A Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen–Gasoline Blends in SI Engine Performance and Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
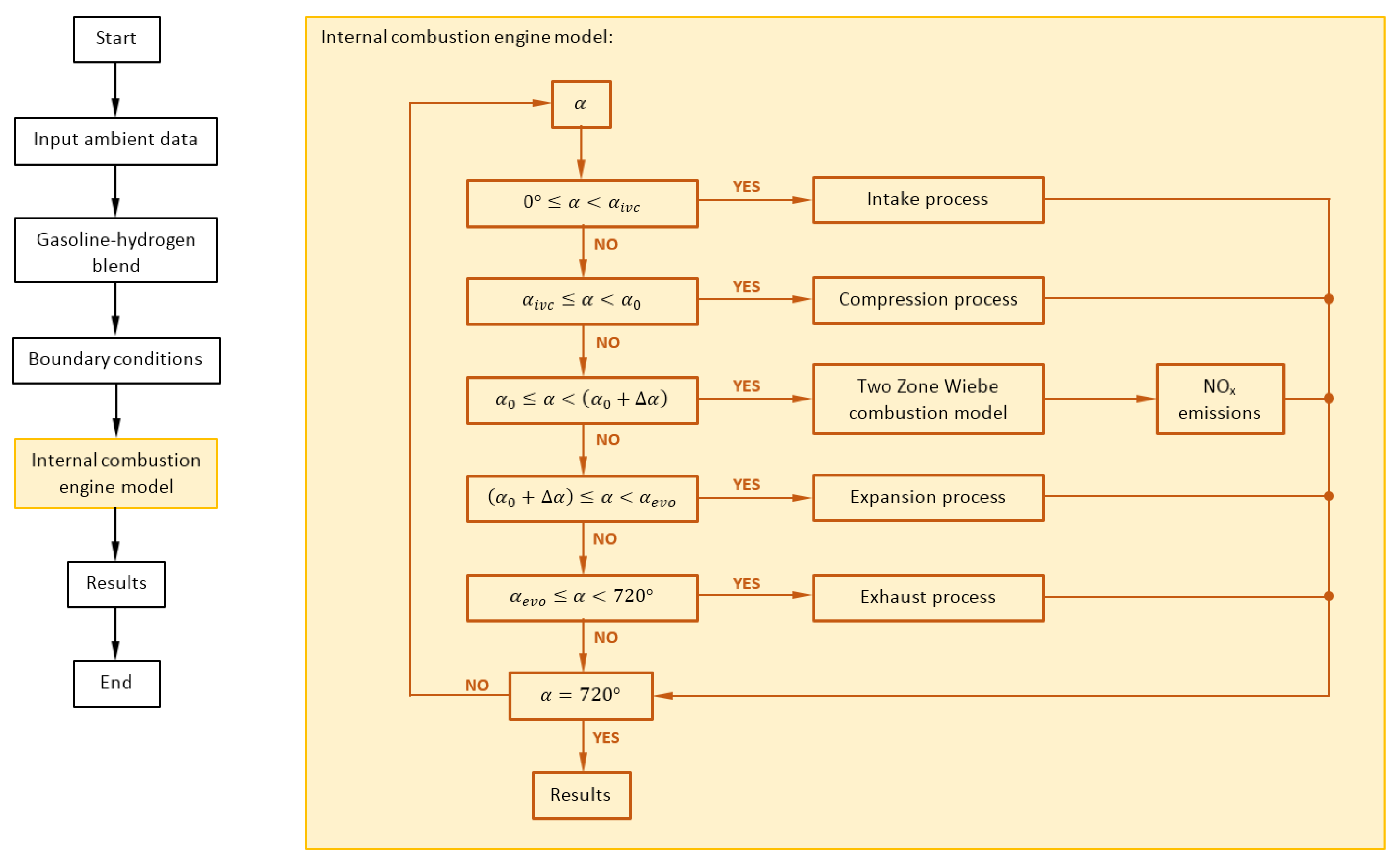
2. Methodology
2.1. Fuel System Model
2.2. Control Unit Model
2.3. Combustion Model
2.4. NOx Model
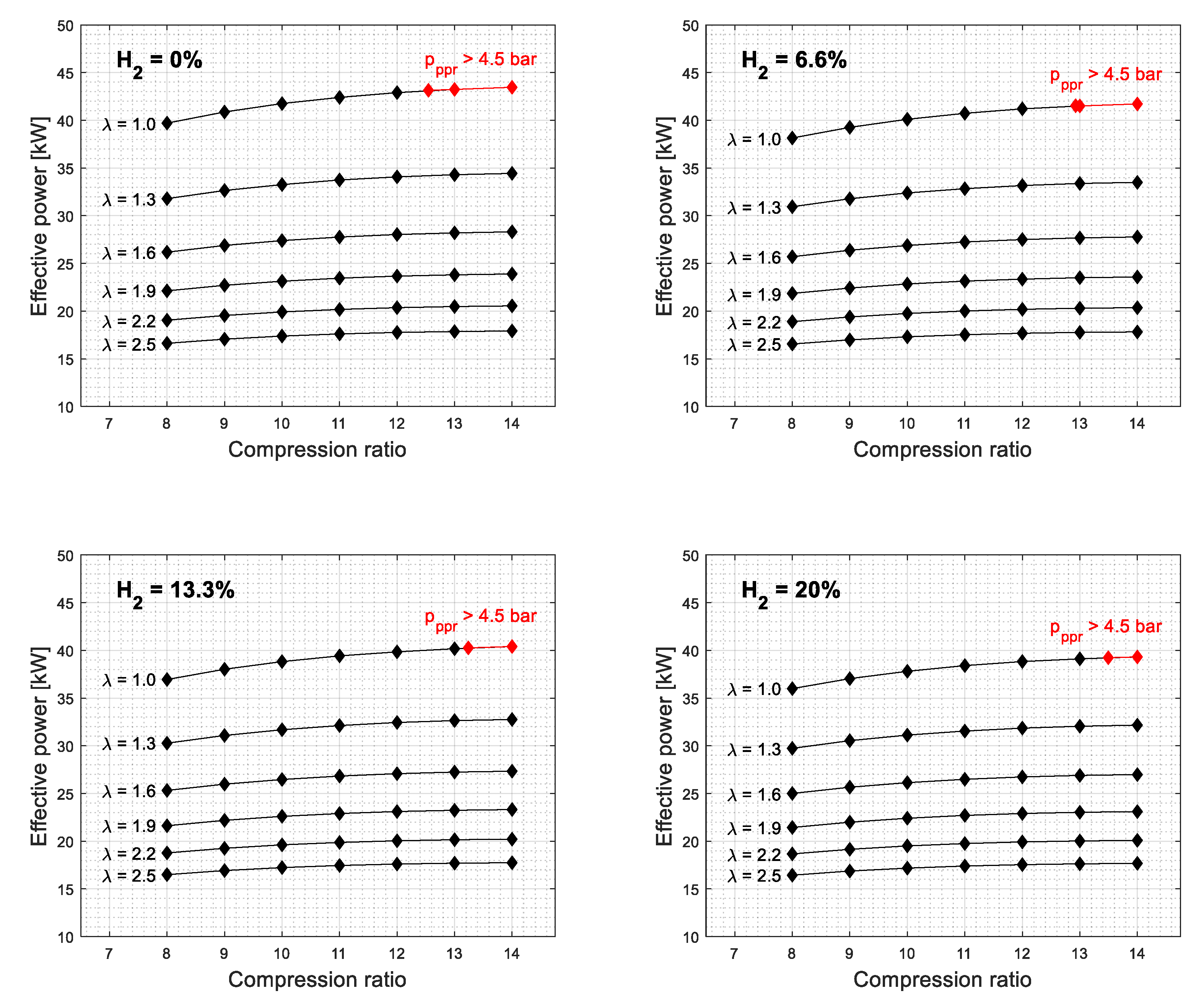
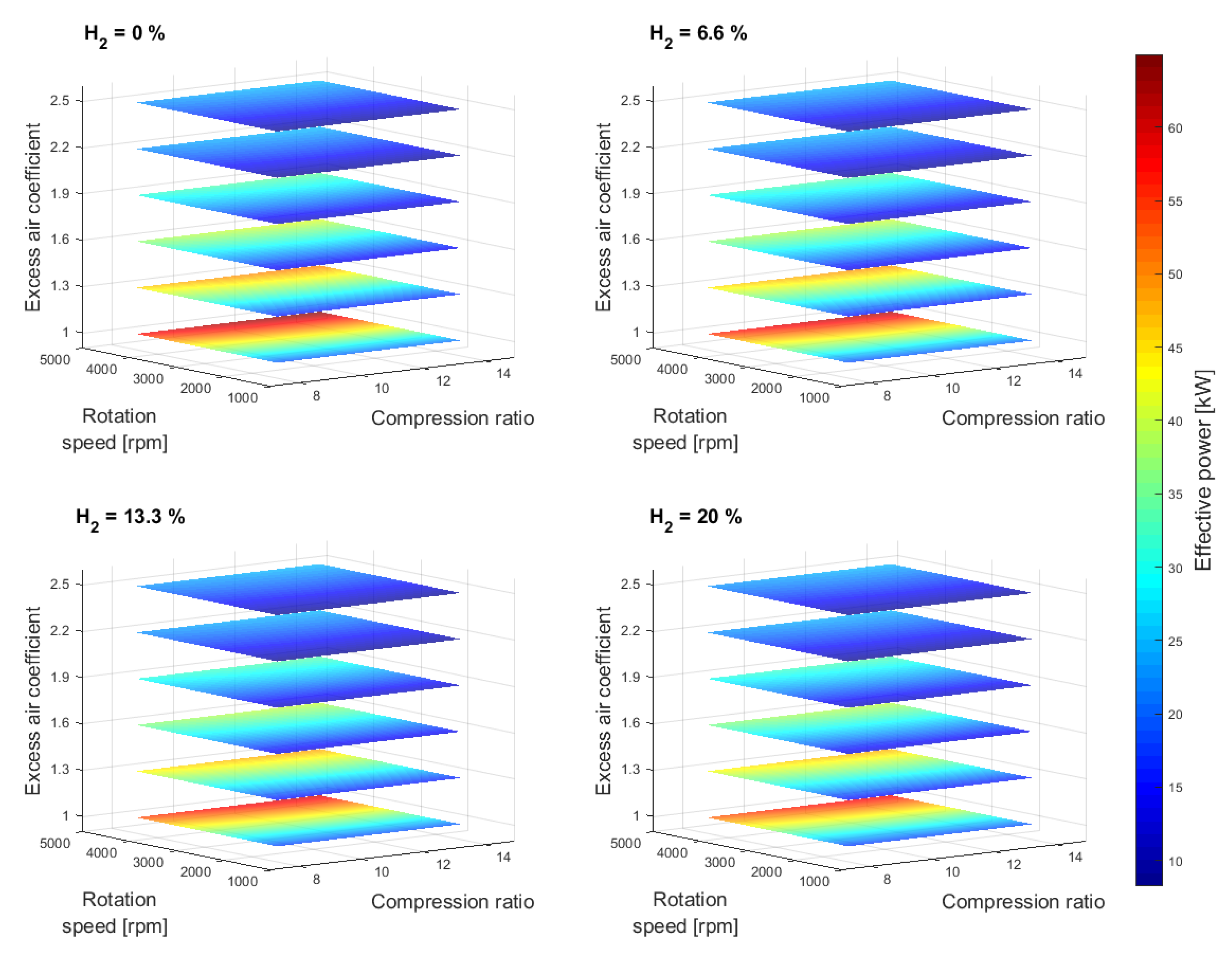
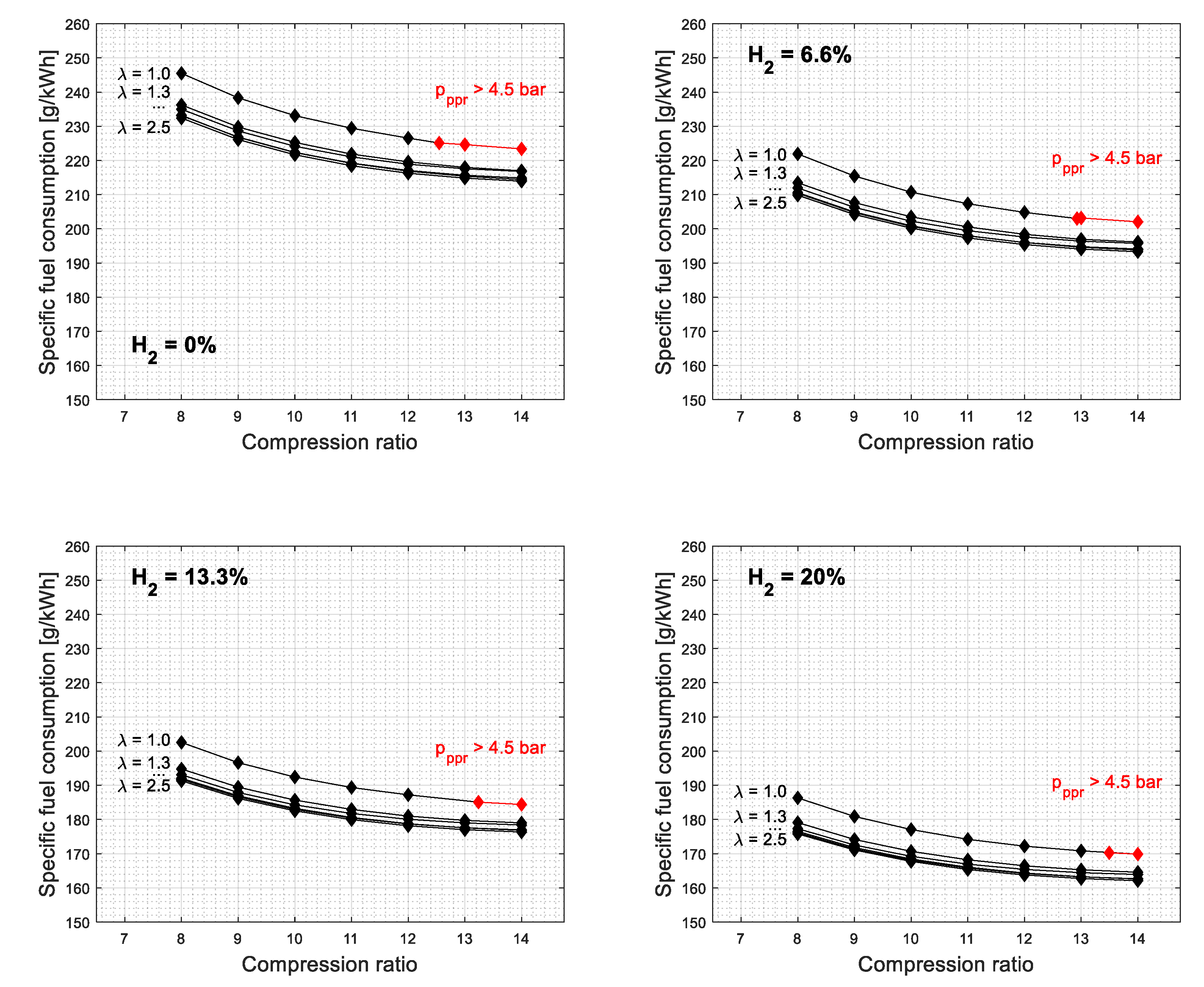
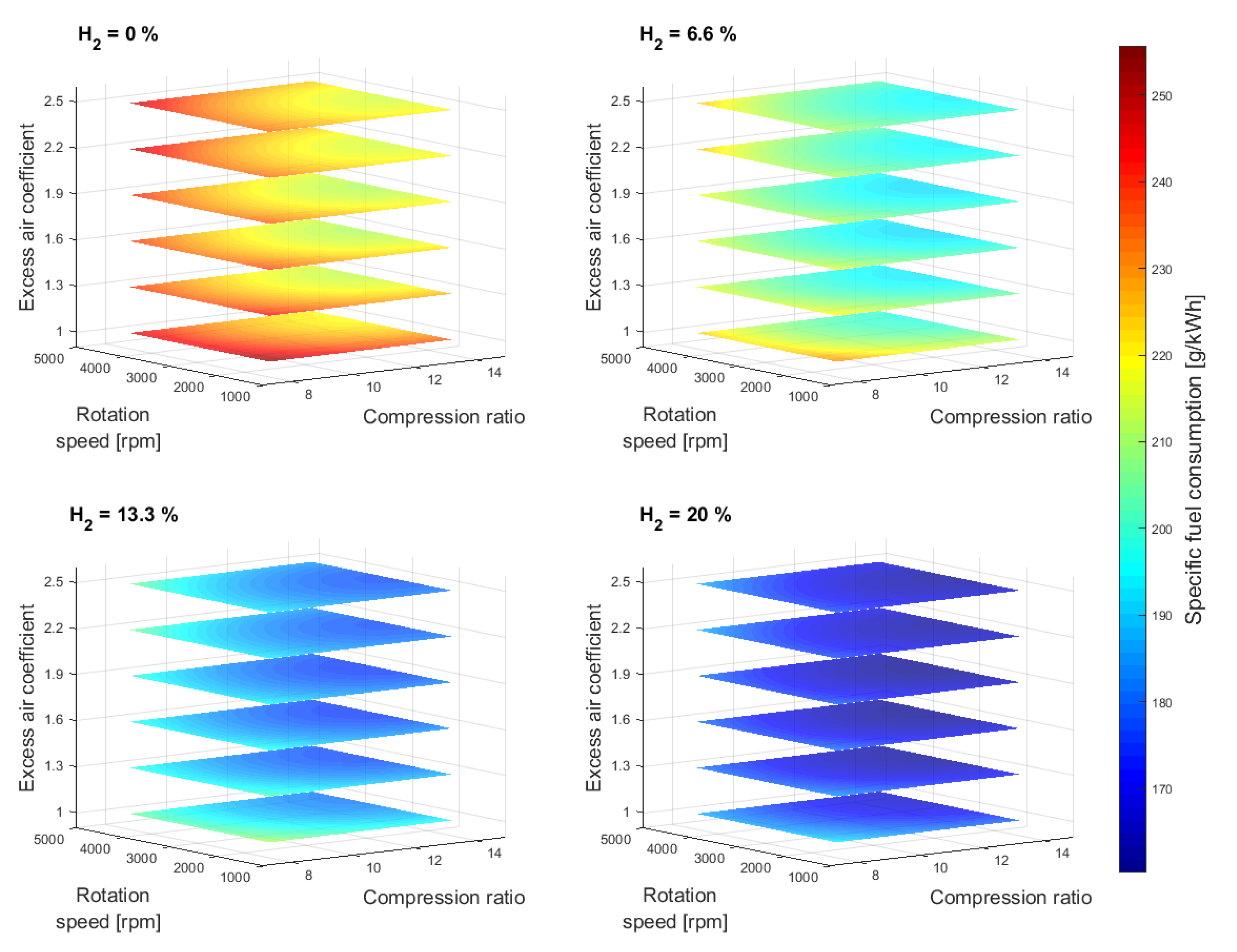
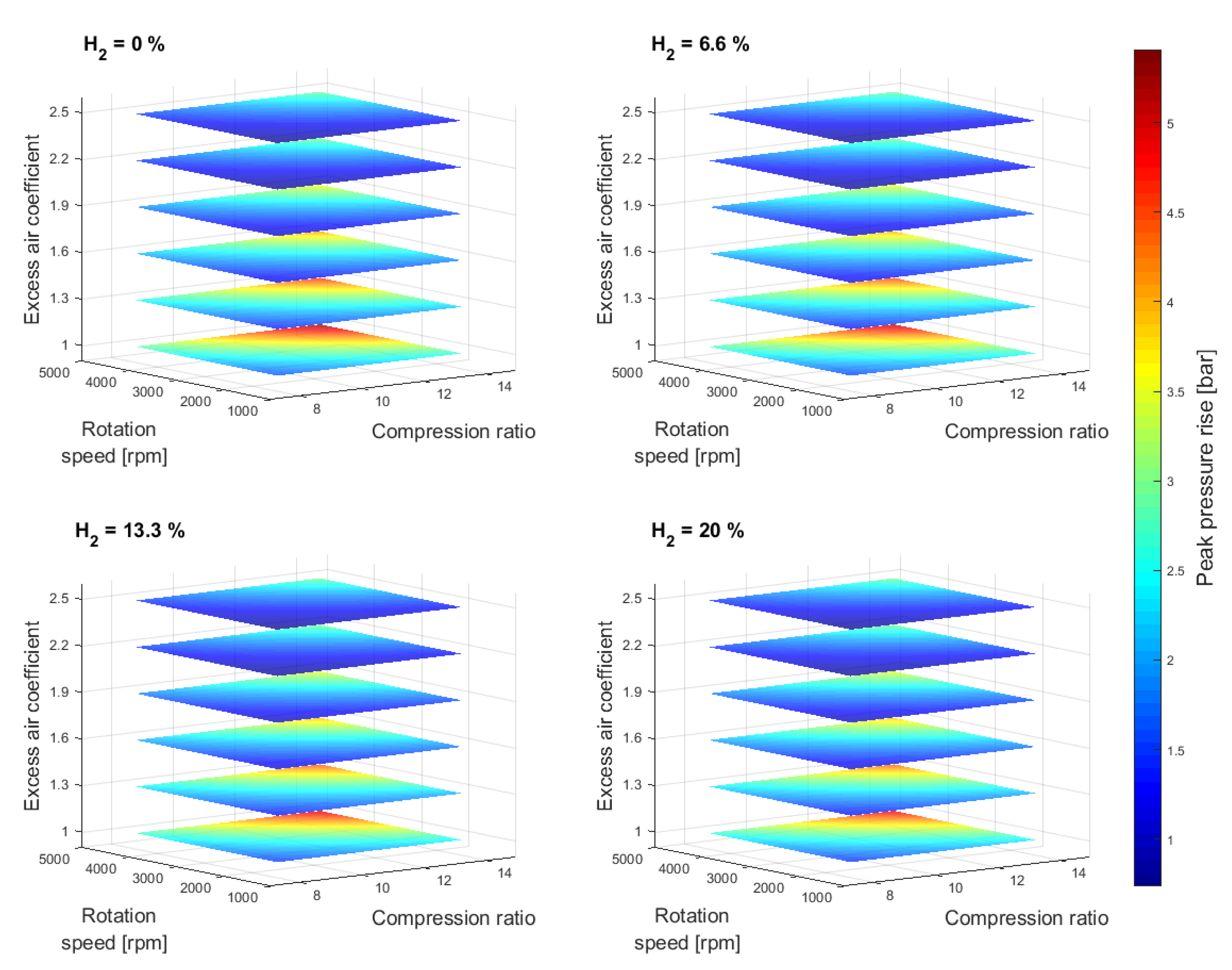
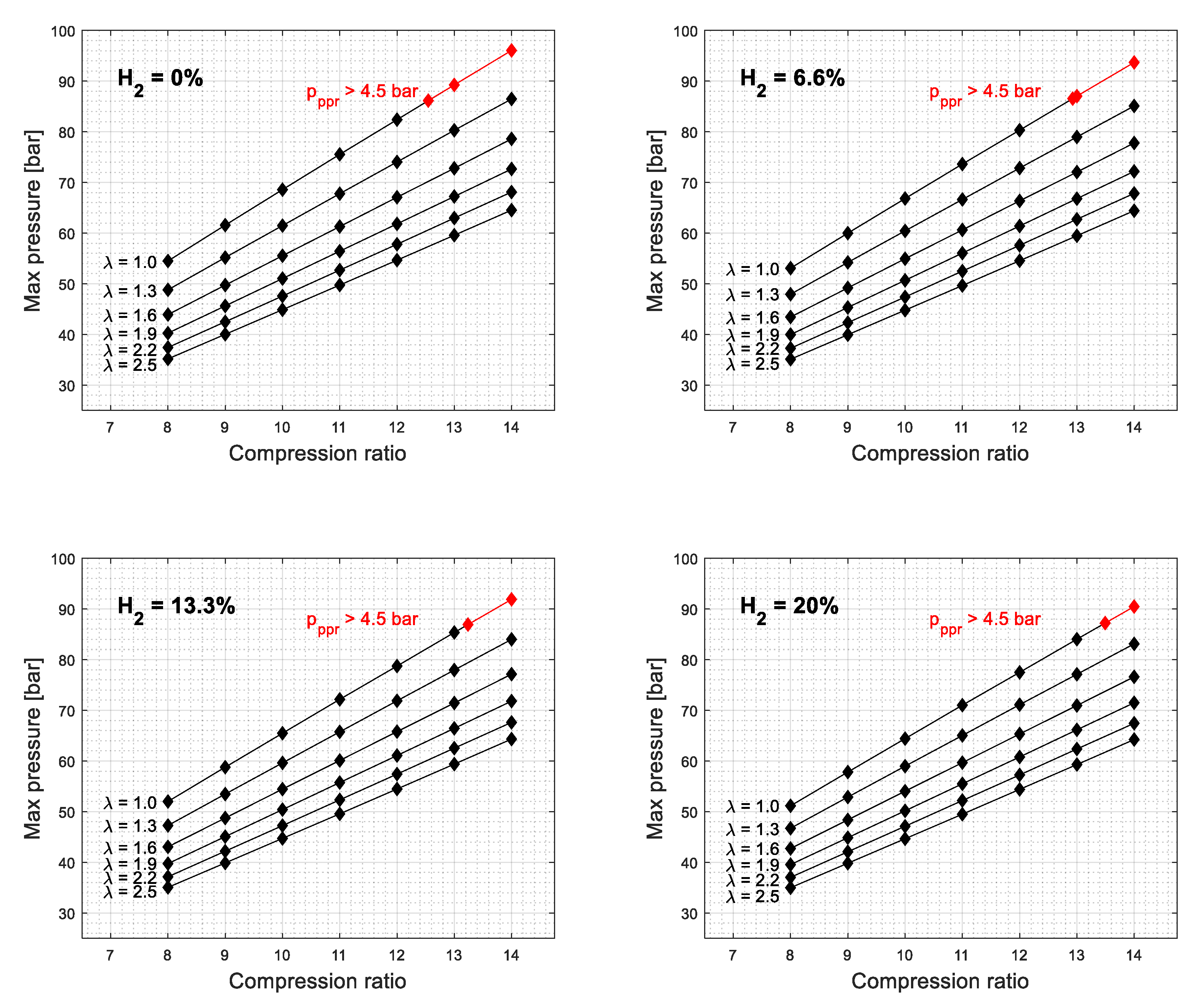
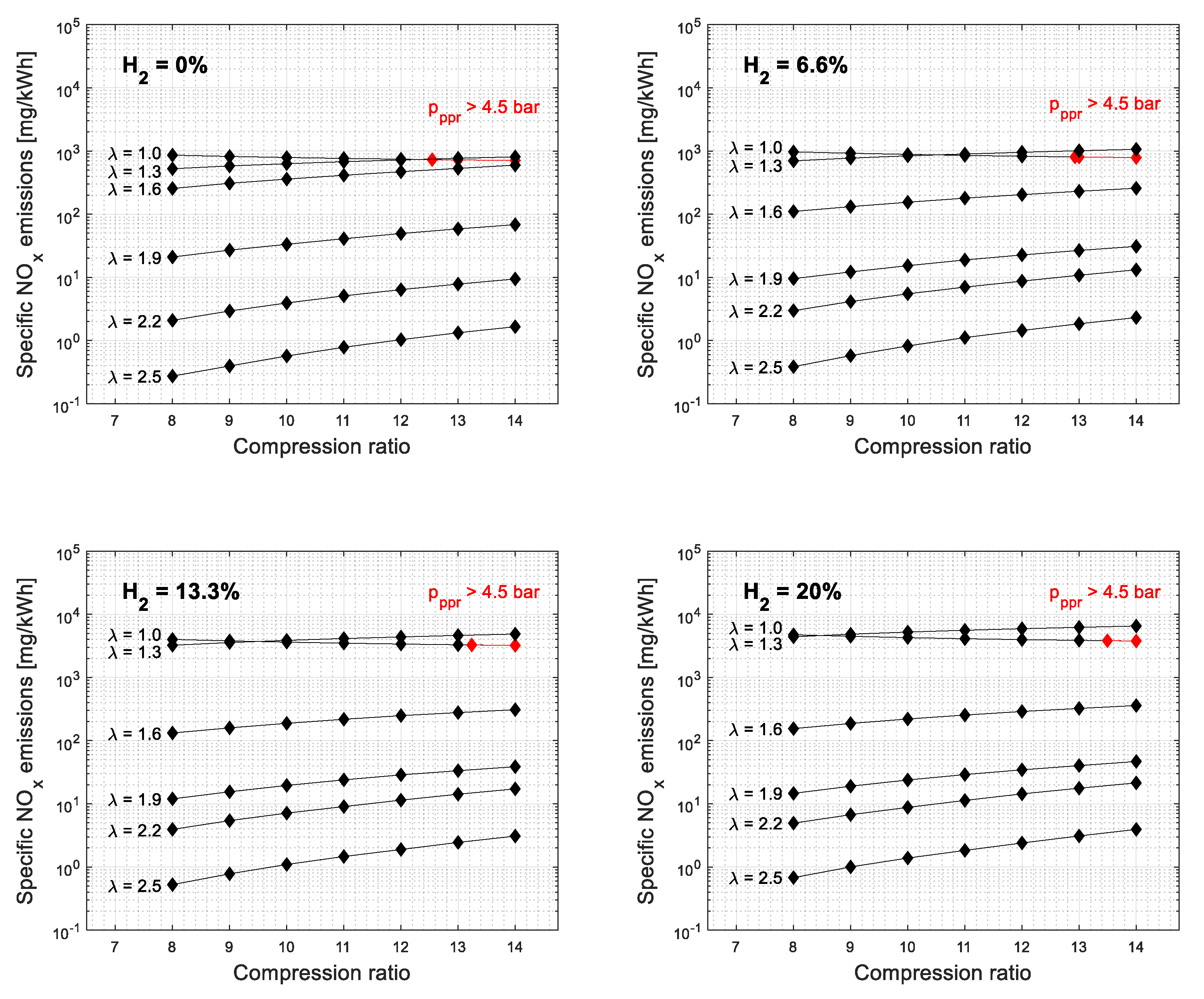
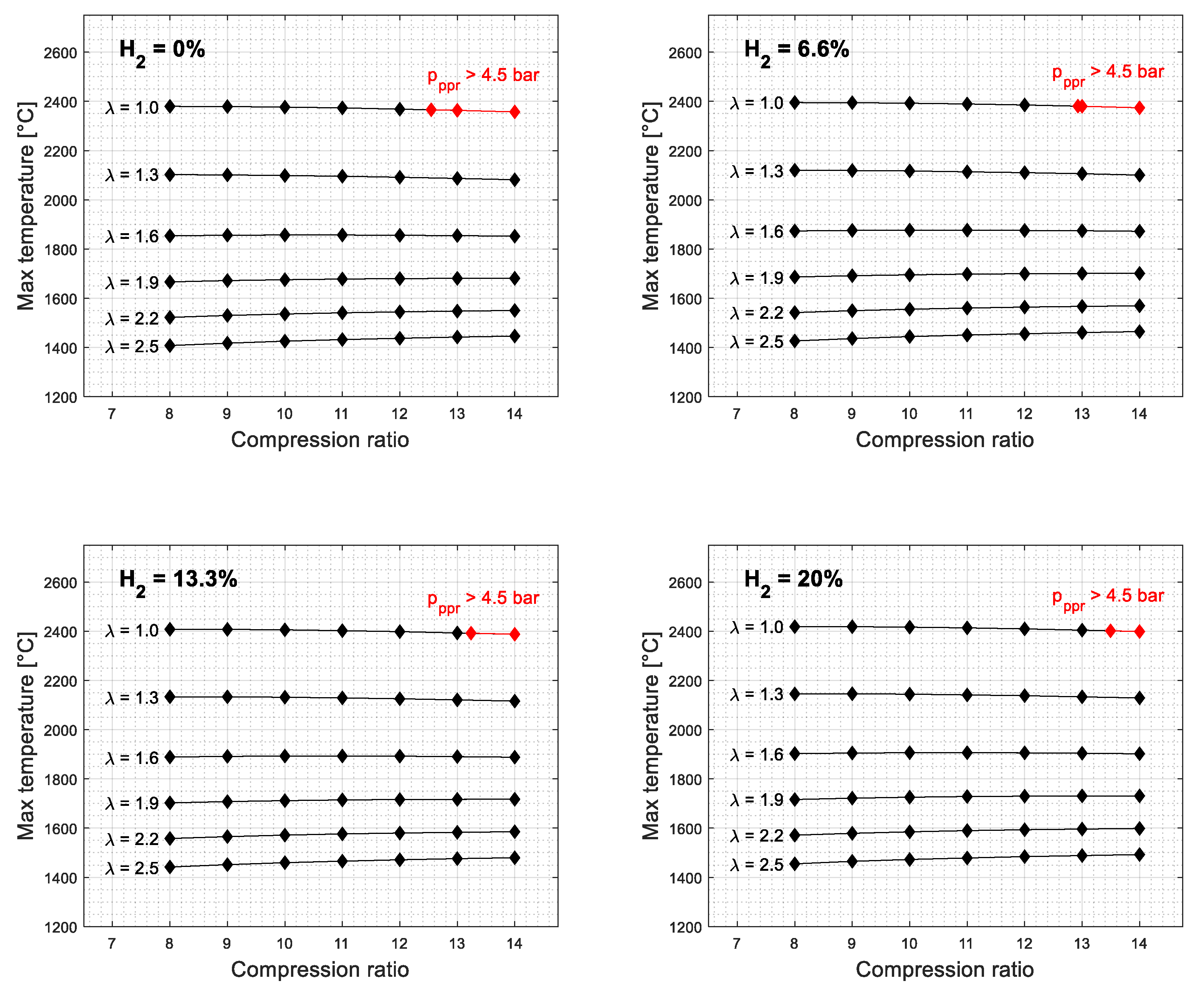
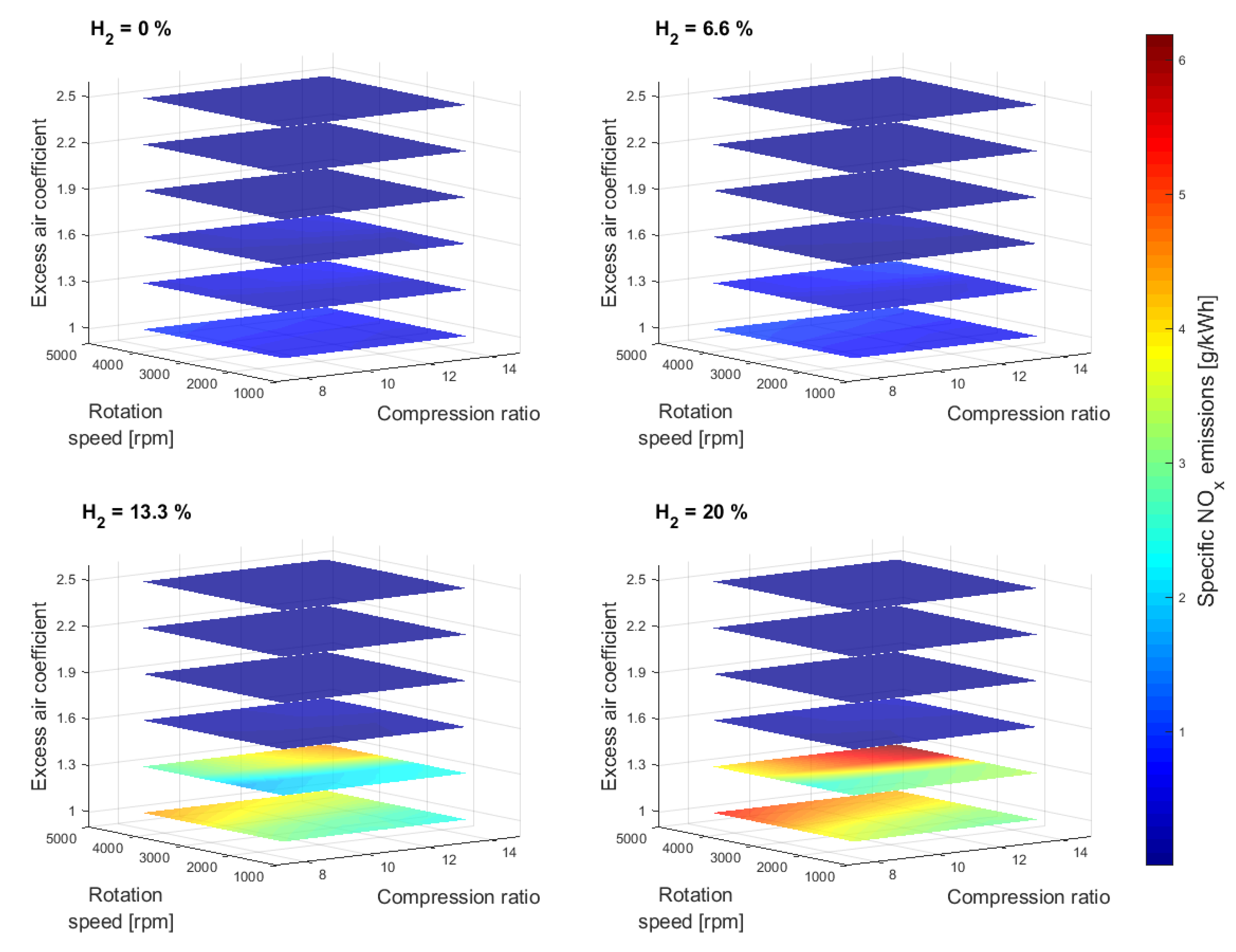
3. Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robbins, A. How to understand the results of the climate change summit: Conference of Parties21 (COP21) Paris 2015. J. Public Health Policy 2016, 37, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Beaumont, L.; Bernacchi, C.J.; Byrne, M.; Cheung, W.; Conant, R.T.; Cotrufo, F.; Feng, X.; Janssens, I.; Jones, H. Essential outcomes for COP26. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desantes, J.; Molina, S.; Novella, R.; Lopez-Juarez, M. Comparative global warming impact and NOX emissions of conventional and hydrogen automotive propulsion systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.