Implementation of a Microgrid System with a Four-Phase Inductor Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter for EV Charging Stations
Abstract
1. Introduction
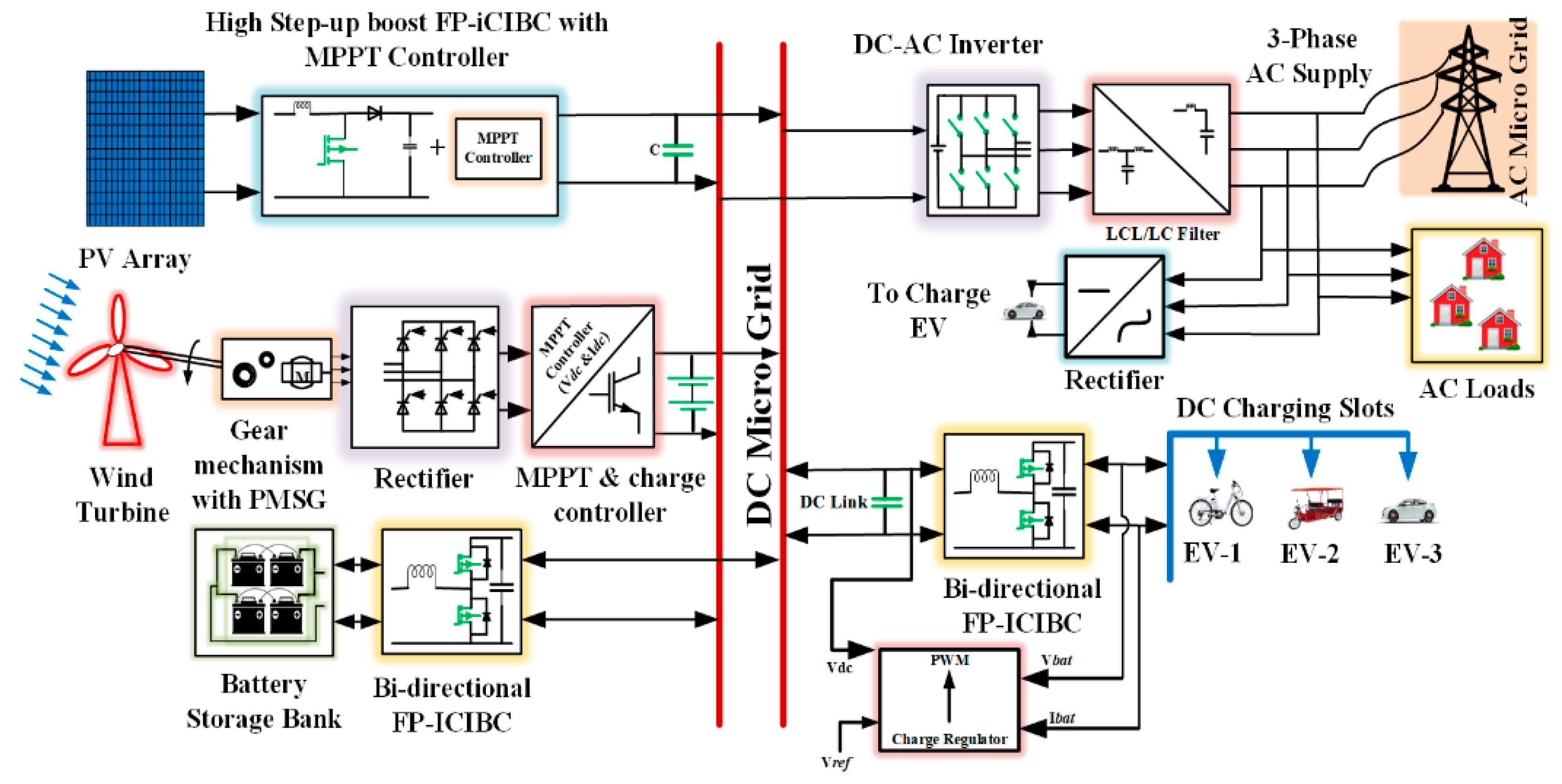
2. Proposed System Configuration
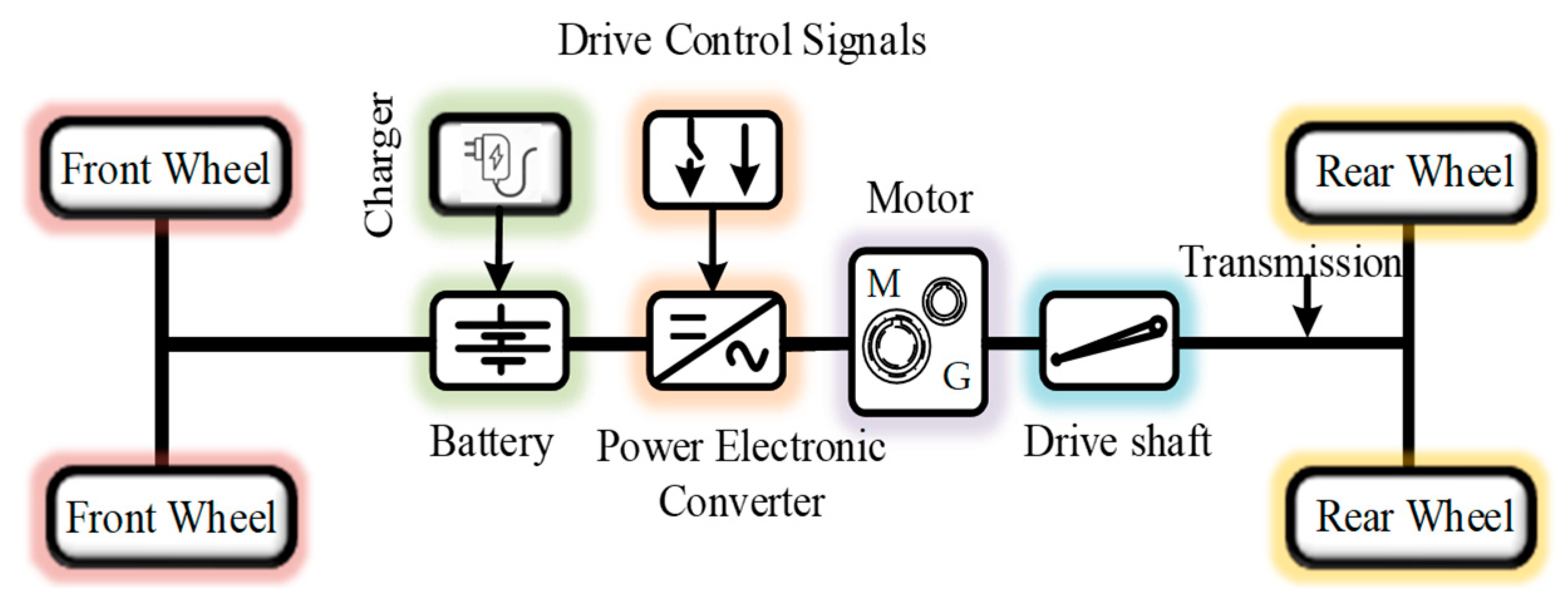
2.1. EV Structure
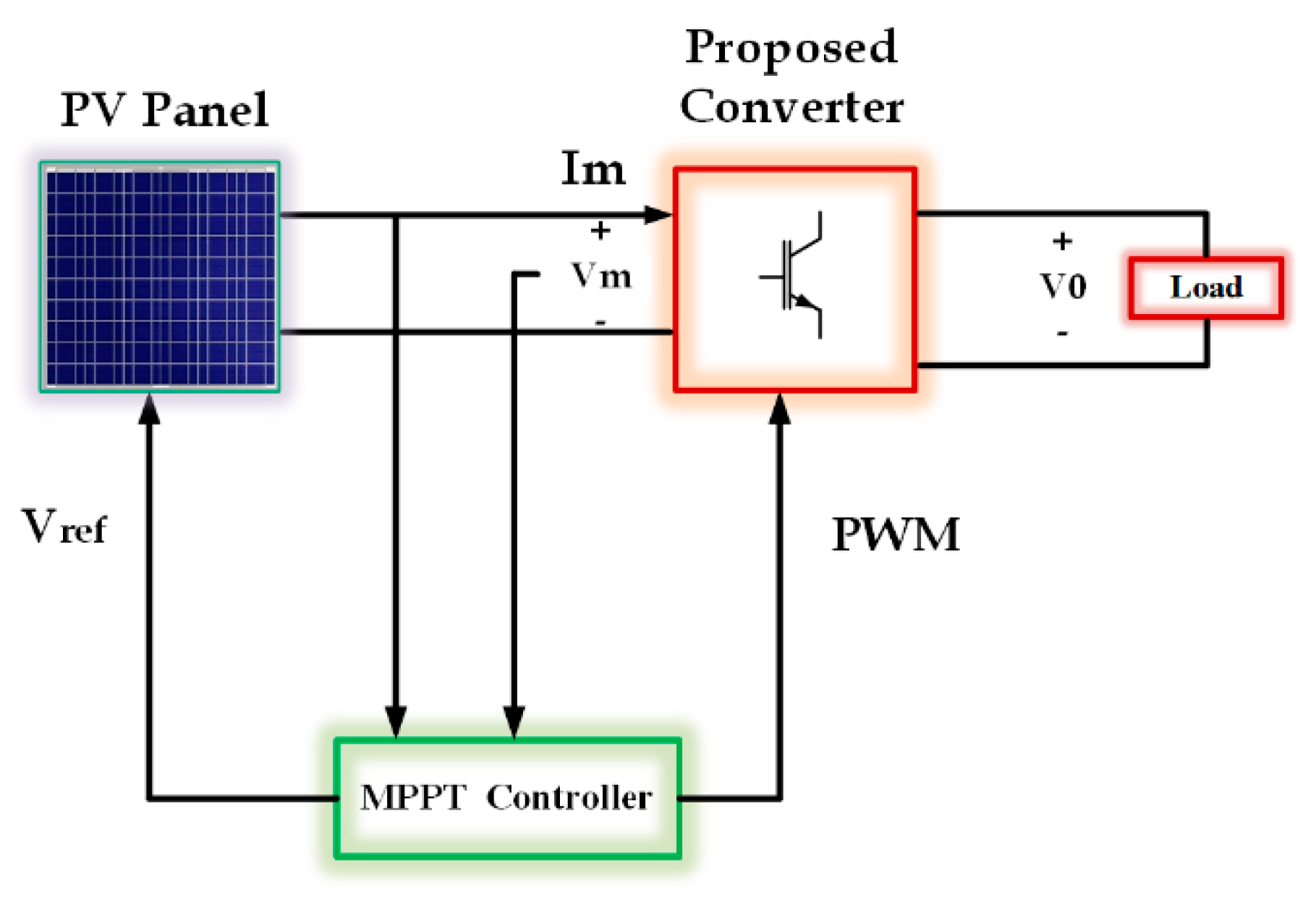
