Thermal and Thermo-Hydraulic Performance of a Semi-Circular Solar Air Collector Utilizing an Innovative Configuration of Metal Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This study develops a detailed three-dimensional model of the SCSAC using the COMSOL Multiphysics software version 6.2, including many operational and geometrical parameters, such as solar irradiation, ambient temperature, wind speed, SCSAC dimensions, and metal foam materials with different specifications. The methodology employed for heat generation within metal foams was originally developed and formulated by the authors.
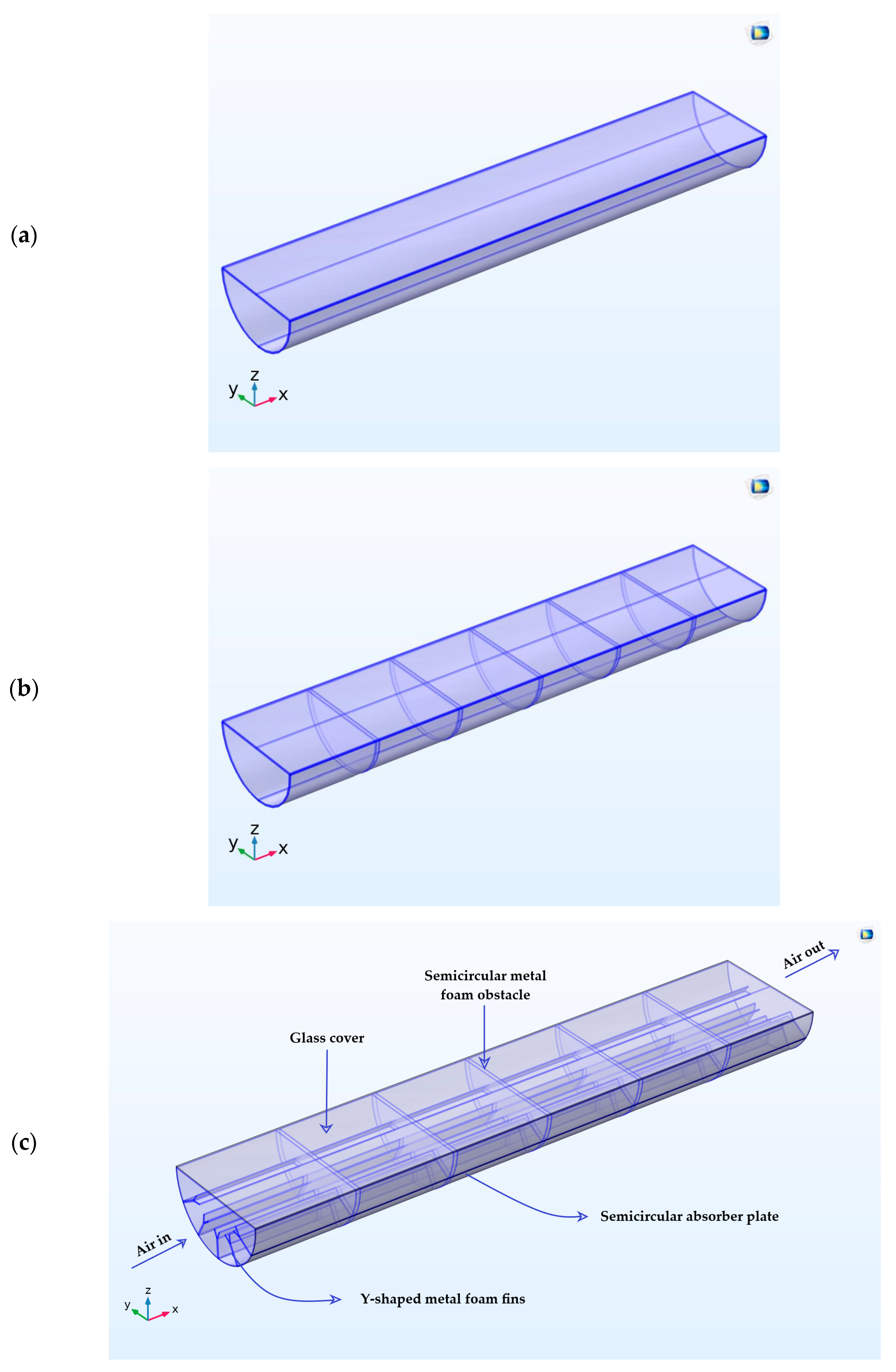
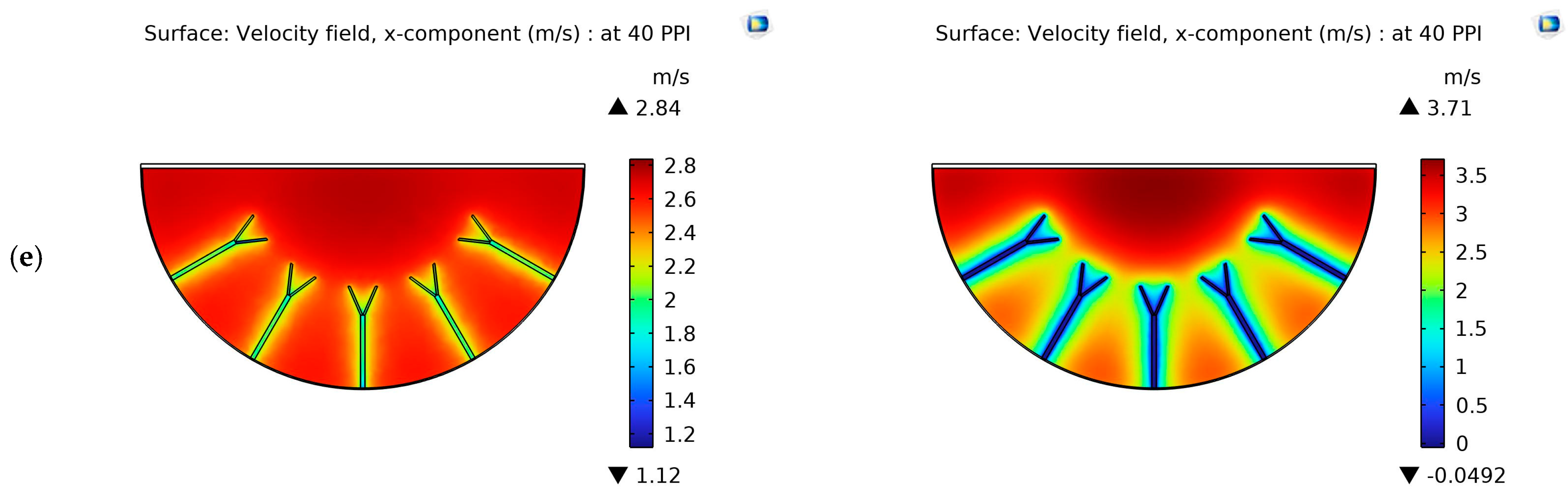
- The influence of the configuration and distribution of metal foams in air ducts on thermal performance was studied. The purpose of utilizing semicircular metal foam obstacles is to inhibit the development of the thermal boundary layer, hence enhancing the heat transfer coefficient. Additionally, the purpose of employing Y-shaped metal foam fins is to induce turbulence, hence improving the heat transfer coefficient. Accordingly, the thermal performance will be improved.
2. Methodology
2.1. Geometry and System Description
2.2. System Modelling
2.2.1. Fluid Flow Model
2.2.2. Heat Transfer Model
2.3. Mathematical Model
- (a)
- Steady-state incompressible flow.
- (b)
- The flow analysis covers entrance and fully developed regions.
- (c)
- The flow is modeled as turbulent flow because of the following:
- The obstruction of metal foam.
- The Reynolds numbers at the entrance of the air passage are mostly in the turbulent region.
- (d)
- The thermo-physical properties of the working fluid (air) are constant.
- (e)
- The properties of metal foams are uniform, homogeneous, and isotropic.
- (f)
- The bottom and side edges are well-insulated.
- (g)
- The radiation heat losses from the bottom side are neglected.
- (h)
- There is no air leakage.
