The Effect of Bakery Waste Addition on Pine Sawdust Pelletization and Pellet Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
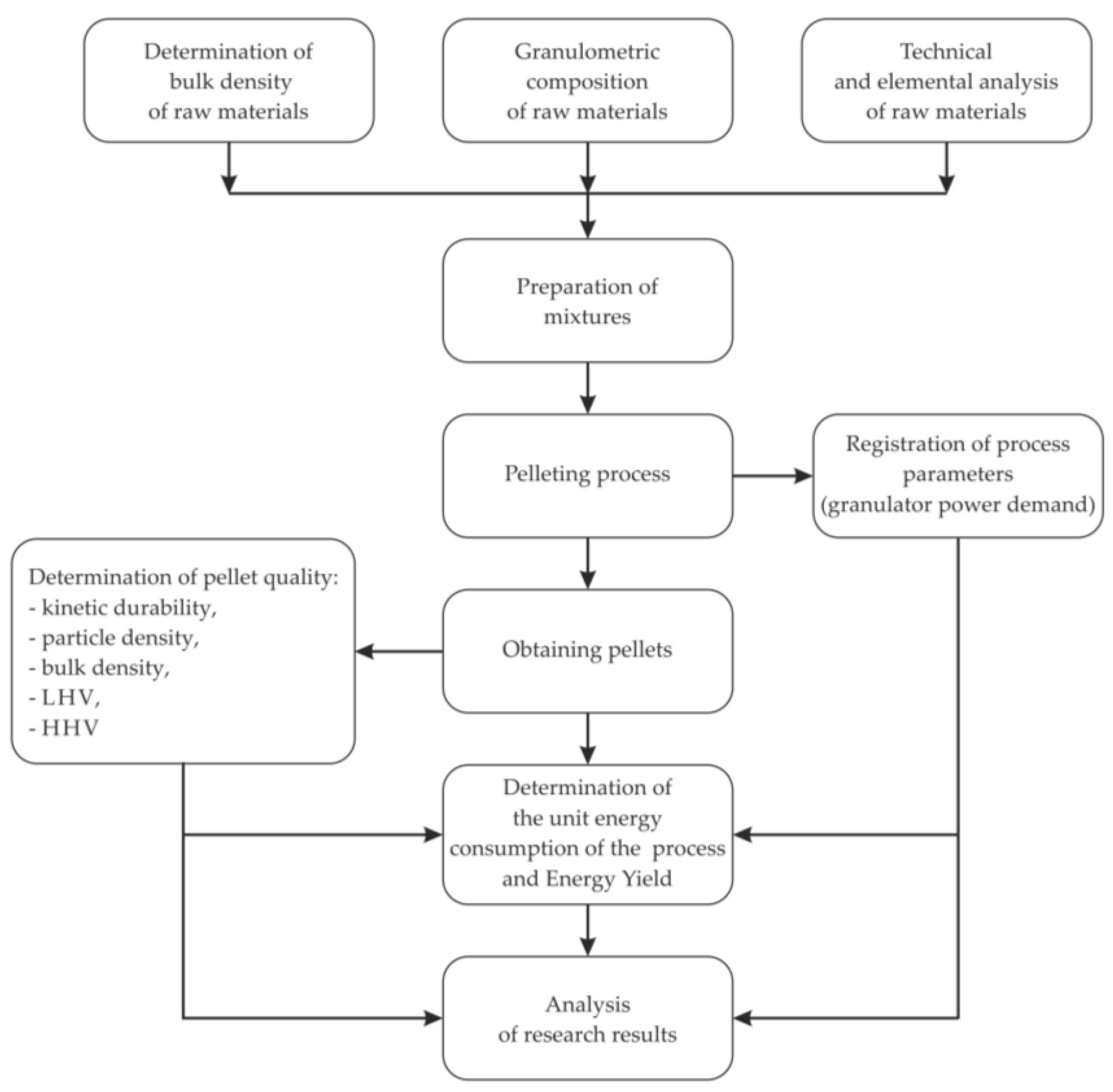
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Raw Materials
2.3. Bulk Density and Granulometric Composition of Raw Materials
2.4. Mixture Preparation
2.5. Pressure Agglomeration Process
2.6. Pellet Density and Bulk Density
2.7. Kinetic Durability of Pellets
3. Results and Discussion
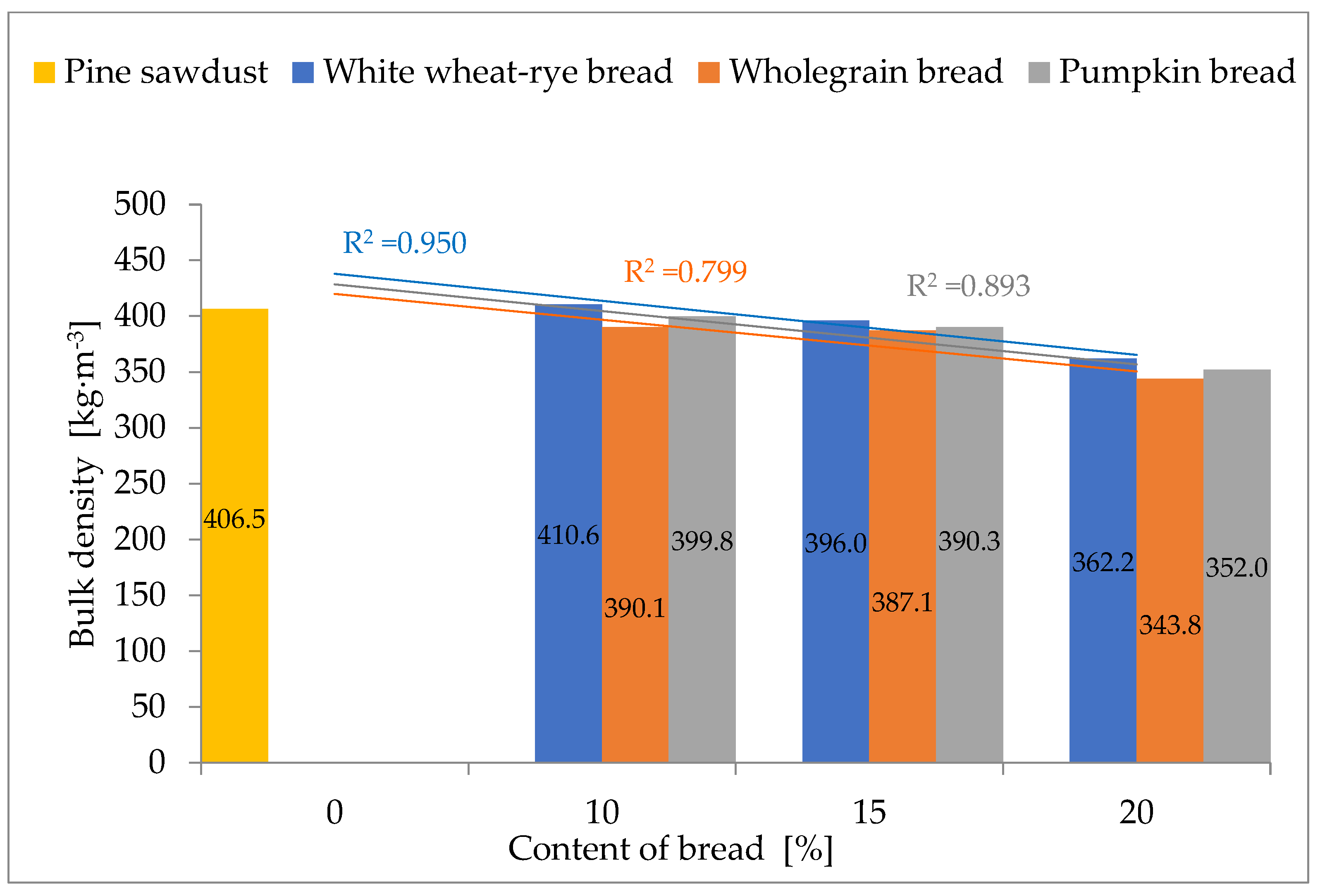
3.1. Properties of Raw Materials and Mixtures
3.2. Properties of Pellets
3.3. Energy Indicators
3.4. Economical Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zakari, A.; Khan, I.; Tan, D.; Alvarado, R.; Dagar, V. Energy Efficiency and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Energy 2022, 239, 122365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, D. Biofuels from Renewable Sources, a Potential Option for Biodiesel Production. Bioengineering 2022, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, M. Renewable Energy for Sustainable Development in India: Current Status, Future Prospects, Challenges, Employment, and Investment Opportunities. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2020, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W.; Nowak, M.; Bojarski, W. Anaerobic Digestion and Composting as Methods of Bio-Waste Management. Agric. Eng. 2023, 27, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweiri, F.; Khan, S.A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Saeed, M.; Zeyad, M.; Mashaly, R.; Hamad, S. Environment and Sustainability Approach to Manage Sweet Bakery Waste Product. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Pietrzak, W. Zagospodarowanie Odpadowego Pieczywa Do Produkcji Bioetanolu. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2011, 18, 105–118. [Google Scholar]
- Żukiewicz, K.; Słowik, T.; Dudziak, A. Preventing Food Waste in the Food Retail Sector in the Light of the Current Legislation in Poland. Agric. Eng. 2022, 26, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdeș, M.; Zăbavă, B.