The Concept of an Infrastructure Location to Supply Buses with Hydrogen: A Case Study of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Characteristics of West Pomeranian Voivodship in Poland
3.2. Methodology Used to Conduct the Research
- 1.
- Solaris Urbino 18 hydrogen FCEVs produced in Poland will be operated (Table 4). Green hydrogen will be used for fuelling operations.
- 2.
- The stations will be located in the two biggest cities of West Pomeranian Voivodeship: Szczecin and Koszalin. These cities were chosen considering their size (over 100,000 inhabitants) and importance in the voivodeship. Szczecin is the capital and the largest city in the voivodeship. Koszalin takes second place in terms of the number of inhabitants in the analysed voivodeship [74,75].
- 3.
- The stations could be located near areas with heavy traffic. It was assumed that they would be used by hydrogen-powered buses and passenger cars.
- 4.
- 5.
- The number of hydrogen refuelling stations will be calculated for 2025 and 2040.
- 6.
- The location of stationary stations for fuelling vehicles with hydrogen will be proposed. Each station should include the following elements: dispenser, compressor, and stationary tanks. One station may include several dispensers.
- —registered buses in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, pcs.,
- —registered buses in Poland, pcs.
- Lstv—number of hydrogen refuelling stations per voivodeship, pcs.,
- Lsp—number of stations planned for analysed time period, pcs.
- Pbrc—percentage share of buses registered in a particular city against the number of buses registered in the analysed cities, pcs.
- —number of buses planned for Szczecin and Koszalin (per phase: 2025, 2030, 2040), pcs.,
- —estimated average daily mileage per bus (can be based, e.g., on data from public transport operators), km,
- —average hydrogen consumption rate for typical hydrogen buses, kg H2/100 km.
- —required dispensing rate, kg/hour,
- —total daily demand for hydrogen, kg (),
- —available refuelling window, hours.
- —target utilization rate, %.
- —required corrected dispensing rate, kg/hour,
- —refuelling rate per one dispenser, kg/hour.
4. Results
4.1. Calculation of the Number of Hydrogen Refuelling Stations for the West Pomeranian Voivodeship
- For 2025:
- For 2040:
4.2. The Concept of Hydrogen Refuelling Stations Location in Szczecin
- —percentage share of the population of a selected district of Szczecin in relation to population of the entire city, %,
- —number of planned stations in the city, pcs.
4.3. The Concept of Hydrogen Refuelling Station Location in Koszalin
4.4. Calculation of Hydrogen Amount Needed for Buses Operation
- 1.
- The number of hydrogen-powered buses () planned for 2025, 2030, 2040 is as follows:
- Szczecin city:
- -
- 2025: 10 buses,
- -
- 2030: 20 buses,
- -
- 2040: 30 buses,
- Koszalin city:
- -
- 2025: 5 buses,
- -
- 2030: 10 buses,
- -
- 2040: 15 buses.
- 2.
- Estimated average daily mileage per bus (): 200 km/day.
- 3.
- Average hydrogen consumption rate for a typical hydrogen- powered bus (): 8 kg H2/100 km.
- 1.
- The estimated daily hydrogen demand () for 2040 is used.
- 2.
- Typical refuelling time per bus refuelling: 15 min.
- 3.
- Available refuelling window (): 10 h (600 min) of refuelling time.
- 4.
- Target utilization rate for dispensers: 70% utilization rate for dispensers.
- 5.
- Refuelling rate per one dispenser (): 30 kg/hour.
- 6.
- Hydrogen should be stored within the station to cover 1–3 days demand.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Prioritize strategic locations—ensure that hydrogen refuelling stations are located near major public transport routes to maximize accessibility and usage by public transport vehicles. When choosing a dispenser, special attention should be paid to the pressure at which the vehicle is powered with hydrogen. The safety of hydrogen fuelling is extremely important and should be ensured so that the operation of hydrogen stations and the subsequent operation of vehicles takes place in a way that does not threaten the life of society.
- Pay dedicated attention to public awareness campaigns—implement educational programs to inform the public about the benefits and use of hydrogen-powered vehicles and refuelling stations, fostering acceptance and encouraging utilization.
