Abstract
The European Commission has recently announced two guiding principles for EU product policy: First, product policy shall ensure that the performance of front-runner products in terms of sustainability becomes the norm, and second, the effectiveness of the current Ecodesign legislative framework is going to be significantly improved. Within this paper, already existing front-runner approaches and recent and ongoing product policy-making processes were reviewed. Based on the results, an EU front-runner approach is outlined. The presented approach (i) refers to performance levels of the best products already available on the market, (ii) aggregates information in existing databases, and (iii) works semi-automated. Together, all three attributes have a high potential to facilitate and accelerate the specification of appropriate minimum requirements for products at the EU level. This way, EU policymakers can deliver on the core objectives of the Ecodesign legislative framework much better. The basic mechanism and its legal entrenchment of the approach are illustrated for the energy efficiency of energy-related products. In addition, the Front-Runner Approach can be applied to any product group in the scope of the upcoming Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation and to a wide range of product-related minimum requirements, such as durability, reparability, or recycled content. The study’s objective is to suggest a tailor-made and dynamic approach to keep the EU product legislation up to date using innovative technology based on the investigation of current regulations and identify the gap. Experiences from three international case studies suggest that a front-runner approach to setting energy-performance standards can drive innovation and reduce energy consumption via promoting energy-efficient products; transparency about available products is one of the key factors and can be established by a database. The EU front-runner approach comprises extending the existing energy label database (or making use of the digital product passport) and introducing a legislative procedure that triggers changes in the energy efficiency requirements in the specific EU regulations if the database shows that a certain threshold value is reached. Challenges such as limited EU staff capacities and opportunities such as increased dynamic are discussed.
1. Introduction
Improving energy efficiency has been identified by the European Commission as a key dimension to moderate the energy demand and to cut greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to achieve a reduction in energy consumption by at least 32.5% by 2030 [1]. Following the principles of the Green Deal, the EU Commission is seeking to reduce the energy consumption of the EU even further by setting binding targets at the EU level, namely, primary energy consumption by 39% and final energy consumption by 36% by 2030 [2]. Towards achieving these targets, the EU Commission [1] classifies increasing energy efficiency as the easiest way of mitigating GHG emissions while also reducing consumer expenditures. On top of climate change threats, recent geopolitical events, such as the recent energy crisis in the course of the war in Ukraine jeopardizing energy security in Europe, have elevated the importance of energy efficiency measures.
Since 2005, the EU Commission has been equipped with the Ecodesign Directive 2009/125/EC [3] (formerly 2005/32/EC) to define Ecodesign requirements that improve the environmental performance of energy-related products. Energy-related products either consume energy or affect the energy consumption of other products or systems. The focus is to set energy efficiency-related minimum requirements for different product groups such as information and communications technology (ICT), home appliances, and investment goods [4,5,6,7,8]. The Directive aims to reduce energy consumption and thus contribute to the energy and climate goals of the EU; new requirements are currently being extended to resource efficiency. Today, 31 regulations with energy efficiency requirements are already implemented. Energy-related savings are regularly modeled and quantified within the framework of the “Ecodesign Impact Accounting” [9]. The savings achieved in relation to the total EU electricity consumption resulting from these minimum requirements for energy efficiency in 2020 were determined as 334 TWh [10]. This is roughly equivalent to the total European hydro (375 TWh) or wind (398 TWh) energy production in the same year [11]. However, the experience gathered so far from the implementation of product requirements and labeling has also shown that the existing saving potentials have not been effectively and efficiently exploited for many of the Ecodesign product groups [12].
Corresponding legislation needs years and preparatory and retards revision studies. As an example, the review process of the Ecodesign regulation on displays took 96 months compared to the theoretical minimum of 42 months [12]. Hinchliffe and Akkerman [13] analyzed the limitations of the resources that are available for conducting review studies. In some cases, the next level of the minimum requirements of a product group was achieved or even significantly exceeded by the products available on the market long before the requirements took effect. Therefore, dynamic updates of product requirements are fundamental to ensure that these requirements are efficient themselves and fulfill the intention of the legal framework. For example, the savings potential of >70% of the measures announced in the 3rd Ecodesign Working Plan 2016–2019 [14] had not been realized by the end of 2021 [15]. Possible reasons are the increasing number of regulated product groups, more types of product efficiency requirements (energy-, material-, and resource efficiency), and the complexity of products (digitalization, IoT, etc.).
