Process Optimization of Pellet Manufacturing from Mixed Materials in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Pellet Density and Durability Test Methods
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Interaction Effects on Pellet Density
3.2. Interaction Effects on Pellet Durability
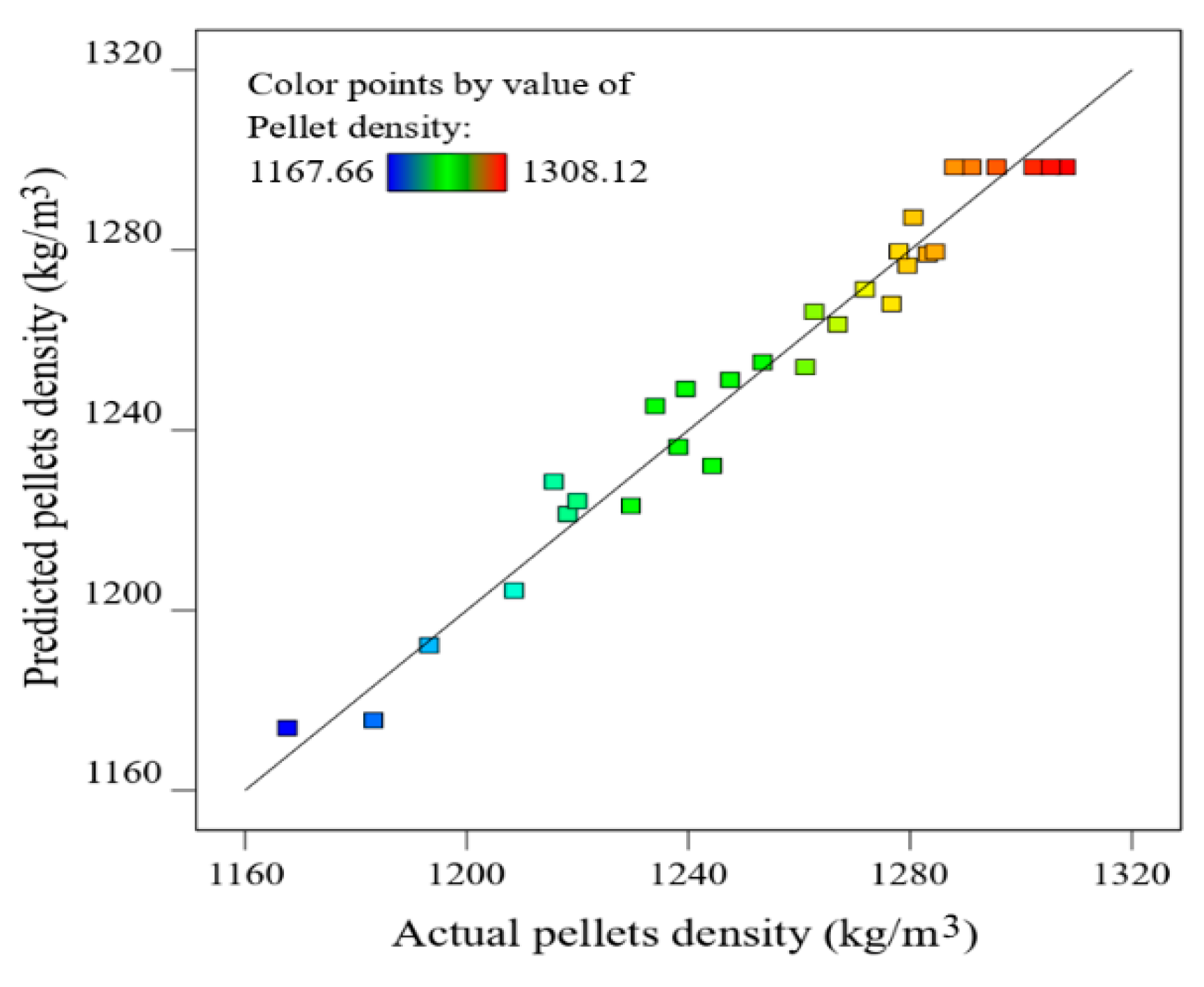
3.3. Optimization and Model Verification
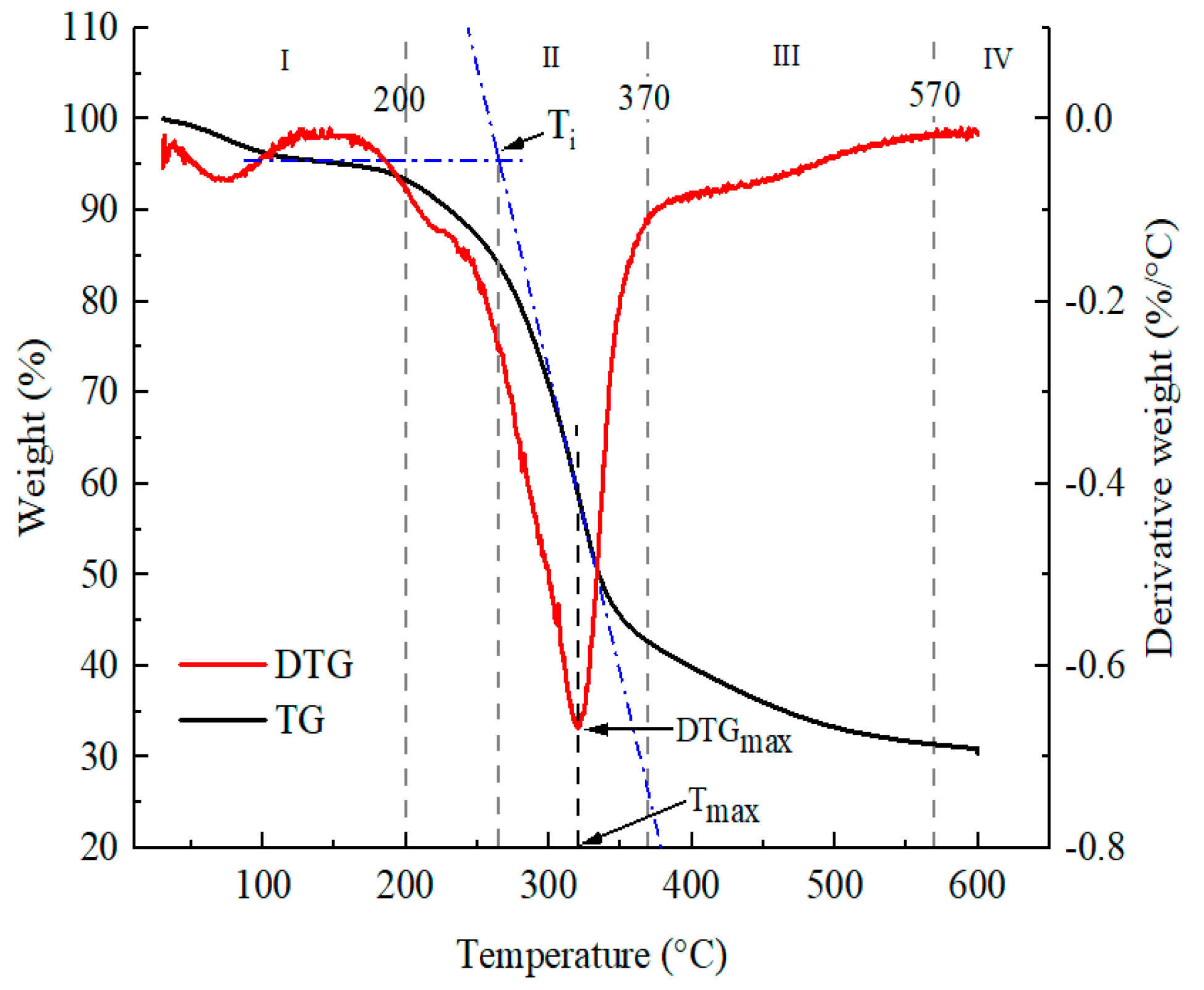
3.4. TG/DTG r Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Mathematical regression models were established, and the R2 values for the regression models were 0.97 for pellet density and 0.94 for pellet durability, accurately predicting these properties under optimal conditions.
- (2)
- Based on p-values, pelleting time, molding pressure, ultrasonic power, and mixing ratio had significant effects on pellet density. Mixing ratio, ultrasonic power, molding pressure, and pelleting time significantly influenced pellet durability. The interaction effects between mixing ratio and pelleting time, as well as molding pressure and pelleting time, were statistically significant for pellet density. Meanwhile, the interaction effects between the mixing ratio and molding pressure, as well as the mixing ratio and ultrasonic power, had an extremely significant impact on pellet durability.