- Conduct regular assessment—continuously monitor and evaluate the operational statistics of hydrogen-powered buses and adjust the placement and number of refuelling stations accordingly to meet changing demand and urban mobility patterns.
- It is important to engage local government, transportation authorities, and private stakeholders in the planning and development phases to create a cohesive strategy that aligns with the national hydrogen strategy and regional goals.
- Elaborate plan for future expansion—design the initial stations with future scalability in mind, allowing for easy expansion to accommodate anticipated increases in hydrogen demand and the growth of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
- Address economic and legal challenges—identify potential financial, regulatory, and legal barriers to the establishment of hydrogen refuelling infrastructure and work proactively to address these issues through policy advocacy and partnerships.
- Implement pilot projects—consider initiating pilot projects in the city to test the feasibility and operational effectiveness of hydrogen refuelling stations before broader implementation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drożdż, W.; Kinelski, G.; Czarnecka, M.; Wójcik-Jurkiewicz, M.; Maroušková, A.; Zych, G. Determinants of Decarbonization—How to Realize Sustainable and Low Carbon Cities? Energies 2021, 14, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamier-Gliszczynski, N.; Wyszomirski, A.; Balewski, C.; Kłodawski, M. Green Public Transport in Poland—Planning the Process of the Electrification of the Bus Fleet of Vehicles. Energies 2024, 17, 6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, B.; Stecuła, K.; Olczak, P.; Kulpa, J.; Stecuła, B. Exploring the Green Horizon: Recent Research on Renewable Energy in Poland—A Review. Energies 2025, 18, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Roccotelli, M.; Sahu, U.K. Hydrogen Fuel for Future Mobility: Challenges and Future Aspects. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, H.; Saidur, R.; Razali, N.; Anuar, F.S.; Saleman, A.R.; Islam, M.R. An overview of hydrogen as a vehicle fuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5511–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowska, M.; Błoński, K.; Mańkowska, M.; Rzeczycki, A. Research on the Concept of Hydrogen Supply Chains and Power Grids Powered by Renewable Energy Sources: A Scoping Review with the Use of Text Mining. Energies 2022, 15, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowska, M.; Rzeczycki, A.; Sowa, M.; Drożdż, W. Functional Model of Power Grid Stabilization in the Green Hydrogen Supply Chain System—Conceptual Assumptions. Energies 2023, 16, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyza, D.; Gołda, P.; Sendek-Matysiak, E. Use of hydrogen in public transport systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Cho, S.H.; Cho, S.M.; Na, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.K. Review of hydrogen infrastructure: The current status and roll-out strategy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Révész, Á.; Gajdics, M. Improved h-storage performance of novel mg-based nanocomposites prepared by high-energy ball milling: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, G.; Brew, A.; Hunter, K.; Sharman, J.; Wright, E. Specific adsorption of perchlorate anions on pt{hkl} single crystal electrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13689–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaïci, W.; Michela, L. Hydrogen gas refueling infrastructure for heavy-duty trucks: A feasibility analysis. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2021, 144, 070906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Rogié, B.; Kærn, M.; Rothuizen, E. A first study of the potential of integrating an ejector in hydrogen fuelling stations for fuelling high pressure hydrogen vehicles. Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 113958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvillo, C.; Sánchez-Miralles, Á.; Villar, J. Energy management and planning in smart cities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, H.; He, G. Development of fuelling protocols for gaseous hydrogen vehicles: A key component for efficient and safe hydrogen mobility infrastructures. Clean Energy 2023, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polish Hydrogen Strategy to 2030 with an Outlook to 2040. Annex to Resolution No. 149 of the Council from 2 November 2021. (Item 1138). Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/klimat/polska-strategia-wodorowa-do-roku-2030 (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Position of the Minister of Climate and Environment in Poland. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/klimat/Stanowisko-w-sprawie-stosowania-przepisow-i-norm-technicznych-w-trakcie-procesu-inwestycyjnego-budowy-stacji-tankowania-wodoru (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Garabedian, H.; Wight, G.; Borland, N.; Dreier, K. Wind to wheels hydrogen project. World Electr. Veh. J. 2008, 2, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negurescu, N.; Pană, C.; Popa, M.; Cernat, A. Performance comparison between hydrogen and gasoline fuelled s.i. engine. Therm. Sci. 2011, 15, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, H.; Börner, S.; Hendrick, P.; Recker, E. Modification and testing of an engine and fuel control system for a hydrogen fuelled gas turbine. Prog. Propuls. Phys. 2011, 2, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendek-Matysiak, E.; Pyza, D. Prospects for the development of electric vehicle charging infrastructure in Poland in the light of the regulations in force. Arch. Transp. 2021, 57, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Filina-Dawidowicz, L.; Sęk, J.; Trojanowski, P.; Wiktorowska-Jasik, A. Conditions of Decision-Making Related to Implementation of Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles in Urban Transport: Case Study of Poland. Energies 2024, 17, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenberghen, T.; López, E. Overcoming barriers to the implementation of alternative fuels for road transport in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ally, J.; Pryor, T. Accelerating hydrogen implementation by mass production of a hydrogen bus chassis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akac, A.; Tsiatsiou, K.; Angelakakis, A. A review on best practices using hydrogen fuel-cell electric vehicles in public transport. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1123, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; You, S.; Hu, Z.; Wen, Y. Coordinated operation of hydrogen refuelling and fast charging combo station under normal and contingent conditions. Energy Convers. Econ. 2020, 1, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Kendall, K.; Yan, X. China progress on renewable energy vehicles: Fuel cells, hydrogen and battery hybrid vehicles. Energies 2018, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xylia, M.; Leduc, S.; Patrizio, P.; Kraxner, F.; Silveira, S. Locating charging infrastructure for electric buses in Stockholm. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 78, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunith, A.; Mendelevitch, R.; Goehlich, D. Electrification of a city bus network—An optimization model for cost-effective placing of charging infrastructure and battery sizing of fast-charging electric bus systems. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2017, 11, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potoglou, D.; Song, R.; Santos, G. Public charging choices of electric vehicle users: A review and conceptual framework. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 121, 103824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizes, B.; Soares, J.; Costa, A.; Pinto, T.; Lezama, F.; Novais, P.; Vale, Z. Electric Vehicles’ User Charging Behaviour Simulator for a Smart City. Energies 2019, 12, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutjar, M.; Kowald, M. The configuration of charging stations: What do potential users want? Travel Behav. Soc. 2023, 32, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowska, M.; Kogut-Jaworska, M.; Borawski, M.; Piwowarski, M. The significance of formal & legal factors in selecting a location for a hydrogen buffer to stabilize the operation of power distribution networks. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tan, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Gao, W. Willingness of chinese households to pay extra for hydrogen-fuelled buses: A survey based on willingness to pay. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1109234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar Singla, M.; Safaraliev, M.; Singh, K.; Odinaev, I.; Abdel Menaem, A. Advancements and challenges of fuel cell integration in electric vehicles: A comprehensive analysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 88, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Advantages and Technological Progress of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, F. Electric Vehicles: Benefits, Challenges, and Potential Solutions for Widespread Adaptation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisel, M.; Schmidt, J.; Kolbe, L. Finding suitable locations for charging stations. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference (IEVC), Florence, Italy, 17–19 December 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.; Salazar, M.; Rajagopal, R.; Pavone, M. Joint optimization of autonomous electric vehicle fleet operations and charging station siting. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairand, J.; González, M.; Kumar, R.; Vyas, S.; Escrivá-Escrivá, G. Coordinated siting and sizing of electric taxi charging stations considering traffic and power systems conditions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Madrid PowerTech, Madrid, Spain, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, D. Locating multiple types of charging facilities for battery electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 103, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Torcat, A.; Charry-Sanchez, J.; Elkamel, A.; Flett, P. A multi-period power infrastructure and charging station network planning model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Energy 2019, Västerås, Sweden, 12–15 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. Investigation for size and location of electric vehicle charging station accompanying vrp index and commissioning cost. Int. J. Emerg. Electr. Power Syst. 2023, 25, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, N.; Sudabattula, S.; Suresh, V. Optimal placement of electric vehicle charging station in distribution system using meta-heuristic techniques. Math. Model. Eng. Probl. 2022, 9, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowski, P.; Filina-Dawidowicz, L. Diagnostic and repair centers locating methodology for vehicles carrying sensitive cargo. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 55, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasolenko, O.; Lobashov, O.; Bugayov, I.; Gyulyev, N.; Filina-Dawidowicz, L. Designing the conditions of road traffic in the cities taking into account the human factor. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Cracow, Poland, 5–7 June 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.; Stecuła, K.; Grebski, W.W. Methods and Techniques Supporting Energy and Media Savings in Maintenance of Public Transport Buses—State of the Art and Recommendations. Energies 2024, 17, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvardson, J.; Jensen, J. Analysing improvements to on-street public transport systems: A mesoscopic model approach. Public Transp. 2017, 9, 385–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z. Remote Fault Diagnosis for the Powertrain System of Fuel Cell Vehicles Based on Random Forest Optimized with a Genetic Algorithm. Sensors 2024, 24, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffar, M.; Aziz, N. Urban form and economic sustainability in housing projects. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2021, 68, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekmann, A.; Sujan, V. Optimizing long term hydrogen fueling infrastructure plans on freight corridors for heavy duty fuel cell electric vehicles. Sae Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2023, 5, 2405–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butturi, M.; Gamberini, R. The potential of hydrogen technologies for low-carbon mobility in the urban-industrial symbiosis approach. Int. J. Energy Prod. Manag. 2022, 7, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, F.; Agoston, P.; Minx, J.; Canadell, J.; Andrew, R.; Quéré, C.; Peters, G.; Sharifi, A.; Yamagata, Y.; Dhakal, S. Urban infrastructure choices structure climate solutions. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, D.; Kuria, J. Potential for transition to low-carbon urban road transport in developing countries: Insights from literature. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 6, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C. Hydrogen Power Focus Shifts from Cars to Heavy Vehicles. Engineering 2020, 6, 1333–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2023/1804 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 September 2023 on the Deployment of Alternative Fuels Infrastructure, and Repealing Directive 2014/94/EU (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/1804/oj (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- United Nations Climate Change. The Paris Agreement. What Is the Paris Agreement? Available online: https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/paris-agreement (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- EU Economy and Society to Meet Climate Ambitions. European Green Deal: Commission Proposes Transformation of EU Economy and Society to Meet Climate Ambitions. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/IP_21_3541 (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Ustawa z dnia 21 listopada 2024 r. o zmianie Ustawy o elektromobilności i paliwach alternatywnych oraz niektórych innych ustaw (D.U. 2024 r. poz. 1853). Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20240001853 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Zero emissions powertrains. Product catalogue 2023. Available online: https://www.solarisbus.com/public/assets/content/pojazdy/Katalogi_2023/EN_Zeroemisyjne_1920_x_1080.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Solarisbus Parameters. Available online: https://ecity.solarisbus.com/en/hydrogen-bus (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Solarisbus Urbino 18 Hydrogen. Bus of the Year 2025. Available online: https://magazine.solarisbus.com/en/solaris-urbino-18-hydrogen-bus-of-the-year-2025/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Solarisbus Parameters. Available online: https://www.solarisbus.com/en/vehicles/hydrogen (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Nesobus Parameters. Available online: https://www.nesobus.pl/en/#/technical-information (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Solarisbus Parameters. Available online: https://www.solarisbus.com/public/assets/Biuro_prasowe/2021_10_Transexpo_Kielce/Technical_Details_Urbino_12_hydrogen_Transexpo_EN.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Solarisbus Parameters. Available online: https://www.solarisbus.com/public/assets/Biuro_prasowe/2022_09_14_Premiera_Urbino_18_hydrogenST/Technical_data_Urbino_18_hydrogen.pdf.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Portal H2poland.eu. Available online: https://h2poland.eu/pl/kategorie/transport/wodorowe-autobusy (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Electrical Vehicles Increasingly Popular. A Record was Set in April. Available online: https://www.gramwzielone.pl/auto-ekologiczne/20316086/elektryki-coraz-bardziej-popularne-w-kwietniu-padl-rekord (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Statistical Yearbook of the Western Pomeranian Voivodeship 2024. Available online: https://szczecin.stat.gov.pl/publikacje-i-foldery/roczniki-statystyczne/rocznik-statystyczny-wojewodztwa-zachodniopomorskiego-2024,6,24.html (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Google Maps. West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/place/Wojew%C3%B3dztwo+zachodniopomorskie/@52.5811811,18.1723548,6.58z/data=!4m6!3m5!1s0x4700e5366f382f2f:0x1020e32ad0ec110!8m2!3d53.4657891!4d15.1822581!16zL20vMDE4eG5j?entry=ttu&g_ep=EgoyMDI1MDYwNC4wIKXMDSoASAFQAw%3D%3D (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Center for Economic Initiatives of West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Available online: https://cig.wzp.pl/region-2/infrastruktura/transport-drogowy (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Transport in West Pomeranian Voivodship 2023. Available online: https://szczecin.stat.gov.pl/publikacje-i-foldery/transport-i-lacznosc-gospodarka-morska-zegluga/transport-w-wojewodztwie-zachodniopomorskim-w-2023-r-,5,15.html (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Poland’s Central Statistical Office Population. Population Status and Structure and Natural Movement by Territory in 2024 (as of 30 June 2024). Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/obszary-tematyczne/ludnosc/ludnosc/ludnosc-stan-i-struktura-ludnosci-oraz-ruch-naturalny-w-przekroju-terytorialnym-w-2024-r-stan-w-dniu-30-06,6,37.html (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Available online: https://bip.wzp.pl/artykul/wojewodztwo-zachodniopomorskie (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Koszalin in Numbers. Available online: https://www.polskawliczbach.pl/Koszalin (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Central Statistical Office in Poland. Local data bank. Available online: https://bdl.stat.gov.pl/bdl/dane/podgrup/tablica (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Google Maps. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps/@53.8058687,15.6224472,9.58z?entry=ttu&g_ep=EgoyMDI1MDYwNC4wIKXMDSoASAFQAw%3D%3D (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Jan Kasprowicz Park in Szczecin. Available online: https://rowery.wzp.pl/2137-pomorze-zachodnie-park-im-jana-kasprowicza-w-szczecinie (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- The Roads and Public Transport Authority in Szczecin. Available online: https://www.zditm.szczecin.pl/en/passenger/timetables/by-line (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Open Street Maps. Available online: www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Szczecin Municipal Office Public Information Office. Available online: https://bip.um.szczecin.pl/files/46FDB3E68DA645FEB0BCE80984EE9904/26589%20dostepna%20cyfrowo.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- The Pomeranian Dukes Park. Available online: https://rowery.wzp.pl/en/3599-pomorze-zachodnie-the-pomeranian-dukes-park (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Map of bus stations in Koszalin. Available online: http://mapka.mzk.koszalin.pl (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Deep reinforcement learning-based energy management strategy for fuel cell buses integrating future road information and cabin comfort control. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 321, 119032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yi, F.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, D.; Wu, G. Hydrogen leakage source positioning method in deep belief network based on fully confined space Gaussian distribution model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 63, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, A.; Perez Carrera, C.; Pappalardo, C.M.; Guida, D.; Berardi, V.P. A Comprehensive Literature Review on Hydrogen Tanks: Storage, Safety, and Structural Integrity. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony Jose, S.; Gallant, A.; Gomez, P.L.; Jaggers, Z.; Johansson, E.; LaPierre, Z.; Menezes, P.L. Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Batteries 2025, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Rial, R. Biofuels versus climate change: Exploring potentials and challenges in the energy transition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 196, 114369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, A.F.; Ateş, N.; Alotaibi, S.; Alzahrani, T.; Amsal, A.M.; Elsayed, S.K. Sustainable hybrid systems for electric vehicle charging infrastructures in regional applications. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Viktor, P.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mahmood Ali, B.; Algburi, S.; Alzoubi, H.M.; Khudhair Al-Jiboory, A.; Zuhair Sameen, A.; Salman, H.M.; Jaszczur, M. The renewable energy role in the global energy Transformations. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 48, 100545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Users Type | Selected Station Location Preferences |
|---|---|
| Bus operators | Costs, bus lines congestion, accessibility, strategic location, energy storage systems, infrastructure compatibility, station power and charge efficiency, safety of performed operations, etc. |
| Individual/residential users | Prices, location, accessibility, convenience, and charging point information and payment system, charging station level of service, charging power, comfort and amenities, etc. |