The study’s objective is to suggest a tailor-made and dynamic approach to keep the EU product legislation up to date using innovative technology based on the investigation of current regulations and identify the gap. An initial outline has already been presented [16] and is further described and discussed.
This study starts with a description of the type of delays in the legislative process for setting Ecodesign requirements in the EU. In addition, existing dynamic front-runner approaches established in Japan, South Korea, and China are analyzed and summarized. Finally, an approach tailored to the EU context is proposed, which intends to be more dynamic and to keep EU product legislation up to date considering product innovation and recent market developments. This approach is then called the “EU front-runner”.
2. Methods
Two methodological approaches were combined in this study: First, preparatory studies and reviews in the wake of the revision of the Ecodesign legislative framework, as well as product-specific energy-efficiency requirements, were analyzed (Section 3.1). This step focused on market analysis and the criteria based on which minimum efficiency requirements are currently derived. Second, case studies of already existing front-runner policy approaches designed to stimulate the continuous improvement in energy efficiency of energy-related products were identified and analyzed in depth for their opportunities and obstacles (Section 3.2). The findings from the first two steps were then used as input for in-depth discussions among experts from the authors’ institutions with the aim of developing an EU front-runner approach. The results of this step are outlined in Section 3.3. Within this study, conceptual work is presented that may have to be refined for implementation. Therefore, opportunities and threats of the EU front-runner approach are discussed but need to be outlined in-depth in further studies.
3. Results
3.1. Missed Energy Saving Potentials in EU Product Policy
Until 2022, existing Ecodesign regulations in the EU have led to an annual 10% energy consumption reduction (170 Mt CO2eq) for the energy-related products in scope [17]. By 2030, these savings could reach 18% (266 Mt CO2eq) [9]. However, evidence from the implementation and review process of the Ecodesign Directive [3] and the Energy Labeling Regulation [18] has shown that for a significant number of covered product groups, the existing saving potentials have not always been effectively and efficiently tapped. This results primarily from unambitious requirements, delayed implementation and updating of requirements, and product non-compliance [3].
Concerning unambitious requirements, Siderius and Nakagami [19] argue that the benefits of a more ambitious Ecodesign scheme are large. Elevating energy savings by just a few percent could result in additional energy savings of 5–10 TWh. Letschert et al. [20] claim that an additional 2700 Mt CO2 could be saved between 2015 and 2030 if a selection of energy-intensive products in Europe, including, e.g., boilers, dryers, washing machines, and heat pumps, had to meet the level of Best-Available Techniques. Schlegel et al. and Scott et al. [21,22] argue that widening the scope of Ecodesign regulations from energy efficiency to including material efficiency has great emission reduction potential. Scott et al. [22] found that over 40% of production emissions (2061 Mt CO2eq) are embodied in material-intensive products consumed in the EU. Furthermore, product developments are not sufficiently taken into account in the process of developing minimum requirements, leading to products reaching the minimum requirement well in advance of the target year [12,19,23].
Delays in setting and reviewing minimum product requirements result in missed potential from products remaining exempt from the legislation, as well as products with low environmental performance that stay on the market. Consequently, the savings potential of more than 70% of the measures announced in the 3rd Ecodesign Working Plan 2016–2019 had not been realized by the end of 2021 [15]. Furthermore, the 4th Ecodesign and Energy Labeling Working Plan, which was expected to cover a period starting from 2020, was delayed by two years. In March 2022, it was finally published [24]. Schweitzer et al. [15] estimate that these delays equal up to 10 Mt CO2eq annually.
Non-compliant products still available on the market after passing the target year result in further missed energy efficiency potential. The EU Commission [25] estimates that in 2019, 10–25% of the products on the market were non-compliant. This would correspond to missed energy savings of 10% or 174.8 TWh/year by 2020 [12].
Many factors limit the exploitation of energy-saving potentials and contribute to these delays. The main reasons addressed by literature are time-consuming market analyses for new product groups and lengthy review processes [12,23,26,27], lack of complete or up-to-date information [13,19], workload and resource constraints [3,28], increased product complexity [13,16], conflicting stakeholder interests [23,27], a consolidated publication procedure instead of individual publication of measures once developed [12,26], and a lack of quick internal procedures within the EU Commission [28].
3.2. Existing Approaches
In the following sub-sections, existing approaches in different countries, including Japan, South Korea, and China, are briefly described.
