Abstract
NOx is one of the main sources of pollutants for motor vehicles. Nowadays, many diesel vehicle manufacturers may use emission-cheating equipment to make the vehicles meet compliance standards during emission tests, but the emissions will exceed the standards during actual driving. In order to strengthen the supervision of diesel vehicles for emission monitoring, this article intends to establish a model that can predict the transient emission characteristics of heavy-duty diesel vehicles and provide a solution for remote online monitoring of diesel vehicles. This paper refers to the heavy-duty vehicle National VI emission regulations and uses vehicle-mounted portable emission testing equipment (PEMS) to conduct actual road emission tests on a certain country’s VI heavy-duty diesel vehicles. Then, it proposes a new feature engineering processing method that uses gray correlation analysis and principal component analysis to eliminate invalid data and reduce the dimensionality of the aligned data, which facilitates the rapid convergence of the model during the training process. Then, a double-hidden-layer BP (Back propagation) neural network was established, and the improved gray wolf algorithm was used to optimize the threshold and weight of the neural network, and a heavy-duty diesel vehicle NOx emission prediction model was obtained. Through the training of the network, the root mean square error (RMSE) of the improved model on the test set between the predicted value and the true value is 1.9144 (mg/s), and the coefficient of determination (R2) is 0.87024. Compared with single-hidden-layer network and double-hidden-layer BP neural network models, the accuracy of the model has been improved. The model can well predict the actual road NOx emissions of heavy-duty diesel vehicles.
1. Introduction
With the continuous development of China’s economy, the number of automobile owners is increasing day by day, leading to a pressing environmental issue: automobile exhaust emissions. The Annual Report on Environmental Management of China’s Mobile Sources (2021) released by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment revealed that in 2020, diesel trucks emitted a staggering 481.7 million tons of nitrogen oxides (NOx), accounting for 78.5% of total automobile emissions [1]. In light of the national comprehensive clean diesel vehicle and clean diesel engine action, it has become particularly crucial to implement effective testing of heavy-duty diesel vehicle emissions. There are three primary emission testing techniques for heavy-duty vehicles: engine bench test, actual road test, and chassis dynamometer test [2,3,4]. However, engine bench tests and chassis dynamometer tests, being conducted indoors, may not fully represent the real emissions of the vehicles [5,6]. To address this limitation, this paper utilizes a portable emission testing system (PEMS) installed on heavy-duty diesel vehicles to measure the genuine emission levels during real-world driving conditions and to monitor the emissions of heavy-duty diesel vehicles [7,8]. The use of PEMS on heavy-duty diesel vehicles offers a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of emissions, providing valuable insights for effective environmental management and emissions reduction strategies.
Diesel vehicle emissions are affected by multiple factors, including engine operating conditions, fuel mixture, etc. This complexity and nonlinearity make it challenging to build accurate prediction models. In the RDE experiment, in addition to the factors of the vehicle itself, other related factors are the driver’s driving behavior, road conditions, and environmental conditions. The traditional model will be limited by various factors when predicting emissions, but the data-driven model will not have such limitations. Tang et al. [9] established a BP neural network model based on engine bench test data, using fuel consumption, load, and other parameters as inputs, and CO, HC, and NOx as outputs. The model’s predicted values for CO, HC, and NOx showed a strong agreement with the experimental values, indicating better consistency. Fu et al. [10] employed an artificial neural network algorithm and reported that the root mean square error between the values of fuel consumption rate and gaseous emissions predicted by the trained network closely approximated zero when compared to the experimentally measured values. Furthermore, Wang et al. [11] devised a fusion method combining mutual information (MI) and BP neural network (BPNN). This approach involved sorting all the measured signals based on MI values and categorizing the most significant parameters according to their physical importance. The inputs for the model were then selected from these categorized groups, resulting in a reduction of approximately 15% in mean absolute deviation and root mean square error compared to the static MAP (Mutual Information Analysis and Projection) method. The various studies mentioned above demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of neural network models in predicting and analyzing pollutant emissions from diesel vehicles, contributing to the development of better emission control strategies and environmental protection efforts. Jonghak Lee et al. [12] used PEMS equipment to conduct RDE tests on diesel engines on real roads, collected road environment, atmosphere, and post-processing performance factors, and used RDE test data and artificial neural networks with various statistical parameters for evaluation. The results show that the artificial neural network can give a good prediction of pollutant emissions. Hao Yu et al. [13] established a NOx and PN prediction model based on the GA-BP algorithm to solve the problem of expensive road testing of light vehicles. The model’s predicted values of NOx and PN have a high degree of linear correlation with the true values.
The data-driven emission model [14,15,16,17,18] has the advantages of a short development cycle and low development cost, effectively reducing the time and cost involved in the development process. Part of the above research is based on deep learning models built for bench tests, which may not be applicable to actual road emissions of complete vehicles. Part of the research is on deep learning models built for actual roads. However, when selecting model input parameters, the number of input feature parameters selected is less, which cannot correctly reflect the actual operating conditions of the vehicle. This article selects 16 parameters related to the vehicle operating conditions as model inputs, and uses gray correlation and principal component analysis to select, eliminate, and reduce the dimensionality of the input features. Most of the models studied above are based on the single-hidden-layer BP network. This paper proposes a double-hidden-layer BP neural network, which has better nonlinear fitting capabilities and a wider range of applications. It also proposes an improved gray wolf optimization algorithm to optimize this double-hidden-layer BP neural network, establishing a model of NOx emission levels of heavy-duty diesel vehicles. This model can provide a reference for online supervision of heavy-duty diesel vehicle emissions and prevent diesel vehicle emissions cheating, which has certain theoretical significance and engineering value.
2. NOx Emission Prediction Model
2.1. Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm
The Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) [19], introduced by Mirjalili in 2014, is a novel meta-inspired search algorithm, similar to the Genetic Algorithm [20] and Particle Swarm Algorithm [21]. The algorithm draws inspiration from the predatory behavior of gray wolves in nature. It exhibits several desirable characteristics, such as strong global search ability, minimal parameter adjustments, robust convergence, and ease of implementation, making it effective in finding optimal solutions.