2.3.1. Energy Balance Technique of SCSAC System
2.3.2. Governing Equations in Free and Porous Regions
2.3.3. Surface-to-Surface Radiation Model
2.4. Performance Evaluation of SCSAC System
Statistical Evaluation of the Studied Parameters with Reference to Model (I)
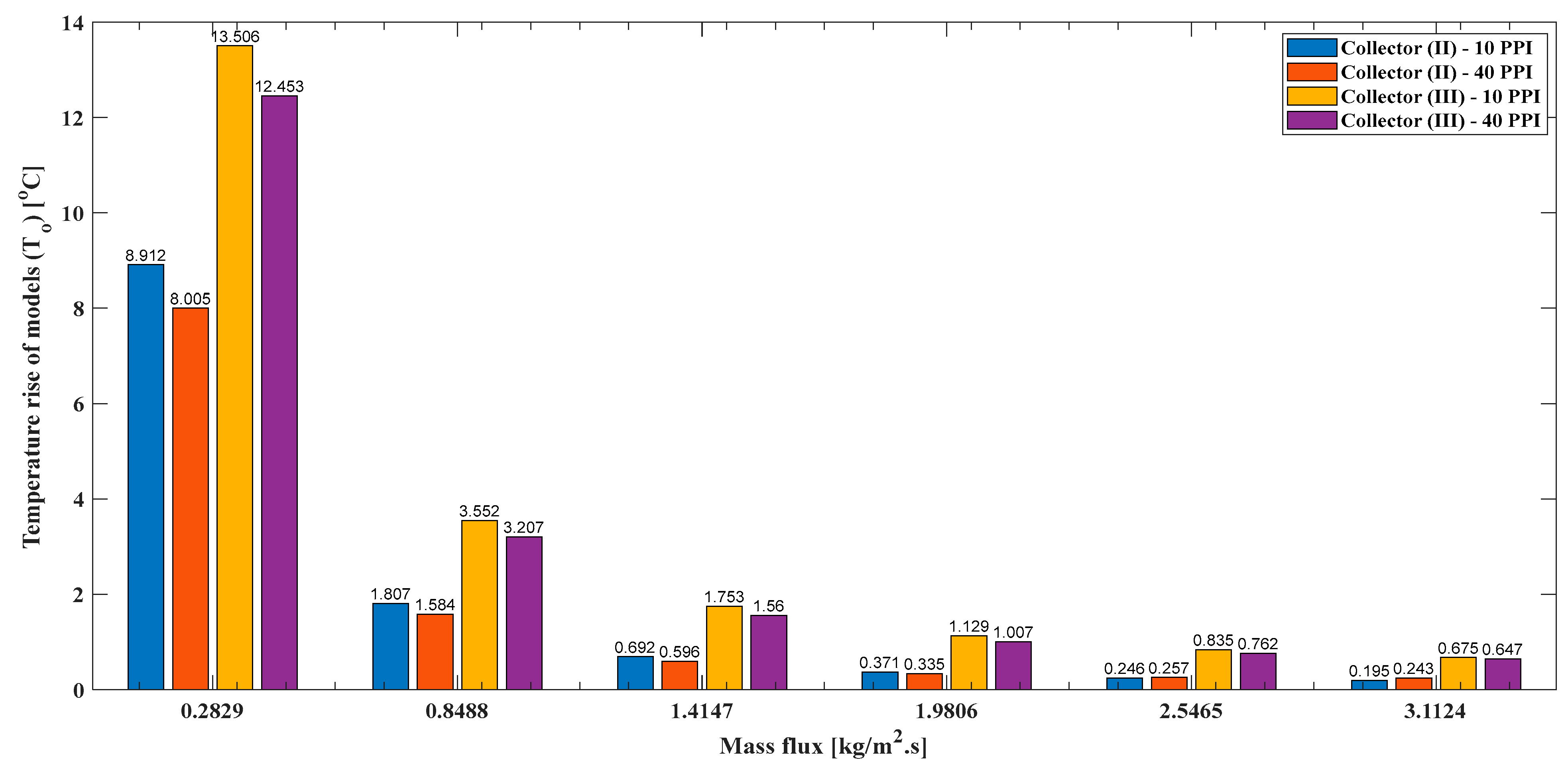
- Outlet air temperature evaluation can be estimated by calculating the outlet air temperature rise of model (II) and model (III) compared to model (I) as follows:
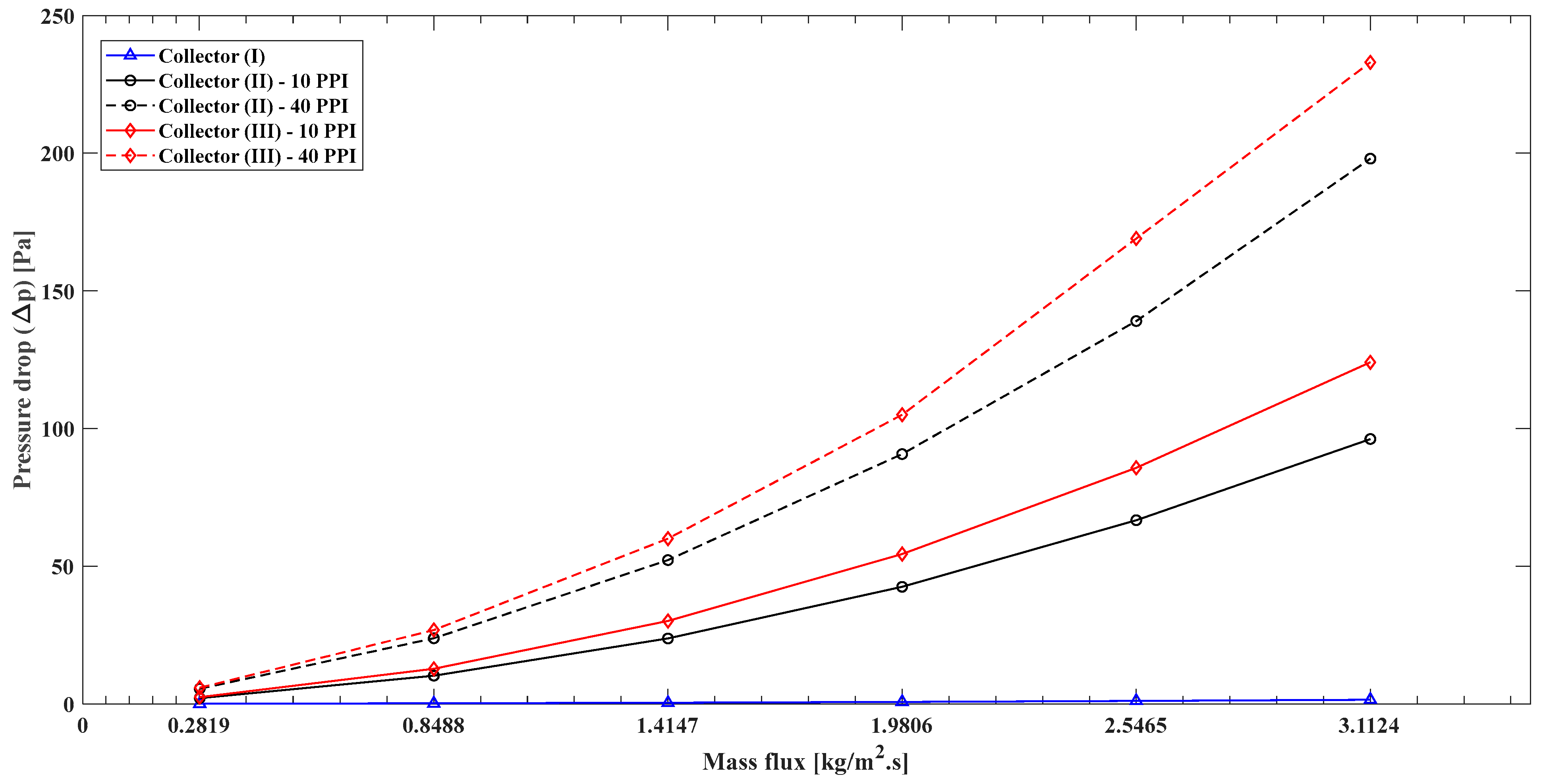
- The pressure drop evaluation can be estimated by calculating the additional pressure drop of model (II) and model (III) compared to model (I) as follows:
- The fan power consumption can be evaluated by calculating the additional fan consumption of model (II) and model (III) compared to model (I) as follows:
- Useful heat gain evaluation can be estimated by calculating the useful heat gain rise of model (II) and model (III) compared to model (I) as follows:
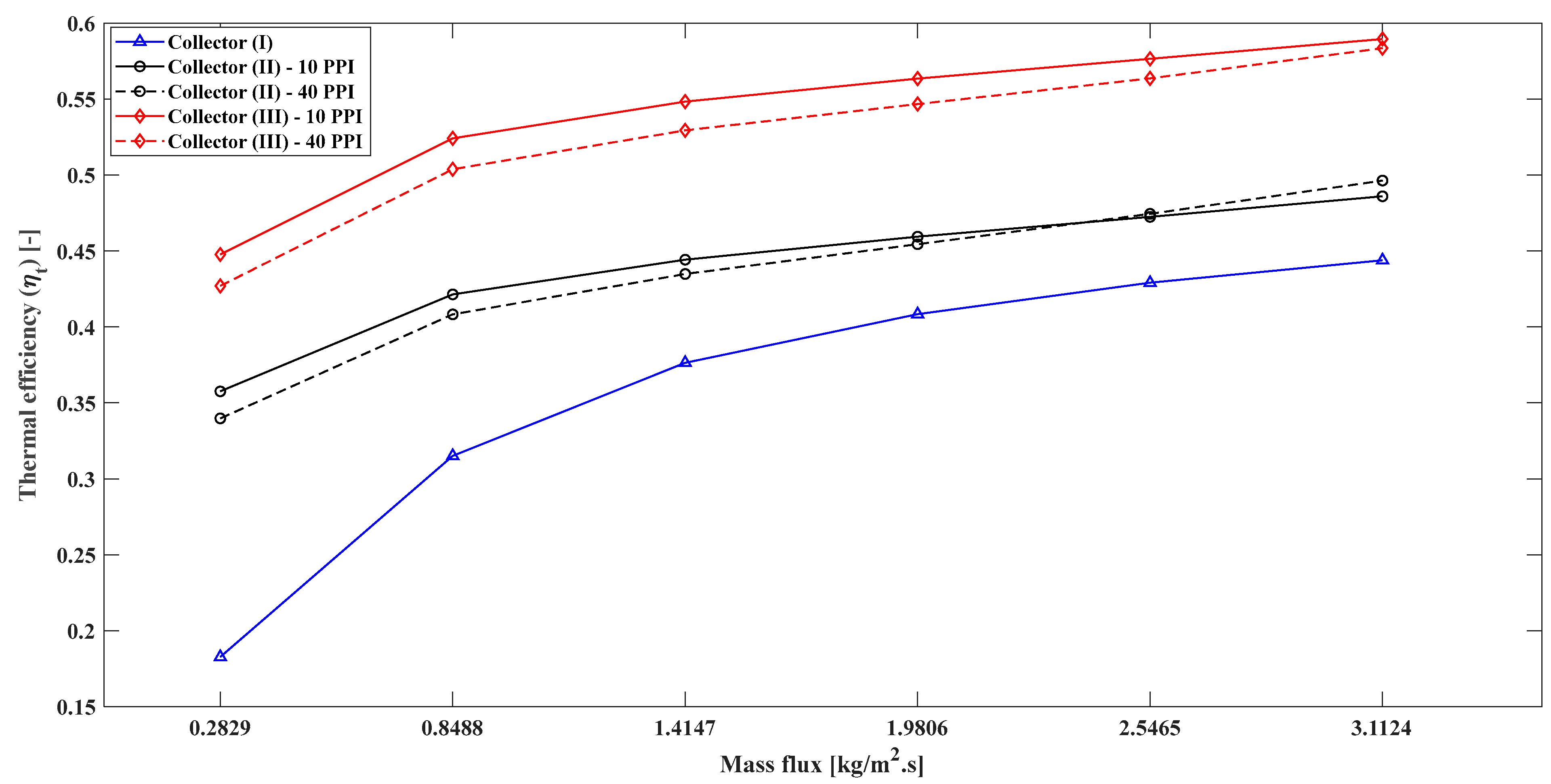
- The percentage enhancement of the thermal efficiency of model (II) and model (III) compared to model (I) can be evaluated as follows:
- The percentage enhancement of thermo-hydraulic efficiency of model (II) and model (III) compared to model (I) can be evaluated as:
3. Numerical Analysis
3.1. Numerical Solution
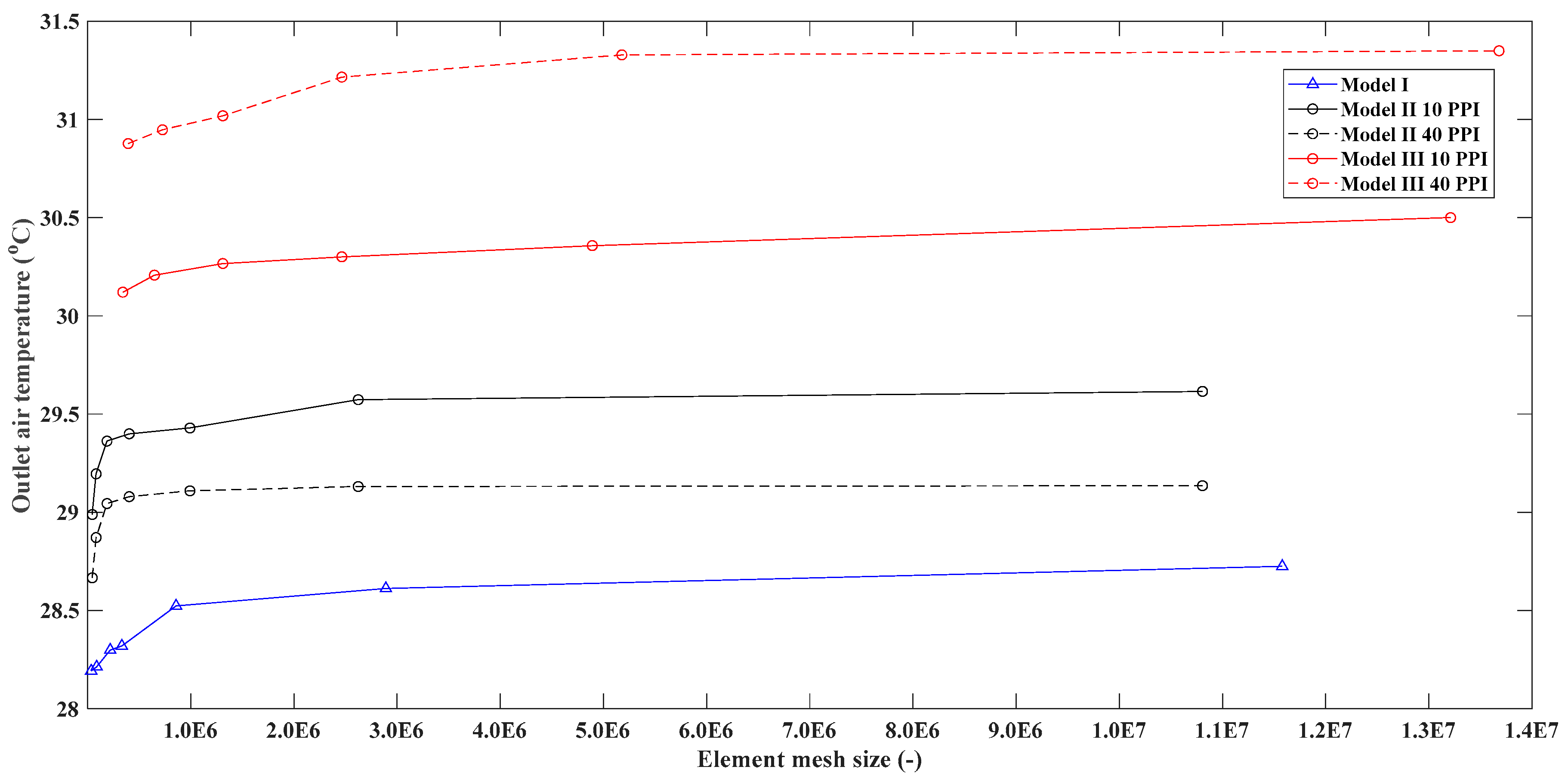
3.2. Grid Independency
3.3. Model Validation
3.4. The Initial and Boundary Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
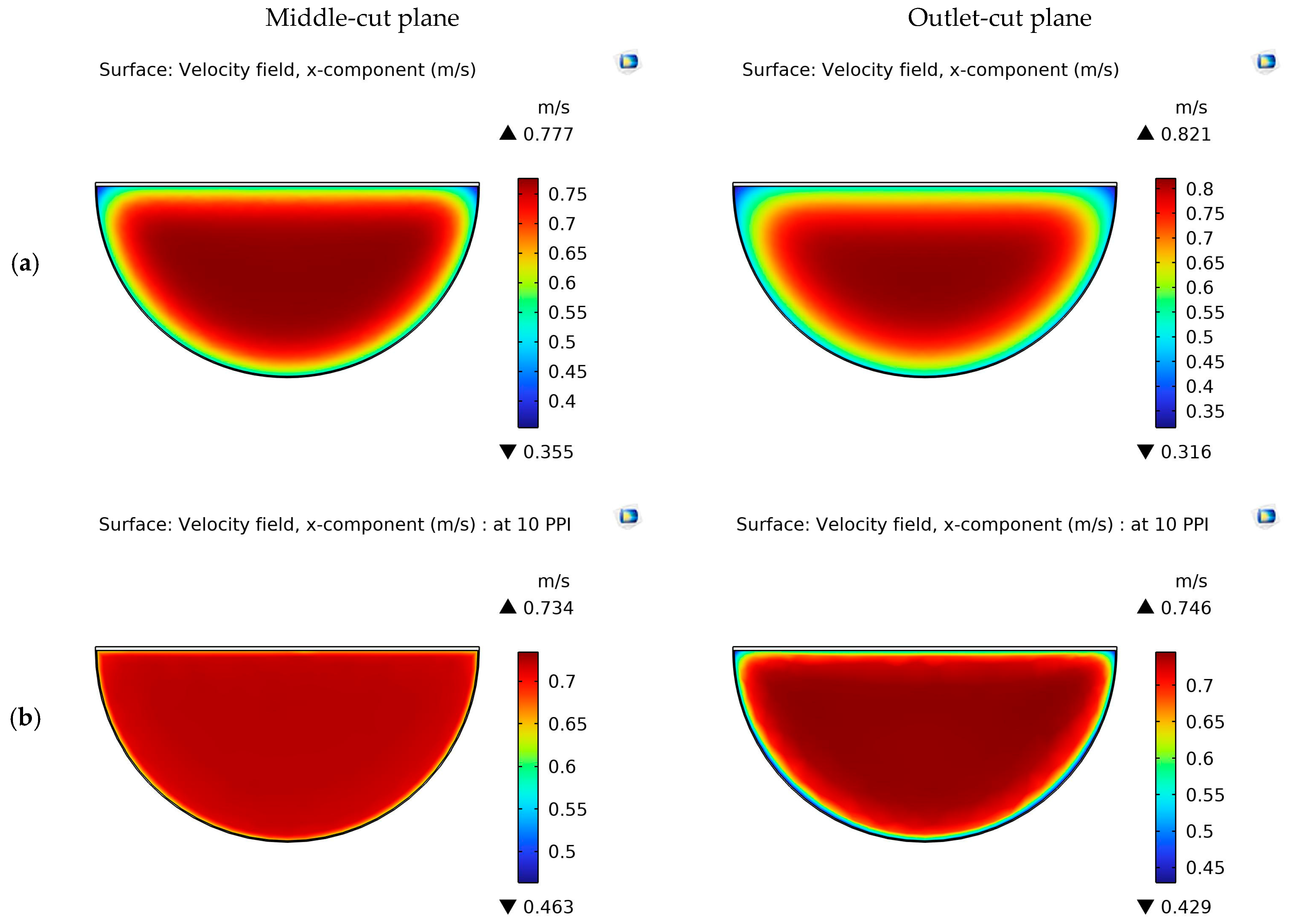
4.1. Velocity Contours
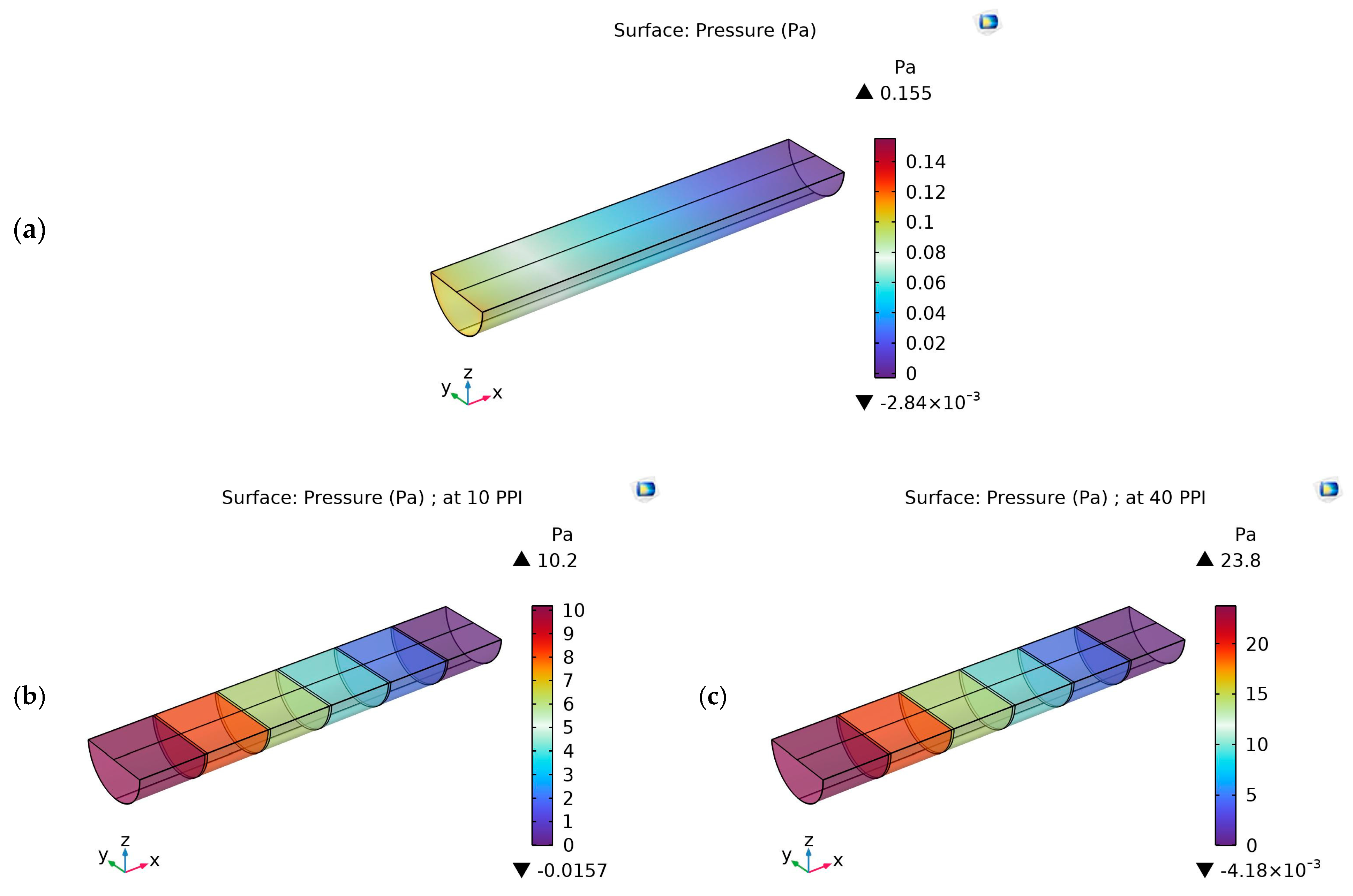
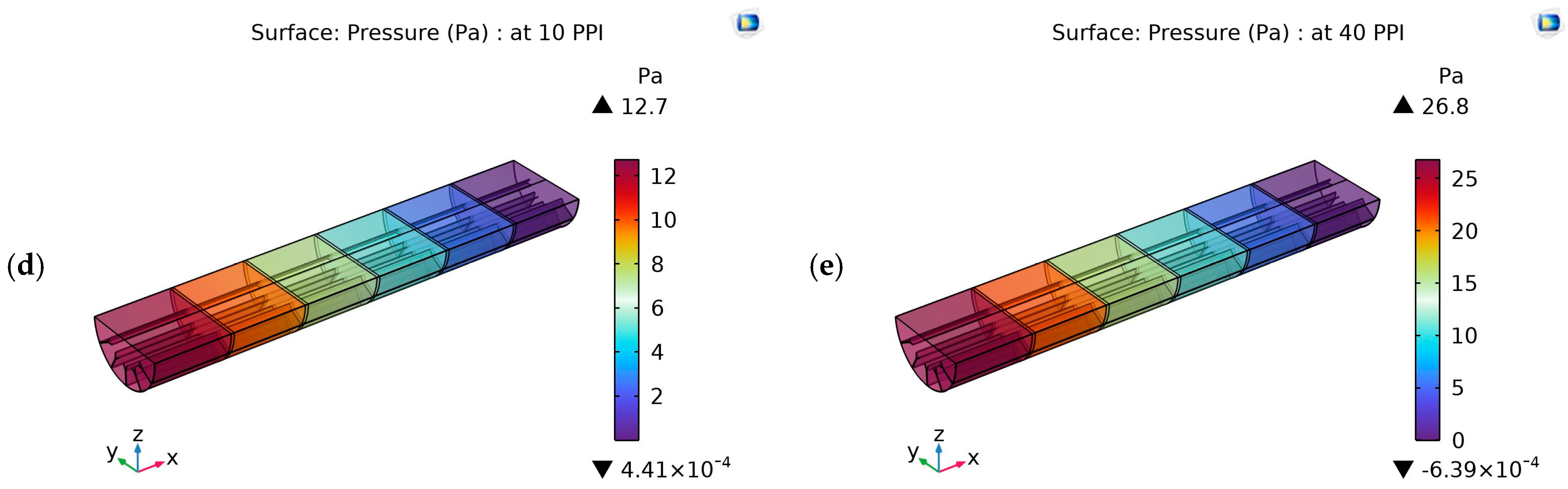
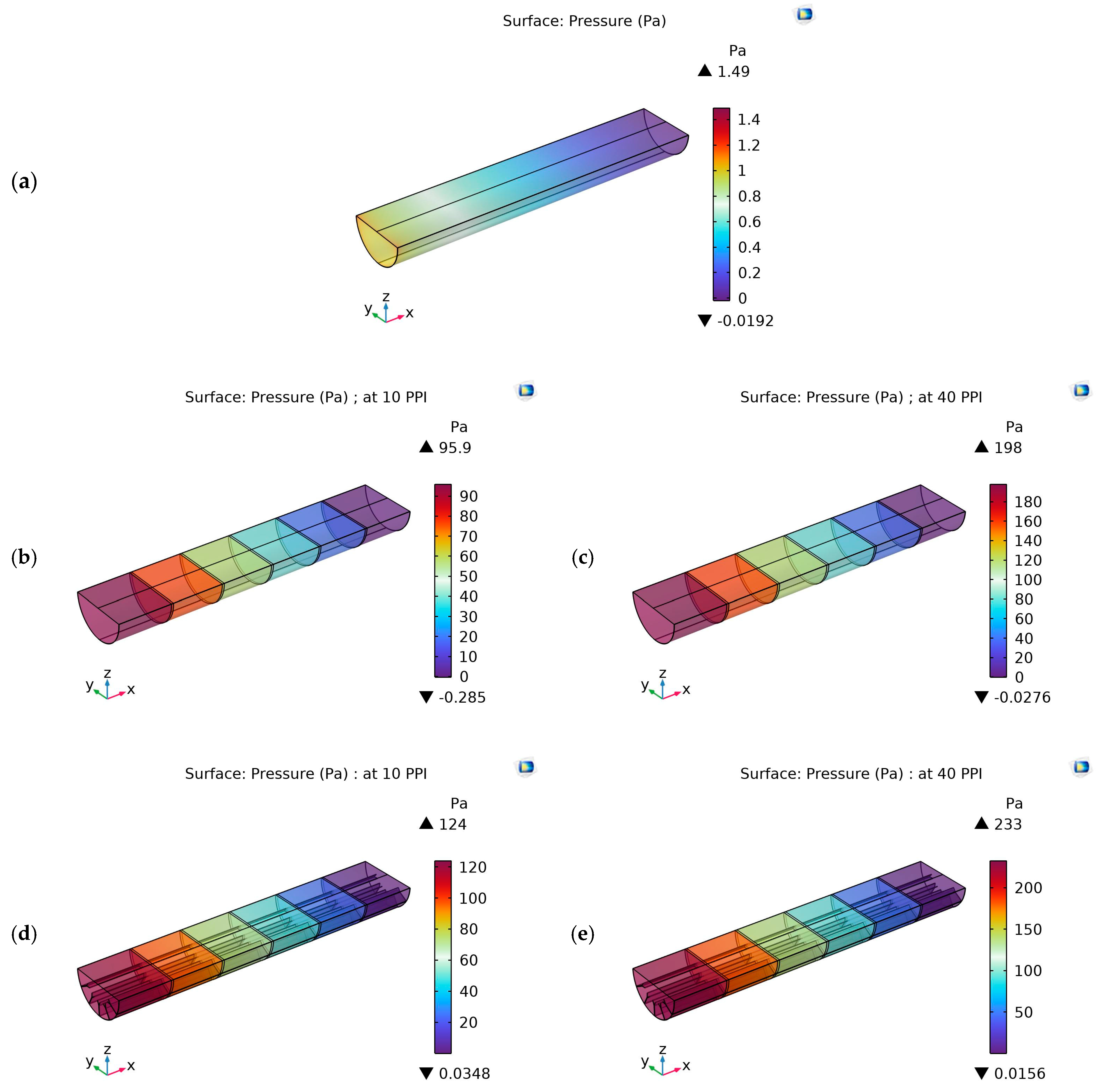
4.2. Pressure Contours
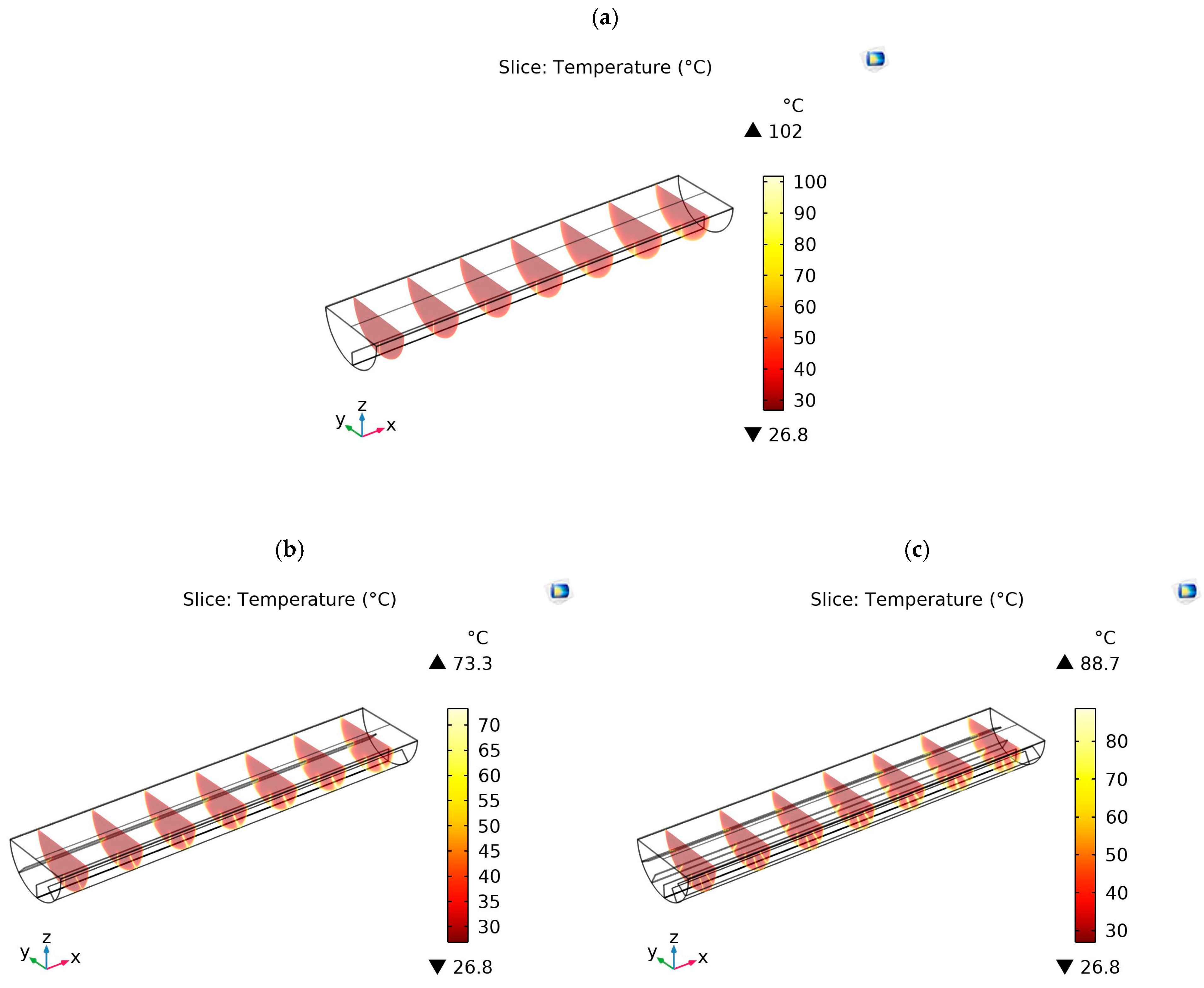
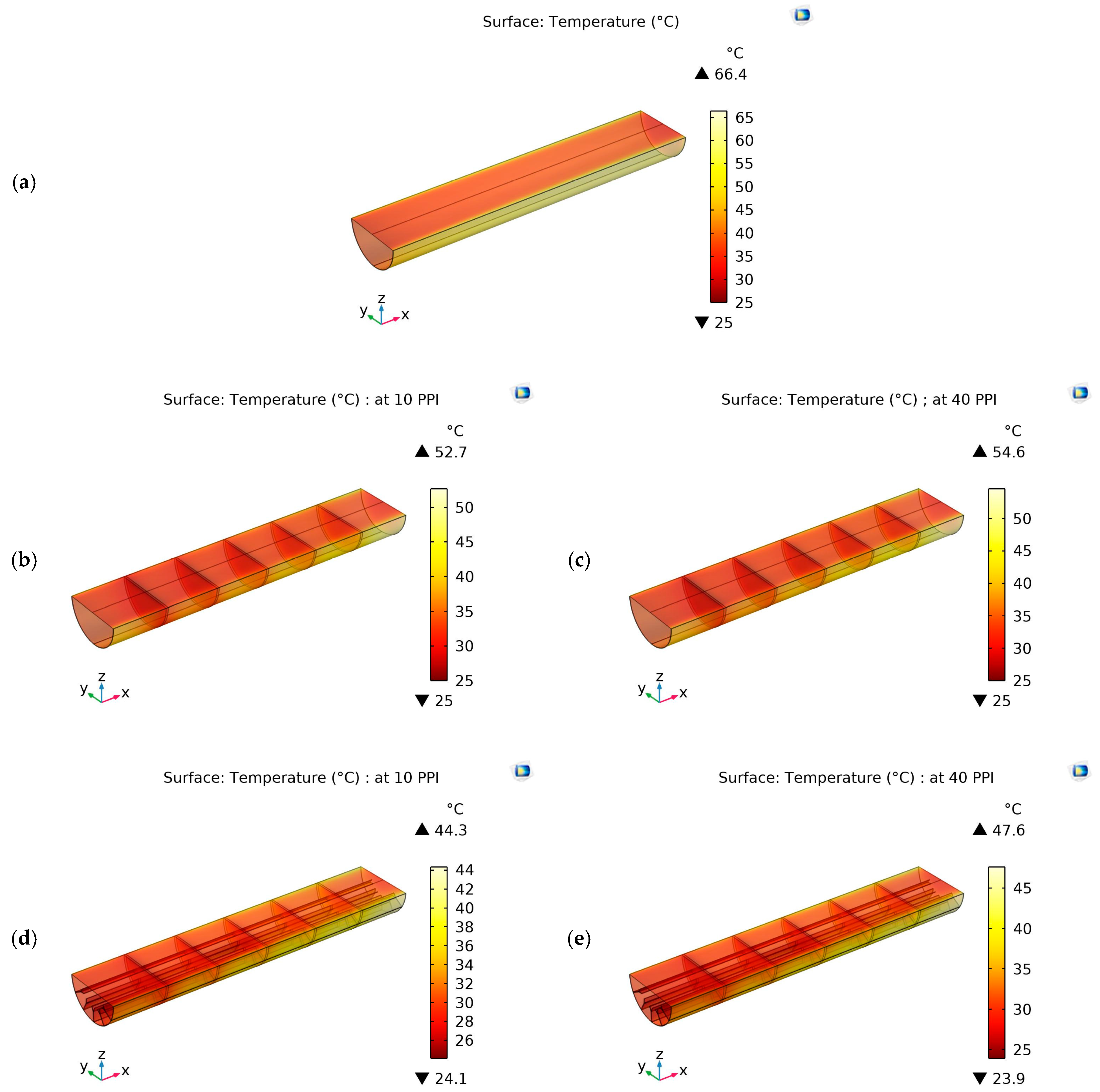
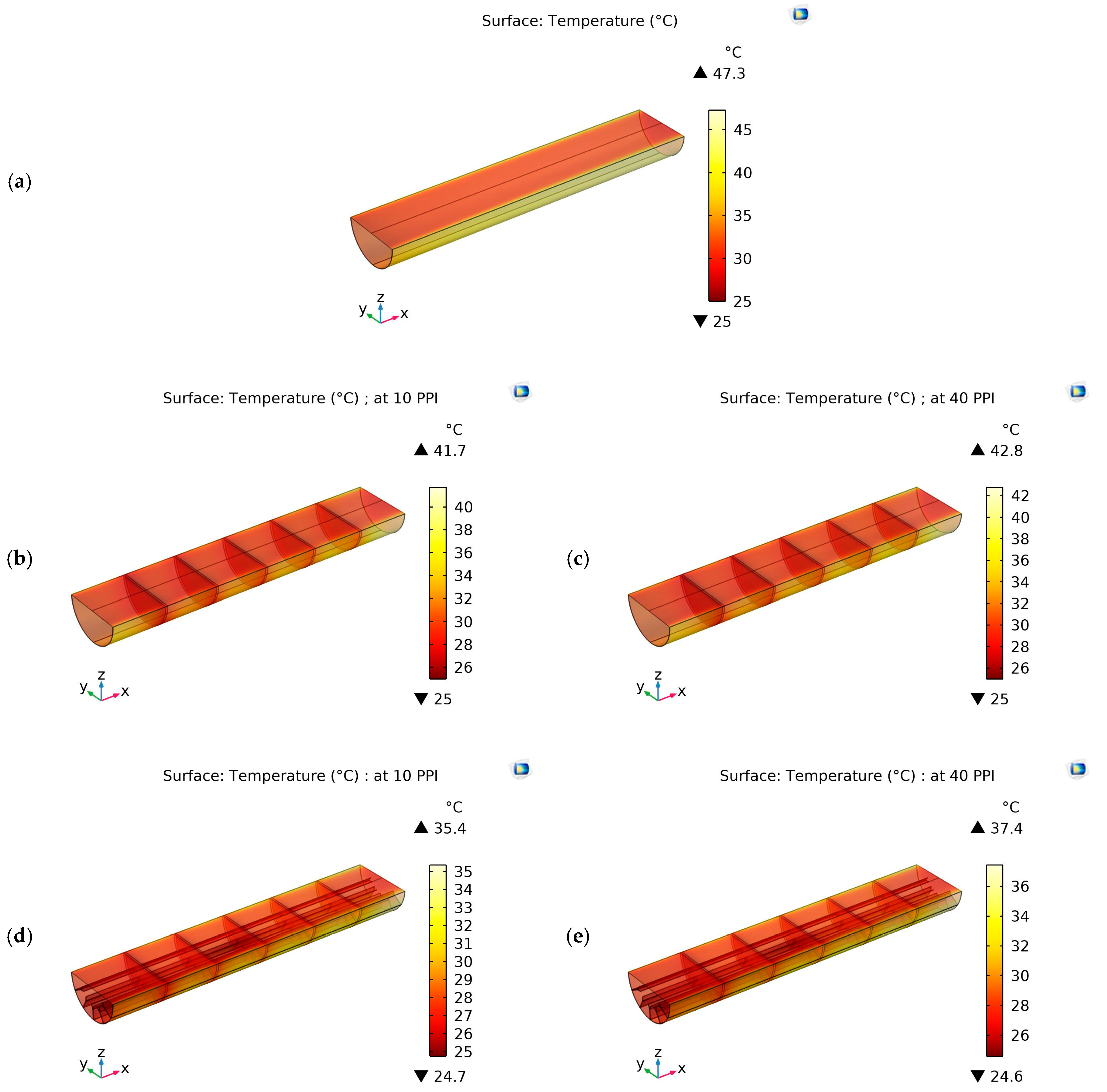
4.3. Temperature Contours
4.4. Outlet Air Temperature
4.5. Pressure Drops
4.6. Fan Power Consumption
4.7. Useful Heat Gain
4.8. Thermal Efficiency
4.9. Thermo-Hydraulic Efficiency
4.10. Average Nusselt Number
4.11. Performance Evaluation Factor (PEF)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclatures
| Area of air duct, | Temperature of absorber plate, | ||
| Area of SCSAC, | Sky temperature, | ||
| Surface area of absorber plate, | Thickness of metal foam fin, | ||
| Model coefficient, =1.44, | Thickness of glass cover, | ||
| Model coefficient, =1.92, | Thickness of absorber plate, | ||
| Model coefficient, =0.09, | Velocity vector, | ||
| Conversion factor, | Initial velocity, | ||
| Forchheimer coefficient, | Wind velocity, | ||