3.2.1. The Japanese Top-Runner Program
Introduced in 1999, Japan’s Top-Runner Program is a regulatory scheme designed to stimulate the continuous improvement in energy efficiency of energy-consuming products in the use phase. It defines minimum energy efficiency targets for electronic consumer goods based on the energy efficiency level of the best-performing product available on the market. Starting with 11 product groups, it was expanded to 31 by 2013 [29]. The Japanese Top-Runner Program goes along with a labeling program, rewarding the best performers.
The program assesses product energy efficiency performance based on a weighted average approach, factoring in all products released to the market per producer [19]. Accordingly, underperforming products may be allowed onto the market as long as the average efficiency of the producer’s products surpasses the minimum requirement. In terms of non-compliance, the program administers a “name and shame” approach. Those producers not meeting the standards risk public denunciation. The Japanese culture and market structure, which are controlled by a few large domestic producers, likely contribute to the effectiveness of this measure [30].
Overall, the Top-Runner Program in Japan has contributed to accelerating energy efficiency improvement for all included electronic products. One specific success story is the case of air conditioners, for which a motor-efficiency increase of 95% was achieved. By 2004, around 70 models, equaling 2 million units, were taken out of production [29]. Kiruna [30] states that the program was successful in establishing uncontested and transparent efficiency targets, which has contributed to reducing investment risk primarily for first movers. However, Kiruna [30] also states that it is difficult to isolate the impacts of the program from already existing market trends. These include technological developments as a result of market competition and the increasing environmental awareness of consumers [31]. Additionally, rebound effects in the form of an increasing number of products per household, larger products, and intensified product usage seem to have increased overall energy use per household [31].
3.2.2. The South Korean Front-Runner Program
The South Korean Front-Runner Program dates back to 1992. The program is composed of various elements, including minimum energy standards, a certification program for high-efficiency products, and the e-Standby program.
Minimum energy standards are mandatory for 37 product groups and primarily target the worst performers. Performance is classified into five categories. The lowest category constitutes the minimum standard. Those not meeting the minimum standard risk penalties of up to EUR 15,000 or being excluded from the market. The certification for high-efficiency products targets the best performers of 45 product groups with a voluntary label. The e-Standby program applies to 22 product groups and issues a mandatory label to those products not meeting energy requirements while in the stand-by modus [32].
Jeong and Kim [33] argue that the South Korean Front-Runner Program is a good example of the effectiveness of consumer information as a policy measure motivating energy efficiency. For over two decades, various energy efficiency labels have guided and influenced consumer behavior. Consumers show an increased willingness to pay for products labeled with either a high-efficiency or voluntary stand-by label.
3.2.3. China’s Leading Energy Efficiency Program
In 2014, the Leading Energy Efficiency Program (LEP) was introduced in China. It complements the “TOP 10,000” Program, including mandatory efficiency targets for the most energy-intensive companies in 19 energy-intensive industries (e.g., steel, ethylene, synthesis ammonia, cement, plate glass, and electrolytic aluminum) [34]. The program aims to motivate technological developments using subsidies (direct subsidies and tax subsidies), which are awarded to the best performers in the market [26]. The selection of the best-performing products is initiated via a voluntary nomination by manufacturers. Selection criteria include energy efficiency as well as aspects related to the product technology and the manufacturer’s competence [35]. The LEP administrates subordinate, sector-specific programs and is combined with a labeling scheme [36].
Nie et al. [37] reason that the subsidies overall enhance the market focus for innovation and contribute to accelerating energy efficiency improvements. This is largely the result of the enhanced competition amongst the best performers. However, focusing on advancing the best performers in the market, this instrument has an adverse effect on the products with lower performance, contributing to a widened gap between the best and least performers. The authors also reason that in case of imperfect market information, the program is bound to fail. This could be the case, for example, when companies prioritize the confidentiality of information over the possibility to receive subsidies. In this context, the size and certainty of the granted subsidy affect the willingness of companies to cooperate.
3.2.4. Summary
The experiences from the three international case studies suggest that a front-runner approach to setting energy-performance standards can drive innovation and reduce energy consumption by promoting energy-efficient products. Several factors are key to the success of such systems. Among these factors is the need for transparency regarding the availability of products on the market. Publicly available databases can be one means to provide more transparency. Current policy developments on digital product passports can further support a sound data basis to support a front-runner approach. Furthermore, to address potential rebound effects, the process of setting minimum requirements needs to be quick and ambitious. The latter could be achieved using a semi- or fully-automated procedure. In the following, we propose such an approach.
