A Method for State of Charge and State of Health Estimation of Lithium Batteries Based on an Adaptive Weighting Unscented Kalman Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The AWUKF algorithm reselects the particles using the unscented transformation, and the adaptive weights are brought into the UKF framework to reduce the sensitivity to noise.
- This algorithm is utilized to attenuate the deviation of the SOC values under measurement and state noise disturbances; moreover, the SOC is used as a basis for estimating the SOH values.
- Simulations are carried out under different experimental conditions to assess the practicality and effectiveness of this algorithm.
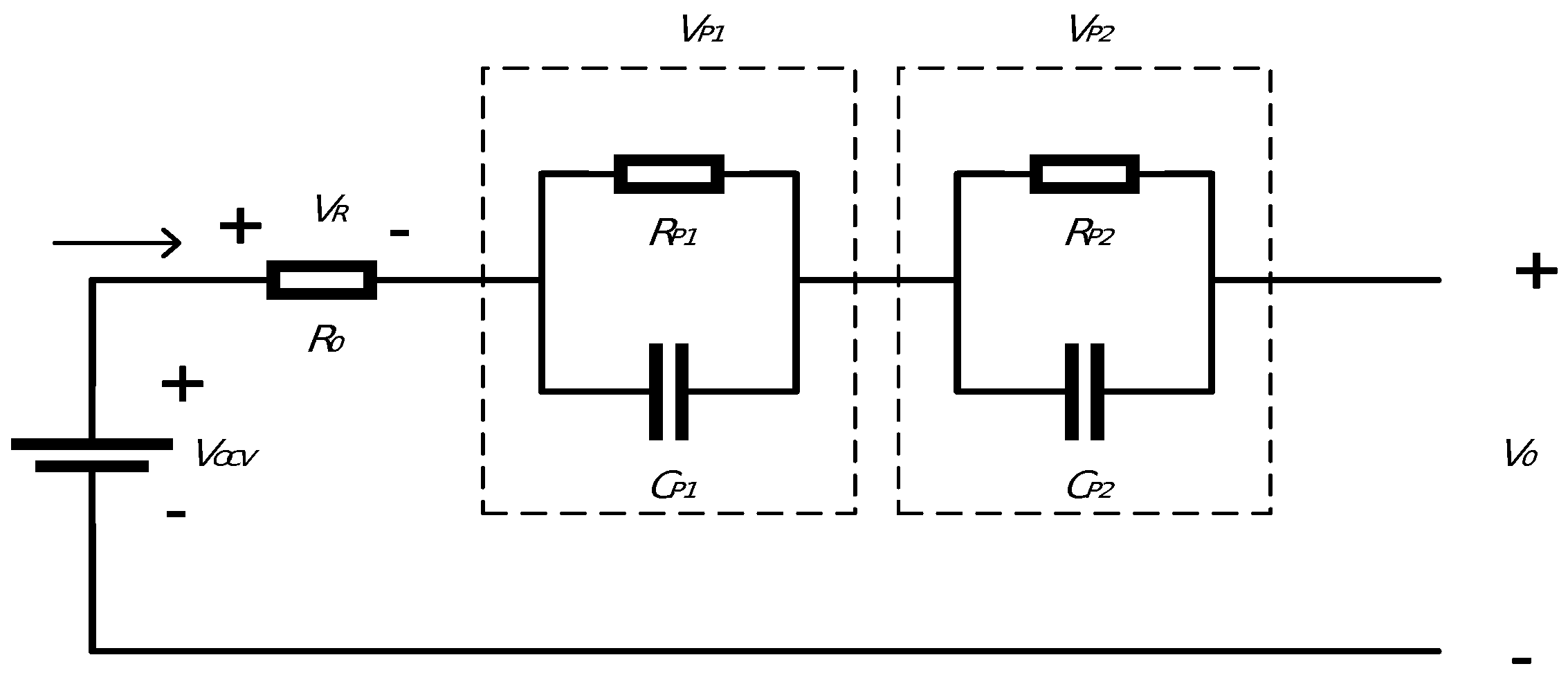
2. Battery Model
2.1. Integral Second-Order RC Model
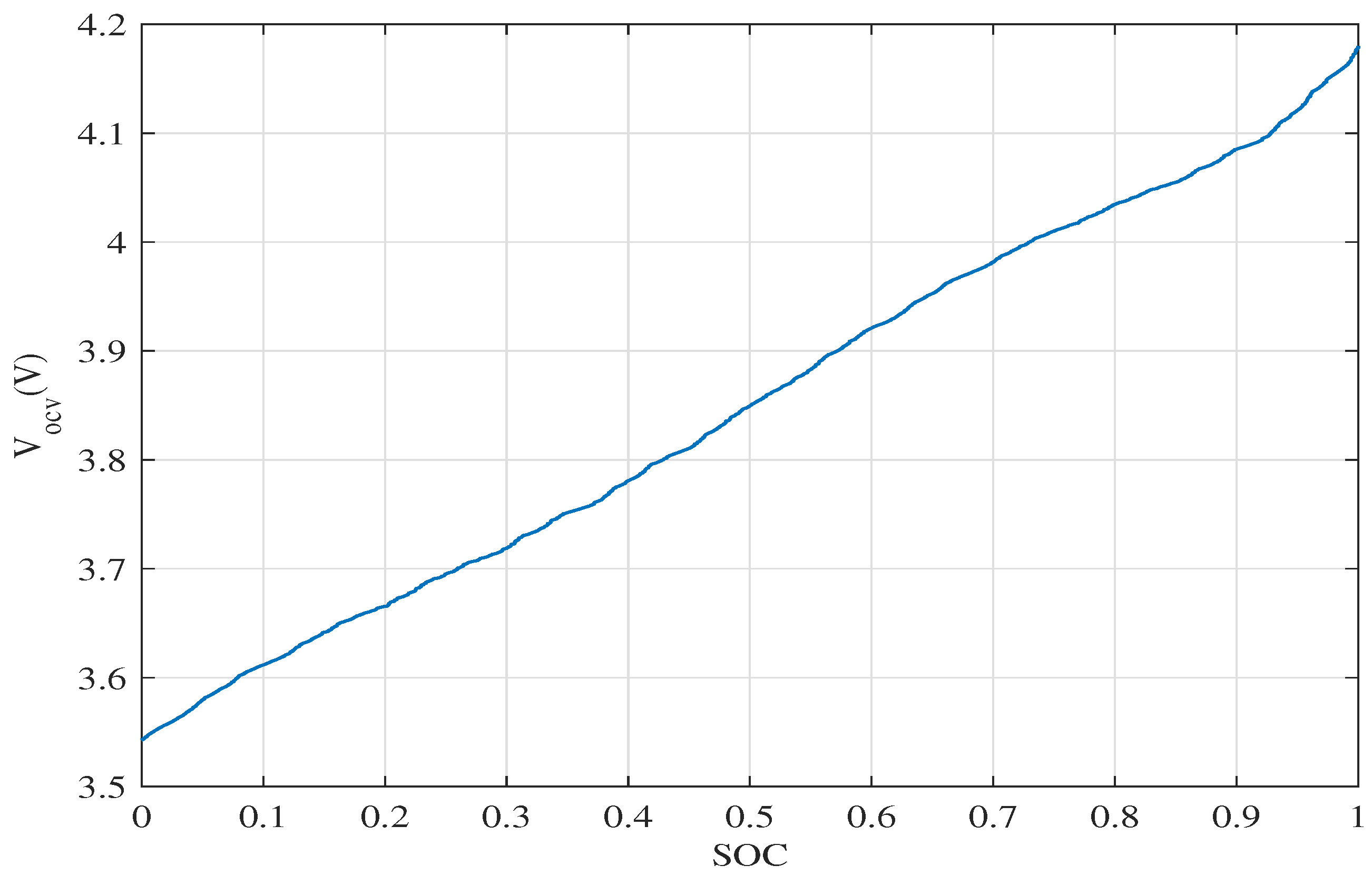
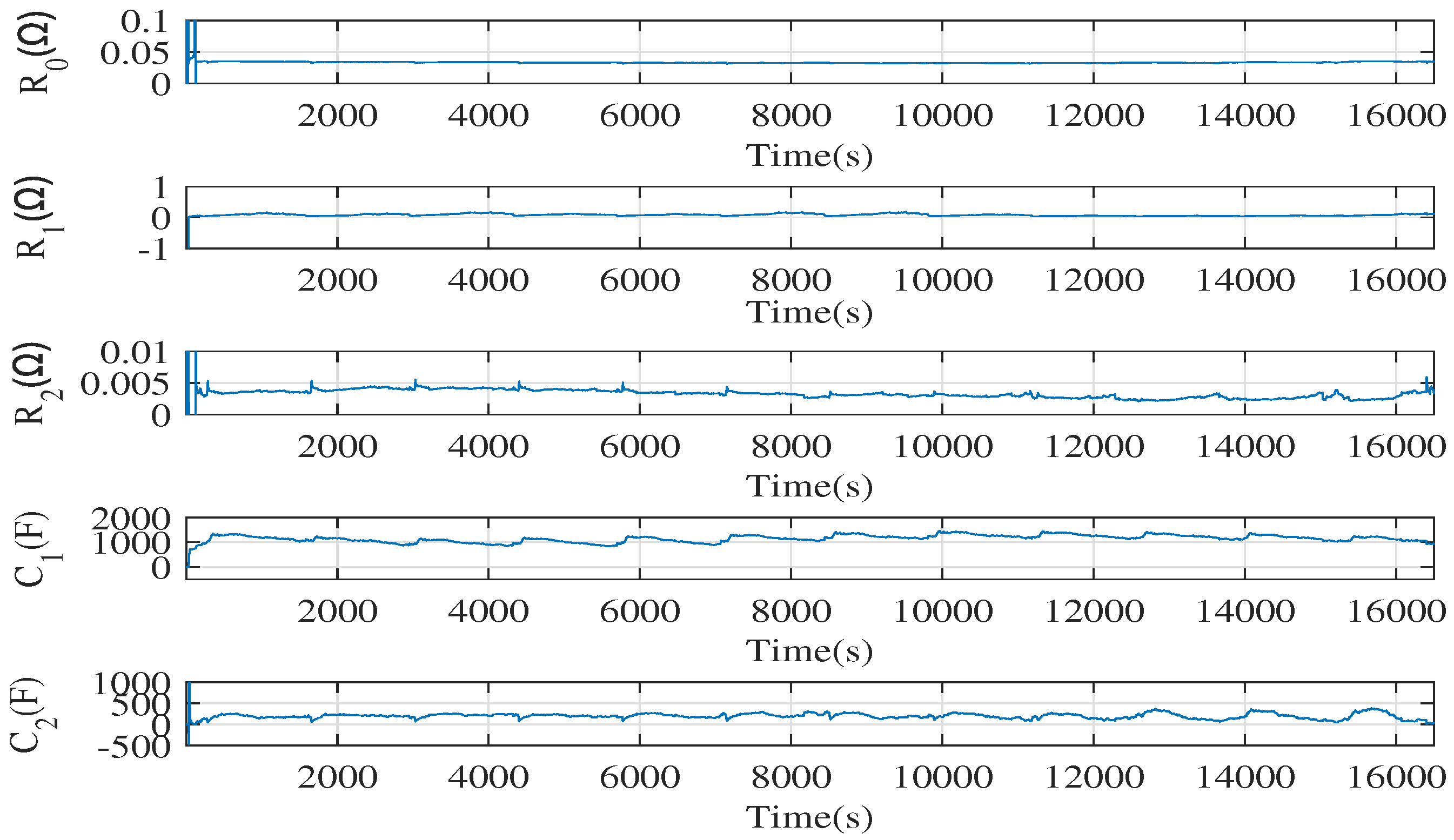
2.2. Parameter Identification Based on MILM Method
3. The SOC and SOH Estimation Method
3.1. SOC Estimation Based on the AWUKF Algorithm
3.2. SOH Estimation
4. Simulation Experiment
4.1. Experimental Condition
4.2. Battery Parameters Identification Results
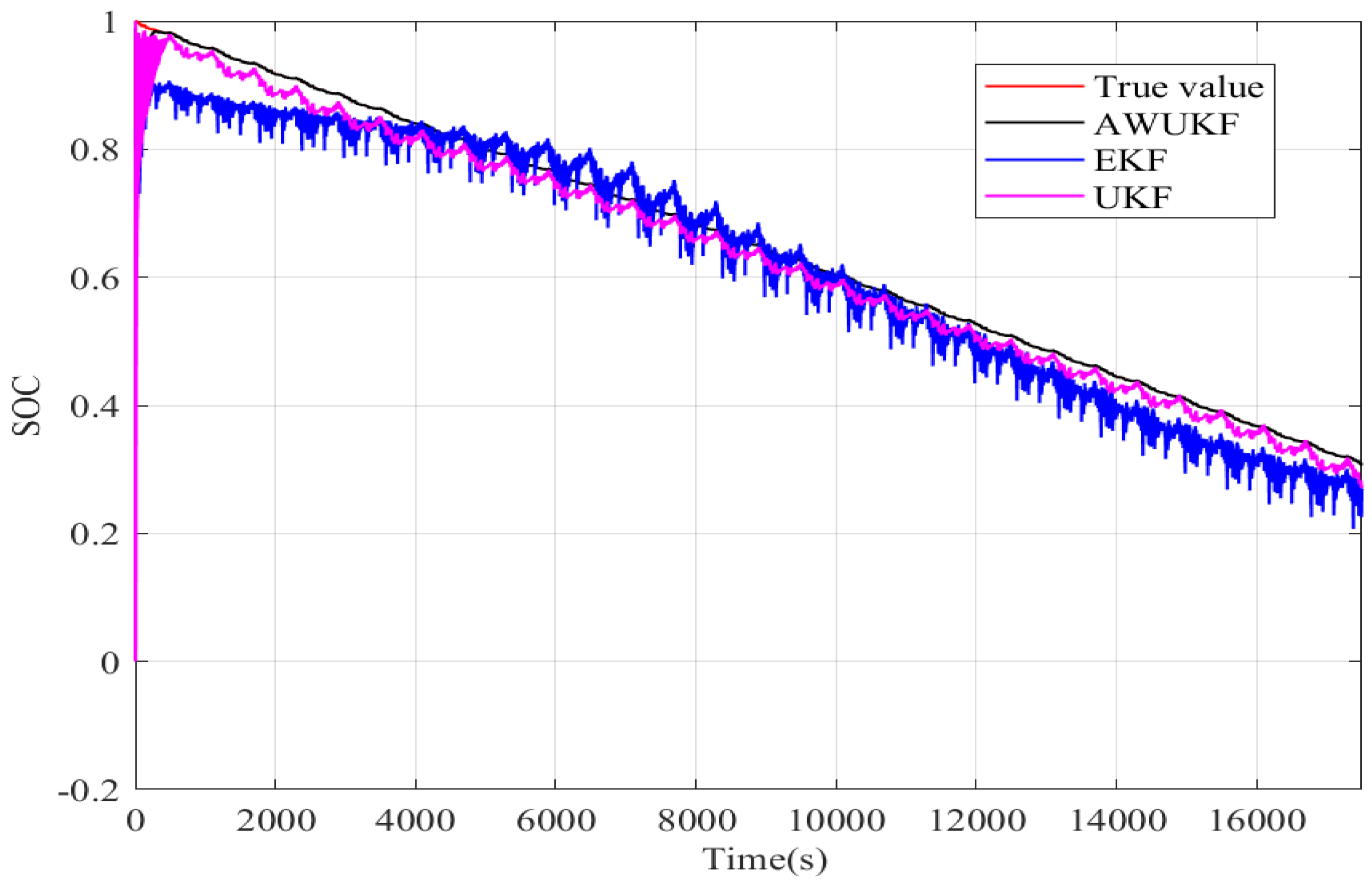
4.3. SOC Prediction Results
4.4. SOH Prediction Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Bai, Y.K.; Zhao, C.Z.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Q. Lithium bonds in lithium batteries. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11192–11195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carkhuff, B.G.; Demirev, P.A.; Srinivasan, R. Impedance-based battery management system for safety monitoring of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6497–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Lee, H. Review on battery thermal management system for electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 149, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Cheng, X.; Lu, Z.Y.; Gu, D.J. SOC estimation of lithium-ion battery pack considering balancing current. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2216–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Yan, G.X. Estimating SOC and SOH of lithium battery based on nano material. Ferroelectrics 2021, 580, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.Q.; Liu, B.C.; Zhang, K.; Ci, S. Toward fast and accurate SOH prediction for lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Ma, R.; Pang, S.Z.; Xu, L.C.; Zhao, D.D.; Wei, J.; Huangfu, Y.G.; Gao, F. A nonlinear observer SOC estimation method based on electrochemical model for lithium-ion battery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.C.; Wang, B.J.; Zhang, H.Z.; Long, C.; Li, H.H. State-of-charge estimation of lithium-ion battery based on a novel reduced order electrochemical model. