Analysis of Solar Radiation Differences for High-Voltage Transmission Lines on Micro-Terrain Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Solar Radiation Calculation Method for Transmission Lines Based on DEM
2.1. Calculation of Solar Position
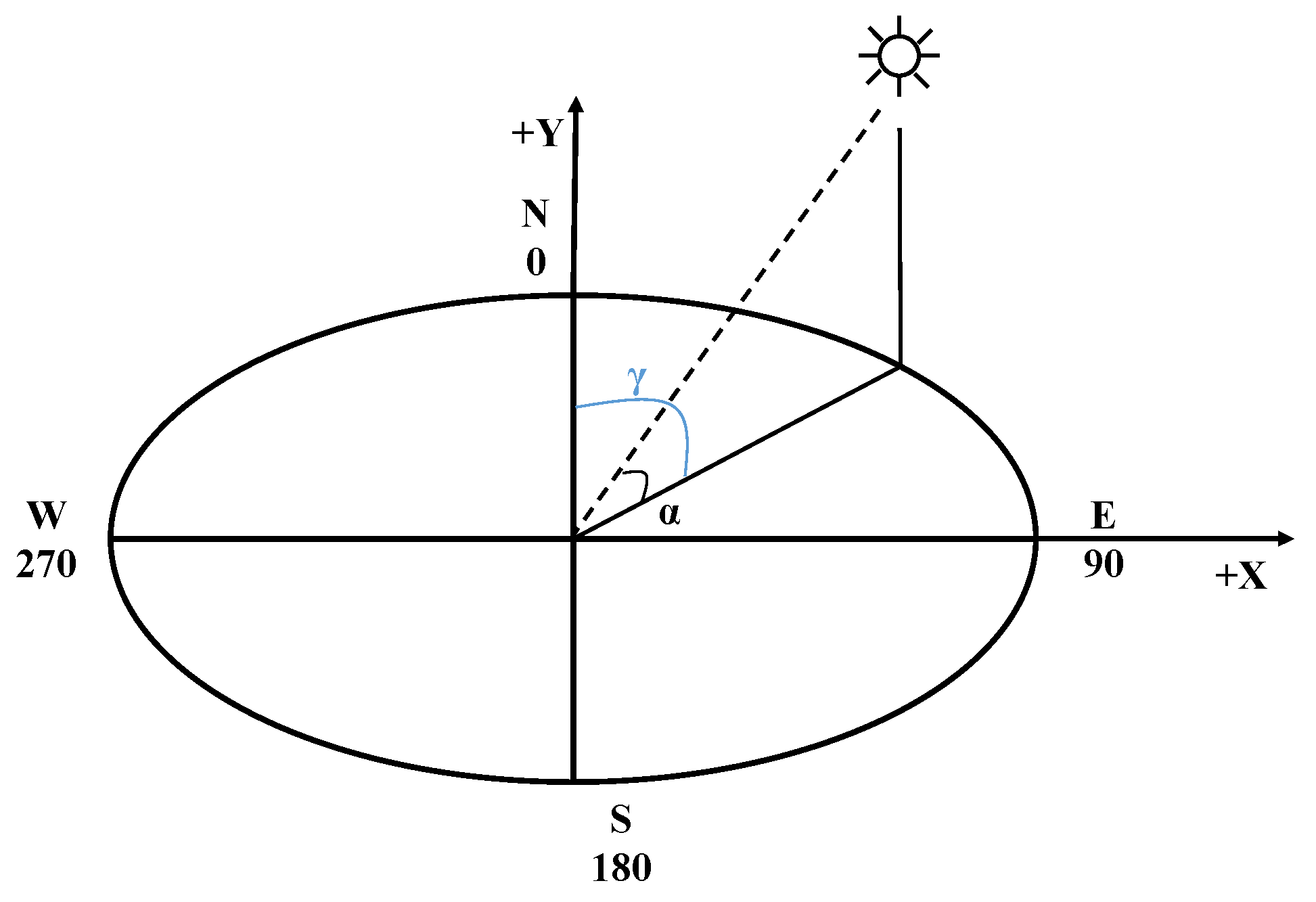
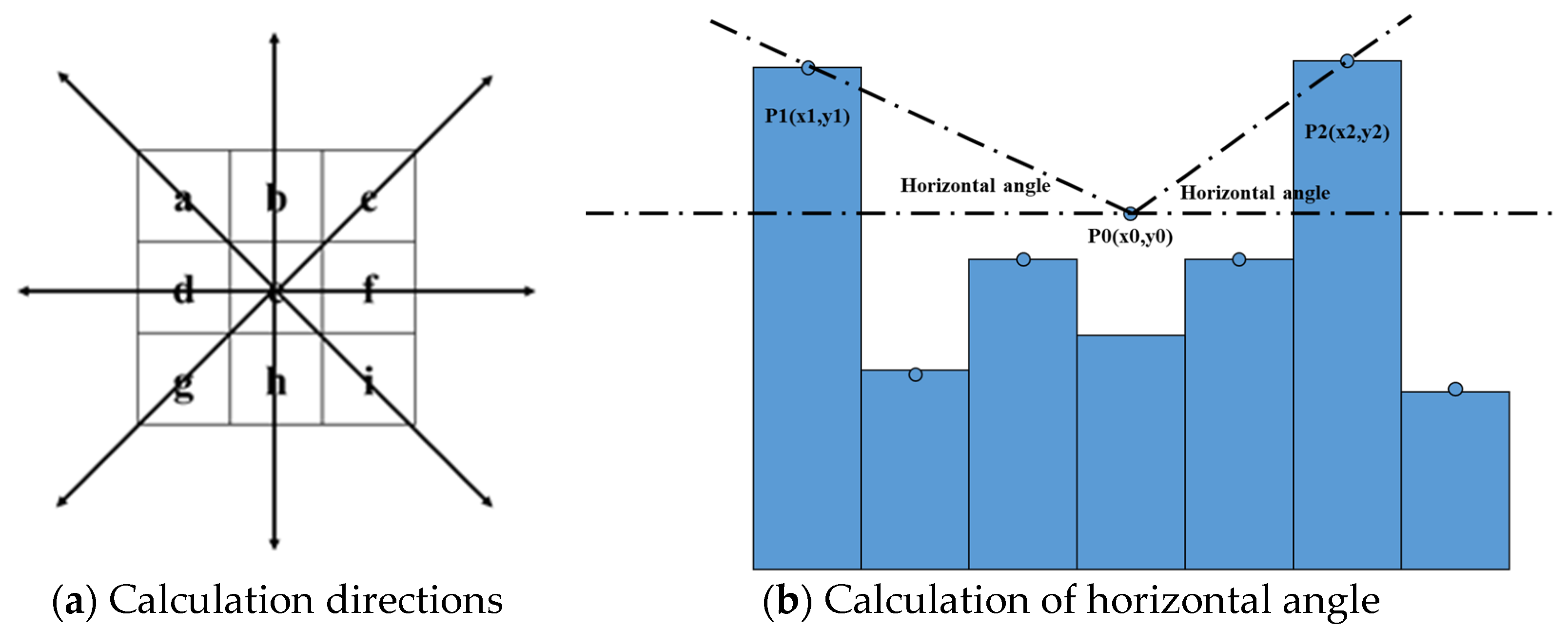
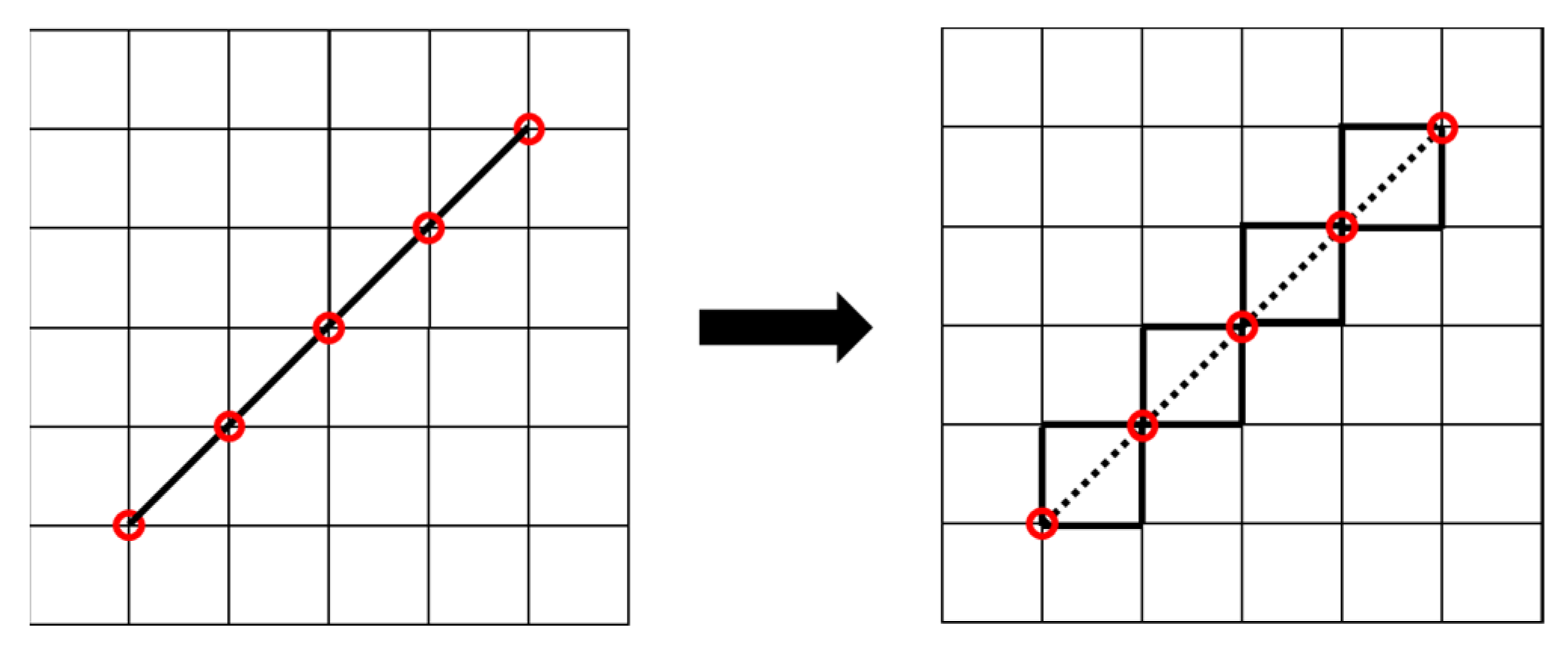
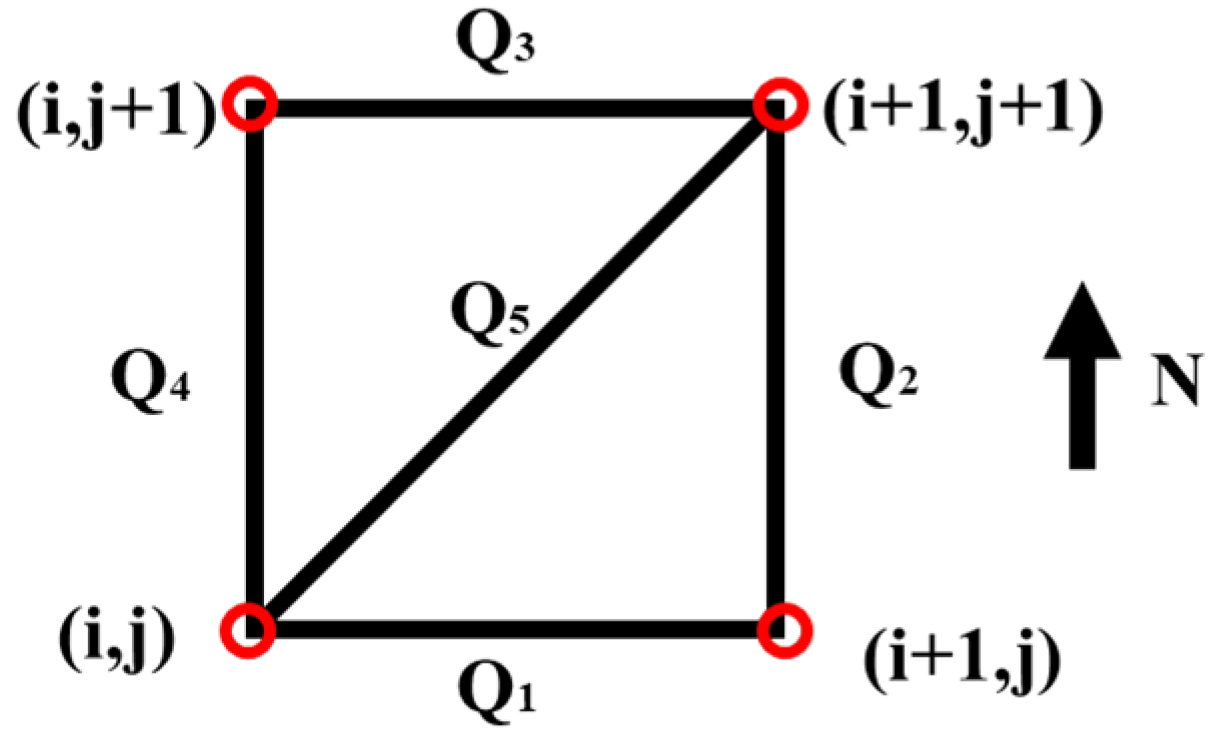
2.2. Viewshed Calculation
2.3. Direct and Scattered Radiation Flux
2.4. Radiative Flux on Transmission Line Surface
2.5. Joule Heating of the Current
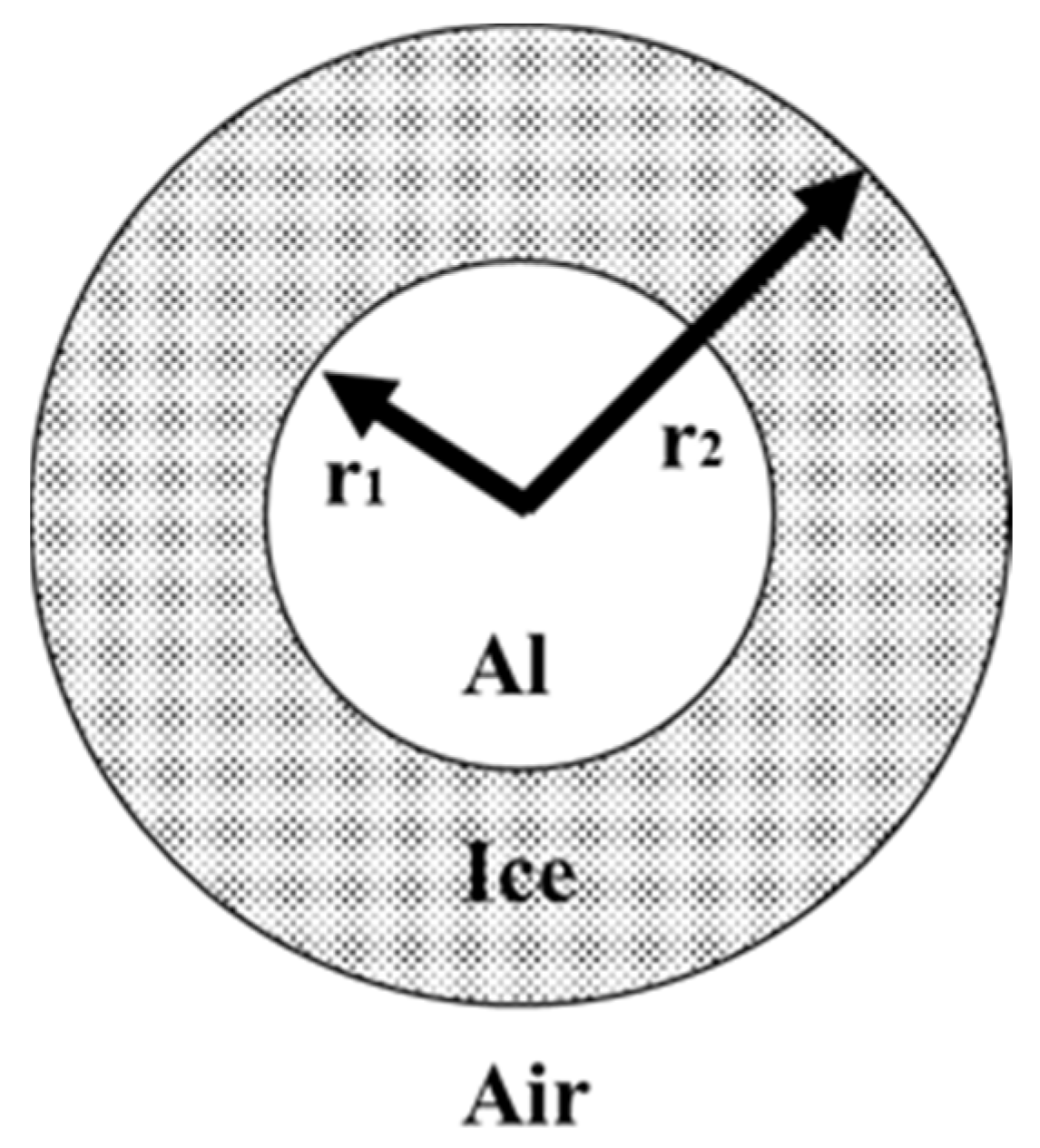
2.6. Heat of Ice Melting
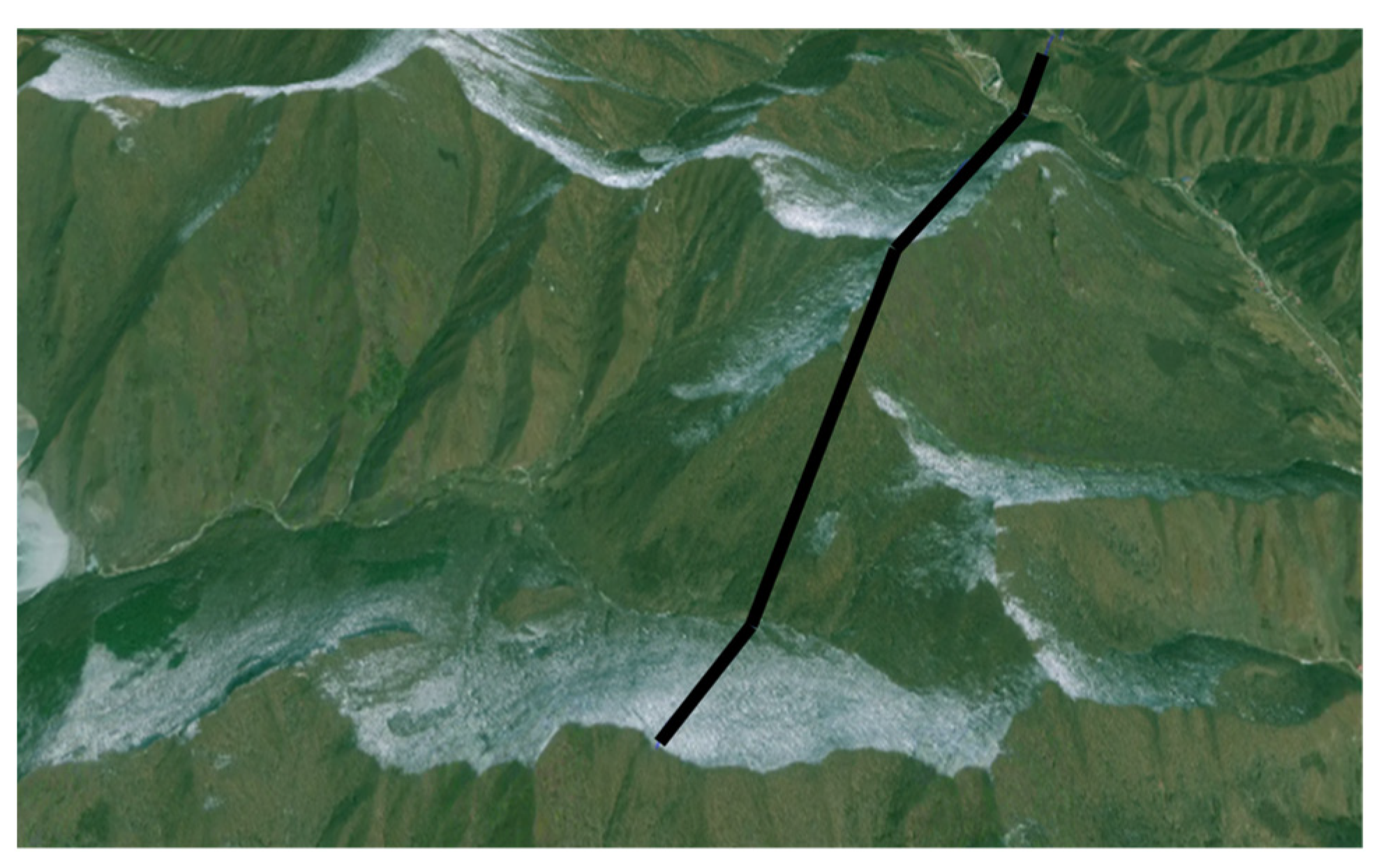
3. Results and Discussion
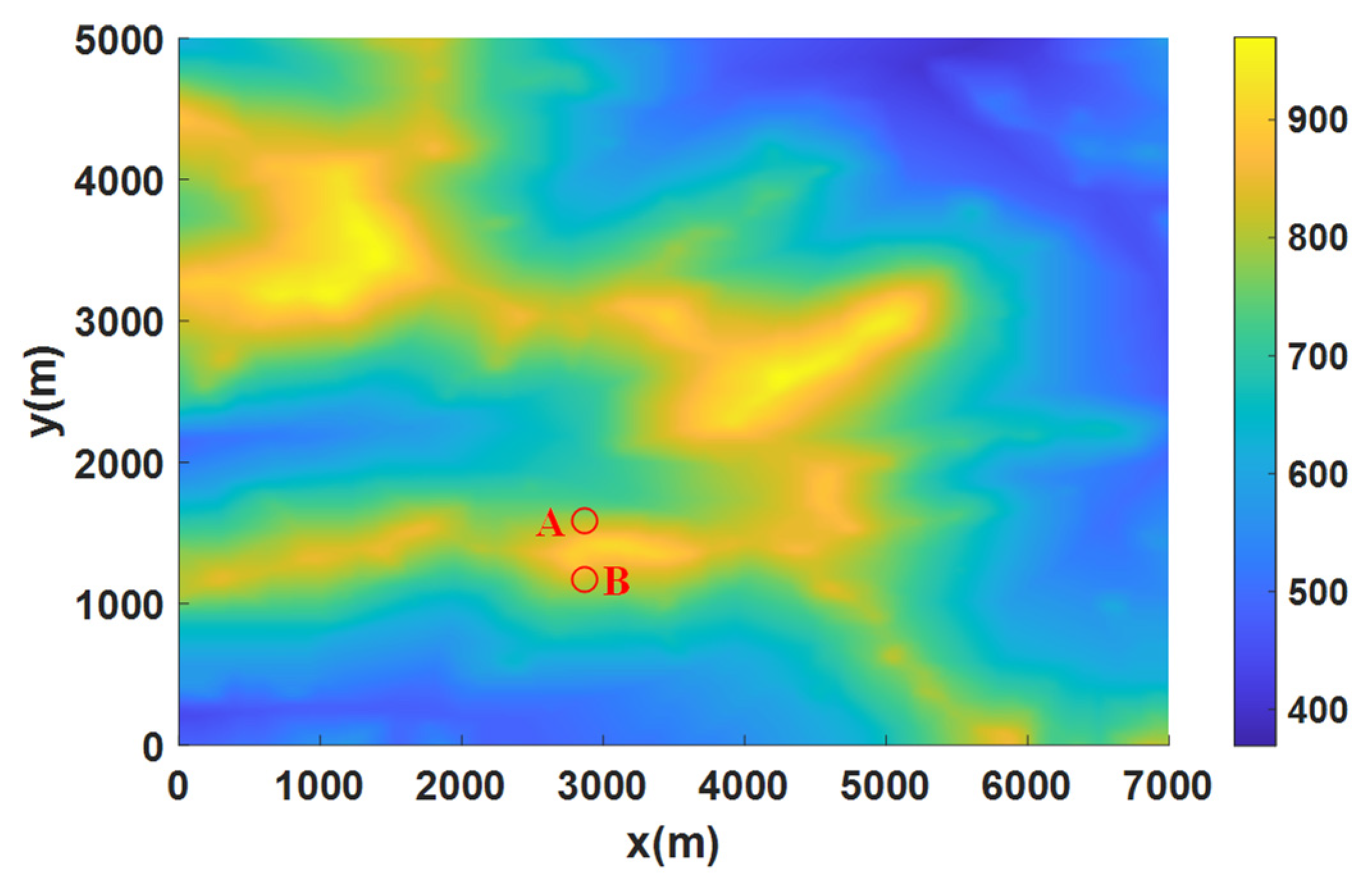
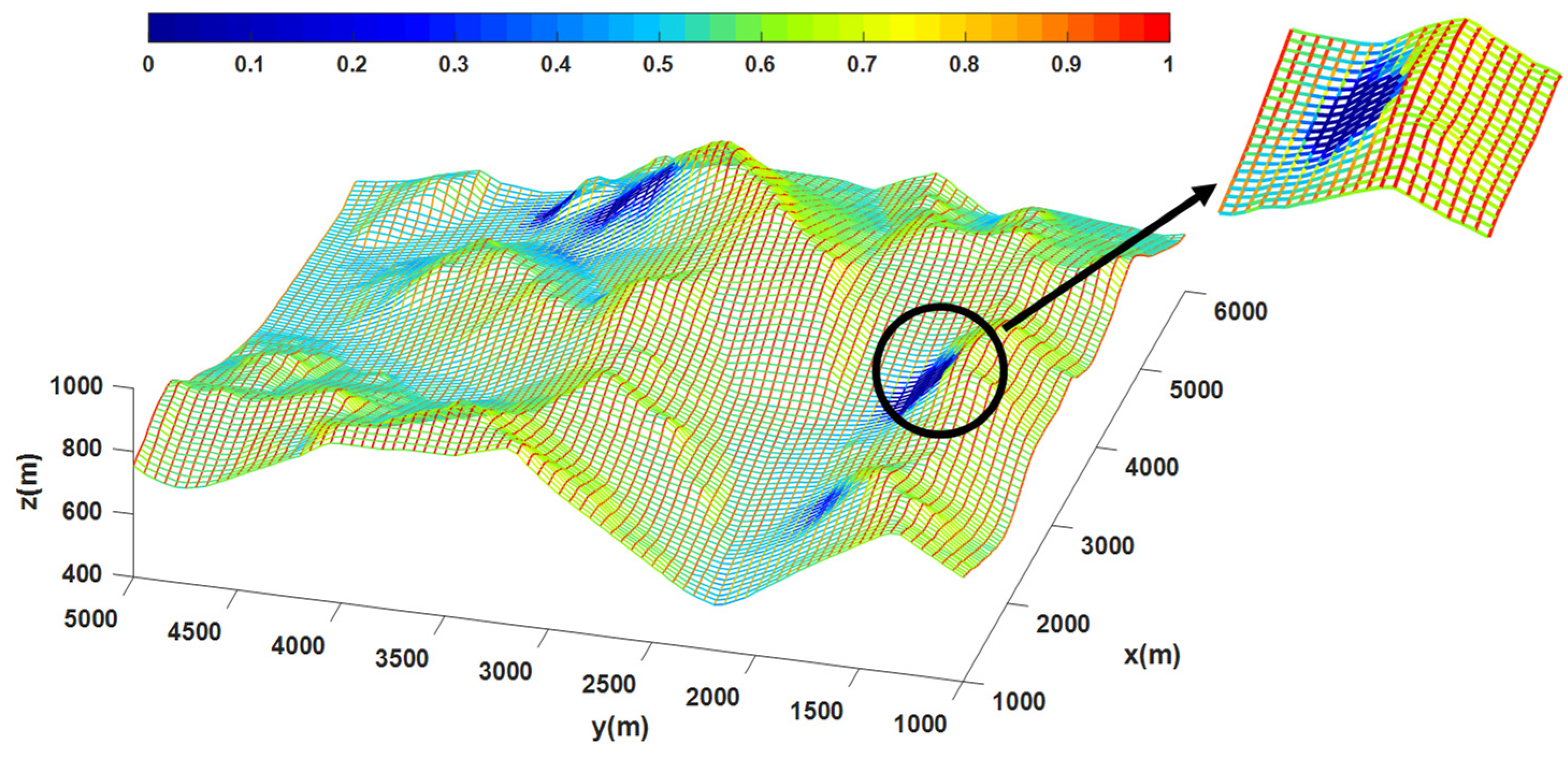
3.1. The Impact of Terrain Shading on Solar Radiation
3.2. Analysis of Factors Affecting Radiation Received by Transmission Lines
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
3.3.1. The Impact of Solar Position
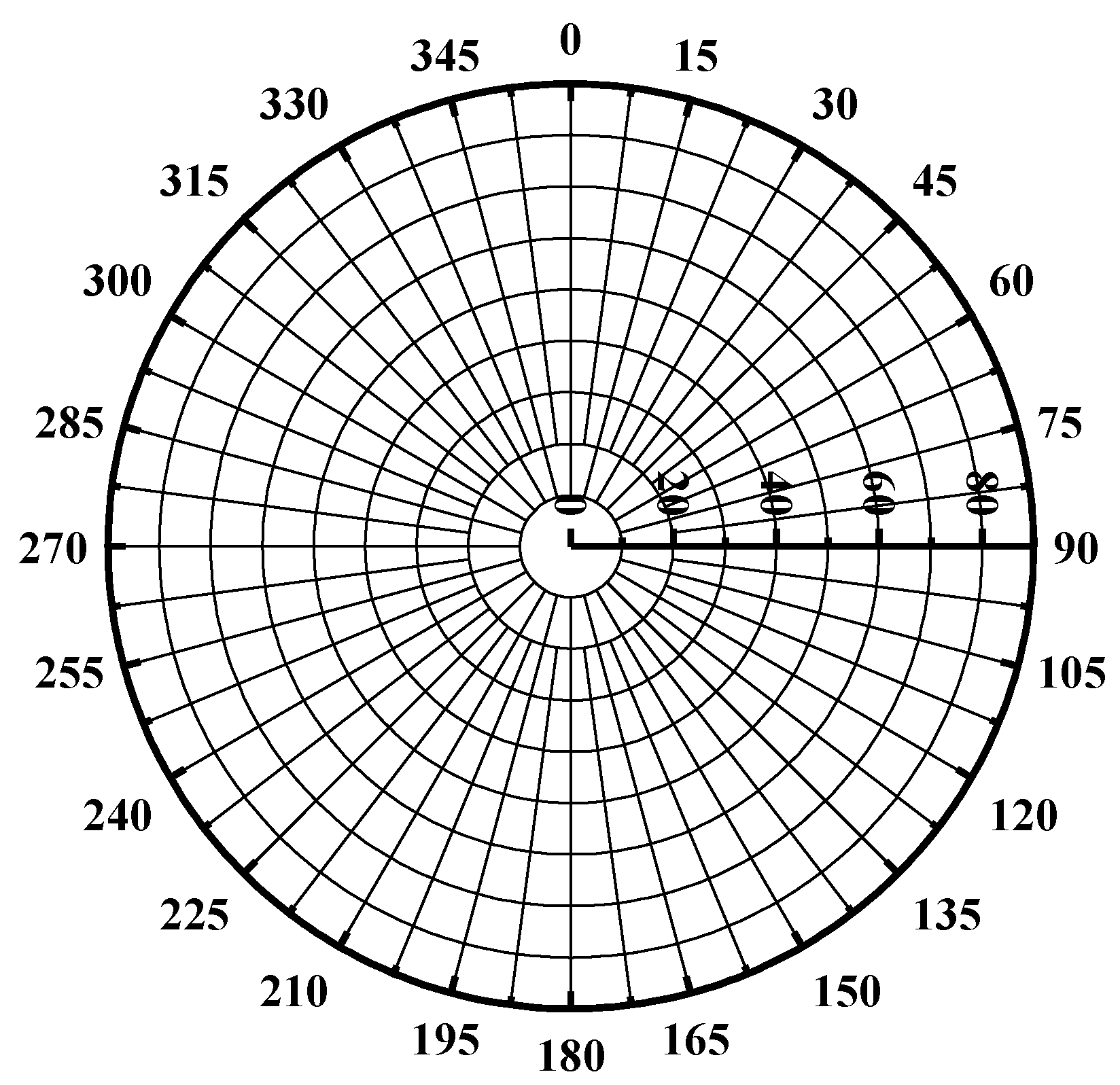
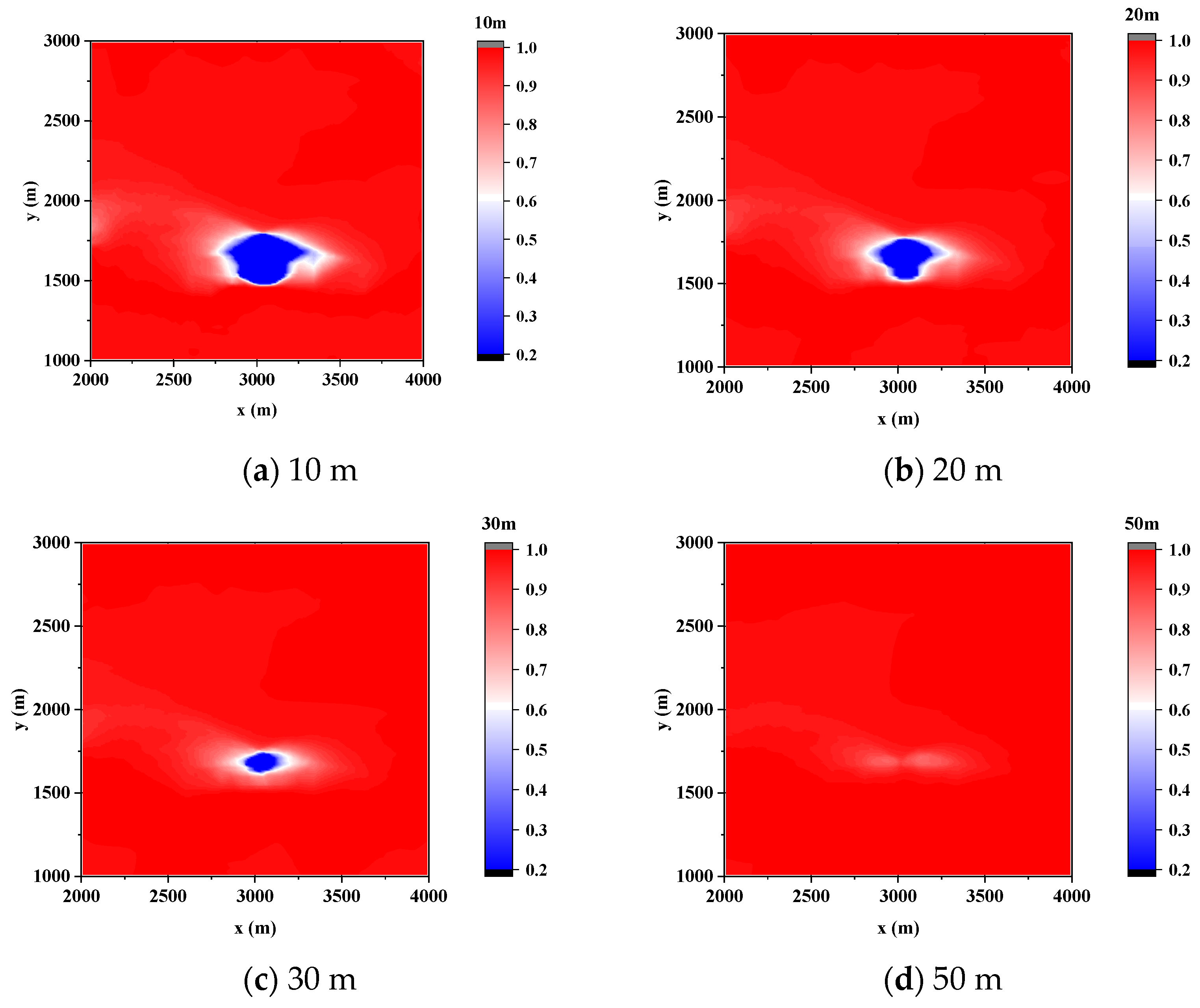
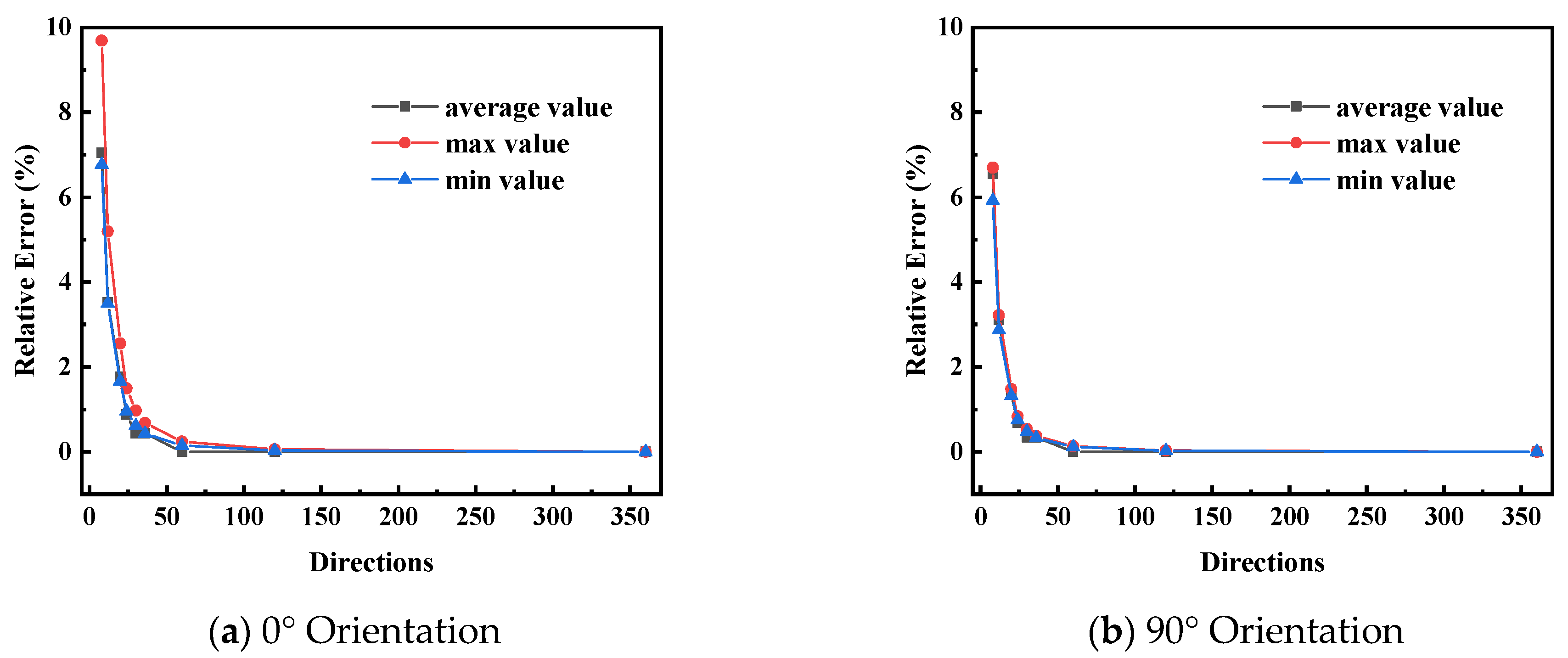
3.3.2. The Azimuthal Resolution
3.4. Equivalent Ice Melting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Qu, X.; Gul, C.; Yang, Y. The Causes and Forecasting of Icing Events on Power Transmission Lines in Southern China: A Review and Perspective. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Virk, M.S.; Liao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, M. Multimodal analysis of saddle micro-terrain prone to wind disasters on overhead transmission lines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 229, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Feng, T. Analysis of ice disasters on ultra-high-voltage direct-current transmission lines. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, R. Linear modeling analysis of the heat balance of the transmission line in high frequency critical ice melting state. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2024, 19, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yue, S.; Zeng, W. A Review of Icing and Anti-Icing Technology for Transmission Lines. Energies 2023, 16, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, W.; Kwon, Y.S.; Li, W.; Yao, S.; Huang, B. Solar deicing nanocoatings adaptive to overhead power lines. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.E.; Perovich, D.K.; Light, B. The spatial distribution of solar radiation under a melting Arctic sea ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L22501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, B.; Grenfell, T.C.; Perovich, D.K. Transmission and absorption of solar radiation by Arctic sea ice during the melt season. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C03023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Arias, J.A.; Tovar-Pescador, J.; Pozo-Vázquez, D.; Alsamamra, H. A comparative analysis of DEM-based models to estimate the solar radiation in mountainous terrain. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 23, 1049–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarslan, E.; Hocaoglu, F.O.; Edizkan, R. Novel short term solar irradiance forecasting models. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Niu, F.; O’neill, Z. Solar radiation prediction using recurrent neural network and artificial neural network: A case study with comparisons. Renew. Energy 2020, 156, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailek, N.; Bouchouicha, K.; Al-Mostafa, Z.; El-Shimy, M.; Aoun, N.; Slimani, A.; Al-Shehri, S. A new empirical model for forecasting the diffuse solar radiation over Sahara in the Algerian Big South. Renew. Energy 2018, 117, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Lin, A.; Wang, L.; Qin, W.; Gong, W. Evaluation of sunshine-based models for predicting diffuse solar radiation in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D. The solar radiation climate of Athens: Variations and tendencies in the period 1992–2017, the brightening era. Sol. Energy 2018, 173, 328–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Chang, J.-F.; Wu, A.-G.; Gao, Z.-K. A novel convolutional neural network framework based solar irradiance prediction method. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 114, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Cui, N.; Hao, W.; Li, H.; Gong, D. High-resolution assessment of solar radiation and energy potential in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 240, 114265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zou, L.; Feng, L.; Wei, J.; Qin, W.; Niu, Z. Prediction of diffuse solar radiation based on multiple variables in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 151–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.E.; Hasenauer, H.; White, M.A. Simultaneous estimation of daily solar radiation and humidity from observed temperature and precipitation: An application over complex terrain in Austria. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 104, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaoui, M.; Bouchouicha, K.; Oulimar, I. Estimation of daily global solar radiation based on MODIS satellite measurements: The case study of Adrar region (Algeria). Measurement 2021, 183, 109802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Sparrow, M. Estimating surface solar radiation over complex terrain using moderate-resolution satellite sensor data. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2005, 26, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; He, Z.; He, L.; Xu, H. Analysis of influence mechanism of spatial distribution of incoming solar radiation based on DEM. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, L.; Maselli, F.; Pieri, M. Improved estimation of global solar radiation over rugged terrains by the disaggregation of Satellite Applications Facility on Land Surface Analysis data (LSA SAF). Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Jia, D.; Jiang, J. Nowcasting of surface solar irradiance using FengYun-4 satellite observations over China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Bueno, L.; Casanova-Mateo, C.; Sanz-Justo, J.; Salcedo-Sanz, S. Machine learning regressors for solar radiation estimation from satellite data. Sol. Energy 2019, 183, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, J.M. Solcast: Validation of a satellite-derived solar irradiance dataset. Sol. Energy 2019, 189, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorga, J.R.S.; Dhurmea, K.R.; Rughooputh, S.; Boojhawon, R. Forecasting mesoscale distribution of surface solar irradiation using a proposed hybrid approach combining satellite remote sensing and time series models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 104, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Deo, R.C.; Downs, N.J.; Raj, N. Self-adaptive differential evolutionary extreme learning machines for long-term solar radiation prediction with remotely-sensed MODIS satellite and Reanalysis atmospheric products in solar-rich cities. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 212, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; She, J.; Peng, X. Assimilating remote sensing data into GIS-based all sky solar radiation modeling for mountain terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yan, G.; Mu, X.