| Type of Vehicle | Advantages | Infrastructure Implication |
|---|---|---|
| FCEVs | Fast refuelling: FCEVs can be refuelled with high-pressure hydrogen gas in several minutes | Hydrogen refuelling stations can potentially service many vehicles per dispenser per day |
| More extended range: FCEVs typically offer ranges of 300–400 km and more | Fewer stations are needed overall to provide coverage, especially on long-distance corridors, compared to shorter-range BEVs | |
| Lower weight sensitivity: hydrogen tanks weigh significantly less than the massive batteries required to give heavy-duty trucks or buses | Infrastructure planning can focus strategically on freight corridors, ports, and distribution hubs, where the value proposition is strongest | |
| Reduced network load at the dispensing point: FCEV does not draw massive instantaneous power from the grid like multiple DC fast chargers operating simultaneously | Planning of station locations focus on the hydrogen supply chain (production, transport, storage) rather than solely on high-power grid upgrades at every station location | |
| Scalable station capacity | Adding more storage and dispensers can potentially scale the vehicle throughput of a hydrogen station more easily than adding multiple Megawatt-level chargers | |
| BEVs | Use of the existing electrical grid, which already exists | Upgraded or existing grid capacity may be used for installing charging stations, not building an entirely new fuel production, transportation, and distribution network |
| Different charging options: BEVs can be charged at home overnight, at various public locations or at other places | Infrastructure planning can include incentives and standards for home/work charging (slow or fast), distributing the load and cost | |
| Energy-efficient charging: using electricity directly from the grid to charge a battery is generally more energy-efficient than using electricity to produce hydrogen | The infrastructure must support a lower total energy demand for the same number of kilometres travelled | |
| Lower station complexity and cost: slower/fast chargers may be installed in different locations | Chargers are generally less complex and expensive per unit than high-pressure hydrogen refuelling stations currently | |
| Market adoption: BEVs have a significant head start in market adoption | There is an established demand to justify investment |
| Parameter | Description | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen storage capacity | Amount of hydrogen stored in onboard tanks | 37.5 kg (5 rooftop tanks, Type IV) |
| Range | Maximum driving distance on a full hydrogen tank | Up to 350 km (Solaris Urbino 12) ~300 km (NesoBus) |
| Refuelling Time | Time required to refuel the hydrogen tanks to full | Approximately 8–15 min |
| Efficiency | The efficiency of converting hydrogen energy into electricity | Around 45–60% |
| Electric Motor Power | Power output of the electric traction motor | 160–180 kW |
| Battery Capacity | Capacity of the onboard battery used for boosting and regenerative braking | 30–60 kWh (Li-ion battery) |
| Top Speed | Maximum achievable speed | Around 85 km/h |
| Acceleration | Time to reach operational speed (e.g., 0–50 km/h) | ~20 s |
| Parameter | Solaris Urbino 12 Hydrogen | Solaris Urbino 18 Hydrogen | Nesobus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drive axle | Electric axle with two integrated motors 2 × 125 kW | Portal axle Central engine standard | Model AVE 130 AxTrax |
| Hydrogen fuel cell, kW | 70 | 100 | 70 |
| Hydrogen tank type | Type 4, composite tanks | Composite tanks | Type 4, composite tanks |
| Hydrogen tank capacity, l | 1560 (5 × 312) | 5 × 312, 3 × 190 | 5 × 312 |
| Batteries, kWh | Solaris High Power, 29.2 | Solaris batteries, about 60 | Type LTO, 2 × 15.2 |
| City with Powiat Status | Area, km2 | Population (30 June 2024), Thousand Persons | Population Density, Persons/km2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Szczecin | 300.55 | 387.7 | 1290 |
| Koszalin | 98.34 | 105.1 | 1069 |
| City with Powiat Status | Percentage Share of Buses Registered, % | Calculated Number of Stations, pcs. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | 2040 | ||
| Szczecin | 79.8 | 1 | 6 |
| Koszalin | 20.2 | 1 | 1 |
| Sum | 100 | 2 | 7 |
