Detailed Controller Synthesis and Laboratory Verification of a Matching-Controlled Grid-Forming Inverter for Microgrid Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- a detailed controller synthesis for a matching-controlled grid-forming inverter is studied and the challenges and requirements to embed the controller in a stand-alone laboratory environment are presented,
- (2)
- implementation of said controller in a laboratory environment comprising DC sources, power electronics for the DC bus control and grid-forming stage, and AC loads in stand-alone operation, and
- (3)
- experimental controller validation comprising blackstart capability, stationary performance, and transient stability accompanied by a systematic sensitivity analysis aiming to enhance the system’s performance.
2. Materials and Methods
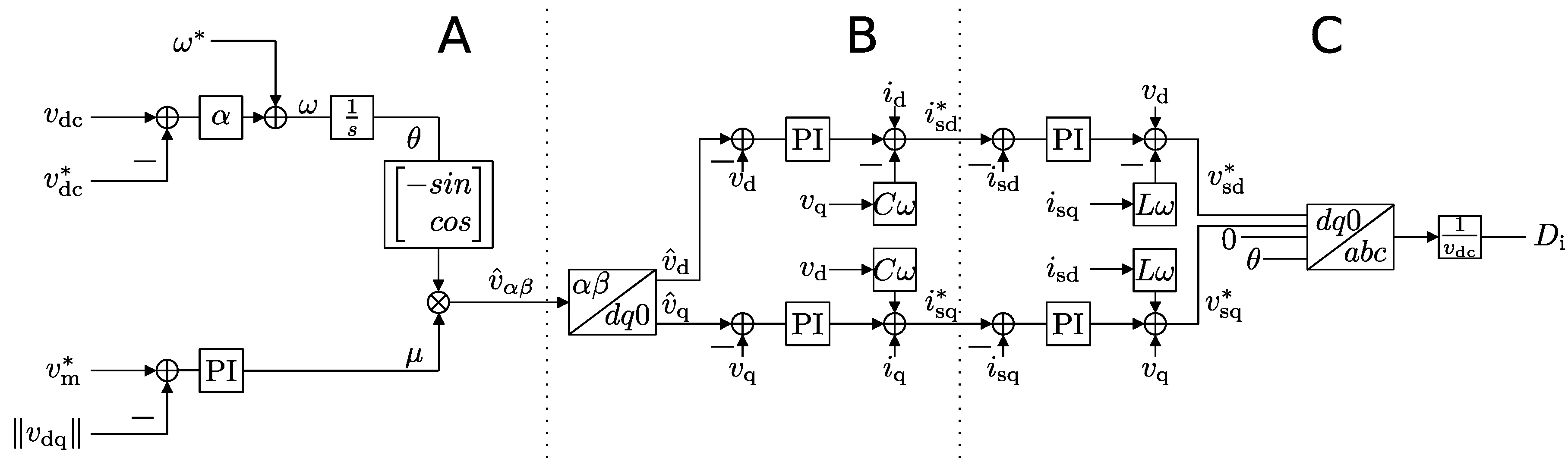
2.1. DC Bus Voltage and Grid-Forming Control
2.2. Controller Implementation
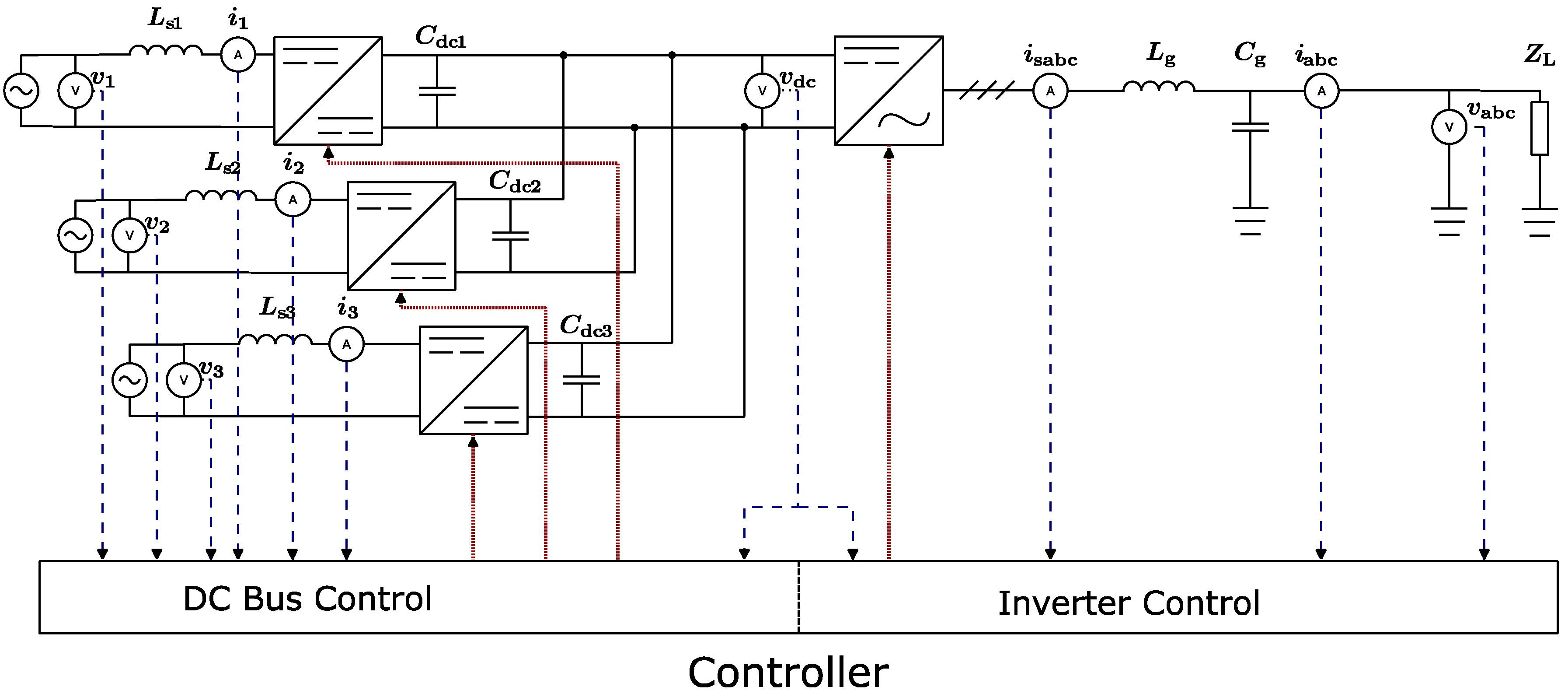
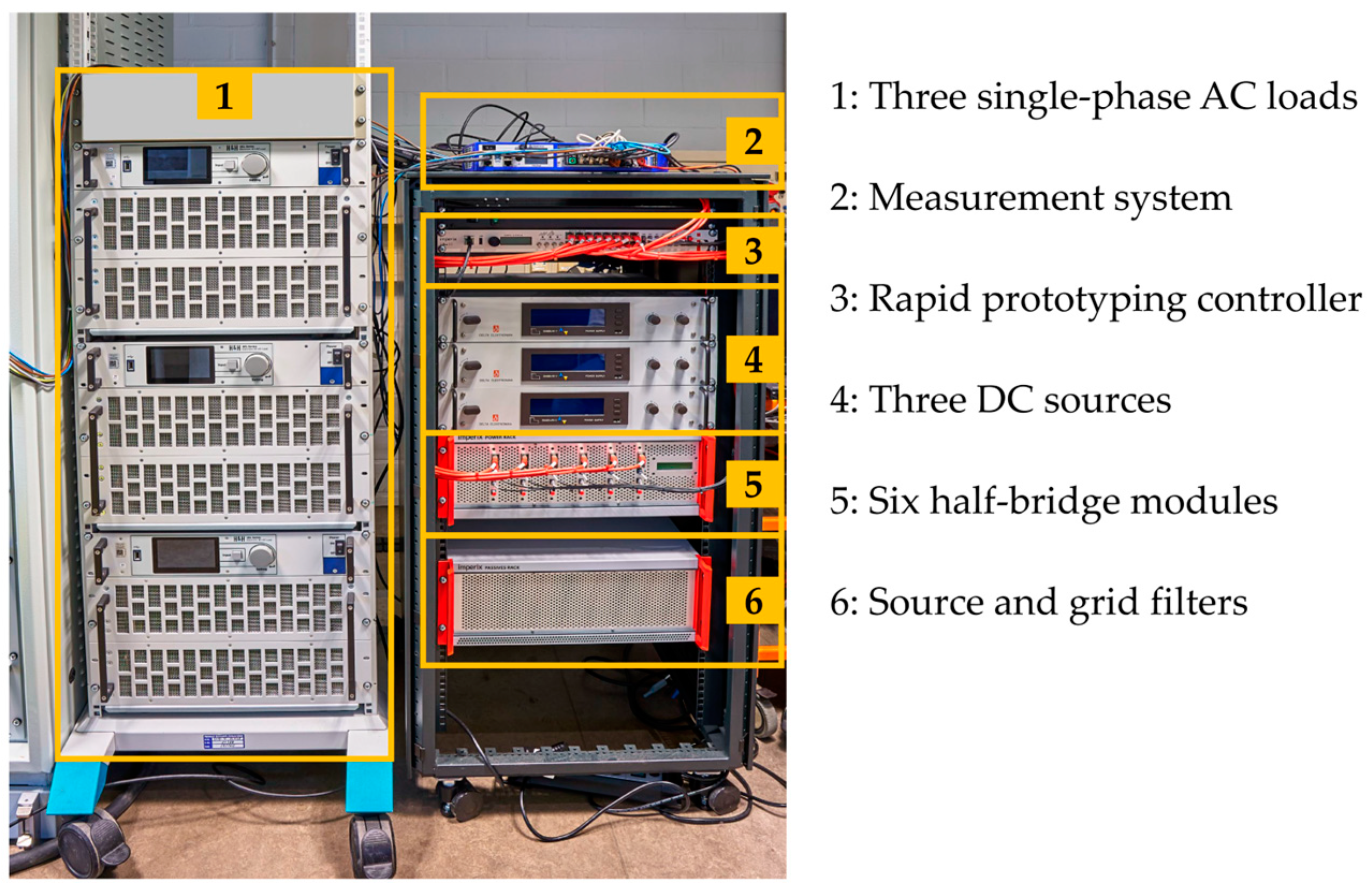
2.3. Experimental Setup
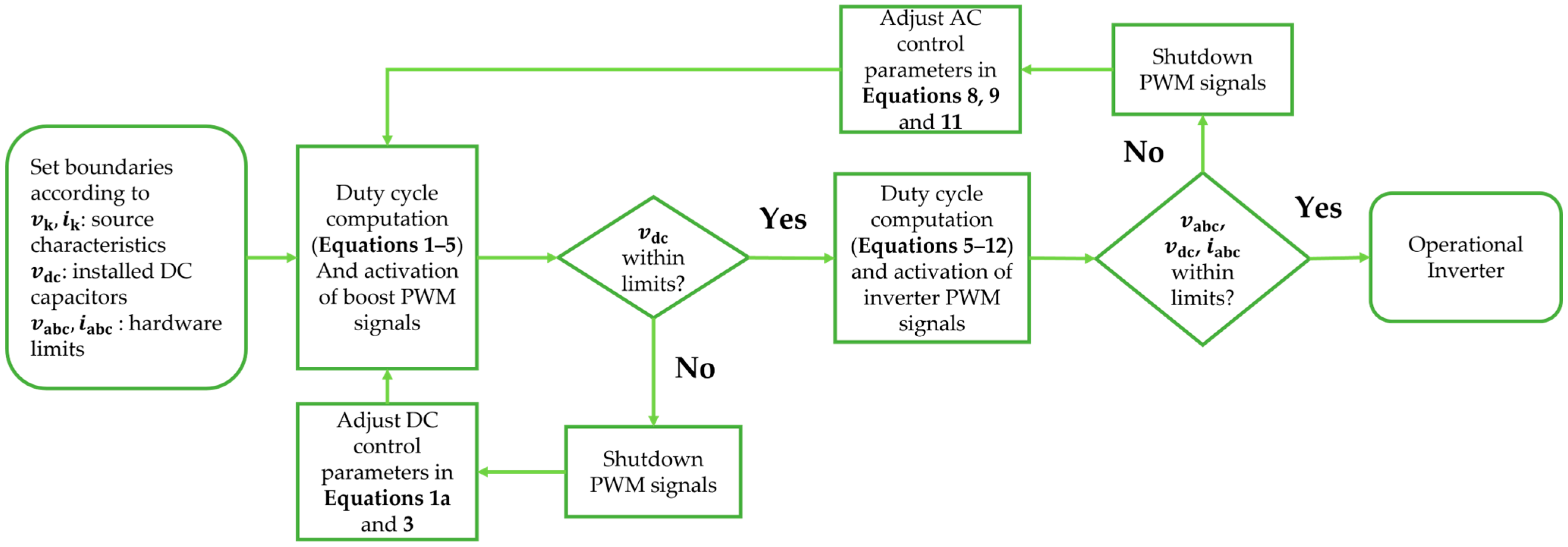
2.4. System Validation
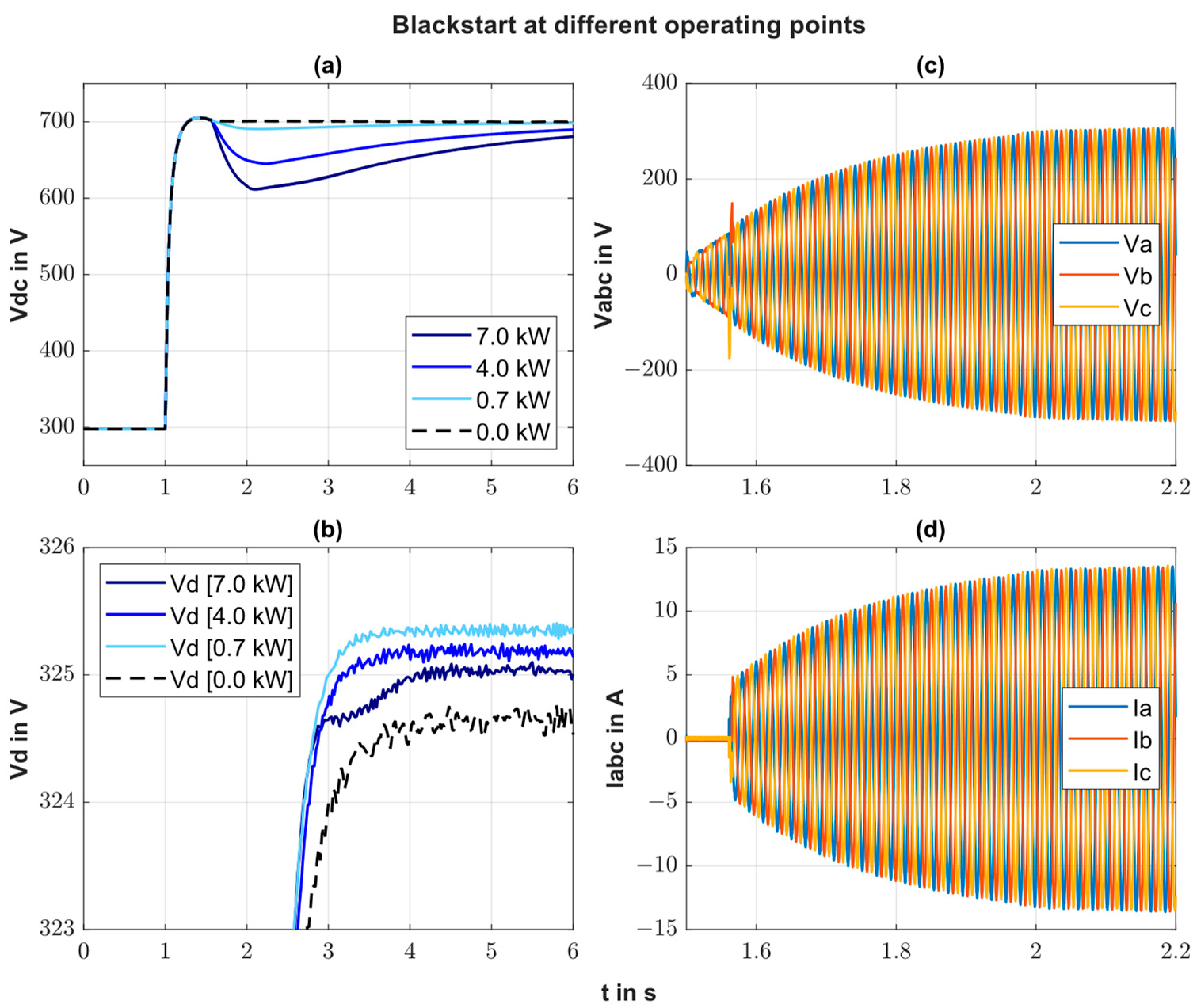
2.4.1. Blackstart
2.4.2. Stationary Behavior
2.4.3. Transient Behavior
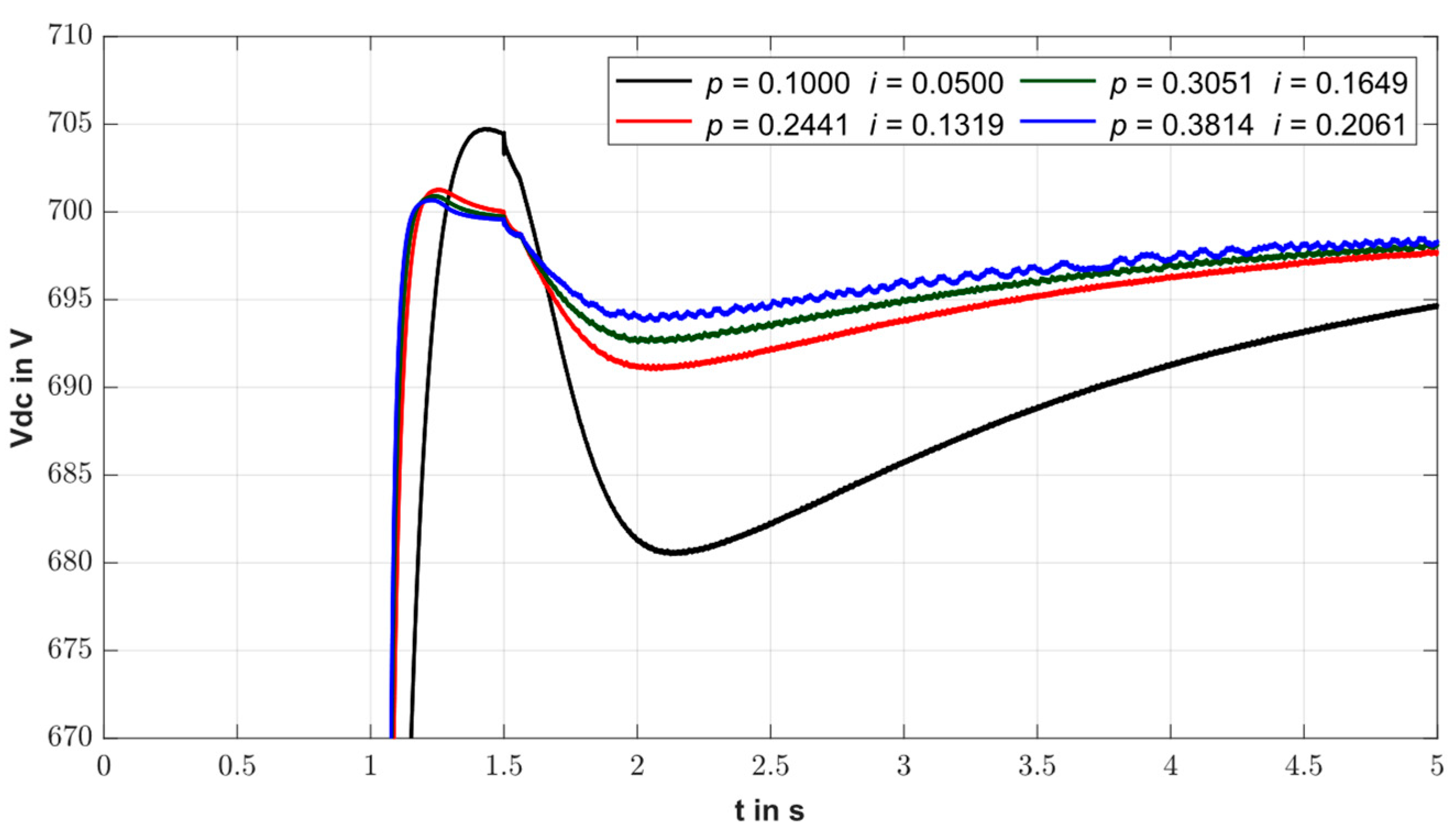
2.4.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Laboratory Validation
3.1. Blackstart
3.2. Stationary Behavior
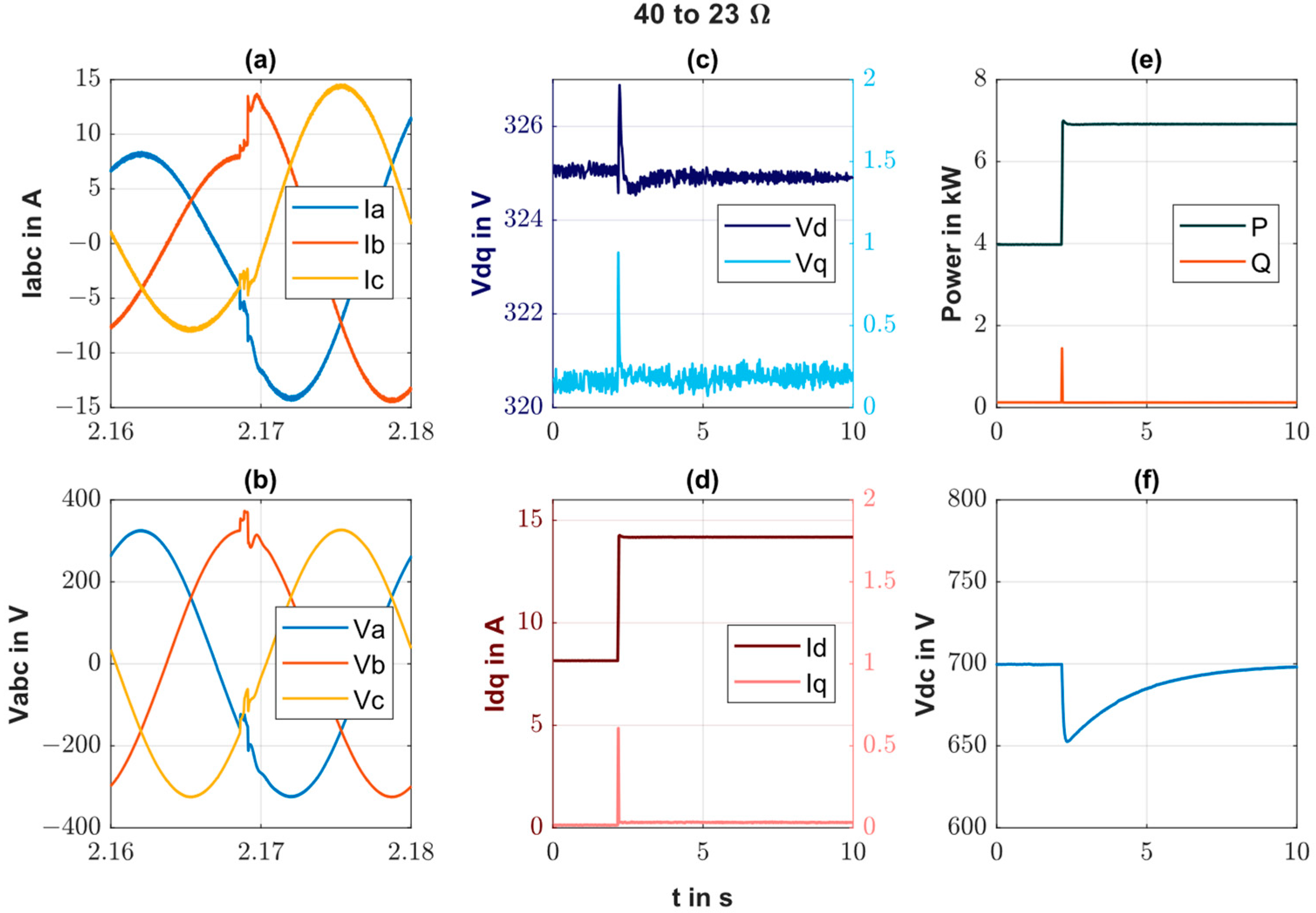
3.3. Transient Behavior
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.4.1. Sensitivity DC Bus Voltage Controller
