Research on Photovoltaic Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Based on Improved Tuna Swarm Algorithm and Adaptive Perturbation Observation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The TSO and P&O algorithms, which are standard in this context, have undergone improvement to enhance both the speed and the accuracy of convergence;
- This MPPT controller employs an intelligent switching technique based on the ITSO and AP&O algorithms. It is designed to address the limitations of traditional MPPT methodologies, which are prone to failure in tracking the MPP and exhibiting erratic behavior in the presence of local shadowing;
- The standard TSO, PSO, GWO, FLC, and AP&O are compared with the proposed algorithm to verify its performance;
- The real-time simulation platform of PV MPPT based on RT-LAB was constructed with the objective of validating the superiority of the proposed MPPT control method.
2. Output Characteristics of PV System under Partial Shade
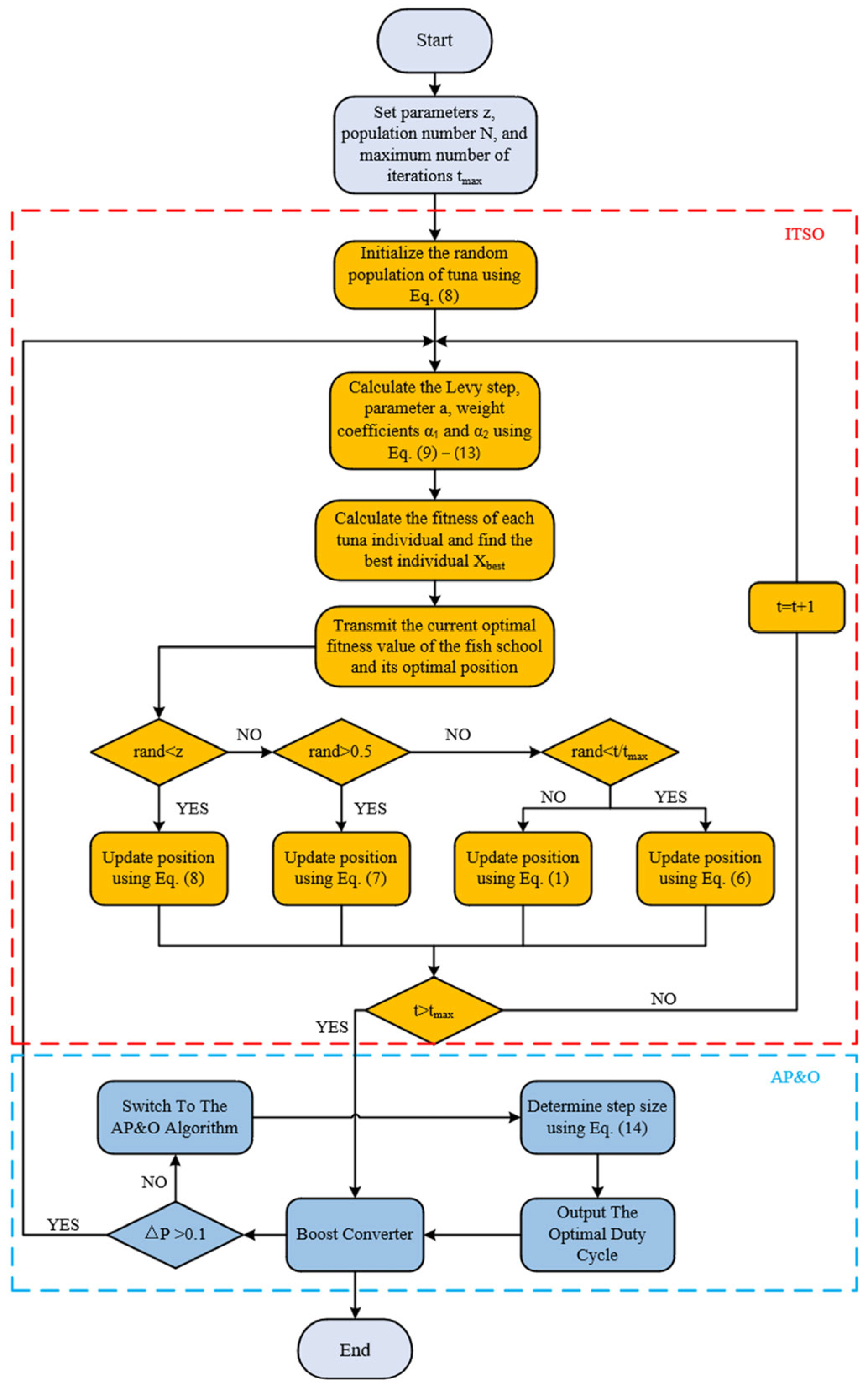
3. MPPT Algorithm Based on ITSO-AP&O
3.1. Tuna Swarm Optimization
3.1.1. Spiral Foraging
3.1.2. Parabolic Foraging
3.2. Improved Tuna Swarm Optimization
SPM Chaotic Map
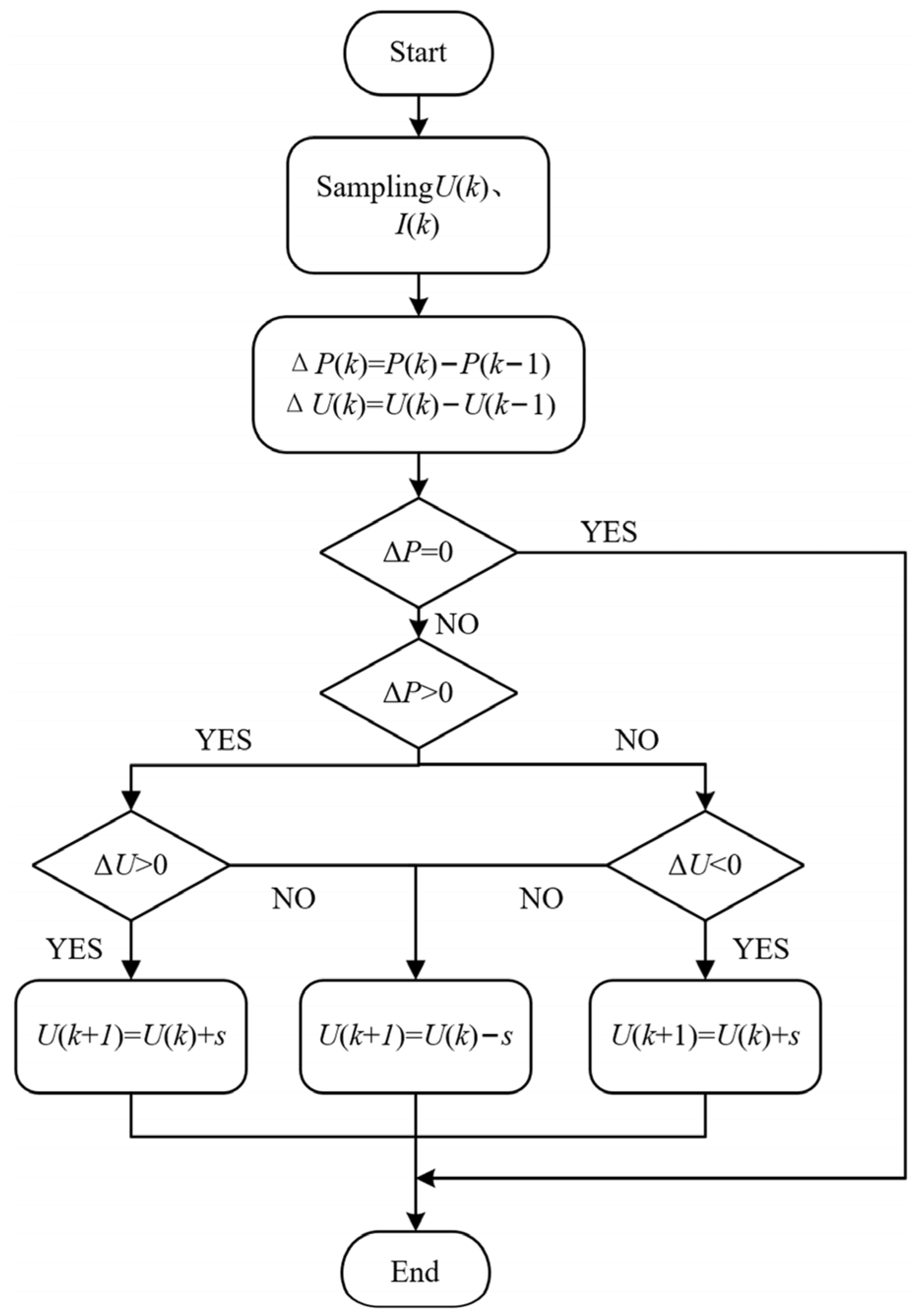
3.3. Adaptive Perturbation and Observation Method
3.4. Application of ITSO-AP&O Algorithm in MPPT
3.4.1. Algorithm Restart Condition
3.4.2. Algorithm Switching Condition
4. Simulation Verification and Analysis
4.1. MPPT Tracking without Shadings
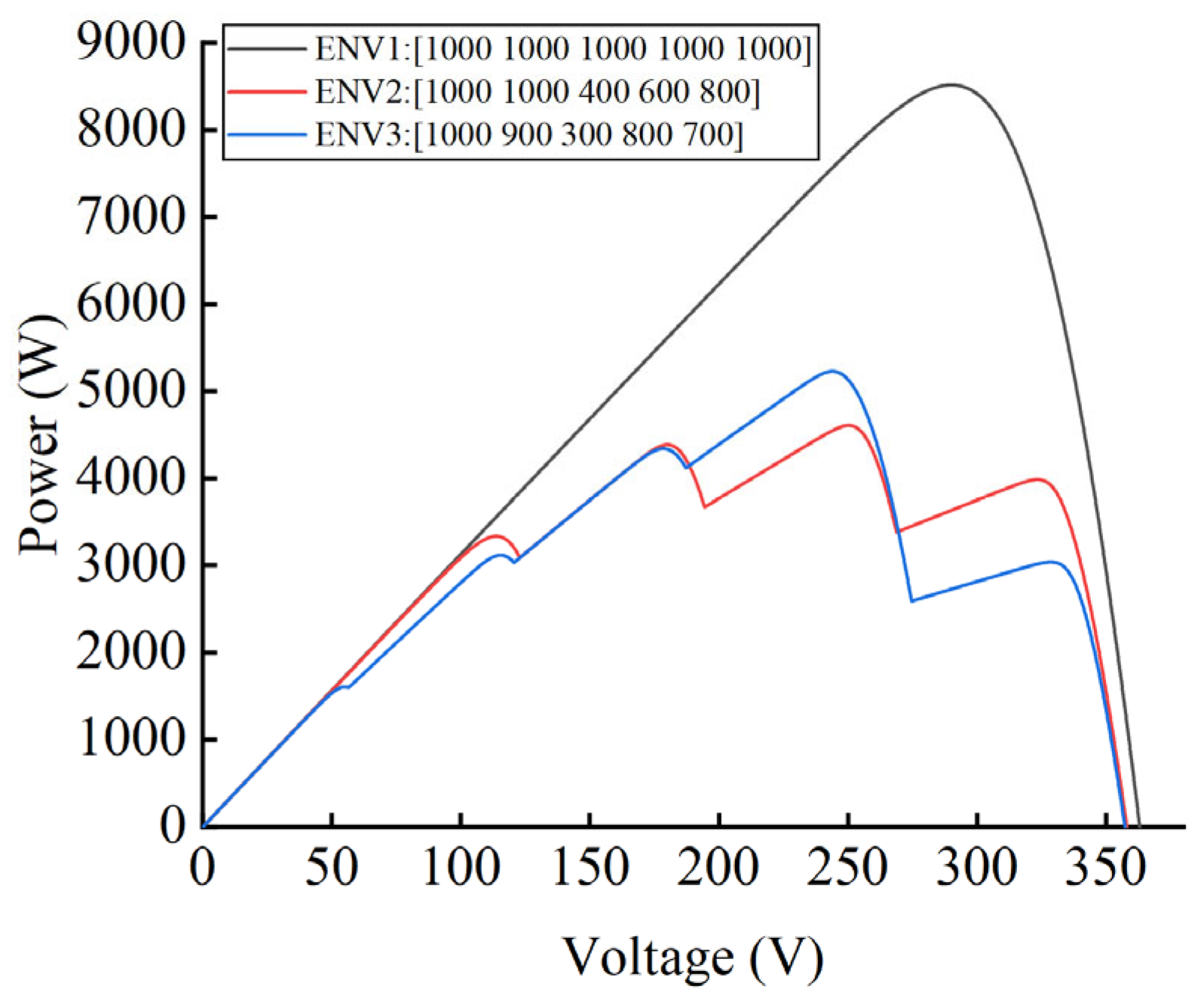