| Heat capacity of air, | Width of SCSAC, | ||
| Sub-grid turbulence generation by PM | Intrinsic average of parameter | ||
| Hydraulic diameter, | |||
| Blackbody hemispherical emissive power | Greek letters | ||
| Height of duct, | Thermal diffusivity, | ||
| Height of metal foam fin, | Absorptivity of glass cover, | ||
| Shape factor, | Absorptivity of absorber plate, | ||
| Irradiation components at a given point | Tilt angle of solar collector, | ||
| Combined HTC, | Turbulence dissipation rate TDR, | ||
| Forced convection HTC, | Emissivity of glass cover, | ||
| Natural convection HTC, | Emissivity of absorber plate, | ||
| Identity tensor, | Thermal efficiency, | ||
| Solar intensity, | Thermo-hydraulic efficiency, | ||
| Viscous stress tensor, | Permeability of metal foam, | ||
| Turbulent kinetic energy, | Air thermal conductivity, | ||
| Characteristic length of collector, | Thermal conductivity of air in PM, | ||
| Length of SCSAC, | Thermal conductivity of PM, | ||
| Mass flux, | Dynamic viscosity, | ||
| Mass flow rate, | Turbulent dynamic viscosity, | ||
| Normal vector | Kinetic viscosity, | ||
| Pressure, | Density of air inside the duct, | ||
| Pumping power, | Density of air outside the SAC, | ||
| Fan power consumption, | Stefan Boltzmann constant, | ||
| Prandtl number, | Stress tensor of TKE, =1.0, | ||
| Wetted perimeter, | Stress tensor of TDR, =1.3, | ||
| Production of TDR | Transmissivity of glass cover, | ||
| Production of TDR of porous matrix | Porosity of metal foam, | ||
| Production of TKE, due to velocity shear | |||
| Production of TKE of porous matrix | Abbreviations | ||
| Net radiative heat source, | FEM | Finite element method | |
| Heat generation in absorber plate, | FR | Free region | |
| Heat generation in metal foam, | HTC | Heat transfer coefficient | |
| Ra | Rayleigh number , | PR | Porous region |
| Reynolds number, | PARDISO | Parallel sparse direct solver | |
| Temperature, | PPI | Pore per inch | |
| Inlet temperature, | SAC | Solar air collector | |
| Initial temperature, | SCSAC | Semicircular solar air collector | |
| Ambient air temperature, | TDR | Turbulent dissipation rate | |
| Temperature of glass cover, | TKE | Turbulent kinetic energy | |
References