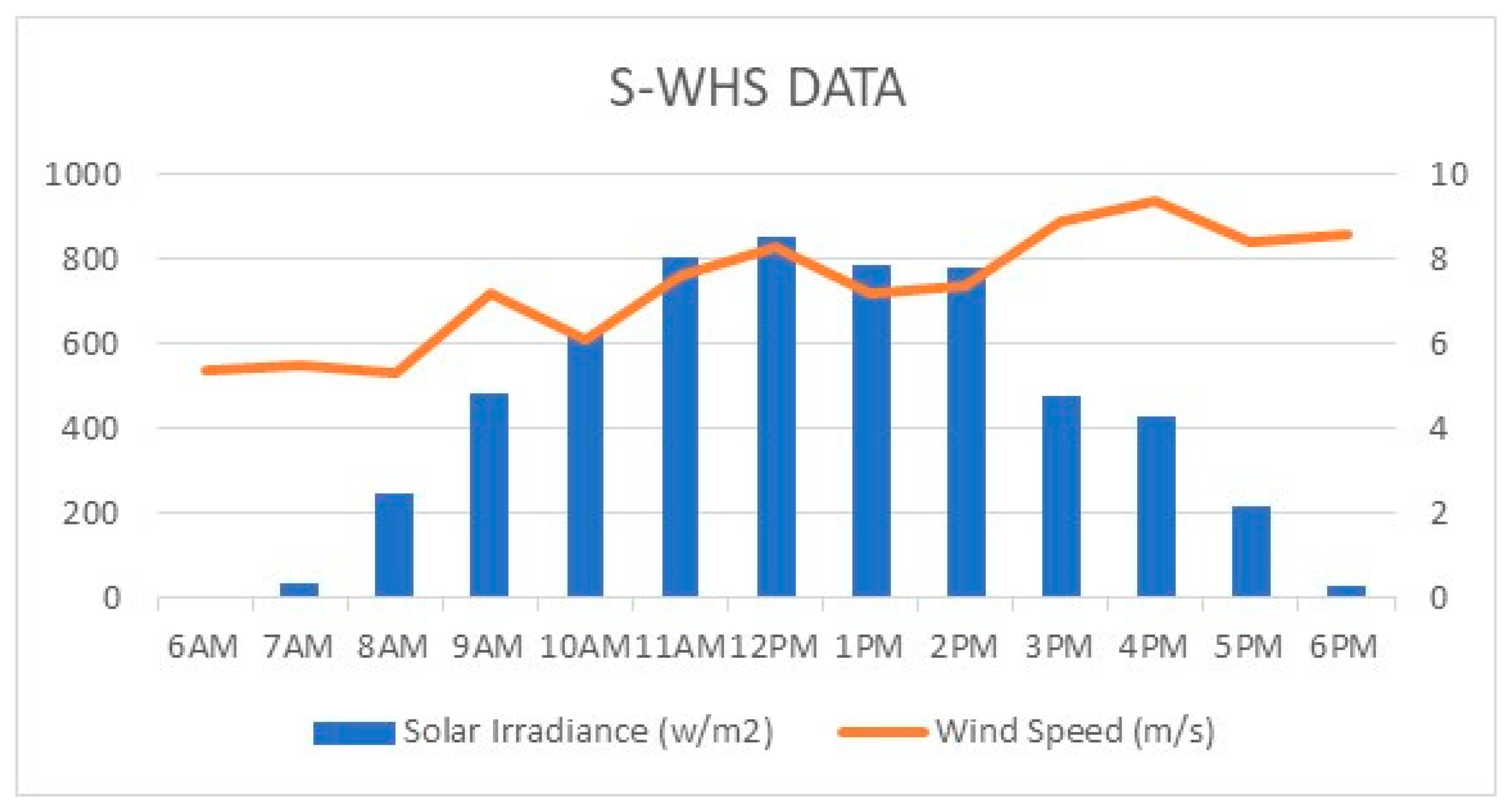
2.2. PV Solar System
2.3. Wind Energy System
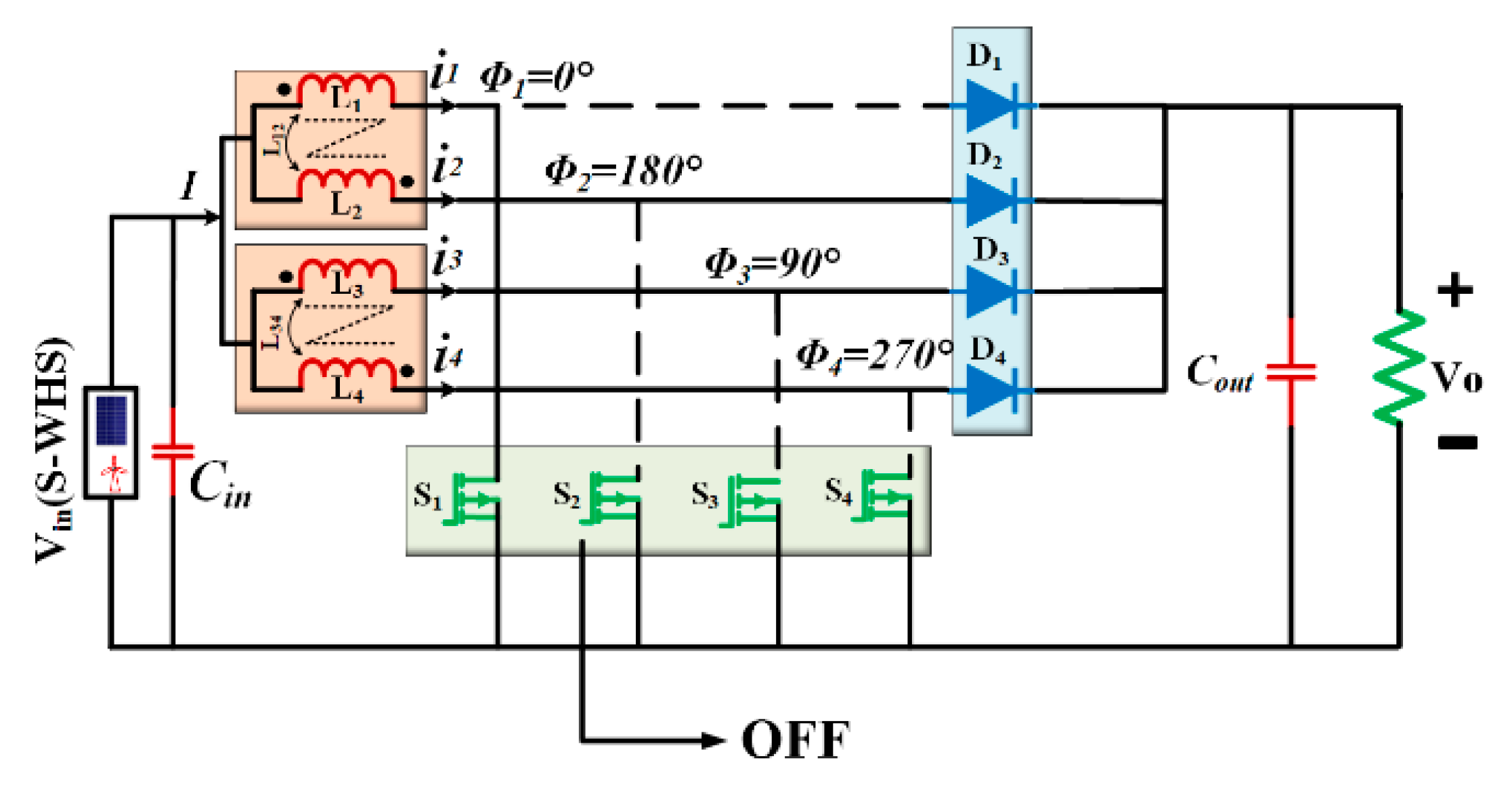
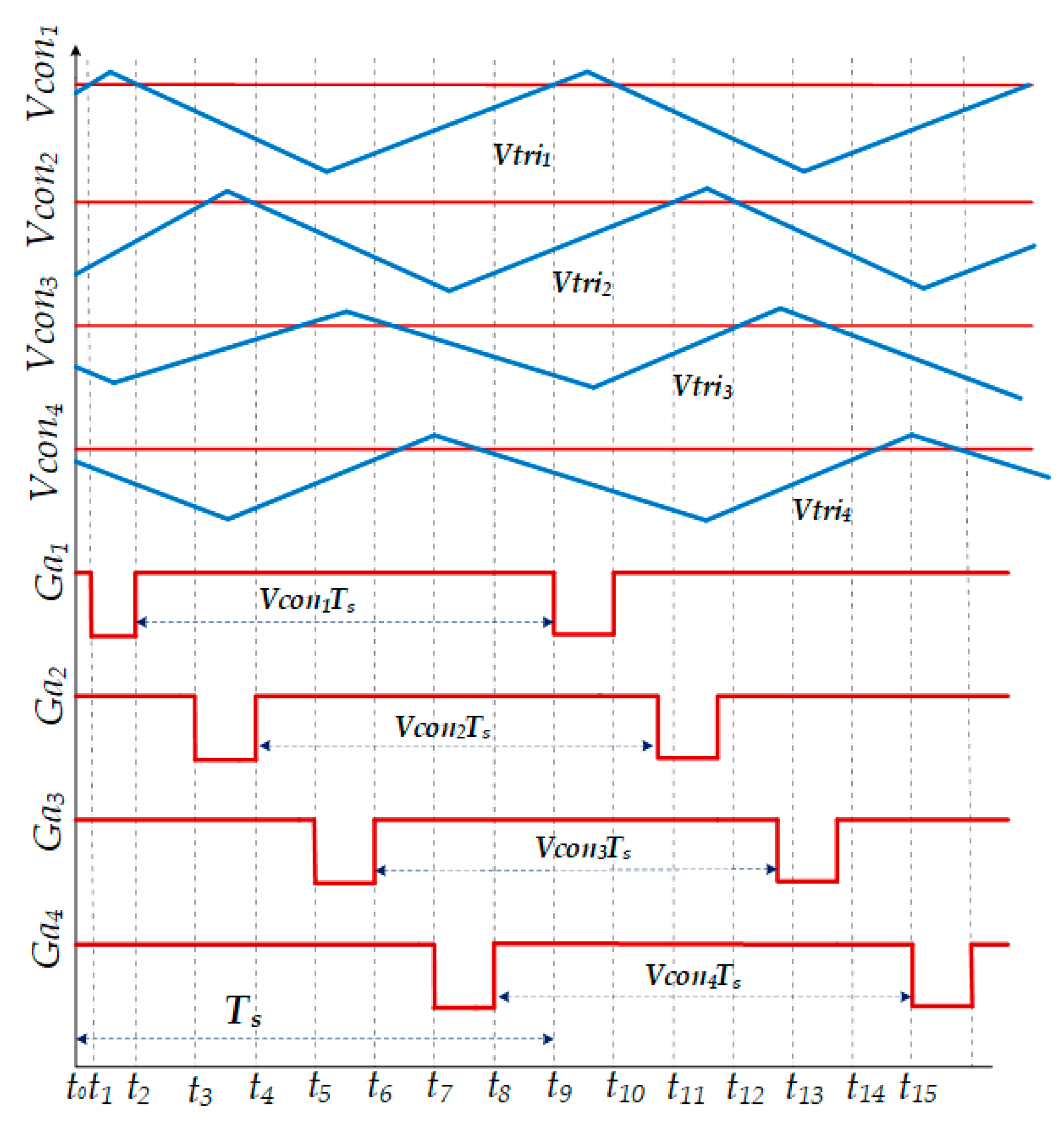
3. Design Structure for Proposed Four-Phase Inductor Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter (FP-ICIBC) and Its Control Strategy
- Case 1: S1 is ON (M1000) and other switches are OFF.