Ș.; Paraschiv, G.; Ionescu, M.; Dincă, M.N.; Moiceanu, G. Food Waste Management for Biogas Production in the Context of Sustainable Development. Energies 2022, 15, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, R.; Krebs, G. The Use of Bakery Wastes in Feedlot Rations for Sheep. Anim. Prod. Aust. 2002, 24, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tulaihan, A.A.; Najib, H.; Al-Eid, S.M. The nutritional evaluation of locally produced dried bakery waste (DBW) in the broiler diets. Pak. J. Nutr. 2004, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, M.R.; Dhakal, H.R. Bakery Waste Is an Alternative of Maize to Reduce the Cost of Pork Production. Nepal. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 20, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; He, H.; Chen, L.; Tian, X.; Hou, P.; Tang, J. A Novel Combination of Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Microbial Fuel Cell for Electricity Production from Bakery Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, M.; Stavraki, C.; Bousoulas, Ι.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M.; Mai, S.; Barampouti, E. Valorisation of Bakery Waste via the Bioethanol Pathway. Energy 2023, 280, 128185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narisetty, V.; Nagarajan, S.; Gadkari, S.; Ranade, V.V.; Zhang, J.; Patchigolla, K.; Bhatnagar, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Kumar, V. Process Optimization for Recycling of Bread Waste into Bioethanol and Biomethane: A Circular Economy Approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 266, 115784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narisetty, V.; Cox, R.; Willoughby, N.; Aktas, E.; Tiwari, B.; Matharu, A.S.; Salonitis, K.; Kumar, V. Recycling Bread Waste into Chemical Building Blocks Using a Circular Biorefining Approach. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 4842–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Brancoli, P.; Narisetty, V.; Wallace, S.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Dubey, B.K.; Kumar, G.; Bhatnagar, A.; Bhatia, S.K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Bread Waste–A Potential Feedstock for Sustainable Circular Biorefineries. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostocki, A.; Unyay, H.; Ławińska, K.; Obraniak, A. Granulates Based on Bio and Industrial Waste and Biochar in a Sustainable Economy. Energies 2022, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obidziński, S.; Hejft, R.; Dołżyńska, M. Badanie Procesu Granulowania Odpadów Zbożowych. Przem. Chem. 2017, 96, 2360–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Khan, N.; Mahajan, V.; Amrutkar, S.; Kumar, D. Bakery Waste: A Promising Unconventional Feed Ingredient for Poultry. IJLSAS 2022, 3, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.K.; Mandø, M.; Rosenørn, A.B. Review of Die Design and Process Parameters in the Biomass Pelleting Process. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerarattananoon, K.; Xu, F.; Wilson, J.; Ballard, R.; Mckinney, L.; Staggenborg, S.; Vadlani, P.; Pei, Z.; Wang, D. Physical Properties of Pellets Made from Sorghum Stalk, Corn Stover, Wheat Straw, and Big Bluestem. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, R.; Paczkowski, S.; Knappe, V.; Russ, M.; Wöhler, M.; Pelz, S. Effect of Feedstock Particle Size Distribution and Feedstock Moisture Content on Pellet Production Efficiency, Pellet Quality, Transport and Combustion Emissions. Fuel 2020, 263, 116662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- min Lee, S.; Ahn, B.J.; Choi, D.H.; Han, G.-S.; Jeong, H.-S.; Ahn, S.H.; Yang, I. Effects of Densification Variables on the Durability of Wood Pellets Fabricated with Larix kaempferi C. and Liriodendron tulipifera L. Sawdust. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, D.; Israelsson, S.; Öhman, M.; Dahlqvist, S.-A.; Gref, R.; Boman, C.; Wästerlund, I. Effects of Raw Material Particle Size Distribution on the Characteristics of Scots Pine Sawdust Fuel Pellets. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djatkov, D.; Martinov, M.; Kaltschmitt, M. Influencing Parameters on Mechanical–Physical Properties of Pellet Fuel Made from Corn Harvest Residues. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Meng, D.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X. Effects of Pelletizing Conditions on the Structure of Rice Straw-Pellet Pyrolysis Char. Fuel 2020, 264, 116909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubwama, M.; Yiga, V.A. Characteristics of Briquettes Developed from Rice and Coffee Husks for Domestic Cooking Applications in Uganda. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewiarz, M.; Mudryk, K.; Wróbel, M.; Frączek, J.; Dziedzic, K. Parameters Affecting RDF-Based Pellet Quality. Energies 2020, 13, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Mahajani, S.M.; Arora, A. Production and Utilization of Fuel Pellets from Biomass: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, N.Y.; Afzal, M.T. Effect of Particle Size on Mechanical Properties of Pellets Made from Biomass Blends. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Gil, M.; Rubiera, F.; Pevida, C. Pelletization of Wood and Alternative Residual Biomass Blends for Producing Industrial Quality Pellets. Fuel 2019, 251, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chandra, R.P.; Sokhansanj, S.; Saddler, J.N. Influence of Steam Explosion Processes on the Durability and Enzymatic Digestibility of Wood Pellets. Fuel 2018, 211, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Ogunfayo, I.; Hall, M.R.; Snape, C.; Quick, W.; Weatherstone, S.; Eastwick, C. Changes in Mechanical Properties of Wood Pellets during Artificial Degradation in a Laboratory Environment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 148, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooyserkani, Z.; Kumar, L.; Sokhansanj, S.; Saddler, J.; Bi, X.T.; Lim, C.J.; Lau, A.; Melin, S. SO2-Catalyzed Steam Pretreatment Enhances the Strength and Stability of Softwood Pellets. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukam, A.; Berghel, J.; Henrikson, G.; Frodeson, S.; Ståhl, M. A Review of the Mechanism of Bonding in Densified Biomass Pellets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 148, 111249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, T.R.; Nanda, S.; Meda, V.; Dalai, A.K. Densification of Waste Biomass for Manufacturing Solid Biofuel Pellets: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 231–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M.A.; Irfan, M.; Tabish, A.N.; Mahmood Khan, H.; Waqas Iqbal, M.; Fatima, H.; Iqbal, T. Effect of Pretreatment Parameters and Binder Concentration on the Densification of Wood Residue. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, e14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 14780:2017; Solid Biofuels—Sample Preparation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- EN 932-1:1996; Tests for General Properties of Aggregates—Part 1: Methods for Sampling. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 1996.
