Enhancing the Methane Yield of Salicornia spp. via Organosolv Fractionation as Part of a Halophyte Biorefinery Concept
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Halophyte Plant Material and Residues Used for the Biogas Potential Tests
2.2. Biomethane Potential Test Set-Up
2.3. Biomass Compositional Analysis
2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.5. Theoretical Biomethane Potential
3. Results and Discussion
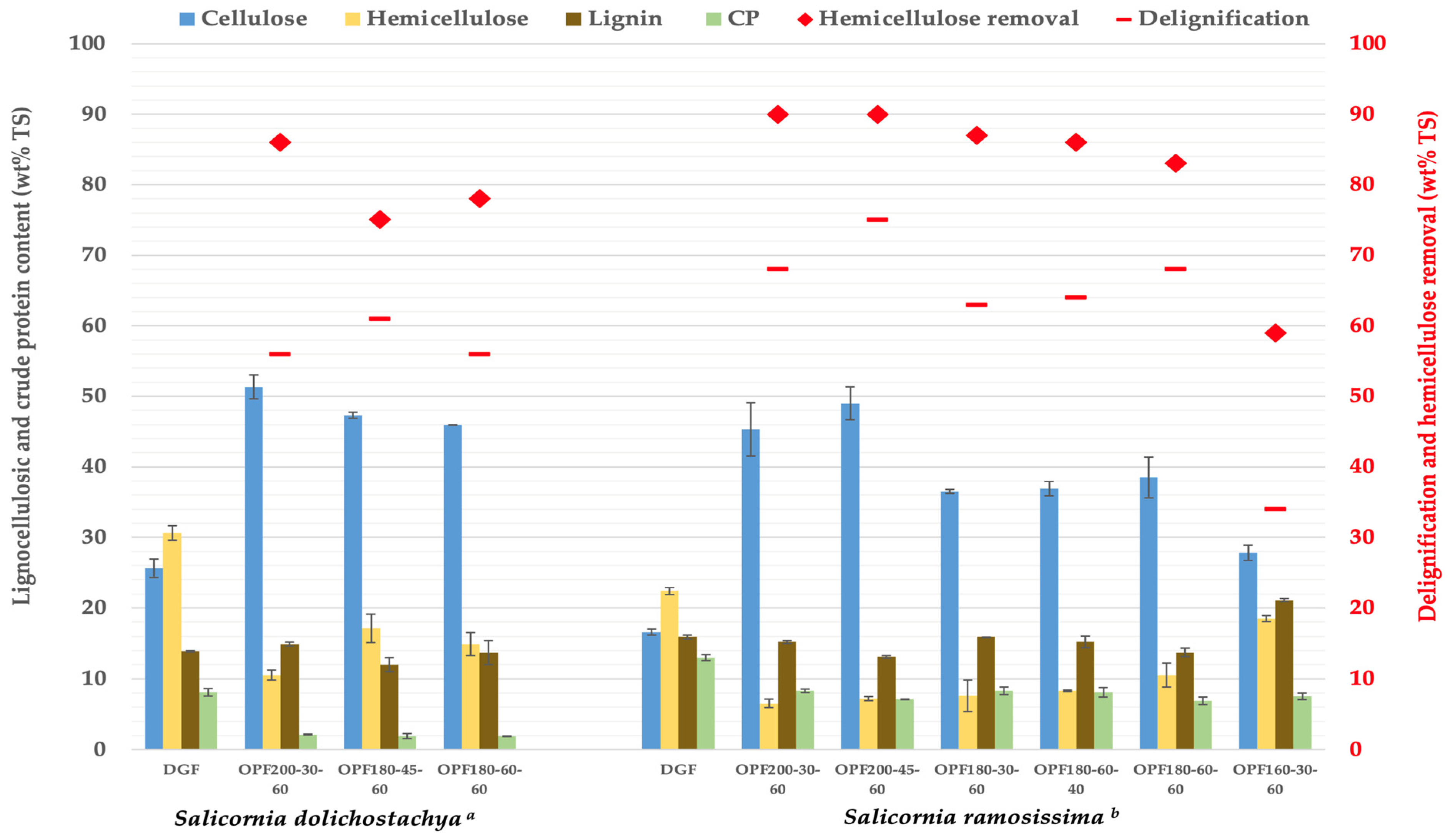
3.1. Biomass Composition
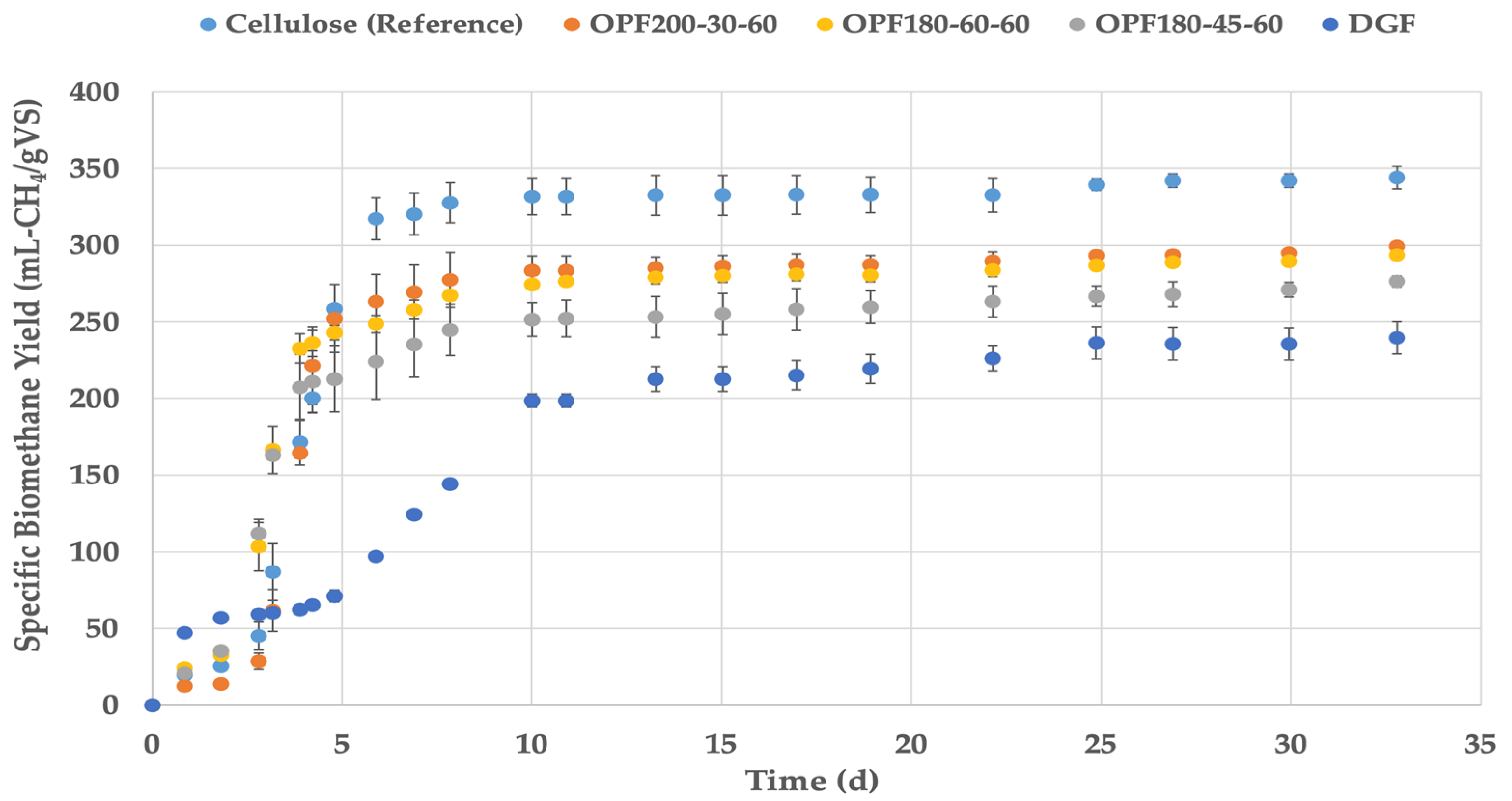
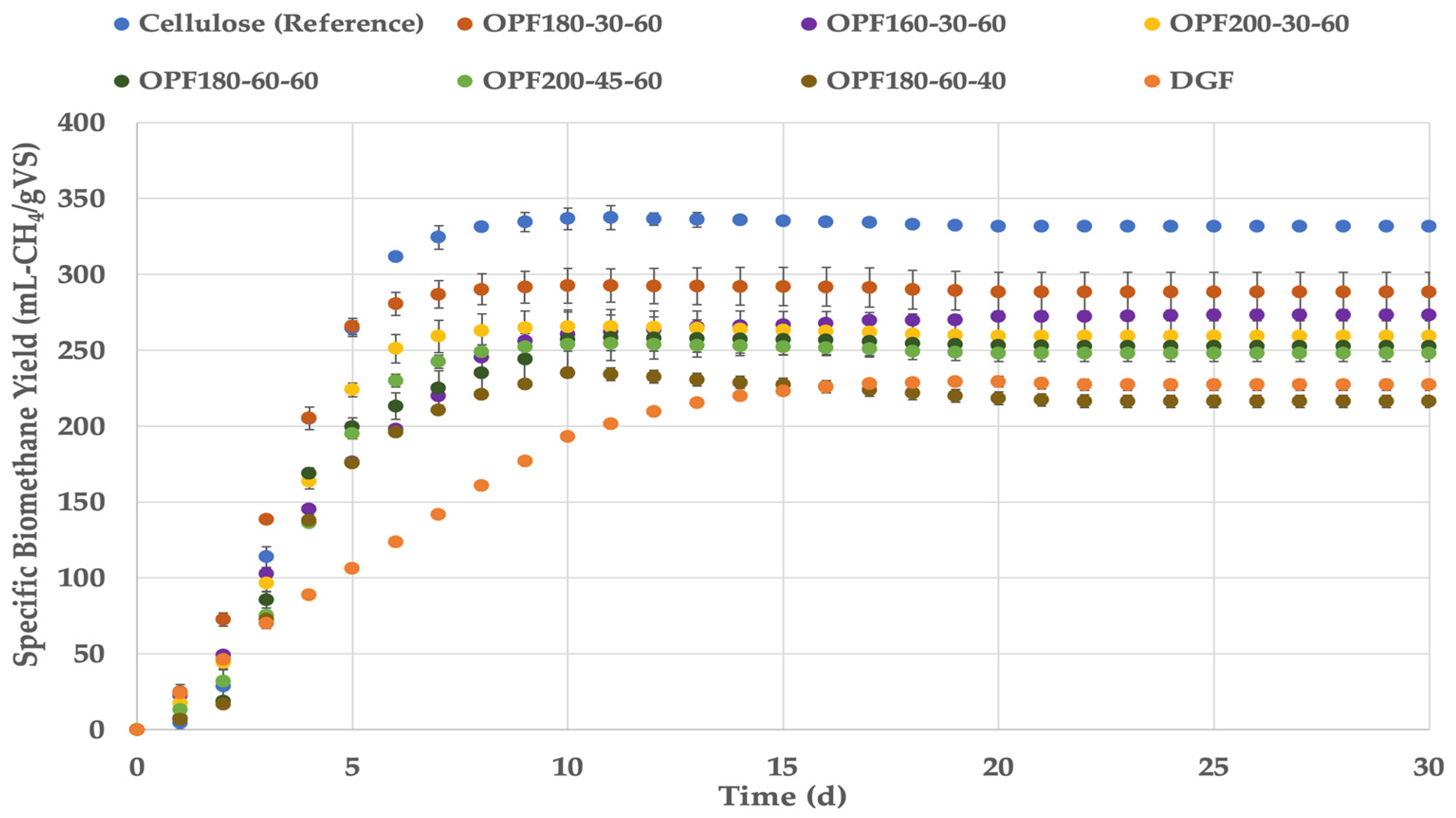
3.2. Experimental and Theoretical Methane Potential and Biodegradability of Salicornia spp. Fibers
3.3. Comparison to Other Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giordano, R.; Aliotta, G.E.; Johannesen, A.S.; Voetmann-Jensen, D.; Laustsen, F.H.; Andersen, L.A.; Rezai, A.; Fredsgaard, M.; Lo Vecchio, S.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; et al. Effects of Salicornia-Based Skin Cream Application on Healthy Humans’ Experimental Model of Pain and Itching. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkko, L.S.S.; Turcios, A.E.; Kohnen, S.; Chaturvedi, T.; Papenbrock, J.; Thomsen, M.H. Cultivation and Characterisation of Salicornia Europaea, Tripolium Pannonicum and Crithmum Maritimum Biomass for Green Biorefinery Applications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkko, L.S.S.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Trentin, R.; Fredsgaard, M.; Chaturvedi, T.; Custódio, L.; Thomsen, M.H. Bioactive Extracts from Salicornia Ramosissima J. Woods Biorefinery as a Source of Ingredients for High-Value Industries. Plants 2023, 12, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, C.