Reconstruction of Lake-Level Changes by Sedimentary Noise Modeling (Dongying Depression, Late Eocene, East China)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Gamma Ray Logging
3.2. Time Series Analyses Methods
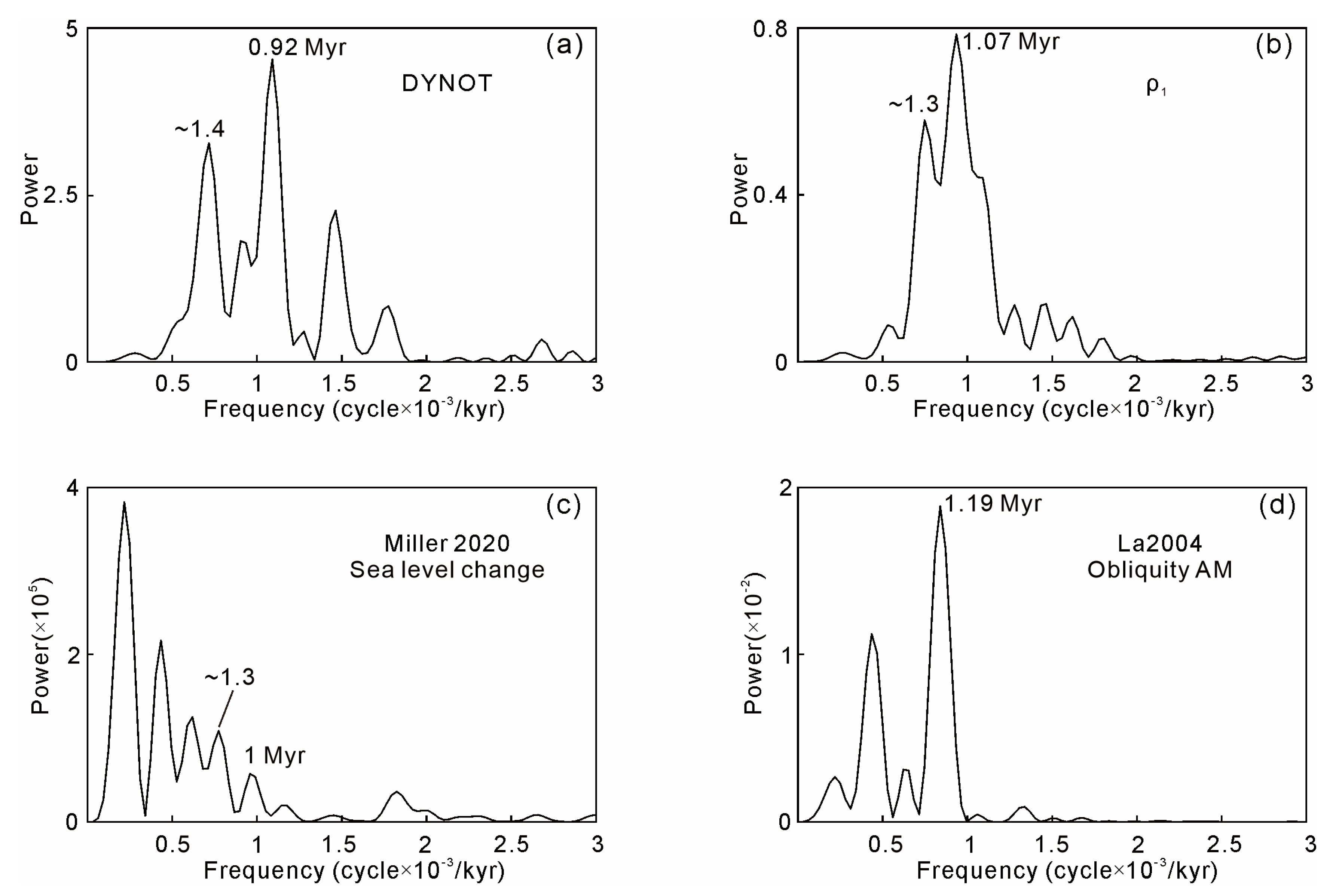
3.3. Sedimentary Noise Modelling
4. Results
4.1. Time Series Analysis
4.2. Astronomical Tuning
4.3. Sedimentary Noise Modeling of Lake-Level Changes
5. Discussion
5.1. An Astronomical Time Scale (ATS) in the Dongying Depression
5.2. Verification of Sedimentary Noise Model for Reconstructing Lake Levels
5.3. Astronomical Forcing on Lake-Level Fluctuations in the Dongying Depression
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilgen, F.; Schwarzacher, W.; Strasser, A. Concepts and definitions in cyclostratigraphy (second report of the cyclostratigraphy working group). SEPM. Spec. Publ. 2004, 81, 303–305. [Google Scholar]
- Strasser, A.; Hilgen, F.J.; Heckel, P.H. Cyclostratigraphy-concepts, definitions, and applications. Newsl. Stratigr. 2006, 42, 75–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnov, L.A. Cyclostratigraphy and astrochronology in 2018. In Stratigraphy & Timescales; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, S.R. Cyclostratigraphy and the problem of astrochronologic testing. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 190–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, A.; Hillgärtner, H.; Pasquier, J. Cyclostratigraphic timing of sedimentary processes: An example from the Berriasian ofthe Swiss and French Jura Mountains. SEPM. Spec. Publ. 2004, 81, 135–151. [Google Scholar]
- De Vleeschouwer, D.; Whalen, M.T.; Day, J.E.; Claeys, P. Cyclostratigraphic calibration of the Frasnian (Late Devonian) time scale (western Alberta, Canada). Bulletin 2012, 124, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hesselbo, S.P. Pacing of the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (Early Jurassic) from astronomical correlation of marine sections. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenio, B.D.; Fischer, A.G.; Silva, I.P.; Weissert, H.; Ferreri, V. Cyclostratigraphy: Approaches and case histories. SEPM. Spec. Publ. 2004, 81, 1–311. [Google Scholar]
- Wagreich, M.; Hohenegger, J.; Neuhuber, S. Nannofossil biostratigraphy, strontium and carbon isotope stratigraphy, cyclostratigraphy and an astronomically calibrated duration of the Late Campanian Radotruncana calcarata Zone. Cretac. Res. 2012, 38, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Browning, J.V.; Schmelz, W.J.; Kopp, R.E.; Mountain, G.S.; Wright, J.D. Cenozoic sea-level and cryospheric evolution from deep-sea geochemical and continental margin records. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Bao, X.; Yang, Y. Charging of the Neogene Penglai 19-3 field, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Oil accumulation in a young trap in an active fault zone. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, H.; Xu, C.; Yang, X.; Du, X. Reconstructing provenance interaction of multiple sediment sources in continental down-warped lacustrine basins: An example from the Bodong area, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2020, 113, 104142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Kemp, D.B.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, M. Astronomical forcing and sedimentary noise modeling of lake-level changes in the Paleogene Dongpu Depression of North China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 535, 116116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer-Pietras, K.M. Insolation forcing of sub-lacustrine debris flows–Could monsoon intensification have played a role? Eocene lacustrine Green River Formation, Piceance Creek Basin, Colorado. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 553, 109738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Hinnov, L.A.; Jiang, G.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Wan, X.; Wang, C. Cyclostratigraphy and orbital tuning of the terrestrial upper Santonian–Lower Danian in Songliao Basin, northeastern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 407, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Z.; Li, B.; He, Q.; Bian, X. A Brief Introduction To The Cenozoic Astrostratigraphic Time Scale For The Dongying Depression, Shandong. J. Stratigr. 