Multi-Objective Optimization of the Microchannel Heat Sink Used for Combustor of the Gas Turbine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optimization Methodology
2.1. Design Variables and Objective Function
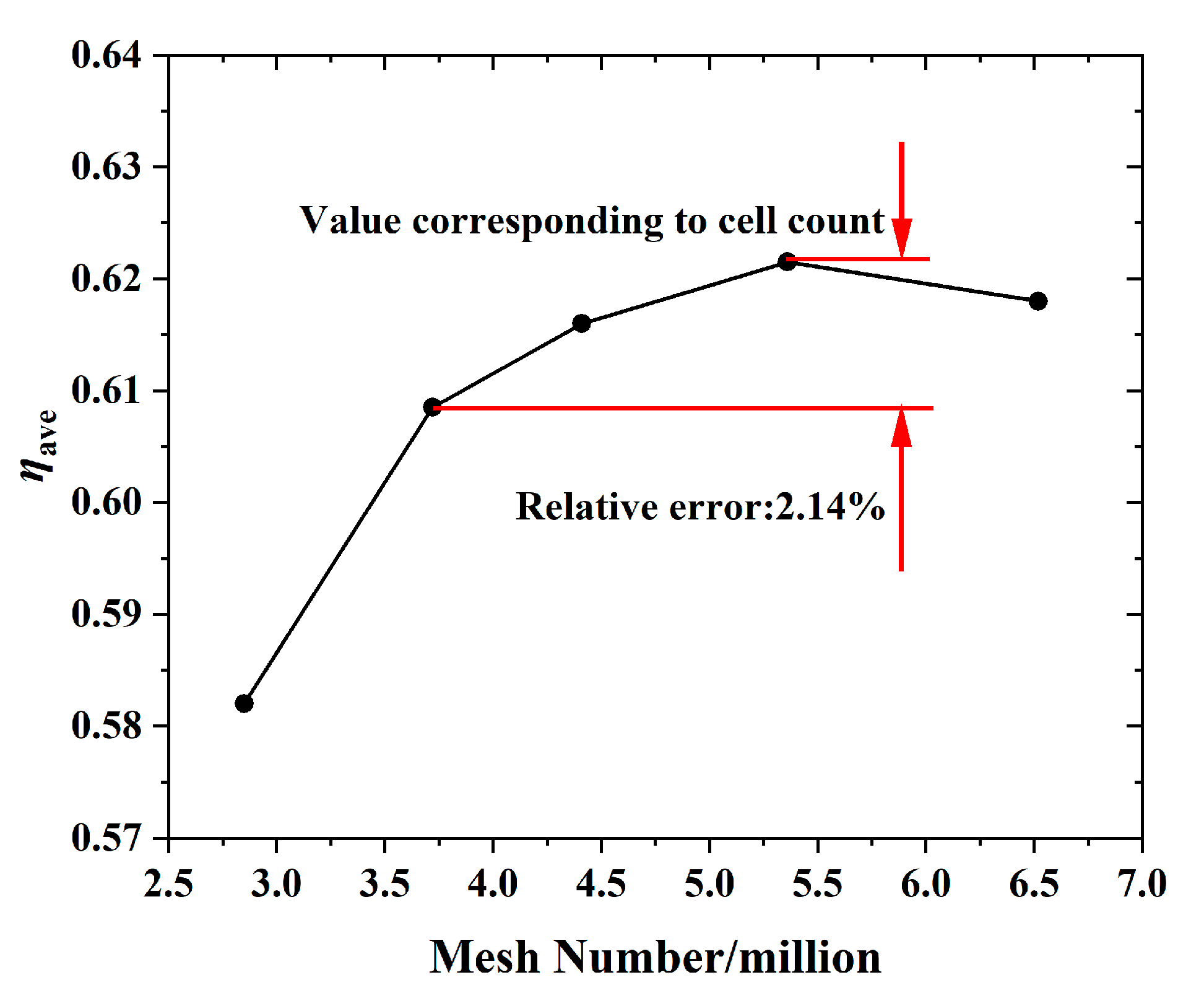