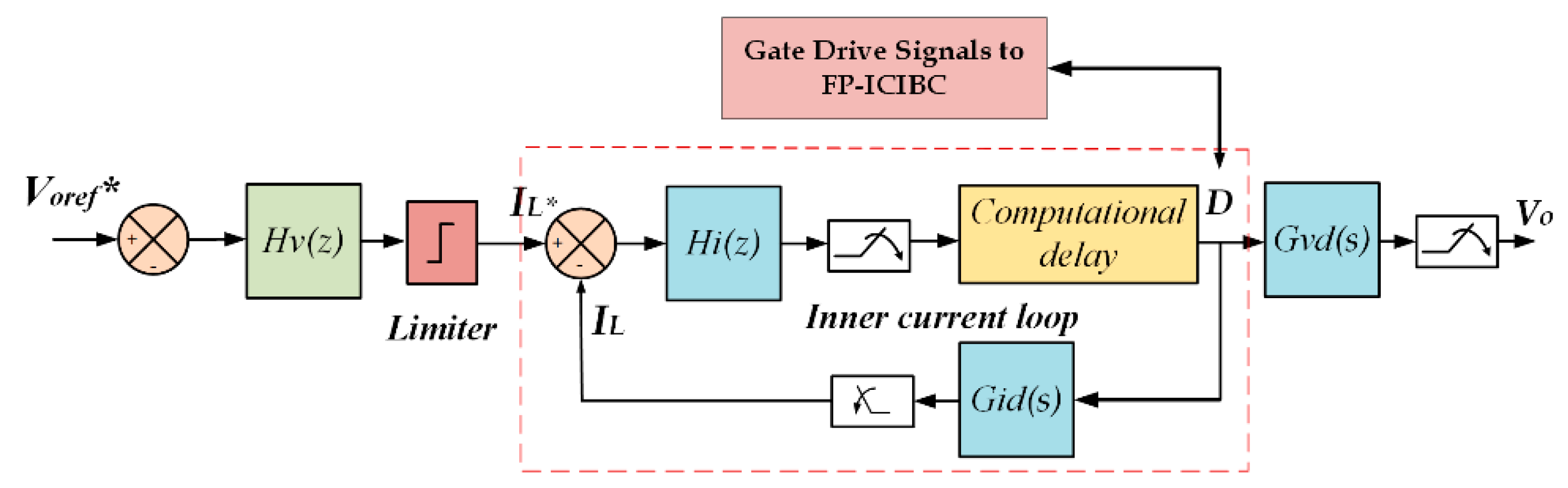
Digital 2PI Controller for FP-ICIBC
4. Power Management of Proposed Hybrid System and Simulation Analysis
4.1. Case Studies for Different Load Conditions
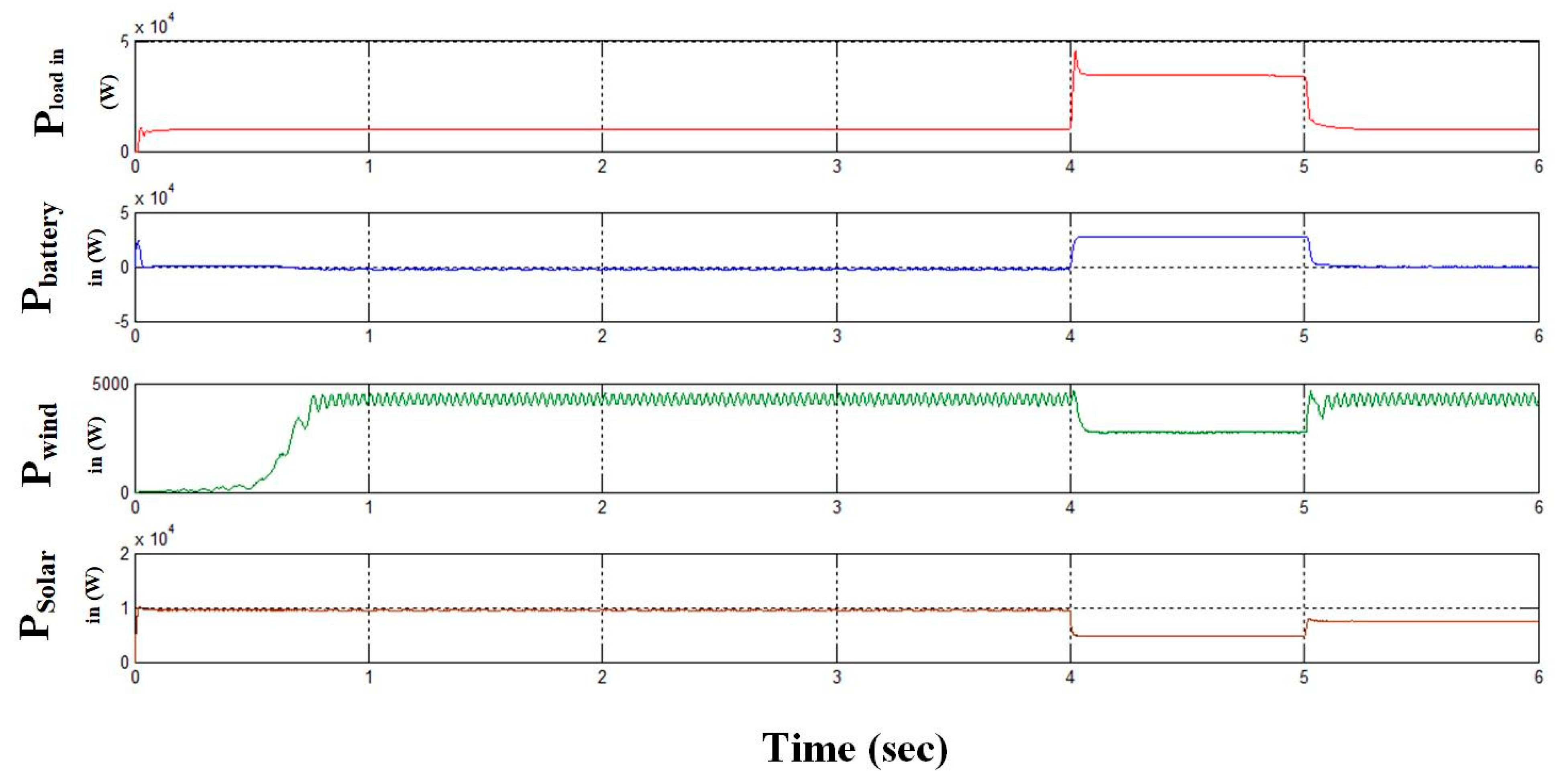
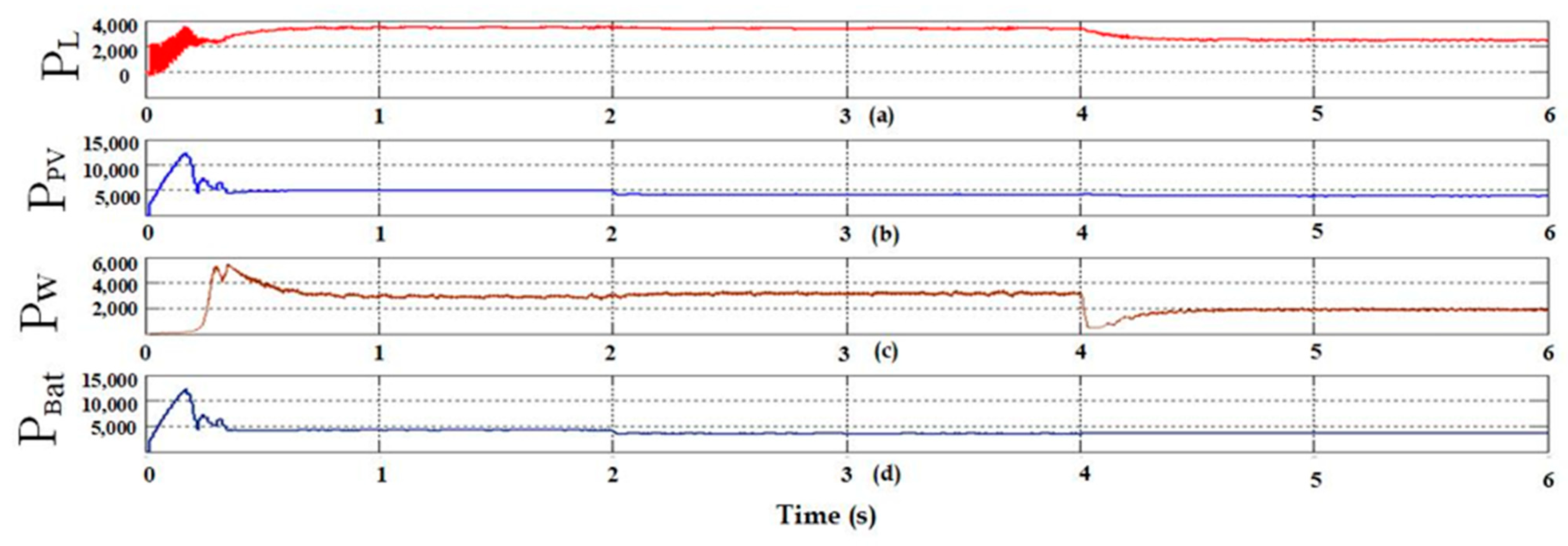
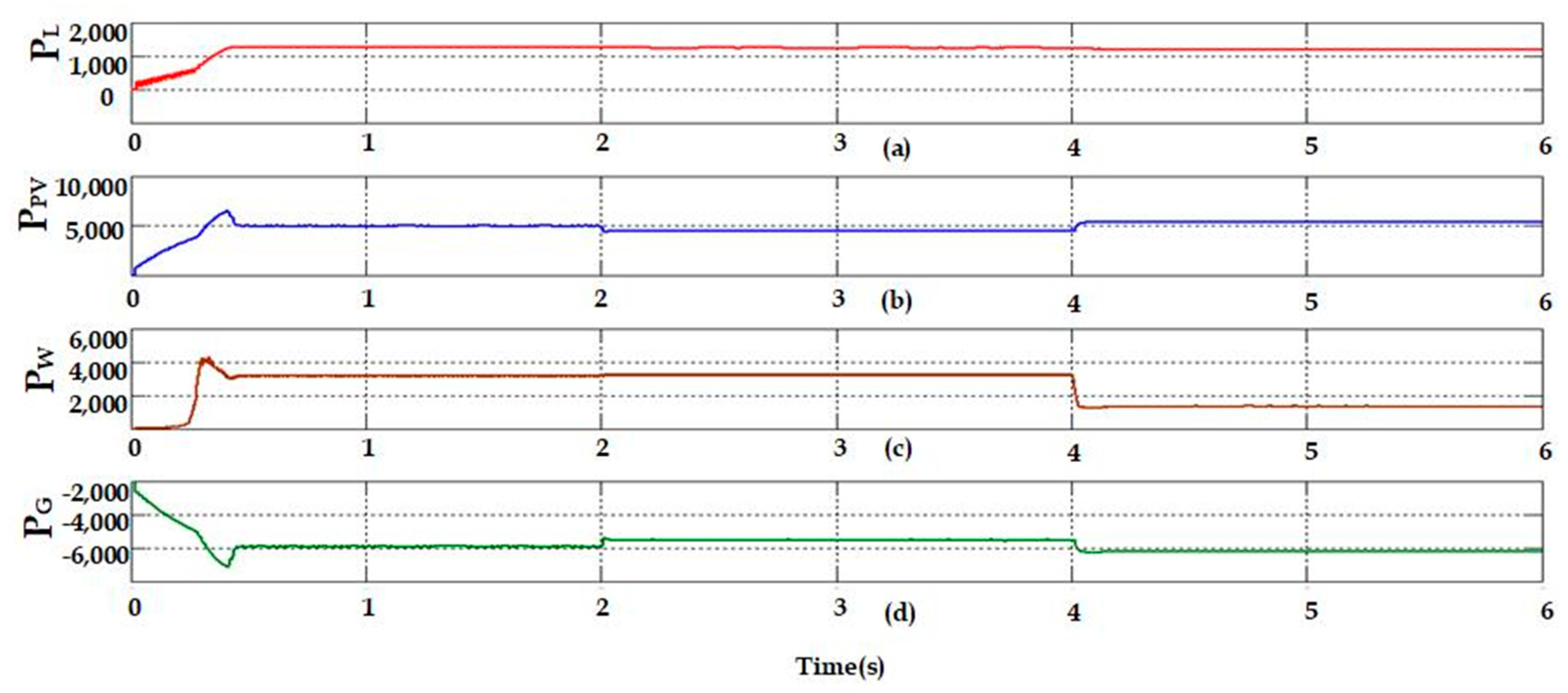
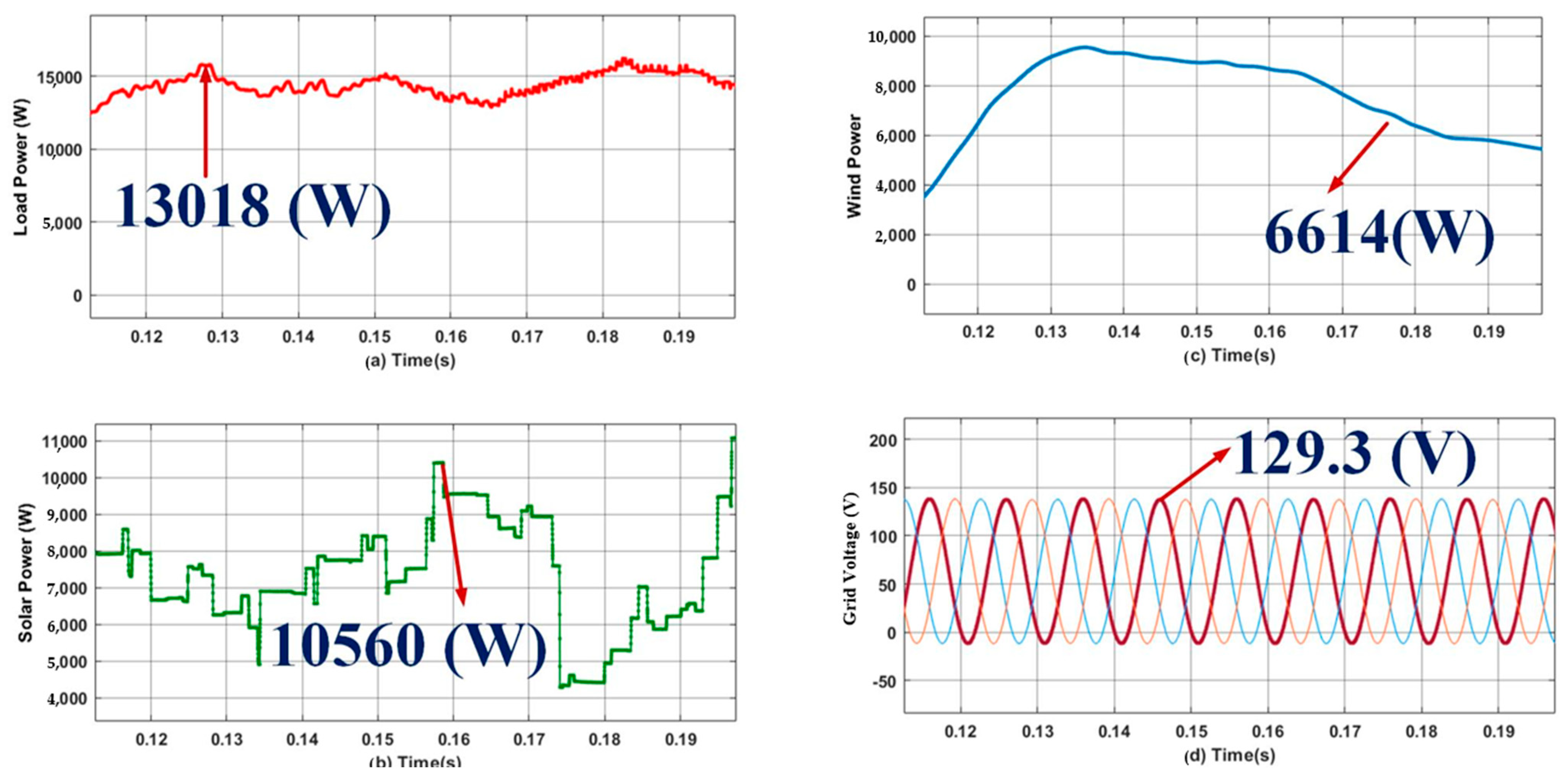
- Case 1: analysis of S-WHS without load sharing.
