- Functional modification enables the precise control of CO2 capture capacity;
- Solvent system optimization improves mass transport properties;
- Interface engineering enhances catalyst selectivity;
2.4. Other Electrolytes
3. Electrolyte Engineering for Product-Selective eCO2RR
3.1. pH-Mediated Control of Electrolytes in CO2 Electroreduction
3.2. Concentration Effects of Electrolytes on eCO2RR
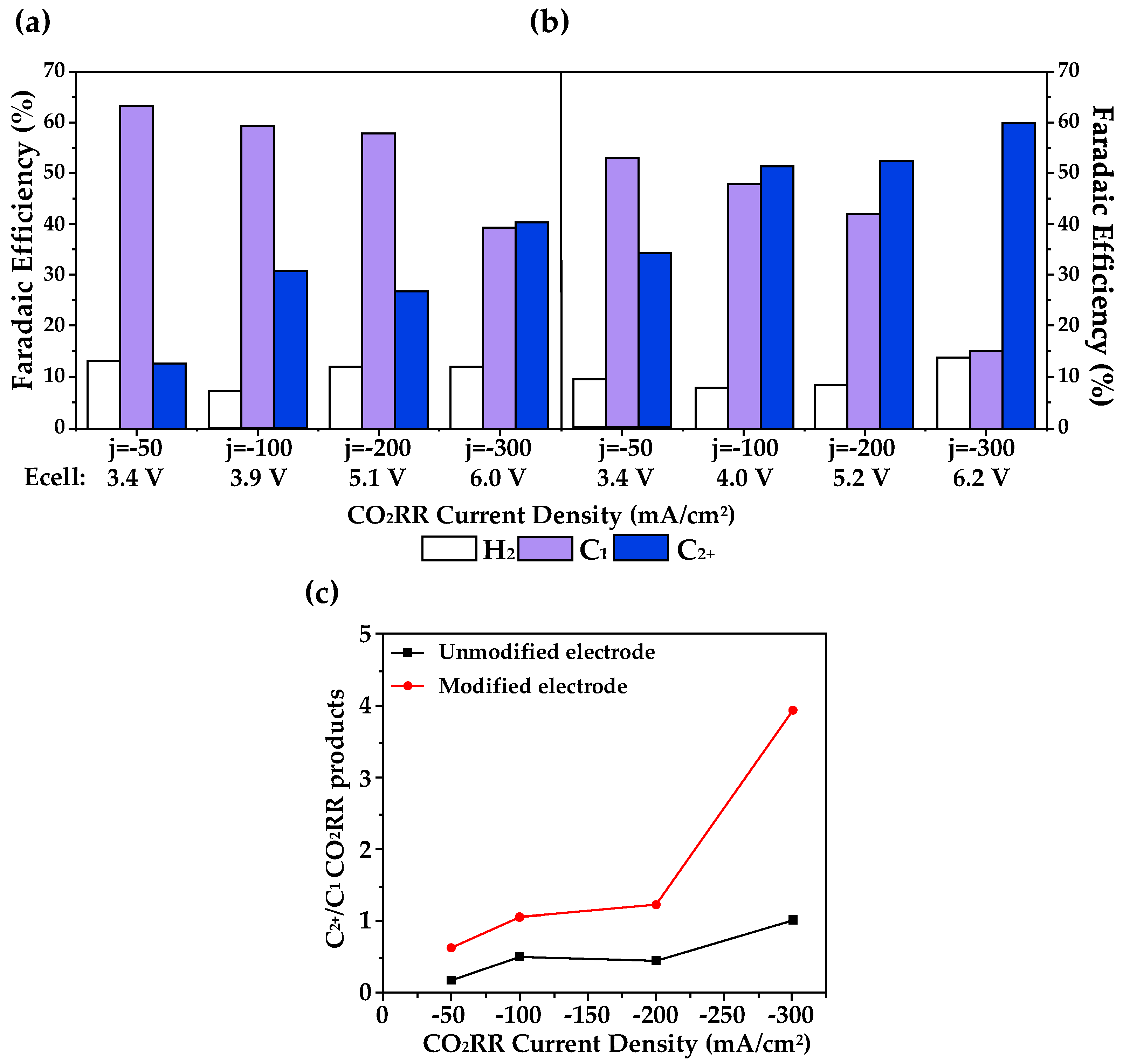
3.3. Cation–Anion Synergistic Effects in eCO2RR
3.4. Design Strategies for Dopant Engineering
- Cationic CTAB lowers the proton concentration via hydrophobic chains, yielding 50% HCOOH FE [15];
- Double-charged quaternary ammonium salts tune product selectivity (28% C2H4 with C8 chains vs. 41% CO with C2 chains) [66];
- Hydrophobic [NTF2]− enriches CO2 for 38.7% HCOOH FE [15];
- Immobilized imidazolium cations achieve 85% HCOOH selectivity in acidic media [67];
- Lewis acids (e.g., boric acid) form [B(OCH2CH2O)2]− chelates for 85% ethylene glycol FE [68].
3.5. Rational Screening Strategies
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
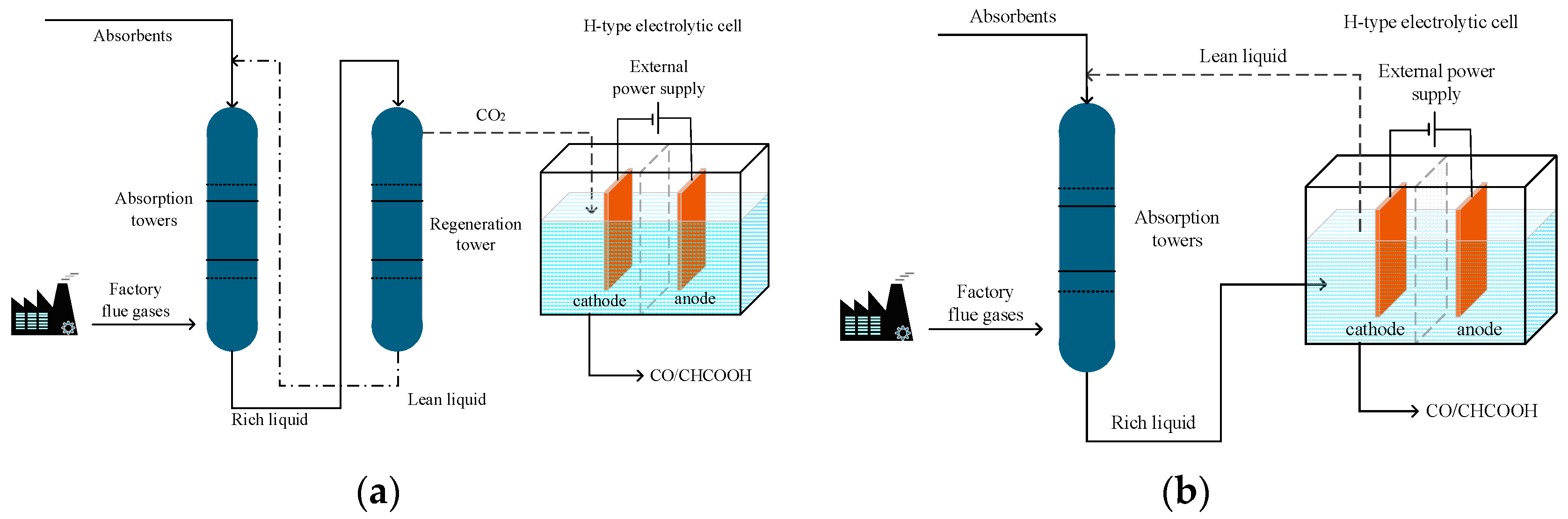
4. Application of ICCU
5. Conclusions
6. Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, S.J.; Caldeira, K.; Matthews, H.D. Future CO2 emissions and climate change from existing energy infrastructure. Science 2010, 329, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubou, H. A Review of Global CO2 Emissions and Total Energy Consumption. SEA—Pract. Appl. Sci. 2021, 9, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangnan, T.; Yuan, A.; Jing, J.; Yang, L.; Jingkui, T.; Desheng, C. Technical Solution for Decarburization in Context of Carbon Neutrality. Distrib. Energy 2021, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenmin, B.; Huihong, L.; Keyu, C.; Zhibin, Z. Recent Progress on Chemical Conversion of Carbon Dioxide. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2018, 47, 70–72+76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiusong, H.; Shujuan, W.; Junjie, X. Review of Integrated CO2 Capture and Electrochemical Reduction Utilization System. J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2022, 28, 679–686, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=79O6ZE_Rn2rjpMW-EUVEPf89BAarlDojvBOqQ2WVVO1TLiNwGZjpMO3RaLpDUhUcTDcQRUguToVe8T0-0W68Xp4RV-ygIKCDfsWm1t7gK0fsMlPKrbbdGMNmOngtwuZi2TrJuqTtEZsJHYFk47_suXe87kZYvvFnO9MPItsSE6F_jYKSiC7qdn3fWoXnfFVme2RNH0wfTC4=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, S.; Xu, Q.C.; Moss, A.B.; Mirolo, M.; Deng, W.Y.; Chorkendorff, I.; Drnec, J.; Seger, B. How alkali cations affect salt precipitation and CO2 electrolysis performance in membrane electrode assembly electrolyzers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, D.F.; Rothenberg, G.; Garcia, A.C. Investigating proton shuttling and electrochemical mechanisms of amines in integrated CO2 capture and utilization. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Gao, H.S.; Feng, J.Q.; Zeng, S.J.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.C.; Ren, B.Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, X.P. Aromatic Ester-Functionalized Ionic Liquid for Highly Efficient CO2 Electrochemical Reduction to Oxalic Acid. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 4900–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.E.; Li, F.W.; Ozden, A.; Rasouli, A.S.; de Arquer, F.P.G.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, S.Z.; Luo, M.C.; Wang, X.; Lum, Y.W.; et al. CO2 electrolysis to multicarbon products in strong acid. Science 2021, 372, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, M.; Fiorentin, M.R.; Risplendi, F.; Raffone, F.; Sommer, T.; García-Melchor, M.; Cicero, G. Efficient mapping of CO adsorption on Cu1-xMx bimetallic alloys via machine learning. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 14148–14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Mao, Y.; Sultan, S.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z. Performance enhancement of desorption reactor in the electrochemically mediated amine regeneration CO2 capture process: Thru modelling, simulation, and optimization. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Q.; Zhang, L.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Cao, Z.W.; Yu, W.G.; Zhu, X.F.; Yang, W.S. Alkaline-earth elements (Ca, Sr and Ba) doped LaFeO3-δ cathodes for CO2 electroreduction. J. Power Sources 2019, 443, 227268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.H.; Cao, M.X.; Cai, W.M.; Xu, C.X.; Xu, J.W.; Huang, Z.Y. Ionic Liquids Modulating Local Microenvironment of Ni-Fe Binary Single Atom Catalyst for Efficient Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Small 2024, 20, 2308522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yamauchi, H.; Wang, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Kim, J.; Gordiz, K.; Huang, B.T.; Xu, H.B.; Zheng, D.J.; Wang, X.; et al. CO2-to-methanol electroconversion on a molecular cobalt catalyst facilitated by acidic cations. Nat. Catal. 2024, 7, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Han, X.; Thoi, V.S. Modulating the Electrode-Electrolyte Interface with Cationic Surfactants in Carbon Dioxide Reduction. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrodi, B.; Kecsenővity, E.; Samu, A.; Halmágyi, T.; Rojas-Carbonell, S.; Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Janáky, C. High carbonate ion conductance of a robust PiperION membrane allows industrial current density and conversion in a zero-gap carbon dioxide electrolyzer cell. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4098–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Q.; Barile, C.J. Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Polycrystalline Copper by Modulating Proton Transfer with Fluoropolymer Composites. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2022, 5, 4712–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichou, E.; Perazio, A.; Adjez, Y.; Gomez-Mingot, M.; Schreiber, M.W.; Sánchez-Sánchez, C.M.; Fontecave, M. Tuning Selectivity of Acidic Carbon Dioxide Electrolysis via Surface Modification. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 7060–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathunge, C.M.; Ovalle, V.J.; Waegele, M.M. Probing promoting effects of alkali cations on the reduction of CO at the aqueous electrolyte/copper interface. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 30166–30172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, G.P.; Bruening, M.A.; Musgrave, C.B.; Goddard, W.A.; Peters, J.C.; Agapie, T. Potassium ion modulation of the Cu electrode-electrolyte interface with ionomers enhances CO2 reduction to C2+ products. Joule 2024, 8, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, F.S.; Lackner, K.S. Capturing carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere. World Resour. Rev. 2004, 16, 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, G.; Keith, D.W. An air-liquid contactor for large-scale capture of CO2 from air. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 4380–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Hori, Y. Product Selectivity Affected by Cationic Species in Electrochemical Reduction of Co2 and Co at a Cu Electrode. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 64, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayemoba, O.; Cuesta, A. Spectroscopic Evidence of Size-Dependent Buffering of Interfacial pH by Cation Hydrolysis during CO2 Electroreduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27377–27382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringe, S.; Clark, E.L.; Resasco, J.; Walton, A.; Seger, B.; Bell, A.T.; Chan, K. Understanding cation effects in electrochemical CO2 reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3609–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z. Research of Carbon Capture Processusing Ammonia as Absorbent Based on antisolvent Crystallization. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Du, Q.; Shan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Direct CO2 electroreduction from NH4HCO3 electrolyte to syngas on bromine-modified Ag catalyst. Energy 2021, 216, 119250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.; Shan, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xie, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Effect of halogen-modification on Ag catalyst for CO2 electrochemical reduction to syngas from NH4HCO3 electrolyte. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.M.; Samu, G.F.; Balog, A.; Csapó, E.; Janáky, C. Composition-Dependent Electrocatalytic Behavior of Au-Sn Bimetallic Nanoparticles in Carbon Dioxide Reduction. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunwell, M.; Lu, Q.; Heyes, J.M.; Rosen, J.; Chen, J.G.G.; Yan, Y.S.; Jiao, F.; Xu, B.J. The Central Role of Bicarbonate in the Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide on Gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3774–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoxu, Z. Study on CO2 Capture from Flue Gas by Chemical Absorption. 2016. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=79O6ZE_Rn2qzeHMgbHg9U6nzARWtygqYJWSamoyN1lHOUCXiVWfWS-XBWXwRu2G7MznMssLS64gQdCYgwSAPTcKKW71JER4SCTox8ETt2Dzmc-j0NehD8I-rozjEM7Y7K212aZaVfzwLz2bKN3ckXAcqlfu3h1qOKD-MW9NydZn1dkuzatlDGerHqEV15gP20BqGOSZYGa4=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Liang, Z.W.; Rongwong, W.; Liu, H.L.; Fu, K.Y.; Gao, H.X.; Cao, F.; Zhang, R.; Sema, T.; Henni, A.; Sumon, K.; et al. Recent progress and new developments in post-combustion carbon-capture technology with amine based solvents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control. 2015, 40, 26–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuilova, A.; Koiwanit, J.; Piewkhaow, L.; Wilson, M.; Chan, C.W.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P. Life Cycle Assessment of Post-Combustion CO2 Capture and CO2-Enhanced Oil Recovery based on the Boundary Dam Integrated Carbon Capture and Storage Demonstration Project in Saskatchewan. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies (GHGT), Austin, TX, USA, 5–9 October 2014; pp. 7398–7407. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Electrochemical Reduction of Ethanolamine CO2 Capture Solution Energy Transfer Enhancement and Full Life Cycle Assessment. Chongqing Univ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.K.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.J. Active chemisorption sites in functionalized ionic liquids for carbon capture. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4307–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Gui, C.; Sun, L.; Hu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Yu, G. Energy Applications of Ionic Liquids: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 12170–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, L.A.; Hancu, D.; Beckman, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Green processing using ionic liquids and CO2. Nature 1999, 399, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.L.; Maginn, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Solubilities and thermodynamic properties of gases in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7315–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.P.; Zeng, S.J.; Liu, H.Z.; Feng, J.Q.; Gao, H.S.; Bai, L.; Dong, H.F.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhang, X.P. Insights into Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction in Ionic Liquids: Carbon Dioxide Activation and Selectivity Tailored by Ionic Microhabitat. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 3191–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, B.A.; Salehi-Khojin, A.; Thorson, M.R.; Zhu, W.; Whipple, D.T.; Kenis, P.J.A.; Masel, R.I. Ionic Liquid-Mediated Selective Conversion of CO2 to CO at Low Overpotentials. Science 2011, 334, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.R.; Song, J.L.; Xie, C.; Hu, Y.; Han, B.X. Highly efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2 into formic acid over lead dioxide in an ionic liquid-catholyte mixture. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Shi, J.; Shen, F.X.; Zhen, J.Z.; Li, Y.F.; Shi, F.; Yang, B.; Jia, Y.J.; Dai, Y.N.; Hu, Y.Q. Selection of Low-Cost Ionic Liquid Electrocatalyst for CO2 Reduction in Propylene Carbonate/Tetrabutylammonium Perchlorate. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gan, Z.D.; Xin, S.X.; Fang, W.H.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.L.; Cui, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, X.P. High performance carbon dioxide electroreduction in ionic liquids with in situ shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, E.D.; Mayton, R.D.; Ntai, I.; Davis, J.H. CO2 capture by a task-specific ionic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Jia, C.; Dong, H.F.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, S.J. A Novel Dual Amino-Functionalized Cation-Tethered Ionic Liquid for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 5835–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Feng, J.Q.; Zhang, X.P.; Gao, H.S.; Jin, S.M.; Liu, L.; Shen, W.F. Efficient Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to CO in Ionic Liquids. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 9873–9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, D.X.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.X.; Li, H.P.; Dong, W.W.; Zhang, R.J.; Feng, C.Y. Efficient Electroreduction of CO2 to CO on Porous ZnO Nanosheets with Hydroxyl Groups in Ionic Liquid-based Electrolytes. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 2570–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Kang, X.C.; Jiao, J.P.; Xing, X.Q.; Yin, Y.Y.; Jia, S.Q.; Chu, M.E.; Han, S.T.; Xia, W.; Wu, H.H.; et al. Ternary Ionic-Liquid-Based Electrolyte Enables Efficient Electro-reduction of CO2 over Bulk Metal Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 11512–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, Y.; Yoshii, K.; Gunji, T.; Takeda, S.; Takeichi, N. Electrodeposition of Cu with Amino Acids toward Electrocatalytic Enhancement of CO2 Reduction Reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 054507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, P.S.; Singh, A.R.; Chan, K.R. pH Effects on Hydrogen Evolution and Oxidation over Pt(111): Insights from First-Principles. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6194–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitopi, S.; Bertheussen, E.; Scott, S.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Engstfeld, A.K.; Horch, S.; Seger, B.; Stephens, I.E.L.; Chan, K.; Hahn, C.; et al. Progress and Perspectives of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper in Aqueous Electrolyte. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Fang, W.S.; Cen, Y.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Hu, Y.M.; Xia, B.Y. Reaction Environment Regulation for Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction in Acids. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2024, 63, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.Q.; Gao, S.T.; Shi, J.L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.B. Developing micro-kinetic model for electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide on copper electrode. J. Catal. 