Abstract
The thermal structure of the lithosphere is key to understanding its thickness, properties, evolution, and geothermal resources. Cratons are known for their low heat flow and deep lithospheric roots. However, present-day cratons in East China have geothermal characteristics that are highly complex, with variable heat flow values, diverging from the typical thermal state of cratons. In this study, we conducted a detailed analysis of the geothermal geological background of the cratons in East China, summarizing the thermal state and tectono-thermal processes of different tectonic units, calculating the temperature at various depths, and discussing differences in temperature and thermal reservoirs at different depths. The observed lithospheric thermal thickness within the North Jiangsu Basin and the Bohai Bay Basin is notably reduced in comparison to that of the Jianghan Basin and the Southern North China Basin. The phenomenon of craton destruction during the Late Mesozoic emerges as a pivotal determinant, enhancing the geothermal resource prospects of both the Bohai Bay Basin and the North Jiangsu Basin. Our findings contribute significantly to the augmentation of theoretical frameworks concerning the origins of heat sources in global cratons. Furthermore, they offer invaluable insights for the methodical exploration, evaluation, advancement, and exploitation of geothermal resources.
1. Introduction
Cratons, often perceived as the epitome of stability within the solid lithosphere, are characterized by features such as low density, low heat flow, and a significantly thick lithosphere [1,2,3]. However, recent advancements in research have begun to challenge this long-standing assumption, providing substantial evidence that cratons may not be as immutable as previously thought. It has been observed that several cratons across the globe have been subject to lithospheric thinning, or in some cases, complete craton destruction [4,5,6,7]. China hosts three cratons: the Tarim Craton, the North China Craton, and the Yangtze Craton. Various studies by different scholars in petrology, geochemistry, structural geology, and geophysics have shown that the cratons in East China (east of the North–South Gravity Gradient Zone), particularly the North China Craton, have undergone significant lithospheric thinning over hundreds of kilometers since the early Paleozoic [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. This phenomenon has led to fundamental changes in the physical and chemical properties of the lithospheric mantle. Additionally, studies in geothermal science [5,17,18] also reveal that the present-day heat flow in the cratons in East China presents anomalies, deviating from the thermal state typically observed in cratons (Figure 1).
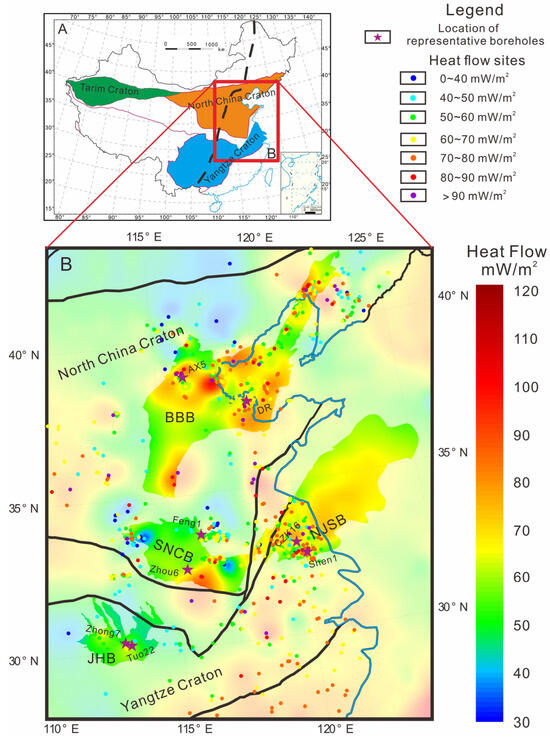
Figure 1.
Tectonic background and geothermal heat flow map of the cratons in East China. The heat flow data in the figure are sourced from [19,20,21,22], and we refer to to [19] for the construction of boundaries. The bold, black, dashed lines in (A) represent the North–South Gravity Gradient Zone. In (B), we have made the areas outside the North Jiangsu Basin (NJSB), the Bohai Bay Basin (BBB), the Jianghan Basin (JHB), and the Southern North China Basin (SNCB) 70 percent transparent in our geodetic heat flow map in order to differentiate the thermal backgrounds of the priority study areas.
Previous studies on the thermal structure of the lithosphere in East China have largely depended on the one-dimensional steady-state heat conduction equation (e.g., [23,24]). Drawing from insights into the lithospheric thermal structure in East China, He et al. [23] suggested that the thermal lithospheric thickness in East China typically ranges from 60 to 100 km, with the Moho temperature ranging from 500 to 850 °C, showing a “hot mantle–cold crust” structural type. Zang et al. [24] utilized 1° × 1° heat flow data, calculating the lithospheric thermal structure in the North China region, with the lithospheric bottom boundary at depths of 60–180 km and the Moho temperature fluctuating between 450 and 750 °C. Integrating various geological and geophysical data, Wang et al. [25] ascertained the thermal-rheological structure of the North China lithosphere, indicating that the lithospheric thickness in Eastern North China is concentrated between 80 and 110 km. In recent years, studies focusing on the heat flow of secondary tectonic units such as basins have demonstrated diverse lithospheric thermal thicknesses. The Bohai Bay Basin (BBB) displays a thermal lithospheric thickness ranging from 60 to 110 km, with an average heat flow value between 60 and 70 mW·m−2 [26,27,28]. The Southern North China Basin (SNCB) presents heat flow values and thermal lithospheric thicknesses of 56 mW·m−2 and 110–140 km, respectively [29,30,31]. The Jianghan Basin (JHB) in the Central Yangtze Craton reveals a geothermal heat flow value of 52 mW·m−2 and a thermal lithospheric thickness of 100–160 km [32,33]. The North Jiangsu Basin (NJSB) in the Lower Yangtze Craton boasts an average heat flow value of 67 mW·m−2, with a thermal lithospheric thickness of 78–85 km [22,34,35]. However, the majority of these studies lack a cohesive framework and do not analyze the geothermal genesis of cratons in East China. Concurrently, the densely inhabited and economically advanced cratons in East China require clean energy sources such as geothermal resources. Research on the variability in the regions’ deep temperatures and geothermal resource potential will aid in tackling this challenge.
In this study, we examined the heat flow data of cratons in East China and, utilizing data from the major basins (SNCB, NJSB, JHB, and BBB), provided a comprehensive analysis of the tectono-thermal processes in different tectonic units. We investigated and mapped out the variations in deep temperature and geothermal resource potential across different tectonic units. Our results serve to enhance theoretical frameworks for geothermal accumulation patterns and genesis theories in cratons. From an application perspective, our findings offer valuable insights for the exploration, assessment, development, and utilization of geothermal resources in the populous regions of East China. This research contributes actively towards achieving China’s “carbon neutrality” and “peak carbon” goals, supporting the nation’s pursuit of sustainable development and environmental responsibility.