2.2. Brief Description of CFD Modeling
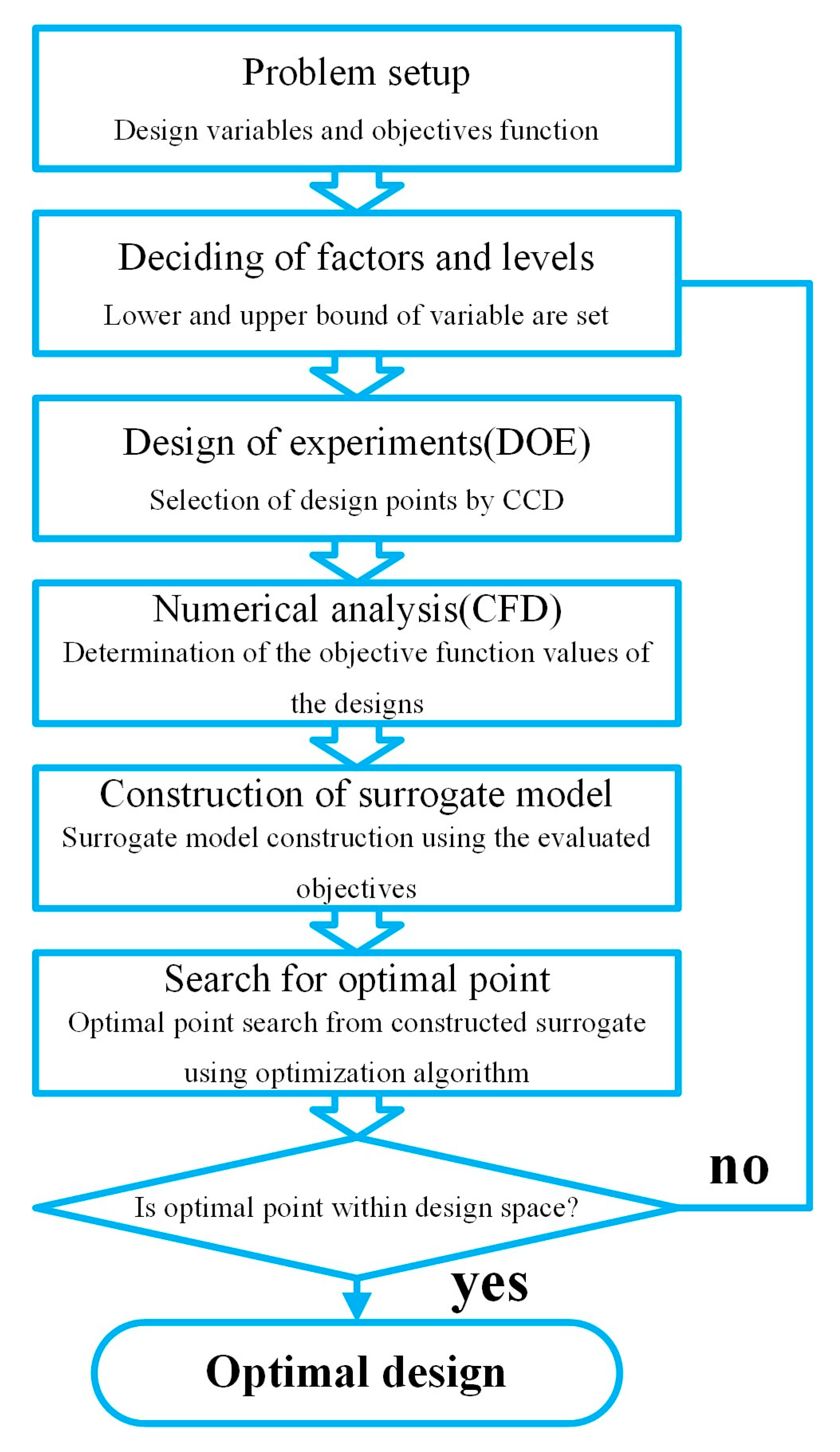
2.3. Brief Description of Optimization Flow Chart
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Optimization Results
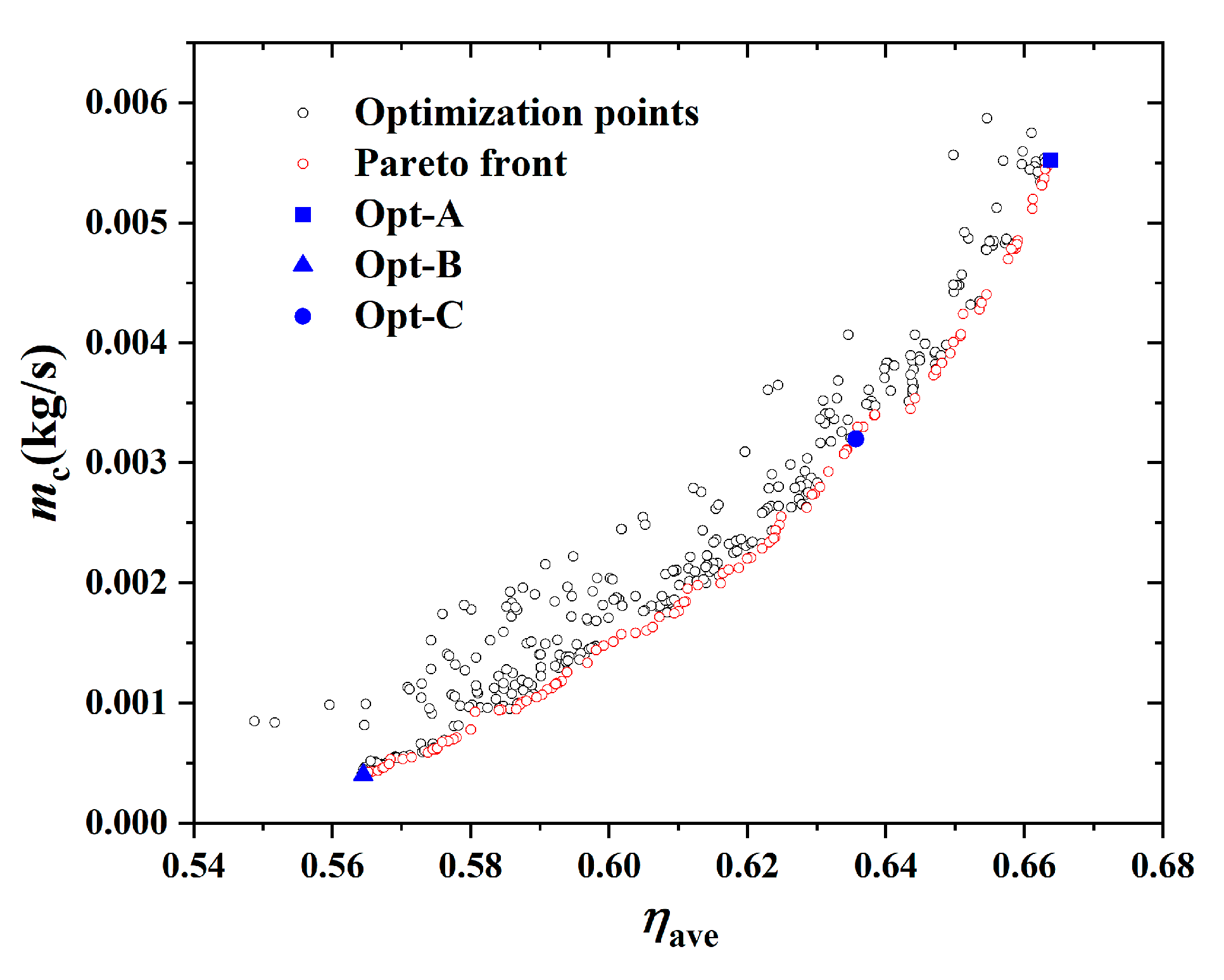
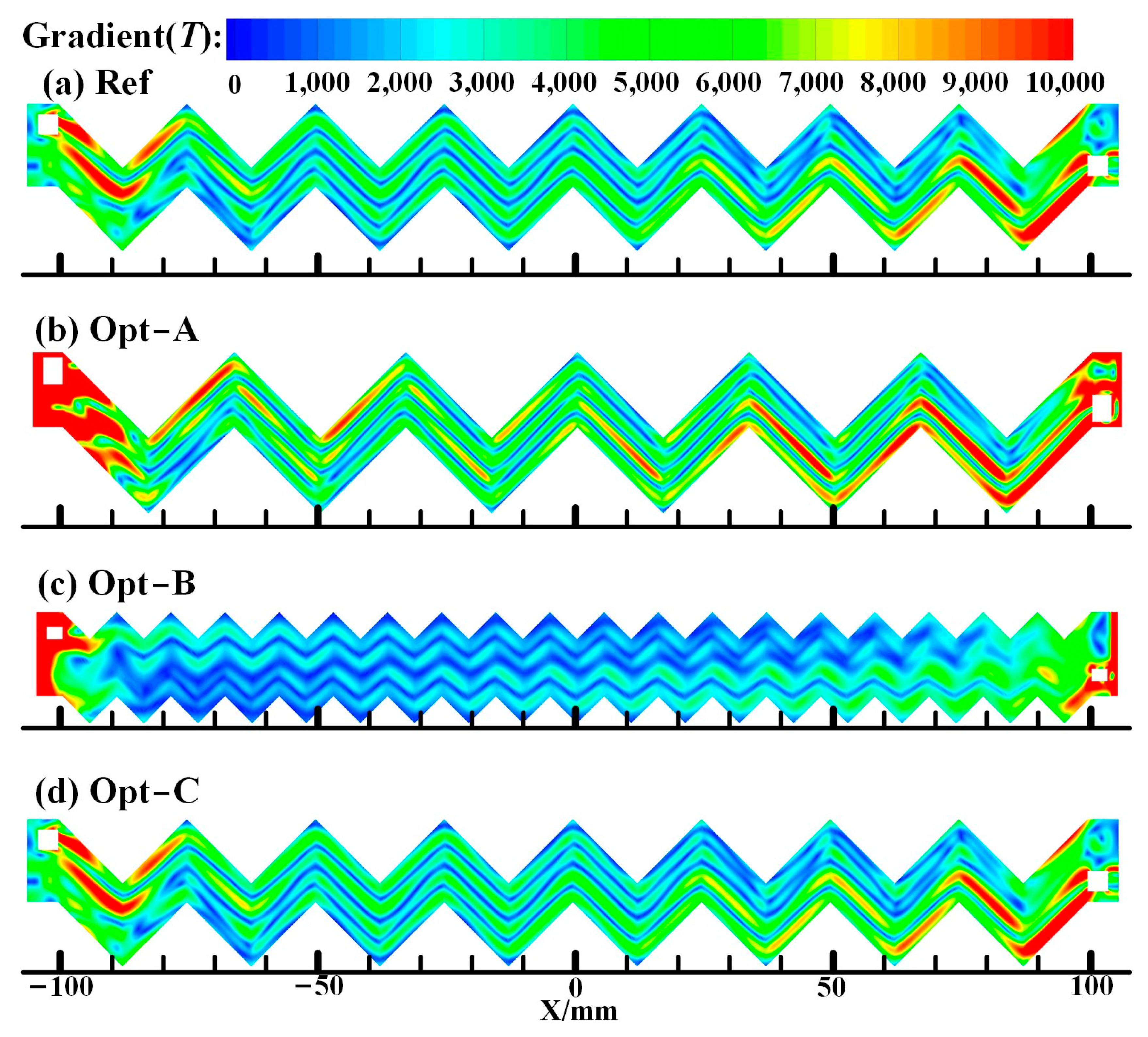
