A Review of End-of-Life Scenarios for Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
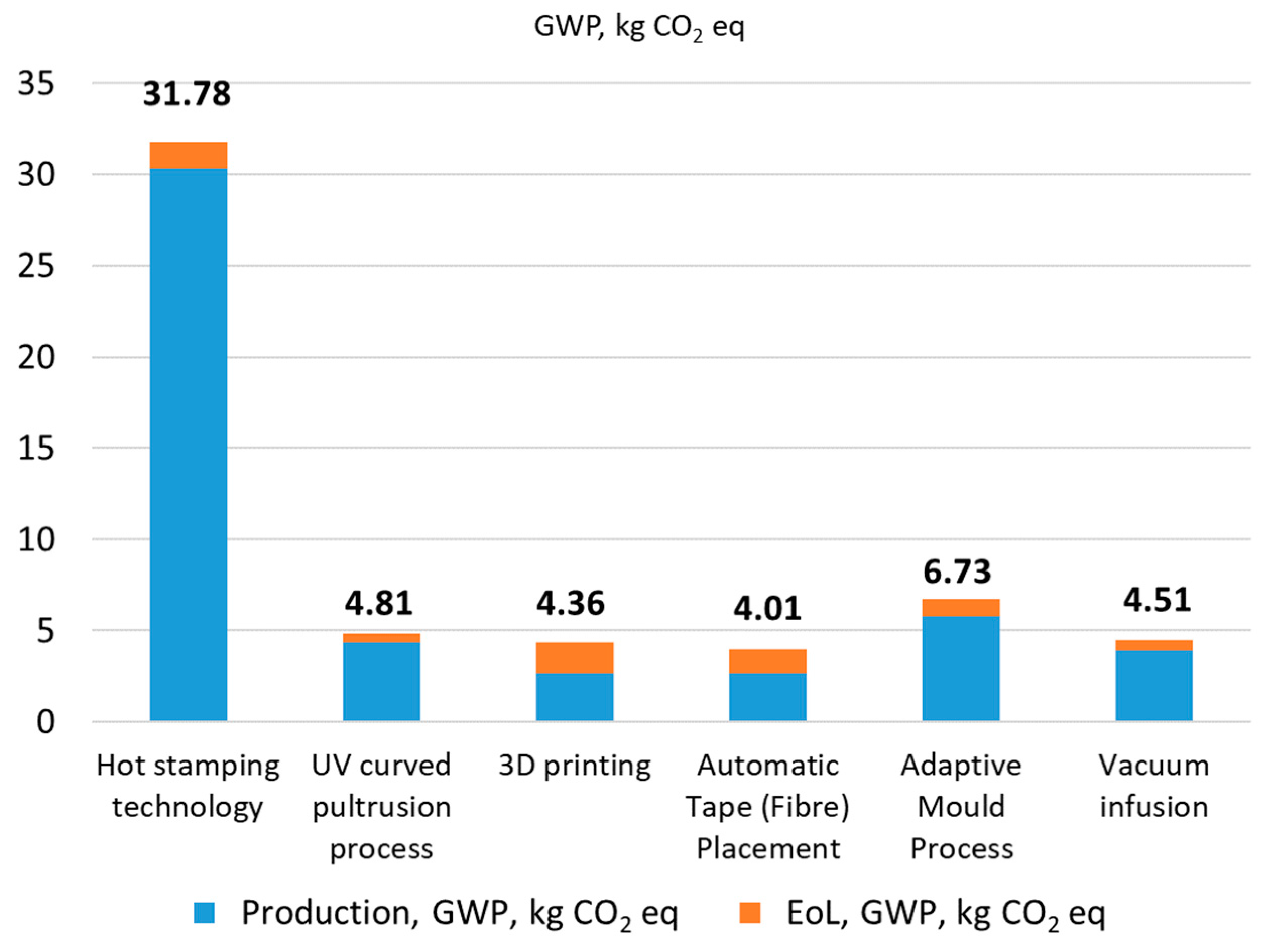
1.1. FRP Technologies in Fibre4Yards Project
- -
- Hot stamping, employed by INEGI (Institute of Science and Innovation in Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Porto, Portugal); thermoplastic composite sheets are hot stamped into a mould to give them the appropriate shape; the first step is prepreg uncoiling via the automatic taper lay-up (ATL) process and spot welding; next, the blank is moved the die to be 2D shape formed via the application of heat and pressure in a flat plate hot-press; after this, the previously melted component is heated by IR and pressed into a 3D shape.