2. Geologic Setting
The North China Craton, Yangtze Craton, and Tarim Craton collectively constitute the fundamental framework of the Chinese mainland. The North–South Gravity Gradient Zone extends from Southern China into Russian territory, covering approximately 4000 km. Geophysical observations, including Bouguer gravity anomalies, reveal significant differences in tectonic regimes on the eastern and western sides of the gravity gradient zone [36]. The focus of this study is primarily centered on the cratons in East China, encompassing the eastern block of the North China Craton and the central–southern region of the Yangtze Craton (Figure 1). The North China Craton is acknowledged as one of the oldest cratons globally, comprising the eastern block, central orogenic belt, and western block [37]. The region of Western Liaoning and Eastern Hebei contains a geological record with crustal remnants dating back over 3.8 billion years [38]. The Yangtze Craton, predominantly situated in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, is home to the Kongling Complex, located in the northern margin of the Lower Yangtze Craton, representing the oldest exposed rocks in the Yangtze Craton and widely regarded as its continental nucleus. These rocks chronicle multiple episodes of crustal growth and reworking in the Yangtze Craton since the Archean Eon [39]. In contrast to the conventional stability associated with cratons, the eastern block of the North China Craton underwent craton destruction in the Late Cretaceous [11,40,41,42,43,44].
The SNCB and BBB constitute the two major basins of the eastern block of the North China Craton, adjoining from north to south. Throughout the Cenozoic evolution of these basins, they have shown similarities in their structures, and their evolutionary stages are essentially synchronized [45]. These basins experienced the Paleogene rifting and extension stage and the Neogene to Quaternary post-rift subsidence stage, resulting in sedimentary sequences, including the deposition of fluvial–lacustrine clastic rocks in the Paleogene and the formation of terrestrial-sourced clastic rocks in the Neogene to Quaternary periods [45].
The JHB and NJSB are characteristic basins of the Middle–Lower Yangtze Craton. The JHB is identified as a Cretaceous to Neogene basin located in the central part of the Yangtze Plate, nestled between the Qinling–Dabie Orogenic Belt and the Jiangnan Uplift, as well as the Huangling Uplift [46]. It has been shaped by multiple phases of tectonic movements [46]. The NJSB serves as the terrestrial portion of the North Jiangsu–South Yellow Sea continental basin, a Cenozoic basin distinguished by a structural pattern of “one uplift and two depressions” (the Jianhu uplift, the Yanfu depression, and the Dongtai depression) [47]. The basement is comprised primarily of a suite of Ediacaran and Paleozoic marine carbonate rocks and clastic rocks [20].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Geothermal Database
3.1.1. Terrestrial Heat Flow
Terrestrial heat flow is defined as the heat transferred from the Earth’s interior to the surface per unit time and unit area, which subsequently dissipates into the atmosphere. In contrast to temperature and geothermal gradients, terrestrial heat flow provides a more precise representation of the thermal state of a region. Prior research has meticulously explored the heat flow in BBB [26,27,28], SNCB [29,30,31], JHB in the Central Yangtze Craton [32,33], and NJSB in the Lower Yangtze Craton [20,22] within the cratons in East China. Employing a compilation of the latest heat flow data, we have produced a heat flow map for the study area (Figure 1B). Overall, the terrestrial heat flow in the cratons in East China deviates from the typical thermal state of cratons, exhibiting characteristics of a higher heat flow background. In the northern segment of the eastern block of the North China Craton and the Lower Yangtze Craton, there is a high heat flow, while in the Central Yangtze and Southern North China regions, there is a lower heat flow background with sporadic areas of heat flow anomalies. These anomalies can be attributed to the “thermal refraction” effect caused by the enrichment of ore deposits in the shallow crust [48], as observed in the southern part of the SNCB.
3.1.2. Type and Temperature of Thermal Reservoir
The cratons in East China mainly host two sets of geothermal reservoirs: shallow Cenozoic clastic rock reservoirs and deep carbonate rock reservoirs. Our compilation of representative temperature–depth curves for different tectonic units in the study area (Figure 2) indicates significant variations in reservoir temperature and geothermal gradients among different tectonic units. At a depth of 1000 m, the temperatures in BBB and NJSB can reach 50–60 °C. This is followed by the JHB, which has a slightly lower temperature. SNCB displays the lowest temperature, around 40 °C. As depth increases, temperature generally shows a gradual upward trend. At equivalent depths, temperatures are the lowest in SNCB, followed by slightly higher values in JHB, and NJSB and BBB exhibit highest temperatures.
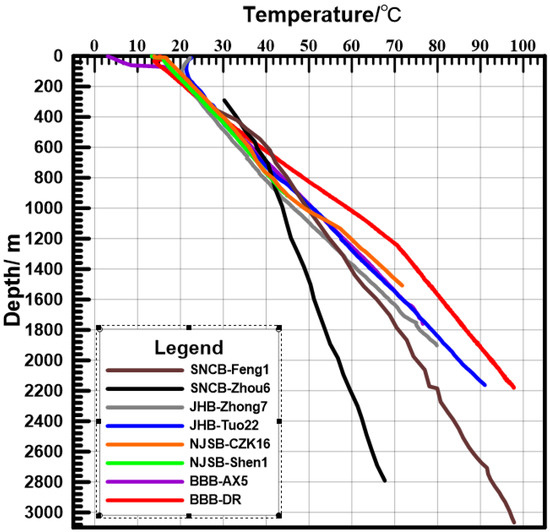
Figure 2.
Representative thermometric curves of major tectonic units in the cratons in East China. The data of BBB-AX5 are from [49]; those of BBB-DR are from [50]; those of JHB-Tuo22 and JHB-Zhong7 are from [32,33]; and those of NJSB-CZK16 and NJSB-Shen1 are from [20,22] (see Figure 1 for specific well locations).
During the Cenozoic era, the Eastern North China Craton saw the deposition of massive clastic rocks. Among them, the Neogene Guantao Formation and Minghuazhen Formation are recognized as excellent geothermal reservoirs and are widespread in BBB and SNCB [51]. Additionally, recent research has highlighted the widespread occurrence of carbonate rock reservoirs in BBB, featuring a minimum burial depth of only 500 m. The geothermal systems generally follow a distribution trend in the NNE to NE directions. The Paleogene and Neogene formations act as cap rocks, exhibiting low levels of rock thermal conductivity. In the Lower Paleozoic, particularly in the Middle Cambrian Wumishan Formation, the thermal conductivity of limestone is remarkably high, ranging from 2.5 to 4.2 W·m−1·K−1, forming high-quality geothermal reservoirs [51]. In particular, in BBB, the temperature range for the Minghuazhen Formation is 31–46 °C, that for the Guantao Formation is 42–67 °C, and that for carbonate rock reservoirs is 40–130 °C [51].
Similar to BBB, the thermal reservoirs in NJSB are predominantly classified into two types: shallow Cenozoic sandstone reservoirs and Ediacaran–Paleozoic carbonate rock reservoirs. An abundance of geophysical profiles and sedimentological evidence suggest that the deep carbonate rock reservoirs in NJSB have a wide distribution and large scale, encompassing almost the entire basin. They represent high-quality deep geothermal reservoirs. Specifically, for the Yancheng Formation, the temperature range is 20–60 °C, for the Sanduo Formation, it is 50–80 °C, for the Dainan Formation, it is 60–110 °C, and for the carbonate rock reservoirs, it is 80–200 °C [20].