2021, 393, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Z.; Xuan, J.; Wang, H. In-Situ Observation of the pH Gradient near the Gas Diffusion Electrode of CO2 Reduction in Alkaline Electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15438–15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.H.; Xu, A.N.; Chan, K.R.; Hu, X.L. A Cation Concentration Gradient Approach to Tune the Selectivity and Activity of CO2 Electroreduction. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2022, 61, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.C.; Guo, W.X.; Gebbie, M.A. Tuning Ionic Screening To Accelerate Electrochemical CO2 Reduction in Ionic Liquid Electrolytes. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 9706–9716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Liao, X.Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.M.; Liu, K.; Fu, J.W.; Liu, M. Near-Electrode Concentration Gradients of Bicarbonate and pH within Porous Gas Diffusion Electrode for Optimized Selective CO2 Electroreduction to C2+ Products. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 12163–12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.S.; Kroschel, M.; Reier, T.; Strasser, P. Controlling the selectivity of CO2 electroreduction on copper: The effect of the electrolyte concentration and the importance of the local pH. Catal. Today 2016, 260, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbie, M.A.; Liu, B.C.; Guo, W.X.; Anderson, S.R.; Johnstone, S.G. Linking Electric Double Layer Formation to Electrocatalytic Activity. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 16222–16239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, T.; Ngo Thanh, T.; Wang, X.; Ju, W.; Jovanov, Z.; Strasser, P. The product selectivity zones in gas diffusion electrodes during the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5995–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Li, M.R.; Wu, Y.M.; Idros, M.N.; Wang, H.M.; Yago, A.J.; Ge, L.; Wang, G.G.X.; Rufford, T.E. Understanding the Effects of Anion Interactions with Ag Electrodes on Electrochemical CO2 Reduction in Choline Halide Electrolytes. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Z.; Ouyang, Y.X.; Wu, M.L.; Ling, C.Y.; Wang, J.L. Mechanism of surface oxygen-containing species promoted electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.X.; Liu, B.C.; Gebbie, M.A. Suppressing Co-Ion Generation via Cationic Proton Donors to Amplify Driving Forces for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 14243–14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalle, V.J.; Waegele, M.M. Understanding the Impact of N-Arylpyridinium Ions on the Selectivity of CO2 Reduction at the Cu/Electrolyte Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 24453–24460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.C.O.; Dattila, F.; López, N.; Koper, M.T.M. The Role of Cation Acidity on the Competition between Hydrogen Evolution and CO2 Reduction on Gold Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, W.A.; Sajevic, U.; Mammadzada, R.; Nikolaienko, P.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J. Tethered Alkylammonium Dications as Electrochemical Interface Modifiers: Chain Length Effect on CO2 Reduction Selectivity at Industry-Relevant Current Density. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 30107–30116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichou, E.; Adjez, Y.; Li, Y.; Gömez-Mingot, M.; Fontecave, M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, C.M. Smart Electrode Surfaces by Electrolyte Immobilization for Electrocatalytic CO2 Conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2824–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Calvinho, K.U.D.; Dhiman, M.; Laursen, A.B.; Gu, H.F.; Santorelli, D.; Clifford, Z.; Dismukes, G.C. Tunable product selectivity on demand: A mechanism-guided Lewis acid co-catalyst for CO2 electroreduction to ethylene glycol. EES Catal. 2024, 2, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lees, E.W.; Goldman, M.; Salvatore, D.A.; Weekes, D.M.; Berlinguette, C.P. Electrolytic conversion of bicarbonate into CO in a flow cell. Joule 2019, 3, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.C.; Lee, G.; Yuan, T.G.; Wang, Y.; Nam, D.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; de Arquer, F.P.G.; Lum, Y.; Dinh, C.T.; Voznyy, O.; et al. CO2 Electroreduction from Carbonate Electrolyte. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Rong, Y.W.; Li, X.; Sang, J.Q.; Wei, P.F.; An, Q.D.; Gao, D.F.; Wang, G.X. Molecular Enhancement of Direct Electrolysis of Dilute CO2. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Wang, Q.; Qu, Z.G.; Zhang, H.J. Enabling direct flue gas electrolysis by clarifying impurity gas effects on CO2 electroreduction. Nano Energy 2025, 134, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.K.; Zheng, J.J.; Luo, X.Y.; Lin, W.J.; Ding, F.; Li, H.R.; Wang, C.M. Tuning Anion-Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Improved SO2 Capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2013, 52, 10620–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.; Ramírez, A.; Pérez-Fortes, M. Learning from the past: Limitations of techno-economic assessments for low-temperature CO2 electrolysis. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2025, 213, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villadsen, S.N.B.; Kaab, M.A.; Nielsen, L.P.; Moller, P.; Fosb, P.L. New electroscrubbing process for desulfurization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 278, 119552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijian, L.; Yuping, G.; Ling, L.; Guojun, K.; Xi, C.; Miaomiao, L.; Juanjuan, Z.; Feng, W. Research status and future development direction of CO2 absorption technology for organic amine. Clean Coal Technol. 2022, 28, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, X.T.; Ju, C.; Xia, R.K.; Tan, A.D.; Xu, C.; Liu, J.G. Study of dynamic thermal behavior and control strategies for membrane electrode assembly of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 102, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wack, Y.; Sollich, M.; Salenbien, R.; Diriken, J.; Baelmans, M.; Blommaert, M. A multi-period topology and design optimization approach for district heating networks. Appl. Energy 2024, 367, 123380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.Q.; Xia, B.K.; Yang, K.; Li, D.; Shao, T.Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Duan, J.J. Techno-economic Analysis and Carbon Footprint Accounting for Industrial CO2 Electrolysis Systems. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 17997–18008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.C.; Liu, R.; Yi, S.J. Integrating communication networks with reinforcement learning and big data analytics for optimizing carbon capture and utilization strategies. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 108, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
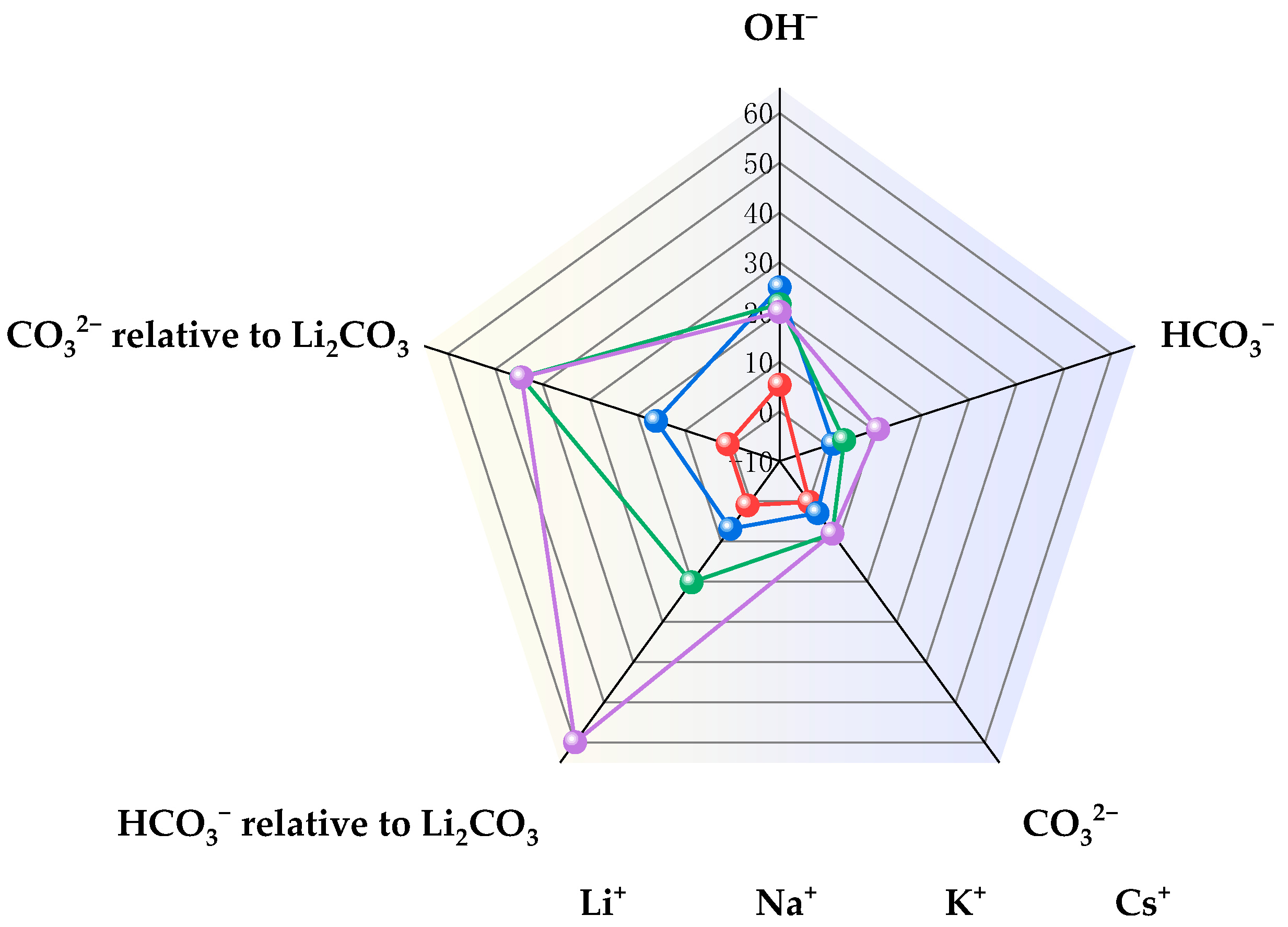
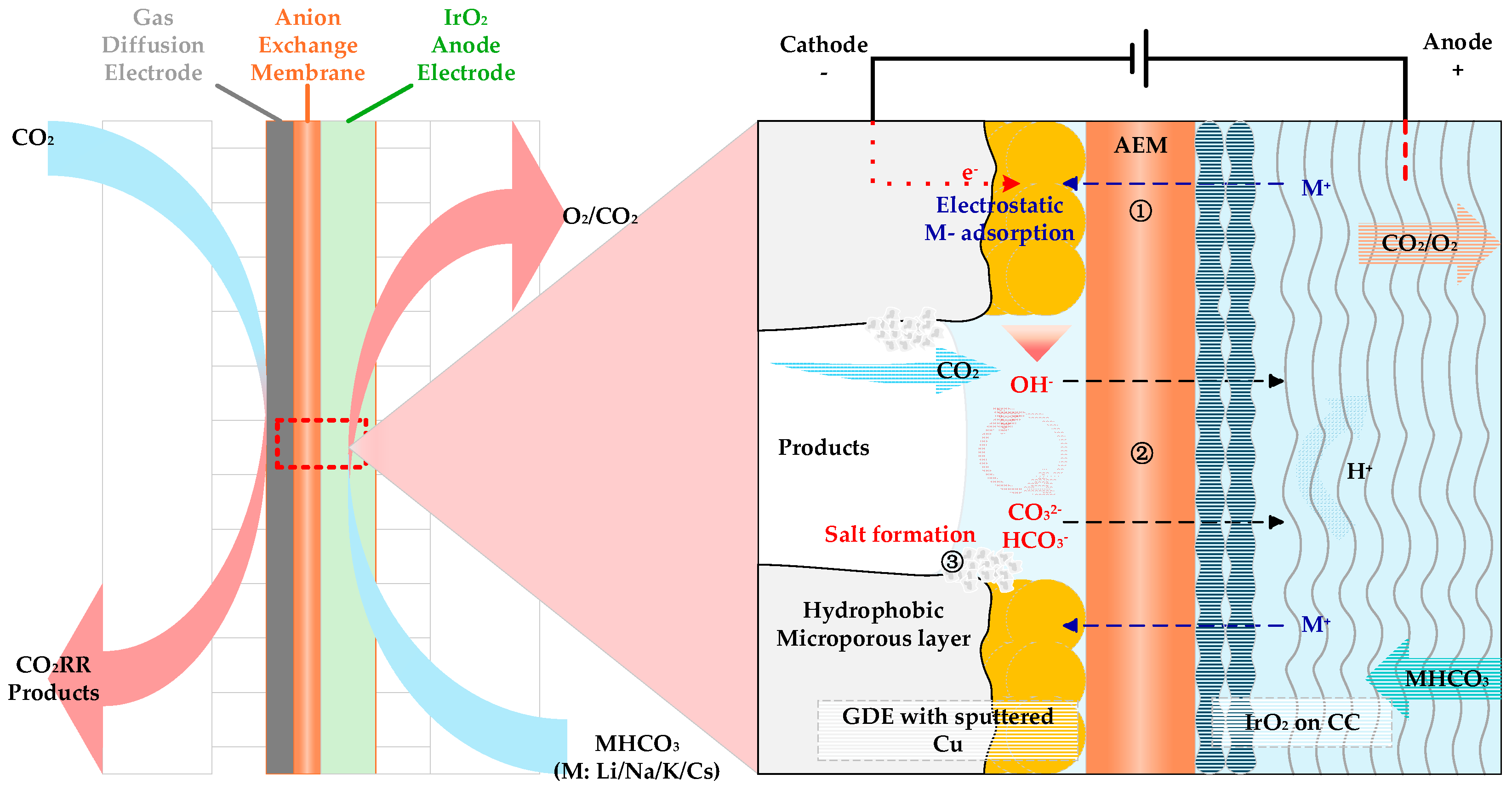
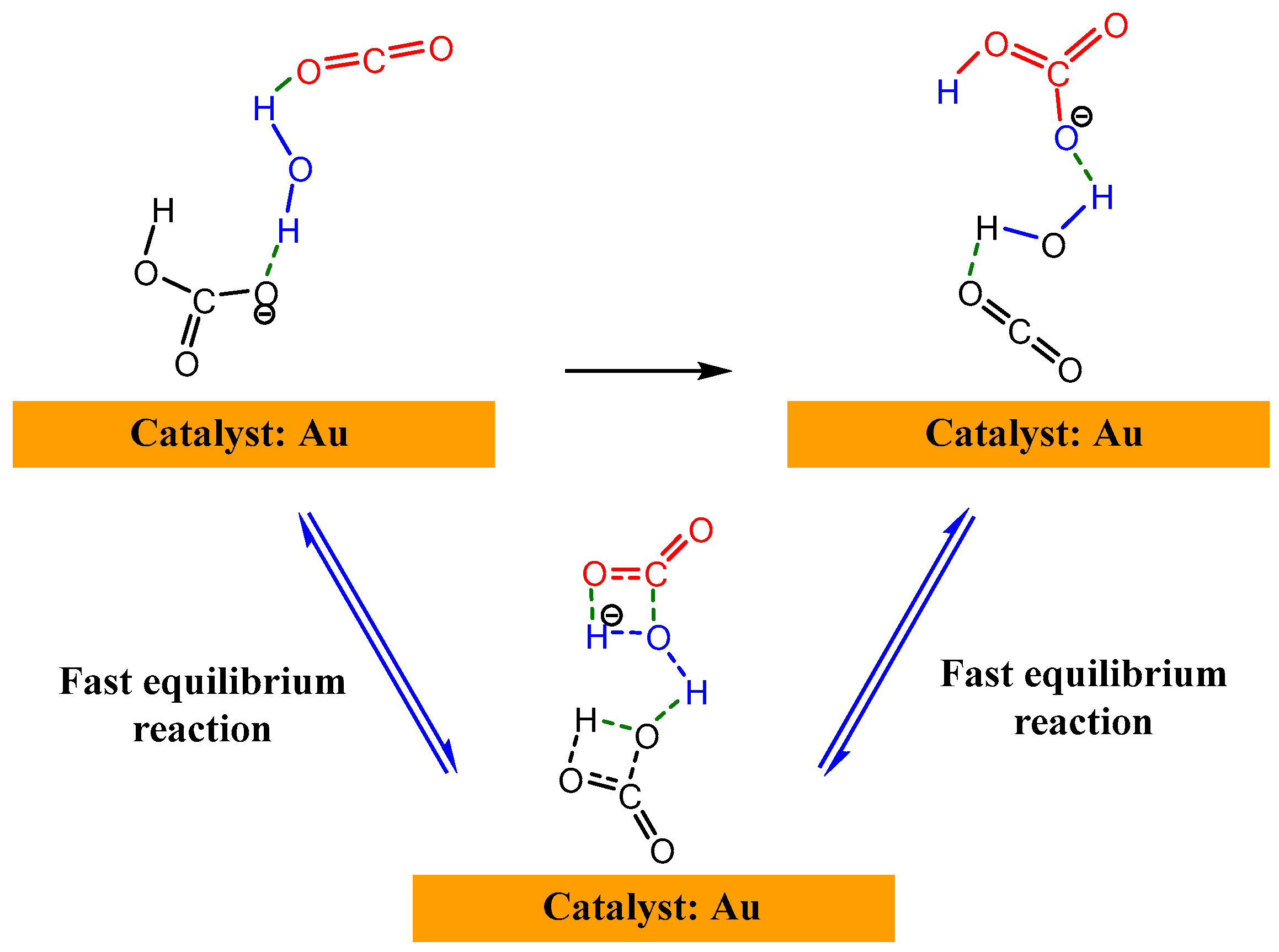

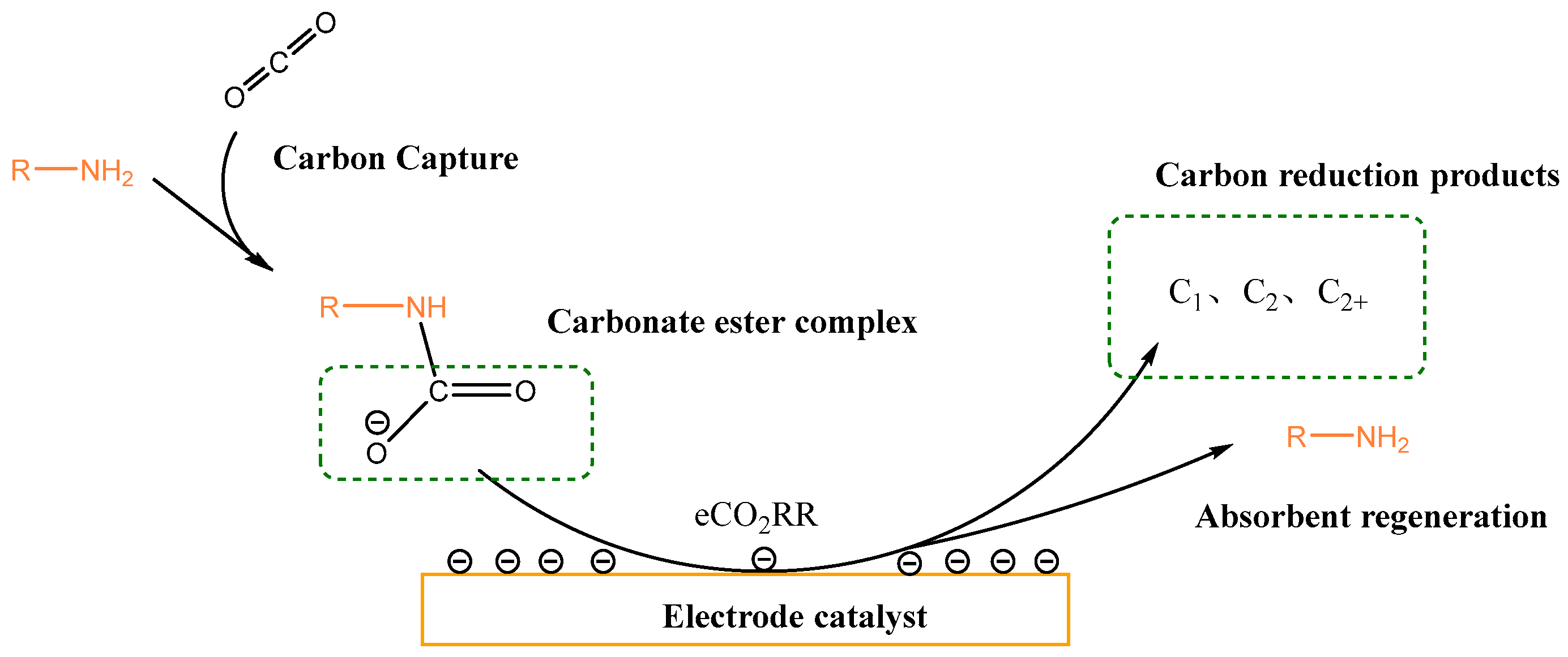
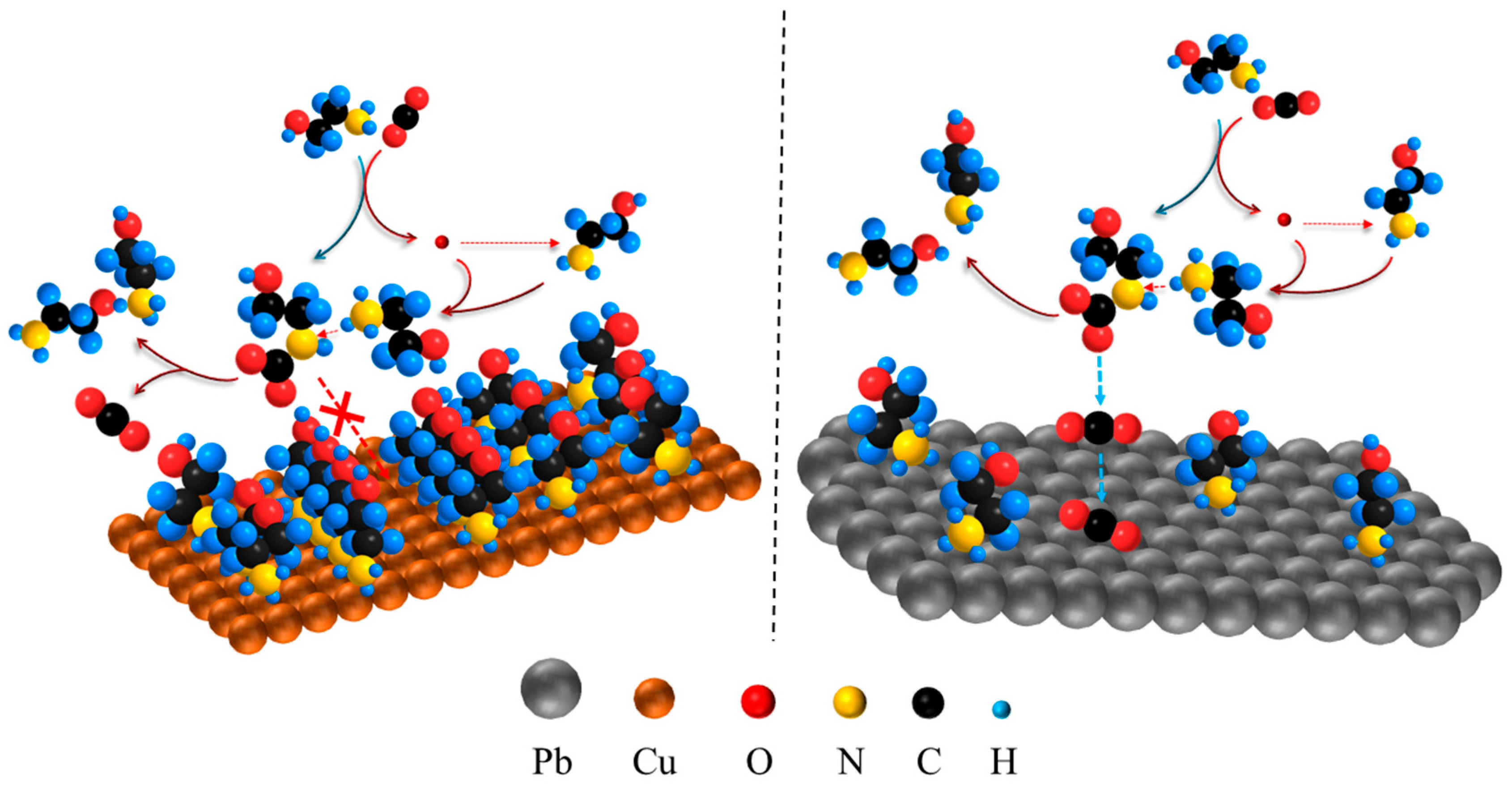
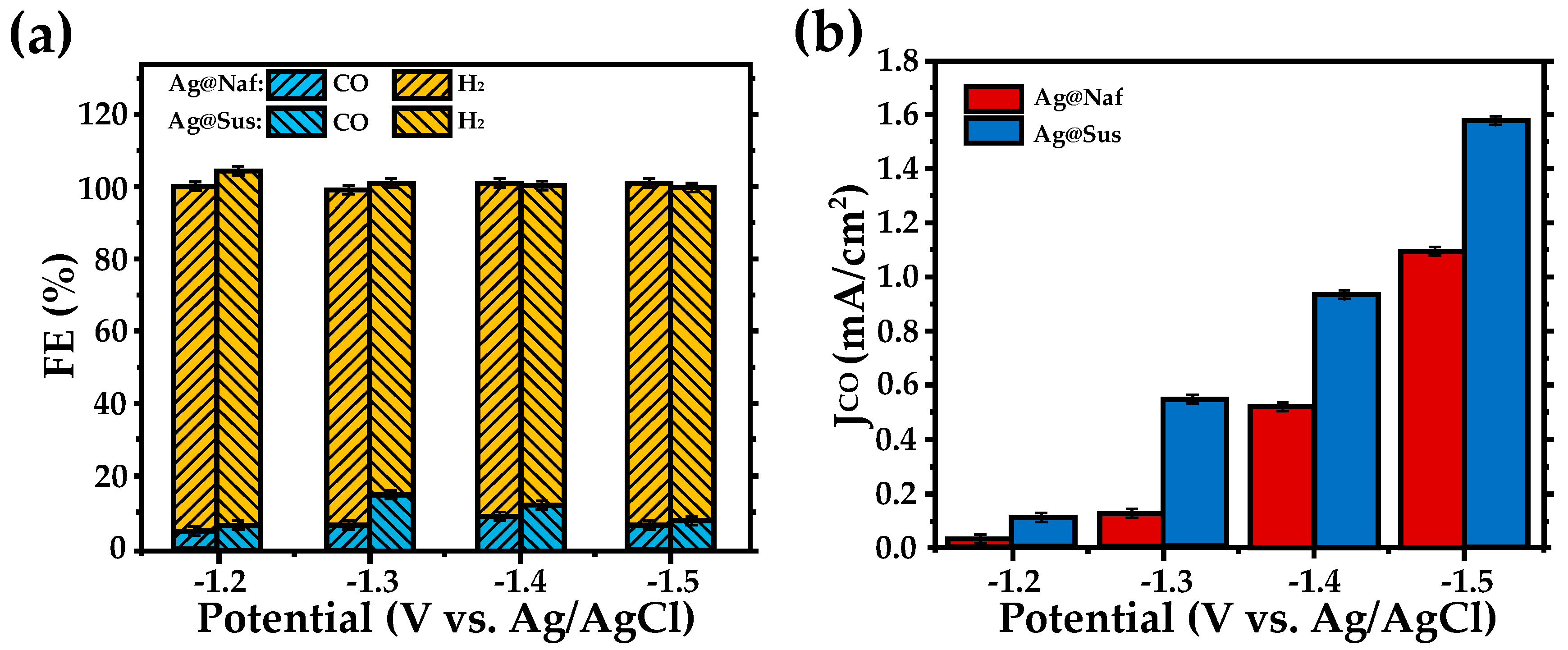
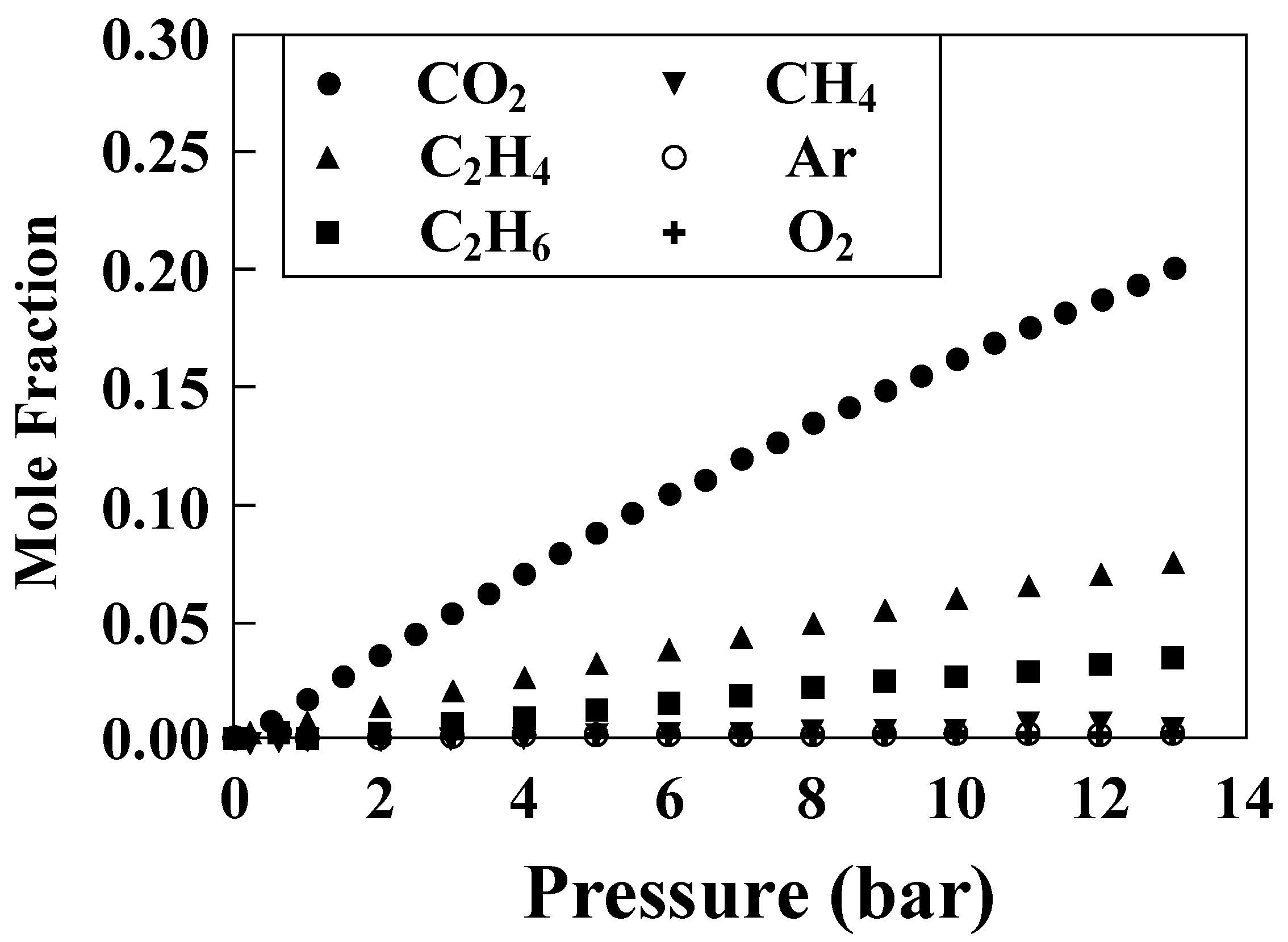
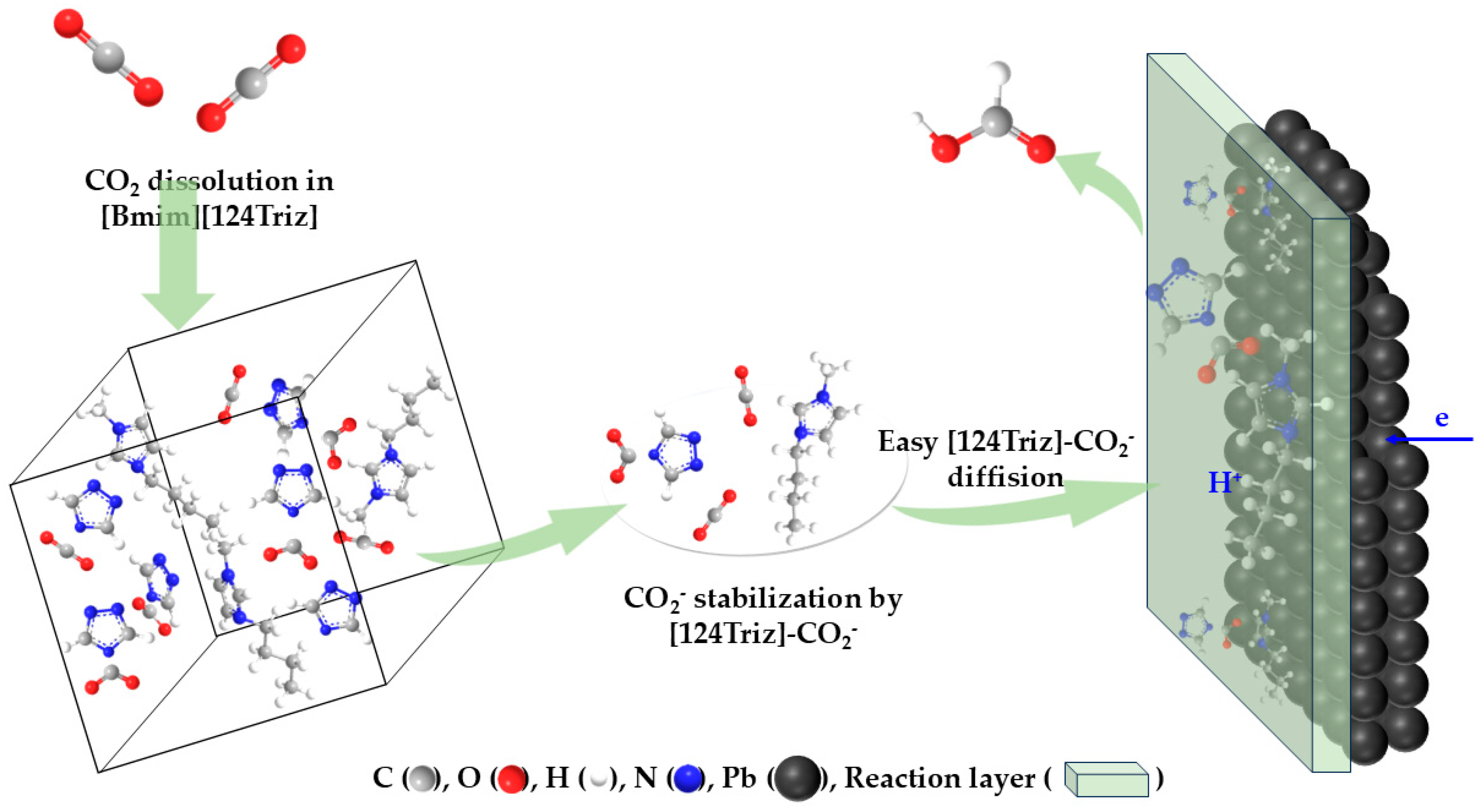
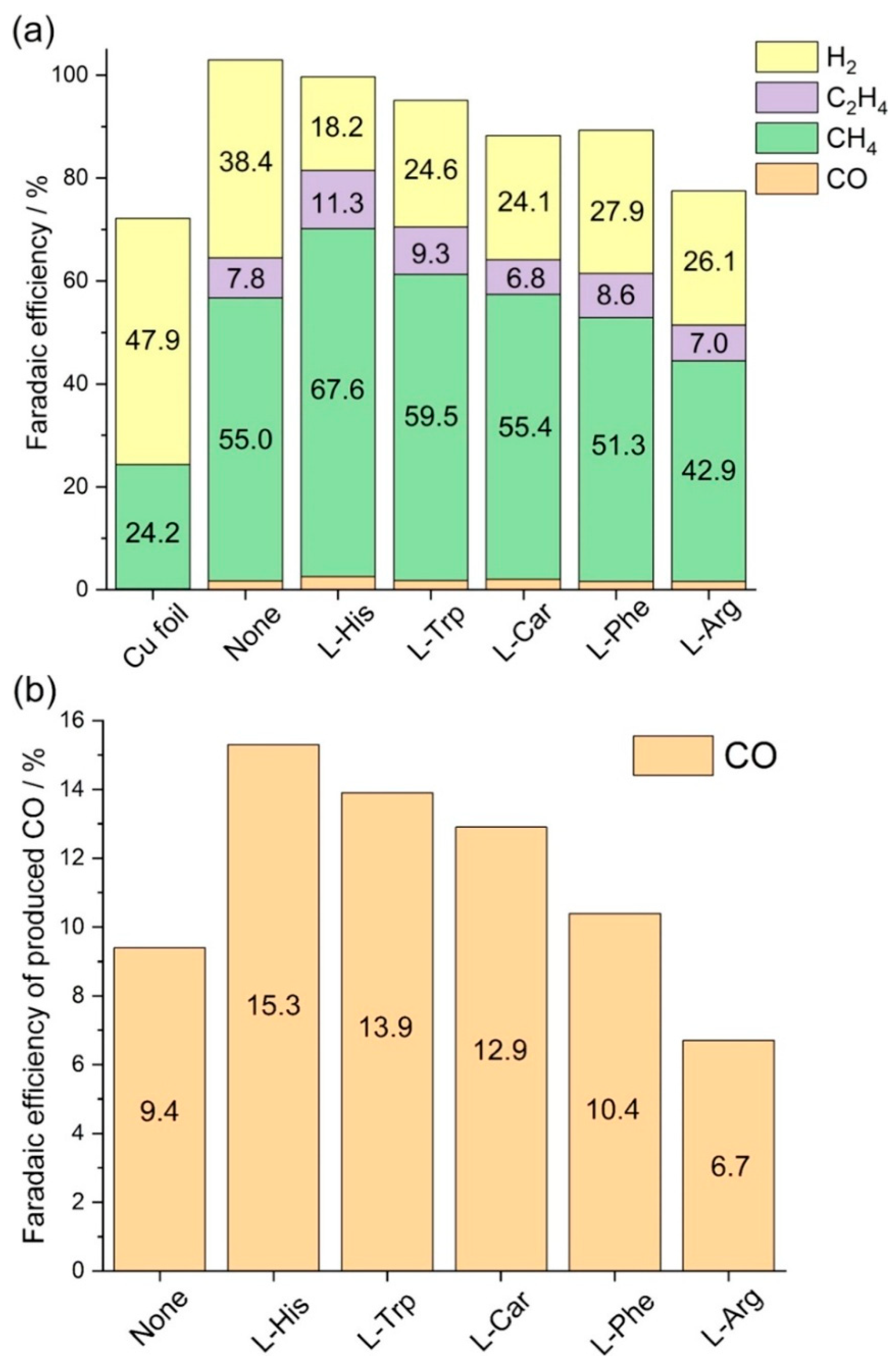
| Entry | Electrolytes | j (mA·cm−2) | FECO (%) | FEHCOOH (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3 M BminBF4/0.2 M C12minBF4/MeCN (1) | 83.6 ± 1.3 | 99.5 ± 0.2 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.5 M C12minBF4/MeCN (2) | 48.3 ± 2.6 | 99.2 ± 0.4 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.5 M BminBF4/MeCN (3) | 63.2 ± 3.2 | 78.2 ± 1.3 | 3.6 ± 2.6 |
| 4 | 0.4 M BminBF4/0.1 M C12minBF4/MeCN | 77.8 ± 1.5 | 98.3 ± 0.8 | 1.0 ± 0.5 |
| 5 | 0.2 M BminBF4/0.3 M C12minBF4/MeCN | 72.4 ± 1.0 | 98.8 ± 0.2 | 0 |
| 6 | 0.1 M BminBF4/0.4 M C12minBF4/MeCN | 66.5 ± 3.1 | 98.3 ± 0.5 | 0 |
| Electrolyte Type | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Bicarbonates |
|
|
| Amines |
| |
| ILs |
|
|
| Emerging Systems |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, G.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research on the Characteristics of Electrolytes in Integrated Carbon Capture and Utilization Systems: The Key to Promoting the Development of Green and Low-Carbon Technologies. Energies 2025, 18, 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123039
You G, Li Y, Dong L, Li Y, Zhang Y. Research on the Characteristics of Electrolytes in Integrated Carbon Capture and Utilization Systems: The Key to Promoting the Development of Green and Low-Carbon Technologies. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123039
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Guoqing, Yunzhi Li, Lihan Dong, Yichun Li, and Yu Zhang. 2025. "Research on the Characteristics of Electrolytes in Integrated Carbon Capture and Utilization Systems: The Key to Promoting the Development of Green and Low-Carbon Technologies" Energies 18, no. 12: 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123039
APA StyleYou, G., Li, Y., Dong, L., Li, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Research on the Characteristics of Electrolytes in Integrated Carbon Capture and Utilization Systems: The Key to Promoting the Development of Green and Low-Carbon Technologies. Energies, 18(12), 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123039