3.3. Drafting an EU Front-Runner Approach
3.3.1. Data Sources
For establishing a front-runner approach, constantly updated databases on the efficiencies of products placed on the market are fundamental. Updated databases are needed to find the front-runners of the product group, i.e., the products with the best available performance. Starting from the products’ efficiencies, the new minimum requirement for the entire product group can be derived.
The EPREL (European Product Registry for Energy Labeling, https://eprel.ec.europa.eu/screen/home, accessed on 23 August 2023) database represents an efficient basis for this approach. The database is mandatory for 15 product groups for which an EU energy labeling obligation is in force. In addition, it includes a significant number of products with Ecodesign requirements. Finally, EPREL gives a comprehensive overview of the products on the EU market. A process to verify the database entries was recently discussed and implemented by the EU Commission, contributing to the validity of the data available via the platform. Therefore, it would be reasonable and expedient to use this already established infrastructure to provide the efficiencies of all product groups for which requirements under the Ecodesign legislative framework are set.
In addition to EPREL, further legislative developments might create data sources. One example is the digital product passport and the obligation to inform the EU Commission about the quantities of products placed on the market as part of the EU Commission’s proposal for sustainable product regulation [3]. For the time being, the focus could be on the aspect of energy efficiency for which methodologies in policy making are furthest developed. In the future, the principle could be applied to other environmental performance criteria as well.
3.3.2. Legislative Procedure
Up to now, the revision of minimum energy efficiency requirements requires a revision of the whole respective implementing regulation. This leads to the entire comitology procedure, including preparatory work/studies, which is finally very time-consuming and an additional burden according to personnel resources by the EU Commission, the member states, and all stakeholders involved in the process. It, therefore, seems to be adequate and appropriate to adapt the energy efficiency-related minimum requirements separately from the regular full revisions. As a consequence, the minimum energy efficiency requirements can be updated or continued at shorter intervals or even by using an annual omnibus regulation) Basic changes, such as the introduction of new measurement or calculation methods, would remain the subject of comprehensive revisions, which may then occur in longer intervals as is currently established. The dynamic approach can also be revised, e.g., if the development of the market occurs to be slower than expected.
3.3.3. Key Elements
Legislation should be able to react to product innovations and market developments in a reasonable time. In the context of energy-efficiency-related Ecodesign requirements, this could be achieved by a procedure that regularly updates the energy efficiency requirements of the implementing regulation of the specific product group, either via updating individual implementing regulations or an omnibus regulation for multiple product groups.
In a first step, the front-runner approach should be enabled by the framework regulation, i.e., the proposed future European Sustainable Product Regulation [3]. This comprises, for example, introducing a dynamic front-runner procedure in addition to the current static scheme to set performance requirements.
In the second step, the front-runner principle needs to be specified: The EU Commission needs to be assigned to annually assess the energy efficiency of product groups based on information from databases. Then, the EU Commission needs to be empowered to adapt the performance requirements according to the identified efficiency improvements in a simplified written procedure.
On this basis, we propose to establish the following parameters in the secondary legislation for each product group:
- A threshold representing a critical share of products on the market reached a certain efficiency level (e.g., an energy efficiency gap of x% between the front-runner products and the existing minimum requirement). When the threshold is reached, an adjustment of the energy efficiency requirement is triggered.
- A mechanism to specifically determine the new minimum requirements, calculated on the basis of the average energy efficiency of the top y% of the most efficient products.
- An appropriate transition period until the new requirement applies.