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayenne, A.; Turcios, A.E.; Thomsen, M.H.; Rocha, R.J.M.; Papenbrock, J.; Uellendahl, H. Halophytes as Feedstock for Biogas Production: Composition Analysis and Biomethane Potential of Salicornia spp. Plant Material from Hydroponic and Seawater Irrigation Systems. Fermentation 2022, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Norrrahim, M.F.; Huzaifah, M.R.M.; Farid, M.A.A.; Shazleen, S.S.; Misenan, M.S.M.; Yasim-Anuar, T.A.T.; Naveen, J.; Norizan, M.N.; Rani, M.S.A.; Hakimi, M.I.; et al. Greener Pretreatment Approaches for the Valorisation of Natural Fibre Biomass into Bioproducts. Polymers 2021, 13, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.G.; Meng, X.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. The Critical Role of Lignin in Lignocellulosic Biomass Conversion and Recent Pretreatment Strategies: A Comprehensive Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G.; Lens, P. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Materials to Enhance Their Methane Potential. In Renewable Energy Technologies for Energy Efficient Sustainable Development; Sinharoy, A., Lens, P.N.L., Eds.; Applied Environmental Science and Engineering for a Sustainable Future; Springer eBooks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 85–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmatz, A.A.; Masarin, F.; Brienzo, M. Lignin Removal and Cellulose Digestibility Improved by Adding Antioxidants and Surfactants to Organosolv Pretreatment of Sugarcane Bagasse. Bioenergy Res. 2021, 15, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandla, M.L.; Martín, C.; Jönsson, L.J. Analytical Enzymatic Saccharification of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Conversion to Biofuels and Bio-Based Chemicals. Energies 2018, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, K.; Shafiei, M.; Kumar, R. Progress in Physical and