The primary geothermal reservoirs in JHB comprise Paleogene and Neogene sandstone and glutenite, forming low-temperature hot water reservoirs. The Paleogene Qianjiang Formation is identified as a saline lake facies deposit, with a thickness of approximately 3500 m. It stands as the largest Paleogene saline lake facies depression in China. The surrounding temperature gradient is between 2.3 and 4.0 °C/100 m. The water temperature of the Neogene hot water reservoir ranges from 25 to 69 °C, while the Paleogene hot brine water temperature ranges from 60 to 95 °C [33].
3.1.3. Crustal Structure and Thermophysical Parameters
Delineating the crustal structure is essential for the study of the lithospheric thermal structure. Crustal structural classification (including Moho depth) of representative tectonic units in the cratons in East China is largely based on recent geophysical profiles and existing research outcomes [20,22,30,32,52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. Their detailed stratigraphic results are depicted in Table 1. In contrast to the relatively uniform thermal state in JHB, notable differences in the thermal state of uplift and depression areas in NJSB, SNCB, and BBB are observed. Hence, separate statistics were compiled for these areas. Comprehensive studies on thermal conductivity in NJSB reveal that the thermal conductivity of carbonate rocks in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic exceeds that in the Proterozoic and Cenozoic strata [20,22], dominating the regional temperature field. Consequently, measured values (thermal conductivity and heat production values for the Cenozoic, Mesozoic, Paleozoic, and Ediacaran strata are 1.77, 2.60, 3.69, and 3.70 W·m−1·K−1 and 1.47, 1.54, 1.80, and 0.54 μW·m−3, respectively) were utilized for the shallow sedimentary layers in NJSB [20,22]. For parameter selection in other regions and the assignment of thermal properties of the deep crust and mantle, we refer to the results provided by [59] (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Crustal layering structure and thermophysical parameters of major tectonic units in the cratons in East China. (D1, Sedimentary layer; D2, Upper crust; D3, Middle crust; D4, Lower crust; in the abbreviations, the last letter U stands for the uplift area and the D stands for the depression (e.g., NJBU, North Jiangsu Basin Uplift)).
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Changes in Vertical Heat Flow
Surface heat flow is segmented into two components: (1) the heat accumulation due to the decay of radioactive elements in the crust (crustal heat flow, ); and (2) the heat flow from the deep Earth, known as mantle heat flow (), which encompasses the heat generated by radioactive decay in the lithospheric mantle. While this component of heat is relatively minor, its importance for the stability of the lithosphere cannot be overstated. Thus, examining the lithospheric thermal structure is inherently an investigation into the vertical variation in heat production.
Utilizing crustal layering, we obtain the heat contributions from radioactive heat production in different layers (). Employing the “backstripping method”, we ascertain the heat flow values at the bottom of each layer. Hence, the mantle heat flow is determined by Equation (1) [60]:
3.2.2. Temperature Curve of the Lithosphere
In accordance with one-dimensional steady-state heat conduction equation, the temperature at a certain depth within the lithosphere is calculated with Equation (2):
and represent the temperature at the top and bottom of layer (°C), respectively; is the heat flow at the top of layer (mW·m−2); denotes the thickness (km); is the overall thermal conductivity of the rock (W·m−1·K−1) (temperature correction is necessary; see Methods of Thermal Structures for more details); and is the rate of heat generation by the rock in layer (μW·m−3).
Given the gradual increase in deep-seated temperature, the impact of thermal conductivity on temperature warrants consideration. As thermal conductivity varies with temperature, by incorporating the radiative heat transfer effects at high temperature, we adjust the thermal conductivity of deep-seated rocks using Equation (3) [61]:
Here, denotes the thermal conductivity at room temperature, and b and c are identified as experimental constants. To secure the optimal fitting parameter values, experimental outcomes from [62] (b1 = 0.0015 K−1) were applied for correcting the upper crust, while those from [63] (b2 = 0.0001 K−1) were employed for correcting the middle–lower crust and mantle lithosphere. When temperature surpasses 800 °C, a value of c = 1 × 10−10 W·m−1·K−4 was applied to correct the radiative thermal conductivity [64].
3.2.3. Calculation of Thermal Lithosphere Thickness
In the prevalent literature on the temperature distribution at different depths, the metric of lithospheric thermal thickness is derived by defining the base of the lithosphere as the solidus temperature of the mantle, approximated at 1200 °C [65], 1250 °C [66], or 1300 °C [67], or through comparison with the solidus line of basaltic rocks [68]. We utilize Equations (4) and (5) to delineate the upper and lower bounds of the lithospheric insulation line, thereby determining the thermal thickness [69]:
Upper limit: T1 = 1200 + 0.5,
Lower limit: T2 = 1300 + 0.4·Z,
4. Results
4.1. Contribution of Heat Flow from the Crust and Mantle
Our analysis of the heat flow contributions of different lithospheric radioactive heat-producing elements, the crustal heat flow, the mantle heat flow, and the ratio of crust to mantle heat flow in the main tectonic units of the study area is detailed in Table 2 and Figure 3. The crustal heat flow quantifies the heat contribution of radioactive elements in the crust of a tectonic unit. Research highlights that the high crustal heat flow (~30 mW·m−2) in the NJSB is attributed to a deeper crustal thickness. The BBB and SNCB, which are both part of the eastern block of the North China Craton, share similar crustal structural characteristics, with crustal heat flows ranging between 27 and 28 mW·m−2. Among the locations studied, the JHB exhibits the lowest crustal heat flow contribution of 26 mW·m−2.

Table 2.
Thermal structure characteristics of lithosphere in major tectonic units of the cratons in East China. (D1, Sedimentary layer; D2, Upper crust; D3, Middle crust; D4, Lower crust; in the abbreviations, the last letter U stands for the uplift area and the D stands for the depression (e.g., NJBU, North Jiangsu Basin Uplift)).
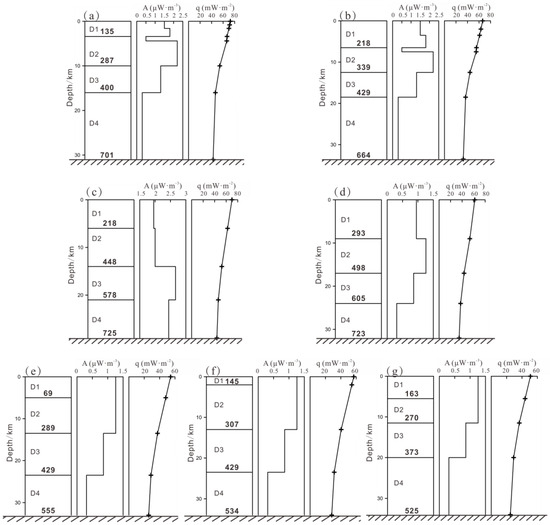
Figure 3.
Crust thermal structure of the major tectonic units of the cratons in East China. (a) NJSBU; (b) NJSBD; (c) JHB; (d) BBBU; (e) BBBD; (f) SNCBD; (g) SNCBD. (Abbreviations are consistent with those in Table 2. Text in bold within the Earth’s crust layers indicates temperature data at the bottom boundary of each layer).