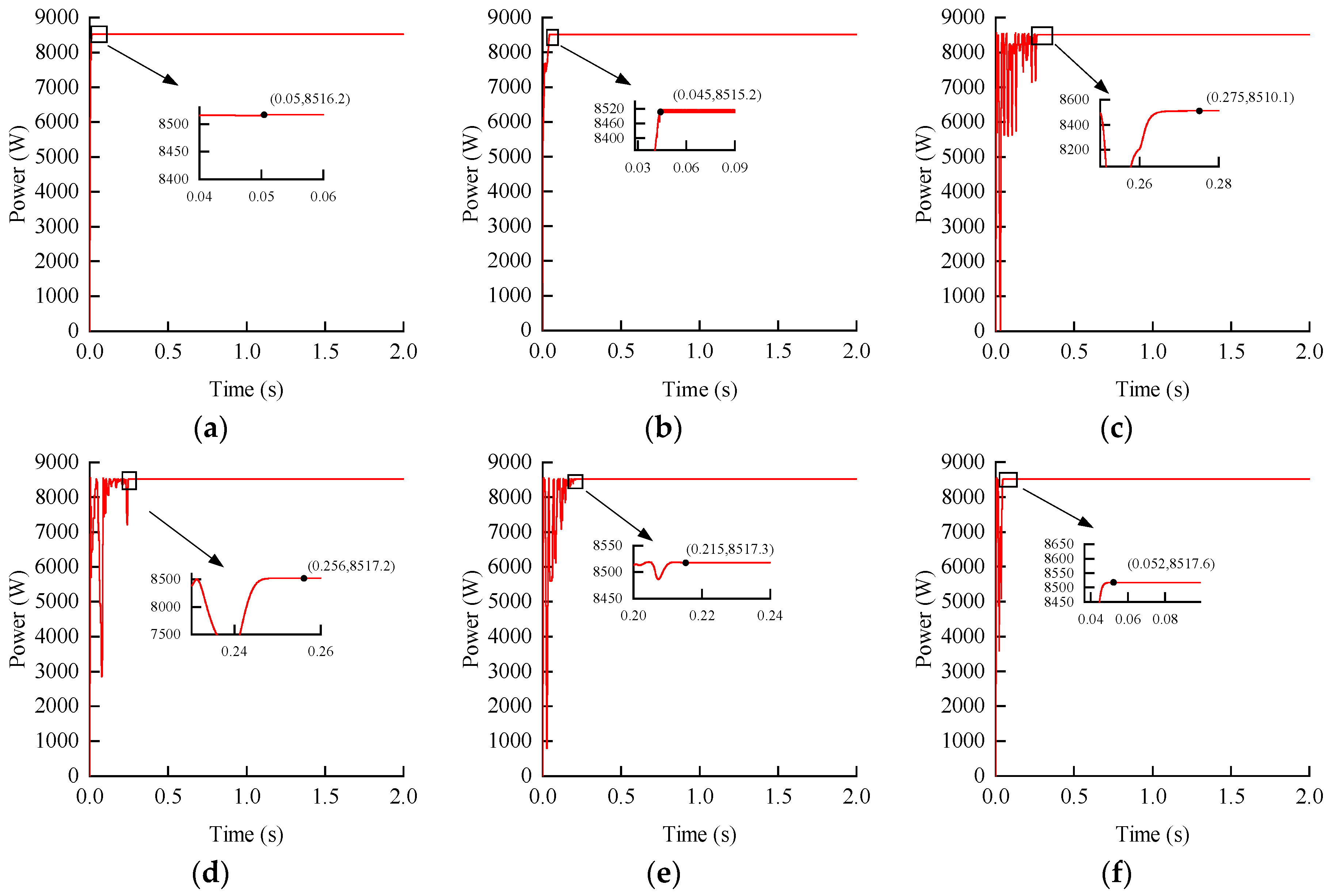
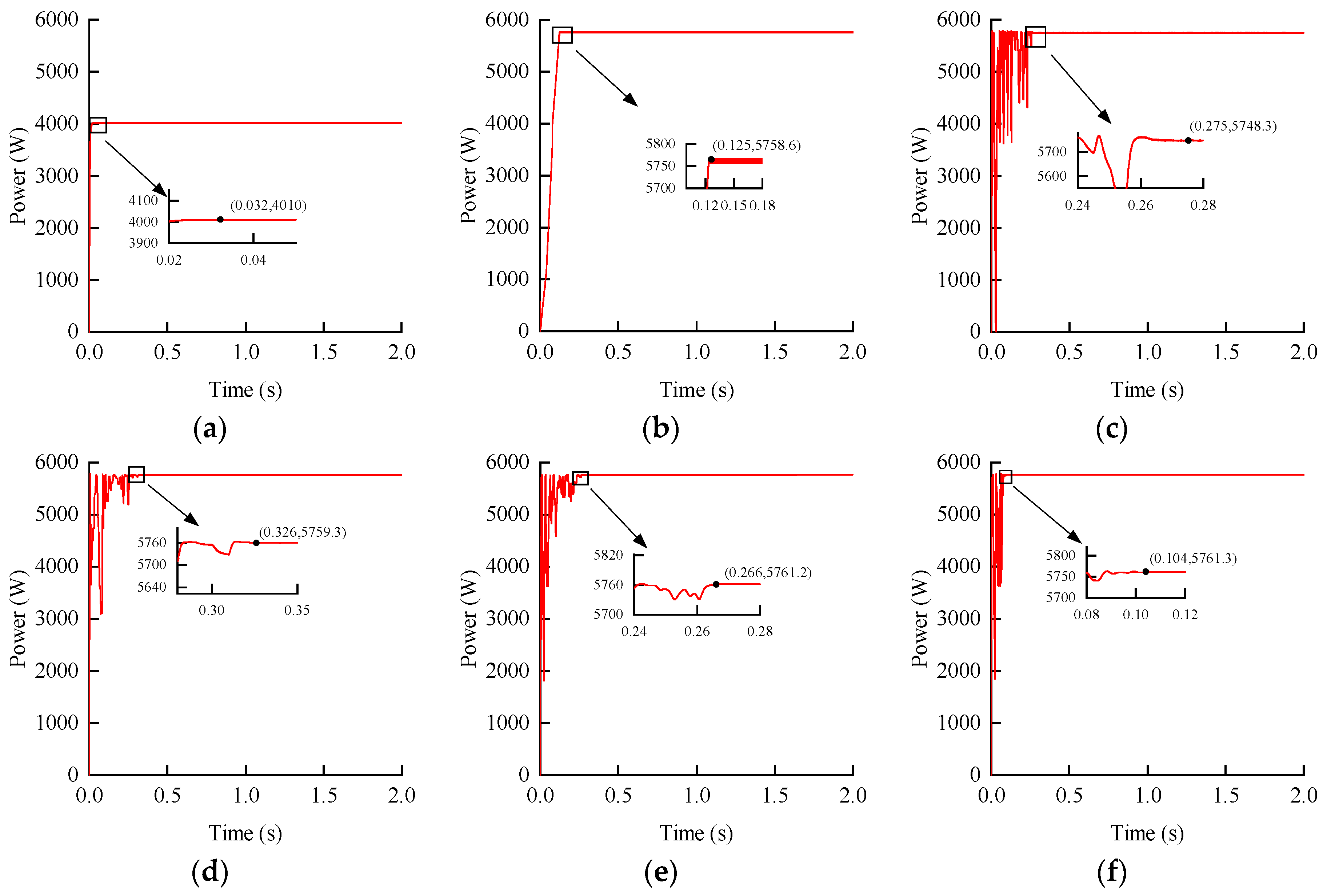
4.2. MPPT Tracking in the Case of Static Partial Shading
4.3. MPPT Tracking in the Case of Dynamic Partial Shading
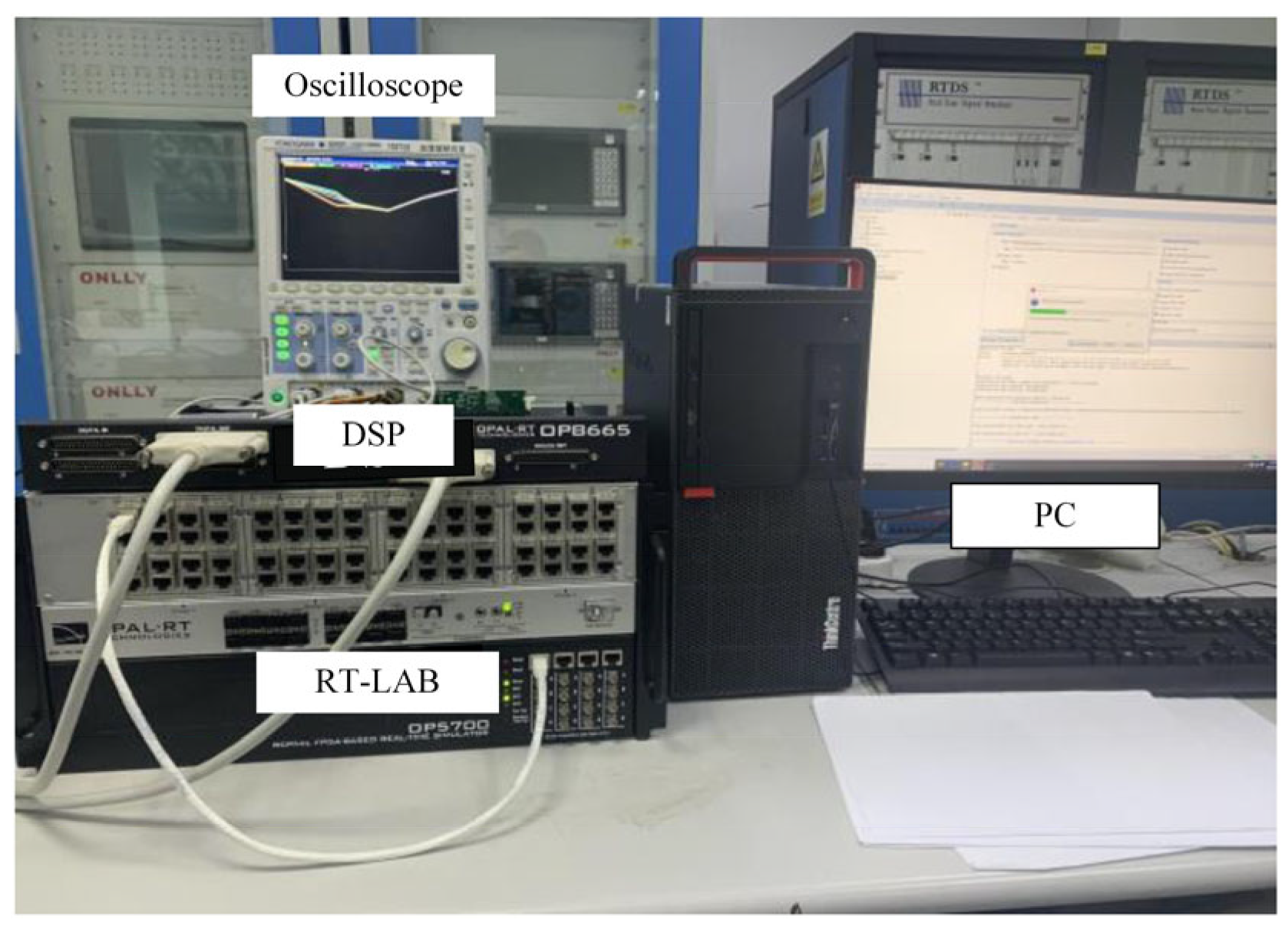
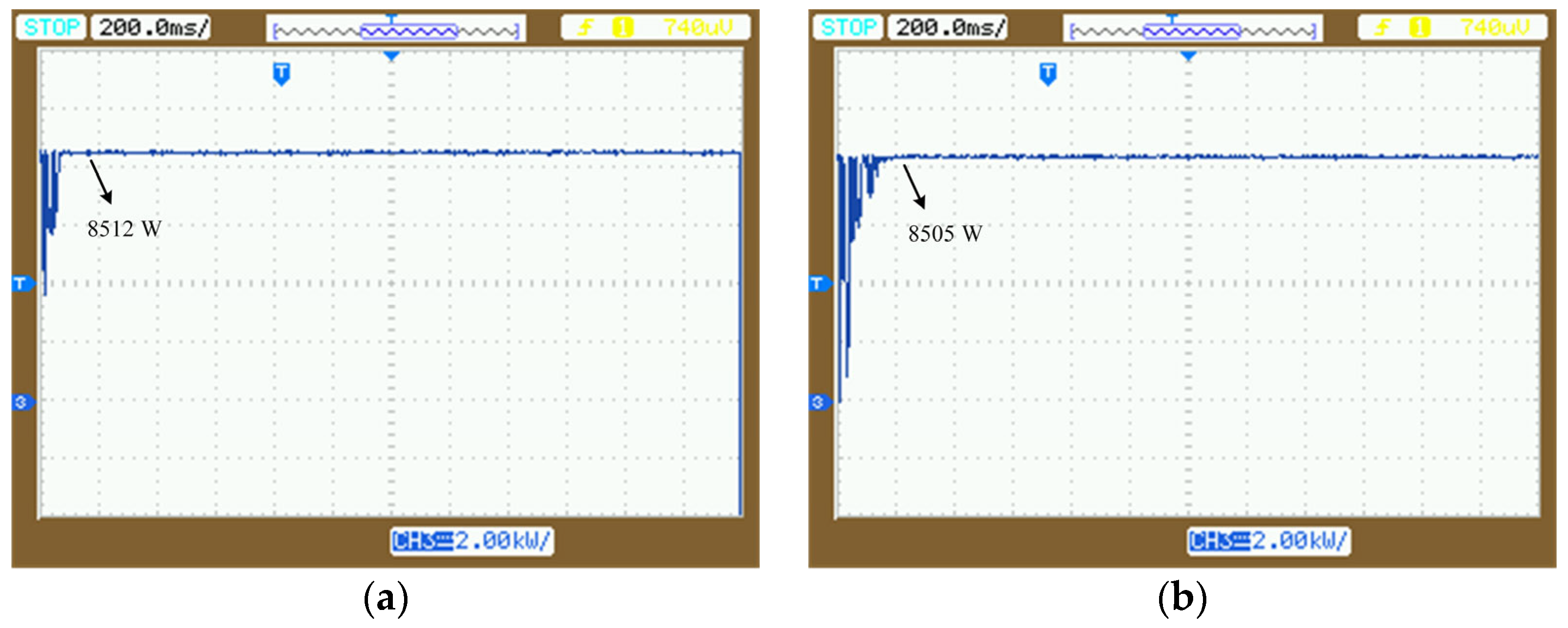
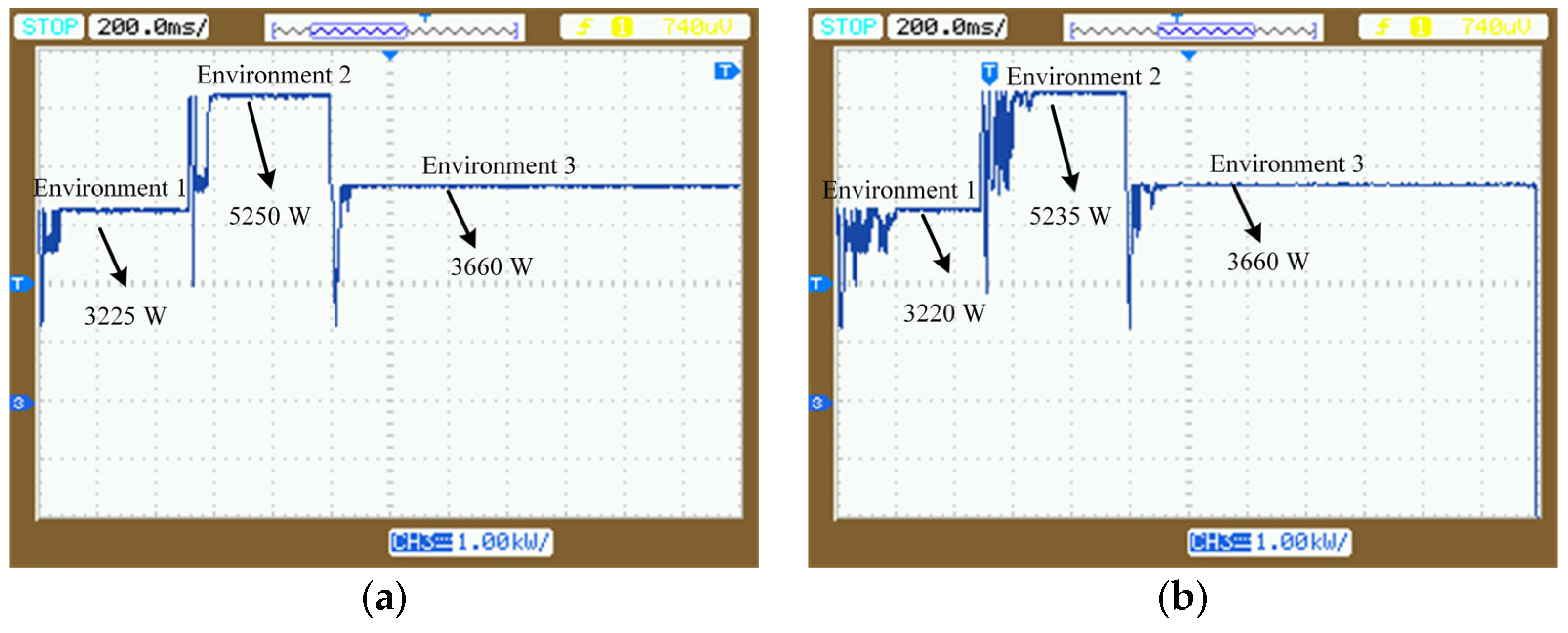
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Afshan, S.; Awosusi, A.A.; Abbas, S. Transition towards sustainable energy: The role of economic complexity, financial liberalization and natural resources management in China. Resour. Policy 2023, 83, 103631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouhi, A.; Rehman, S.; Buker, M.S.; Said, Z. Up-to-date literature review on Solar PV systems: Technology progress, market status and R&D. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132339. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.; Cui, L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, K.; Zhou, L.; Huang, H. Classification and summarization of solar photovoltaic MPPT techniques: A review based on traditional and intelligent control strategies. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, A.K.; Karuppiah, N.; Selvaraj, T.; Balachandran, P.K.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Senjyu, T. A comparative analysis of maximum power point techniques for solar photovoltaic systems. Energies 2022, 15, 8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellakhi, A.; El Beid, S.; Abouelmahjoub, Y.; Mchaouar, Y. Optimization of power extracting from photovoltaic systems based on a novel adaptable step INC MPPT approach. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.O.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Classification and evaluation review of maximum power point tracking methods. Sustain. Futures 2020, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhukya, L.; Kedika, N.R.; Salkuti, S.R. Enhanced maximum power point techniques for solar photovoltaic system under uniform insolation and partial shading conditions: A review. Algorithms 2022, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasim, M.S.; Amjad, M.; Abbasi, M.A.; Bhatti, A.R.; Rasool, A. An improved grasshopper-based MPPT approach to reduce tracking time and startup oscillations in photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Shu, H.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Sun, L. Comprehensive overview of maximum power point tracking algorithms of PV systems under partial shading condition. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirateruna, E.S.; Millenia, A.F.A. Design of MPPT PV using particle swarm optimization algorithm under partial shading condition. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Robot. 2022, 4, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahhir, S.; Chtita, S.; Chouder, A.; El Hammoumi, A. Enhanced energy output from a PV system under partial shaded conditions through Grey wolf optimizer. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 9, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, U.; Singh, V.; Kumar, B.; Rani, A. An improved MVO assisted global MPPT algorithm for partially shaded PV system. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 38, 6715–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanidhi, B.; Ramasamy, L.; Samuel, C.R.; Vasanth, M. Development of novel Cuckoo search optimization-based controller for partially shaded Photovoltaic system. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 45, 4447–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhang, L. A differential evolution optimization-based black widow spider method in PV systems under shading conditions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 148, 110927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.; Kumar, C.; Anbarasan, A.; Sowmya, R. A new maximum power point tracking technique based on whale optimisation algorithm for solar photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2022, 43, 5627–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.H.; Khan, N.M.; Mirza, A.F.; Mansoor, M.; Akhtar, N.; Qadir, M.U.; Khan, N.A.; Moosavi, S.K.R. A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm based MPPT control technique for PV systems under complex partial shading condition. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101367. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, S.; Chiu, C.S.; Ngo, T.D. A novel horse racing algorithm based MPPT control for standalone PV power systems. Energies 2022, 15, 7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagadurga, T.; Narasimham, P.; Vakula, V.S. Global maximum power point tracking of solar photovoltaic strings under partial shading conditions using cat swarm optimization technique. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Ye, Q.; Jiang, K.; Mo, X.; Shen, G. An improved MPPT method for photovoltaic systems based on mayfly optimization algorithm. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charin, C.; Ishak, D.; Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Ismail, B.; Alsuwian, T.; Alhawari, A.R.H. Modified levy-based particle swarm optimization (MLPSO) with boost converter for local and global point tracking. Energies 2022, 15, 7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibi, R.; EL Bachtiri, R.; El Hammoumi, K.; Yagoubi, M. Photovoltaic system’s MPPT under partial shading using TS fuzzy robust control. IFAC-Pap. 2022, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Gaur, P. Radial basis function neural network technique for efficient maximum power point tracking in solar photo-voltaic system. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, B.C.; Lai, Y.C.; Lin, C.E. A deep reinforcement learning-based MPPT control for PV systems under partial shading condition. Sensors 2020, 20, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.S. PSO and ANN based hybrid MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic array under partial shading condition. Eng. Int. 2020, 8, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, M.K.; Pradhan, C.; Calay, R.K. A computational intelligence based maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic power generation system with small-signal analysis. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 2023, 44, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldino AL, M.; Freitas, C.M.; Monteiro, L.F.C. Analysis of the hybrid PSO-InC MPPT for different partial shading conditions. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 22, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Han, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Han, B.; Tang, A. Tuna swarm optimization: A novel swarm-based metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 9210050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.N.M.; Radzi, M.A.M.; Azis, N.; Shafie, S.; Zainuri, M.A.A.M. An enhanced adaptive perturb and observe technique for efficient maximum power point tracking under partial shading conditions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacca, G.; dos Santos Junior, V.C.; de Melo, V.V. An improved Jaya optimization algorithm with Lévy flight. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tian, J. An improved nonlinear tuna swarm optimization algorithm based on circle chaos map and levy flight operator. Electronics 2022, 11, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerxun, W.; Xu, C.; Guo, H.; Guo, L.; Zeng, N.; Cheng, Z. An ultra-short-term wind speed prediction model using LSTM based on modified tuna swarm optimization and successive variational mode decomposition. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 3001–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Gu, M.