- Obidziński, S.; Dołżyńska, M.; Stasiełuk, W. Production of Fuel Pellets from a Mixture of Sawdust and Rye Bran; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 214, p. 012073. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17828; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Bulk Density. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 18847; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Particle Density of Pellets and Briquettes. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Thomas, M.; van der Poel, A.F.B. Physical Quality of Pelleted Animal Feed 1. Criteria for Pellet Quality. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 61, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-R-64834:1998; Pasze-Badanie Wytrzymałości Kinetycznej Granul. PKN: Warszawa, Poland, 1998.
- Jadwisieńczak, K.; Obidziński, S.; Choszcz, D. Assessment of the Physical and Energetic Properties of Fuel Pellets Made from Sage Waste Biomass with the Addition of Rye Bran. Materials 2022, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J.; Wasilewski, J.; Zając, G.; Kuranc, A.; Koniuszy, A.; Hawrot-Paw, M. Evaluation of Particulate Matter (PM) Emissions from Combustion of Selected Types of Rapeseed Biofuels. Energies 2022, 16, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaluk, O.; Havrysh, V.; Nitsenko, V. Energy and Environmental Assessment of Straw Production for Power Generation. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 228, 01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Várhegyi, G.; Chen, H.; Godoy, S. Thermal Decomposition of Wheat, Oat, Barley, and Brassica Carinata Straws. A Kinetic Study. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, J.; Zając, G.; Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J.; Kuranc, A. Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emission Levels during the Combustion of Selected Types of Agricultural Biomass. Energies 2022, 15, 7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermyagina, E.; Mendoza Martinez, C.; Lahti, J.; Nikku, M.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen-Mänttäri, M.; Vakkilainen, E. Characterization of Pellets Produced from Extracted Sawdust: Effect of Cooling Conditions and Binder Addition on Composition, Mechanical and Thermochemical Properties. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 164, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabjańska-Świeca, G.; Hrabak, J.; Zapała, E.; Patyna, I. Oznaczanie Zawartości Siarki w Biomasie Energetycznej z Zastosowaniem Wybranych Metod Analitycznych. Karbo 2013, 2, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Gaze, B.; Noszczyk, T.; Romański, L.; Dyjakon, A.; Kułażyński, M. Określenie Dominującego Mechanizmu Powstawania NOx w Kotłach Małej Mocy Zasilanych Biomasą. Przem. Chem. 2020, 99, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obernberger, I.; Thek, G. Physical Characterisation and Chemical Composition of Densified Biomass Fuels with Regard to Their Combustion Behaviour. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 27, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 14961; Solid Biofuels—Fuel Specifications and Classes—Part 1: General Requirements. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2010.