The mantle heat flow () is defined as a geophysical parameter that evaluates the intensity of deep mantle activity in a region and represents a crucial component of the overall geothermal heat flow. In our research, the mantle heat flow values were determined for representative tectonic units in the Eastern North China Craton (Table 2). The highest mantle heat flow occurs in the uplift area of the BBB and the uplift area of the NJSB, reaching 44 mW·m−2 and 43 mW·m−2, respectively. Following these, the mantle heat flow values for the depression areas of the BBB and the NJSB are both over 30 mW·m−2; when compared to that of the JHB, the mantle heat flow in the SNCB is higher (27 mW·m−2). These findings suggest that among the tectonic units in the Eastern North China Craton, the mantle heat flow in the BBB and the NJSB is significantly elevated. Horizontally, a gradual decrease in mantle heat flow values is observed from east to west. For example, moving from the Eastern NJB and BBB to the central areas of the SNCB and JHB, the mantle heat flow values gradually diminish.
The distribution and ratio of crust to mantle heat flow can quantitatively illustrate the surface heat flow distribution of tectonic units. Based on the regional thermal state and the proportion of crust to mantle heat flow, the thermal structure of regional tectonic units can be categorized as “hot crust and cold mantle” or “hot mantle and cold crust” [23]. In scenarios in which the overall regional heat flow surpasses the plate–scale average heat flow or matches it, if the mantle heat flow exceeds 50%, the mantle is deemed “hot” relative to the crust, signifying it is the “hot mantle and cold crust” type [23]. Conversely, if the proportion of crustal heat flow in the total heat flow surpasses 50%, it is classified as the “hot crust and cold mantle” type. In our analysis, based on the heat flow distribution of different tectonic units, the crust to mantle heat flow ratio for each major tectonic unit was calculated (Table 2). The results reveal significant variations in the crust to mantle heat flow ratio across different regions, oscillating between 0.6 and 1.7 overall. The BBB shows the lowest crust to mantle heat flow ratio, with most areas below 0.8. Next, the NJSB features a crust to mantle heat flow ratio ranging from 0.7 to 0.9, typifying a “hot mantle and cold crust” thermal structure. In the central regions, the SNCB and JHB possess a crust to mantle heat flow ratio ranging from 1 to 1.1, signaling a transitional “warm crust and warm mantle” thermal structure. It is crucial to note that although the NJSB aligns with the “hot mantle and cold crust” type in terms of its crust to mantle heat flow ratio, it displays both a high mantle heat flow and a high crustal heat flow.
4.2. Comparison of Lithospheric Thermal Thicknesses
We have created a lithospheric thermal thickness map for different tectonic units in the study area and adjacent regions (Figure 4, Table 2). Our analysis demonstrates that the BBB possesses an extremely thin thermal lithospheric thickness, with a thickness of only 73 km in the uplift areas. Contrastingly, the thermal thickness in the uplift areas of the NJSB is 78 km. The SNCB showcases a lithospheric thermal thickness of about 130 km, whereas the lithospheric thermal thickness in the JHB of the Middle Yangtze Craton is slightly thicker (146 km). In domains with a thin thermal thickness, the temperature at the base of the lithosphere tends to be lower, such as the average temperature at the base of the lithosphere in the uplift areas of the NJSB, which is 1286 °C. Conversely, in areas characterized by a thicker thermal lithospheric thickness, such as the average temperature at the base of the lithosphere in the JHB, the temperature increases to 1315 °C.
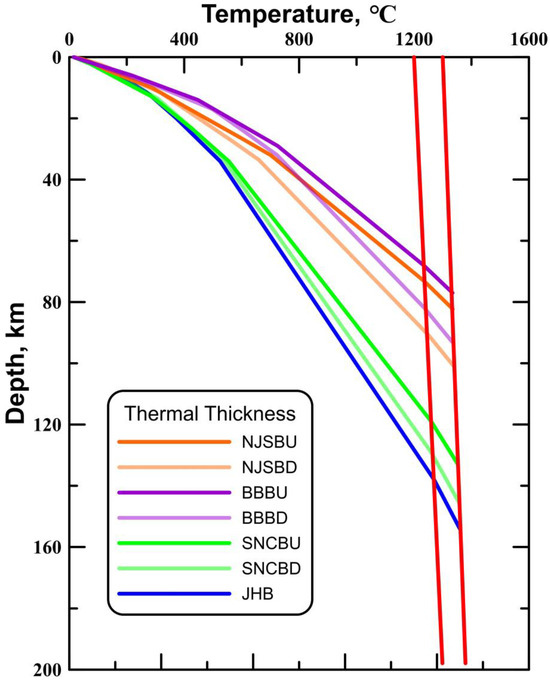
Figure 4.
Thickness of thermal lithosphere in major tectonic units in the cratons in East China.
4.3. Lithospheric Temperature Variations at Different Depths and Implications for Geothermal Resource Potential
The Moho temperature variance indirectly reflects the thermal state of a region, with a higher Moho temperature generally indicating a greater potential for geothermal resources. Utilizing Equations (1)–(3), we calculated the temperature at different lithospheric layer boundaries (the base of the sedimentary layer, base of the upper crust, base of the middle crust, base of the lower crust, and base of the lithosphere) and will now highlight the Moho temperature (Table 2, Figure 3).
The BBB exhibits the highest Moho temperature, exceeding 720 °C. The NJSB has a Moho temperature in the uplift areas exceeding 700 °C and ranging from approximately 660 to 670 °C in the depression areas. The lowest Moho temperatures are found in the SNCB, where the temperatures at the base of the lower crust generally fall below 550 °C, differing by more than 150 °C from the highest temperature observed in the BBB.
Additionally, we determined the temperature values and geothermal gradients at depths of 5 km, 10 km, 15 km, 20 km, 25 km, and 30 km for the major tectonic units in the cratons in East China (Table 3, Figure 5). Our findings indicate that, at the same depth, the uplift areas tend to exhibit higher temperature values compared to the depression areas within the same tectonic unit. The region with the highest temperature is the uplift area of the BBB.

Table 3.
Temperature and gradient values at different depths of main tectonic units in cratons in East China.
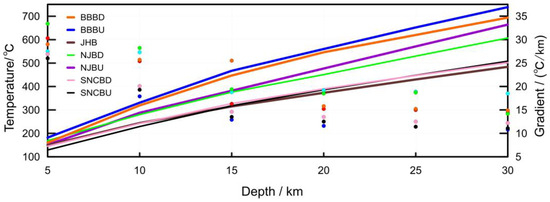
Figure 5.
Temperature and gradient values versus depth of main tectonic units in cratons in East China. (The lines and dots represent variations in temperature and gradients, respectively).
At a depth of 5 km, the uplift area of the BBB exhibits the highest temperature and geothermal gradient values, reaching 182 °C and 33.4 °C/km, respectively. The depression area of the NJSB is next, with a temperature reaching 169 °C at a depth of 5 km. The lowest temperature at a depth of 5 km is found in the depression area of the SNCB, registering merely 129 °C, which is 53 °C lower than the highest value. At a depth of 10 km, all regions show temperatures exceeding 200 °C, with the uplift and depression areas of the BBB generally surpassing 300 °C. The temperature difference between the different regions reaches a maximum of 102 °C. At a depth range of 20 km, the temperature in the BBB reaches around 550 °C, followed by the NJSB, which has a significantly higher temperature compared to that of the other tectonic units. With increasing depth, the geothermal gradient values tend to decline. For instance, in the uplift area of the BBB, the geothermal gradient decreases from 33 °C/km at a depth of 5 km to 14 °C/km at a depth of 30 km. Within the shallower depths up to 10 km, the geothermal gradient values are generally above 20 °C/km; yet, beyond 20 km, the gradient values drop below 20 °C/km. The reduction in the geothermal gradient for different tectonic units ranges mostly above 50% at depths from 5 km to 30 km.