Mirjalili conducted tests to verify the performance of the GWO algorithm compared to the Particle Swarm and Genetic Algorithms in terms of optimization functions. The results demonstrated that the GWO algorithm outperformed the other two algorithms in terms of both convergence speed and algorithm stability.
Gray wolves in nature are social carnivores at the top of the food chain. Figure 1 exhibit a well-organized social structure with a strict hierarchy and division of labor. The social hierarchy of gray wolves is strictly divided into four categories, which are defined as , , and wolves. The hunting process mainly includes three processes: surrounding, hunting, and attacking. The ω wolf completes this behavior under the joint guidance of , , and wolves. The specific principles are as follows.
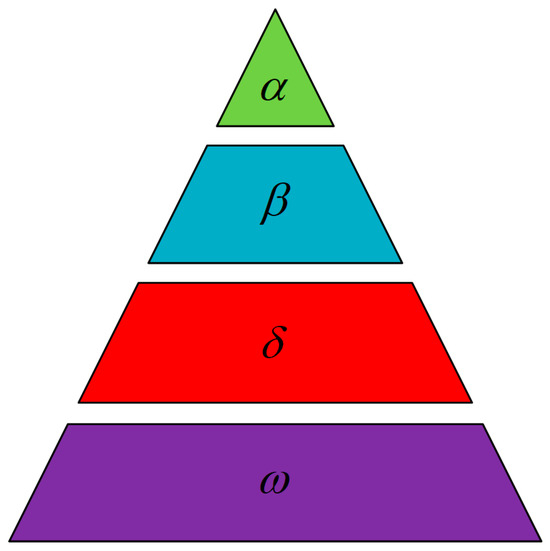
Figure 1.
Social hierarchy of the gray wolf.
The hunting process of the gray wolf consists of three main stages: encirclement, hunting, and attacking. The ω wolf, along with the α, β, and δ wolves, is jointly guided through this behavior.
2.1.1. Surrounding Prey
The gray wolf population size is defined as N, and the spatial dimension of activity is defined as D. The gray wolf population is doted by , where represents the position of the i-th gray wolf in the population, with each solution indicating the location of an individual wolf. The mathematical model for the hunting behavior of gray wolves is denoted as follows:
In the formula, D represents the distance between the gray wolf and the prey. denotes the location of the gray wolf after generations, while represents the location of the gray wolf after t iterations. The hunting process involves pursuing a target, denoted as , and represents the number of iterations. C and A are coefficients representing group synergy, and they are represented by the following equations:
In the formula, the magnitude of parameter is expressed as a linear decrease from 2 to 0 over the course of the iterations. The values of and are random numbers between [0, 1]. denotes the current iteration number, while denotes the maximum number of iterations.
2.1.2. Hunting
The position of prey is the global optimal solution. The wolves can quickly surround the prey under the guidance of α, β, and δ wolves, and adjust the position of ω wolves in the wolf pack. The mathematical model is as follows.
In the formula, , , and respectively represent the distances between the α, β, and δ wolves and other wolves. , , and represent the current positions of the α, β, and δ wolves, respectively. , , and are random numbers, and represents the current position of an individual gray wolf in the pack.
In the formula, , , and represent the distances that individual ω wolves in the pack move towards the α, β, and δ wolves, respectively. represents the final position that the ω wolf will reach after this movement during the generation as shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
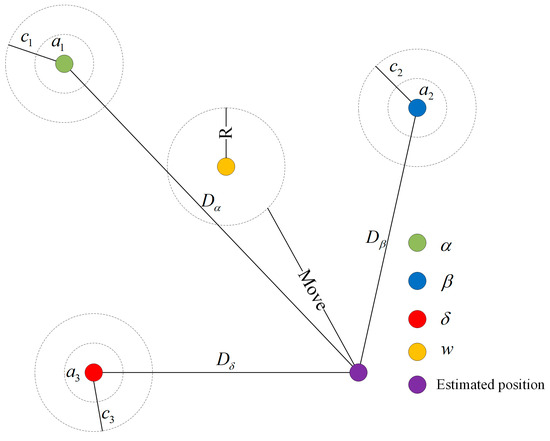
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of gray wolf location update in the gray wolf algorithm.
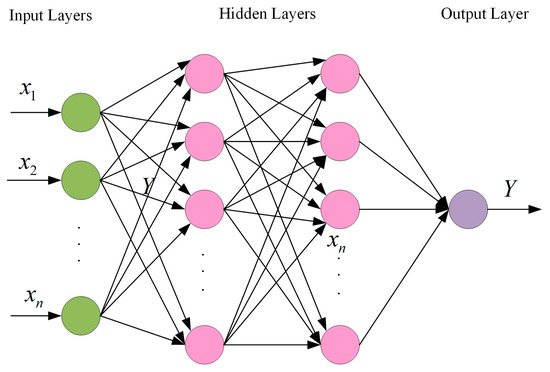
Figure 3.
Structure of a double-hidden-layer BP neural network.
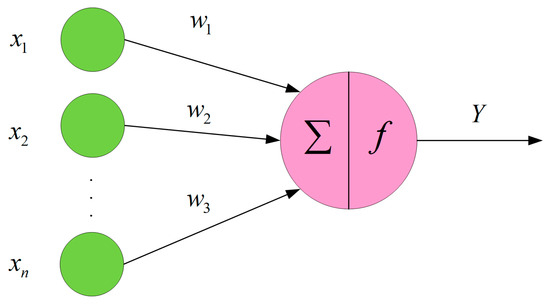
Figure 4.
Topological structure of neurons.
2.1.3. Attacking Prey
During the hunting process, if the prey stops moving, the gray wolf attacks the prey to complete the hunt. Throughout the hunting process, the value of decreases from 2 to 0. Additionally, the value of A varies within the interval [−a, a]. The position of the gray wolf during each iteration is always at any position between its current location and the position of the prey. When the absolute value of A is greater than one, the population engages in a global search. On the other hand, when the absolute value of A is less than one, the population performs a local search. The gray wolf ultimately attacks the prey at this point, signifying the successful completion of the hunt.