- Al-Bakri, B.A.R.; Rasham, A.M.; Al-Sulttani, A.O. Thermal Performance of Multiple-Pass Solar Air Heater with Pin Fins. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2022, 17, 2192–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Ling, X. Analysis of heat transfer and flow characteristics over serrated fins with different flow directions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyam, A.; Chand, P. Experimental investigations on thermal performance of solar air heater with wavy fin absorbers. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 55, 2651–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Dhruw, L.; Chander, S. Experimental investigation of a double pass converging finned wire mesh packed bed solar air heater. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabhane, M.G.; Kanase-Patil, A.B. Experimental analysis of double flow solar air heater with multiple C shape roughness. Sol. Energy 2017, 155, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.; Hamed, M.H.; Omara, Z.; Kandeal, A. Influence of fin height on the performance of a glazed and bladed entrance single-pass solar air heater. Sol. Energy 2018, 162, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chand, P. Performance prediction of extended surface absorber solar air collector with twisted tape inserts. Sol. Energy 2018, 169, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Abou Al-sood, M.M.; Omara, Z.M.; Bek, M.A.; Kabeel, A.E. Performance evaluation of a new counter flow double pass solar air heater with turbulators. Sol. Energy 2018, 173, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyam, A.; Chand, P. Effect of wavelength and amplitude on the performance of wavy finned absorber solar air heater. Renew. Energy 2018, 119, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarminzi, M.A.S.M.; Razak, A.A.; Azmi, M.A.A.; Fazlizan, A.; Majid, Z.A.A.; Sopian, K. Comparative study on thermal performance of cross-matrix absorber solar collector with series and parallel configurations. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 25, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasham, A.M.; Al-Bakri, B.A.R. Thermal Performance of Double-Pass Counter Flow and Double-Parallel Flow Solar Air Heater with V-Grooved Absorber Plate; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Farhan, A.A.; Sahi, H.A. Energy Analysis of Solar Collector With perforated Absorber Plate. J. Eng. 2017, 23, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.K.; Rasham, A.M.; Alshadeedi, B.M. Finite Element Modeling of Finned Double-Pass Solar Air Heaters; IEEE: Lahore, Pakistan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kabeel, A.; Khalil, A.; Shalaby, S.; Zayed, M. Experimental investigation of thermal performance of flat and v-corrugated plate solar air heaters with and without PCM as thermal energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 113, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuşka, M.; Şevik, S. Energy, exergy, economic and environmental (4E) analyses of flat-plate and V-groove solar air collectors based on aluminium and copper. Sol. Energy 2017, 158, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoli, S.; Lu, R.; Xu, D.; Yu, P. Thermal performance improvement of a solar air heater fitted with winglet vortex generators. Sol. Energy 2018, 159, 966–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, N.A.; Shbailat, S.J. Energy and Exergy Analysis of Dual Channel Solar Air Collector with Different Absorber Plates Geometry. J. Eng. 2018, 24, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.T.; Mustafa, A.T. Numerical Simulation of Thermal-Hydrodynamic Behavior within Solar Air Collector. J. Eng. 2018, 24, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.M.; Gaddoa, A.A. Outdoor Testing of a Zig-Zag SolarAir heater with and without Artificial Roughness on Absorber Plate. J. Eng. 2019, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-C.; Huang, P.-C. Numerical study of heat transfer enhancement for a novel flat-plate solar water collector using metal-foam blocks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 6734–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nima, M.A.; Ali, A.M. Effect of Metal Foam Insertion on Thermal Performance of Flat-PlateWater Solar Collector Under Iraqi Climate Conditions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 4863–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nima, M.A.; Ali, A.M. Numerical Study of Heat Transfer Enhancement for a Flat Plate Solar Collector by Adding Metal Foam Blocks. J. Eng. 2017, 23, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Experimental and numerical investigations of a single and double pass porous serpentine wavy wiremesh packed bed solar air heater. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1361–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, S.Y.; Farhan, A.A. Performance augmentation of a solar air heater using herringbone metal foam fins: An experimental work. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 45, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobair, H.K.; Nima, M.A. The indirect solar dryers with innovative solar air heaters designs: A review article. Heat Transf. 2023, 52, 2400–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, D.; Layek, A.; Kumar, P.M. Performance analysis of trapezoidal corrugated solar air heater with sensible heat storage material. Energy Procedia 2017, 109, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. Thermal performance of curved-slope solar collector. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 150, 119295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Meng, T.; Jing, C.; Hu, J.; Qian, S. Experimental and numerical investigation on thermal performance of PV-driven aluminium honeycomb solar air collector. Sol. Energy 2020, 204, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, C.; Moummi, N.; Brima, A.; Moummi, A. Experimental study of new solar air heater design. Int. J. Green Energy 2016, 13, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, H.; Ralston, T.; Kim, S.W. A novel gridded solar air heater and an investigation of its conversion efficiency. Sol. Energy 2016, 136, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Liu, F.; Wang, D. Experimental study on the performance of spiral solar air heater. Sol. Energy 2019, 182, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A.; Mesgarpour, M. Experimental analysis and numerical modeling of solar air heater with helical flow path. Sol. Energy 2018, 162, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; You, S.; Wu, Z.; Fan, M.; Wang, L.; Wei, S. A comparative study on the performance of a novel triangular solar air collector with tilted transparent cover plate. Sol. Energy 2021, 227, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Thermal performance analysis of semicircular and triangular cross-sectioned duct solar air heaters under external recycle. J. Energy Storage 2018, 20, 316–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sulttani, A.O.; Ahsan, A.; Al-Bakri, B.A.; Hason, M.M.; Daud, N.N.N.; Idrus, S.; Alawi, O.A.; Macioszek, E.; Yaseen, Z.M. Double-slope solar still productivity based on the number of rubber scraper motions. Energies 2022, 15, 7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, P.; Li, Q.; Zheng, R.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; He, B.; Bao, J.; Tan, D. A coupled LBM-LES-DEM particle flow modeling for microfluidic chip and ultrasonic-based particle aggregation control method. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 143, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, P.; Li, Q.; Yin, Z.; Zheng, R.; Wu, J.; Bao, J.; Bai, W.; Qi, H.; Tan, D. Multi-field coupling particle flow dynamic behaviors of the microreactor and ultrasonic control method. Powder Technol. 