- -
- The UV curved pultrusion process (Robtrusion®), proposed by the IRURENA Group (Azpeitia, Spain); UV curing of pultruded profiles enables the production of profiles with a curved longitudinal axis using a robotic pulling system; initially, the fibres are strengthened by bathing in resin; the impregnated reinforcements are pulled into the mould, which is only used to shape the profile cross-section; the profile is hardened with UV radiation and shaped using a robot arm that grabs the profile and pulls it in accordance with the specific geometry required for the profile; the last step is to manually cut the profile.
- -
- 3D printing(IRURENA Group (Azpeitia, Spain)), reported by 10XL (Rivierdijk, The Netherlands), specializes in proprietary large-scale hybrid printers; this is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file by building objects layer by layer of material.
- -
- Adaptive mould used by Curve Works (Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands); in this process, the moulds for composite manufacturing are adjusted to any given geometry; at first, the structure is divided into panels within a 3D Computer-Aided Design (CAD) program; the adaptive mould shapes itself automatically to the design according to the geometry saved in the CAD file.
- -
- Vacuum infusion applied by the NAVAL Group (Nantes, France), whereby a vacuum is used to draw resin into a dry fibre reinforcement, resulting in a void-free composite structure; the first step involves fixing the fibres and core material to the mould; next, the resin feeding line is installed, which includes a vacuum line, valves and a vacuum bag, which must be properly sealed [3].
1.2. Recycling Methods of FRP
1.2.1. Chemical Recycling
1.2.2. Thermal Recycling
1.2.3. Mechanical Recycling
1.3. End-of-Life for FRP Materials
2. Survey of LCA Methodologies
2.1. Life Cycle Assessment Methodology
- Goal Definition and Scoping describe the analysed product, process or activity; the purpose, scope and functional unit are defined, which establish a reference to which the inputs and outputs are related; and system boundaries are determined (which processes are included in the analysis).
- The Inventory Analysis. This step helps with identifying and quantifying inputs (e.g., row materials, energy and water usage) and outputs (e.g., emissions, solid waste disposal and wastewater discharges). This is a technical process of inventory of all relevant data for each process within the defined system boundaries.
- The Impact Assessment assesses the potential effects of energy, water and material usage and the emissions identified in the inventory analysis based on selected environmental impact categories (e.g., global warming, human health). This step includes obligatory and optional sub-phases: classification, characterization, normalization and weighting consistent with ISO standards.
- The Interpretation step analyses the results from which to draw conclusions and identify significant environmental impacts.
2.2. End-of-Life for Fibre4Yards Technologies
3. LCA Analysis of FRP Technologies
4. Conclusions
- Meeting environmental regulations and sustainability targets (Environmental limits).
- Adapting to evolving laws and policies related to waste management and recycling (Governmental legislation).
- Implementing a C2C strategy (cradle-to-cradle) to transform FRP waste into a valuable product (Circular Economy approach).
- Addressing limitations in fibre properties, e.g., strength and durability (Interior fibre properties).
- Developing efficient methods for handling FRP waste during recycling (composite Processing Techniques).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sevigné-Itoiz, E.; Mwabonje, O.; Panoutsou, C.; Woods, J. Life cycle assessment (LCA): Informing the development of a sustainable circular bioeconomy? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajula, T.; Behm, K.; Vatanen, S.; Saarivuori, E. Managing the Life Cycle to Reduce Environmental Impacts. In Dynamics of Long-Life Assets: From Technology Adaptation to Upgrading the Business Model; Grösser, S.N., Reyes-Lecuona, A., Granholm, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switherland, 2017; pp. 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Sobulska, M.; Pietrzak, M.; Zbiciński, I. Application of Life Cycle Assessment to Analysis of Fibre Composite Manufacturing Technologies in Shipyards Industry. Processes 2024, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favi, C.; Germani, M.; Luzi, A.; Mandolini, M. A design for EoL approach and metrics to favour closed-loop scenarios for products A design for EoL approach and metrics to favour closed-loop scenarios for products. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2017, 10, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenboom, J.G.; Langer, R.; Traverso, G. Bioplastics for a circular economy. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the Environment—Review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-Attiya, W.A.K.A. An overview of the environmental pollution and health effects associated with waste landfilling and open dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravanian, A.; Ravari, S.O. Types of Contamination in Landfills and Effects on The Environment: A Review Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 614, 012083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, P.O.; Edokpayi, J.N.; Odiyo, J.O. Health and Environmental Risks of Residents Living Close to a Landfill: A Case Study of Thohoyandou Landfill, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/98/oj (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S. Waste Management for Polymers in Food Packaging Industries. In Plastic Films in Food Packaging; Ebnesajjad, S., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 249–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, N.; Last, N.; Morris, K.C. A process model representation of the end-of-life phase of a product in a circular economy to identify standards needs. Front. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 3, 988073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, L.M.; Mejía-Gutiérrez, R.; Nadeau, J.P.; Pailhès, J. Life cycle analysis in preliminary design stages. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference on Mechanical, Design Engineering & Advanced Manufacturing, Toulouse, France, 28 January–17 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Suhariyanto, T.T.; Wahab, D.A.; Rahman, M.N.A. Product Design Evaluation Using Life Cycle Assessment and Design for Assembly: A Case Study of a Water Leakage Alarm. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolz, M.; Martinez, X.; Sá, D.; Silva, J.; Jurado, A. Composite materials, technologies and manufacturing: Current scenario of European union shipyards. Ships Offshore Struct. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Youn, J.R.; Gutowski, T.G. Life cycle energy analysis of fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; McKechnie, J.; Turner, T.A.; Pickering, S.J. Energy and environmental assessment and reuse of fluidised bed recycled carbon fibres. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fazio, D.; Boccarusso, L.; Formisano, A.; Viscusi, A.; Durante, M. A Review on the Recycling Technologies of Fibre-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Materials Used in Industrial Fields. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziparaskeva, G.; Papamichael, I.; Voukkali, I.; Loizia, P.; Sourkouni, G.; Argirusis, C.; Zorpas, A.A. End-of-Life of Composite Materials in the Framework of the Circular Economy. Microplastics 2022, 1, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibre4Yards Project. Available online: https://www.fibre4yards.eu (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Pietrzak, M.; Zbiciński, I. Effect of Recycling on the Environmental Impact of a High-Efficiency Photovoltaic Module Combining Space-Grade Solar Cells and Optical Micro-Tracking. Energies 2023, 16, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, X.; Sá, D.; Silva, J.; Alvarez-Buylla, S. FIBRE4YARDS: Fibre Composite Manufacturing Technologies for the Automation and Modular Construction in Shipyards. Mater. Compuestos 2022, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, C. Recyclable and reformable epoxy resins based on dynamic covalent bonds—Present, past, and future. Polym. Test. 2022, 105, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensadoun, F.; Vanderfeesten, B.; Verpoest, I.; Van Vuure, A.W.; Van Acker, K. Environmental impact assessment of end of life options for flax-MAPP composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharde, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Mechanothermal and chemical recycling methodologies for the Fibre Reinforced Plastic (FRP). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraboli, P.; Kawakami, H.; Wade, B.; Gasco, F.; DeOto, L.; Masini, A. Recyclability and reutilization of carbon fiber fabric/epoxy composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Choi, H.O.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Ju, C.S. Circulating flow reactor for recycling of carbon fiber from carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Pinkard, B.R.; Novosselov, I.V. Recycling of carbon fiber reinforced polymers in a subcritical acetic acid solution. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, C.C.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Recycling of woven carbon-fibre-reinforced polymer composites using supercritical water. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.N.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.; Yang, B.; Kim, J.; Jung, Y.C. Application of supercritical water for green recycling of epoxy-based carbon fiber reinforced plastic. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 173, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.J.; Oliveux, G.; Leeke, G.A. Optimisation of solvolysis for recycling carbon fibre reinforced composites, In Proceedings of the ECCM 2016—Proceeding of the 17th European Conference on Composite Materials, Munich, Germany, 26–30 June 2016.