| District | Number of Settlements, pcs. | Population of Each District (31 December 2023), Persons | Percentage Share of Population of Each District, % | Calculated Number of Stations, pcs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Śródmieście | 10 | 105,800 | 30 | 2 |
| Północ | 7 | 637 | 16 | 1 |
| Zachód | 9 | 112,602 | 32 | 2 |
| Prawobrzeże | 11 | 76,860 | 22 | 1 |
| No. | Station Location | Order of Station Implementation | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Street/Avenue | District | |||
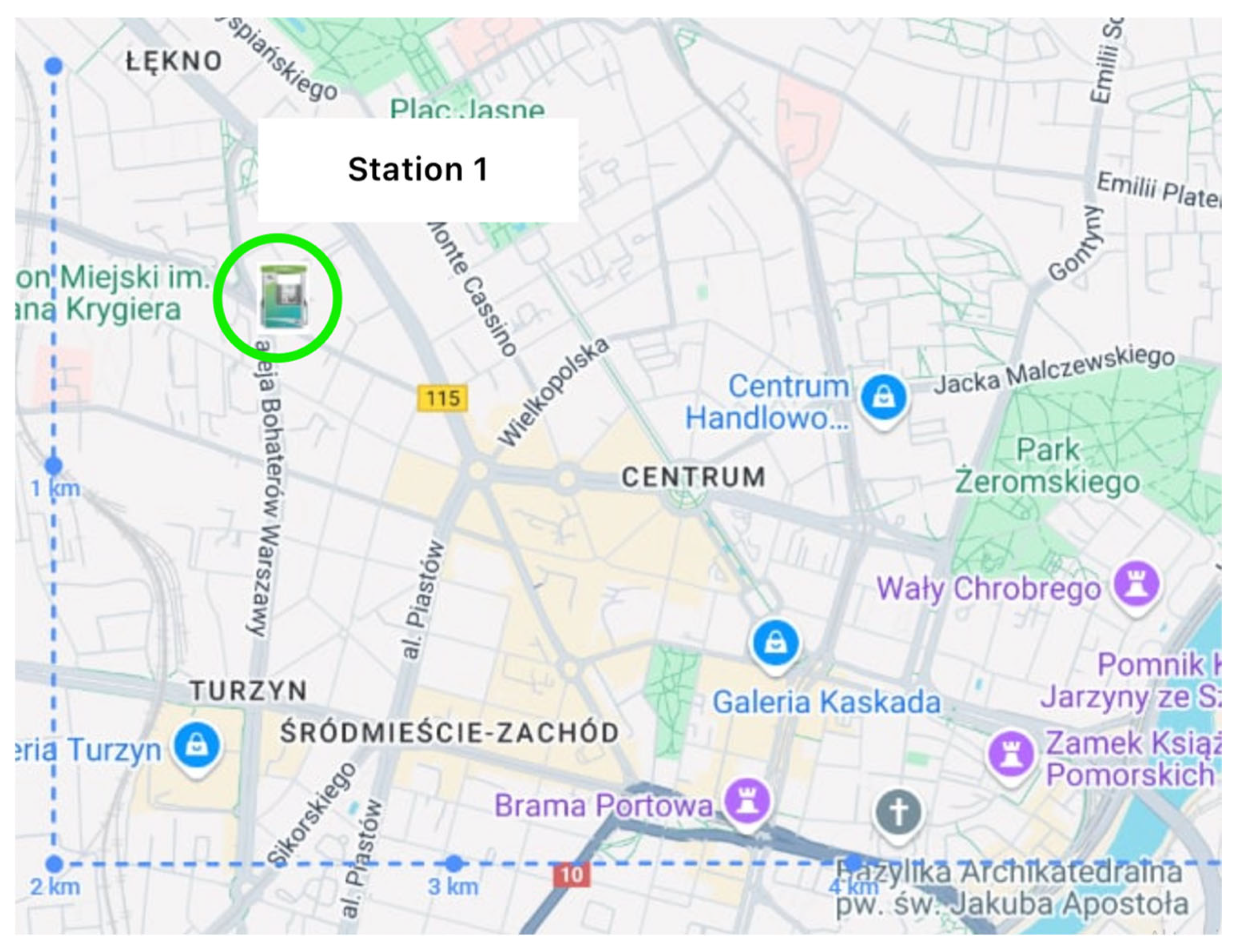
| 1 | Adama Mickiewicza Str. | Śródmieście | 1 | The station may be located near a section of the public transport network, which includes lines such as 60, 67, 86. |
| 2 | Wojska Polskiego Ave. | Zachód | 2 | The station may be located near a section of the public transport network, which includes lines such as 53, 60. |
| 3 | 1 Maja Str. | Śródmieście | 3 | The station may be located near a section of the public transport network, which includes lines such as 53, 58, 60, 63. |
| 4 | Profesora Ludwika Janiszewskiego Str. | Zachód | 4 | The station may be located near a section of the public transport network, which includes lines such as 53, 61. |
| 5 | Goleniowska Str. | Prawobrzeże | 5 | The station may be located near a section of the public transport network, which includes lines such as 64, 96, C. |
| 6 | Bogumińska Str. | Północ | 6 | The station may be located near a section of the public transport network, which includes lines such as 101, 107, 63. |
| City with Powiat Status | 2025 | 2030 | 2040 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Szczecin | 160 | 320 | 480 |
| Koszalin | 80 | 160 | 240 |
| City with Powiat Status | Daily Demand, kg/day | Dispensing Rate Required, kg/hour | Number of Dispensers, pcs. | Days of Storage, Number of Days | Hydrogen Storage Capacity, kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Szczecin | 480 | 69 | 3 | 1 | 480 |
| 2 | 960 | ||||
| 3 | 1440 | ||||
| Koszalin | 240 | 34 | 2 | 1 | 240 |
| 2 | 480 | ||||
| 3 | 720 |
| Selected Cities and Towns | Area, km2 | Population (30 June 2024), Thousand Persons | Registered Buses (2023), pcs. | Proposed Number of Stations, pcs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Szczecin | 300.55 | 387.7 | 1.718 | 3 |
| Koszalin | 98.34 | 105.1 | 1.443 | 1 |
| Stargard | 48.08 | 66.272 | 528 | 1 |
| Kołobrzeg | 25.67 | 43.364 | 26 | 1 |
| Świnoujście | 197.20 | 38.728 | 138 | 1 |
| City | Location Description | Location Visualization |
|---|---|---|
| Świnoujście | Barlickiego Street. Near the port and ferry crossing. Proximity to the main public transport hub, with convenient connections to the main route towards Szczecin. |  |
| Kołobrzeg | Trzebiatowska Street. Near the MZK bus depot and the ring road. The direct vicinity of the bus depot—optimal for logistics and refuelling. Regional road DW102 is close, and the S6 expressway is easily accessible. | 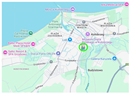 |
| Stargard | Broniewskiego Street. In the immediate vicinity of the MPK Stargard bus depot, adjacent to national road DK10 and near DK20. | 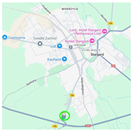 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filina-Dawidowicz, L.; Miłek, D.; Baziukė, D. The Concept of an Infrastructure Location to Supply Buses with Hydrogen: A Case Study of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland. Energies 2025, 18, 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123026
Filina-Dawidowicz L, Miłek D, Baziukė D. The Concept of an Infrastructure Location to Supply Buses with Hydrogen: A Case Study of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123026
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilina-Dawidowicz, Ludmiła, Dawid Miłek, and Dalia Baziukė. 2025. "The Concept of an Infrastructure Location to Supply Buses with Hydrogen: A Case Study of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland" Energies 18, no. 12: 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123026
APA StyleFilina-Dawidowicz, L., Miłek, D., & Baziukė, D. (2025). The Concept of an Infrastructure Location to Supply Buses with Hydrogen: A Case Study of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in Poland. Energies, 18(12), 3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123026