2007, 31, 423–429, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Algeo, T.J.; Liu, H.; Hao, Y.; Du, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, P.; Guo, L.; Peng, L. High-resolution astrochronological record for the Paleocene-Oligocene (66–23Ma) from the rapidly subsiding Bohai Bay Basin, northeastern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 510, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Hao, Y. Terrestrial sedimentary responses to astronomically forced climate changes during the Early Paleogene in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 502, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Z. Cyclostratigraphy and astronomical tuning of the middle eocene terrestrial successions in the Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 174, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, A.; Ma, C. Astrochronology of a middle Eocene lacustrine sequence and sedimentary noise modeling of lake-level changes in Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2022, 585, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, M.; Ogg, J.G.; Zhang, C.; Feng, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. East Asian lake hydrology modulated by global sea-level variations in the Eocene warmhouse. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2023, 602, 117925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zou, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, L. Significant progress of continental petroleum geological theory in basins of Central and Western China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hinnov, L.A.; Huang, C.; Ogg, J.G. Sedimentary noise and sea levels linked to land–ocean water exchange and obliquity forcing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, M.; Kemp, D.B.; Boulila, S.; Ogg, J.G. Sedimentary noise modeling of lake-level change in the Late Triassic Newark Basin of North America. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2022, 208, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradstein, F.; Ogg, J.G.; Schmitz, M.D.; Ogg, G.M. The Geologic Time Scale; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2012; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, Y. Sequence stratigraphy and architectural variability in Late Eocene lacustrine strata of the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China. Sediment. Geol. 2013, 295, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yan, J.; Yuan, W.; Chen, S.Y. Sedimentary Facies Types of The Third Member of The Shahejie Formation in The Paleogene of The Dongying Depression, The Bohaiwan Basion and Third Distribution Characters on Plane. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2005, 27, 55–61, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. High Frequency Sequence Stacking Mode of Dongying Delta-turbidite Fans and Lithological Trap. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2005, 23, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten, H.; Wonik, T. Cyclostratigraphic studies of sediments from Lake Van (Turkey) based on their uranium contents obtained from downhole logging and paleoclimatic implications. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 1639–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ogg, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hinnov, L.; Chen, Z.; Zou, Z. Astronomical tuning of the end-Permian extinction and the Early Triassic Epoch of South China and Germany. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 441, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Ogg, J.G.; Zhu, J.; Lin, S.; Yang, D.; Zhao, P.; Kong, L. Astronomical time scale of the Paleogene lacustrine paleoclimate record from the Nanxiang Basin, central China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 532, 109253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleverand, W.S. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.P.; Hinnov, L.A. Rock Magnetic Cyclostratigraphy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Kump, L.R.; Hinnov, L.A.; Mann, M.E. Tracking variable sedimentation rates and astronomical forcing in Phanerozoic paleoclimate proxy series with evolutionary correlation coefficients and hypothesis testing. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 501, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.J. Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Lees, J.M. Robust estimation of background noise and signal detection in climatic time series. Clim. Chang. 