Chemical Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass. In Biofuel Technologies: Recent Developments; Gupta, V., Tuohy, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 53–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Liu, Y.; Uchida, S.; Kawarada, K.; Ukagami, Y.; Ichinose, H.; Kaneko, S.; Fukuda, K. Effects of Cellulose Crystallinity, Hemicellulose, and Lignin on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Miscanthus sinensis to Monosaccharides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabelo, S.C.; Nakasu, P.Y.S.; Scopel, E.; Araújo, M.F.; Cardoso, L.H.; Da Costa, A.C. Organosolv Pretreatment for Biorefineries: Current Status, Perspectives, and Challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bhagia, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pu, Y.; Dunlap, J.R.; Li, S.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Yoo, C.G. Effects of the Advanced Organosolv Pretreatment Strategies on Structural Properties of Woody Biomass. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 146, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Iqbal, T.; Khan, M.J. Recent Advances in the Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Biofuels and Value-Added Products. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 20, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Rahman, S.; Raynie, D.E. Recent Advances of Greener Pretreatment Technologies of Lignocellulose. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 3, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Enhanced Biogas Production. Prog. Energ. Combust. Sci. 2014, 42, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. Increased Biogas Production from Wheat Straw by Chemical Pretreatments. Renew. Energy 2018, 119, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, G.; Papirio, S.; Lens, P.N.L.; Esposito, G. Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Materials Using Ethanol-Organosolv Pretreatment. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongbuekeaw, T.; Sawangkeaw, R.; Chaiprapat, S.; Charnnok, B. Conversion of Rubber Wood Waste to Methane by Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2020, 11, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, S.M.; Zilouei, H.; Karimi, K.; Asadinezhad, A. Enhanced Biogas Production from Sunflower Stalks Using Hydrothermal and Organosolv Pretreatment. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 76, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohamadsadeghi, S.; Karimi, K.; Zamani, A.; Amiri, H.; Horváth, I.S. Enhanced Solid-State Biogas Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass by Organosolv Pretreatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 350414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monção, M.; Wretborn, T.; Rova, U.; Matsakas, L.; Christakopoulos, P. Salicornia dolichostachya Organosolv Fractionation: Towards Establishing a Halophyte Biorefinery. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28599–28607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monção, M.; Thoresen, P.P.; Wretborn, T.; Lange, H.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Patel, A. A Novel Biorefinery Concept Based on Marginally Used Halophyte Biomass. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 3902–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verein Deutscher Ingenieure. VDI 4630: Fermentation of Organic Materials: Characterisation of the Substrate, Sampling, Collection of Material Data, Fermentation Tests; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN 12880; Characterization of sludges—Determination of dry residue and water content. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2000.