2.2. BP Neural Network
The BP neural network is a feed-forward neural network based on supervised learning and error backpropagation. With the aid of a transfer function, it can achieve mapping from input to output. The BP neural network utilizes the gradient descent method to optimize the weights and thresholds during training, aiming to improve the fitting between the predicted values and the actual output values [22,23,24]. The structure of the neural network comprises three main layers: the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer. The neural network’s structure and schematic diagram are as follows:
In the formula, represents the activation function, means output, means input, means weight, and means bias.
In a BP neural network, every neuron is entirely connected to the neurons of the previous layer. Each neuron passes its output through weighted connections to the neurons of the next layer, and then this output is compared with a threshold value. Subsequently, the value of the neurons in the next layer is determined by applying an activation function, introducing non-linearity to the network. This process continues, and the values are passed layer by layer as input through the network, allowing for the flow of information and computation until reaching the output layer.
2.3. Improvement of Gray Wolf Optimization Neural Network
2.3.1. Gray Wolf Improvements
To enhance the accuracy of the BP neural network in predicting the actual road emissions of heavy-duty diesel vehicles, the gray wolf algorithm is utilized to optimize the initial weights and thresholds of the BP neural network. The optimized initial weights and thresholds are then used to reconstruct the BP neural network, which is subsequently trained to predict the NOx emissions of heavy-duty diesel vehicles. However, during the optimization process, the gray wolf algorithm may encounter local optima, which can impact its performance. The critical factors affecting the gray wolf algorithm include the initialization of the gray wolf population, the search mechanism, and the update strategy of the control parameters [25,26]. To address these challenges, improvements are made in the following aspects:
(1) Population initialization improvement
In the gray wolf algorithm, the population is initially generated randomly, which can lead to poor diversity and a higher risk of falling into local optima during the optimization process. To address this issue and enhance the algorithm’s performance, chaotic mapping is introduced for initializing the gray wolf population. By incorporating chaotic mapping, the diversity of the initial population is increased, promoting better exploration of the solution space. Among the commonly used chaotic mappings, Circle mapping is adopted for this improvement. The formula for Circle mapping is as follows:
In the formula, represents the gray wolf position, where = 0.5, = 2.2.
(2) Gray wolf parameter a improved
The cosine function combined with random distribution is used to adjust the gray wolf parameter . The improved a has a random distribution, which can well balance global and local searches, and avoids the linear reduction of a from easily falling into a local optimum during the optimization process.
In the formula, is the current number of iterations, is the maximum number of iterations, represents a uniformly distributed random number between 0 and 1, is a random number subject to a normal distribution, and is the standard deviation, which is used to measure the deviation of the control parameter from its mathematical expectation.
(3) Gray wolf location update formula improvements
Using the weighted sum of the best position to update the position can effectively prevent the search process from falling into the local optimum. The gray wolf can find the global optimum point in the iterative process. The formula is as follows:
2.3.2. Gray Wolf Optimization BP Neural Network Model Building
Defining the parameters N and in the gray wolf algorithm. Among them, N represents the population number of the gray wolf population, and R represents the search space dimension of the gray wolf individual. The position of each gray wolf represents the weight and threshold of the BP neural network, and the optimal alpha wolf position is found in the iterative process, which is the optimal neural network weight and threshold. The input layer nodes, first-hidden-layer nodes, second-hidden-layer nodes, and output layer nodes of the BP neural network are respectively set to , , , and , and the calculation formula of search space is as follows:
The specific steps of improving gray wolf optimization BP neural network to predict NOx emissions [27,28,29,30,31]:
(1) Normalize the data, scramble the data, and divide them into a training set and a test set.
(2) Initialize the gray wolf population, use the chaotic map to initialize the gray wolf, and use for the gray wolf individual position, where represents the i-th gray wolf individual position, contains six parameters of the double-hidden-layer BP neural network: the weight between the input layer and hidden layer 1, the threshold of hidden layer 1, the weight of hidden layer 1 and hidden layer 2, the threshold of hidden layer 2, the weight between hidden layer 2 and output layer, and the threshold of output layer.
(3) Use the location information of each gray wolf to construct a BP neural network, train the network, and use the root mean square error between the trained network prediction output and the real value to construct the fitness function:
In the formula, represents the predicted value of the neural network for the i-th sample, while denotes the true value of the neural network for the same i-th sample. The variable represents the total number of samples used for evaluation.
(4) Calculate the fitness value of each individual in the first-generation gray wolf population according to the above formula, and select the three gray wolves with the highest fitness values as α, β, and δ wolves, and the rest as ω wolves.
(5) During each iteration, the wolves in the gray wolf algorithm update the values of the parameters , , and . Subsequently, the BP neural network is reconstructed based on the new gray wolf parameters, and the network is trained. After training, the fitness value of each gray wolf in the updated wolf pack is calculated using the specified formula. This fitness value is used to determine the new α, β, δ, and ω wolves within the pack based on their fitness levels.
(6) The process involves judging whether the maximum number of iterations is reached. If the maximum number of iterations is reached, the position of the alpha wolf at this time is recorded. This position corresponds to the optimal weight and threshold of the BP neural network, representing the solution found by the gray wolf algorithm. If the maximum number of iterations is not yet reached, the algorithm returns to step (5) to continue iterating.
(7) The BP neural network is constructed using the neural network weights and thresholds obtained through the improved gray wolf algorithm. After constructing the network, it is trained using the training data to learn the relationships between the input features and the corresponding NOx output.
Improved gray wolf optimized BP neural network to predict NOx emission flow chart (Figure 5):
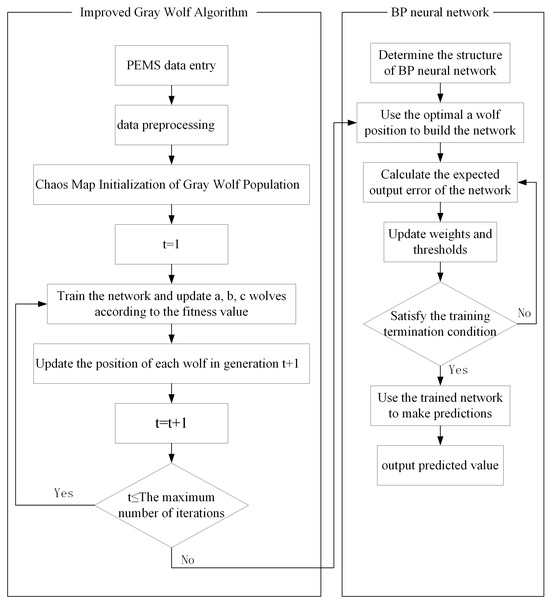
Figure 5.