1996, 33, 409–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hinnov, L.; Kump, L. Acycle: Time-series analysis software for paleoclimate research and education. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 127, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, J.; Robutel, P.; Joutel, F.; Gastineau, M.; Correia, A.C.M.; Levrard, B. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 428, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, H.; Cai, Z.; Guan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Sun, Z.C.; Yang, S.Z. Tertiary in Petroliferous Regions of China (IV): The Bohai Gulf Basin; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1994; 240p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.; Wang, F.; Zheng, H.; Fu, J. Cenozoic volcanic rocks and its relations to basin evolution and oil accumulation in dongying sag. Earth Sci. 1997, 22, 157–164, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, P.E.; Kent, D.V. Milankovitch climate forcing in the tropics of Pangaea during the Late Triassic. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1996, 122, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauth, M.H.; Maslin, M.A.; Deino, A.; Strecker, M.R. Late cenozoic moisture history of East Africa. Science 2005, 309, 2051–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulila, S.; Galbrun, B.; Miller, K.G.; Pekar, S.F.; Browning, J.V.; Laskar, J.; Wright, J.D. On the origin of Cenozoic and Mesozoic “third-order” eustatic sequences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovane, L.; Florindo, F.; Sprovieri, M.; Pälike, H. Astronomic calibration of the late Eocene/early Oligocene Massignano section (central Italy). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhold, T.; Röhl, U. Orbital pacing of Eocene climate during the Middle Eocene Climate Optimum and the chron C19r event: Missing link found in the tropical western Atlantic. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2013, 14, 4811–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, J.E.; Wendler, I. What drove sea-level fluctuations during the mid-Cretaceous greenhouse climate? Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 441, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Algeo, T.J.; Lu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Identifying marine incursions into the Paleogene Bohai Bay Basin lake system in northeastern China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2018, 200, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagreich, M.; Lein, R.; Sames, B. Eustasy, its controlling factors, and the limno-eustatic hypothesis-concepts inspired by Eduard Suess. Austrian J. Earth Sci. 2014, 107, 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sames, B.; Wagreich, M.; Wendler, J.E.; Haq, B.U.; Conrad, C.P.; Melinte-Dobrinescu, M.C.; Hu, X.; Wendler, I.; Wolfgring, E.; Yilmaz, I.Ö. Short-term sea-level changes in a greenhouse world—A view from the Cretaceous. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 441, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, K.; Yaltirak, C.; Alpar, B. The relationship between the tectonic setting of the Lake Iznik basin and the middle strand of the North Anatolian Fault. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 18, 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Xu, Y. The subduction of the west Pacific plate and the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, H.; Feng, X.; Wei, P. Reconstruction of Lake-Level Changes by Sedimentary Noise Modeling (Dongying Depression, Late Eocene, East China). Energies 2023, 16, 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052216
Sun Z, Jiang T, Zhu H, Feng X, Wei P. Reconstruction of Lake-Level Changes by Sedimentary Noise Modeling (Dongying Depression, Late Eocene, East China). Energies. 2023; 16(5):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052216
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhongheng, Tao Jiang, Hongtao Zhu, Xinluo Feng, and Pengli Wei. 2023. "Reconstruction of Lake-Level Changes by Sedimentary Noise Modeling (Dongying Depression, Late Eocene, East China)" Energies 16, no. 5: 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052216
APA StyleSun, Z., Jiang, T., Zhu, H., Feng, X., & Wei, P. (2023). Reconstruction of Lake-Level Changes by Sedimentary Noise Modeling (Dongying Depression, Late Eocene, East China). Energies, 16(5), 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052216