Abstract
This paper investigates the Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) factors influencing occupant satisfaction in commercial buildings in Iran, contrasting the views of building experts (architects and engineers) with those of building occupants. Employing the fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (FAHP), this study focuses on the four primary IEQ factors: thermal comfort, indoor air quality, visual comfort, and acoustic comfort. The study aims to bridge the gap between expert evaluations and occupant perceptions of IEQ factors in commercial buildings in Iran. By examining the disparities in prioritising IEQ factors between these two groups, the study sheds light on the complexities of IEQ assessment and highlights the importance of considering diverse perspectives in optimising indoor environments. Our methodology includes a survey conducted among 30 building experts (15 architects and 15 building engineers) and 102 occupants, employing FAHP to derive the relative importance weights of each IEQ factor. The results highlight significant disparities between architects, engineers, and occupants in prioritising these factors. Architects emphasise visual comfort (42%), while engineers and occupants view thermal comfort (53% and 41%) as the most crucial factor for occupant satisfaction. The study underscores the complexity of IEQ in commercial buildings and the diverse perspectives influencing its assessment. It contributes to the broader discourse on optimising IEQ, emphasising the need for a comprehensive approach that encompasses both technical expertise and occupant experience.
1. Introduction
Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) plays a pivotal role in shaping the experiences and satisfaction levels of occupants in commercial buildings [1]. The impact of poor IEQ extends far beyond mere discomfort, significantly affecting occupants, businesses, and broader societal aspects. For occupants, substandard IEQ can lead to a range of health issues, from immediate effects like headaches, eye irritation, and fatigue to long-term consequences such as respiratory diseases and exacerbated allergies [2]. This deterioration in health can result in increased absenteeism and reduced productivity, directly affecting business operations [3]. Businesses, in turn, face the economic repercussions of poor IEQ through higher healthcare costs, decreased work output, and potential legal liabilities [4]. Furthermore, buildings with poor IEQ often consume more heating, ventilation, and air conditioning energy, leading to increased operational costs and a larger carbon footprint, exacerbating environmental concerns [5].
The essence of IEQ encompasses a broad range of environmental factors, each contributing uniquely to individuals’ overall well-being and productivity within these spaces. Based on a Study by Roumi et al. [6], major environmental comfort factors affecting overall occupant satisfaction are thermal comfort (TC), indoor air quality (IAQ), visual comfort (VC), and acoustic comfort (AC).
Among the critical factors affecting IEQ, TC received the most interest from researchers [7,8]. It involves the maintenance of an indoor climate that balances heat produced by the human body with that in the surrounding environment to achieve a state of physical and psychological comfort [9]. The significance of thermal comfort is particularly highlighted in commercial buildings where diverse activities and varying occupancy levels can impact the thermal environment, influencing occupant satisfaction. Examining the effects of three different temperature settings (17 °C, 21 °C, and 28 °C), Lan et al. [10] found that deviations from a thermally neutral environment led to a decline in neurobehavioral performance. Additionally, individuals experienced heightened negative emotions and were required to exert greater effort to maintain their performance levels in conditions of thermal discomfort.
IAQ is a critical aspect concerning the cleanliness of the air within a building and its impact on the health and comfort of occupants [11]. Factors such as ventilation and air freshness are crucial in determining IAQ. The air quality inside a building can directly affect occupants’ respiratory and mental health [12]. By studying real-scale experiments in meeting rooms, Wu et al. discovered a 1% decrease in overall performance for every 10 μg/m3 rise in PM2.5 levels [13]. Additionally, with every 10% increase in air quality dissatisfaction, there was a 1.1% reduction in productivity performance. Conducting online monitoring of IAQ is crucial in many industries. In a recent study by Wan et al. [14], novel laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and single-particle aerosol mass spectrometry technologies were developed to detect indoor air pollution from electronic welding operations.
VC relates to the quality of light within indoor environments. It encompasses aspects such as natural daylight, artificial lighting, glare control, and colour rendering, all essential for performing visual tasks efficiently and comfortably [15]. Appropriate visual comfort can reduce eye strain, improve mood, and increase productivity among building occupants [16]. Aries et al. [17] have highlighted a notable correlation between the quality and type of views and the perceived discomfort experienced by individuals. Yang and Mak [18] stated that the quality of artificial lighting and daylight availability constitute primary parameters for visual comfort. Concurrently, Hamedani et al. [16] have demonstrated that reflections and glare are significant factors that adversely affect occupants by causing annoyance or discomfort, which diminishes their satisfaction and productivity.
The importance of AC in commercial buildings is often overlooked [19]. It refers to controlling unwanted sound and noise to create an environment conducive to communication and concentration [20]. Factors influencing acoustic comfort include building design, construction materials, and interior space layout. Studying 181 factory workers, Akbari et al. [21] showed a significant negative relationship between noise level and human productivity. Also, Felipe Contin de Oliveira et al. [22] expressed that chatting, telephone ringing and irrelevant speech are the primary noise sources causing stress, productivity loss, and discomfort due to lack of privacy and distraction in offices.
The interplay of these four IEQ factors creates a complex matrix that defines the quality of the indoor environment. Therefore, understanding and optimising these IEQ factors is crucial for designing and maintaining building environments that are energy-efficient and healthy for their occupants.