Geothermal energy, characterized by its abundance, security, and environmentally friendliness, is deemed a vital future energy source. However, the distribution of medium- to high-temperature geothermal resources is not uniform. Therefore, the geothermal resource potential of regions has become a pivotal area of focus in geological and energy research. Factors influencing a region’s geothermal resource potential include reservoir temperature, reservoir depth, the porosity and permeability of the reservoir, and the volume of the reservoir (such as the Cenozoic clastic rock reservoir in the shallow section and the deep-seated carbonate rock reservoir). For the cratons in East China, especially in the aforementioned basins, which are densely populated, the dominant shallow reservoirs are composed of Cenozoic clastic rocks, while extensive carbonate rock reservoirs are developed at deeper levels. When considering the same exploitation horizon and depth, the temperature of the reservoir emerges as the most critical factor influencing the total geothermal resource quantity for similar target reservoirs per unit area.
Therefore, overall, at various scales, both the NJSB and the BBB are highlighted as prime exploration targets for geothermal resources. For one, this is due to the development of large-scale carbonate rock thermal reservoirs at depths of 2–5 km, which also fall within the critical depth range for geothermal development; additionally, a higher thermal background ensures exceptionally high temperatures at the same depth range. Compared to the BBB, which has been utilized for geothermal purposes for many years, the geothermal development potential of the NJSB may be even more significant. In the JHB, the temperature at a depth of 5 km is also notably close to 150 °C. Should carbonate rock reservoirs be present, its geothermal resource potential could be substantial. In addition, in the NJSB, the temperature within the depression zone at a depth of 5 km is higher than that in the uplift area. In the NJSB, the thermal conductivity of Paleozoic and Ediacaran strata significantly surpasses that of the shallow strata of the Proterozoic and Mesozoic. As the prevalence of strata with a high thermal conductivity increases, their influence over local thermal anomalies also increases, especially in the Dongtai depression on the south side of the Jianhu uplift. Therefore, more comprehensive temperature field simulations are necessary for the precise selection and delineation of geothermal resource target areas.
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Tectonic Activity and Thermal Regime Variability in the Cratons in East China
The differences in the thermal regime of the cratons in East China are mainly reflected in two aspects: their current thermal state and thermal history evolution. The BBB stands as a representative tectonic unit of the eastern block of the North China Craton, with numerous researchers utilizing the thermal state of the BBB as a benchmark for the thermal state of the eastern block of the North China Craton (e.g., [11,18]). Heat flow analyses reveal fundamental differences in the current thermal state between the northern and southern segments of the eastern block of the North China Craton. Similarly, the NJSB in the Lower Yangtze Craton exhibits high heat flow characteristics similar to those of the BBB, while the JHB in the Middle Yangtze Craton demonstrates significant differences in its thermal state when compared to that of the Lower Yangtze Craton.
Both the BBB and NJSB exhibit characteristics of high mantle heat flow, suggesting they have similar deep mantle activities and represent the typical “hot mantle, cold crust” thermal structure. Conversely, the mantle heat flow in the SNCB and JHB is identified as less than 30 mW·m−2, with both sharing similar lithospheric thermal thicknesses, which points to a transitional thermal structure described as “warm crust, warm mantle”.
Serving as representatives of the Eastern North China Craton and the Middle–Lower Yangtze Craton, the BBB and NJB are recognized as typical oil- and gas-bearing basins. The drive for oil and gas exploration and development has catalyzed research into the thermal history of these basins. Currently, methods for examining thermal history encompass paleo-thermometry, geodynamics, and vitrinite reflectance thermometry [70], with paleo-thermometry primarily suited to basin-scale studies. This includes low-temperature thermochronology (such as apatite fission track analyses) and organic matter thermochronology (such as vitrinite reflectance Ro).
Figure 6a summarizes recent studies on the thermal evolution of the BBB and the Lower Yangtze Craton [18,71,72,73]. This synthesis reveals that both showcase a “double-peak” heat flow characteristic. In the BBB, the peak heat flow ages are 107 Ma (with a peak heat flow qmax = 82–88 mW·m−2) and 36 Ma (qmax = 80–89 mW·m−2). In the NJSB, the peak heat flow ages are 129 Ma (qmax = 78–94 mW·m−2) and 58 Ma (qmax = 78–74 mW·m−2). Clearly, these two peaks heat flow events correspond to two tectono-thermal events, with the thermal events in the BBB lagging behind those in the Lower Yangtze Craton. The JHB in the Middle Yangtze Craton is a typical oil and gas basin, while the SNCB in the eastern block of the North China Craton is poor in oil overall. The data on the thermal evolution of these two basins in recent years are summarized in Figure 6b [74,75,76].
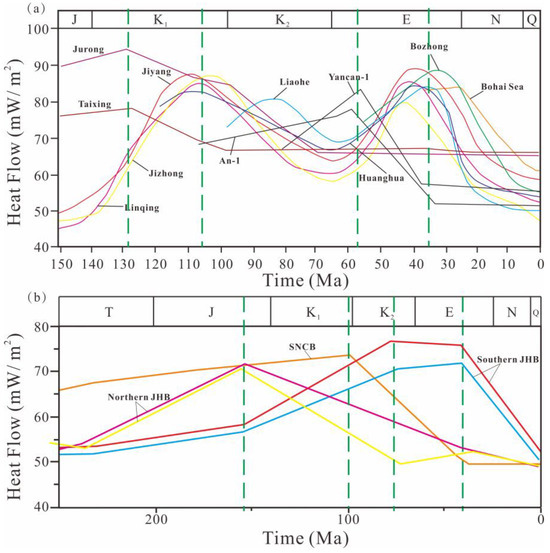
Figure 6.
Thermal history of the Bohai Bay Basin (BBB), the North Jiangsu Basin (NJB), the Southern North China Basin (SNCB), and the Jianghan Basin (JHB). (a): thermal history data from the Bohai and Bozhong Depressions [71,72]; An-1 and Yanshen-1 wells from the Lower Yangtze Craton [73]; other depressions in BBB [18]; (b): thermal history data from SNCB [75]; thermal history data from JHB [74,76].
In the JHB’s northern part, around 157 Ma, the ancient heat flow peaked at 72 mW·m−2. During the Late Cretaceous to Paleogene period, some boreholes evidenced a resurgence in heat flow increases again. Late-stage tectono-thermal events were predominantly observed in the JHB’s southern part, occurring between 78 and 43 Ma, during which the heat flow remained at higher background values (71–76 mW·m−2). Since the late Eocene, the heat flow values in the JHB have gradually decreased.
Research on the heat flow history in the SNCB remains comparatively sparse. For instance, in the Shenqiu Sag, the peak heat flow value reached 74 mW·m−2 at the end of the Early Cretaceous [75]. Additionally, a study on the ancient geothermal gradient in the Zhoukou Depression indicated different areas of the same depression reached the highest thermal evolution stage at different times. For example, the northern Luyi Sag and the western depression experienced tectonic heating and uplift–cooling stages during the Early Cretaceous [29]. The differences in thermal history in different regions of the basin and the relatively lower ancient heat flow increments suggest the limited influence of tectono-thermal events in the Late Mesozoic on these areas in the SNCB and JHB.