3.2. Comparison of Different Optimization Results
4. Conclusions
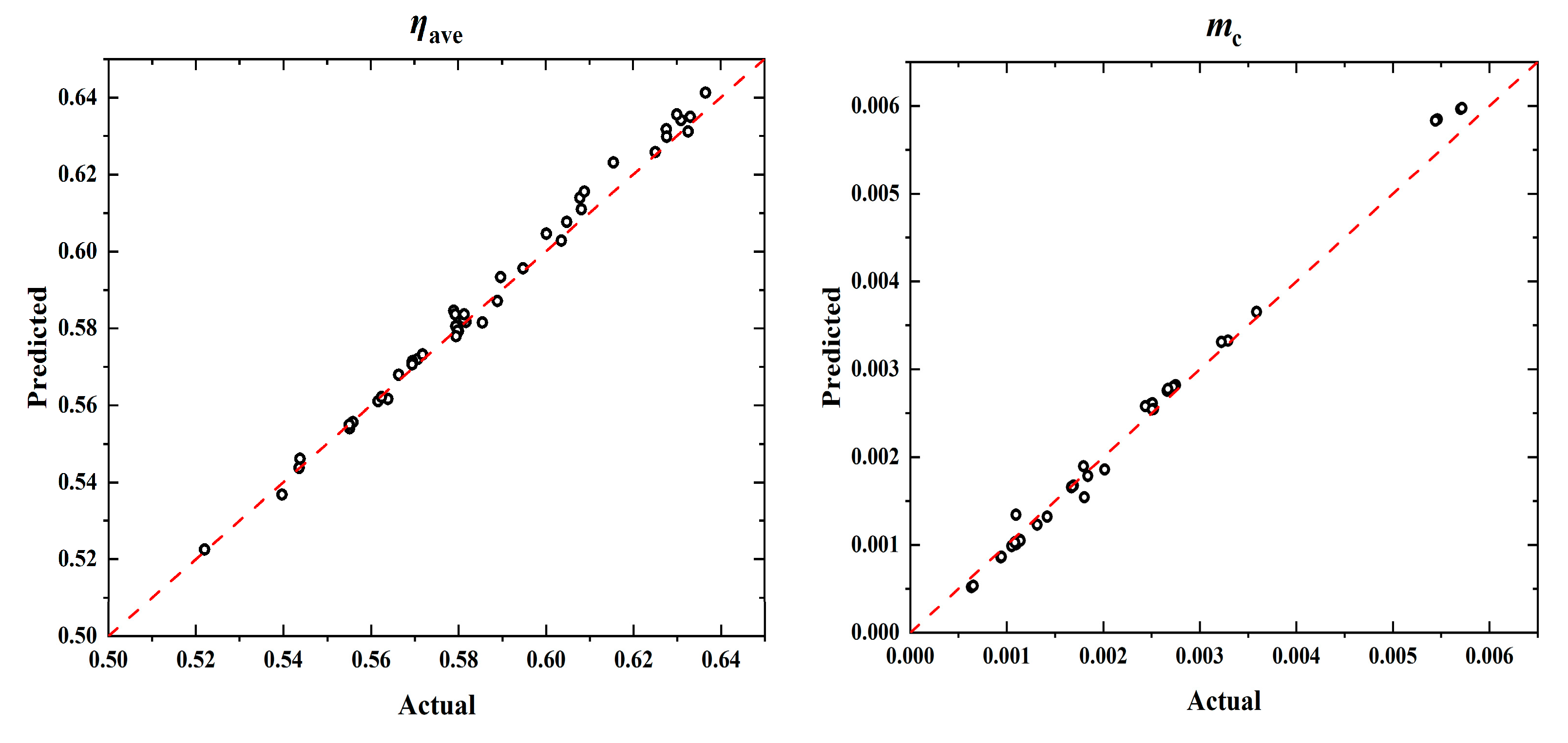
- The established approximation model predicts well based on the error points; the average error of and are 0.39% and 6.75%, respectively.