Flowchart of an improved gray-wolf-optimized BP neural network.
3. Tests and Data Processing
3.1. Test Equipment
The measurement principle, measurement accuracy, linearity, response, and drift of PEMS are specified in the appendix of China’s Type VI light-duty vehicle emission standards. All equipment has been certified by the US Environmental Protection Agency and relevant EU agencies, and the measurement methods of PEMS devices and accuracy meet the requirements of RDE specifications.
In this experiment, the actual road emission test of an N2 heavy-duty diesel vehicle was conducted using the portable emission test equipment (PEMS) manufactured by Horiba Company of Japan (Figure 6). The PEMS device is composed of five modules: the THC analyzer module that uses a heated FID (FA) module to measure THC concentration; the Gas analyzer module (GA) module measures CO, , and NOx concentration; the Central control unit (CC) module receives GPS and OBD information; and the Power exchange unit (PE) power module. Non-Dispersive InfraRed (NDIR) is used to determine CO and concentrations. Chemiluminescence Detection (CLD) is used to determine NOx concentration as shown in Table 1.
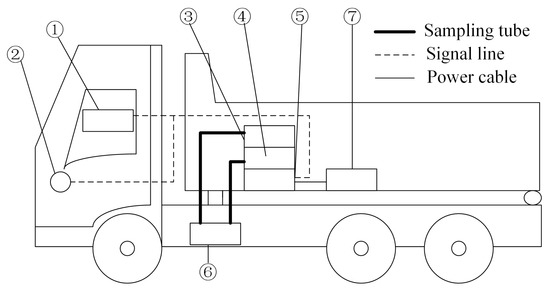
Figure 6.
Sketch of PEMS equipment installation. ① Engineering computer; ② OBD (On-Board Diagnostic); ③ THC analyzer module that uses heated FID (FID analyzer module) (FA); ④ Gas analyzer module (GA); ⑤ Central control unit (CC); ⑥ exhaust pipe; ⑦ Power exchange unit (PE).

Table 1.
OBS-ONE measurement system technical specifications.
3.2. Test Vehicles
The test vehicle was an N2 box-type transportation diesel truck, and the specific parameters of the vehicle are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Vehicle information.
3.3. Road Tests
According to the test requirements stipulated in GB17691-2018 “Heavy-duty Diesel Vehicle Pollutant Emission Limits and Measurement Methods (China Phase VI)”, the composition of the test route should reflect as much as possible the distribution of road conditions during normal use of the vehicle. Vehicle test routes should include urban roads, suburban roads, and expressways. According to the vehicle category, the actual composition ratio is allowed to have a deviation of ±5%. According to regulations, for N2 vehicles, the test road composition is as follows: 45% of urban roads, 25% of suburban roads, and 30% of expressways [32].
In this test, a 2.7 h road test was carried out on the N2 diesel vehicle, with a total test mileage of 115.55 Km. According to the requirements of the regulations, the distribution ratio of road composition in this test is 46.3% in the urban area, 24.5% in the suburbs, and 29.2% in the expressway. The speed diagram of the actual working conditions is shown in Figure 7.
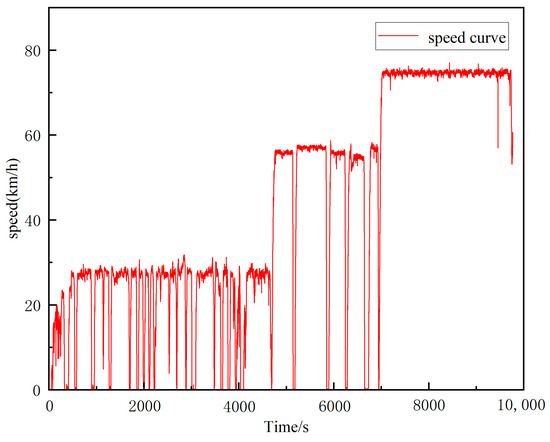
Figure 7.
Test condition diagram.
3.4. Data Pre-Processing
3.4.1. Invalid Data Culling
The National VI Practical Roadworthiness Measurement Methods (PEMS) states that invalid data are not to be used in emissions calculations. The following data are invalid:
- Data during equipment inspection and zero drift verification.
- Data during cold engine start.
- Data that do not meet the test altitude and test ambient temperature requirements.
3.4.2. Data Alignment
Different test modules in the emission testing process have varying response speeds. To minimize time offsets between signals and ensure accurate data alignment, GB17691-2018 “Heavy-duty Diesel Vehicle Pollutant Emission Limits and Measurement Methods (China Phase VI)” prescribes guidelines for aligning the emission-related data after the test. The test data are typically divided into three main parts:
- NOx, CO, and other data collected by the analyzer.
- Data such as exhaust gas mass flow rate and exhaust gas temperature collected by the exhaust gas flowmeter.
- Engine-related data collected by OBD.
To achieve accurate data alignment (Figure 8), is employed as a reference due to its unique absorption peak and lesser susceptibility to pollution compared to other molecules. As a result, serves as the pollutant with the highest test accuracy among the main pollutants. Using as a reference allows for data alignment with other measurements, ensuring the highest correlation coefficient between the data. This alignment process helps to improve the accuracy and reliability of the emission test results for heavy-duty diesel vehicles.
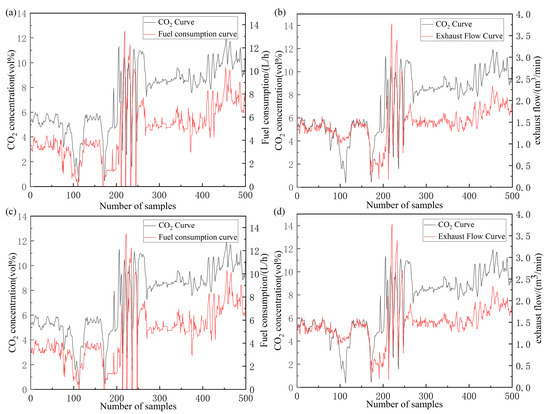
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of data before and after alignment. (a) Schematic diagram before CO2 and fuel consumption rate are aligned; (b) Schematic diagram before CO2 and exhaust flow are aligned; (c) Schematic diagram after aligning CO2 and fuel consumption rate; (d) Schematic diagram after aligning CO2 and exhaust flow.