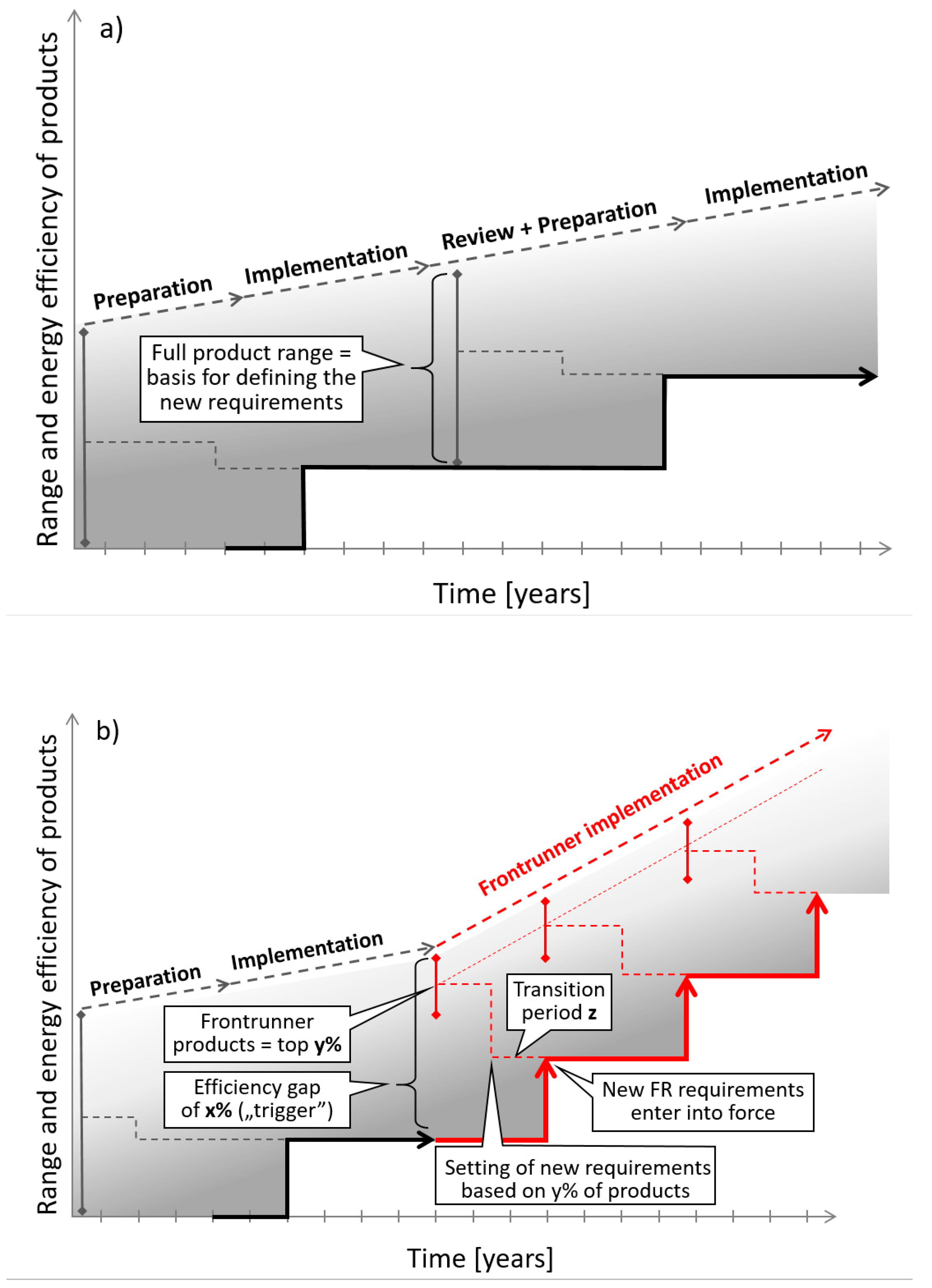
For example, At a certain point in time, the average efficiency of the products within a product group in the EPREL database is, compared to the current requirement, x% more efficient. Then, the requirement is tightened to the average energy efficiency of the y% most efficient products in the EPREL database. The new minimum requirements enter into force after a transition period of z years. Figure 1 illustrates this principle.
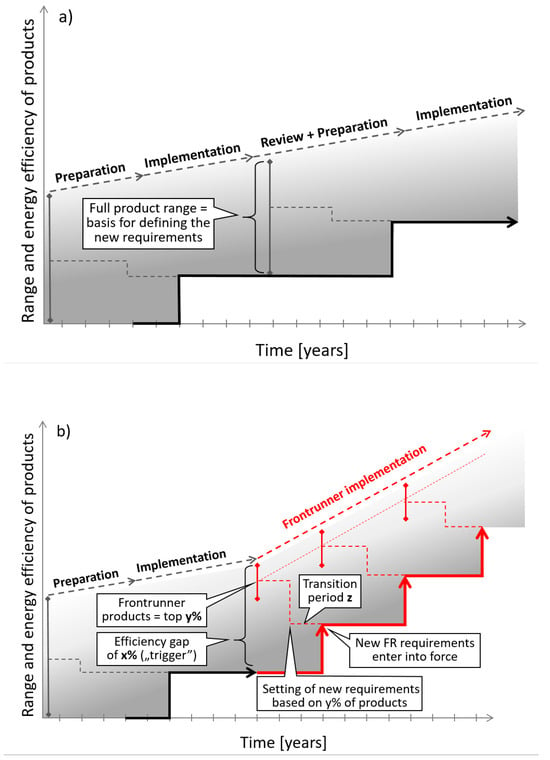
Figure 1.