-M.; Huang, K.; Jia, J.-L.; Su, Y.; Gao, Q.; Liu, X.-J. Improvement of fuel economy of a direct-injection spark-ignition methanol engine under light loads. Fuel 2011, 90, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandaka, B.P.; Kumar, J. Alternative vehicular fuels for environmental decarbonization: A critical review of challenges in using electricity, hydrogen, and biofuels as a sustainable vehicular fuel. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savickas, D.; Steponavičius, D.; Kemzūraitė, A. A novel approach for analysing environmental sustainability aspects of combine harvesters through telematics data. Part II: An IT tool for comparative analysis. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savickas, D.; Steponavičius, D.; Kemzūraitė, A. A novel approach for analysing environmental sustainability aspects of combine harvester through telematics data. Part I: Evaluation and analysis of field tests. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onorati, A.; Payri, R.; Vaglieco, B.M.; Agarwal, A.K.; Bae, C.; Bruneaux, G.; Canakci, M.; Gavaises, M.; Günthner, M.; Hasse, C.; et al. The Role of Hydrogen for Future Internal Combustion Engines; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2022; Volume 23, pp. 529–540. [Google Scholar]
- Assad, M.; Penazkov, O. Comprehensive analysis of the operation of an internal combustion engine fueled by hydrogen-containing mixtures. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 4478–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadidi, B.; Najafi, G.; Yusaf, T. A review of hydrogen as a fuel in internal combustion engines. Energies 2021, 14, 6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.L.; Srna, A.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Kook, S.; Taylor, R.A.; Yeoh, G.H.; Medwell, P.R.; Chan, Q.N. A review of hydrogen direct injection for internal combustion engines: Towards carbon-free combustion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, Z. A comprehensive overview of hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engines: Achievements and future challenges. Energies 2021, 14, 6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, Y.H.; How, H.G.; Le, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Loo, D.L.; Rashid, T.; Sher, F. A review on