In order to intuitively reflect the correlation between the data, the concentration, and exhaust gas quality of 500 sets of data were randomly selected from the data set to align the analyzer data with the exhaust flow meter data, and the concentration and engine fuel consumption rate of 500 sets of data were randomly selected to align the data collected by the exhaust flow meter and OBD. Based on the concentration parameter, the exhaust flow rate and fuel consumption rate data are translated, respectively, and the correlation coefficient is used to represent the alignment degree between the data. The correlation coefficient formula is as follows:
As shown in the figure below Figure 9, the correlation between the data reaches the maxi-mum when the exhaust flow data are shifted by 1 s and the fuel consumption rate data are shifted by 2 s.
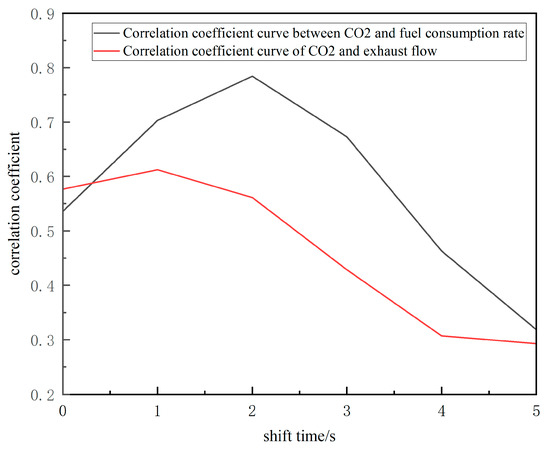
Figure 9.
Correlation coefficients between data versus translation time.
3.4.3. Calculation of NOx Mass Emissions
The NOx emissions of heavy-duty diesel vehicles are usually evaluated by mass emissions as shown in Figure 10. Since the PEMS equipment cannot directly collect the mass emissions of NOx, the mass emissions should be calculated based on the tabular values of the collected data. The regulations stipulate that the original concentration of pollutants arranged according to the conversion time and the mass flow rate of exhaust gas are used to calculate the instantaneous emission mass, the instantaneous value of the entire cycle is integrated, and the integral is multiplied by the u value to obtain the pollutant mass emission (g/s). The calculation formula is as follows:
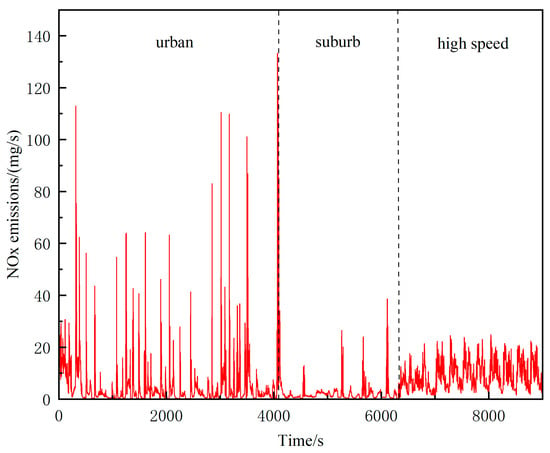
Figure 10.
NOx transient emission value.
In the formula:
—exhaust component density and exhaust density ratio for diesel-fueled NOx with a value is 0.001587;
—Instantaneous concentration of exhaust component, ppm;
—Instantaneous exhaust mass flow rate, Kg/s;
—Sampling frequency, Hz.
3.4.4. Normalization of Data
The dimensions between the input data and the output data are different. In order to eliminate the influence of the dimension between the data and the singular sample data, the input and output data are normalized, and the input matrix and output vector are normalized to [0, 1] respectively. The normalization formula is as follows [33,34]:
In the formula, is the normalized value of the i-th input parameter; is the sample value of the i-th input parameter; is the maximum sample value of the i-th input parameter; is the minimum sample value of the i-th input parameter.
3.5. Neural Network Parameterization
3.5.1. Input and Output Layer Determination
NOx emissions from heavy-duty diesel vehicles are related to many factors, including the working conditions of the engine itself, ambient temperature, and ambient humidity. Based on experience, 16 parameters including speed, exhaust flow, exhaust temperature, exhaust pressure, exhaust diffusion pressure, coolant temperature, engine speed, engine torque, intake pressure, oil pressure, intake manifold temperature, throttle opening, relative humidity of the exhaust pipe environment, absolute humidity of the exhaust pipe environment, intake airflow, and fuel consumption rate under the PEMS test were selected as input parameters. Some data are shown in the Table 3.

Table 3.
Selected PEMS test data.
The gray relational analysis is a statistical method for multi-factor analysis. Its principle is to judge whether the connection is close according to the similarity of the geometric shape of the sequence curve. The data processing flow is as follows [35]:
(1) Determine the parent and subsequence of the analyzed data
In the formula, is the number of samples, is the number of subsequences, is the subsequence, and is the parent sequence.
(2) Applying the homogenization method to dimensionless data
In the formula, is the value before normalization, and is the value after normalization.
(3) Calculation of the gray correlation coefficient
In the formula, is the resolution coefficient, which takes a value within (0, 1). The smaller the , the larger the gap between the correlation coefficients and the stronger the discrimination ability, usually 0.5.
(4) Calculate the gray correlation
According to the above formula, the grey correlation degrees between each sub-sequence and the parent sequence are calculated. Figure 11 reflects the impact of each input feature on NOx emissions. It can be observed from the figure that each feature parameter has a significant influence on the emission characteristics of NOx.