Illustration of the proposed front-runner approach: Part (a) on top shows the current system leading to delays and reduced effectiveness. Part (b) below shows how the front-runner approach can dynamically increase energy efficiency in shorter cycles.
4. Discussion
As this approach is proposed for EU product policy for the first time, the challenges and opportunities associated with its implementation should be carefully considered as far as possible in advance without practical experience.
Its main benefit is the potential to increase the dynamic and, thus, the impact of Ecodesign requirements significantly, as outlined above. Both the missed energy and GHG savings, as well as obstacles in the legislative process, could be tackled. In consequence, more frequent updates of Ecodesign requirements could accelerate product development cycles. The described fast-track for energy efficiency requirements could also be applied to other environmental performance aspects, e.g., recyclability, pollutants, or substances of concern, where feasible. In this way, the front-runner approach could contribute to saving energy and related costs and GHG emissions, reducing resource consumption, and contributing to further environmental improvements needed in the face of accelerating climate change and the energy crisis.
On the contrary, it could be argued that implementing the front-runner approach might lead to a product group developing more slowly than expected or even to technical improvements being intentionally slowed down to manifest the market as it is. However, even for this worst-case scenario, taking the best products as a reference for the next step of performance requirements will exclude less efficient products from the market and thus increase the average efficiency of the remaining products. This increased efficiency will form the basis for the following step. In this way, the level of ambition will still steadily increase, but more slowly. In addition, one approach to avoid this challenge could be to introduce pre-defined steps at which the minimum requirement increases automatically in case a market develops much slower than expected. This backup would be equivalent to the current system of static requirements. Pre-defined steps can serve further important purposes: They provide manufacturers with planning security and provide a benchmark to which the current performance of the product group can be compared.
Regular reviews and updates will continue, but less often. Using this, technical progress in the form of, e.g., new features or better methods to measure energy efficiency can be taken into account in the regulatory process. At the same time, reducing the number of reviews increases the efficiency of the policy process. Additional aspects such as life cycle costs, unintended consequences for the affordability of products, or the performance with regard to other environmental aspects not regulated via the front-runner approach will still have to be investigated during reviews.
A major reason for delays in the current system is the technical complexity of some product groups like space heaters. This can be addressed in the front-runner approach by limiting in-depth technical discussions to full reviews, whereas dynamic updates follow a pre-defined pathway on specific issues. Streamlining such procedures will contribute to the period between raising requirements to be as short as possible and as long as necessary.
With regard to the data basis used to define the front-runner product(s), different approaches are possible. Using sales-weighted data would make the approach more reliable because common (i.e., with a higher market share) products have more impact. On the other hand, sales-weighted market data will slow down the dynamic because the most efficient products (front-runners) usually have small market shares. The market transformation would, therefore, be delayed.
Manipulations of the data basis to select front-runner products, e.g., using a high number of fake entries in existing databases, can still occur and have to be limited by the quality assurance measures established by the EU Commission when developing and maintaining the databases. Other manipulations can be resolved and mitigated during regular revisions.
In a dynamic approach, it needs to be ensured that products for the whole range of the product group are available, i.e., all “sizes” of products in the scope of a regulation. This can be addressed by not referring to a single front-runner product but to a group of best-performing products, as well as via setting the new requirements with a further discount from the front-runner group. Details for this will have to be specified for each product group individually.
The front-runner approach presented in this paper is not a “silver bullet”. Some challenges with regard to setting ambitious Ecodesign requirements remain especially aspects such as limited staff capacities or time-consuming internal procedures of the EU Commission. In addition, the introduction of the front-runner approach itself into the regulatory framework and its implementation for specific product groups will bind staff capacities, which would be relieved only subsequently. Regulating a new product group for which no data are yet available will still require a preparatory study to be done, as well as developing information requirements to create a database that can support a front-runner system.
In any case, the front-runner approach will not result in uncontrollable automatism because a regulatory procedure will still be necessary. This means the EU Commission will remain in charge by having to adopt a front-runner amendment after consulting the respective stakeholders during the established procedures.