Multiple Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) represents a sophisticated and versatile mathematical framework widely adopted for evaluating and choosing alternatives in scenarios where decisions must be made considering various, often conflicting, criteria. This method is particularly crucial in complex decision-making environments where no single criterion can effectively capture the nuances of the alternatives being considered. Over the past few decades, MCDM has evolved significantly in terms of theoretical development and practical applications, making it a vital tool in various fields ranging from engineering and technology to environmental management.
Researchers in the past 20 years have used some MCDM methods. For instance, analytical hierarchical process (AHP) [23,24], a technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS) [25,26,27], preference ranking organisation method for enrichment evaluation (PROMETHEE) [28], ÉLimination et Choix Traduisant la REalité (ELECTRE) [29] and preference analysis for reference ideal solution (PARIS) [30]. These methods have been successfully implemented across diverse industries, reflecting their adaptability and effectiveness in handling complex decision-making scenarios [31].
Saaty developed the AHP method to integrate experts’ viewpoints and pairwise comparison scores into a straightforward hierarchy system [32]. Fuzzy sets were combined with AHP because subjective judgments during comparisons can be imprecise [33]. In other words, since the vagueness and uncertainty of the experts’ viewpoint are significant characteristics of the method, the fuzzy sets theory should correct the lack of precision of human judgments. Fundamentally, the fuzzy AHP (FAHP) method extends a standard AHP method by substituting fuzzy numbers for real numbers in the calculation [33].
The FAHP method has gained popularity due to its ability to handle the vagueness and uncertainty characteristic of expert opinions [34]. Fuzzy AHP enables decision-makers to assess their preferences within a defined range that accommodates uncertainty [35]. FAHP was applied in various industries, for example, agriculture [36], airline retail [37], automobile [38], manufacturing [39], logistics [40], and pharmacy [41]. Also, FAHP has been considered for solving different problems, for instance, machine selection [42], location selection [43], technique selection [44], supplier selection [45], risk analysis [46], and sustainability management [47]. The limitation of the FAHP method is the inconsistency of the expert responses. Therefore, implementing consistency checks is vital for reliable results.
While there has been extensive research using MCDM methods in different industries, a comparison between building experts’ and commercial building occupants’ viewpoints on the impact of IEQ on occupant satisfaction has not been captured. The only partially similar research was conducted by Miao and Ding [48], who invited 60 experts in the construction field to evaluate the importance of the indoor acoustic, luminous, thermal environment, and air quality of different public buildings. Then, they implemented the AHP method to determine the equivalent weights for various indicators. Based on the experts’ opinions, TC and IAQ have accounted for the highest importance in total satisfaction.
The roles and responsibilities of engineers and architects often intersect during the construction process. Architects design buildings to meet client’s demands and are responsible for the aesthetic appearance of the exterior and interior of the building. On the other hand, engineers’ fundamental responsibility is to ensure that the building design is reliable and all relevant building codes are considered. Engineers are concerned with the safety and functionality of buildings. To accomplish this, they select structural materials, specify structural members, and determine electrical, plumbing, ventilation, cooling, heating, and air conditioning systems.
All MCDM methods involve two main steps: calculating the relative weighting of the criterion and selecting the best alternative based on the experts’ pairwise points. We will focus on the first MCDM step, and the viewpoint of different building construction experts (architects and engineers) will be considered and compared to obtain the relative weighting of varying IEQ factors over occupant satisfaction in commercial buildings. To further explore the complexities of IEQ and its impact on occupants, this study aims to address the following research question: To what extent do the prioritizations of Thermal comfort, IAQ, Visual comfort, and Acoustic comfort vary among architects, engineers and building occupants.
The paper is organised as follows: Section 2 discusses the rationale for occupant-centric design. Section 3 explains the methodology employed for data collection and the FAHP. Section 4 showcases the gathered survey responses and a comprehensive discussion of the FAHP calculations. Lastly, Section 5 discusses the perspectives of experts and commercial building occupants, and Section 6 concludes with a summary of the key findings.
2. Rethinking of Building Design
Although the primary design objective of most buildings is to accommodate human occupants by offering healthy, comfortable, and secure environments for diverse purposes, the interaction between humans and buildings is still among the least developed aspects of building science [49]. Various post-occupancy assessments have shown that many buildings frequently fall short of fulfilling the expectations of their occupants (e.g., [50]).
Numerous investigations [19,50,51] have reported varied outcomes yet generally indicate positive advantages from certified buildings (e.g., NABERS). There is a pressing need for further study, not just on the fundamental principles concerning occupant health and IEQ within buildings but also on the methodologies and technologies necessary to apply this knowledge to the design, construction, and operation of buildings [52].
Despite the significant increase in research focusing on building occupants over the last ten years, the design and operation of buildings continue to rely on simplistic assumptions about occupants. These assumptions are increasingly being recognised as misleading [53], examples of which are: (I) The four main IEQ factors (TC, VC, IAQ and AC) can be given equal importance [54]; (II) Providing an ideal indoor environment is considered to negate the necessity of granting occupants the ability to control their environment [55]; (III) Buildings have a consistent distribution of occupants and are nearly fully occupied for the entire day [56]; (IV) The ideal conditions for indoor environments are defined solely by physical parameters such as air temperature, relative humidity, airspeed, sound pressure level, illuminance, and contaminant concentration [57]; (V) Managing buildings with the average occupant in mind is sufficient for ensuring comfort [58].