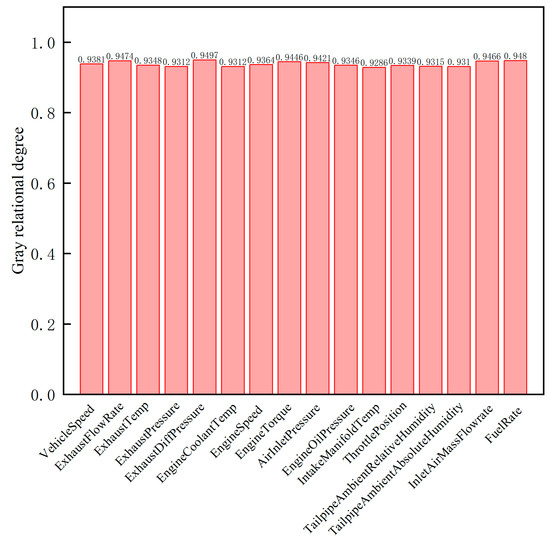
Figure 11.
Gray correlation matrix.
Figure 12 is the correlation matrix among the aforementioned 16 input parameters. It can be observed that there is a high linear correlation between some of the data, such as the engine torque and fuel consumption rate reaching 0.97. This indicates the existence of redundancy among the input parameters. Moreover, as the 16 feature parameters serve as inputs for the neural network, the network is relatively complex, leading to a longer training time. Therefore, it is necessary to perform dimensionality reduction on the collected data.
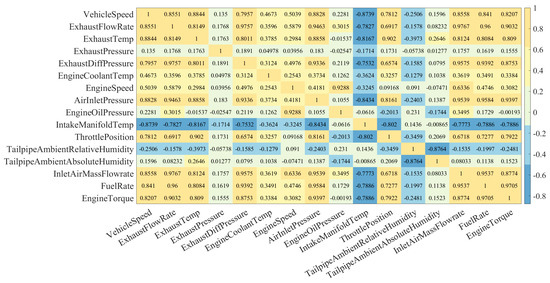
Figure 12.
Matrix of input parameter correlation coefficients.
The principal component analysis is a commonly used data dimensionality reduction method, the number of principal components is selected through the variance contribution ratio, and the principal components are linear combinations of the original variables, these linear combinations can mostly reflect the original data [36]. The steps of principal component analysis are as follows:
(1) Decentralization and standardization of feature data
The 16 and characteristic parameters are respectively averaged, and each characteristic parameter is subtracted from its mean value, and then the data are standardized.
In the formula, is the standardized data, is the mean value of the original data, is the standard deviation of the original data.
(2) Data Dimension Reduction
The correlation coefficient matrix between the variables is calculated for the processed data and the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the correlation coefficient matrix are calculated.
In the formula, is the number of samples. There are eigenvalues of the correlation coefficient matrix, which are , , …, , and the corresponding eigenvectors are , , …, .
The computed eigenvalues are sorted in descending order, the top k groups with the largest variance contribution are selected, and their corresponding k eigenvectors are multiplied with the original data to obtain new data with only k eigenstate.
Figure 13 reflects the variance contribution rate of each principal component and the cumulative variance contribution rate of the first n principal components. In order to more accurately represent the original data, the first 10 sets of data were selected, and at this point, the cumulative variance contribution rate is 99%. In order to reflect the raw data more accurately, the first 10 data sets were selected, at which point the cumulative variance contribution was 99%.
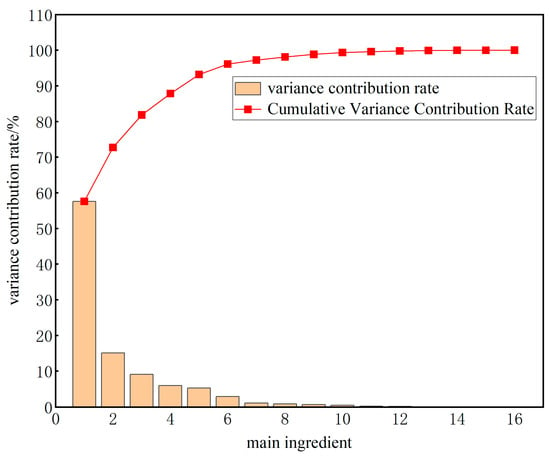
Figure 13.
PCA principal component contribution.
The principal component feature vector is a linear combination of the original data and the feature vector. The K-dimension principal component is used to represent the M-dimension feature parameter data as much as possible, expressed as follows:
In the formula, is the corresponding eigenvector after the eigenvalues are arranged in descending order, is the standardized data, and is the main component.
3.5.2. Determination of the Number of Hidden Layers and the Number of Neurons
The number of hidden layers and the number of neurons have a significant impact on the network accuracy, training time, and convergence speed. It is crucial to choose a reasonable number of hidden layers and neurons. Usually, single-hidden-layer networks are weak in nonlinear mapping ability, and in order to achieve the intended mapping effect, dual-hidden-layer neural networks are chosen. Dual-hidden-layer neural networks can fit any smooth mapping with any accuracy with the assistance of appropriate activation functions. The number of neurons is also crucial; too few and the network learns poorly and fails to achieve the intended mapping; too many and the network is over-trained and generalizes poorly.
In the formula, is the number of nodes in the input layer, is the number of nodes in the hidden layer, is the number of nodes in the output layer, and the value of ranges from 0 to 10.
The network trained by the number of neurons determined by the empirical formula cannot be mapped well, according to the trial-and-error method to constantly adjust the number of neurons training, and finally determine the number of neurons in the first hidden layer is 40, the number of neurons in the second hidden layer is 20, at this time the model has a good generalization ability.
3.5.3. Model Transfer Function Selection
The structure of the double-hidden-layer BP neural network is the input layer to hidden layer 1, hidden layer 1 to hidden layer 2, and hidden layer 2 to the output layer. Through several simulations and analyses, the logsig function is selected from the input layer to the implied layer 1, the logsig function is selected from implied layer 1 to implied layer 2, and the purelin function is selected from implied layer 2 to the output layer.
4. Analysis of Forecast Results
From the fitness curve, it can be seen that the improved Grey Wolf Algorithm stabilizes at a fitness value of 2.42 after 185 iterations. At this point, the optimal position of the alpha wolf is , which corresponds to the optimal initial weights and thresholds for the BP neural network. When these parameters are used in the training of the BP neural network, the model exhibits good accuracy, as reflected in the graph below, with a root mean square error (RMSE) of 1.9144 (mg/s). Within the permissible error range, this model is capable of accurately predicting diesel vehicle NOx emissions (Figure 14 and Figure 15).