- The length of the “zigzag” (Z) and the periodic width (W) have a significant influence on the and ; to be specific, more zigzags and bigger periodic width obtain a worse cooling effect and consume less .
- The error of CFD values and predicted value by optimization is small, and an optimal structure produces an increase of 2.76% in and an increase of 44.8% in with respect to Ref case.
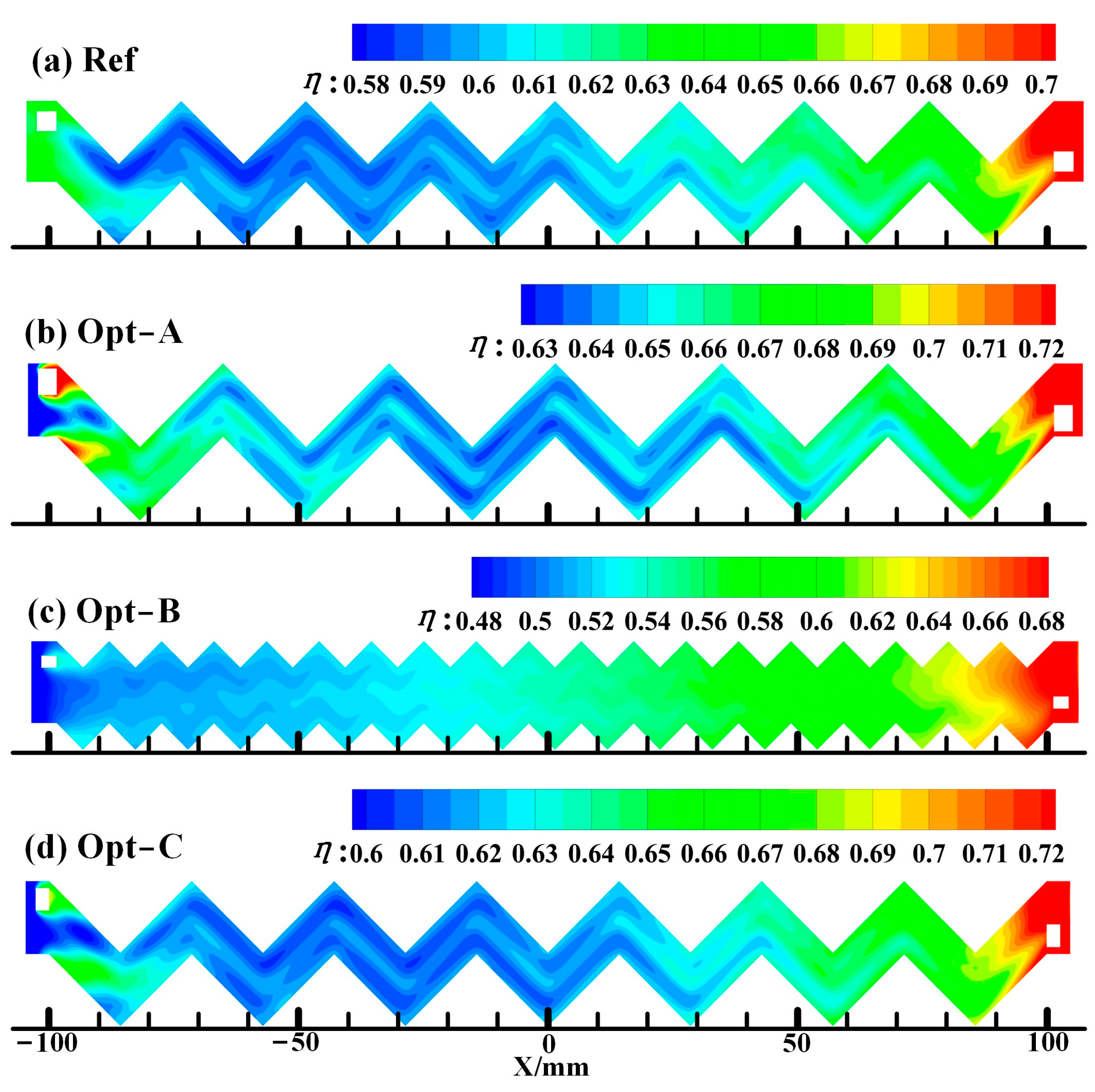
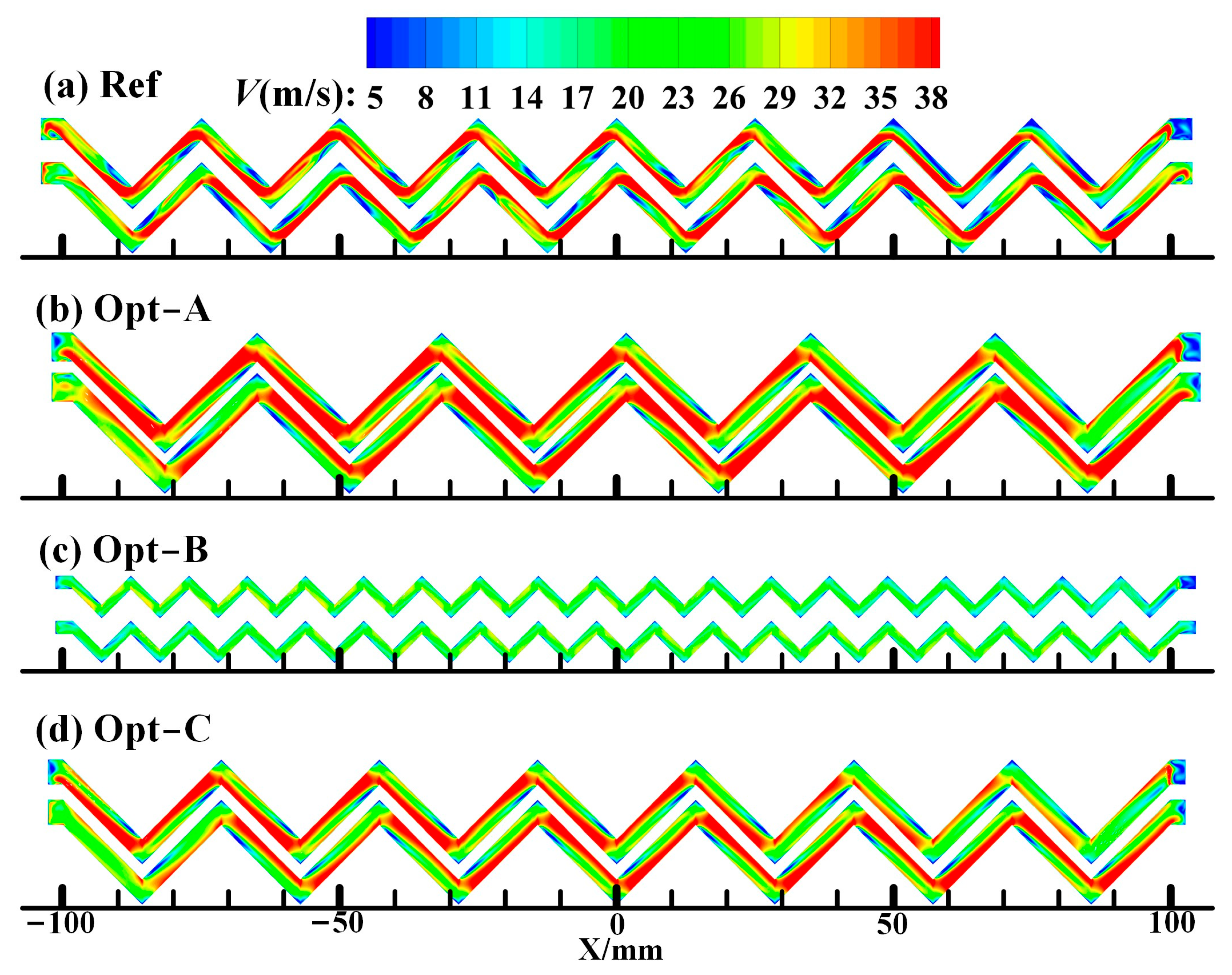
- The structure of Opt-A possesses a smaller W and bigger Z; it can be seen that Opt-A yields higher local . The structure of Opt-B possesses a bigger W and Z; it can be seen that along the direction, the cooling effectiveness decreases, and the phenomenon of high cooling effectiveness at the corresponding position of the internal channels disappears, which implies that the more zigzags, the less , and the worse the cooling effect.
- Topology optimization can automatically generate free-form and efficient structures, and this numerical method has been introduced into the field of thermal fluid structure design in recent years. It is expected that the flow and heat transfer characteristics of the channels can be further improved by topological optimization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuckerman, D.B.; Pease, R.F. High-performance heat sinking for VLS. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1981, 2, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqiuddin, N.H.; Saw, L.H.; Yew, M.C.; Yusof, F.; Ng, T.C.; Yew, M.K. Overview of micro-channel design for high heat flux application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Mahabunphachai, S. Feasibility investigations on a novel micro-manufacturing process for fabrication of fuel cell bipolar plates: Internal pressure-assisted embossing of micro-channels with in-die mechanical bonding. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Menon, S.; Lavrich, Z.; Wang, H.; Hagen, C.L. Design, simulation, and testing of a novel micro-channel heat exchanger for natural gas cooling in automotive applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinlola, M.A.; Shire, G.S.F.; Moss, R.W. The significance of scaling effects in a solar absorber plate with micro-channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 90, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradikazerouni, A.; Afrand, M.; Alsarraf, J.; Mahian, O.; Wongwises, S.; Tran, M.-D. Comparison of the effect of five different entrance channel shapes of a micro-channel heat sink in forced convection with application to cooling a supercomputer circuit board. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 150, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnasegaran, P.; Mohammed, H.A.; Shuaib, N.H.; Saidur, R. The effect of geometrical parameters on heat transfer characteristics of microchannels heat sink with different shapes. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 37, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshvaght-Aliabadi, M.; Rad, S.E.H.; Hormozi, F. Al2O3–water nanofluid inside wavy mini-channel with different cross-sections. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. Influence of geometric parameters on flow and heat transfer performance of micro-channel heat sinks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shi, M.; Wu, J. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of heat and fluid flow in noncircular microchannel heat sinks. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 36, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-C.; Jang, J.-H.; Yeh, H.-W.; Wu, M.-S. The heat transfer characteristics of liquid cooling heatsink containing microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.L.; Xia, G.D.; Liu, X.F.; Li, Y.F. Exergy analysis and performance evaluation of flow and heat transfer in different micro heat sinks with complex structure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 84, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, A.M.; Mohd-Ghazali, N.; Ahmad, R. Optimization of an ammonia-cooled rectangular microchannel heat sink using multi-objective non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA2). Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 48, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halelfadl, S.; Adham, A.M.; Mohd-Ghazali, N.; Maré, T.; Estellé, P.; Ahmad, R. Optimization of thermal performances and pressure drop of rectangular microchannel heat sink using aqueous carbon nanotubes based nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 62, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, S. Numerical study on layout of micro-channel heat sink for thermal management of electronic devices. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 88, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafai, K.; Zhu, L. Analysis of two layered micro!channel heat sink concept in electronic cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J. Numerical simulation of stacked microchannel heat sink with mixing-enhanced passive structure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 34, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-C.; Muezzin, F.N.A. Heat transfer of a parallel flow two-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 49, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-C.; Yan, W.-M.; Li, W.-P. Analysis of heat transfer characteristics of double-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3090–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-C.; Yan, W.-M.; Wang, X.-D.; Huang, Y.-X. Optimal design of geometric parameters of double-layered microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Zhao, J.Y.; Tseng, K.J. Parametric study on the performance of double-layered microchannels heat sink. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bakhit, H.; Fakheri, A. Numerical simulation of heat transfer in simultaneously developing flows in parallel rectangular ducts. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Teo, C.J.; Lee, P.S.; Chew, Y.T.; Shu, C. Fluid flow and heat transfer in wavy microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2760–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamanroy, Z.; Khoshvaght-Aliabadi, M. Analysis of straight and wavy miniature heat sinks equipped with straight and wavy pin-fins. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 146, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodnianská, Z.; Kotšmíd, S. Intensification of convective heat transfer in new shaped wavy channel configurations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 162, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Chander, S. Thermal performance of a fully developed serpentine wavy channel solar air heater. J. Energy Storage 2019, 25, 100896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, Z.L.; Lee, P.S.; Singh, P.K.; Mou, N. Investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer in wavy micro-channels with alternating secondary branches. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.A.; Gunnasegaran, P.; Shuaib, N.H. Numerical simulation of heat transfer enhancement in wavy microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakanova, A.; Keian, C.C.; Zhao, J. Performance improvements of microchannel heat sink using wavy channel and nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.A.; Gunnasegaran, P.; Shuaib, N.H. Influence of channel shape on the thermal and hydraulic performance of microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangthongsuk, W.; Wongwises, S. An experimental investigation on the heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of nanofluid flowing in microchannel heat sink with multiple zigzag flow channel structures. Exp. Therm Fluid Sci. 2017, 87, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Xia, G.D.; Li, Y.F.; Jia, Y.T.; Wang, J. Effects of structural parameters on fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics in microchannel with offset zigzag grooves in sidewall. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Xia, G.D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Jia, Y.T.; Zong, L.X. An experimental study on hydrothermal performance of microchannel heat sinks with 4-ports and offset zigzag channels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 152, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Fletcher, D.F.; Haynes, B.S. Experimental study of transient behaviour of laminar flow in zigzag semi-circular microchannels. Exp. Therm Fluid Sci. 2015, 68, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Leung, W.W.-F. Flow and mixing in rotating zigzag microchannel. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Cao, B.; Wu, X.; Zhao, X. The experimental study of the heat ransfer performance of a zigzag-serpentine microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 163, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, H.; Moghimi, M.A.; Meyer, J.P. Shape optimisation of wavy mini-channel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 122, 105172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampio, K.; Karvinen, R. Optimization of convectively cooled heat sinks. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 79, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, T.-H.; Yan, W.-M. Optimization of thermal resistance and bottom wall temperature uniformity for double-layered microchannel heat sink. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 93, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakanova, A.; Yin, S.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.M.; Leong, K.C. Optimization and comparison of double-layer and double-side micro-channel heat sinks with nanofluid for power electronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 65, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, T. A novel passive micromixer designed by applying an optimization algorithm to the zigzag microchannel. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, J.; Abbassi, A.; Saffar-Avval, M. Optimization of conjugate heat transfer in wavy walls microchannels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 82, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normah, G.-M.; Oh, J.-T.; Chien, N.B.; Choi, K.