- DIN EN 12879; Characterization of sludges—Determination of the Loss on Ignition of Dry Mass. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2001.
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.J.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.W.; Crocker, D.P. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure; Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Buswell, A.M.; Mueller, H.F. Mechanism of Methane Fermentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, W.C. Energy Recovery from Sanitary Landfills—A Review; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; Fernández-Cegrí, V.; De La Rubia, M.A.; Borja, R.; Béline, F.; Cavinato, C.; Demirer, G.N.; Fernández, B.; Fernández-Polanco, M.; Frigon, J.-C.; et al. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) of Solid Organic Substrates: Evaluation of Anaerobic Biodegradability Using Data from an International Interlaboratory Study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcios, A.E.; Cayenne, A.; Uellendahl, H.; Papenbrock, J. Halophyte Plants and Their Residues as Feedstock for Biogas Production—Chances and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, T.; Amon, B.; Kryvoruchko, V.; Zollitsch, W.; Mayer, K.; Gruber, L. Biogas Production from Maize and Dairy Cattle Manure—Influence of Biomass Composition on the Methane Yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, T.; Christiansen, A.; Gołębiewska, I.; Thomsen, M.H. Salicornia Species; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, P.; Ottesen, V.; Opedal, M.T.; Moe, S.T. Morphology of Lignin Structures on Fiber Surfaces after Organosolv Pretreatment. Biopolymers 2022, 113, e23520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pu, Y.; Kumar, R.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Wyman, C.E. Investigation of Lignin Deposition on Cellulose during Hydrothermal Pretreatment, Its Effect on Cellulose Hydrolysis, and Underlying Mechanisms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 111, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.G.; Agrawal, K.; Verma, P. Organosolv Pretreatment: An in-Depth Purview of Mechanics of the System. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2023, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Park, T.; Tong, Y.W.; Yu, Z. The Microbiome Driving Anaerobic Digestion and Microbial Analysis. In Advances in Bioenergy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakas, L.; Nitsos, C.; Raghavendran, V.; Yakimenko, O.; Persson, G.; Olsson, E.; Rova, U.; Olsson, L.; Christakopoulos, P. A Novel Hybrid Organosolv: Steam Explosion Method for the Efficient Fractionation and Pretreatment of Birch Biomass. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsakas, L.; Raghavendran, V.; Yakimenko, O.; Persson, G.; Olsson, E.; Rova, U.; Olsson, L.; Christakopoulos, P. Lignin-First Biomass Fractionation Using a Hybrid Organosolv—Steam Explosion Pretreatment Technology Improves the Saccharification and Fermentability of Spruce Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsakas, L.; Sarkar, O.; Jansson, S.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. A Novel Hybrid Organosolv-Steam Explosion Pretreatment and Fractionation Method Delivers Solids with Superior Thermophilic Digestibility to Methane. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
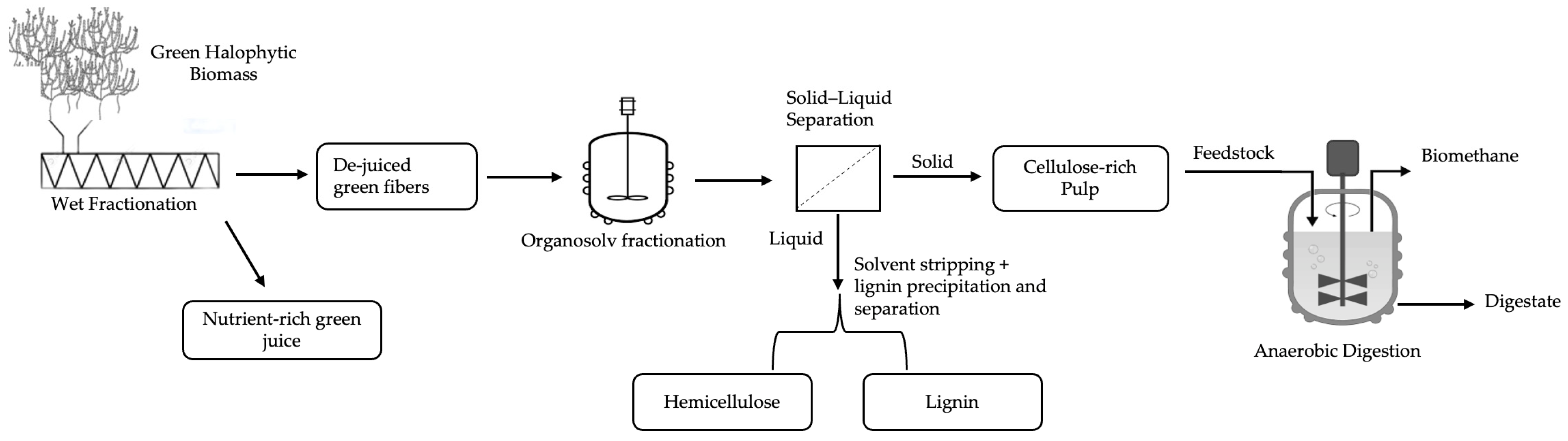
| Sample Notation | Organosolv Treatment Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Time | Solvent Concentration | |
| (°C) | (min) | (% v/v EtOH) | |
| OPF200-30-60 | 200 | 30 | 60 |
| OPF200-45-60 | 200 | 45 | 60 |
| OPF180-30-60 | 180 | 30 | 60 |
| OPF180-45-60 | 180 | 45 | 60 |
| OPF180-60-40 | 180 | 60 | 40 |
| OPF180-60-60 | 180 | 60 | 60 |
| OPF160-30-60 | 160 | 30 | 60 |
| Halophyte Samples | TS | VS | VS | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% FM | wt% FM | wt% TS | wt% TS | |
| S. dolichostachya (S. dol) | ||||
| SdolDGF | 92.7 (0.1) | 88.0 (0.2) | 95.0 (0.2) | 5.0 (0.2) |
| SdolOPF200-30-60 | 95.9 (0.1) | 89.7 (0.2) | 93.5 (0.2) | 6.5 (0.2) |
| SdolOPF180-45-60 | 93.5 (0.1) | 87.9 (0.5) | 94.0 (0.6) | 6.1 (0.6) |
| SdolOPF180-60-60 | 93.5 (0.1) | 87.7 (0.3) | 93.7 (0.2) | 6.3 (0.2) |
| S. ramosissima (S. ram) | ||||
| SramDGF | 92.4 (0.03) | 81.1 (0.1) | 87.8 (0.1) | 12.2 (0.1) |
| SramOPF200-30-60 | 97.6 (0.02) | 93.8 (0.2) | 96.1 (0.2) | 3.9 (0.2) |
| SramOPF200-45-60 | 95.7 (0.1) | 91.9 (0.1) | 96.2 (0.04) | 3.8 (0.04) |
| SramOPF180-30-60 | 97.2 (0.01) | 93.1 (0.3) | 95.8 (0.3) | 4.2 (0.3) |
| SramOPF180-60-40 | 96.3 (0.01) | 94.3 (0.02) | 98.0 (0.02) | 2.0 (0.02) |
| SramOPF180-60-60 | 96.2 (0.03) | 93.2 (0.03) | 96.8 (0.04) | 3.2 (0.04) |
| SramOPF160-30-60 | 94.9 (0.02) | 92.6 (0.04) | 97.6 (0.02) | 2.4 (0.02) |