- (3)
- The optimal conditions obtained were a mixing ratio of 25%, molding pressure of 4 MPa, pelting time of 37 s, and ultrasonic power of 200 W.
- (4)
- The combustion of the optimized pellet was divided into four stages, including the drying stage, volatilizing combustion stage, lignin decomposition, coke combustion stage, and burnout stage. The maximum weight loss rate was 0.6659%/°C, with the corresponding temperature of 320 °C. Ignition temperature and burnout temperature were 266 °C and 570 °C, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Yi, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Research progress of fueling utilization technology of corn straw. J. Wuhan Polytech. Univ. 2022, 41, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, L.; Zhao, L.; Meng, H.; Yao, Z. Study on straw multi-use potential in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, H.; Meng, H.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhao, L. Analysis of long-term mechanism for development of straw industry in northeast China under guidance of “Green-concept”. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, R.; Shahi, D.K.; Mahapatra, P.; Singh, C.S.; Naik, S.K.; Thombare, N.; Singh, A.K. Management of crop residues with special reference to the on-farm utilization methods: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 181, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M. Possibility of utilizing agriculture biomass as a renewable and sustainable future energy source. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, M.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. A Review on the Effects of Pretreatment and Process Parameters on Properties of Pellets. Energies 2022, 15, 7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styks, J.; Wróbel, M.; Frączek, J.; Knapczyk, A. Effect of Compaction Pressure and Moisture Content on Quality Parameters of Perennial Biomass Pellets. Energies 2020, 13, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Liu, Y.; Ali, B.; Mao, X.; Hussain, S.; Fu, J.; Ao, W.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; et al. Pyrolysis of pellets prepared from pure and blended biomass feedstocks: Characterization and analysis of pellets quality. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Investigation on characteristics of corn stover and sorghum stalk processed by ultrasonic vibration-assisted pelleting. Renew. Energy 2017, 101, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Z.; Meng, H.; Cong, H.; Cong, H. Design and experiment of biomass briquetting machine with vertical double circular mould. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrin, A.B.; Ma, A.N.; Choo, Y.M.; Mohamad, S.; Rohaya, M.H.; Azali, A.; Zainal, Z. Oil Palm Biomass As Potential Substitution Raw Materials For Commercial Biomass Briquettes Production. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 5, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sui, J.; Wang, L.; Song, J. The Effect of Urea Pretreatment Combined with Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting on Pellet Solid Density and Durability. Processes 2023, 11, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Deines, T.D.; Pei, Z.J.; Wang, D. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting of Biomass a Designed Experimental Investigation on Pellet Quality and Sugar Yield. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Erie, PA, USA, 12–15 October 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Pei, Z.J.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.R.; Cong, W.; Zhang, M.; Deines, T. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting of Cellulosic Biomass for Biofuel Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2011, 133, 011012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Deines, T.W.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Peiieting of Wheat Straw: A Designed Experimentai Investigation on Pellet Quality and Sugar Yield. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2012, 134, 061013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zhang, P.; Pei, Z.J. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted pelleting of wheat straw: A predictive model for pellet density using response surface methodology. Biofuels 2014, 3, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Heng, L.; Zhang, P.; Pei, Z.J.; Wang, D.; Wilson, J.; Zhou, J. Comparison of two pelleting methods for cellulosic ethanol manufacturing: Ultrasonic vibration-assisted pelleting vs. ring-die pelleting. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2015, 6, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chang, S.; Pei, Z.J.; Wang, D. Optimization of Input Variables in Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Pelleting of Cellulosic Biomass Using Multiple Response Surface Methodology. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Madison, WI, USA, 10–14 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Cong, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, D. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted pelleting for cellulosic biofuels manufacturing: A study on in-pellet temperatures. Renew. Energy 2015, 76, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted pelleting for cellulosic biofuel manufacturing: Investigation on power consumption. Renew. Energy 2013, 55, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, M.-X.; Zhang, P.-X.; Ji, H.-W.; Wu, Y.-C.; Liu, Z.-S.; Lu, Q. The individual and interactive effects of acid and basic oxides on ash fusibility during oxy-biomass combustion with recycled SO2. Fuel 2023, 331, 125888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyan, N.; Morey, R.V. Natural binders and solid bridge type binding mechanisms in briquettes and pellets made from corn stover and switchgrass. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anukam, A.; Berghel, J.; Henrikson, G.; Frodeson, S.; Ståhl, M. A review of the mechanism of bonding in densified biomass pellets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 148, 111249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.Q.; Tang, Y.J.; Fang, Y. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting of Cellulosic Biomass: A Review. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 805–806, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Lang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Liang, N.; Lyu, B.; Yang, C.; Hu, N.; Wu, Y.; et al. Analysis on hot briquetting mechanism of biomass fuel pellets. J. China Coal Soc. 2024, 1–15. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2190.td.20240123.1056.001 (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Yunusa, S.U.; Mensah, E.; Preko, K.; Narra, S.; Saleh, A.; Sanfo, S. A comprehensive review on the technical aspects of biomass briquetting. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, F.; Cong, W.; Zhang, M.; Tang, Y. Investigating pellet charring and temperature in ultrasonic vibration-assisted pelleting of wheat straw for cellulosic biofuel manufacturing. Renew. Energy 2016, 92, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Gao, N.; Song, Q. Pyrolysis of biomass components in a TGA and a fixed-bed reactor: Thermochemical behaviors, kinetics, and product characterization. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 121, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wei, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Comparative analysis of thermal oxidative decomposition and fire characteristics for different straw powders via thermogravimetry and cone calorimetry. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 134, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Liao, J. Experimental Analysis of Biomass Combustion Characteristics Based on Thermogravimetric Analysis. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2018, 45, 43–44. [Google Scholar]







| Sample | C/% | H/% | O/% | N/% | S/% | Ash/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn Stover | 51.43 | 7.13 | 37.64 | 0.79 | 0.38 | 7.89 |
| Rice straw | 47.36 | 7.59 | 39.73 | 0.86 | 0.27 | 6.74 |
| Material Type | Chemical Components (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin | Ash Content | |
| Corn Stover | 38.01 ± 0.41 | 28.04 ± 0.14 | 19.17 ± 0.13 | 3.97 ± 0.71 |
| Rice straw | 31.74 ± 0.2 | 21.29 ± 0.38 | 15.73 ± 0.33 | 9.12 ± 0.52 |
| Level | Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing Ratio (x1)/% | Molding Pressure (x2)/MPa | Pelleting Time (x3)/s | Ultrasonic Power (x4)/W | |
| +2 | 50 | 5 | 50 | 300 |
| +1 | 40 | 4 | 40 | 250 |
| 0 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 |
| −1 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 150 |
| −2 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 100 |
| Run | Mixing Ratio (x1)/% | Molding Pressure (x2)/MPa | Pelleting Time (x3)/s | Ultrasonic Power (x4)/W | Pellet Density y1/(kg/m3) | Pellet Durability y2/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 3 | 50 | 200 | 1277.97 | 90.06 |