- Guo, F.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Gardy, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, X. Upgrading Agro-Pellets by Torrefaction and Co-Pelletization Process Using Food Waste as a Pellet Binder. Renew. Energy 2022, 191, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, K.C. Factors Influencing Pellet Quality. Feed Tech 2001, 5, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ståhl, M.; Berghel, J. Energy Efficient Pilot-Scale Production of Wood Fuel Pellets Made from a Raw Material Mix Including Sawdust and Rapeseed Cake. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4849–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, X.; Lei, W.; Huang, T.; Bai, C. Experimental Investigation on the Energy Consumption, Physical, and Thermal Properties of a Novel Pellet Fuel Made from Wood Residues with Microalgae as a Binder. Energies 2019, 12, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, J. Studia Nad Procesem Granulowania Mieszanek Paszowych. Rozprawy Naukowe; Wyd. AR w Lublinie: Lublin, Poland, 1989; Volume 113, ISBN 0860-4355. [Google Scholar]
- Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J.; Słowik, T.; Zając, G.; Blicharz-Kania, A.; Zdybel, B.; Andrejko, D.; Obidziński, S. Energy Parameters of Miscanthus Biomass Pellets Supplemented with Copra Meal in Terms of Energy Consumption during the Pressure Agglomeration Process. Energies 2021, 14, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.T.; Sepúlveda, F.J.; Arranz, J.I.; Montero, I.; Rojas, C.V. Analysis of Pelletizing from Corn Cob Waste. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 228, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiślak, K.; Sobczak, P.; Kraszkiewicz, A.; Niedziółka, I.; Parafiniuk, S.; Kuna-Broniowska, I.; Tanaś, W.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Obidziński, S. The Use of Lignocellulosic Waste in the Production of Pellets for Energy Purposes. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejft, R.; Obidziński, S. Ciśnieniowa Aglomeracja Materiałów Roślinnych-Innowacje Technologiczno-Techniczne. Część 1. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2012, 57, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.B.; Dubey, B.K. Co-Hydrothermal Carbonization of Food Waste with Yard Waste for Solid Biofuel Production: Hydrochar Characterization and Its Pelletization. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, R.F.; Kosieradzka-Federczyk, A. Paradoksy Ekologiczne. Odpady Miarą Sukcesu i Porażki Cywilizowanej Ludzkości; Wydawnictwo KSAP: Warszawa, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-61713-19-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zarębska, J. Gospodarka o Obiegu Zamkniętym Drogą Do Zrównoważonego Rozwoju. Syst. Wspomagania w Inż. Prod. 2017, 6, 286–295. [Google Scholar]
- SO 17225-2; Solid Biofuels—Fuel Specifications and Classes—Part 2: Graded Wood Pellets. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.



| Type of Added Bakery Waste | Mass Fraction of Bakery Waste [%] | Mass Fraction of Pine Sawdust [%] |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | 100 |
| White wheat–rye bread | 10 | 90 |
| 15 | 85 | |
| 20 | 80 | |
| Wholegrain bread | 10 | 90 |
| 15 | 85 | |
| 20 | 80 | |
| Pumpkin bread | 10 | 90 |
| 15 | 85 | |
| 20 | 80 |
| Share of Fraction Retained on the Sieve [%] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | >4 mm | 3.15 mm | 2 mm | 1 mm | 0.5 mm | 0.25 mm | 0.125 mm | <0.063 mm |
| Pine sawdust | 2.48 | 2.78 | 13.86 | 42.42 | 21.02 | 11.36 | 5.40 | 0.41 |
| White wheat–rye bread | - | - | 0.43 | 5.28 | 27.30 | 45.28 | 16.48 | 4.80 |
| Wholegrain bread | - | - | 1.32 | 20.44 | 46.48 | 29.40 | 1.96 | 0.18 |