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, L.; Chu, Q. Toward operational shortwave radiation modeling and retrieval over rugged terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bárdossy, A.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y. GIS-based modelling of topography-induced solar radiation variability in complex terrain for data sparse region. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2012, 26, 1281–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J.; Frew, J. Rapid calculation of terrain parameters for radiation modeling from digital elevation data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubayah, R.; Rich, P.M. Topographic solar radiation models for GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodysh, J.B.; Omitaomu, O.A.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Neish, B.S. Methodology for estimating solar potential on multiple building rooftops for photovoltaic systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2013, 8, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. A pixel-based approach to estimation of solar energy potential on building roofs. Energy Build. 2016, 129, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Lee, M.; Koo, C.; Jeong, K.; Kim, J. Development of a method for estimating the rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) potential by analyzing the available rooftop area using Hillshade analysis. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscholl, S.; Tasser, E.; Tappeiner, U.; Vigl, L.E. Coupling solar radiation and cloud cover data for enhanced temperature predictions over topographically complex mountain terrain. Int. J. Clim. 2022, 42, 4684–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N. Deriving the slope-mean shielded astronomical solar radiation spectrum and slope-mean possible sunshine duration spectrum over the Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Choi, Y.J.E. Comparative study on shading database construction for urban roads using 3d models and fisheye images for efficient operation of solar-powered electric vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Long, E.; Wei, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, H. A new approach to determine the optimum tilt angle and orientation of solar collectors in mountainous areas with high altitude. Energy 2021, 237, 121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardashov, R.; Eminov, M.; Kara, G.; Kara, E.G.E.; Mammadov, T.; Huseynova, X. The optimum daily direction of solar panels in the highlands, derived by an analytical method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P. A Geometric Solar Radiation Model with Applications in Landscape Ecology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]




| Orientation | Max Value (Wh/m2) | Min Value (Wh/m2) | Average Value (Wh/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 1449 | 227 | 1181 |
| 45° | 1654 | 255 | 1481 |
| 90° | 1955 | 290 | 1792 |
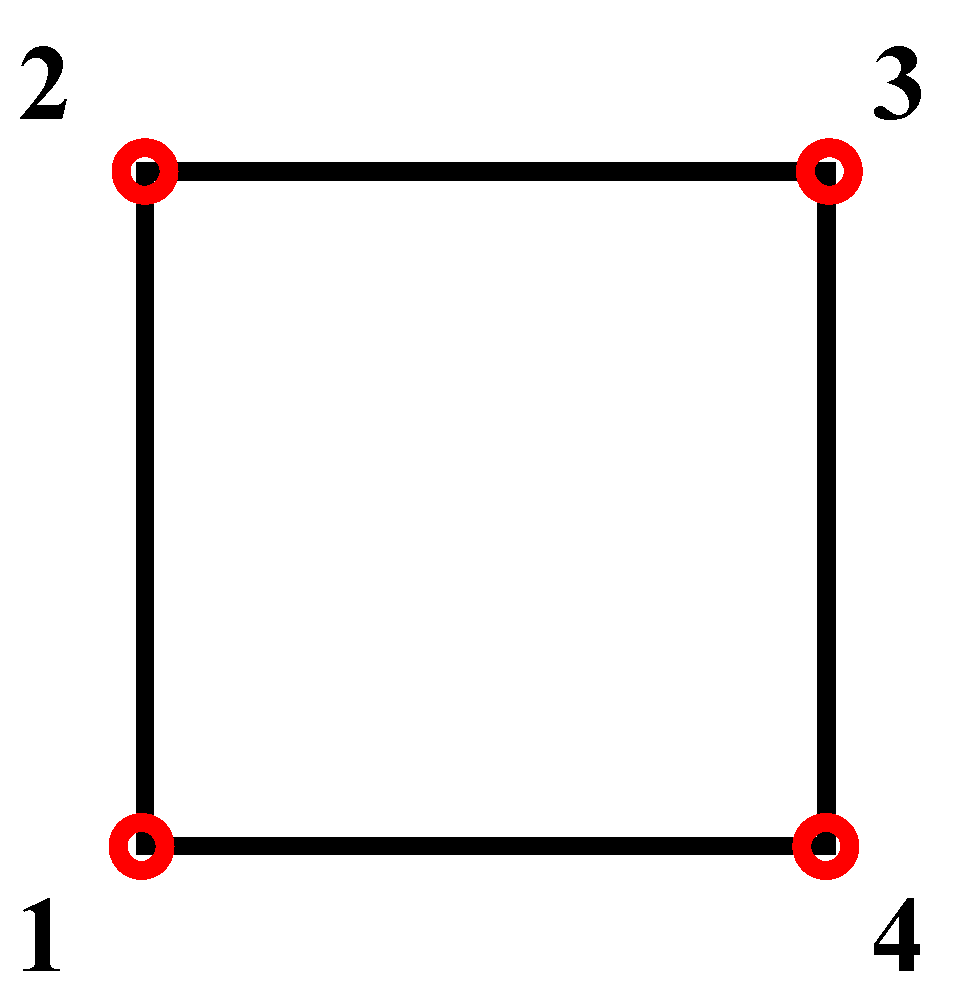