5. Conclusions
In contrast to the current procedure in product regulation, the presented front-runner approach would set minimum requirements in relation to the best-performing products available on the market. This results in requirement levels always being up to date and in line with product innovations and market developments. The approach, therefore, corresponds to the dynamic of the market itself. This enables (i) a more effective and efficient implementation of Ecodesign regulations as today, (ii) significant workload reduction according to the revision procedures (internal procedures may be streamlined, too), as well as (iii) an improvement of the predictability of the overall legislative process for all related stakeholders. However, some challenges in the standard-making process are not addressed by an EU front-runner approach, such as limited staff capacities and time-consuming administrative processes. Similarly, initial preparatory studies are still required, at least to create a database using information requirements that can subsequently support a front-runner approach.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S., M.-C.S., L.R., D.J. and R.M.; Methodology, J.S., M.-C.S., L.R., D.J. and R.M.; Investigation, J.S., M.-C.S., L.R., D.J. and R.M.; Writing—original draft, J.S., M.-C.S. and L.R.; Writing—review and editing, F.H.; Visualization, J.S.; Supervision, T.E., D.J. and F.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the German Environment Agency, grant number 3719373050.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
L.R., F.H., R.M., D.J., and M.-C.S. declare no conflict of interest. As representatives of the funding organization, T.E. and J.S. contributed, as stated above, their experience in the ecodesign processes, however, strictly based on scientific principles according to the internal rules and procedures of the German Environment Agency (Umweltbundesamt), a federal scientific agency.
References
- European Commission. Clean Energy for All Europeans Package. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/topics/energy-strategy/clean-energy-all-europeans-package_en (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and of The Council on Energy Efficiency (Recast) COM/2021/558 Final. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52021PC0558 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. Proposal for a Regulation Establishing a Framework for Setting Ecodesign Requirements for Sustainable Products and Repealing Directive 2009/125/EC. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/publications/proposal-ecodesign-sustainable-products-regulation_en (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/2021 of 1 October 2019 Laying down Ecodesign Requirements for Electronic Displays Pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02019R2021-20191205 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 813/2013 of 2 August 2013 Implementing Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with Regard to Ecodesign Requirements for Space Heaters and Combination Heaters. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32013R0813 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/2023 of 1 October 2019 Laying down Ecodesign Requirements for Household Washing Machines and Household Washer-Dryers Pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02019R2023-20191205 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/1781 of 1 October 2019 Laying down Ecodesign Requirements for Electric Motors and Variable Speed Drives Pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32019R1781 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/424 of 15 March 2019 Laying down Ecodesign Requirements for Servers and Data Storage Products Pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32019R0424 (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Van Holsteijn en Kemna BV. Ecodesign impact Accounting Annual Report 2020—Overview and Status Report. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/568cac02-5191-11ec-91ac-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. Ecodesign and Energy Labelling: Key Tools for Reducing Consumers’ Energy Bills and EU Use of Fossil Fuels. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/ecodesign-and-energy-labelling-key-tools-reducing-consumers-energy-bills-and-eu-use-fossil-fuels-2021-dec-08_de (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Eurostat, Statistical Office of the European Communities. Production of Electricity and Derived Heat by Type of Fuel—Product Data—2022. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-datasets/product?code=nrg_bal_peh (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- European Court of Auditors. EU Action on Ecodesign and Energy Labelling: An Important Contribution to Greater Energy Efficiency Reduced by Significant Delays and Non-Compliance—Special Report 2020. Available online: https://www.eca.europa.eu/Lists/ECADocuments/SR20_01/SR_Ecodesign_and_energy_labels_EN.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Hinchliffe, D.; Akkermann, F. Assessing the review process of EU Ecodesign regulations. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission Ecodesign Working Plan 2016-2019 COM/2016/0773 Final. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52016DC0773 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Schweitzer, J.P.; Toulouse, E.; Zill, M. Delays in Ecodesign Implementation Threaten 55% Climate Target and Cost Citizens Billions. Available online: https://www.coolproducts.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/EEB_ECOS-Delays-in-ecodesign-report.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Schuberth, J.; Ebert, T.; Schlegel, M.C.; Rödig, L.; Jepsen, D. A Front-Runner Approach for EU Product Policy—Impulse for Raising Untapped Energy Saving Potentials. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/a-front-runner-approach-for-eu-product-policy (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- European Commission. Green Deal: New Proposals to Make Sustainable Products the Norm and Boost Europe’s Resource Independence. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_22_2013 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) 2017/1369 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 July 2017 Setting a Framework for Energy Labelling and Repealing Directive 2010/30/EU. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2017/1369/oj (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Siderius, P.J.S.; Nakagami, H. A MEPS is a MEPS is a MEPS: Comparing Ecodesign and Top Runner schemes for setting product efficiency standards. Energy Effic. 2013, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letschert, V.; Desroches, L.-B.; Ke, J.; McNeil, M. Energy efficiency—How far can we raise the bar? Revealing the potential of the best available technologies. Energy 2013, 59, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, M.C.; Akkerman, F. One step back, two steps forward—Resource efficiency requirements within Ecodesign. In Proceedings of the ECEEE 2019 Summer Study on Energy Efficiency: Is Efficient Sufficient? Belambra Les Criques, Toulon/Hyères, France, 2 July 2019; pp. 1553–1562. Available online: https://www.eceee.org/library/conference_proceedings/eceee_Summer_Studies/2019/9-improving-energy-efficiency-in-ict-appliances-and-products/one-step-back-two-steps-forward-resource-efficiency-requirements-within-ecodesign/2019/9-004-19_Schlegel.pdf/ (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Scott, K.; Roelich, K.; Owen, A.; Barrett, J. Extending European energy efficiency standards to include material use: An analysis. Clim. Policy 2018, 5, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Evaluation of the Energy Labelling and Ecodesign Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52015SC0143 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission Ecodesign and Energy Labelling Working Plan 2022-2024 2022/C 182/01. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52022XC0504(01) (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Commission. New Energy Efficiency Labels Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/MEMO_19_1596 (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- European Parliamentary Research Service (EPRS). Revision of the Ecodesign Directive: Briefing, Implementation Appraisal. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2022/699502/EPRS_BRI(2022)699502_EN.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Siderius, H.P. Speeding up Adopting Ecodesign and Energy Labelling Measures—Analysis, Challenges and Solutions. eceee 2013 Summer Study on Energy Efficiency: Rethink, Renew, Restart. 2013, pp. 1637–1649. Available online: https://www.eceee.org/library/conference_proceedings/eceee_Summer_Studies/2013/6-appliances-product-policy-and-ict/speeding-up-adopting-ecodesign-and-energy-labelling-measures-analysis-challenges-and-solutions/2013/6-068-13_Siderius.pdf/ (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Molenbroek, E.; Smith, M.; Groenenberg, H.; Waide, P.; Attali, S.; Fischer, C.; Fong, J. Final Technical Report. Evaluation of the Energy Labelling Directive and Specific Aspects of the Ecodesign Directive ENER. C3/2012-523. Ecofys: Utrecht. 2014. Available online: http://www.energylabelevaluation.eu/tmce/Final_technical_report-Evaluation_ELD_ED_June_2014.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). Top Runner Programm: Developing the world’s Best Energy-Efficiency Appliance and More. Available online: https://policy.asiapacificenergy.org/sites/default/files/toprunner2015e.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Kimura, O. Japanese Top Runner Approach for Energy Efficiency Standards; Socio-Economic Research Centre, Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry: Tokyo, Japan, 2010; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, N.; Matsumoto, S. An examination of losses in energy savings after the Japanese Top Runner Program? Energy Policy 2019, 124, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOTIE & Korea Energy Agency. Korea Energy Efficiency Policies: Korea’s Energy Standards & Labeling. Available online: https://eep.energy.or.kr/download/Korean%20Energy%20Efficiency%20Policies%20(2015).pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Jeong, G.; Kim, Y. The effects of energy efficiency and environmental labels on appliance choice in South Korea. Energy Effic. 2015, 3, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Charter. China Energy Efficiency Report: Protocol on Energy Efficiency and Environmental Aspects. Available online: https://www.energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/EERR/EER-China_ENG.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Liang, X.; Zhu, C. Design of China Leading Energy Efficiency Program (LEP) for Equipment and Appliances and Comparative Study of International Experience on Super-Efficient Products. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 94, 012143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Gao, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Ju, Y.; Shen, X. Top-runner incentive scheme in China: A theoretical and empirical study for industrial pollution control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 23, 29344–29356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, P.Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.H. Top Runner program in China: A theoretical analysis for potential subsidies. Energy Strategy Rev. 2018, 21, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).