The consideration of occupants in the decision-making process of building design varies significantly based on the balance of design decisions to meet the overall project goals, the negotiation among team members, how this information is integrated into the design workflow, and the adjustments made as the project evolves. This process involves multiple stakeholders whose interactions are primarily determined by the client’s interests and the established procurement strategy for designing and executing the project [59].
The influence of design decisions on the inhabitants of the constructed environment is predominantly determined by the ability of the client and design team to incorporate the occupants’ needs and desires into the design journey [60]. Information that is mandatory, normative, and business-related, potentially enriched with insights from previous projects and direct consultations with occupants, is deciphered by designers and then manifested in the physical spaces. This process dictates how occupants are expected to use and interact with the building in certain ways and creates possibilities and opportunities for them. Whether knowingly or not, designers place various limitations on occupants, ranging from controls over environmental systems to restrictions on the adaptability and flexibility of space usage. These limitations, often stemming from obligatory and standard business practices and lessons from past projects, restrict how occupants can utilise the building to align with the client’s vision. Frequently, this leads to the exclusion of personal control in favour of automated systems that adhere to energy efficiency criteria.
Consequently, the creation of a building that genuinely reflects the occupants’ way of living is only feasible when designers empathetically align with the occupants’ perspective advocates [61]. This requires an anticipatory approach to understanding the potential expectations and the need for adaptability within spaces, including emotional responses and perceived choices.
Therefore, a fundamental change in perspective is needed, where practitioners move beyond viewing occupants merely as contributors to indoor heat gains and sources of pollutants satisfied with uniform indoor environmental conditions. Instead, it is essential to recognise the complex and dynamic two-way interaction between occupants and buildings.
3. Materials and Methods
A survey is designed to compare four major IEQ factors (TC, IAQ, VC, and AC). Then, the online survey was issued to building experts and commercial building occupants. Afterwards, the consistency of collected responses was analysed, and inappropriate ones were removed. The data collection procedure and FAHP method are explained in the following sections.
3.1. Data Collection
This research utilises a survey approach to investigate the perspectives of building experts and occupants on the influence of four primary IEQ factors on occupant satisfaction within commercial buildings. The questionnaire was designed based on a previous review of 25 IEQ models in commercial buildings by Roumi et al. [6]. A preliminary assessment involving ten participants was conducted to identify technical issues in the questionnaire’s overall design or to detect any consistency problems. The participants found the questionnaire to be concise and understandable.
For this project, participants were recruited through two methods. LinkedIn was employed to gather the perspectives of experts, while on-site advertising was used to collect the viewpoints of occupants for the survey. LinkedIn was utilised to identify and select suitable candidates to ensure that building experts possessed the requisite expertise to effectively assess IEQ factors and parameters. The LinkedIn profiles of potential participants were meticulously reviewed, focusing on their educational qualifications and present professional engagements. Selection criteria for the experts included demonstrable academic or project involvement in the IEQ domain and at least five years of professional experience in architecture, civil, electrical, or HVAC engineering. Once identified as qualified, an invitation email including a short description of the research project and an embedded link to the online survey at the SurveyMonkey website was then sent to potential participants’ LinkedIn pages or work emails. Ninety-five invitations were sent. A follow-up reminder email was sent to potential participants one week after the initial contact.
The research team engaged with occupants from two commercial buildings in Tehran and Kerman to gather insights into the perception of commercial building occupants in different climatic conditions of Iran. Tehran, classified under the Koppen climate classification as a semi-arid climate (BSk), experiences distinct seasons with hot summers and cold winters, receiving moderate rainfall primarily in the spring and autumn. In contrast, Kerman, located in a cold desert climate zone (BWk), according to Koppen, endures more extreme temperature variations with very hot summers, cold winters, and scant rainfall throughout the year, reflecting its more arid conditions. The commercial buildings selected to approach potential participants are illustrated in Figure 1. Those commercial building occupants willing to participate in this study were given a QR code to access and complete the survey online. The human research ethics committee of Griffith University approved this research protocol (Reference ID. 2021/150).
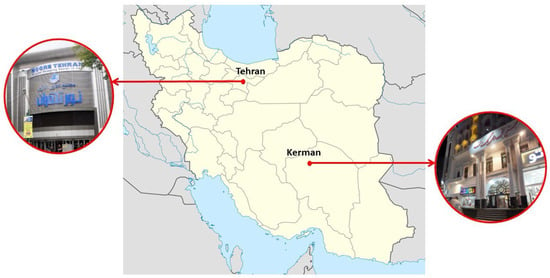
Figure 1.
Location of targeted commercial buildings (left: Noore Tehran Shopping Center; Right: Golestan Passage).
3.2. FAHP Method
The FAHP method developed by Buckley [62] was employed in this study to derive the relative importance weights for each IEQ factor. The FAHP methodology encompasses several stages.
Step 1: As outlined in Section 3.1, experts and occupants evaluated IEQ factors considering their influence on occupant satisfaction. This involved a pairwise comparison of criteria, where respondents were tasked with choosing a linguistic term that most accurately represents the comparative significance of each criterion pair, as depicted in Table 1.