| Halophyte Samples | C | H | N | O | C/N | Empirical Formular |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% TS | ||||||
| S. dolichostachya (S. dol) | ||||||
| SdolDGF | 43.7 (0.3) | 5.9 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 43.6 (0.5) | 33.6 | C39H63N1O29 |
| SdolOPF200-30-60 | 44.0 (0.2) | 6.0 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.01) | 42.7 (0.3) | 129.4 | C151H247N1O110 |
| SdolOPF180-45-60 | 43.2 (0.1) | 5.9 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.01) | 44.0 (0.4) | 139.5 | C163H265N1O124 |
| SdolOPF180-60-60 | 43.4 (0.2) | 5.9 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.01) | 43.6 (0.3) | 140.0 | C163H267N1O123 |
| S. ramosissima (S. ram) | ||||||
| SramDGF | 41.0 (0.4) | 5.6 (0.1) | 2.1 (0.1) | 38.7 (0.5) | 19.7 | C23H38N1O16 |
| SramOPF200-30-60 | 47.9 (0.5) | 6.4 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.04) | 40.0 (0.6) | 36.3 | C42H68N1O27 |
| SramOPF200-45-60 | 49.7(0.1) | 6.4 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.01) | 38.4 (0.7) | 43.6 | C51H79N1O29 |
| SramOPF180-30-60 | 47.1 (0.5) | 6.3 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 40.7 (0.5) | 35.7 | C42H66N1O27 |
| SramOPF180-60-40 | 52.0 (0.7) | 6.5 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 37.7 (0.7) | 40.0 | C47H70N1O25 |
| SramOPF180-60-60 | 48.6 (0.7) | 6.3 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.1) | 40.3 (0.8) | 44.2 | C52H80N1O32 |
| SramOPF160-30-60 | 46.5 (0.4) | 6.1 (0.1) | 1.2 (0.1) | 43.3 (0.5) | 38.8 | C45H71N1O32 |
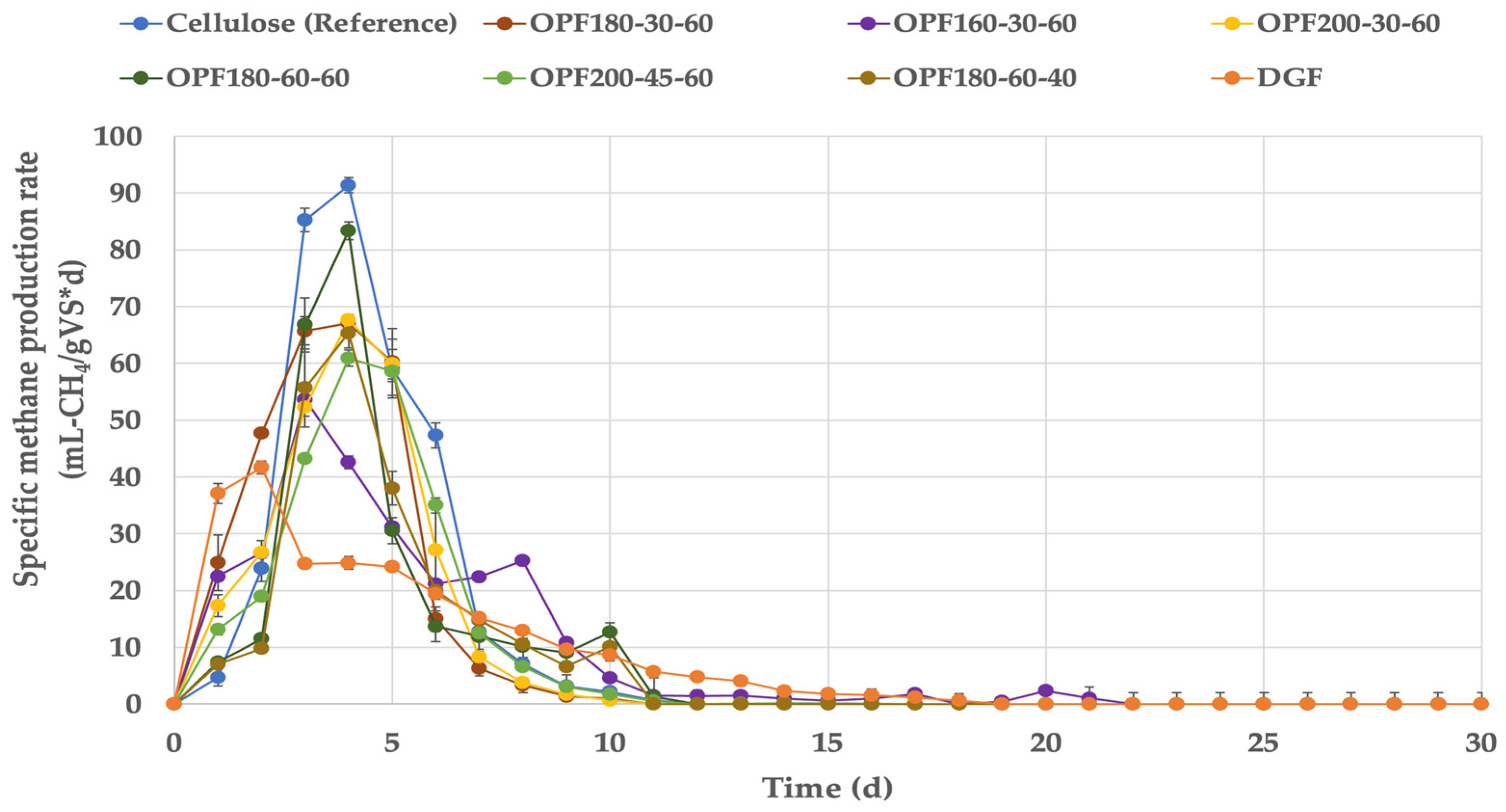
| Halophytic Substrates | BMPEXP | Average CH4 Production Rate | ΔCH4 | TBMP | BD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHNO | OFC | CHNO | OFC | ||||
| mL-CH4/gVS | mL-CH4/(gVS·d) | % | mL-CH4/gVS | % | |||
| S. dolichostachya (S. dol) | |||||||
| SdolDGF | 239.4 (10.5) | 9.5 | - | 435 | 288 | 55 | 83 |
| SdolOPF200-30-60 | 299.3 (2.3) | 28.3 | +25.1 | 459 | 285 | 65 | 105 |
| SdolOPF180-45-60 | 276.4 (3.8) | 25.1 | +15.5 | 441 | 294 | 63 | 94 |
| SdolOPF180-60-60 | 293.6 (2.6) | 27.9 | +23.0 | 447 | 279 | 66 | 105 |
| S. ramosissima (S. ram) | |||||||
| SramDGF | 229.3 (2.8) | 12.1 | - | 449 | 258 | 51 | 89 |
| SramOPF200-30-60 | 265.4 (11.4) | 26.5 | +15.7 | 499 | 267 | 53 | 99 |
| SramOPF200-45-60 | 254.3 (4.7) | 25.4 | +10.9 | 525 | 279 | 48 | 91 |
| SramOPF180-30-60 | 292.7 (10.9) | 29.3 | +28.0 | 487 | 234 | 60 | 125 |