-I.; Robiah, A. Comparison of the optimized thermal performance of square and circular ammonia-cooled microchannel heat sink with genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 102, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Duan, D.; Xi, L.; Gao, J.; Li, Y. Flow and heat transfer characteristics in cooling lamilloy with internal MCs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 201, 123645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Z.; Xu, L.; Xi, L.; Gao, J.; Kou, W.; Jing, X. Study on Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics in Lamilloy Structure with Different Configurations of Internal Minichannels. Energies 2023, 16, 8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-D.; Kim, K.-Y. Surrogate based optimization of a laidback fan-shaped hole for film-cooling. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2011, 32, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Qu, M.; Ukkusuri, S. Optimizing the design of a solar cooling system using central composite design techniques. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijnen, J.P.C. Kriging metamodeling in simulation: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 192, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Moghimi, H.; Nezhad, A.E.; Agelidis, V.G.; Sharaf, A.M. Multi-objective economic emission dispatch considering combined heat and power by normal boundary intersection method. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 129, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Multi-objective genetic optimization of the heat transfer for tube inserted with porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

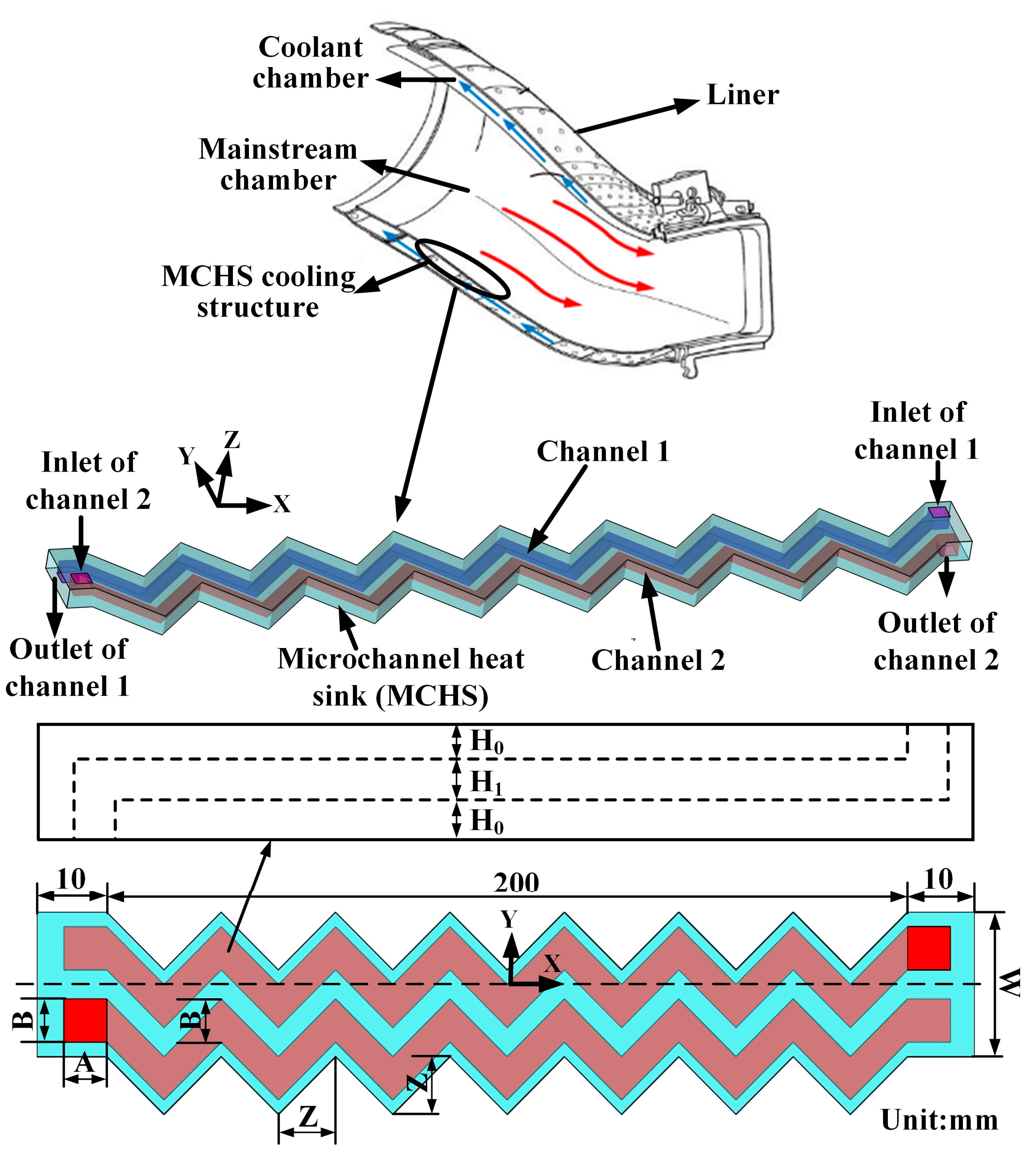
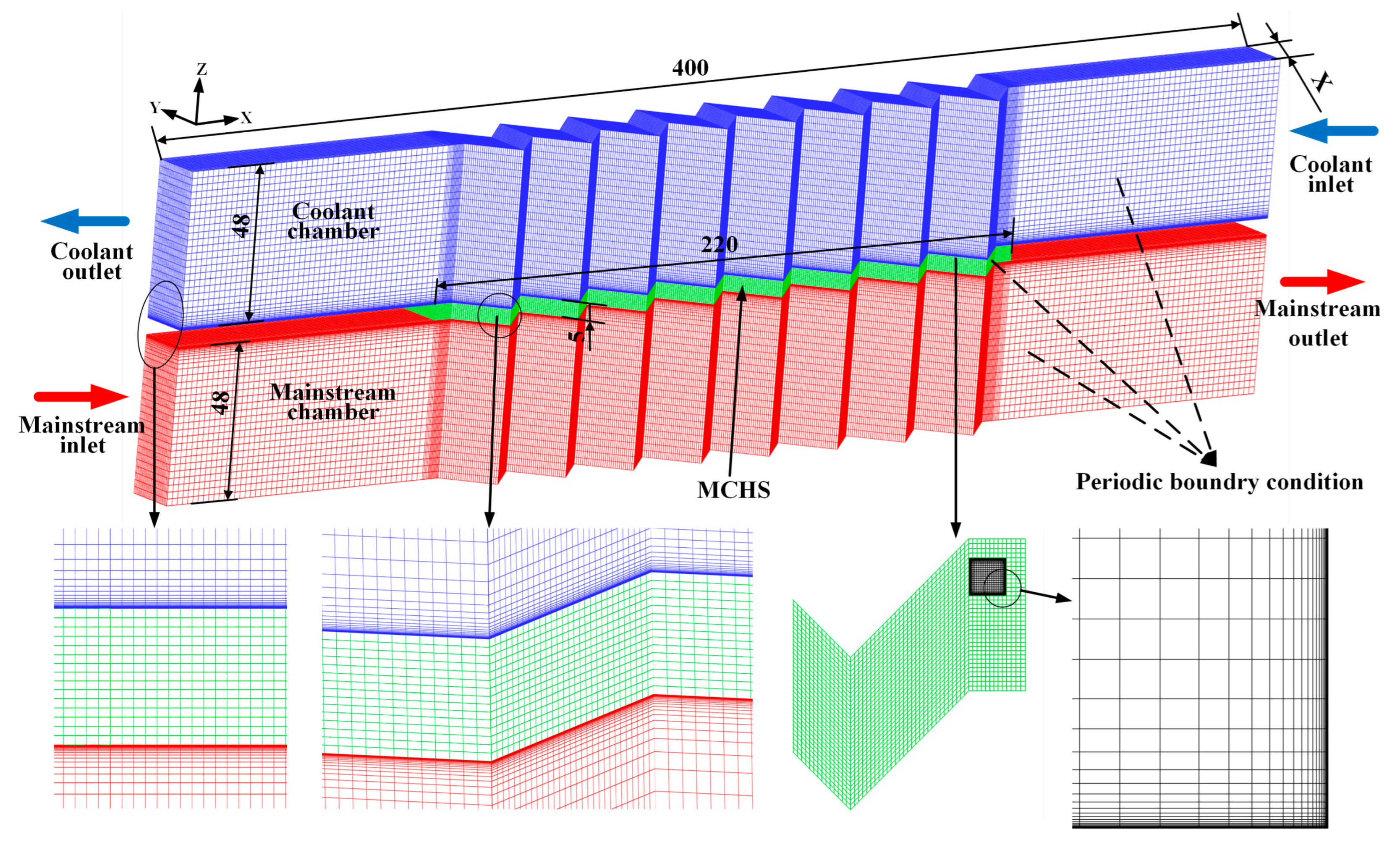

| Parameters | Lower Bound | Central Point | Upper Bound |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| B | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| W | 14 | 16 | 18 |
| H1 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 2 |
| Z | 5 | 12.5 | 20 |
| A | B | W | Z | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4 | 16 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.61553 | 0.00250 |
| 2 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 5 | 0.58179 | 0.00106 |
| 2 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 20 | 0.58975 | 0.00180 |
| 2 | 6 | 14 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.54361 | 0.00094 |
| 6 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 5 | 0.57071 | 0.00110 |
| 2 | 2 | 14 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.57944 | 0.00109 |
| 6 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 20 | 0.57902 | 0.00110 |
| 6 | 6 | 14 | 2 | 5 | 0.54381 | 0.00169 |
| 6 | 6 | 18 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.53975 | 0.00094 |
| 6 | 2 | 14 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.56171 | 0.00066 |
| 2 | 6 | 18 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.60485 | 0.00266 |
| 2 | 6 | 14 | 2 | 20 | 0.63661 | 0.00546 |
| 2 | 6 | 18 | 2 | 5 | 0.58008 | 0.00167 |
| 6 | 6 | 14 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.57931 | 0.00275 |
| 6 | 6 | 18 | 2 | 20 | 0.62764 | 0.00570 |
| 6 | 2 | 18 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.56954 | 0.00114 |
| 2 | 2 | 18 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.55592 | 0.00064 |
| 4 | 2 | 16 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.58126 | 0.00132 |