Table 1.
Linguistic labels and their equivalent triangular fuzzy numbers.
For instance, should a respondent choose the relevant importance as ‘weak’ in response to the question “Which IEQ factor has a greater impact on overall satisfaction, IAQ/Visual comfort?” the corresponding fuzzy triangular scale assigned would be (2, 3, 4). On the other hand, if comparing Visual comfort to IAQ, the fuzzy triangular scale used for this assessment would be (1/4, 1/3, 1/2).
Equation (1) displays the pairwise contribution matrix. In this equation represents the viewpoint of the ath respondent’s preference of ith factor over jth factor, using fuzzy numbers.
The (~) sign indicates the triangular number. For instance, represents the first respondent’s preference for the third factor over the first factor.
Step 2: To have a cumulative overview of all respondents, the arithmetic average of each respondent’s preferences is calculated employing Equation (2). M in this equation represents the total number of respondents.
The updated contribution matrix considering the averaged respondents’ preferences is presented in Equation (3).
Step 3: Equation (4) shows the calculation of the geometric mean of trigonometric fuzzy values of each factor.
Step 4: As presented in Equation (5), the vector summation of is calculated and inversed. Then, the fuzzy triangular number is replaced to make it in increasing order.
Step 5: Using Equation (6), the fuzzy weight of each factor can be calculated.
Step 6: The method presented by Chou and Chang [63] is applied to defuzzify .
Step 7: Finally, all calculated weight factors should be normalised.
3.3. Consistency Evaluation
After the aggregation matrix is formed, it is crucial to verify the consistency of the collected responses. A consistency check is performed on all gathered responses. For instance, if Acoustic comfort is considered more significant than Thermal comfort and Thermal comfort more significant than IAQ, a consistent judgment would also find Acoustic comfort more important than IAQ. Conversely, if IAQ is found to be more important than Acoustic comfort, this would indicate an inconsistency in judgment. The degree of consistency in the decision-maker’s evaluations is assessed by comparing the importance of the categories [64]. This involves calculating the consistency ratio (CR), which is derived from the Consistency Index (CI) and Random Index (RI). RI is determined by the judgment matrix’s size, as described by Saaty [65].
The calculation of the CI involves the Maximum Eigenvalue () and the total number of criteria (n) used for judgments. Then, is derived from the pairwise comparison values obtained from the respondents’ evaluations.
This procedure starts with the transposition of the matrix containing respondents’ judgements alongside the column of priority weights.
Subsequently, is calculated by dividing each element of the Eigen Vector by its corresponding weight in the priority vector. The average of these computed Eigenvalues () yields the Maximum Eigenvalue (). The CR is then calculated by dividing the CI by the RI. Detailed information on the methodology used for consistency checking is available in Saaty’s work [65].
According to Saaty [23], a CR of 0.10 or less indicates that the evaluations within the matrix are acceptable. Conversely, a CR greater than 0.10 signals that the pairwise comparisons lack consistency, necessitating improvements to the evaluation matrix. For a matrix with four criteria, the RI is set at 0.9, as specified by Saaty [23].
4. Results
As mentioned earlier, this study aims to compare the impact of IEQ factors on occupant satisfaction in commercial buildings. Initially, building experts and commercial building residents evaluated the effect of IEQ factors on indoor overall satisfaction using questionnaires. The pairwise comparison matrices that met the consistency criteria are included for further analysis. Viewpoints of 30 building experts (15 architects and 15 engineers) and 102 commercial building occupants were collected from March to August 2022 (Figure 2). The demographic profile of the survey respondents is presented in Table 2.
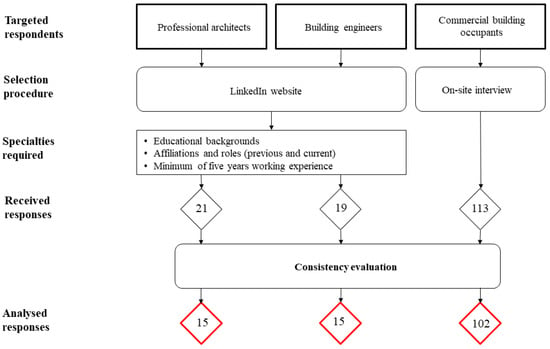
Figure 2.
Data collection method.

Table 2.
Demographic distribution of the survey participants.
Figure 3 displays the age distribution of participants in this study, showing that the majority of building experts were between 31 and 40 years old. In contrast, the predominant age group for commercial building residents was 21–30 years. All expert participants possessed a university degree, whereas 16.7% of commercial building residents held a high-school diploma, as depicted in Figure 4.
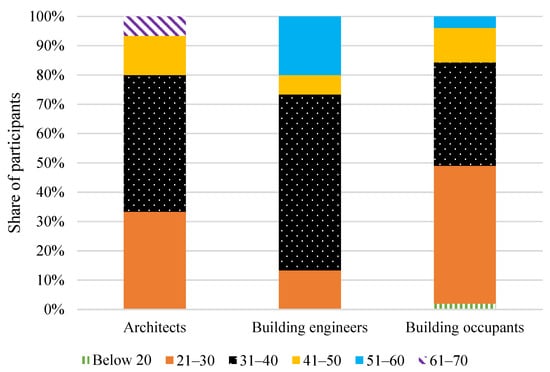
Figure 3.