| SramOPF180-60-40 | 235.2 (3.2) | 23.5 | +2.6 | 541 | 232 | 43 | 101 |
| SramOPF180-60-60 | 258.0 (13.9) | 25.7 | +12.7 | 501 | 246 | 52 | 105 |
| SramOPF160-30-60 | 273.1 (3.8) | 26.1 | +19.2 | 459 | 235 | 60 | 116 |
| Substrates | Organosolv Fractionation Conditions | Solvent-to-Substrate Ratio | Delignification | Methane Yields | ΔCH4 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | mL-CH4/gVS | % | ||||
| S. dolichostachya | 200 °C, 30 min, 60% EtOH | 1:10 | 56 | 299 | +25 | This study |
| S. ramosissima | 180 °C, 30 min, 60% EtOH | 1:10 | 63 | 293 | +28 | |
| Wheat Straw | 180 °C, 60 min, 50% EtOH | 1:10 | 14 | 316 | +15 | [18] |
| Rice Straw | 18 | 332 | +42 | [19] | ||
| Rice Straw | 150 °C, 60 min, 50% EtOH | 1:10 | 14 | 303 | +29 | [19] |
| Rice Straw | 150 °C, 60 min, 75% EtOH, 1% H2SO4 | 1:8 | 22 | 153 | +32 | [22] |
| Sunflower Stalks | 180 °C, 60 min, 50% isopropanol | 1:10 | 26 | 264 | +113 | [21] |
| Cocoa Bean Shells | 180 °C, 60 min, 50% EtOH | 1:10 | 12 | 219 | −5 | [19] |
| Rubber Waste | 210 °C, 30 min, 75% EtOH | 1:10 | 74 | 165 | +179 | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cayenne, A.; Monção, M.; Matsakas, L.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Thomsen, M.H.; Uellendahl, H. Enhancing the Methane Yield of Salicornia spp. via Organosolv Fractionation as Part of a Halophyte Biorefinery Concept. Energies 2024, 17, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051074
Cayenne A, Monção M, Matsakas L, Rova U, Christakopoulos P, Thomsen MH, Uellendahl H. Enhancing the Methane Yield of Salicornia spp. via Organosolv Fractionation as Part of a Halophyte Biorefinery Concept. Energies. 2024; 17(5):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051074
Chicago/Turabian StyleCayenne, Aadila, Maxwel Monção, Leonidas Matsakas, Ulrika Rova, Paul Christakopoulos, Mette H. Thomsen, and Hinrich Uellendahl. 2024. "Enhancing the Methane Yield of Salicornia spp. via Organosolv Fractionation as Part of a Halophyte Biorefinery Concept" Energies 17, no. 5: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051074
APA StyleCayenne, A., Monção, M., Matsakas, L., Rova, U., Christakopoulos, P., Thomsen, M. H., & Uellendahl, H. (2024). Enhancing the Methane Yield of Salicornia spp. via Organosolv Fractionation as Part of a Halophyte Biorefinery Concept. Energies, 17(5), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051074