| 2 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 150 | 1183.19 | 76.77 |
| 3 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 100 | 1220.02 | 79.49 |
| 4 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 300 | 1247.53 | 83.72 |
| 5 | 40 | 2 | 20 | 250 | 1229.65 | 85.50 |
| 6 | 20 | 4 | 40 | 250 | 1280.55 | 95.25 |
| 7 | 40 | 2 | 20 | 150 | 1208.55 | 81.12 |
| 8 | 40 | 2 | 40 | 250 | 1271.88 | 87.75 |
| 9 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1287.96 | 92.67 |
| 10 | 40 | 4 | 20 | 250 | 1239.50 | 82.74 |
| 11 | 30 | 5 | 30 | 200 | 1284.53 | 95.73 |
| 12 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1302.31 | 94.58 |
| 13 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 250 | 1193.27 | 88.89 |
| 14 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1308.12 | 94.49 |
| 15 | 30 | 1 | 30 | 200 | 1215.71 | 85.93 |
| 16 | 20 | 4 | 20 | 150 | 1218.26 | 87.18 |
| 17 | 10 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1233.99 | 90.69 |
| 18 | 30 | 3 | 10 | 200 | 1167.66 | 84.68 |
| 19 | 20 | 2 | 40 | 150 | 1261.12 | 84.39 |
| 20 | 40 | 4 | 20 | 150 | 1238.21 | 82.59 |
| 21 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1291.04 | 92.33 |
| 22 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1295.62 | 89.01 |
| 23 | 20 | 2 | 40 | 250 | 1276.64 | 93.71 |
| 24 | 40 | 4 | 40 | 150 | 1262.71 | 85.95 |
| 25 | 40 | 4 | 40 | 250 | 1279.55 | 86.35 |
| 26 | 30 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1305.38 | 93.62 |
| 27 | 50 | 3 | 30 | 200 | 1266.98 | 82.07 |
| 28 | 20 | 4 | 20 | 250 | 1244.30 | 95.89 |
| 29 | 40 | 2 | 40 | 150 | 1253.38 | 85.98 |
| 30 | 20 | 4 | 40 | 150 | 1283.20 | 90.80 |
| Source | df | Pellet Density | Pellet Durability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | p-Value | Coefficients | Sum of Squares | p-Value | Coefficients | ||
| Model | 14 | 39,395.48 | <0.0001 ** | 1298.41 | 738.34 | <0.0001 ** | 92.78 |
| x1 | 1 | 493.93 | 0.0315 * | 4.54 | 113.27 | <0.0001 ** | −2.17 |
| x2 | 1 | 3908.18 | <0.0001 ** | 12.76 | 74.33 | 0.0003 ** | 1.76 |
| x3 | 1 | 16,786.33 | <0.0001 ** | 26.45 | 67.53 | 0.0004 ** | 1.68 |
| x4 | 1 | 1089.75 | 0.0031 ** | 6.74 | 103.17 | 0.0001 ** | 2.07 |
| x1x2 | 1 | 193.02 | 0.1587 | −3.47 | 49.28 | 0.0016 ** | −1.75 |
| x1x3 | 1 | 768.40 | 0.0097 ** | −6.93 | 0.1127 | 0.8566 | −0.0839 |
| x1x4 | 1 | 4.77 | 0.8188 | 0.5459 | 48.65 | 0.0017 ** | −1.74 |
| x2x3 | 1 | 426.53 | 0.0435 * | −5.16 | 5.76 | 0.2087 | −0.5998 |
| x2x4 | 1 | 35.02 | 0.5370 | −1.48 | 12.04 | 0.0769 | −0.8675 |
| x3x4 | 1 | 6.63 | 0.7872 | −0.6435 | 5.55 | 0.2167 | −0.5889 |
| 1 | 3311.81 | <0.0001 ** | −10.99 | 64.78 | 0.0005 ** | −1.54 | |
| 1 | 3367.57 | <0.0001 ** | −11.08 | 4.94 | 0.2423 | −0.4246 | |
| 1 | 8794.22 | <0.0001 ** | −17.91 | 45.60 | 0.0022 ** | −1.29 | |
| 1 | 6308.41 | <0.0001 ** | −15.17 | 204.51 | <0.0001 ** | −2.73 | |
| Residual | 15 | 1316.09 | -- | -- | 50.05 | -- | |
| Lack of Fit | 10 | 986.60 | 0.3433 | -- | 28.75 | 0.7212 | -- |
| Pure Error | 5 | 329.49 | -- | -- | 21.29 | -- | -- |
| Cor Total | 29 | 40,711.57 | -- | -- | 788.39 | -- | -- |
| Comparison | Process Variables | Pellet Density (kg/m3) | Pellet Durability (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing Ratio/% | Molding Pressure/MPa | Pelleting Time/s | Ultrasonic Power/W | |||
| Predicted value | 24.63 | 3.75 | 36.65 | 212.20 | 1307.39 | 95.89 |
| Experimental value | 25 | 4 | 37 | 200 | 1301.18 | 94.76 |
| Error (%) | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.47 | 1.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Yu, R.; Luo, L.; Shi, H. Process Optimization of Pellet Manufacturing from Mixed Materials in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting. Energies 2024, 17, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092087
Li W, Yu R, Luo L, Shi H. Process Optimization of Pellet Manufacturing from Mixed Materials in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wentao, Rongwei Yu, Lina Luo, and Hongying Shi. 2024. "Process Optimization of Pellet Manufacturing from Mixed Materials in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting" Energies 17, no. 9: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092087
APA StyleLi, W., Yu, R., Luo, L., & Shi, H. (2024). Process Optimization of Pellet Manufacturing from Mixed Materials in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Pelleting. Energies, 17(9), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092087