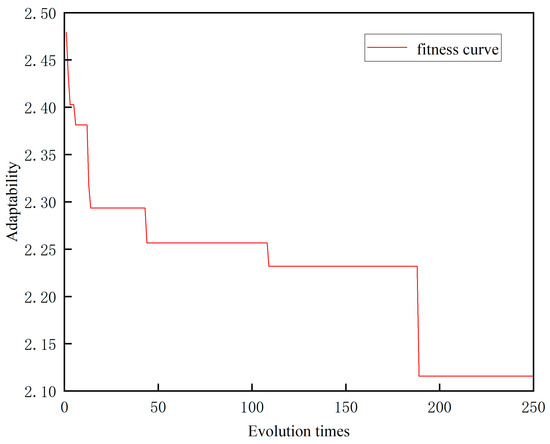
Figure 14.
Evolutionary curve of the improved gray wolf algorithm.
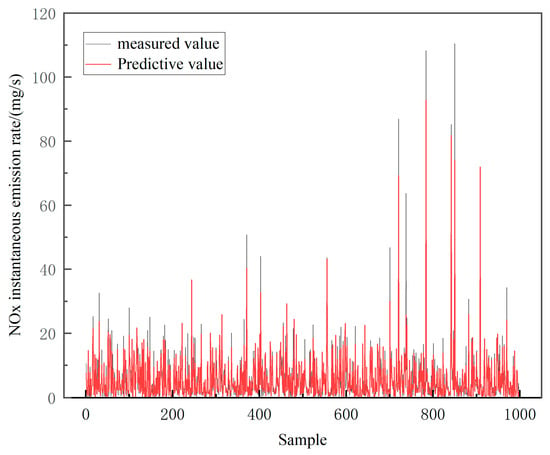
Figure 15.
Comparison of true and predicted values for the test set.
Figure 16, Figure 17 and Figure 18 respectively depict scatter plots of the actual NOx emissions versus predicted NOx emissions on the testing set for the single-hidden-layer BP network model, the double-hidden-layer BP network model, and the improved GWO-optimized BP network model. For the single-hidden-layer BP neural network model, the coefficient of determination (R-squared) on the testing set is 0.71935, and the root mean squared error (RMSE) is 3.42. For the double-hidden-layer BP neural network model, the R-squared on the testing set is 0.8284, with an RMSE of 2.1153. The improved GWO-BP neural network model achieves an R-squared of 0.87024 on the testing set, with an RMSE of 1.9144. Comparing the R-squared values, the improved GWO-BP neural network model shows a 20.98% increase over the single-hidden-layer BP neural network model and a 5.05% increase over the double-hidden-layer BP neural network model. Additionally, the RMSE decreases by 78.6% compared to the single-hidden-layer model and by 10.5% compared to the double-hidden-layer model. From the plot, it is evident that the data points are distributed near the y = x line, indicating that the estimation errors of the model are mainly concentrated between −1 and 1. This suggests high model accuracy and strong fitting capability.
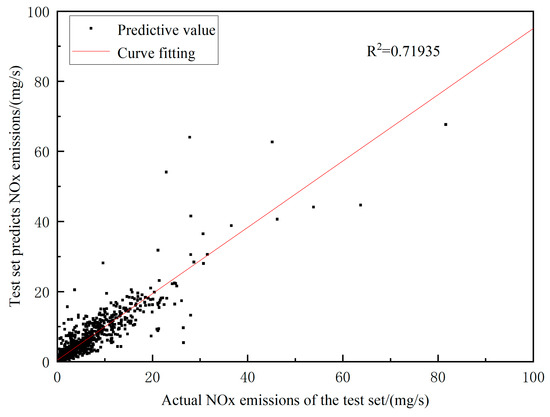
Figure 16.
Predicted value and true value on a single-hidden-layer BP neural network test set.
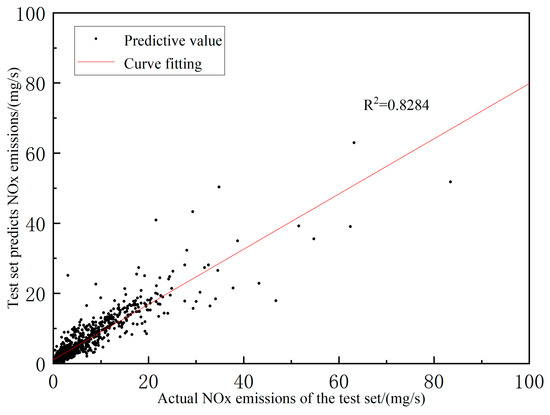
Figure 17.
Predicted value and true value on the test set of a double-hidden-layer BP neural network.
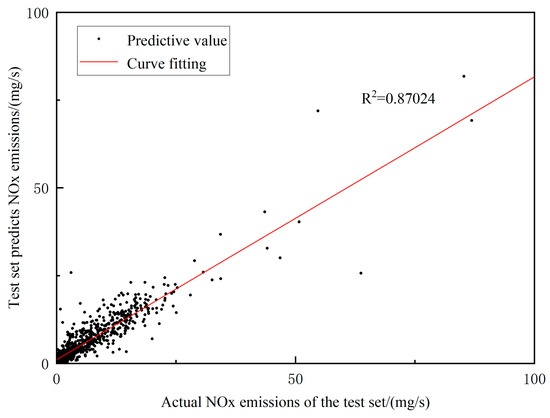
Figure 18.
Predicted and true values on the test set of the improved GWO-BP neural network.
5. Conclusions
(1) The Grey Wolf Algorithm has been improved by utilizing chaotic mapping to initialize the population, ensuring the diversity of the initial population. The adjustment of grey wolf parameter is accomplished using a cosine function combined with a random distribution, effectively balancing the tendency of grey wolves to become trapped in local optima. Furthermore, the grey wolf position updating formula has been modified to prevent it from being trapped in local optima.
(2) Using Practical Emission Measurement System (PEMS) data from actual road tests, the grey correlation degree between NOx and other parameters is analyzed. Then, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is introduced to eliminate invalid data and align the remaining data, reducing their dimensionality. The reduced data are chosen as input, while NOx serves as the output to establish a prediction model. The NOx emission model of a diesel engine based on an improved GWO-BP neural network has a determination coefficient of 0.87024 and root mean square error (RMSE) of 1.9144 (mg/s) on the test set. Compared to the traditional BP neural network model, this model exhibits better predictive accuracy.