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wei, W.; Fan, Z. Bioinspired environment exploration algorithm in swarm based on levy flight and improved artificial potential field. Drones 2022, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
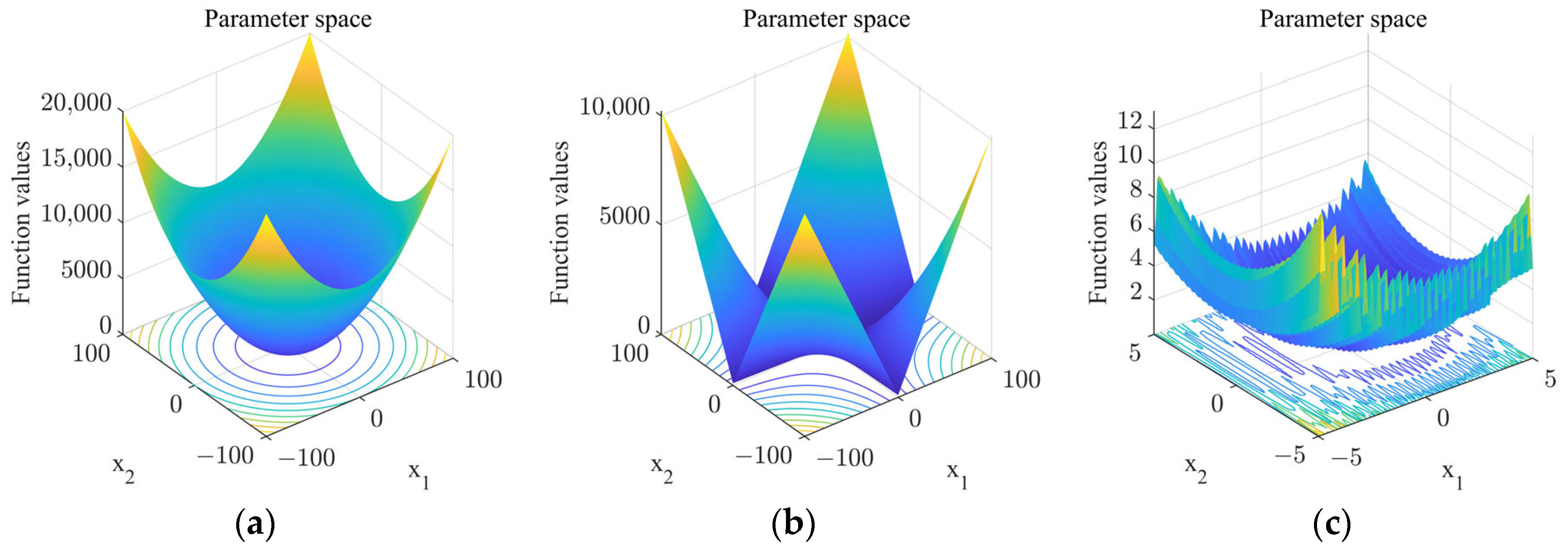
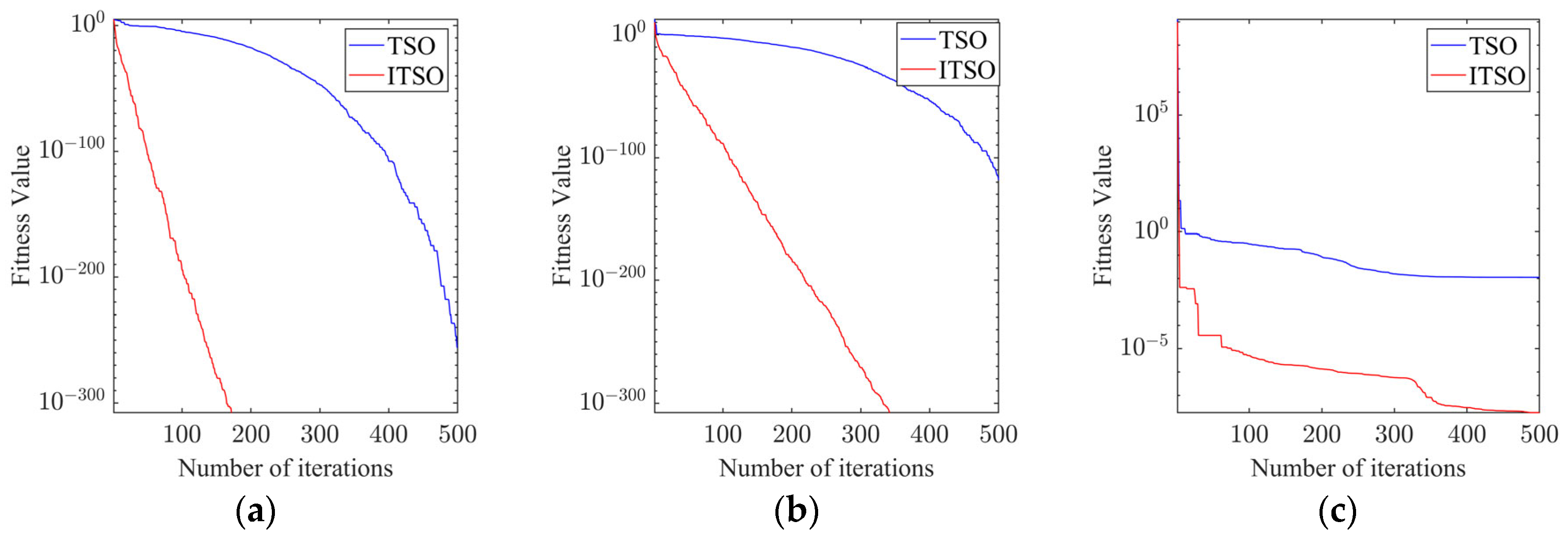

| Function | Performance | ITSO | TSO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere | Optimal value | 0 | 5.78446 × 10−273 |
| Average value | 0 | 7.18554 × 10−227 | |
| Standard deviation | 0 | 0 | |
| Schwefel 2.22 | Optimal value | 0 | 1.16399 × 10−133 |
| Average value | 0 | 5.20219 × 10−118 | |
| Standard deviation | 0 | 2.82359 × 10−117 | |
| Penalized 2 | Optimal value | 4.0874 × 10−9 | 3.5093 × 10−8 |
| Average value | 7.6265 × 10−7 | 1.6872 × 10−5 | |
| Standard deviation | 2.5252 × 10−6 | 3.0156 × 10−5 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum power | 1705.2 W |
| Voltage at MPP | 58 V |
| Current at MPP | 29.4 A |
| Open circuit voltage | 72.6 V |
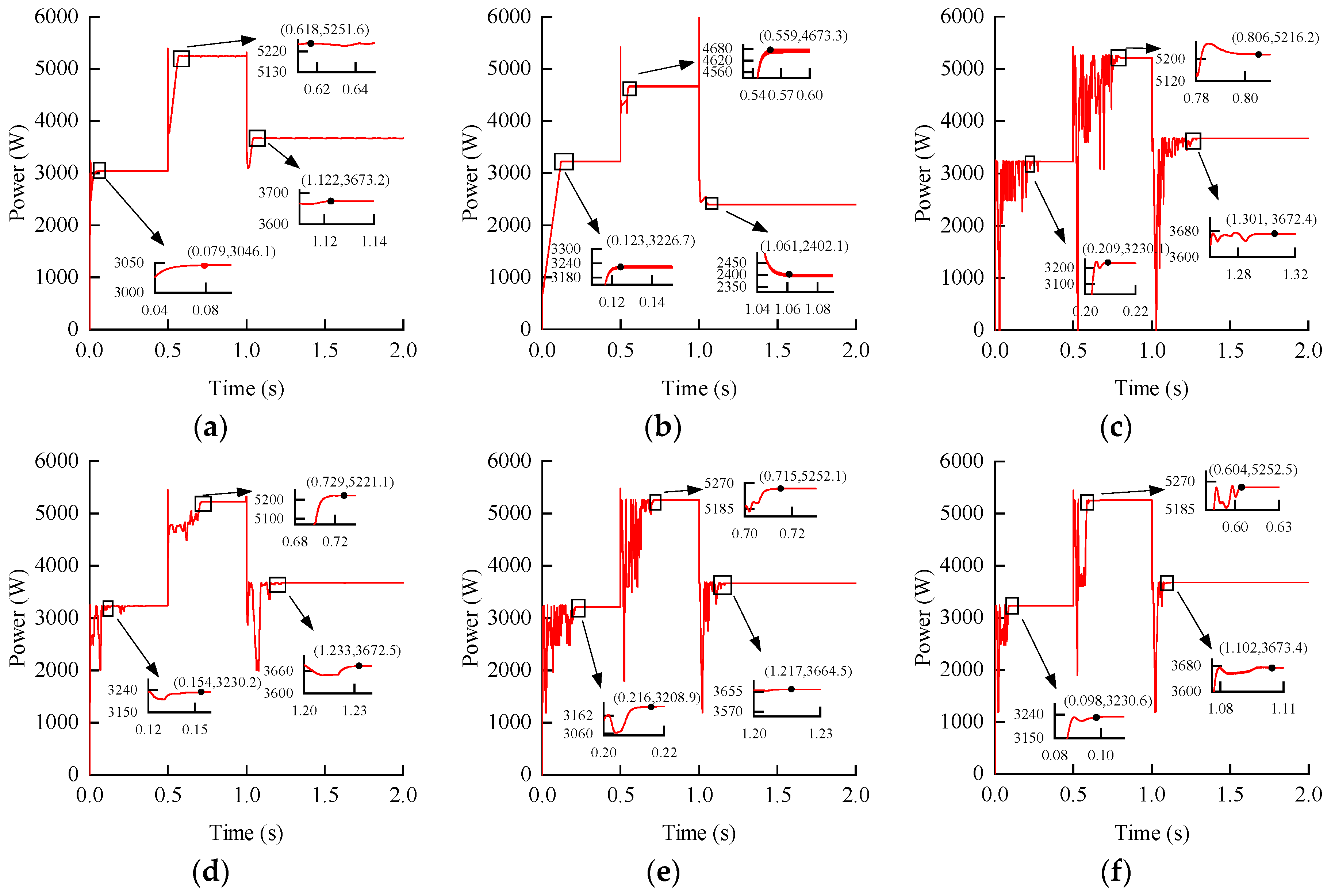
| Environment | Algorithm | Tracking Time (s) | Tracking Power (W) | Tracking Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AP&O | 0.079 | 3046.1 | 94.277 |
| FLC | 0.123 | 3226.7 | 99.867 | |
| PSO | 0.209 | 3230.1 | 99.972 | |
| GWO | 0.154 | 3230.2 | 99.975 | |
| TSO | 0.216 | 3208.9 | 99.316 | |
| ITSO-AP&O | 0.098 | 3230.6 | 99.988 | |
| 2 | AP&O | 0.118 | 5251.6 | 99.954 |
| FLC | 0.059 | 4673.3 | 88.947 | |
| PSO | 0.306 | 5216.2 | 99.281 | |