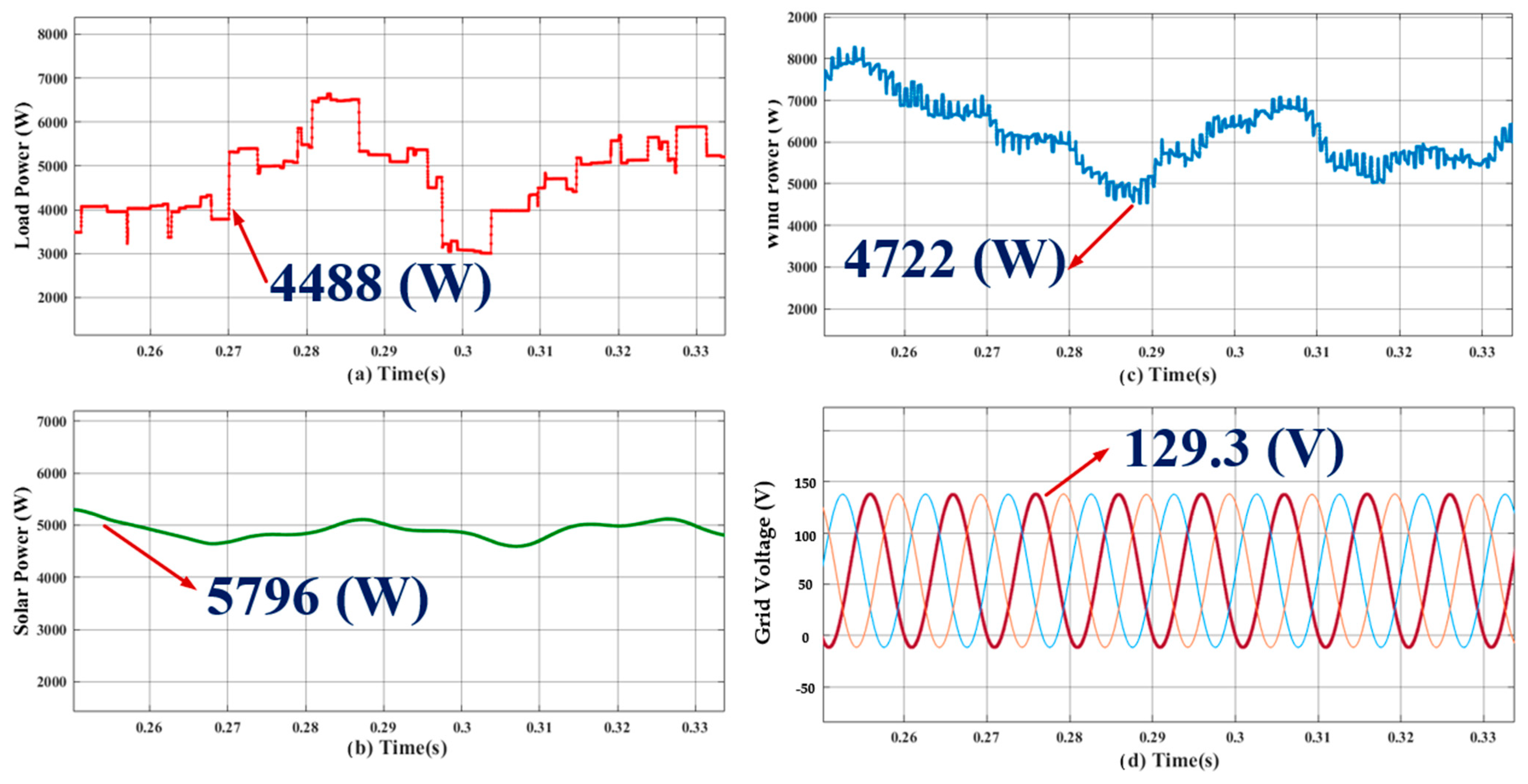
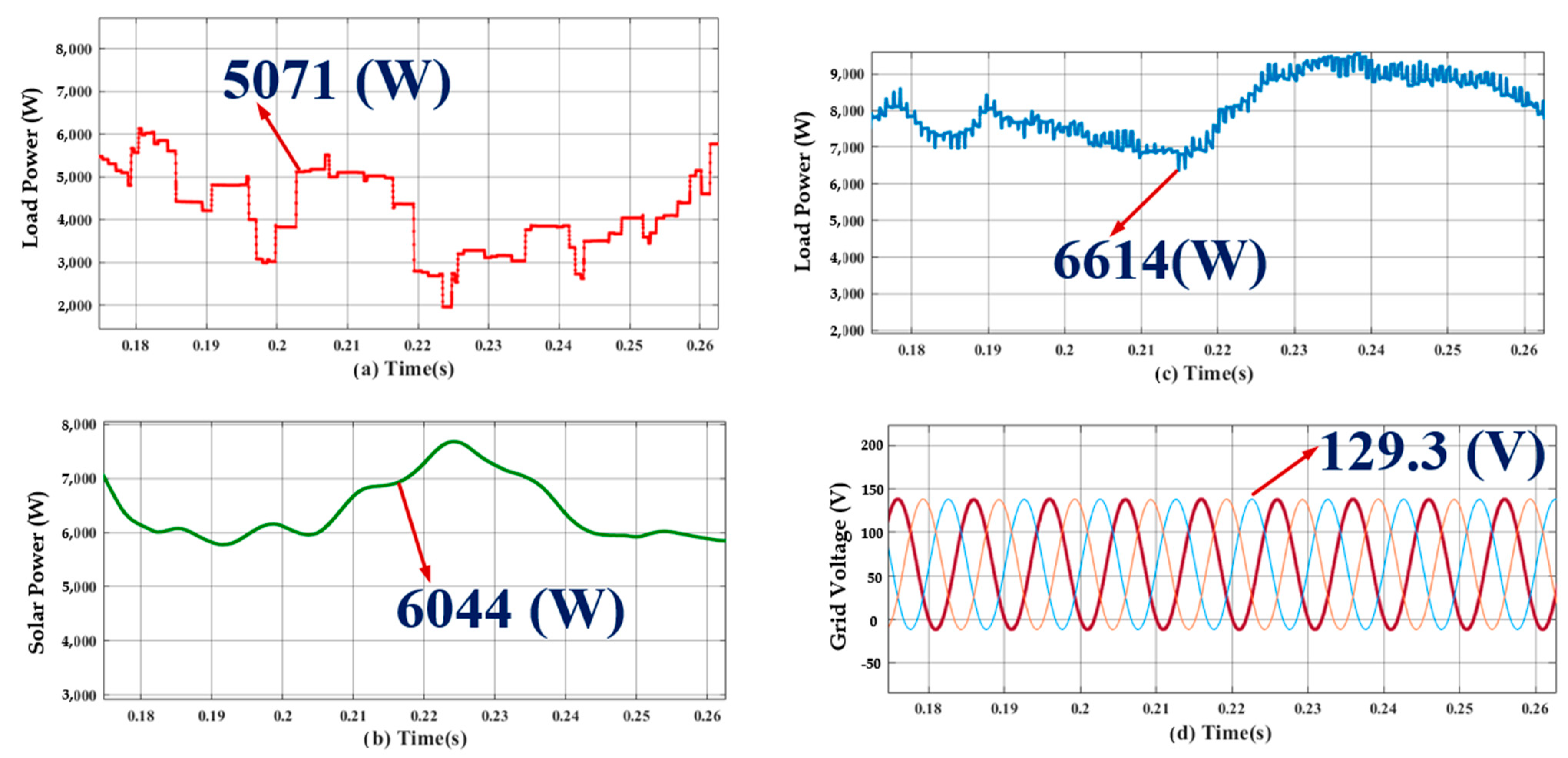
- Case 2: analysis of S-WHS with load sharing (S-WHS > Grid).
- Case 3: analysis of S-WHS with load sharing (S-WHS < Grid).