5.2. Tectonic Indicators and Dynamic Background
Thermal history investigations reveal that the Lower Yangtze Craton underwent a significant tectono-thermal event during the Mesozoic (128–129 Ma), with recorded peak paleo-heat flow values exceeding 90 mW·m−2 (Figure 7a). Additionally, the Lower Yangtze Craton and the northern segment of the eastern block of the North China Craton each recorded two peak thermal events during the Early Cretaceous and Paleogene, respectively. The times of reaching the peak paleo-heat flow values for these two events differ by about 20 Ma (Figure 7a), suggesting a potential disparity in the timing of craton destruction between them.
Early Cretaceous magmatism is widespread in East China, with the primary epoch of rock formation concentrated around 115–135 Ma [11,77] (Figure 7b). Following its late or post-peak period of magmatic activity, East China experienced a series of extensional structures, including metamorphic core complexes and extensional domes [78] (Figure 7c). Chronological analyses of the magmatic activity, ductile deformation, and extensional structure of the Lower Yangtze Craton and the eastern block of the North China Craton suggest that the tectono-thermal events in the Lower Yangtze Craton occurred slightly earlier than those in the eastern block of the North China Craton (Figure 7), as observed in volcanic rocks from the Lu-Zong Basin (127–135 Ma) and others. Recent reconstructions of the paleogeography of the ancient Pacific Plate (Izanagi Plate) propose [79,80,81] that around 140 Ma, the Izanagi Plate subducted in a north–northeast (NNE) direction [41,82], with the age of the oceanic crust getting progressively older moving towards the west. Due to the differences in the ages of the original oceanic crust and the NNE-directed subduction of the Izanagi Plate [80,81], the Lower Yangtze Craton might have experienced extensional tectonics and magmatic activity prior to the Eastern North China Craton. In summary, statistical studies of regional thermal history, magmatic activity, and the chronology of extensional structures [20,22,73] suggest that the subduction of the Izanagi Plate led to slightly different timings for the intense, non-steady-state mantle flows beneath the Lower Yangtze Plate and the Eastern North China Craton. Consequently, the destruction of the Lower Yangtze Craton occurred slightly earlier than the craton destruction in East China.
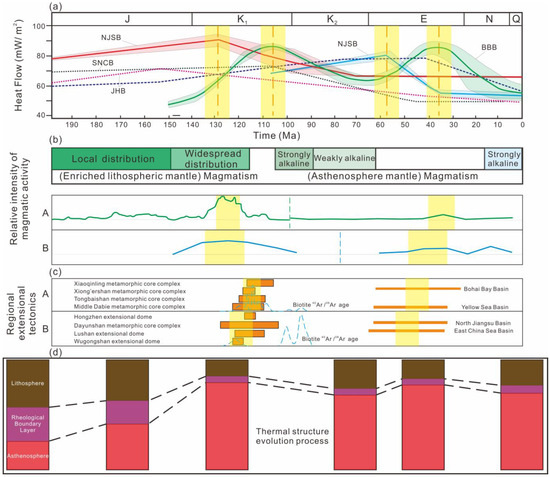
Figure 7.
Differences in thermal regime transition between the Eastern North China Craton and the Lower Yangtze Craton in Mesozoic and Cenozoic. (a) Thermal history pathway; (b) relative intensity of magmatism (modified from [11]); (c) regional extensional tectonics (modified from [78]); and (d) dynamics of thermal lithosphere thickness (modified from [17]) for the eastern block of the North China Craton and the Lower Yangtze Craton since 200 Ma. ‘A’ and ‘B’ in (b,c) represent the eastern block of the North China Craton and the Middle and Lower Yangtze Cratons, respectively.
During the Cenozoic, magmatic activity in East China was significantly diminished, and basalt became the predominant magmatic rock type (Figure 7b). There was also a noticeable decline in regional extensional strength from the subduction of the Pacific Plate compared to the Mesozoic [83], which primarily influenced the development of basins in East China, such as the BBB, the North Yellow Sea Basin, the North Jiangsu–South Yellow Sea Basin, and East China Sea Basin (Figure 7c). In general, the Lower Yangtze Craton experienced the aforementioned tectono-thermal events earlier than the Eastern North China Craton, and this corresponds to the differences in the timings of the Cenozoic thermal regime transition between the Eastern North China Craton and the Lower Yangtze Craton (Figure 7a).
6. Conclusions
This investigation into the lithospheric thermal structure of major tectonic units in the cratons in East China has led to the following conclusions.
The lithospheric thermal thickness of the NJSB and BBB ranges from 73 to 102 km and from 68 to 93 km, respectively, with mantle heat flow values ranging from 35 to 43 mW·m−2 and from 35 to 44 mW·m−2, indicative of a typical “hot mantle–cold crust” thermal structure. Conversely, the JHB and SNCB show distinctly different lithospheric thermal characteristics, indicating a distinct thermal state. The temperature differences gradually increase at increasing depths.
We determined the temperature at different lithospheric layer boundaries. The BBB exhibits the highest Moho temperature, surpassing 720 °C. The NJSB has a Moho temperature in the uplift areas exceeding 700 °C and ranging from approximately 660 to 670 °C in the depression areas. The lowest Moho temperatures are observed in the SNCB, where the temperature at the base of the lower crust generally falls below 550 °C, differing by more than 150 °C from the highest temperature observed in the BBB. Additionally, we calculated the temperature values and geothermal gradients at depths of 5 km, 10 km, 15 km, 20 km, 25 km, and 30 km for the major tectonic units in the cratons in East China. The results indicate that, at an identical depth, uplift areas typically exhibit higher temperatures compared to those of depression areas within the same tectonic unit. With increasing depths, the temperature gradient generally tends to decrease.
