Heat Exchanger Networks: Applications for Industrial Integrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
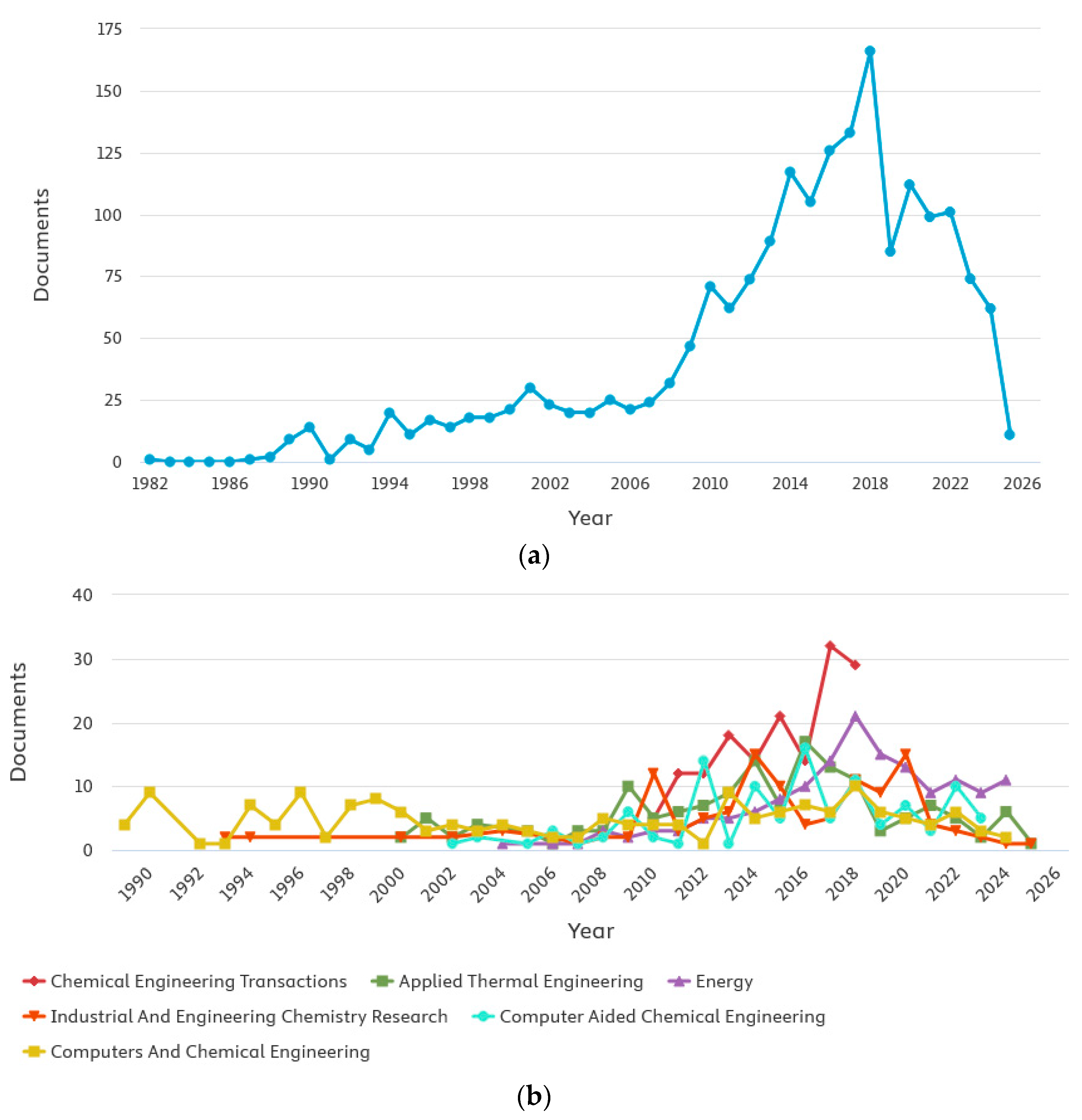
2. Bibliometric Study
- Reports on the practical experiences as well as guidelines in several countries;
- Industrial symbiosis tools and optimization;
- The topic of HI and, more recently, the simultaneous integration of heat and work;
- Integration and management of water/wastewater and material.