2025, 454, 120731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zuo, W.; Li, Q.; Zhou, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-objective optimization of liquid cooling plate partially filled with porous medium for thermal management of lithium-ion battery pack by RSM, NSGA-II and TOPSIS. Energy 2025, 318, 134853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zuo, W.; Li, Q.; Zhou, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. Performance enhancement studies on the liquid cooling plate fully filled with porous medium for thermal management of lithium-ion battery pack. J. Energy Storage 2025, 116, 116072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.; Gao, J.; Yang, X.; He, Q. Evaluation on solar-biogas heating system for buildings: Thermal characteristics and role of heat storage sectors. Appl. Energy 2025, 390, 125817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Dhiman, P. Thermal Performance Analysis of a Rectangular Longitudinal Finned Solar Air Heater with Semicircular Absorber Plate. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2016, 138, 011006-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Mahajan, R.L. Metal Foam and Finned Metal Foam Heat Sinks for Electronics Cooling in Buoyancy-Induced Convection. J. Electron. Packag. 2006, 128, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, T.L.; Lavine, A.S.; Incropera, F.P.; Dewitt, D.P. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Lemos, M.J. Turbulence in Porous Media: Modeling and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A.; Nield, D.A. Convection in Porous Media, 5th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, B.; Abdenour, S.; Oualid, C.; Marwani, H.M.; Sami, R.; Aljuraide, N.I.; Althomali, R.H.; Rahman, M.M.; Ali, M.M.; El Bouz, M.A. Three-dimensional transient CFD modeling of multiple finned aluminum foam heat sinks in a horizontal channel. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 78, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chamoli, S.; Lu, R.; Chen, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, P. Numerical optimization of design parameters for a modified double-layer microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 138, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
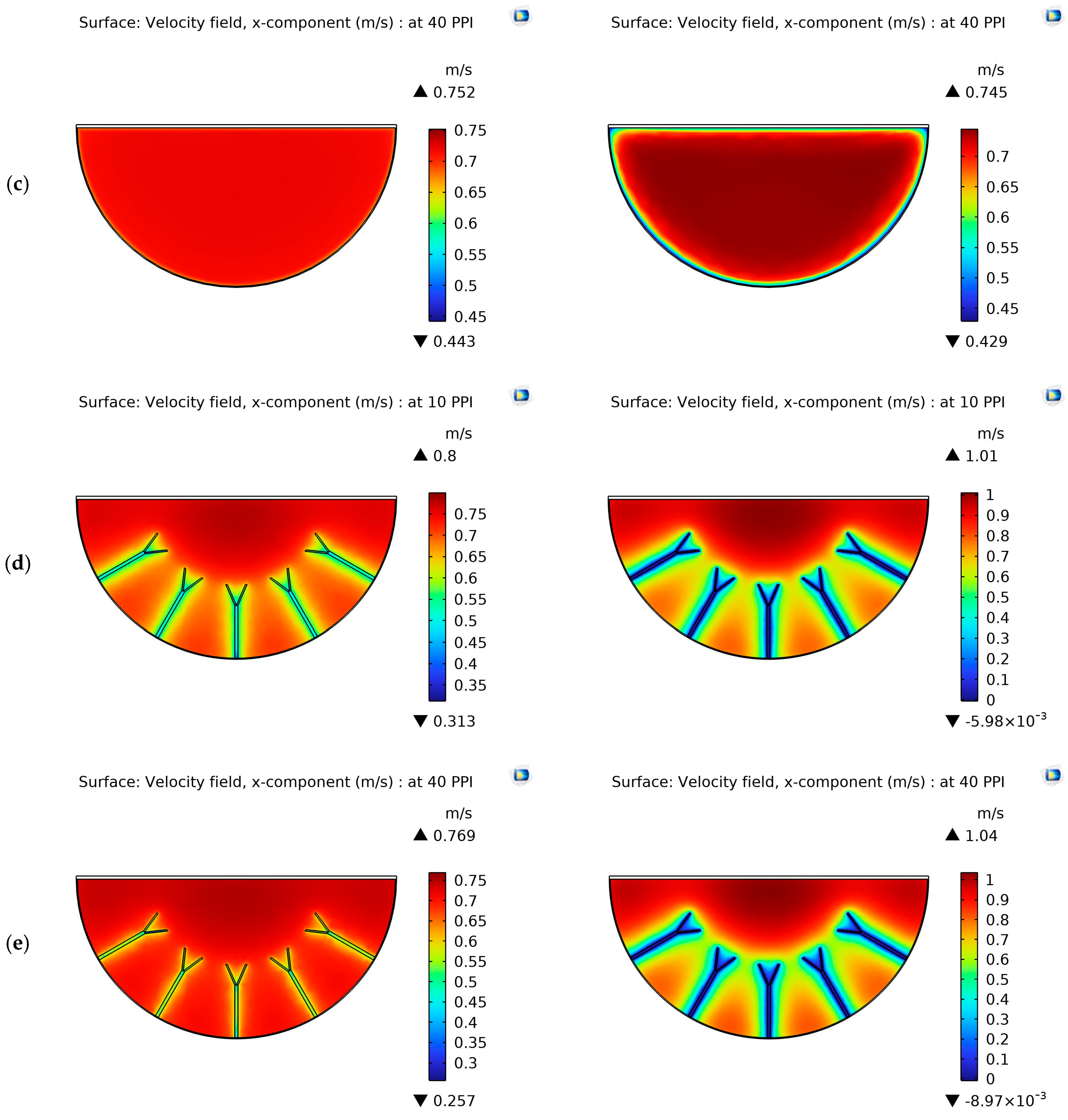
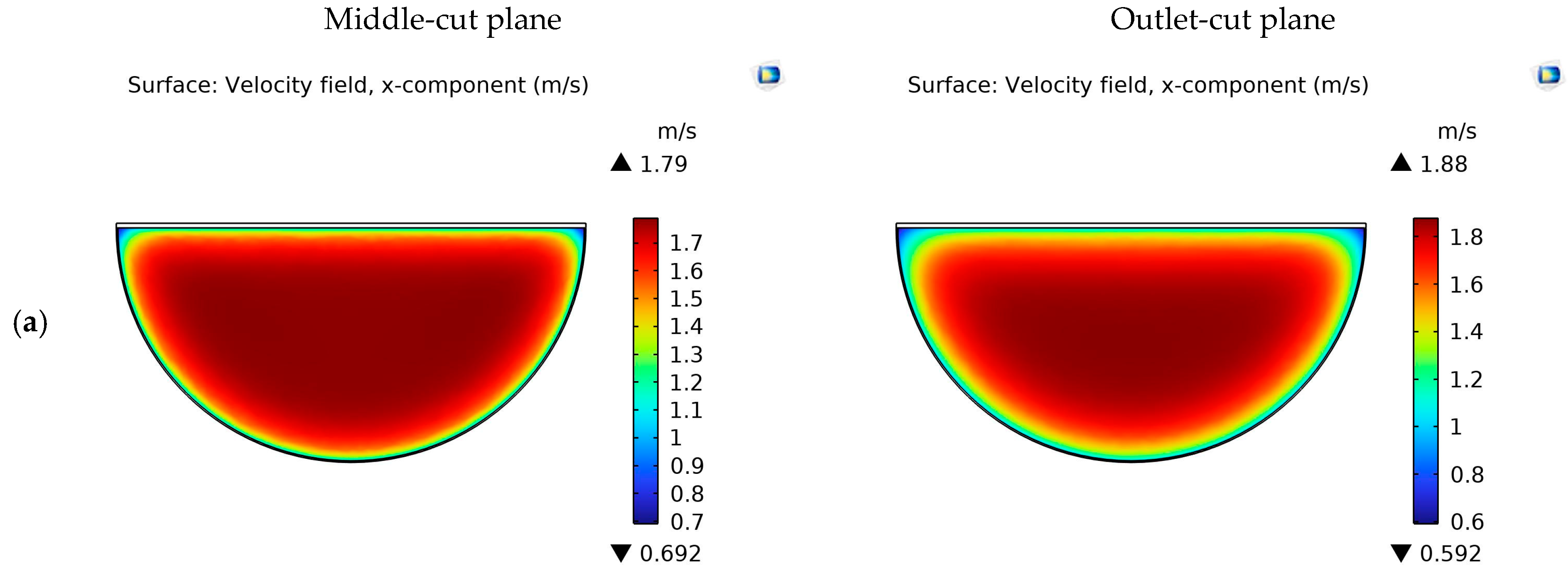
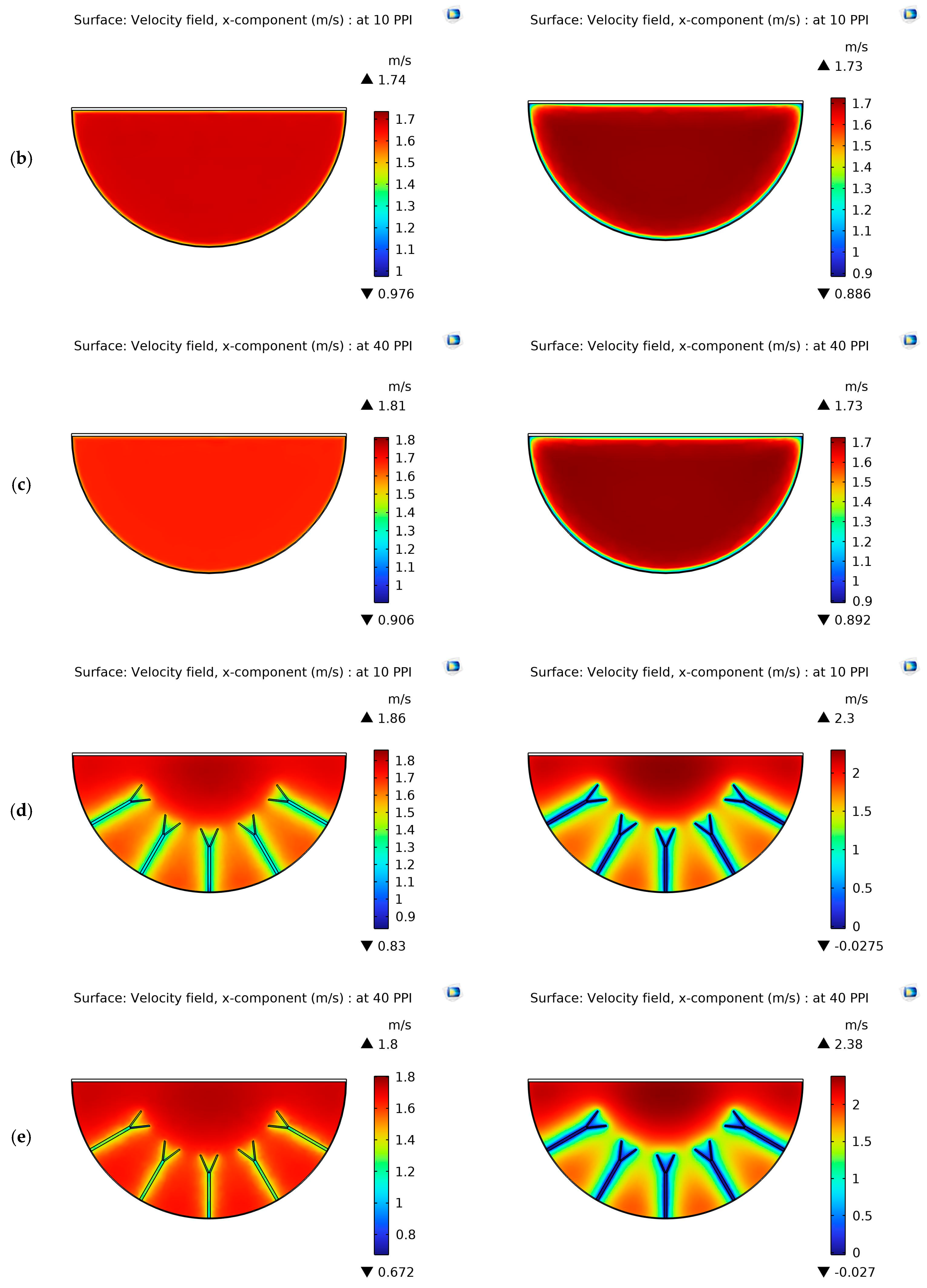
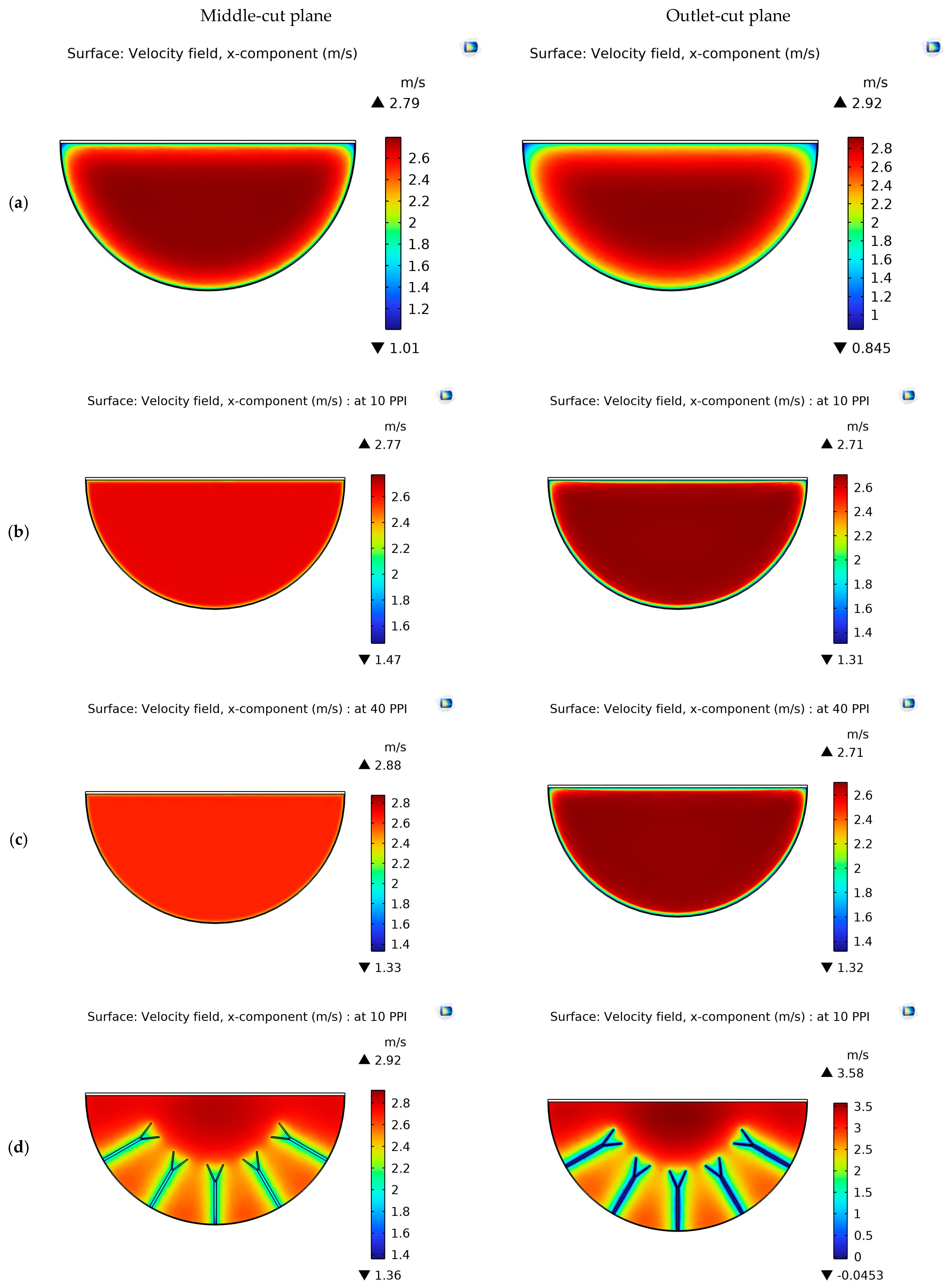








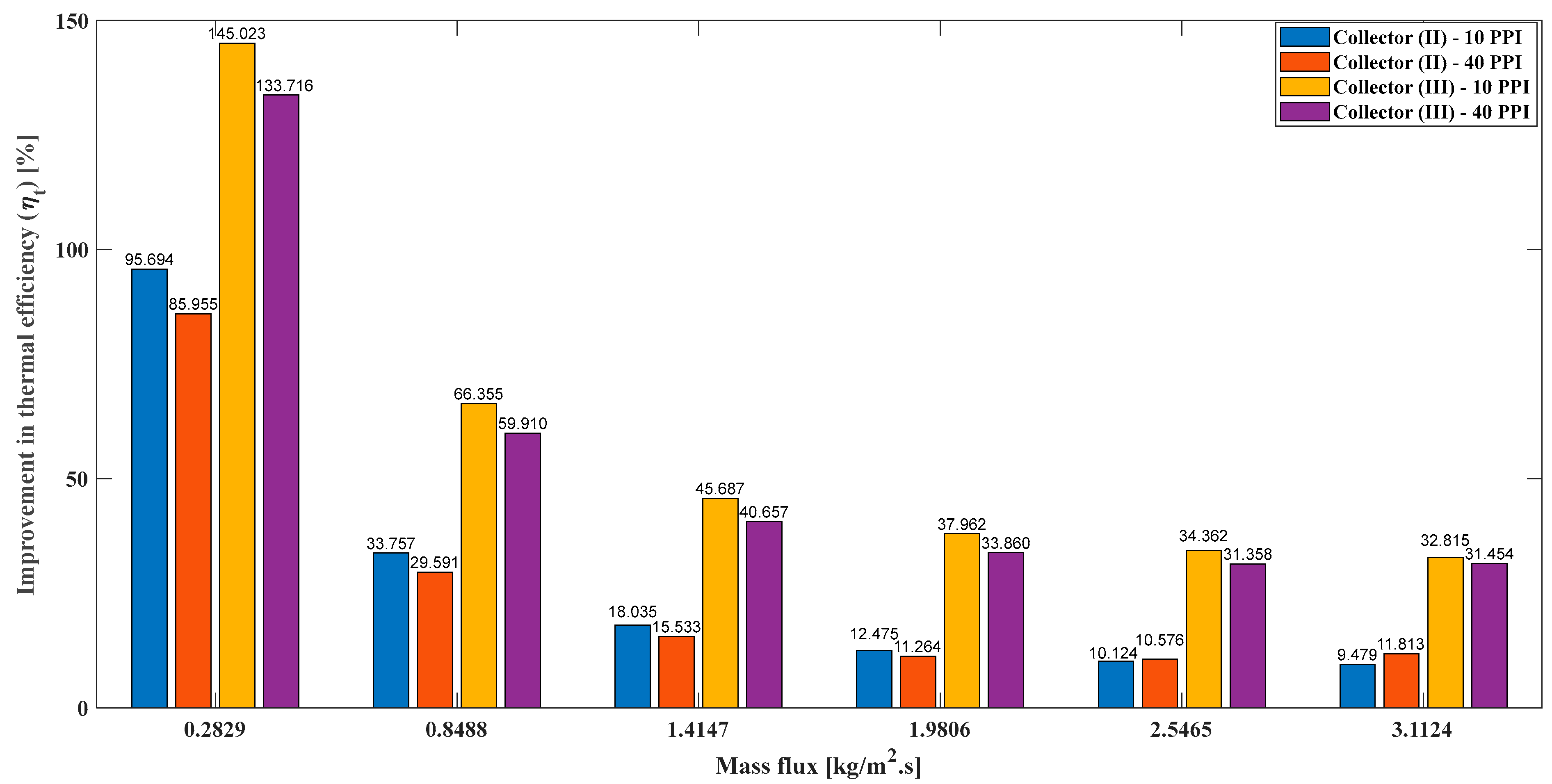

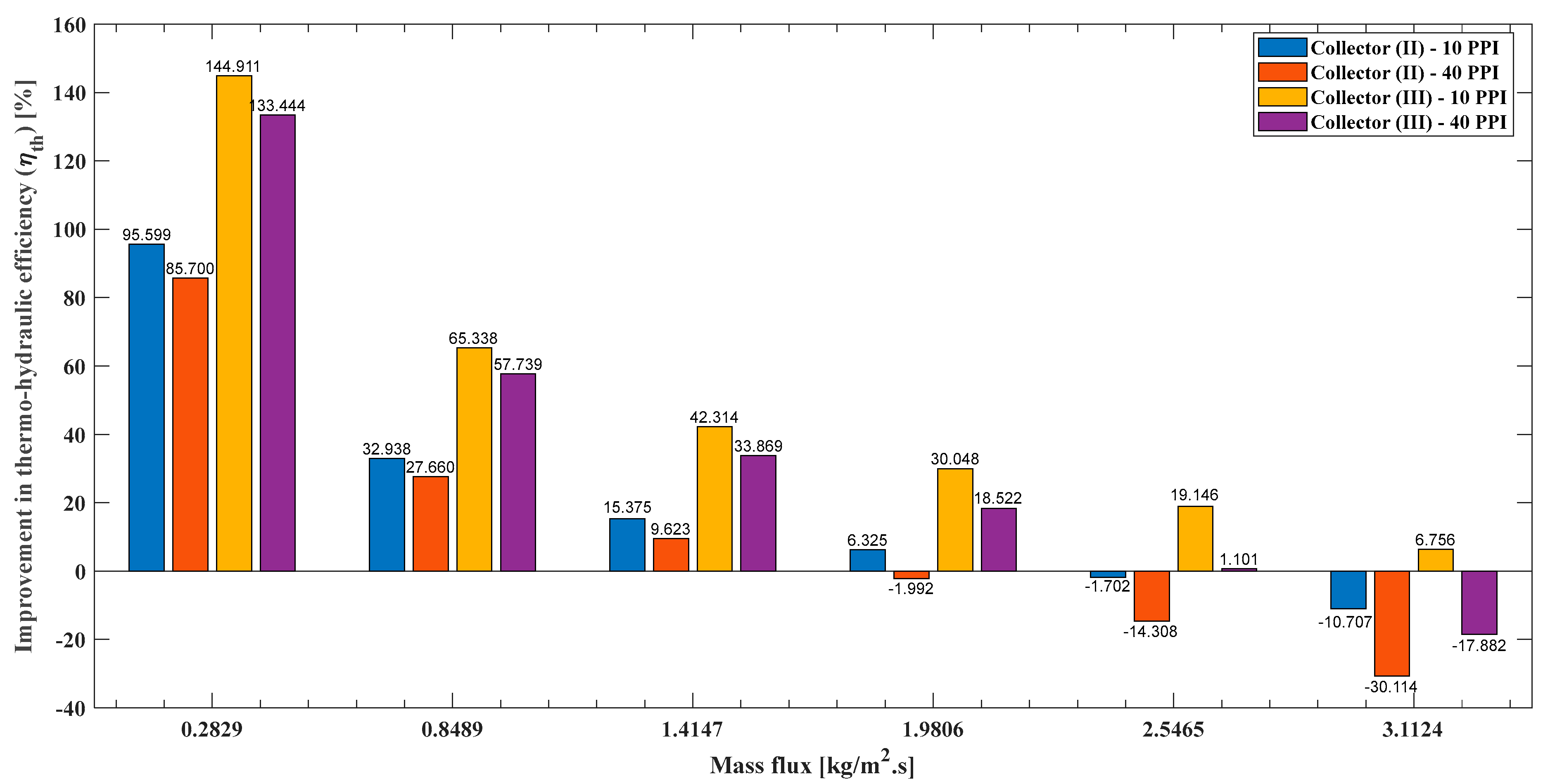

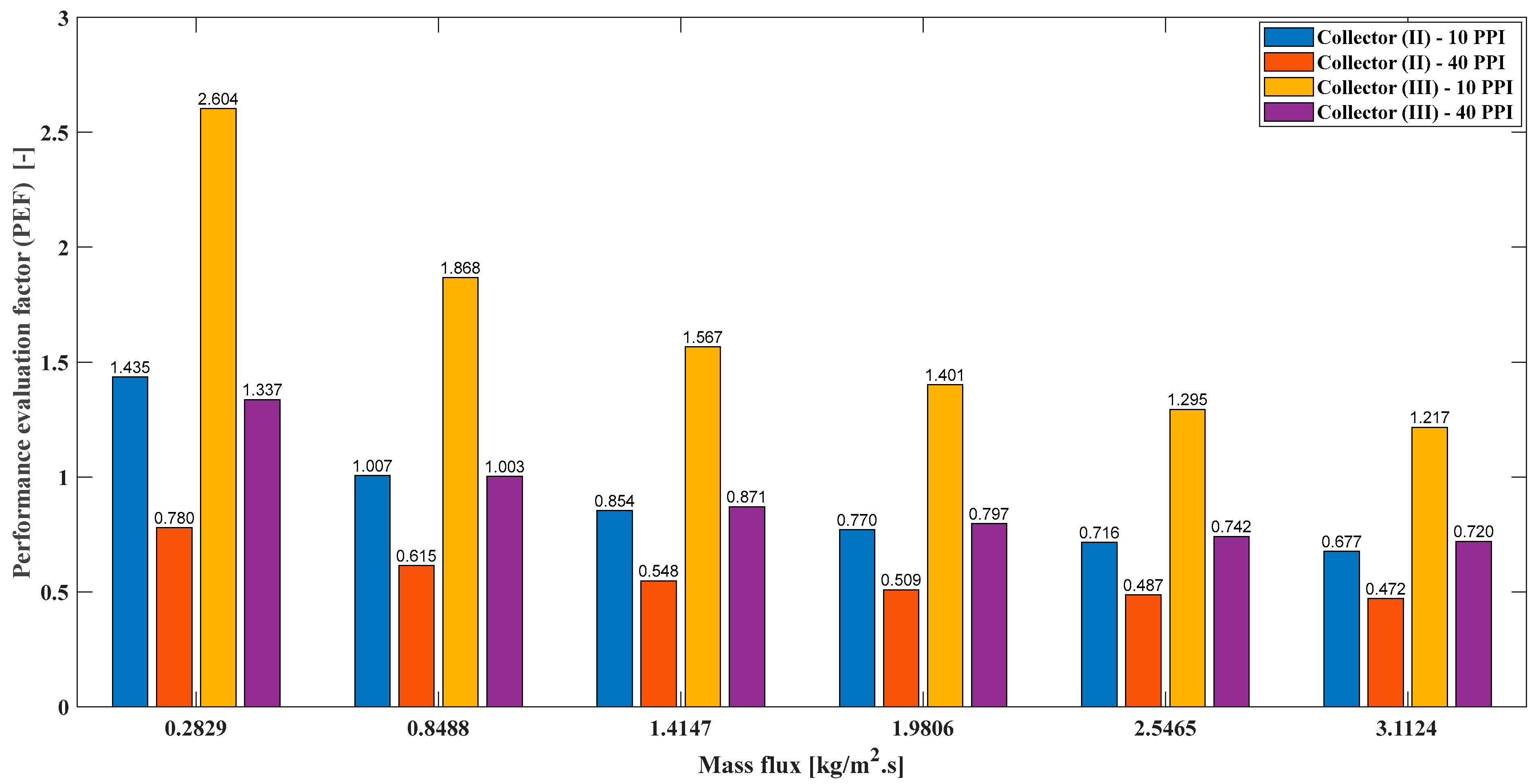
| System and Operating Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Collector length | 1.5 |
| Collector width (diameter) | 0.3 |