| 4 | 4 | 16 | 2 | 12.5 | 0.63305 | 0.00329 |
| 4 | 4 | 16 | 1.6 | 20 | 0.62767 | 0.00322 |
| 6 | 4 | 16 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.60016 | 0.00251 |
| 4 | 4 | 16 | 1.6 | 5 | 0.58557 | 0.00142 |
| 4 | 6 | 16 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.63262 | 0.00359 |
| 4 | 4 | 16 | 1.2 | 12.5 | 0.59487 | 0.00184 |
| 4 | 4 | 14 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.62507 | 0.00252 |
| 2 | 4 | 16 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.60784 | 0.00244 |
| 4 | 4 | 18 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.60890 | 0.00251 |
| 6 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 5 | 0.57986 | 0.00110 |
| 6 | 6 | 14 | 2 | 20 | 0.63098 | 0.00572 |
| 2 | 2 | 14 | 2 | 20 | 0.60358 | 0.00180 |
| 2 | 6 | 18 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.55515 | 0.00094 |
| 6 | 2 | 14 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.57955 | 0.00114 |
| 2 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 5 | 0.57189 | 0.00105 |
| 2 | 6 | 14 | 2 | 5 | 0.56640 | 0.00167 |
| 6 | 6 | 18 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.58139 | 0.00273 |
| 6 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 20 | 0.58894 | 0.00202 |
| 2 | 6 | 14 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.60821 | 0.00267 |
| 6 | 6 | 18 | 2 | 5 | 0.56392 | 0.00168 |
| 2 | 2 | 14 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.56251 | 0.00063 |
| 6 | 2 | 18 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.55513 | 0.00065 |
| 6 | 6 | 14 | 1.2 | 5 | 0.52198 | 0.00094 |
| 2 | 6 | 18 | 2 | 20 | 0.63001 | 0.00544 |
| 2 | 2 | 18 | 1.2 | 20 | 0.56951 | 0.00109 |
| N | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z | 20.0 | 16.67 | 14.29 | 12.5 | 11.11 | 10.0 | 9.09 | 8.33 | 7.69 | 7.14 | 6.67 | 6.25 | 5.88 | 5.56 | 5.26 | 5.0 |
| Design Variables | (kg/s) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | W | Z | CFD | NSGA-II | CFD | NSGA-II | |||
| Ref | median | 4 | 4 | 16 | 1.6 | 12.5 | 0.616 | — | 0.00250 | — |
| Opt-A | 3.76 | 5.23 | 14.51 | 1.91 | 16.67 | 0.658 | 0.664 | 0.00604 | 0.00552 | |
| Opt-B | 3.09 | 2.40 | 16.25 | 1.31 | 5.26 | 0.557 | 0.564 | 0.00061 | 0.00040 | |
| Opt-C | compromise | 2.72 | 4.51 | 14.49 | 1.55 | 14.29 | 0.633 | 0.636 | 0.00362 | 0.00320 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Chang, Z.; Xu, L.; Xi, L.; Gao, J.; Zheng, P.; Xu, R. Multi-Objective Optimization of the Microchannel Heat Sink Used for Combustor of the Gas Turbine. Energies 2024, 17, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040818
Zhang X, Yang T, Chang Z, Xu L, Xi L, Gao J, Zheng P, Xu R. Multi-Objective Optimization of the Microchannel Heat Sink Used for Combustor of the Gas Turbine. Energies. 2024; 17(4):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040818
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoming, Tao Yang, Zhenyuan Chang, Liang Xu, Lei Xi, Jianmin Gao, Penggang Zheng, and Ran Xu. 2024. "Multi-Objective Optimization of the Microchannel Heat Sink Used for Combustor of the Gas Turbine" Energies 17, no. 4: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040818
APA StyleZhang, X., Yang, T., Chang, Z., Xu, L., Xi, L., Gao, J., Zheng, P., & Xu, R. (2024). Multi-Objective Optimization of the Microchannel Heat Sink Used for Combustor of the Gas Turbine. Energies, 17(4), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040818