(3) Compared to the traditional BP neural network, the improved Grey Wolf Optimized BP neural network has the advantages of fast convergence, high precision, and less susceptibility to becoming stuck in local optima. It provides a convenient solution for diesel vehicle NOx monitoring.
Author Contributions
Z.W.—Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing—Reviewing and Editing. K.F.—Data curation, Visualization, Writing—Original draft preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the results of this study are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely appreciate all financial and technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. China Mobile Source Environmental Management Annual Report. 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-09/11/content_5636764.htm (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Hao, C.; Ge, Y. Fuel consumption and emission performance from light-duty conventional/hybrid-electric vehicles over different cycles and real driving tests. Fuel 2020, 278, 118340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guor, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, G.Q. Study on exhaust emission test of diesel vehicles based on PEMS. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 166, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Wang, S.; Du, B.; Cui, L.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, W. Study on pollutant emission characteristics of different types of diesel vehicles during actual road cold start. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, X.; Yan, Z. Comparison of fine particles emissions of light-duty gasoline vehicles from chassis dynamometer tests and on-road measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raparthi, N.; Debbarma, S.; Phuleria, H.C. Determination of heavy-duty vehicle emission factors from highway tunnel measurements in India: Laboratory vs. real-world study. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Pei, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, F.; Qin, J. The impact of the variation in driving conditions on the NOx emissions characteristics in PEMS test for heavy-duty vehicle. J. Eng. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Bonnel, P.; Kühlwein, J.; Provenza, A.; Lambrecht, U.; Alessandrini, S.; Carriero, M.; Colombo, R.; Forni, F.; Lanappe, G.; et al. Will Euro 6 reduce the NOx emissions of new diesel cars?–Insights from on-road tests with Portable Emissions Measurement Systems (PEMS). Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Xu, Y.C.; Yao, S.D.; Li, C.Y.; Li, N. Prediction of emission performance in a diesel engine fuelled with bio-diesel based on double-hidden layer BP neural network. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 278, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sunden, B. Application of artificial neural network to forecast engine performance and emissions of a spark ignition engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 201, 117749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Awad, O.I.; Liu, S.; Shuai, S.; Wang, Z. NOx emissions prediction based on mutual information and back propagation neural network using correlation quantitative analysis. Energy 2020, 198, 117286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kwon, S.; Kim, H.; Keel, J.; Yoon, T.; Lee, J. Machine learning applied to the NOx prediction of diesel vehicles under real driving cycle. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chang, H.; Wen, Z.; Ge, Y.; Hao, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, J. Prediction of Real Driving Emission of Light Vehicles in China VI Based on GA-BP Algorithm. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, Y.; Wadhwa, G.; Sri Preethaa, K.R.; Paul, A. Forecasting Carbon Dioxide Emissions of Light-Duty Vehicles with Different Machine Learning Algorithms. Electronics 2023, 12, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Sáez, A.; Rattá, G.A.; Barrios, C.C. Prediction of exhaust emission in transient conditions of a diesel engine fueled with animal fat using Artificial Neural Network and Symbolic Regression. Energy 2018, 149, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çay, Y.; Korkmaz, I.; Çiçek, A.; Kara, F. Prediction of engine performance and exhaust emissions for gasoline and methanol using artificial neural network. Energy 2013, 50, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J. Assessing fuel economy and NOx emissions of a hydrogen engine bus using neural network algorithms for urban mass transit systems. Energy 2023, 275, 127517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Rajakarunakaran, S.; Thirugnanasambandam, M.; Devaraj, D. Artificial neural network model to predict the diesel electric generator performance and exhaust emissions. Energy 2015, 83, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.; Rowe, J.E. Genetic Algorithms: Principles and Perspectives: A Guide to GA Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A Tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, R. Neural Networks: A Systematic Introduction; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; McClelland, J.L. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition: Foundations; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 318–362. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, B.; Trivedi, B. Optimizing back propagation parameters for anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE-International Conference on Research and Development Prospectus on Engineering and Technology (ICRDPET), Tamilnadu, South India, 29–30 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hatta, N.M.; Zain, A.M.; Sallehuddin, R.; Shayfull, Z.; Yusoff, Y. Recent studies on optimization method of Grey Wolf Optimiser (GWO): A review (2014–2017). Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2651–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igiri, C.P.; Singh, Y.; Poonia, R.C. A review study of modified swarm intelligence: Particle swarm optimization, firefly, bat and gray wolf optimizer algorithms. Recent Adv. Comput. Sci. Commun. (Former. Recent Pat. Comput. Sci.) 2020, 13, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Joint SOH-SOC estimation model for lithium-ion batteries based on GWO-BP neural network. Energies 2022, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Lin, W.; Gulliver, T.A.; Le, K.N. GWO-BP neural network-based OP performance prediction for mobile multiuser communication networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 152690–152700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, L.; Gui, L.; Du, J.; Yin, K.; Do, H.M. Landslide displacement prediction based on variational mode decomposition and WA-GWO-BP model. Landslides 2020, 17, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhao, A. A predictive model of energy consumption for office building by using improved GWO-BP. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Lu, F. Research on SOC estimation of lithium battery based on GWO-BP neural network. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Kristiansand, Norway, 9–13 November 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Limits and Measurement Methods for Emissions from Diesel Fuelled Heavy-Duty Vehicles (CHINA VI). 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqydywrwpfbz/201807/t20180703_445995.shtml (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Gökhan, A.K.S.U.; Güzeller, C.O.; Eser, M.T. The effect of the normalization method used in different sample sizes on the success of the artificial neural network model. Int. J. Assess. Tools Educ. 2019, 6, 170–192. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanja, S.; Das, A. Impact of data normalization on deep neural network for time series forecasting. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.05519. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, R.; Shang, R.; Wu, M.; Peng, C.; Guo, X. Application of gray relational analysis to k-means clustering for dynamic equivalent modeling of the wind farm. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 20154–20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćkiewicz, A.; Ratajczak, W. Principal components analysis (PCA). Comput. Geosci. 1993, 19, 303–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).