Participant categorisation based on age difference.
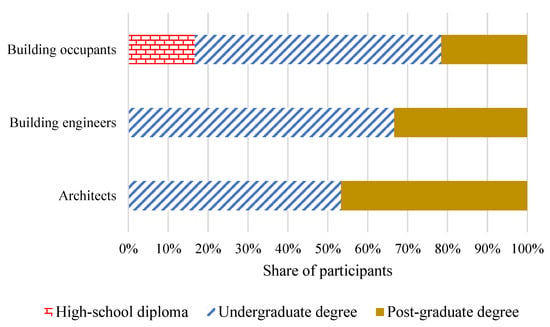
Figure 4.
Participant categorisation based on education.
Figure 5 illustrates the pairwise comparison of experts’ opinions on the effect of IEQ factors on overall occupant satisfaction. In each segment of the horizontal axis, the pairwise comparison is conducted between two IEQ factors. For instance, in the first segment, the importance of IAQ is compared to TC in providing overall occupant satisfaction for occupants. A response of nine means IAQ has an extremely higher impact on occupant satisfaction than TC, and a response of one determines that the effect of TC is extremely higher than that of its counterpart. The outcome of the responses can be summarised as follows:
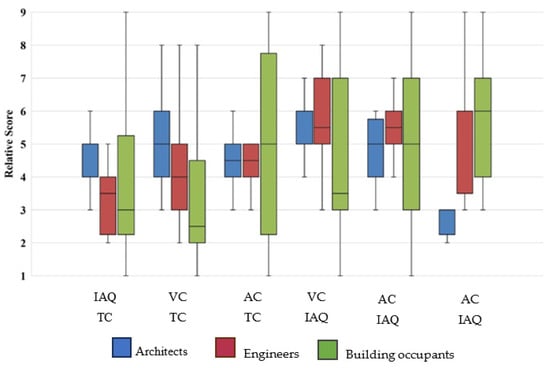
Figure 5.
Pairwise comparison of the IEQ factors’ effect on satisfaction by building experts and commercial building occupants.
- While building engineers and commercial building occupants believed that TC has more impact on occupant satisfaction than other IEQ factors, building architects thought that the influence of VC is higher than the others.
- Architects believe the AC does not contribute much to overall occupant satisfaction compared to VC. In contrast, the building occupants’ survey results demonstrated that the adequacy of AC is more important for actual building residents than the lighting level.
- Response distribution of building experts (blue and red columns) is relatively shorter than the building occupants. The error bars in commercial building occupants’ responses confirm less agreement on pairwise comparisons among them.
Applying the FAHP method, the relative non-fuzzy weight of each IEQ factor is obtained by averaging the fuzzy numbers for each factor. Finally, the normalised weights are calculated and presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Normalised IEQ factor weights.
5. Discussion
The study comprehensively compared the impact of IEQ factors on occupant satisfaction in commercial buildings. This comparison involved establishing weighting factors derived from the responses of building professionals and commercial building occupants. Figure 6 provides insight into the alignment of perspectives between building engineers, architects, and commercial building occupants regarding factors affecting occupant satisfaction. Architects’ views differ considerably from those of building engineers and occupants. As anticipated, architects place the highest importance on visual comfort in influencing occupant satisfaction.
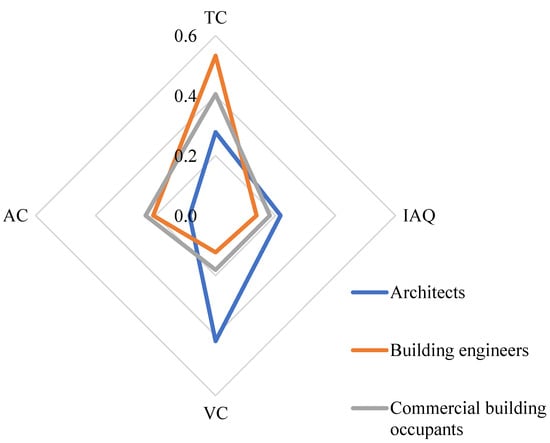
Figure 6.
The normalised weight of the IEQ factors affects occupant satisfaction.
Conversely, building engineers tend to align more closely with the preferences of building occupants, identifying Thermal comfort as the primary IEQ factor contributing to overall satisfaction in commercial buildings. While building occupants’ responses span a wider range due to the larger number of collected responses, they express their preferences cautiously, resulting in a weighting range of 0.18–0.41. In contrast, engineers generally assert that thermal comfort significantly impacts occupant satisfaction, leading to a broader weighting range of 0.12–0.53. Similar trends emerge among building architects who prioritise visual comfort as the most influential factor, assigning it a high weighting of 0.42.
The review of building certification schemes by Wei et al. [51] revealed that the complexity and diversity of parameters used to assess IEQ in commercial buildings are underscored. This research is pivotal as it fills a significant gap in existing literature. Prior to this study, there was a notable absence of research directly comparing the perspectives of building experts and occupants regarding satisfaction with the indoor environment in commercial buildings. This study not only adds to the existing body of knowledge but also paves the way for future research and practical applications focused on optimising IEQ from a more inclusive and occupant-centred perspective.