| Number of Y-shaped fins | 5 |
| Fin height | 0.05 |
| Fin thickness | 0.003 |
| Thickness of absorber plate, | 0.001 |
| Fin distribution angles | |
| Thermal conductivity of absorber plate | 238 |
| Thermal conductivity of glass cover | 1.4 |
| Absorptivity of absorber plate | 0.95 |
| Absorptivity of glass cover | 0.05 |
| Emissivity of absorber plate | 0.94 |
| Emissivity of glass cover | 0.90 |
| Transmissivity of glass cover | 0.875 |
| The intensity of solar radiation reaching the SCSAC | 750 |
| Ambient temperature | 25 |
| Wind speed | 1 |
| MF Samples | Density | Porosity (%) | Permeability | Forchheimer Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 238 | 2700 | 900 | 10 | 90.85 | 1.62 | 0.078 |
| 2 | 40 | 95.85 | 0.54 | 0.086 |
| 0.025 | 1 | 35.3199 | 36.3060 | 2.7919 |
| 3 | 37.6624 | 36.6460 | 2.6987 | |
| 5 | 40.1088 | 41.5210 | 3.5209 | |
| No. | Section/Condition | Fluid Flow Model | Heat Transfer Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Condition | ||
| 2 | Inlet section | ||
| 3 | Inside face of glass cover | No slip conditions | - |
| 4 | Interface surfaces between FR and PR | Continuity of | Continuity of and |
| 5 | Outlet section | ; ; | |
| 6 | Outside face of glass cover | - | Equation (1) |
| 7 | Absorber plate | No slip conditions | |
| 8 | Metal foam obstacles | - | |
| 9 | Bottom plate | Included in (4) | Insulated wall |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Bakri, B.A.R.; Rasham, A.M.; Al-Sulttani, A.O. Thermal and Thermo-Hydraulic Performance of a Semi-Circular Solar Air Collector Utilizing an Innovative Configuration of Metal Foams. Energies 2025, 18, 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102501
Al-Bakri BAR, Rasham AM, Al-Sulttani AO. Thermal and Thermo-Hydraulic Performance of a Semi-Circular Solar Air Collector Utilizing an Innovative Configuration of Metal Foams. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102501
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Bakri, Basim A. R., Ali M. Rasham, and Ali O. Al-Sulttani. 2025. "Thermal and Thermo-Hydraulic Performance of a Semi-Circular Solar Air Collector Utilizing an Innovative Configuration of Metal Foams" Energies 18, no. 10: 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102501
APA StyleAl-Bakri, B. A. R., Rasham, A. M., & Al-Sulttani, A. O. (2025). Thermal and Thermo-Hydraulic Performance of a Semi-Circular Solar Air Collector Utilizing an Innovative Configuration of Metal Foams. Energies, 18(10), 2501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102501