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Demir, I.; Cao, D.C.; Jost, D.; Ringbeck, F.; Junker, M.; Sauer, D.U. Data-driven systematic parameter identification of an electrochemical model for lithium-ion batteries with artificial intelligence. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 44, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Xu, C.F.; Su, H.Y. Neural Network-Based State of Charge Observer Design for Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Chen, H.C.; Tsai, M.Y. AC Impedance-based Online State-of-charge Estimation for Li-ion Batteries. Sens. Mater. 2018, 30, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Manzo, S.; Greenwood, P.; Chen, R. An Impedance Model for EIS Analysis of Nickel Metal Hydride Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, F.; Schaltz, E.; Stroe, D.I.; Gismero, A.; Farjah, E. An Enhanced Equivalent Circuit Model with Real-Time Parameter Identification for Battery State-of-Charge Estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.W.; Chen, H. Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Gauss-Hermite Particle Filter. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.W. Multi-objective decision analysis for data-driven based estimation of battery states: A case study of remaining useful life estimation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 14156–14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukouvala, F.; Hasan, M.M.F.; Floudas, C.A. Global optimization of general constrained grey-box models: New method and its application to constrained PDEs for pressure swing adsorption. J. Glob. Optim. 2017, 67, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.H. A novel approach of battery pack state of health estimation using artificial intelligence optimization algorithm. J. Power Sources 2018, 376, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Wang, S.L.; Fan, Y.C.; Xia, L.L.; Qiu, J.S. A novel fuzzy-extended Kalman filter-ampere-hour (F-EKF-Ah) algorithm based on improved second-order PNGV model to estimate state of charge of lithium-ion batteries. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2022, 50, 3811–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, C. Influence diagnostics in support vector machines. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2020, 49, 757–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talha, M.; Asghar, F.; Kim, S.H. A neural network-based robust online SOC and SOH estimation for sealed lead-acid batteries in renewable systems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Q.; Luo, M.J.; She, L.Y.; Cui, X.Y. Joint estimation of ternary lithium-ion battery state of charge and state of power based on dual polarization model. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 1128–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.Q.; Yin, S.Q. The multi-innovation extended Kalman filter algorithm for battery SOC estimation. Ionics 2020, 26, 6145–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Din, M.S.; Hussein, A.A.; Abdel-Hafez, M.F. Improved battery SOC estimation accuracy using a modified UKF with an adaptive cell model under real EV operating conditions. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.M.; Chen, H.B.; Yao, G.Y. Hierarchical gradient based and hierarchical least squares based iterative parameter identification for CARARMA systems. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Separable Newton recursive estimation method through system responses based on dynamically discrete measurements with increasing data length. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Chen, T. Combined parameter and output estimation of dual-rate systems using an auxiliary model. Automatica 2004, 40, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, X. Two-stage gradient-based iterative algorithms for the fractional-order nonlinear systems by using the hierarchical identification principle. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2022, 36, 1778–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Chen, T. Parameter estimation of dual-rate stochastic systems by using an output error method. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Two-stage auxiliary model gradient-based iterative algorithm for the input nonlinear controlled autoregressive system with variable-gain nonlinearity. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 30, 5492–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ding, F. Multi-innovation gradient-based iterative identification methods for feedback nonlinear systems by using the decomposition technique. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2023, 33, 7755–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Chen, F. Model transformation based distributed stochastic gradient algorithm for multivariate output-error systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2023, 54, 1484–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Y.J.; Ding, F.; Yang, E.F. Hierarchical gradient-based iterative parameter estimation algorithms for a nonlinear feedback system based on the hierarchical identification principle. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 43, 124–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, Y. Maximum likelihood extended gradient-based estimation algorithms for the input nonlinear controlled autoregressive moving average system with variable-gain nonlinearity. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2021, 31, 4017–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, G.; Ding, F.; Liu, Q.; Yang, E. Iterative parameter identification algorithms for transformed dynamic rational fraction input-output systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 434, 115297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liu, S.D.; Shu, J.; Wan, X.K. Hierarchical recursive least squares estimation algorithm for secondorder Volterra nonlinear systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 3940–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.H. Filtered auxiliary model recursive generalized extended parameter estimation methods for Box-Jenkins systems by means of the filtering identification idea. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2023, 33, 5510–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Luan, X.; Yang, E. Highly-efficient filtered hierarchical identification algorithms for multiple-input multiple-output systems with colored noises. Syst. Control Lett. 2024, 186, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Pan, J.; Ding, W. Partially-coupled least squares based iterative parameter estimation for multi-variable output-error-like autoregressive moving average systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 3040–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Li, J.; Yao, Z.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Si, R.C.; Diao, Y.P. Research on battery SOH estimation algorithm of energy storage frequency modulation system. Energy Rep. 2021, 8, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavand, A.; Khajehoddin, S.A.; Ardakani, M.; Tabesh, A. Online estimations of li-ion battery soc and soh applicable to partial charge/discharge. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayamy, M.; Nasiri, A.; Okoye, O. Development of an Equivalent Circuit for Batteries Based on a Distributed Impedance Network. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 6119–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.J.; Qiu, S.L.; Li, G. Simulation of second-order RC equivalent circuit model of lithium battery based on variable resistance and capacitance. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.C.; Li, Z.X.; Liu, B.L.; Wang, K.S. SOC estimation of lithium-ion battery considering the influence of discharge rate. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chu, X.M.; Liu, C.G.; Liu, J.L.; Mou, J.M. Parameter identification of ship motion model based on multi innovation methods. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Ma, J.X.; Xiong, W.L. Expectation-maximization algorithm for bilinear state-space models with time-varying delays under non-Gaussian noise. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 2706–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Ding, F. A novel coupled recursive multivariate nonlinear time-series modelling method by using interactive identification. Appl. Math. Modell. 2024, 127, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Nouri, H. Identification and U-control of a state-space system with time-delay. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2022, 36, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Liu, X.M. The filtering-based maximum likelihood iterative estimation algorithms for a special class of nonlinear systems with autoregressive moving average noise using the hierarchical identification principle. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2019, 33, 1189–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Ling, K.V. Online network-based identification and its application in satellite attitude control systems. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 2530–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.Q.; Ji, Y. Parameter estimation of fractional-order Hammerstein state space system based on the extended Kalman filter. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Ding, F.; Hayat, T. A novel nonlinear optimization method for fitting a noisy Gaussian activation function. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2022, 36, 690–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Li, M.H. Unbiased recursive least squares identification methods for a class of nonlinear systems with irregularly missing data. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 2247–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Q. Novel parameter estimation method for the systems with colored noises by using the filtering identification idea. Syst. Control Lett. 2024, 186, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Shao, B.; Xiang, J.X.; Zhang, Q. Attitude control of quadrotor UAVs based on adaptive sliding mode. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 2698–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Pan, J.; Chen, G. Sliding mode dual-channel disturbance rejection attitude control for a quadrotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 10489–10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, J. A novel quadruple boost nine level switched capacitor inverter. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 18, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Wu, T. Fault diagnosis of lithium-ion batteries based on wavelet packet decomposition and Manhattan average distance. Int. J. Green. Energy 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, S. CFSA-Net: Efficient large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation based on cross-fusion self-attention. Comput. Mat. Contin. 2023, 77, 2677–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Zhou, F.F.; Yan, H.C.; Huang, W.C.; Luo, G. Noise and interference suppression control method of DC-DC buck converters based on cascaded filter LADRC. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2024, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, G.S.; Liu, W.Q.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Ren, L. Data-Driven Tracking Control Based on LM and PID Neural Network with Relay Feedback for Discrete Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11587–11597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Least squares parameter estimation and multi-innovation least squares methods for linear fitting problems from noisy data. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 426, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Parameter estimation for nonlinear functions related to system responses. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 1780–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Separable multi-innovation Newton iterative modeling algorithm for multi-frequency signals based on the sliding measurement window. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 41, 805–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.M.; Liu, X.M. Auxiliary model-based multi-innovation recursive identification algorithms for an input nonlinear controlled autoregressive moving average system with variable-gain nonlinearity. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2022, 36, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Ji, Y.; Ma, C.Q. Joint two-stage multi-innovation recursive least squares parameter and fractional-order estimation algorithm for the fractional-order input nonlinear output-error autoregressive model. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 1650–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Shu, J. Gradient-based parameter estimation for an exponential nonlinear autoregressive time-series model by using the multi-innovation. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. Multivariable CAR-like system identification with multi-innovation gradient and least squares algorithms. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.J.; Ding, F. Decomposition- and gradient-based iterative identification algorithms for multivariable systems using the multi-innovation theory. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 2971–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; He, Y.; Wang, L.J. Maximum likelihood based multi-innovation stochastic gradient identification algorithms for bilinear stochastic systems with ARMA noise. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 2690–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, H.; Ding, F. Adaptive multi-innovation gradient identification algorithms for a controlled autoregressive autoregressive moving average model. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pu, Y.; Guo, L.X.; Cao, J.F.; Zhu, Q.M. Second-order optimization methods for time-delay autoregressive exogenous models: Nature gradient descent method and its two modified methods. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Hierarchical gradient- and least-squares-based iterative estimation algorithms for input-nonlinear output-error systems by using the over-parameterization. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2024, 34, 1120–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Shao, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y. Filtered generalized iterative parameter identification for equation-error autoregressive models based on the filtering identification idea. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2024, 38, 1363–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Dai, W.; Zhu, Q.M.; Nouri, H. Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient identification algorithm for estimating a bilinear state-space model with moving average noise. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 420, 114794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Jiang, X.; Wan, X.K.; Ding, W. A filtering based multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithm for multivariable control systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F. Decomposition and composition modeling algorithms for control systems with colored noises. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2024, 38, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Joint iterative state and parameter estimation for bilinear systems with autoregressive noises via the data filtering. ISA Trans. 2024, 147, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Ma, H.; Pan, J.; Yang, E.F. Hierarchical gradient- and least squares-based iterative algorithms for input nonlinear output-error systems using the key term separation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 5113–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.M.; Ding, F.; Pan, F.; Yang, E.F. Hierarchical recursive least squares parameter estimation methods for multiple-input multiple-output systems by using the auxiliary models. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2023, 37, 2983–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.P. Control algorithms of magnetic suspension systems based on the improved double exponential reaching law of sliding mode control. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2018, 16, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luan, X. Recursive identification methods for general stochastic systems with colored noises by using the hierarchical identification principle and the filtering identification idea. Annu. Rev. Control 2024, 57, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L. Model recovery for multi-input signal-output nonlinear systems based on the compressed sensing recovery theory. J. Frankl. Inst. 2022, 359, 2317–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






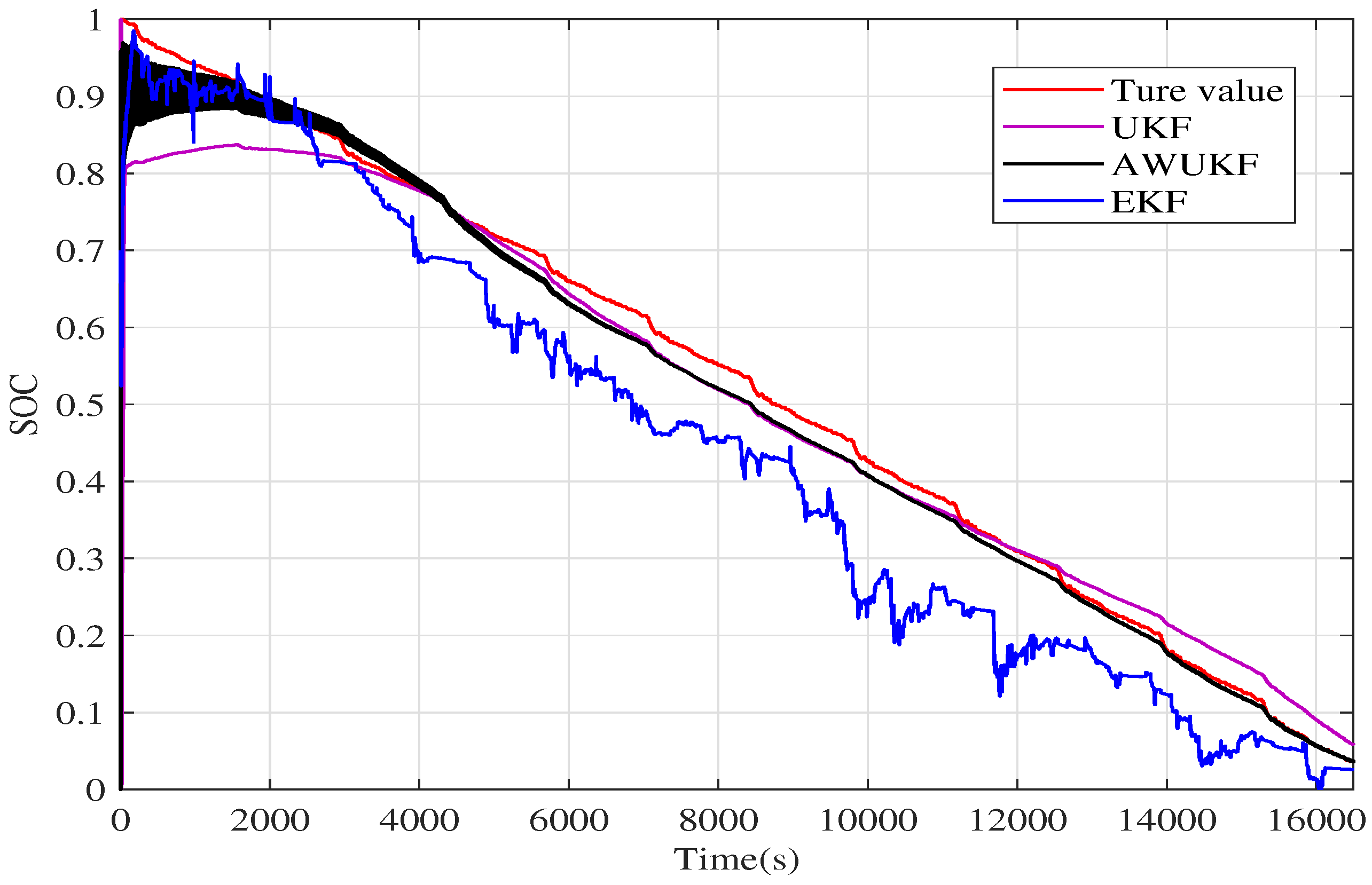

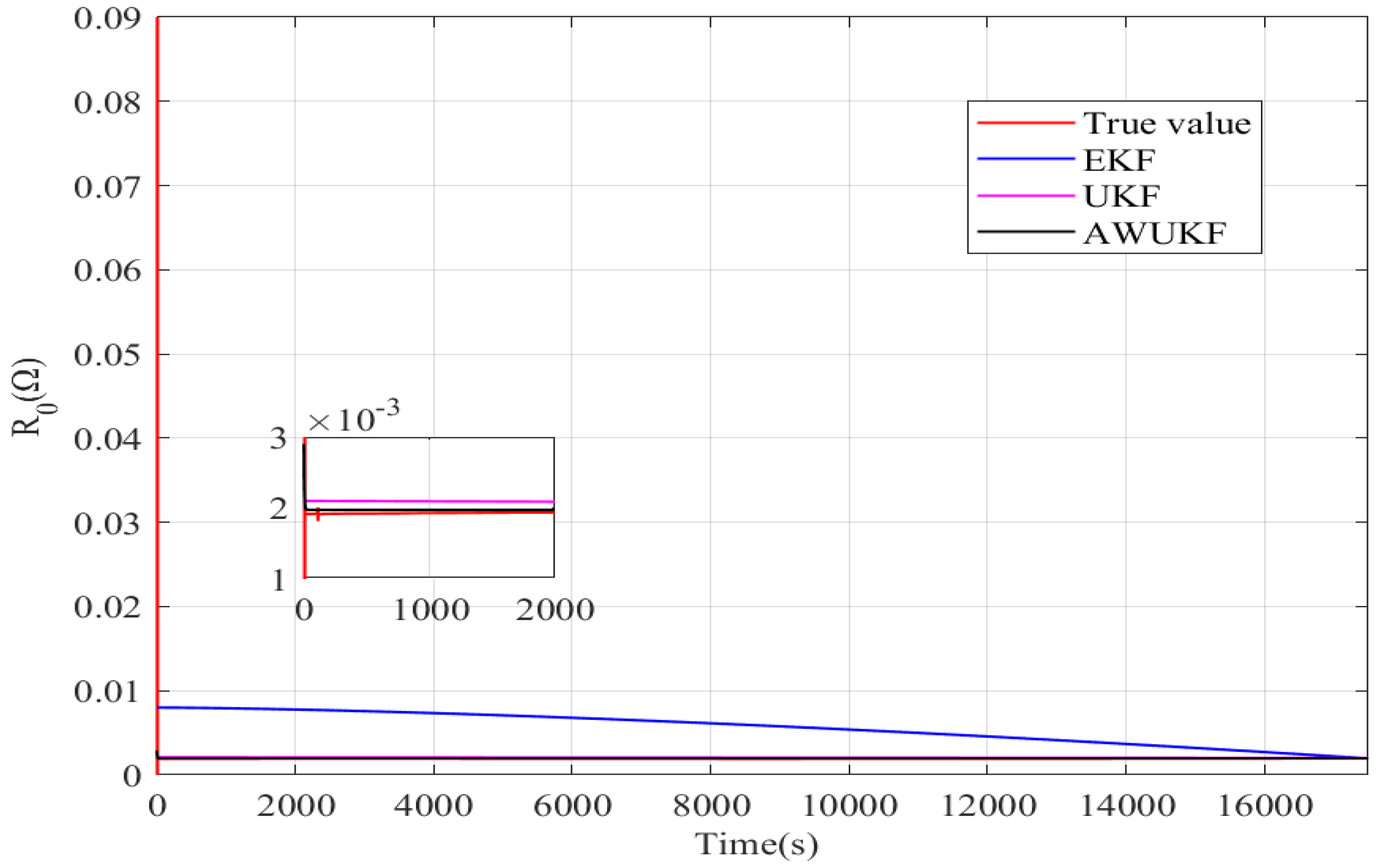



| Information | Type | Data |
|---|---|---|
| Rate | Voltage | 3.2 V |
| Operation | Voltage | 2.7 V–4.2 V |
| Capacitance | 3600 mAh | |
| Rate | Charge current | 0.72 A |
| Max | Discharge current | 3.6 A |
| RMSE | MAE | |
|---|---|---|
| AWUKF | 0.0133 | 0.0011 |
| UKF | 0.0299 | 0.0211 |
| EKF | 0.0442 | 0.0350 |
| RMSE | MAE | |
|---|---|---|
| AWUKF | 0.0285 | 0.0188 |
| UKF | 0.0584 | 0.0324 |
| EKF | 0.0907 | 0.0774 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, F.; Ma, C.; Ji, Y. A Method for State of Charge and State of Health Estimation of Lithium Batteries Based on an Adaptive Weighting Unscented Kalman Filter. Energies 2024, 17, 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092145
Fang F, Ma C, Ji Y. A Method for State of Charge and State of Health Estimation of Lithium Batteries Based on an Adaptive Weighting Unscented Kalman Filter. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092145
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Fengyuan, Caiqing Ma, and Yan Ji. 2024. "A Method for State of Charge and State of Health Estimation of Lithium Batteries Based on an Adaptive Weighting Unscented Kalman Filter" Energies 17, no. 9: 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092145
APA StyleFang, F., Ma, C., & Ji, Y. (2024). A Method for State of Charge and State of Health Estimation of Lithium Batteries Based on an Adaptive Weighting Unscented Kalman Filter. Energies, 17(9), 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092145