This research reveals significant discrepancies between the perceptions of building experts (architects and engineers) and actual building occupants regarding IEQ factors. Among the four major aspects of IEQ, architects placed more emphasis on visual comfort; however, engineers believed thermal comfort was the most significant factor influencing occupant satisfaction. The result of this study aligned with a study in Australia [66], implying the focus of professional architects is on lighting and the visual comfort of the occupants. In fact, architects are trained to emphasise building design’s aesthetic and functional aspects, including how spaces are lit and perceived visually. This focus on visual comfort could stem from an architectural perspective that places a high value on natural light, views, and the overall visual impact of a space, considering these elements crucial for creating inviting and stimulating environments. Also, architects’ preference for visual comfort may be influenced by their understanding of how light and sightlines contribute to a space’s perceived quality and usability. Engineers, with a focus on the technical and functional performance of buildings, may prioritise thermal comfort as it relates to energy efficiency, building systems, and sustainability objectives. Occupants’ preference for thermal comfort likely arises from immediate physical experiences within a space, affecting their comfort, health, and satisfaction. The day-to-day lived experience of occupants makes thermal comfort a tangible and immediate concern, directly influencing their perception of a building’s performance. Further exploration into these differences could involve examining the educational background and professional ideologies of architects compared to engineers, the societal and economic pressures influencing design and construction decisions, and the evolving expectations of occupants regarding workplace and living environments.
This study stands out for its focus on the perspectives of building experts, such as architects and engineers, and commercial building occupants. This approach is distinct from other studies, primarily focusing on expert opinions [48,67,68]. This research used the FAHP to rank IEQ factors to bridge the gap between expert opinions and occupant experiences in commercial buildings. This dual perspective offers a more holistic understanding of IEQ, capturing both technical expertise and actual user experience, which is a novel approach compared to other studies.
The present research results can be compared with those of previously published studies. The study by Chiang and Lai [67] consulted twelve experts to develop an IEQ index based on a combined effect of various categories of the physical environment, weighted according to their impact on occupants’ health and well-being. Their approach similarly recognises the multidimensional nature of IEQ factors. However, it does not encompass the occupant’s perspective. The findings of Si et al. [68] reveal regional differences in prioritising IEQ factors. UK experts prioritised thermal comfort and IAQ. However, engineers viewed all IEQ factors in China equally, and planners and designers emphasised IAQ, indicating a potential cultural and regional influence in IEQ assessment. This aspect suggests that geographical and cultural contexts can significantly influence perceptions of the importance of IEQ factors.
6. Conclusions
This study has contributed to understanding IEQ and its impact on occupant satisfaction within commercial buildings. A comprehensive analysis using the FAHP unveiled the differing perspectives of building experts and occupants on the importance of IEQ factors. Notably, the research has highlighted a divergence in the prioritisation of these factors, with architects emphasising visual comfort, while engineers and occupants have identified thermal comfort as a key contributor to occupant satisfaction. This divergence underscores the complexity of assessing and optimising IEQ, emphasising the need for a multifaceted approach that incorporates diverse viewpoints.
The findings of this study are instrumental in advancing the dialogue on building design and operation, advocating for a more occupant-centric approach that appreciates the nuanced preferences and experiences of building users. By bridging the gap between expert opinions and actual occupant experiences, this research provides valuable insights that can guide the development of more effective, sustainable, and occupant-friendly building environments.
Considering the observed potential influence of cultural and regional factors on IEQ prioritisation, future research should delve deeper into these dimensions. Comparative studies across various geographical locations could reveal unique preferences and requirements, informing more localised and effective IEQ strategies. Additionally, monitoring changes in occupant satisfaction and IEQ factor prioritisation over time, especially in response to building modifications or shifts in occupant demographics, could offer further insights into the dynamic nature of occupant–building interaction.
Incorporating the insights gained from this study, it becomes evident that the key to creating buildings that truly serve their occupants lies in adopting a design philosophy that places the occupant at the heart of every decision. This approach demands a shift in how designers conceptualise their role in the building process and reevaluation of the traditional dynamics between clients, designers, and occupants.