Based on the study of the tectonic evolution and thermal history of the cratons in East China since the Mesozoic, combined with paleogeographic reconstructions of East Asia and the (ancient) Western Pacific coast, this research posits that the destruction of the Lower Yangtze Craton (or the NJSB) and the northern segment of the Eastern North China Craton (or the BBB) likely unfolded in a sequential manner. The southern segment of the Eastern North China Craton (or the SNCB) and the Yangtze Craton (or the JHB) may have only experienced lithospheric thinning. The better geothermal resource potential in the BBB and NJSB Basins is intimately linked to the craton destruction during the Late Mesozoic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. (Yibo Wang) and J.W.; methodology, J.W. and Y.W. (Yibo Wang); validation, J.W., Y.W. (Yibo Wang), L.H., L.W., J.G., J.C., Z.W. and Y.W. (Yaqi Wang); formal analysis, J.W.; investigation, J.W.; resources, J.W.; data curation, J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W., Y.W. (Yibo Wang) and L.H.; writing—review and editing, L.W., J.G., J.C., Z.W., Y.W. (Yaqi Wang) and S.H.; visualization, J.W. and Y.W. (Yibo Wang); supervision, L.H., S.H. and Y.W. (Yibo Wang); project administration, L.H., S.H. and Y.W. (Yibo Wang); funding acquisition, S.H. and Y.W. (Yibo Wang). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutralization Science and Technology Innovation Special Fund of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. BE2022859, BE2022034), Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42302341), and State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution (SKL-K202304).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Carlson, R.W.; Irving, A.J.; Schulze, D.J.; Hearn, B.C. Timing of lithospheric mantle modification beneath the Wyoming Craton. Int. Kimberl. Conf. Ext. Abstr. 2003, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, F.; Jaupart, C. Temperature and rheological properties of the mantle beneath the North American craton from an analysis of heat flux and seismic data. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peslier, A.H.; Woodland, A.B.; Bell, D.R.; Lazarov, M. Olivine water contents in the continental lithosphere and the longevity of cratons. Nature 2010, 467, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusky, T.M.; Windley, B.F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, P. Flat slab subduction, trench suction, and craton destruction: Comparison of the North China, Wyoming, and Brazilian cratons. Tectonophysics 2014, 630, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Qiu, N.S. Heat flow and destabilized cratons: A comparative study of the North China, Siberian, and Wyoming cratons. Int. Geol. Rev. 2017, 59, 884–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, O.P.; Dwivedi, S.K. Decratonised lithosphere associated with mantle plume upwelling in the Singhbhum craton, eastern India based on geophysical and geodynamic perspective. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 246, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Cao, Z.B.; Peng, L.H.; Liu, L.J.; Chen, L.; Lundstrom, C.; Peng, D.D.; Yang, X.T. Secular craton evolution due to cyclic deformation of underlying dense mantle lithosphere. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, T.Y. Distinct lateral variation of lithospheric thickness in the Northeastern North China Craton. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 267, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Zhang, A.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Ryan, C.G. Phanerozoic evolution of the lithosphere beneath the Sino-Korean Craton. In Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies, M.A.; Fan, W.; Zhang, M. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120 km of Archaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1993, 76, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Xu, Y.G.; Wilde, S.A.; Walker, R.J. Destruction of the North China Craton in the Mesozoic. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 47, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G. Thermo-tectonic destruction of the Archaean lithospheric keel beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China: Evidence, timing and mechanism. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zhao, Y.; Davis, G.A.; Ye, H.; Wu, F. Temporal and spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatism and deformation in the North China Craton: Implications for lithospheric thinning and decratonization. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 131, 49–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, M.; Song, S.G. Catastrophic craton destruction via wholesale lithosphere delamination. Geology 2023, 51, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q.H.; Xia, Q.K. Craton destruction induced by drastic drops in lithospheric mantle viscosity. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2022EA002455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Bao, X.W. Phanerozoic evolution of lithospheric structures of the North China Craton. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.J.; Zhang, L.Y. Thermal evolution of cratons in China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 164, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.S.; Zuo, Y.H.; Xu, W.; Li, W.Z.; Chang, J.; Zhu, C.Q. Meso-Cenozoic lithosphere thinning in the eastern North China Craton: Evidence from thermal history of the Bohai Bay Basin, North China. J. Geol. 2016, 124, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.Z.; Hu, S.B.; Shi, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.T.; Hu, D. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: Updated dataset and tectonic implications. Tectonophysics 2019, 753, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L.J.; Guan, J.P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.T.; Hu, J.; Hu, S.B. Exploration process and genesis mechanism of deep geothermal resources in the North Jiangsu Basin, East China: From nothing to something. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 784600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Furlong, K.; Fuchs, S.; He, L.J.; Hu, S.B. Terrestrial heat flow variation with depth caused by anomalously high radiogenic heat production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Hu, D.; Guan, J.P.; Wang, L.J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.T.; Jiang, G.Z.; Hu, J.; Tang, B.N.; Zhu, C.Q.; et al. The present-day geothermal regime of the North Jiangsu Basin, East China. Geothermics 2020, 88, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.J.; Hu, S.B.; Wang, J.Y. Characteristics of the lithospheric thermal structure in the eastern continental region of China. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2001, 11, 966–969. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, S.X.; Liu, Y.G.; Ning, J.Y. Thermal Structure of the Lithosphere in North China. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2002, 45, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, Y.M.; Feng, Y.S. Three-Dimensional Thermo-Rheological Structure of the Lithosphere in the North China Craton Determined by Integrating Multiple Observations: Implications for the Formation of Rifts. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 969–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Wang, L.S.; Gong, Y.L.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Han, Y.B. Thermo-rheological structure of the lithosphere of the Jiyang depression and its geodynamic significance. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2005, 35, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Zou, H.Y. Presentday Geothermal Structure of Lithosphere and the Cenozoic Tectonothermal Evolution of Bohai Basin. Geoscience 2013, 27, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.H.; Qiu, N.S.; Chang, J.; Hao, Q.Q.; Li, Z.X.; Li, J.W.; Li, W.Z.; Xie, C.H. Meso-Cenozoic Lithospheric Thermal Structure in the Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 87, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.G.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhao, J.F.; Liu, Y.T. A Study on Geothermal Field and Its Geological Significance in Southern Area of the North China Craton. Geol. Rev. 2009, 55, 428–434. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, L.S.; Liu, S.W.; Li, C.; Ding, Z.Y. Thermo-Rheological Structure of the Lithosphere in the South Huabei Basins. Geol. J. China Univ. 2006, 12, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, L.S.; Liu, S.W.; Li, C.; Ding, Z.Y. Geothermal Field in the South Huabei Basins. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 604–608. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Q.Y.; He, L.J. Deep Temperature and Thermal Structure along the Fengjie-Guanyindang Geotraverse in Mid-Upper Yangtze Area. Chin. J. Geol. 2014, 49, 799–811. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, C.Q.; Shan, J.N.; Hu, S.B. Borehole Temperature Logging and Terrestrial Heat Flow Distribution in Jianghan Basin. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2010, 45, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.S.; Shi, Y.S. Geothermal Research in Hydrocarbon Basins; Nanjing University Press: Nanjing, China, 1989; pp. 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.S.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.S.; Wang, Y.H. Distribution of geothermal fields and geodetic heat flow density in the Lower Yangzi region. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 1995, 38, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.F.; Xu, Y.G.; Chen, Y. Formation mechanism of the north–south gravity lineament in East China. Tectonophysics 2021, 818, 229074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.C.; Zhai, M.G. Lithotectonic elements of Precambrian basement in the North China Craton: Review and tectonic implications. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1207–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Wan, Y.S.; Wu, J.S.; Wilde, S.A.; Dong, C.Y.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yin, X.Y. Archean Crustal Evolution and the Oldest Rocks in the North China Craton. Geol. Bull. China 2007, 26, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H. Crust Evolutional Process of Yangtze Craton during Archean-Paleoproterozoic Period. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.R.