| GWO | 0.229 | 5221.1 | 99.374 | |
| TSO | 0.215 | 5252.1 | 99.964 | |
| ITSO-AP&O | 0.104 | 5252.5 | 99.971 | |
| 3 | AP&O | 0.122 | 3673.2 | 99.951 |
| FLC | 0.061 | 2402.1 | 65.363 | |
| PSO | 0.301 | 3672.4 | 99.929 | |
| GWO | 0.233 | 3672.5 | 99.932 | |
| TSO | 0.217 | 3664.5 | 99.714 | |
| ITSO-AP&O | 0.102 | 3673.4 | 99.956 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; He, Y.; Li, M. Research on Photovoltaic Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Based on Improved Tuna Swarm Algorithm and Adaptive Perturbation Observation Method. Energies 2024, 17, 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122985
Li X, He Y, Li M. Research on Photovoltaic Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Based on Improved Tuna Swarm Algorithm and Adaptive Perturbation Observation Method. Energies. 2024; 17(12):2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122985
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianqi, Ye He, and Maojun Li. 2024. "Research on Photovoltaic Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Based on Improved Tuna Swarm Algorithm and Adaptive Perturbation Observation Method" Energies 17, no. 12: 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122985
APA StyleLi, X., He, Y., & Li, M. (2024). Research on Photovoltaic Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Based on Improved Tuna Swarm Algorithm and Adaptive Perturbation Observation Method. Energies, 17(12), 2985. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122985