Although the findings are not statistically demonstrative, they offer insights into the relative importance of proposed IEQ factors, depending on professional backgrounds. The results are relevant to a broad spectrum of building stakeholders, including designers, consultants, researchers, and residents. Professional building managers could utilise the weighting priorities to gauge occupant demands or guide private building owners during renovations or purchases. Finally, the findings offer valuable perspectives for legislative efforts and could influence future building-related education.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: F.M.S.; methodology: F.M.S. and S.R.; formal analysis: F.M.S. and S.R.; investigation: F.M.S.; writing—original draft preparation: F.M.S.; writing—review and editing: M.S.Z. and M.A.A.G.; visualisation: F.M.S.; supervision: M.S.Z. and M.A.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Roumi, S.; Zhang, F.; Stewart, R.A. Global Research Trends on Building Indoor Environmental Quality Modelling and Indexing Systems—A Scientometric Review. Energies 2022, 15, 4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimlyat, P.S.; Kandar, M.Z. Appraisal of indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in healthcare facilities: A literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, S.; Sugiuchi, M.; Arata, S. Office thermal environment that maximizes workers’ thermal comfort and productivity. Build. Environ. 2023, 233, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Vine, E.L. A scoping study on the costs of indoor air quality illnesses: An insurance loss reduction perspective. Environ. Sci. Policy 1999, 2, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmadi, E.; McLellan, B.; Ogata, S.; Tezuka, T. An integrated, socially equitable design for sustainable water and energy supply in Iran. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 81, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumi, S.; Zhang, F.; Stewart, R.A.; Santamouris, M. Commercial building indoor environmental quality models: A critical review. Energy Build. 2022, 263, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; He, Y.; Hao, X.; Li, N.; Su, Y.; Qu, H. Optimal temperature ranges considering gender differences in thermal comfort, work performance, and sick building syndrome: A winter field study in university classrooms. Energy Build. 2022, 254, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhlenkamp, M.; Schmidt, M.; Wesseling, M.; Wick, A.; Gores, I.; Müller, D. Thermal comfort in environments with different vertical air temperature gradients. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Tartarini, F.; Parkinson, T.; Cooper, P.; de Dear, R. Thermal comfort in a mixed-mode building: Are occupants more adaptive? Energy Build. 2019, 203, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Wargocki, P.; Lian, Z. Quantitative measurement of productivity loss due to thermal discomfort. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, K.W. Indoor air quality and its effects on humans—A review of challenges and developments in the last 30 years. Energy Build. 2016, 130, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezis, I.; Biskos, G.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Kalantzi, O.-I. Particulate matter and health effects in offices—A review. Build. Environ. 2019, 156, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Weng, J.; Xia, B.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Q. The Synergistic Effect of PM2.5 and CO2 Concentrations on Occupant Satisfaction and Work Productivity in a Meeting Room. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, E.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Xie, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. The online in situ detection of indoor air pollution via laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and single particle aerosol mass spectrometer technology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 174, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Shokri, E. Daylight illuminance in urban environments for visual comfort and energy performance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedani, Z.; Solgi, E.; Skates, H.; Hine, T.; Fernando, R.; Lyons, J.; Dupre, K. Visual discomfort and glare assessment in office environments: A review of light-induced physiological and perceptual responses. Build. Environ. 2019, 153, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aries, M.B.C.; Veitch, J.A.; Newsham, G.R. Windows, view, and office characteristics predict physical and psychological discomfort. J. Environ. Psychol. 2010, 30, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Mak, C.M. Relationships between indoor environmental quality and environmental factors in university classrooms. Build. Environ. 2020, 186, 107331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumi, S.; Stewart, R.A.; Zhang, F.; Santamouris, M. Unravelling the relationship between energy and indoor environmental quality in Australian office buildings. Sol. Energy 2021, 227, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, G.; Ciaburro, G.; Trematerra, A. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Noise Detection in Open-Plan Offices Using Recursive Partitioning. Buildings 2018, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, J.; Dehghan, H.; Azmoon, H.; Forouharmajd, F. Relationship between Lighting and Noise Levels and Productivity of the Occupants in Automotive Assembly Industry. J. Environ. Public Health 2013, 2013, 527078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipe Contin de Oliveira, S.; Aletta, F.; Kang, J. Self-rated health implications of noise for open-plan office workers: An overview of the literature. Build. Acoust. 2023, 30, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T. Decision making with the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, C.; Beskese, A.; Temur, G.T. Sustainability analysis of different hydrogen production options using hesitant fuzzy AHP. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18059–18076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.; Shankar, R. An STEEP-fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS framework for evaluation and selection of thermal power plant location: A case study from India. Energy 2012, 42, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.-C. Facility Location Selection Using Fuzzy Topsis under Group Decisions. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl.-Based Syst. 2002, 10, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Mardani, A.; Turskis, Z.; Jusoh, A.; Nor, K.M.D. Development of TOPSIS Method to Solve Complicated Decision-Making Problems—An Overview on Developments from 2000 to 2015. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2016, 15, 645–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, B.; Almasri, A.; Uzun Ozsahin, D. Preference Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment Evaluation (Promethee). In Application of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in Environmental and Civil Engineering; Uzun Ozsahin, D., Gökçekuş, H., Uzun, B., LaMoreaux, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, B.; Bwiza, R.A.; Uzun Ozsahin, D. ELimination Et Choix Traduisant La REalité (ELECTRE). In Application of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis in Environmental and Civil Engineering; Uzun Ozsahin, D., Gökçekuş, H., Uzun, B., LaMoreaux, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardil, C. Aircraft Selection Process Using Preference Analysis for Reference Ideal Solution (PARIS). Int. J. Aerosp. Mech. Eng. 2020, 159, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sah, B.; Singh, A.R.; Deng, Y.; He, X.; Kumar, P.; Bansal, R.C. A review of multi criteria decision making (MCDM) towards sustainable renewable energy development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; RWS: Chalfont St. Peter, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Eckert, C.M.; Earl, C. A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubler, S.; Robert, J.; Derigent, W.; Voisin, A.; Le Traon, Y. A state-of the-art survey & testbed of fuzzy AHP (FAHP) applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 65, 398–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, A.H.; Ojokoh, B.A.; Adetunmbi, A.O. Performance analysis of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process multi-criteria decision support models for contractor selection. Sci. Afr. 2020, 9, e00471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, S.M.; Behzadian, M.; Samizadeh, R.; Ignatius, J. A fuzzy hybrid group decision support system approach for the supplier evaluation process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 73, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J.; Fahim, P.B.M.; Tavasszy, L. Supplier selection in the airline retail industry using a funnel methodology: Conjunctive screening method and fuzzy AHP. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 8165–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, K.; Fröhling, M.; Breun, P.; Schultmann, F. Assessing social risks of global supply chains: A quantitative analytical approach and its application to supplier selection in the German automotive industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, M.B.; Kilic, H.S. A two stage approach for supplier selection problem in multi-item/multi-supplier environment with quantity discounts. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, A.Y.; Oztekin, A.; Gumus, A.T.; Gunasekaran, A. A hybrid data analytic methodology for 3PL transportation provider evaluation using fuzzy multi-criteria decision making. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 6097–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezad, A.; Seif, A.; Esfandiari, N. Supplier evaluation and selection with QFD and FAHP in a pharmaceutical company. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 68, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameshwaran, R.; Praveen Kumar, S.; Saravanakumar, K. An integrated fuzzy MCDM based approach for robot selection considering objective and subjective criteria. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 26, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Chaudhary, N.; Saxena, N. Selection of warehouse location for a global supply chain: A case study. IIMB Manag. Rev. 2018, 30, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balusa, B.C.; Gorai, A.K. Sensitivity analysis of fuzzy-analytic hierarchical process (FAHP) decision-making model in selection of underground metal mining method. J. Sustain. Min. 2019, 18, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Govindan, K.; Gold, S. Multi-tier sustainable global supplier selection using a fuzzy AHP-VIKOR based approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 195, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Barua, M.K. Risk analysis in green supply chain using fuzzy AHP approach: A case study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, A.; Costa, R.; Levialdi, N.; Menichini, T. A fuzzy analytic hierarchy process method to support materiality assessment in sustainability reporting. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 121, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Ding, Y. Indoor environmental quality in existing public buildings in China: Measurement results and retrofitting priorities. Build. Environ. 2020, 185, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, R.; Aziminezhad, M. Human-building interaction: A bibliometric review. Build. Environ. 2023, 242, 110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.; Siu-Yu Lau, S. Post-occupancy evaluation of the thermal environment in a green building. Facilities 2013, 31, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wargocki, P.; Zirngibl, J.; Bendžalová, J.; Mandin, C. Review of parameters used to assess the quality of the indoor environment in Green Building certification schemes for offices and hotels. Energy Build. 2020, 209, 109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuimara, T.; Gunay, B.; Day, J.; Burpee, H. Designing for Occupants: A Review of the Integrated Design Practice. In Proceedings of the ACEEE 2018 Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Buildings-Making Efficiency Easy and Enticing, Pacific Groove, CA, USA, 12–17 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, T.; Yan, D.; D’Oca, S.; Chen, C.-F. Ten questions concerning occupant behavior in buildings: The big picture. Build. Environ. 2017, 114, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Marjanovic-Halburd, L. Criteria weighting for green technology selection as part of retrofit decision making process for existing non-domestic buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Schiavon, S.; Brager, G. Personal comfort models—A new paradigm in thermal comfort for occupant-centric environmental control. Build. Environ. 2018, 132, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, M.; Kloppenborg Møller, J.; Calì, D.; Carlucci, S. Human-in-the-loop methods for occupant-centric building design and operation. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, D. Integrated analysis of energy, indoor environment, and occupant satisfaction in green buildings using real-time monitoring data and on-site investigation. Build. Environ. 2020, 182, 107014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANSI/ASHRAE. STANDARD 55, Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2004; Available online: www.ashrae.org (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Bleil de Souza, C.; Tucker, S.; Belafi, Z.D.; Reith, A.; Hellwig, R.T. Occupants in the Building Design Decision-Making Process. In Occupant-Centric Simulation-Aided Building Design; O’Brien, W., Tahmasebi, F., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, C.; Day, J.; Agee, P.; Wener, R.; Jin, Q.; Senick, J. Methods to Obtain the Occupant Perspective; Routledge: London, UK, 2023; pp. 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J. The Ecological Approach to Visual Perception: Classic Edition; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, J.J. Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1985, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-W.; Chang, Y.-C. The implementation factors that influence the ERP (enterprise resource planning) benefits. Decis. Support Syst. 2008, 46, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaro, J.; Mwasha, A.; Williams, R.G.; Zico, R. An Integrated Criteria Weighting Framework for the sustainable performance assessment and design of building envelope. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Some Mathematical Concepts of the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Behaviormetrika 1991, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumi, S.; Zhang, F.; Stewart, R.A.; Santamouris, M. Weighting of indoor environment quality parameters for occupant satisfaction and energy efficiency. Build. Environ. 2023, 228, 109898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.; Lai, C.-M. A study on the comprehensive indicator of indoor environment assessment for occupants’ health in Taiwan. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Marjanovic-Halburd, L.; Nasiri, F.; Bell, S. Assessment of building-integrated green technologies: A review and case study on applications of Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) method. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).