production and implementation of hydrogen as a green fuel in internal combustion engines. Fuel 2023, 333, 126525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y. Investigation on the cold start characteristics of a hydrogen-enriched methanol engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14466–14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ji, C.; Wang, S. Combustion analysis and emissions characteristics of a hydrogen-blended methanol engine at various spark timings. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 4707–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, H.; Saidur, R.; Razali, N.; Anuar, F.S.; Saleman, A.; Islam, M. An overview of hydrogen as a vehicle fuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5511–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, R.D. Directions in internal combustion engine research. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciniviz, M.; Köse, H. Hydrogen use in internal combustion engine: A review. Int. J. Automot. Eng. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.-h.; Sun, B.-g. Effect of the Miller cycle on the performance of turbocharged hydrogen internal combustion engines. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 123, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X. Lean burn performance of a hydrogen-blended gasoline engine at the wide open throttle condition. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoee, A.; Bakhshan, Y.; Aval, S.M.; Gharehghani, A. An improvement of a lean burning condition of natural gas/diesel RCCI engine with a pre-chamber by using hydrogen. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 166, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwaja, S.; Naber, J.D. Dual nature of hydrogen combustion knock. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 12489–12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, S. Recent progress in the use of hydrogen as a fuel for internal combustion engines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hamada, K.I.; Aziz, A.R.A. Characterization of the time-averaged overall heat transfer in a direct-injection hydrogen-fueled engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4816–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalcı, T.; Karagöz, Y. Experimental investigation of the combustion characteristics, emissions and performance of hydrogen port fuel injection in a diesel engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18480–18489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, F.; Megaritis, A. Experimental investigation of the effects of separate hydrogen and nitrogen addition on the emissions and combustion of a diesel engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 10126–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, A.A.; Alabduly, A.J.; Alkhedhair, A.M.; Alqahtani, N.B.; Albishi, M.S. Effect of operation under lean conditions on NOx emissions and fuel consumption fueling an SI engine with hydrous ethanol–gasoline blends enhanced with synthesis gas. Energy 2022, 238, 121694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akansu, S.O.; Tangöz, S.; Kahraman, N.; İlhak, M.İ.; Açıkgöz, S. Experimental study of gasoline-ethanol-hydrogen blends combustion in an SI engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 25781–25790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajes, J.; Novella, R.; Gomez-Soriano, J.; Barbery, I.; Libert, C. Advantages of hydrogen addition in a passive pre-chamber ignited SI engine for passenger car applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 13219–13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouadi, A.; Bentahar, F. Combustion study of a spark-ignition engine from pressure cycles. Energy 2016, 101, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.B. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pirouzpanah, V.; Saray, R.K.; Sohrabi, A.; Niaei, A. Comparison of thermal and radical effects of EGR gases on combustion process in dual fuel engines at part loads. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Anderson, D.; Hoffman, M.; Prucka, R.; Filipi, Z. A phenomenological combustion analysis of a dual-fuel natural-gas diesel engine. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2017, 231, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Renganathan, M. NOx emission control strategies in hydrogen fuelled automobile engines. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 20, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reaction Equation | k0 (cm3, mol, s) | a (-) | TA (K) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | N2 + O = NO + N | 4.93 × 1013 | 0.0472 | 38,048.01 | |
| R2 | O2 + N = NO + O | 1.48 × 108 | 1.5 | 2859.01 | |
| R3 | N + OH = NO + H | 4.22 × 1013 | 0 | 0 | |
| R4 | N2O + O = NO + NO | 4.58 × 1013 | 0 | 12,130.6 | |
| R5 | O2 + N2 = N2O + O | 2.25 × 1010 | 0.825 | 50,569.7 | |
| R6 | OH + N2 = N2O + H | 9.14 × 107 | 1.148 | 36,190.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurić, Z.; Vidović, T.; Šimunović, J.; Radica, G. A Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen–Gasoline Blends in SI Engine Performance and Emissions. Energies 2024, 17, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071557
Jurić Z, Vidović T, Šimunović J, Radica G. A Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen–Gasoline Blends in SI Engine Performance and Emissions. Energies. 2024; 17(7):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071557
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurić, Zdeslav, Tino Vidović, Jakov Šimunović, and Gojmir Radica. 2024. "A Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen–Gasoline Blends in SI Engine Performance and Emissions" Energies 17, no. 7: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071557
APA StyleJurić, Z., Vidović, T., Šimunović, J., & Radica, G. (2024). A Comprehensive Analysis of Hydrogen–Gasoline Blends in SI Engine Performance and Emissions. Energies, 17(7), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071557