- Yan, H.; Lu, C.X.; Jing, D.Q.; Chang, C.B.; Liu, N.X.; Hou, X.L. Recycling of carbon fibers in epoxy resin composites using supercritical 1-propanol. New Carbon Mater. 2016, 31, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, I.; Hiramatsu, M.; Shimamura, Y.; Awaya, T.; Sako, T. Chemical recycling of carbon fiber reinforced plastic using supercritical methanol. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 91, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Pickering, S.J.; Lester, E.H.; Warrior, N.A. Decomposition of epoxy resin in supercritical isopropanol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Di Bartolo, A.; Dintcheva, N.T. Matrix and Filler Recycling of Carbon and Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Hadigheh, S.A.; Wei, Y. Recycling of glass fibre reinforced polymer (GFRP) composite wastes in concrete: A critical review and cost benefit analysis. Structures 2023, 53, 1540–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppannan Gopalraj, S.; Kärki, T. A review on the recycling of waste carbon fibre/glass fibre-reinforced composites: Fibre recovery, properties and life-cycle analysis. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; De Marco, I.; Caballero, B.M.; Laresgoiti, M.F.; Legarreta, J.A.; Cabrero, M.A.; González, A.; Chomón, M.J.; Gondra, K. Recycling by pyrolysis of thermoset composites: Characteristics of the liquid and gaseous fuels obtained. Fuel 2000, 79, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahil, M.A.; Williams, P.T. Recycling of carbon fibre reinforced polymeric waste for the production of activated carbon fibres. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 91, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.M.; Martinho, A.; Oliveira, J.P. Recycling of Reinforced Glass Fibers Waste: Current Status. Materials 2022, 15, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, S.J.; Kelly, R.M.; Kennerley, J.R.; Rudd, C.D.; Fenwick, N.J. A fluidised-bed process for the recovery of glass fibres from scrap thermoset composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.J.; Turner, T.A.; Meng, F.; Morris, C.N.; Heil, J.P.; Wong, K.H.; Melendi, S. Developments in the fluidised bed process for fibre recovery from thermoset composites. In Proceedings of the CAMX 2015—Composites and Advanced Materials Expo, Dallas, TX, USA, 26–29 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, P.; Wa, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, J.; Duan, G. A physical process for recycling and reusing waste printed circuit boards, In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Electronics and the Environment, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 10–13 May 2004. [CrossRef]
- Oliveux, G.; Dandy, L.O.; Leeke, G.A. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: Review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Karl, C.W.; Gagani, A.I.; Jørgensen, J.K. Composite material recycling technology—State-of-the-art and sustainable development for the 2020s. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, S.; Pinho, S.T. Recycling carbon fibre reinforced polymers for structural applications: Technology review and market outlook. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. Life cycle assessment of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011, 16, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, R.; McKechnie, J. Environmental and financial performance of mechanical recycling of carbon fibre reinforced polymers and comparison with conventional disposal routes. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R. Introductory Chapter: Recycling and Reuse of End-of-Life Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymers. In Recent Developments in the Field of Carbon Fibers; Khanna, R., Cayumil, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gen2Carbon Website. Available online: https://www.gen2carbon.com (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Hermansson, F.; Janssen, M.; Svanström, M. Prospective study of lignin-based and recycled carbon fibers in composites through meta-analysis of life cycle assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witik, R.A.; Payet, J.; Michaud, V.; Ludwig, C.; Månson, J.A.E. Assessing the life cycle costs and environmental performance of lightweight materials in automobile applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 1694–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overly, J.G.; Dhingra, R.; Davis, G.A.; Das, S. Environmental evaluation of lightweight exterior body panels in new generation vehicles. SAE Trans. 2002, 111, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witik, R.A.; Teuscher, R.; Michaud, V.; Ludwig, C.; Månson, J.A.E. Carbon fibre reinforced composite waste: An environmental assessment of recycling, energy recovery and landfilling. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 49, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Prabhakara, H.M.; Bramer, E.A.; Dierkes, W.; Akkerman, R.; Brem, G. A critical review on recycling of end-of-life carbon fibre/glass fibre reinforced composites waste using pyrolysis towards a circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.A.; Rodríguez, O.; Alguacil, F.J.; García-Díaz, I.; Centeno, T.A.; García-Fierro, J.L.; González, C. Recovery of carbon fibres by the thermolysis and gasification of waste prepreg. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 104, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgini, L.; Benelli, T.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Leonardi, C.; Zattini, G.; Minak, G.; Dolcini, E.; Cavazzoni, M.; Montanari, I.; Tosi, C. Recovery of carbon fibers from cured and uncured carbon fiber reinforced composites wastes and their use as feedstock for a new composite production. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PwC Sustainable Performance and Strategy, 2016. Life Cycle Assessment of CFGF—Continuous Filament Glass Fibre Products, Report Prepared for GlassFibreEurope. Available online: https://glassfibreeurope.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/GFE_LCA-report-2023-February-2023.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Jones, N.; Williams, P.T. Recycling of fibre-reinforced polymeric waste by pyrolysis: Thermo-gravimetric and bench-scale investigations. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2003, 70, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudersbach, M.; Jürgens, M.; Pohler, M.; Spierling, S.; Venkatachalam, V.; Endres, H.J.; Barner, L. Life Cycle Assessment in a Nutshell—Best Practices and Status Quo for the Plastic Sector. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 2300466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppannan Gopalraj, S.; Deviatkin, I.; Horttanainen, M.; Kärki, T. Life Cycle Assessment of a Thermal Recycling Process as an Alternative to Existing CFRP and GFRP Composite Wastes Management Options. Polymers 2021, 13, 4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kočí, V.; Picková, E. Life cycle perspective of liquid epoxy resin use in the automotive industry. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marson, A.; Masiero, M.; Modesti, M.; Scipioni, A.; Manzardo, A. Life Cycle Assessment of Polyurethane Foams from Polyols Obtained through Chemical Recycling. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