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 376–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Xu, Y.G. Magmatic perspective on subduction of Paleo-Pacific plate and initiation of big mantle wedge in East Asia. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 213, 103473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y. Formation time of the big mantle wedge beneath East China and a new lithospheric thinning mechanism of the North China craton—Geodynamic effects of deep recycled carbon. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, C.; Gu, C.C.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.J.; Su, N.; Xiao, S.Y. Oceanic plate subduction history in the western Pacific Ocean: Constraint from late Mesozoic evolution of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 386–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.X.; Xu, Y.G. The subduction of the west Pacific plate and the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhao, J.F.; Deng, Y.; Guo, P.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, J.Q. Genetic causes of oil-rich and-poor reservoirs: Implications from two Cenozoic basins in the eastern North China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 48, 1506–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.X.; Gao, Z.W.; Zhang, J. Structure model and evolution of the jianghan basin and relation with moderate to strong earthquakes. Earthquake 2021, 29, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.M.; Chen, W.; Li, H.Y.; Duan, H.L. Strike⁃slip structures and hydrocarbon accumulation in complex fault blocks in Subei Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2023, 45, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Wang, J.A. The Terrestrial Heat Flow in Anhui Province; Cultural Relics Press: Beijing, China, 1982; pp. 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.T.; Rao, S.; Xiao, H.P.; Wang, Y.B.; Jiang, G.Z.; Hu, S.B.; Zhang, C. Terrestrial heat flow of Jizhong depression, China, Western Bohai Bay basin and its influencing factors. Geothermics 2021, 96, 102210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.Z.; Tang, X.Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, P.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhao, P.; Hu, S.B. High-quality heat flow determination from the crystalline basement of the south-east margin of North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Jiang, G.Z.; Zhang, C.; Tang, X.C.; Hu, S.B. Estimating geothermal resources in Bohai Bay Basin, East China, using Monte Carlo simulation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, C.; He, L.J. Lithospheric thermal structure of the North China Craton and its geodynamic implications. J. Geodyn. 2016, 102, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H.; Liu, B.J.; Zhao, J.R.; Liu, B.F.; Zhang, C.K.; Pan, S.Z.; Lin, J.Y.; Guo, W.B. 2-D P-Wave Velocity Structure of Lithosphere in the North China Tectonic Zone: Constraints from the Yancheng-Baotou Deep Seismic Profile. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R. Seismic Study of Crust and Upper Mantle Structure and Tectonics in Middle-to-Lower Yangtze Craton and Its Adjacent Regions. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, F.Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Duan, Y.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Lin, J.Y. Seismic Structure of the Lithosphere beneath Eastern North China Craton Results from Long Distance Deep Seismic Sounding. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2015, 58, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bai, Z.M. P-wave velocity structure of the Lower Yangtze crust: Reinterpretation of the Fuli Ji-Fengxian seismic bathymetry profile. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, Z.J.; Tian, X.B.; Liu, B.F.; Bai, Z.M.; Lü, Q.T.; Teng, J.W. Crustal Structure beneath the Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt and Its Surrounding Areas: Constraints from Active Source Seismic Experiment along the Lixin to Yixing Profile in East China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 918–930. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Teng, J.W. Crustal and upper-earth slow structure of the Suixian-Ma’anshan belt and some features of the southern section of the Zhenglu tectonic belt. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 1989, 32, 648–659. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Hu, S.B.; Wang, Z.T.; Jiang, G.Z.; Hu, D.; Zhang, K.S.; Gao, P.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T. Heat flow, heat production, thermal structure and its tectonic implication of the southern Tan-Lu Fault Zone, East–Central China. Geothermics 2019, 82, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D. Thermal gradients in the continental crust. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1986, 24, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, I.T.; Golovanova, I.V.; Khachay, Y.V.; Druzhinin, V.S.; Kosarev, A.M.; Schapov, V.A. Low geothermal heat flow of the Urals fold belt—Implication of low heat production, fluid circulation or palaeoclimate? Tectonophysics 1997, 276, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rao, R.U.M. Geothermal Investigations In The 1993 Latur Earthquake Area, Deccan Volcanic Province, India. Tectonophysics 1999, 306, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.; Šafanda, J. Geothermal modeling along a two-dimensional crustal profile in Southern Portugal. J. Geodyn. 2002, 34, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, J.F.; Simmons, G. Thermal conductivity of Earth materials at high temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 6966–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, S.; Rabinowicz, M.; Grégoire, M.; Chevrot, S. Differences between Archean and Proterozoic lithospheres: Assessment of the possible major role of thermal conductivity. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2006, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.J.; Hyndman, R.D.; Flück, P. Heat flow, heat generation, and crustal temperature in the northern Canadian Cordillera: Thermal control of tectonics. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2316–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemieva, I.M.; Mooney, W.D. Thermal thickness and evolution of Precambrian lithosphere: A global study. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2001, 106, 16387–16414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.J.; Hu, S.B.; Yang, W.C.; Wang, J.Y. Radiogenic heat production in the lithosphere of Sulu ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 277, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; McDonough, W.F.; O’Connell, R.J. Thermal structure, thickness and composition of continental lithosphere. Chem. Geol. 1998, 145, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, A.L.; Wildman, M.; Stevens, G.A.L.; Murray, K.E. Thermal history modeling techniques and interpretation strategies: Applications using QTQt. Geosphere 2023, 19, 493–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.B.; Sullivan, P.B.O.; Raza, A.; Kohn, B.P. Thermal history and tectonic subsidence of the Bohai Basin, northern China: A Cenozoic rifted and local pull-apart basin. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2001, 126, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.B.; Zhang, R.Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Cai, D.S. Thermal history and tectonothermal evolution evolution characteristics of the Bohai Basin. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 1999, 42, 748–755. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, P. The Application of the Thermometric Indicators to the Study of Thermal Evolution in the Lower-Yangtze Region; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2005; (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhao, P.; Sun, Z.X.; Yuan, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.Q. A Study on Maturity Evolution of Lower Silurian Marine Hydrocarbon Source Rocks and Thermal History in the Southern Jianghan Basin. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2010, 53, 2918–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.L.; Gao, H.P.; Jiang, W. Thermal History Modeling of Permian Source Rocks in Tanzhuang-Shenqiu Sag. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2010, 32, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.S.; Zhu, C.Q.; Hu, S.B. Heat Flow History, Tectono-Sedimentary Evolution and Thermal Events of the Jianghan Basin. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 934–939. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhang, X.O.; Yang, J.H. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in East China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Charles, N.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Faure, M.; Wu, L.; Wang, F.; Li, Q.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.C. Late Mesozoic compressional to extensional tectonics in the Yiwulüshan massif, NE China and their bearing on the Yinshan–Yanshan orogenic belt. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Gurnis, M.; Ma, P.F.; Zhang, B. Reconstruction of northeast Asian deformation integrated with western Pacific plate subduction since 200 Ma. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 175, 114–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.D.; Seton, M.; Zahirovic, S.; Williams, S.E.; Cannon, J. Ocean Basin Evolution and Global-Scale Plate Reorganization Events Since Pangea Breakup. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2016, 44, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seton, M.; Müller, R.D.; Zahirovic, S.; Gaina, C.; Torsvik, T.; Shephard, G.; Talsma, A.; Gurnis, M.; Turner, M.; Maus, S. Global continental and ocean basin reconstructions since 200. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 113, 212–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Guo, P.Y.; Niu, Y.L. Eastern China Continental Lithosphere Thinning Is a Consequence of Paleo-Pacific Plate Subduction: A Review and New Perspectives. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Pang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, D. Coupling between Cenozoic Extensional Exhumation in North China and the Subduction of the Pacific Plate. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2023, 620, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).