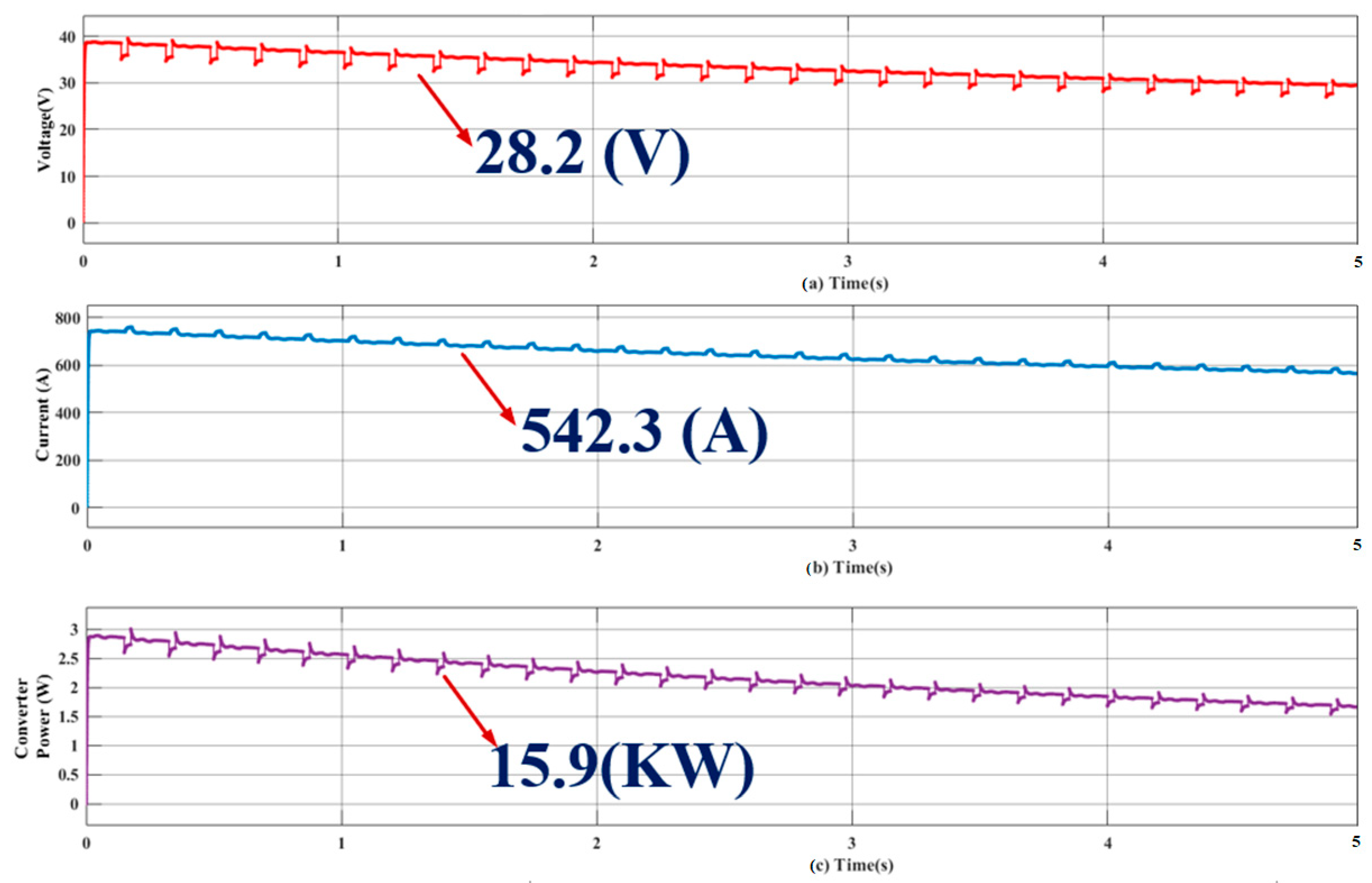
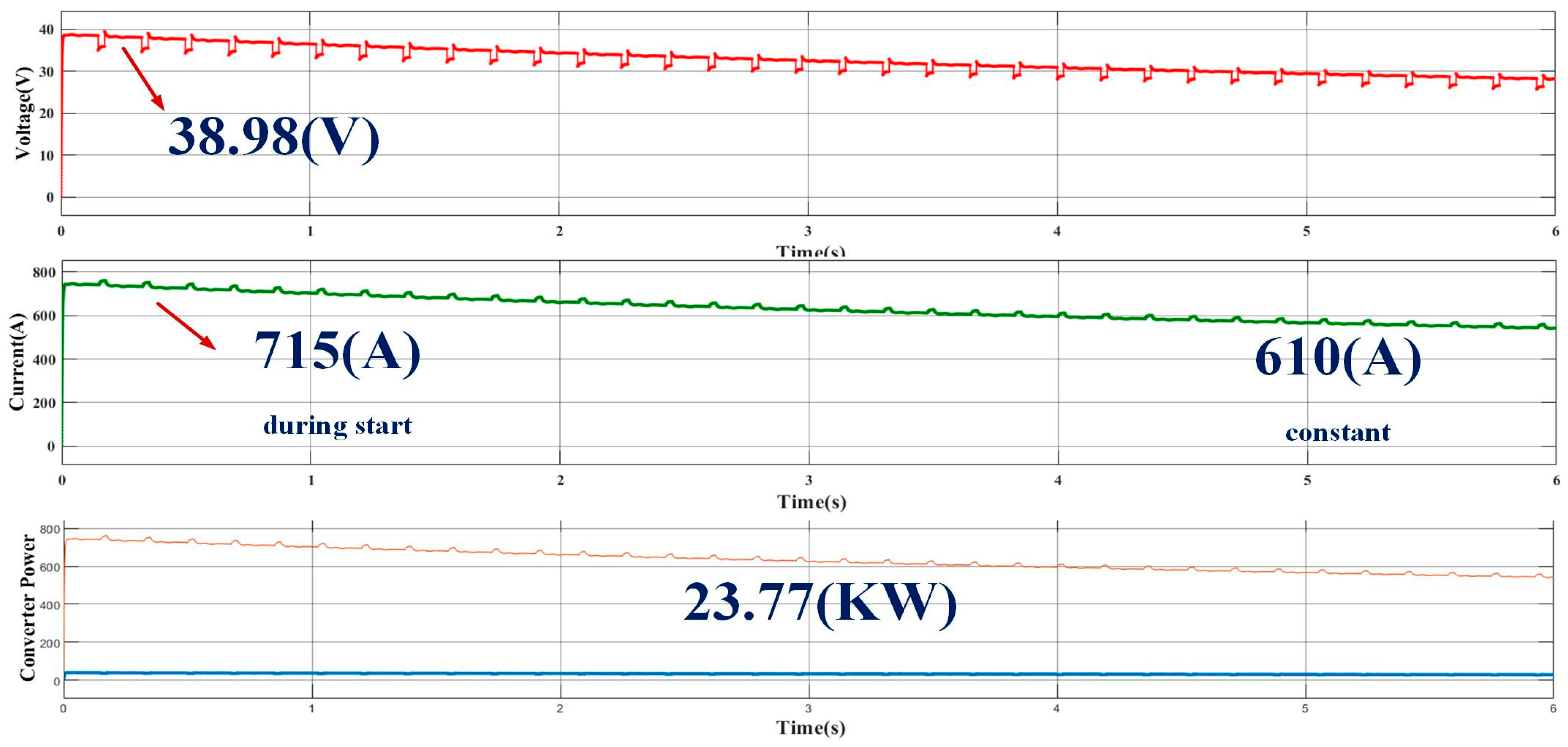
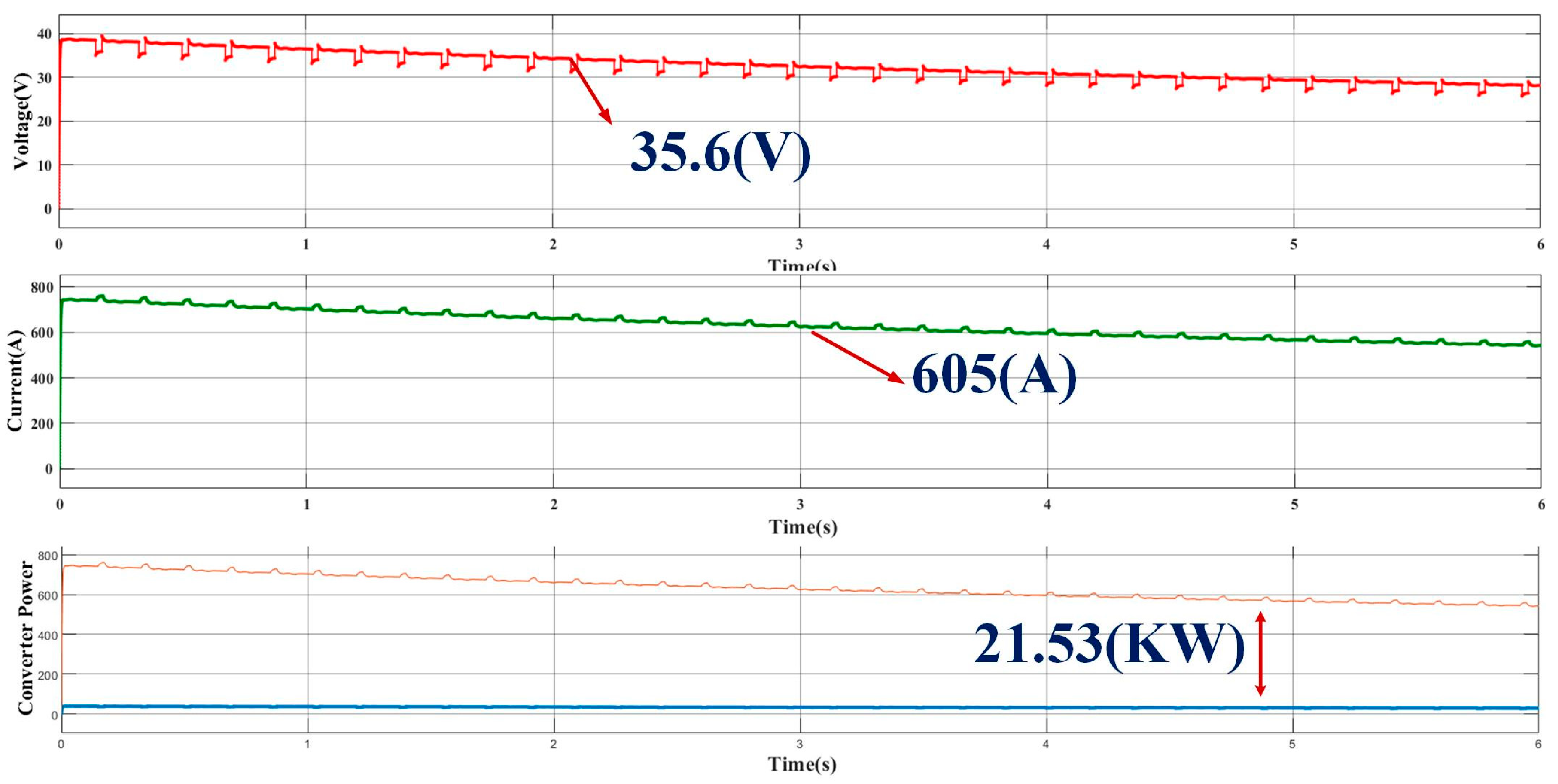
4.1.1. Analysis of Proposed Hybrid System Operated to Charge Two-Wheeler Electric Bike System
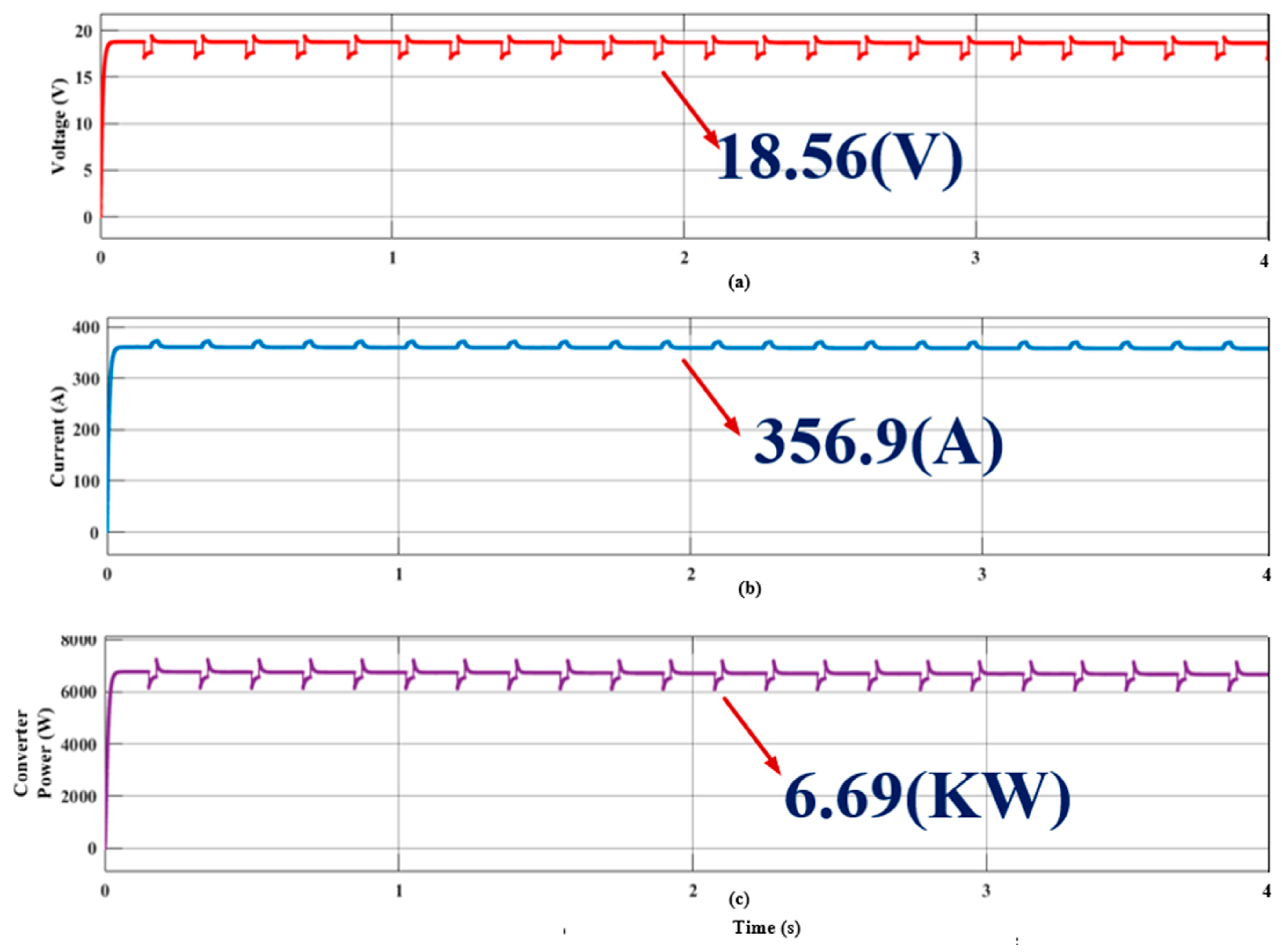
4.1.2. Analysis of Proposed Hybrid System Operated to Charge Four-Wheeler Electric Car System
4.1.3. Analysis of Proposed Hybrid System Operated to Charge Multiple Vehicles at a Time
4.2. Mathematical Model Analysis for EV Charging Rate
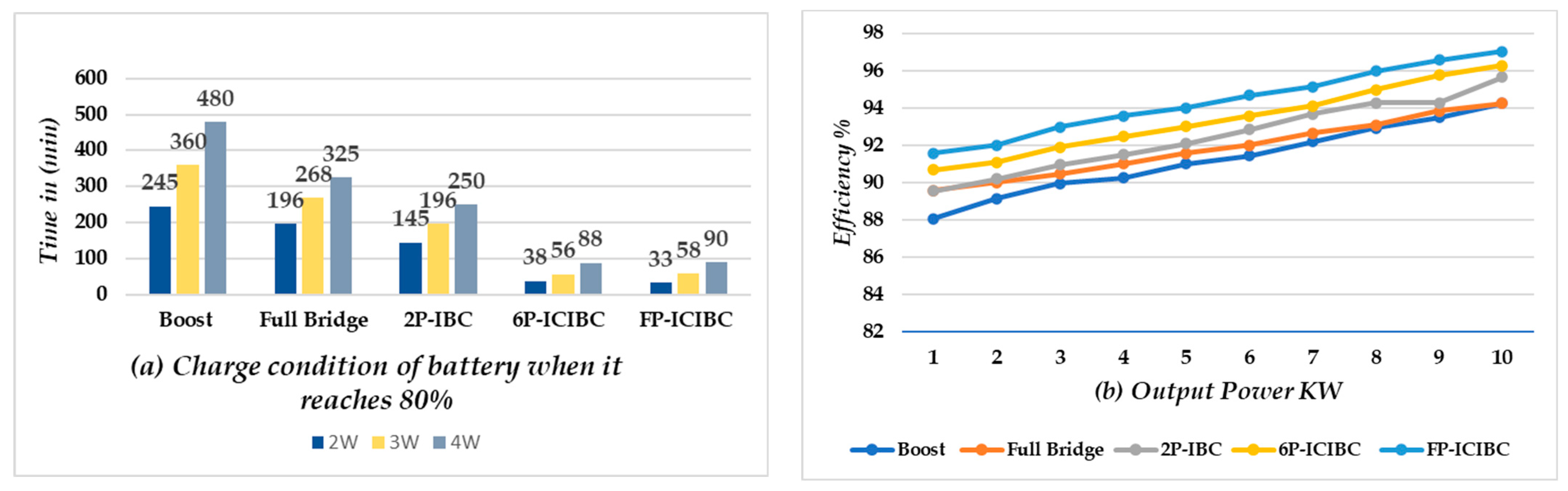
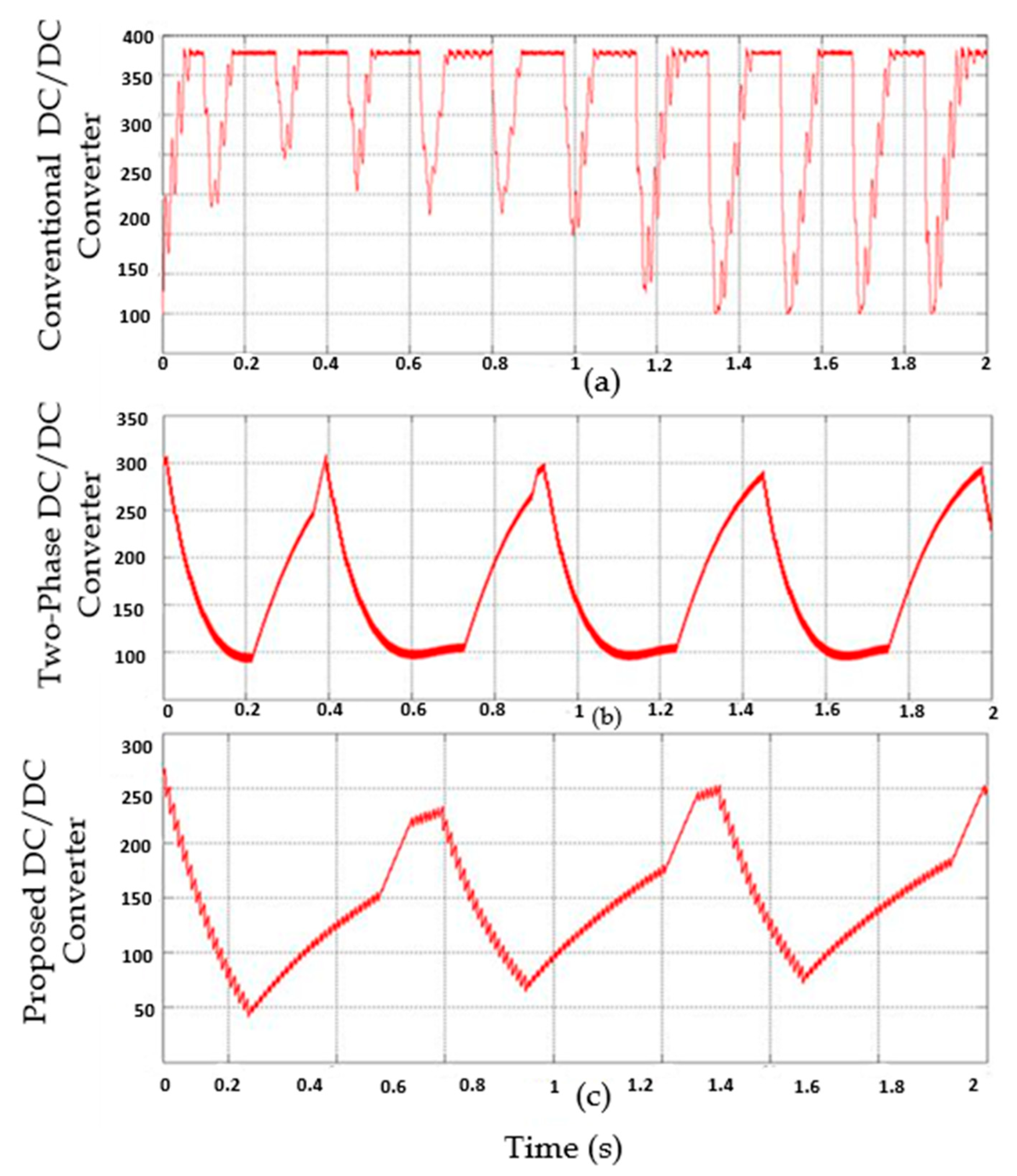
4.3. Performance Analysis of Proposed FP-ICIBC under Voltage Ripples
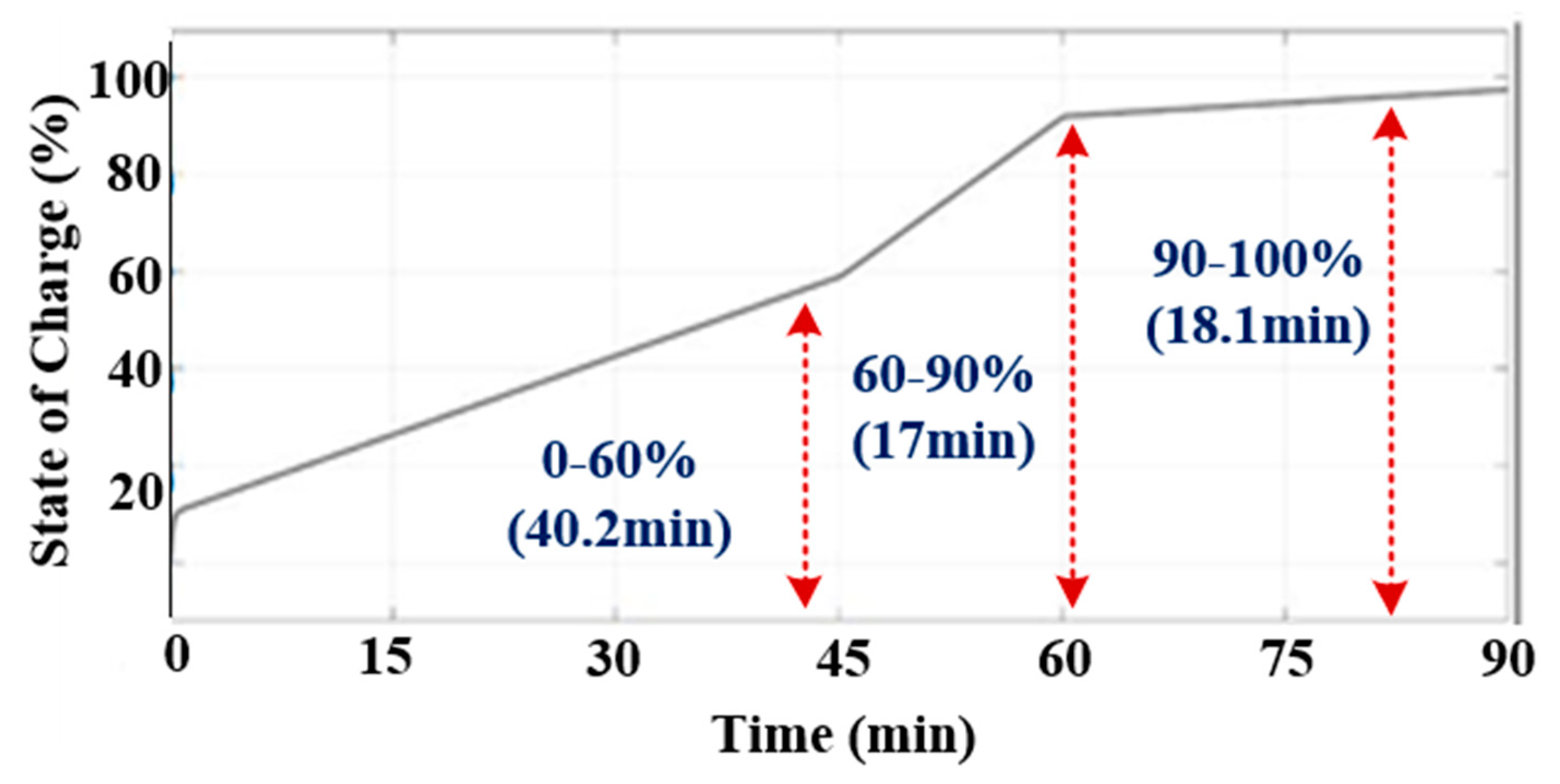
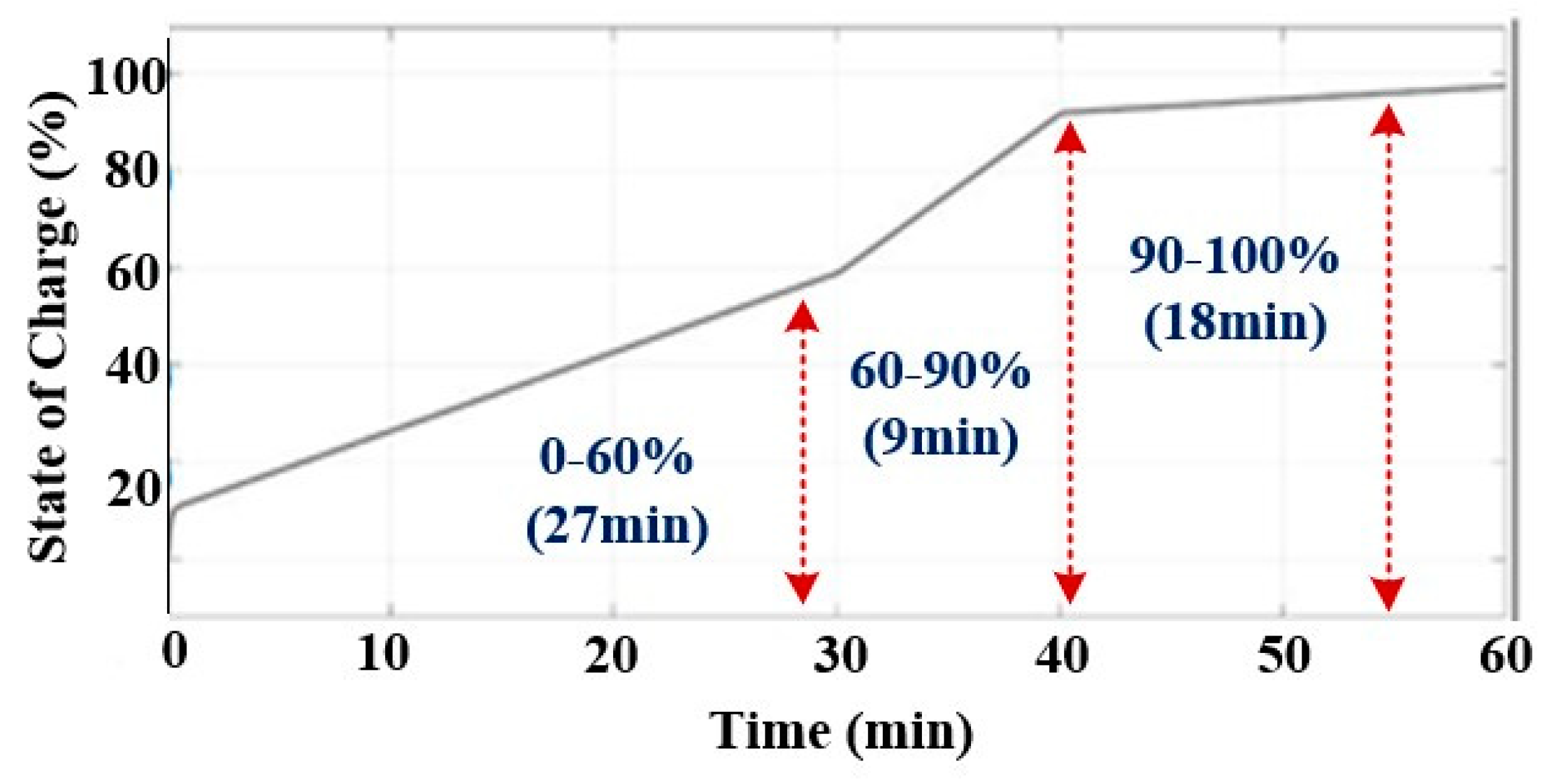
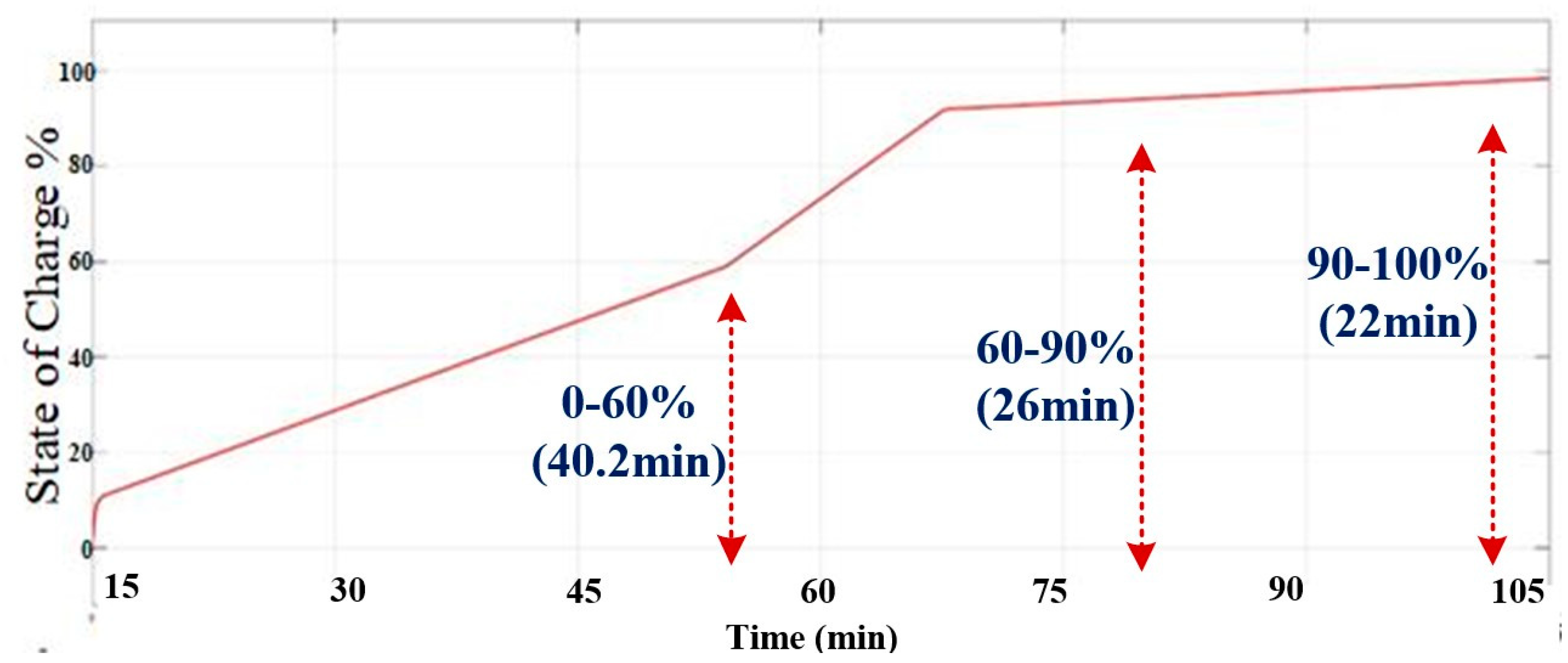
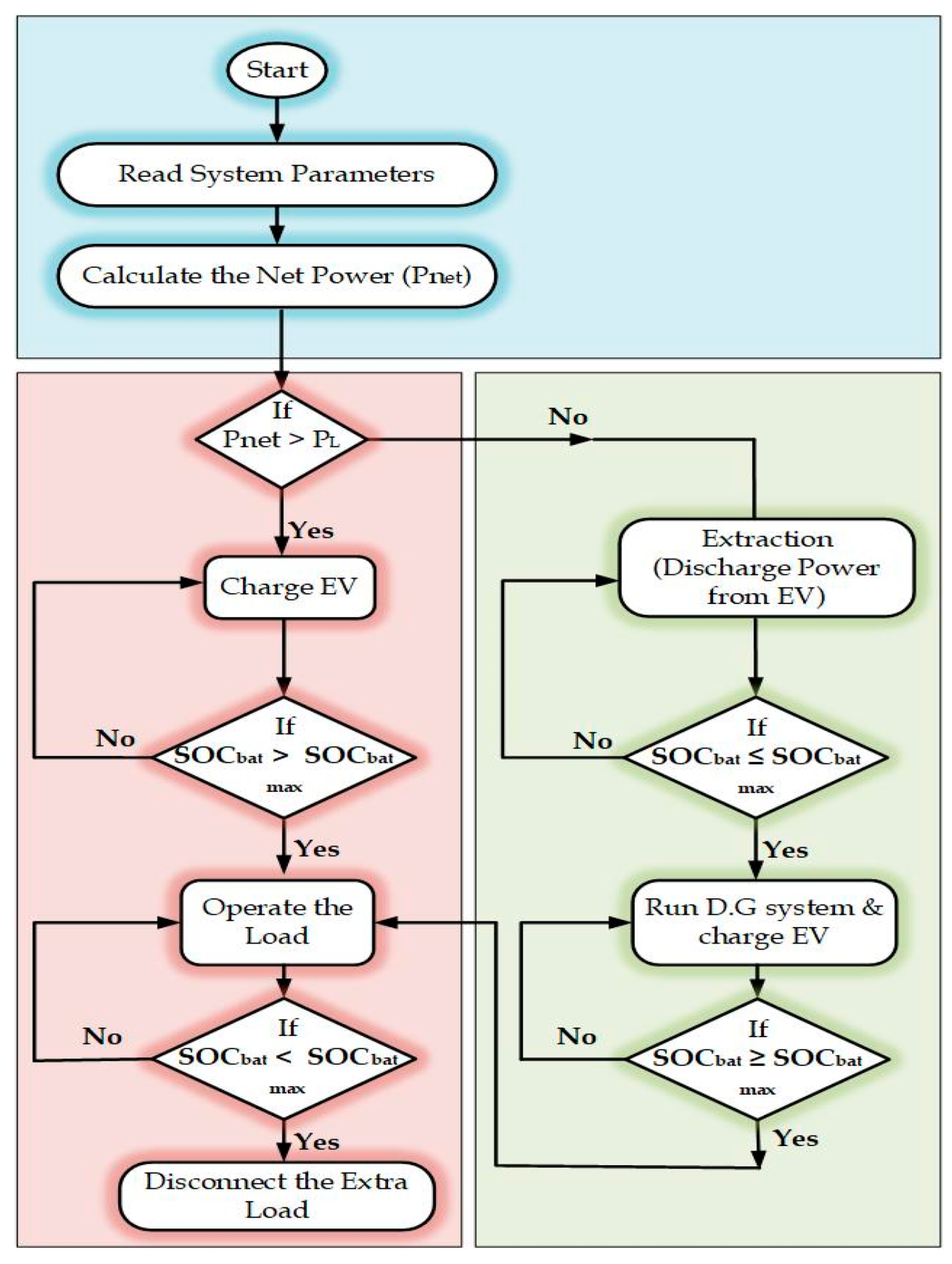
4.4. Procedure Followed to Charge an EV (Buffering)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| AC/DC | Alternating Current/Direct Current |
| AMM | Amorphous Magnetic Materials |
| CBC | Conventional Boost Converter |
| Cin/Cout | Input/Output Capacitors |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CS | Charging Stations |
| D | Duty cycle |
| DC | Direct Current |
| DTC | Direct Torque Control |
| EMI | Electromagnetic Interference |
| EV | Electric Vehicles |
| EVCS | Electric Vehicle Charging Stations |
| FC | Fuel Cell |
| Fsw | Switching Frequency |
| GHG | Green House Gas |
| Gi/Gv | Gate current/voltages |
| Current/Change in current/Change in Current peak to peak | |
| IBC | Interleaved Boost Converter |
| ICE | Internal Combustion Engines |
| I2R | Power loss |
| K | coupling coefficient |
| Kp/Ki | Proportional/Integral gain |
| Ls/Leq/LM | Self-Inductance/Equivalent Inductance/Mutual Inductance |
| MPPT | Maximum Power Point Tracking |
| NFR | Nanocrystalline Flake Ribbon |
| NPC | Neutral Point Clamped |
| PI | Proportional Integral |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| Pout | Output Power |
| PQ | Power Quality |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| S | Switch |
| SoC | State of Charge |
| SPV | Solar Photovoltaic |
| S-WHS | Solar Wind Hybrid Systems |
| Ts | Switching time |
| R/L/C | Resistance/Inductance/Capacitance |
| Vin/Vout/Vref | Input/Output Voltage/reference Voltage |
| ZOH | Zero-order Hold |
| Change in Voltage | |
| η | Efficiency |
References
- Ye, H.; Jin, G.; Fei, W.; Ghadimi, N. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1556–7036. [Google Scholar]
- Brenna, M.; Foiadelli, F.; Leone, C.; Longo, M. Electric Vehicles Charging Technology Review and Optimal Size Estimation. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 2539–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.A.; Carli, G.; Azeez, N.A.; Williamson, S.S. Modeling, Design, Control, and Implementation of a Modified Z-Source Integrated PV/Grid/EV DC Charger/Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 5213–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chauhan, P.; Singh, N.J. Feasibility of Grid-connected Solar-wind Hybrid System with Electric Vehicle Charging Station. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Kouro, S.; Wu, B. Charging Architectures for Electric and Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. In Technologies and Applications for Smart Charging of Electric and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles; Veneri, O., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alghaythi, M.L.; O’Connell, R.M.; Islam, N.E.; Khan, M.M.S.; Guerrero, J.M. A High Step-Up Interleaved DC-DC Converter with Voltage Multiplier and Coupled Inductors for Renewable Energy Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 123165–123174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Keypour, R.; Savaghebi, M.; Golalipour, K. Probabilistic Optimal Bi-level Scheduling of a Multi-Microgrid System with Electric Vehicles. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 2421–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prem, P.; Sivaraman, P.; Raj, J.S.S.S.; Sathik, M.J.; Almakhles, D. Fast charging converter and control algorithm for solar PV battery and electrical grid integrated electric vehicle charging station. Automatika 2020, 61, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, A.; Abapour, M.; Sabahi, M. Reliability Evaluation of Conventional and Interleaved DC–DC Boost Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Zhao, R.; Gladwin, D.T. Vehicle-to-Vehicle charging system fundamental and design comparison. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 13–15 February 2019; pp. 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Wu, B.; Kouro, S.; Yaramasu, V.; Wang, J. Electric Vehicle Charging Station Using a Neutral Point Clamped Converter with Bipolar DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Su, B. Practical Implementation of an Interleaved Boost Converter for Electric Vehicle Applications. J. Power Electron. 2015, 15, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosai, H.; McNeal, S.; Jordan, B.; Scofield, J.; Ray, B.; Turgut, Z. Coupled Inductor Characterization for a High Performance Interleaved Boost Converter. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4812–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; McCann, R. Analysis and simulation of a multiple input interleaved boost converter for renewable energy applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 36th International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 September–2 October 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovsky, M.; Guidi, G.; Kawamura, A. Assessment of Coupled and Independent Phase Designs of Interleaved Multiphase Buck/Boost DC–DC Converter for EV Power Train. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, W.; Yamamoto, M.; Imaoka, J.; Velandia, F.; Cortes, C.A. Efficiency optimization of a two-phase interleaved boost DC-DC converter for Electric Vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the2016 IEEE 8th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Hefei, China, 22–26 May 2016; pp. 2474–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazy, O.; Van Mierlo, J.; Lataire, P. Analysis, Modeling, and Implementation of a Multidevice Interleaved DC/DC Converter for Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4445–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, Y.; Breining, P.; Schiefer, M.; Doppelbauer, M. Experimental Study of the Amorphous Magnetic Material for High-Speed Sleeve-Free PM Rotor Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 4422–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Long, T. Permeability-Adjustable Nanocrystalline Flake Ribbon in Customized High-Frequency Magnetic Components. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 39, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubert, T.; Mindl, P.; Čeřovský, Z. Design of Control and Switching Frequency Optimization of DC/DC Power Converter for Super-capacitor. Automatika 2016, 57, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Salhi, I.; Laghrouche, S.; Ait-Amirat, Y.; Djerdir, A. Robust control of four-phase interleaved boost converter by considering the performance of PEM fuel cell current. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 38827–38840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.bikedekho.com/tvs/iqube-electric/specifications (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Eswar, K.N.D.V.S.; Doss, M.A.N.; Jayapragash, J. Design of Zeta Converter Integrated with Renewable Source PV and Hybrid Energy Storage Systems for Industrial/Domestic Applications. In International Symposium on Sustainable Energy and Technological Advancements; Panda, G., Alhelou, H.H., Thakur, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 303–317. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://evfunda.com/bajaj-re-electric-auto-rickshaw/ (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Available online: https://www.cardekho.com/tata/nexon-ev (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- Chakraborty, S.; Vu, H.-N.; Hasan, M.M.; Tran, D.-D.; Baghdadi, M.E.; Hegazy, O. DC-DC Converter Topologies for Electric Vehicles, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles and Fast Charging Stations: State of the Art and Future Trends. Energies 2019, 12, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, S.; Uddin, M.B. Analysis the performance of interleaved boost converter. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information & Communication Technology (iCEEiCT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 13–15 September 2018; pp. 547–551. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, V.J.; Keerthi, G.; Mahalingam, P. Interleaved quadratic boost DC–DC converter with high voltage gain capability. Electr. Eng. 2020, 102, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, S.; Rahiman, Z.; Chenniappan, S.; Sundaram, E.; Subramaniam, U.; Padmanaban, S. Efficient Multi-Phase Converter for E-Mobility. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Operating States | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | Operating States | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode-1 0 < D1(t) + D2(t) + D3(t) + D4(t) ≤ 1 | 1000 | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | Mode-3 2 < D1(t) + D2(t) + D3(t) + D4(t) ≤ 3 | 1011 | ✓ | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 0000 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | 1001 | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | ||
| 0100 | ✖ | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | 1101 | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ✓ | ||
| 0000 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | 1100 | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ||
| 0010 | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | ✖ | 1110 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ||
| 0000 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | 0110 | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ||
| 0001 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | 0111 | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 0000 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | 0011 | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Mode-2 1 < D1(t) + D2(t) + D3(t) + D4(t) ≤ 2 | Mode-4 3 < D1(t) + D2(t) + D3(t) + D4(t) ≤ 4 | ||||||||||
| 1000 | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | 0111 | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 1100 | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | 1111 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 0100 | ✖ | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | 1011 | ✓ | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 0110 | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | 1111 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 0010 | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | ✖ | 1101 | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ✓ | ||
| 0011 | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | 1111 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 0001 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | 1110 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ||