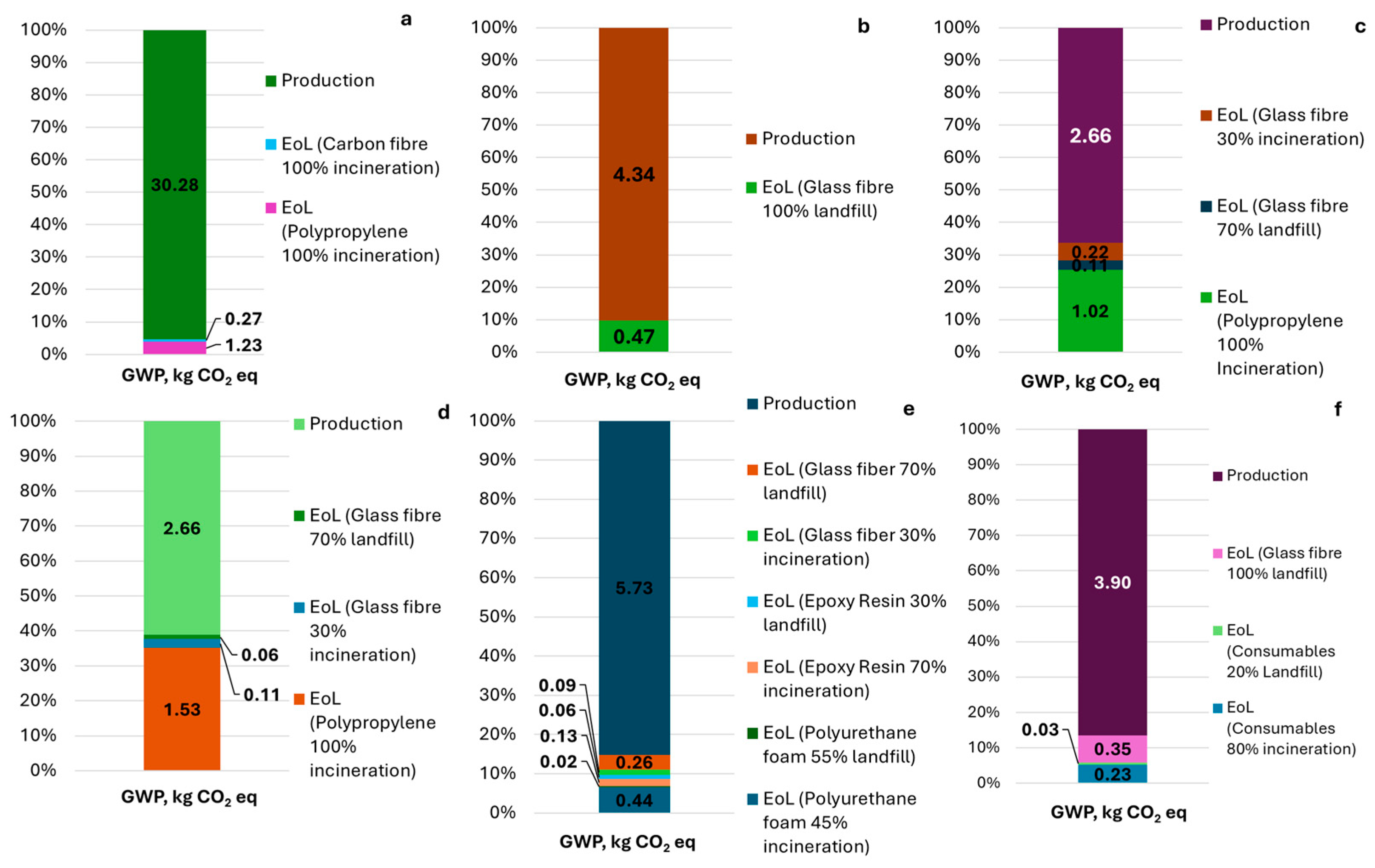
| Material | End-of-Life Scenario | Recycling Method | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fibre | |||
| Carbon fibre reinforced polymer | Scenario 1 59% recycling, 41% incineration Scenario 2 100% incineration, Scenario 3 100% landfill | Thermal recycling | [38] |
| Carbon fibre | 100% Incineration | n/a | [52,53] |
| Carbon fibre reinforced polymers | 100% landfill | n/a | [52,54] |
| Carbon fibre reinforced polymers | Scenario 1 100% pyrolysis Scenario 2 100% incineration, Scenario 3 100% landfill | Pyrolysis | [54,55] |
| Carbon fibre reinforced polymers | Scenario 1 24% recycled and may be used in CF production, 19% recycled and may be used in another application, 57% landfilled or incinerated | Mechanical recycling | [49,52] |
| Scenario 2 100% incineration, | n/a | ||
| Scenario 3 100% landfill | n/a | ||
| Polybenzoxazine resin with woven carbon fibre | 100% pyrolysis with pyrolysis product yield: Solid (activated carbon fibres may be used for composite production) 70–83.6% Oil 14–24.6% Gas 0.7–3.8% | Pyrolysis in a fixed-bed reactor | [40,56] |
| Polybenzoxazine resin with carbon fibre | 100% pyrolysis with pyrolysis product yield: Solid (recovered fibres) 58.4–61.5% Oil 28.5–30.7% Gas 10–10.9% | Thermolysis and gasification | [56,57] |
| Epoxy composite with carbon fibre | 100% pyrolysis with pyrolysis product yield: Solid (recovered fibres) 65–70% Oil 10–15% Gas 15–20% | Pyrolysis process | [56,58] |
| Glass Fibre | |||
| Waste from glass fibre manufacture | 54% non-hazardous waste to landfill 44% waste sent to recycling 1.7% non-hazardous waste to incineration 0.4% hazardous waste landfilled | n/a | [59] |
| Epoxy resin with GF and CF (45%) Polypropylene resin with GF tape (75%) | 100% pyrolysis with pyrolysis product yield: Solid (recovered fibres) 65.3–81.7% Oil 18–31.7% Gas 0.2–3% 100% pyrolysis with pyrolysis product yield: Solid (recovered fibres) 78.9% Oil 20% Gas 1.1% | Pyrolysis | [56,60] |
| Material | End of Life | Literature/Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | 100% Incineration | 10XL data |
| Carbon fibre | 100% Incineration | [52,62] |
| Glass fibre | 100% Landfill | NAVAL group data |
| Polypropylene | 100% Incineration | 10XL data |
| Glass fibre Glass fibre ash | 30% Incineration, 70% Landfill | 10XL data |
| Glass fibre | 30% Incineration, 70% Landfill | 10XL data |
| Epoxy resin | 70% Incineration, 30% Landfill | [63] |
| Polyurethane foam | 45% Incineration, 55% Landfill | [64] |
| Glass fibre | 100% Landfill | Naval group data |
| Consumables | 80% Incineration, 20% Landfill | Naval group data |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziemińska-Stolarska, A.; Sobulska, M.; Pietrzak, M.; Zbiciński, I. A Review of End-of-Life Scenarios for Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Materials. Energies 2024, 17, 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153713
Ziemińska-Stolarska A, Sobulska M, Pietrzak M, Zbiciński I. A Review of End-of-Life Scenarios for Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Materials. Energies. 2024; 17(15):3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiemińska-Stolarska, Aleksandra, Mariia Sobulska, Monika Pietrzak, and Ireneusz Zbiciński. 2024. "A Review of End-of-Life Scenarios for Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Materials" Energies 17, no. 15: 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153713
APA StyleZiemińska-Stolarska, A., Sobulska, M., Pietrzak, M., & Zbiciński, I. (2024). A Review of End-of-Life Scenarios for Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Materials. Energies, 17(15), 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153713