| Pumpkin bread | - | - | 0.94 | 12.54 | 45.80 | 31.86 | 8.28 | 0.20 |
| Parameter | Unit | Pine Sawdust | White Wheat–Rye Bread | Wholegrain Bread | Pumpkin Bread |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk density | kg·m−3 | 116.6 ± 1.3 a | 577.0 ± 5.2 b | 554.4 ± 3.5 c | 526.7 ± 2.5 d |
| Moisture | % | 10.65 ± 0.03 a | 7.36 ± 0.01 b | 6.37 ± 0.04 c | 6.98 ± 0.02 c |
| Ash | % | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 2.67 ± 0.03 b | 3.06 ± 0.03 c | 3.36 ± 0.10 d |
| VM | % | 74.02 ± 0.05 a | 68.74 ± 0.26 b | 71.33 ± 0.38 c | 70.40 ± 0.27 d |
| FC | % | 14.88 ± 0.08 a | 21.23 ± 0.26 b | 19.24 ± 0.42 c | 19.26 ± 0.39 c |
| C | % | 47.40 ± 0.11 a | 39.52 ± 0.11 b | 40.33 ± 0.08 c | 39.31 ± 0.06 d |
| H | % | 7.196 ± 0.784 a | 8.537 ± 0.037 b | 8.488 ± 0.030 bc | 8.413 ± 0.050 c |
| N | % | 0.290 ± 0.027 a | 1.813 ± 0.029 b | 1.537 ± 0.045 c | 1.580 ± 0.037 c |
| S | % | 0.049 ± 0.006 a | 0.192 ± 0.006 b | 0.159 ± 0.007 c | 0.192 ± 0.009 b |
| HHV | kJ·kg−1 | 19,229 ± 38 a | 15,646 ± 73 b | 16,425 ± 39 c | 16,037 ± 60 d |
| LHV | kJ·kg−1 | 17,593 ± 38 a | 14,190 ± 79 b | 14,401 ± 39 c | 14,751 ± 59 d |
| Parameter | Unit | Pine Sawdust | White Wheat–Rye Bread | Wholegrain Bread | Pumpkin Bread | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content addition | % | 100 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 10 |
| Power demand | W | 2110 | 2045 | 1872 | 1773 | 1829 | 1798 | 1700 | 1805 | 1738 | 1642 |
| Energy consumption unit ECU | Wh·kg−1 | 52.75 | 51.12 | 46.80 | 44.32 | 45.72 | 44.95 | 42.51 | 45.12 | 43.45 | 41.05 |
| Decrease in ECU compared to pine sawdust | % | - | ↓ 3.08 | ↓ 11.28 | ↓ 15.97 | ↓ 13.32 | ↓ 14.79 | ↓ 19.43 | ↓ 14.45 | ↓ 17.63 | ↓ 22.18 |
| Decrease in ECU compared to the 10% mixture | % | - | - | ↓ 8.46 | ↓ 13.30 | - | ↓ 1.69 | ↓ 7.05 | - | ↓ 3.71 | ↓ 9.03 |
| LHV | kJ·kg−1 | 17,593 | 17,308 | 17,034 | 16,938 | 17,239 | 17,167 | 16,988 | 17,375 | 17,098 | 17,073 |
| Energy Yield | Wh·kg−1 | 4834 | 4757 | 4685 | 4661 | 4743 | 4724 | 4676 | 4781 | 4706 | 4701 |
| Decrease in EY compared to pine sawdust | Wh·kg−1 | - | ↓ 77 | ↓ 149 | ↓ 173 | ↓ 91 | ↓ 110 | ↓ 158 | ↓ 53 | ↓ 128 | ↓ 133 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obidziński, S.; Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J.; Zając, G.; Kowczyk-Sadowy, M.; Krasowska, M.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Cwalina, P.; Faszczewski, D.; Wasilewski, J. The Effect of Bakery Waste Addition on Pine Sawdust Pelletization and Pellet Quality. Energies 2024, 17, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020523
Obidziński S, Szyszlak-Bargłowicz J, Zając G, Kowczyk-Sadowy M, Krasowska M, Sienkiewicz A, Cwalina P, Faszczewski D, Wasilewski J. The Effect of Bakery Waste Addition on Pine Sawdust Pelletization and Pellet Quality. Energies. 2024; 17(2):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020523
Chicago/Turabian StyleObidziński, Sławomir, Joanna Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, Grzegorz Zając, Małgorzata Kowczyk-Sadowy, Małgorzata Krasowska, Aneta Sienkiewicz, Paweł Cwalina, Damian Faszczewski, and Jacek Wasilewski. 2024. "The Effect of Bakery Waste Addition on Pine Sawdust Pelletization and Pellet Quality" Energies 17, no. 2: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020523
APA StyleObidziński, S., Szyszlak-Bargłowicz, J., Zając, G., Kowczyk-Sadowy, M., Krasowska, M., Sienkiewicz, A., Cwalina, P., Faszczewski, D., & Wasilewski, J. (2024). The Effect of Bakery Waste Addition on Pine Sawdust Pelletization and Pellet Quality. Energies, 17(2), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020523