3. Industrial Symbiosis and Eco-Industrial Parks
3.1. Industrial Symbiosis
3.2. Eco-Industrial Parks
- Fairfield (Baltimore, Maryland), which mainly contains petroleum and organic chemical companies. The Baltimore Development Corporation developed the EIP concept with the assistance of Cornell University.
- The Brownsville Regional Industrial Symbiosis Project (Brownsville, TX, USA) is pursuing the idea of a “virtual EIP” that links industries that are not necessarily located in the same area.
- Cape Charles Sustainable Technologies Industrial Park (Cape Charles, VA, USA).
- Chattanooga (TN, USA) has several defined goals, such as developing multi-purpose facilities, affordable housing, and a clean public transport system based on electric buses.
- Project objectives (for the Netherlands, the economic and environmental aspects are valued equally, while in the USA, the prime objective is creating local jobs, and economic aspects are weighted more than environmental aspects).
- Initiators and finance (in the Netherlands, the initiators are local entrepreneur/employer associations in close cooperation with the government who also participate financially in the development process, whereas in the USA, the local industry is more passive, and the local government is the main initiator of such projects).
- Public participation (local non-governmental organizations and local communities are actively involved in developing the USA EIP projects. In the Netherlands, the companies and direct stakeholders carry out the EIP development process).
4. Integration Options Within Eco-Industrial Parks
4.1. Heat Integration in Eco-Industrial Parks
4.2. Heat and Work Integration in Eco-Industrial Parks
4.3. Water and Material Stream Integration in Eco-Industrial Parks
5. Challenges in Designing HENs for Industrial Parks
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, D.Z. Global Experiences with Special Economic Zones, Focus on China and Africa; World Bank Policy Research Working Paper; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Frosch, R.A.; Gallopoulos, N.E. Strategies for Manufacturing. Sci. Am. 1989, 261, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, J.; Gertler, N. Industrial Ecology in Practice: The Evolution of Interdependence at Kalundborg. J. Ind. Ecol. 1997, 1, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graedel, T.; Allenby, B. Industrial Ecology; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, D. Industrial Symbiosis and Eco-Industrial Development: An Introduction. Geogr. Compass 2008, 2, 1138–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertow, M.R. Industrial symbiosis: Literature and taxonomy. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2000, 25, 313–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, D.R.; Laybourn, P. Redefining Industrial Symbiosis: Crossing Academic–Practitioner Boundaries. J. Ind. Ecol. 2012, 16, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, E.A.; Moran, S.R.; Holmes, D.B.; Martin, S. Fieldbook for the Development of Eco-Industrial Parks; Indigo Development: Oakland, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, E.A. Eco-Industrial Handbook for Asian Developing Countries; Report to the Asian Development Bank, Environment Department: Metro Manila, Philippines, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor, T.; Adam, E.; Bates, M. Drivers and limitations for the successful development and functioning of EIPs (eco-industrial parks): A literature review. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 61, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeres, R.R.; Vermeulen, W.J.V.; De Walle, F.B. Eco-industrial park initiatives in the USA and the Netherlands: First lessons. J. Clean. Prod. 2004, 12, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, R.P.; Cohen-Rosenthal, E. Designing eco-industrial parks: A synthesis of some experiences. J. Clean. Prod. 1998, 6, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chertow, M.; Song, Y. Developing country experience with eco-industrial parks: A case study of the Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B. Eco-industrial parks: National pilot practices in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Côté, R.P.; Fujita, T. Assessment of the National Eco-Industrial Park Standard for Promoting Industrial Symbiosis in China. J. Ind. Ecol. 2009, 13, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Park, J.Y.; Park, H.-S. A review of the National Eco-Industrial Park Development Program in Korea: Progress and achievements in the first phase, 2005–2010. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.U.; Jeong, J.H.; Jeong, S.K. Assessing the performance of carbon dioxide emission reduction of commercialized eco-industrial park projects in South Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wu, H.; Jin, H.; Yang, M. System study of combined cooling, heating and power system for eco-industrial parks. Int. J. Energy Res. 2008, 32, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Yoon, S.-G.; Chae, S.H.; Park, S. Economic and environmental optimization of a multi-site utility network for an industrial complex. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipólito-Valencia, B.J.; Rubio-Castro, E.; Ponce-Ortega, J.M.; Serna-González, M.; Nápoles-Rivera, F.; El-Halwagi, M.M. Optimal design of inter-plant waste energy integration. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 62, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhole, V.R.; Linnhoff, B. Total site targets for fuel, co-generation, emissions, and cooling. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1993, 17, S101–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemeš, J.; Dhole, V.R.; Raissi, K.; Perry, S.J.; Puigjaner, L. Targeting and design methodology for reduction of fuel, power and CO2 on total sites. Appl. Therm. Eng. 1997, 17, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Hirochi, Y.; Tatsumi, H.; Shire, T. Applying heat integration total site based pinch technology to a large industrial area in Japan to further improve performance of highly efficient process plants. Energy 2009, 34, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, S.-G.; Park, S. Optimization of a waste heat utilization network in an eco-industrial park. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.; Walmsley, M.; Neale, J. Application of heat recovery loops for improved process integration between individual plants at a large dairy factory. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2011, 25, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Dong, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, L.; Du, J. Industrial park heat integration considering centralized and distributed waste heat recovery cycle systems. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-L.; Chang, C.-T.; Jiang, D. A game-theory based optimization strategy to configure inter-plant heat integration schemes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 118, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, C.; Feng, X. A systematic framework for multi-plants Heat Integration combining Direct and Indirect Heat Integration methods. Energy 2015, 90, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.J.; Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q.L. Network Modeling and Design for Low Grade Heat Recovery, Refrigeration, and Utilization in Industrial Parks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9725–9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Chhabra, P.; Garud, S.S.; Aditya, K.; Romagnoli, A.; Comodi, G.; Dal Magro, F.; Meneghetti, A.; Kraft, M. A novel methodology for the design of waste heat recovery network in eco-industrial park using techno-economic analysis and multi-objective optimization. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, D. Modeling, Estimation, and Control of Waste Heat Recovery Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, K.H.; Klemeš, J.J.; Wan Alwi, S.R.; Abdul Manan, Z. Industrial implementation issues of Total Site Heat Integration. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 61, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, P.Y.; Wan Alwi, S.R.; Klemeš, J.J.; Varbanov, P.S.; Abdul Manan, Z. Algorithmic targeting for Total Site Heat Integration with variable energy supply/demand. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 70, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varbanov, P.S.; Klemeš, J.J. Integration and management of renewables into Total Sites with variable supply and demand. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 35, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiete, M.; Ludwig, J.; Schultmann, F. Intercompany Energy Integration: Adaptation of Thermal Pinch Analysis and Allocation of Savings. J. Ind. Ecol. 2012, 16, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspelund, A.; Berstad, D.O.; Gundersen, T. An Extended Pinch Analysis and Design procedure utilizing pressure based exergy for subambient cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 2633–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, T.; Berstad, D.O.; Aspelund, A. Extending pinch analysis and process integration into pressure and fluid phase considerations. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2009, 18, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsung, A.; Aspelund, A.; Gundersen, T.; Barton, P.I. Synthesis of heat exchanger networks at subambient conditions with compression and expansion of process streams. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 2090–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razib, M.S.; Hasan, M.M.F.; Karimi, I.A. Preliminary synthesis of work exchange networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 37, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, V.C.; Ravagnani, M.A.S.S.; Caballero, J.A. Simultaneous synthesis of work exchange networks with heat integration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 112, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Gundersen, T. Sub-ambient heat exchanger network design including compressors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 137, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Gundersen, T. Correct integration of compressors and expanders in above ambient heat exchanger networks. Energy 2016, 116, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Smith, R. Wastewater minimisation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1994, 49, 981–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhole, V.R.; Ramchandani, N.; Tainsh, R.A.; Wasilewski, M. Make your process water pay for itself. Chem. Eng. 1996, 103, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hallale, N. A new graphical targeting method for water minimisation. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halwagi, M.M.; Gabriel, F.; Harell, D. Rigorous Graphical Targeting for Resource Conservation via Material Recycle/Reuse Networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 4319–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, Z.A.; Tan, Y.L.; Foo, D.C.Y. Targeting the minimum water flow rate using water cascade analysis technique. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Shenoy, U.V. Targeting and design of water networks for fixed flowrate and fixed contaminant load operations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takama, N.; Kuriyama, T.; Shiroko, K.; Umeda, T. Optimal water allocation in a petroleum refinery. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1980, 4, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chang, C.-T.; Ling, H.-C.; Chang. A Mathematical Programming Model for Water Usage and Treatment Network Design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 2666–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva-Argáez, A.; Vallianatos, A.; Kokossis, A. A multi-contaminant transhipment model for mass exchange networks and wastewater minimisation problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1999, 23, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagajewicz, M.; Valtinson, G. On the Minimum Number of Units in Heat Exchanger Networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 16899–16904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelady, E.M.; El-Halwagi, M.M. Design and integration of eco-industrial parks for managing water resources. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2009, 28, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, I.M.L.; Tan, R.R.; Foo, D.C.Y.; Chiu, A.S.F. Game theory approach to the analysis of inter-plant water integration in an eco-industrial park. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, S. Cost allocation evaluation of a multi-plant flexible heat exchanger network design based on fuzzy game. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 175, 108262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviso, K.B.; Tan, R.R.; Culaba, A.B.; Cruz, J.B. Bi-level fuzzy optimization approach for water exchange in eco-industrial parks. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2010, 88, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, M.; Montastruc, L.; Pibouleau, L.; Azzaro-Pantel, C.; Domenech, S. Industrial water management by multiobjective optimization: From individual to collective solution through eco-industrial parks. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 22, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.A.; Boix, M.; Aussel, D.; Montastruc, L.; Domenech, S. Water integration in eco-industrial parks using a multi-leader-follower approach. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 87, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Kulkarni, M.A.; Singh, A.; Huang, Y.L. A game theory based approach for emergy analysis of industrial ecosystem under uncertainty. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2004, 6, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Castro, E.; Ponce-Ortega, J.M.; Serna-González, M.; El-Halwagi, M.M. Optimal reconfiguration of multi-plant water networks into an eco-industrial park. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 44, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnouri, S.Y.; Linke, P.; El-Halwagi, M. Optimal interplant water networks for industrial zones: Addressing interconnectivity options through pipeline merging. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 2853–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.B.; Seager, T.P.; Massard, G.; Nies, L. Information and Communication Technology for Industrial Symbiosis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2010, 14, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, B.; Low, J.S.C.; Juraschek, M.; Herrmann, C.; Tjandra, T.B.; Ng, Y.T.; Kurle, D.; Cerdas, F.; Lueckenga, J.; Yeo, Z.; et al. Collaboration Platform for Enabling Industrial Symbiosis: Application of the By-product Exchange Network Model. Procedia CIRP 2017, 61, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Yang, K.; Che, Y.; Shang, Z.; Tai, J.; Jian, Y. Industrial solid waste flow analysis of eco-industrial parks: Implications for sustainable waste management in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillé, M.; Frayret, J. Industrial Waste Reuse and By-product Synergy Optimization. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskhiri, M.S.; Behera, S.K.; Tan, R.R.; Park, H.-S. Fuzzy optimization of a waste-to-energy network system in an eco-industrial park. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeb Gilani, B.; Morosuk, T. Heat Exchanger Networks: Applications for Industrial Integrations. Energies 2025, 18, 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123021
Saeb Gilani B, Morosuk T. Heat Exchanger Networks: Applications for Industrial Integrations. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123021
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeb Gilani, Bahar, and Tatiana Morosuk. 2025. "Heat Exchanger Networks: Applications for Industrial Integrations" Energies 18, no. 12: 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123021
APA StyleSaeb Gilani, B., & Morosuk, T. (2025). Heat Exchanger Networks: Applications for Industrial Integrations. Energies, 18(12), 3021. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123021