| Orientation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | Max value | 0.26% | 0.20% | 0.20% | 0.26% |
| Min value | 0.25% | 0.19% | 0.19% | 0.25% | |
| 90° | Max value | 0.23% | 0.18% | 0.18% | 0.23% |
| Min value | 0.25% | 0.20% | 0.20% | 0.25% |
| Orientation | Maximum Daily Ice Melting (g) | The Minimum Daily Ice Melting (g) |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 402.1 | 66.5 |
| 45° | 452.4 | 69.8 |
| 90° | 528.7 | 74.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X. Analysis of Solar Radiation Differences for High-Voltage Transmission Lines on Micro-Terrain Areas. Energies 2024, 17, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071684
Zheng H, Wang Y, Xie D, Zhang Z, Jiang X. Analysis of Solar Radiation Differences for High-Voltage Transmission Lines on Micro-Terrain Areas. Energies. 2024; 17(7):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071684
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Hualong, Yizhang Wang, Dexin Xie, Zhijin Zhang, and Xingliang Jiang. 2024. "Analysis of Solar Radiation Differences for High-Voltage Transmission Lines on Micro-Terrain Areas" Energies 17, no. 7: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071684
APA StyleZheng, H., Wang, Y., Xie, D., Zhang, Z., & Jiang, X. (2024). Analysis of Solar Radiation Differences for High-Voltage Transmission Lines on Micro-Terrain Areas. Energies, 17(7), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071684