| 1001 | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | 1111 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Parameters and Its Specifications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S O L A R D A T A | Maximum Power (Pmax) | 15,000 W | W I N D D A T A | Rated Power Output (PRout) | 5000 W |
| Voltage at max. power (Vmax) | 220 V | Peak power output (PPout) | 6800 W | ||
| Current at max. power (Imax) | 6.818 A | Rated voltage (R voltage) | 415 v | ||
| Open circuit voltage (Voc) | 232.32 V | Cut-in (N Cin), Cut-out (Ncout) and wind speed (Nw) | 2, 18, and 8 m/s | ||
| Short circuit current (Isc) | 5.65 A | Rated rotor speed (Nrotor) | 250 rpm | ||
| No. of panels (Np) | 10 | Generator efficiency (η gen) | 0.95 | ||
| No. of strings (Ns) | 1 | Number of blades (Nblades) | 3 | ||
| Cells in string (Ncs) | 10 | Rotor diameter (Dr) | 3600 mm | ||
| Cp value at max. (Cpmax) | 0.18 | ||||
| Parameter Variable | Ratings |
|---|---|
| Rated power output (W) | 3 KW |
| Battery capacity and type | 48 V, 62 Ah, 2.97 kWh, Li-ion |
| Charging condition | Up to 4 h to charge 0–90% |
| Battery type | Li-ion |
| On-board charger | 1.8 kW |
| Parameter Variable | Ratings |
|---|---|
| Rated power output (W) | 4.3 KW |
| Battery capacity and type | 48 V, 91.66 Ah, 4.4 Kwh Li-ion |
| Charging condition | up to 6 h to charge 0–80% |
| Battery type | Li-ion |
| On-board charger | 2.2 KW |
| Parameter Variable | Ratings |
|---|---|
| Rated power output (W) | 4.8 KW |
| Battery capacity and type | 72 V, 298.61 Ah, 21.5 Kwh Li-ion |
| Charging condition | up to 8 h to charge 0–80% |
| Battery type | Li-ion |
| On-board charger | 9.1 kW |
| Type of Converter | Vin(v) | Vout(v) | Iout(A) | N | Fs(Hz) | L(μH) | C(μF) | D | Po(W) | Pl(W) | Pin(W) | η% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boost [26] | 200 | 380 | 13.02 | 1 | 20 | 410 | 780 | 0.5 | 4.94 | 317.54 | 5.26 | 93.97 |
| Full Bridge [27] | 200 | 434 | 13.56 | 2 | 20 | 115 | 250 | 0.5 | 5.80 | 267.34 | 6.15 | 94.24 |
| 2P-IBC [28] | 200 | 435.7 | 13.62 | 4 | 20 | 100 | 235 | 0.5 | 5.93 | 266.88 | 6.19 | 95.66 |
| 6P-IBC [29] | 200 | 500 | 13.98 | 6 | 20 | 85 | 195 | 0.5 | 6.99 | 270 | 7.26 | 96.28 |
| Proposed FP-ICIBC | 232 | 464.4 | 14.125 | 4 | 25 | 66.67 | 168 | 0.5 | 6.56 | 201.48 | 6.76 | 97.02 |
| Parameter | Gain | Rise Time | Voltage Ripple | Charging Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boost [26] | Very low | 1.02 s | 12.5% | Very high |
| Full Bridge [27] | Average | 1.08 s | 12.5% | High |
| 2P-IBC [28] | Max. 2 | 2.02 s | 5.12% | Moderate |
| Proposed FP-ICIBC | High | 1.05 s | <2.9% | Very low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eswar, K.N.D.V.S.; Doss, M.A.N.; Alruwaili, M.; Abdelfattah, W.M. Implementation of a Microgrid System with a Four-Phase Inductor Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter for EV Charging Stations. Energies 2024, 17, 2277. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102277
Eswar KNDVS, Doss MAN, Alruwaili M, Abdelfattah WM. Implementation of a Microgrid System with a Four-Phase Inductor Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter for EV Charging Stations. Energies. 2024; 17(10):2277. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102277
Chicago/Turabian StyleEswar, Kommoju Naga Durga Veera Sai, Mohan Arun Noyal Doss, Mohammed Alruwaili, and Waleed Mohammed Abdelfattah. 2024. "Implementation of a Microgrid System with a Four-Phase Inductor Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter for EV Charging Stations" Energies 17, no. 10: 2277. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102277
APA StyleEswar, K. N. D. V. S., Doss, M. A. N., Alruwaili, M., & Abdelfattah, W. M. (2024). Implementation of a Microgrid System with a Four-Phase Inductor Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter for EV Charging Stations. Energies, 17(10), 2277. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102277