3.4.2. Sensitivity of the AC Voltage Controller
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPC | Direct power control |
| GFLI | Grid-following inverter |
| GFMI | Grid-forming inverter |
| RCP | Rapid control prototyping |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion |
| VOC | Virtual oscillator control |
| VSM | Virtual synchronous machine |
References
- Rocabert, J.; Luna, A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Rodríguez, P. Control of Power Converters in AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4734–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, R.; Wang, X.; Liserre, M.; Lu, X.; Engelken, S. Grid-Forming Converters: Control Approaches, Grid-Synchronization, and Future Trends—A Review. IEEE Open J. Ind. Appl. 2021, 2, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, R.; Wang, X.; Liserre, M.; Lu, X.; Engelken, S. Grid-forming converters: An overview of control approaches and future trends. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 11–15 October 2020; pp. 4292–4299. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Taul, M.G.; Wu, H.; Liao, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Harnefors, L. Grid-Synchronization Stability of Converter-Based Resources—An Overview. IEEE Open J. Ind. Appl. 2020, 1, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arco, S.; Suul, J.A. Virtual synchronous machines—Classification of implementations and analysis of equivalence to droop controllers for microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Grenoble Conference, Grenoble, France, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lasseter, R.H.; Chen, Z.; Pattabiraman, D. Grid-Forming Inverters: A Critical Asset for the Power Grid. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, P.; Nuschke, M.; Strauß, P.; Welck, F. Overview on Grid-Forming Inverter Control Methods. Energies 2020, 13, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, S.; Döhler, J.S.; Oliveira, J.G.; Boström, C. Grid Forming Inverters: A Review of the State of the Art of Key Elements for Microgrid Operation. Energies 2022, 15, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiang, W.; Lin, W.; Wen, J. Grid Forming Converters in Renewable Energy Sources Dominated Power Grid: Control Strategy, Stability, Application, and Challenges. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 1239–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, D.B.; Akrami, M.; Phurailatpam, C.; Me, S.P.; Hadavi, S.; Jayasinghe, G.; Zabihi, S.; Bahrani, B. Grid Forming Inverter Modeling, Control, and Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 114781–114807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.; Astero, P.; Peltoniemi, P.; Lehtonen, M. Promising Grid-Forming VSC Control Schemes Toward Sustainable Power Systems: Comprehensive Review and Perspectives. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 130024–130039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brabandere, K.; Bolsens, B.; van den Keybus, J.; Woyte, A.; Driesen, J.; Belmans, R. A Voltage and Frequency Droop Control Method for Parallel Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.-P.; Hesse, R. Virtual synchronous machine. In Proceedings of the 2007 9th International Conference on Electrical Power Quality and Utilisation (EPQU 2007), Barcelona, Spain, 9–11 October 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Burgos, R.; Cvetkovic, I.; Boroyevich, D.; Mili, L.; Rodriguez, P. Analysis and design of virtual synchronous machine based STATCOM controller. In Proceedings of the COMPEL: 2014 IEEE 15th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics, Santander, Spain, 22–25 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, G.-S.; Colombino, M.; Subotic, I.; Johnson, B.; Gros, D.; Dorfler, F. Dispatchable Virtual Oscillator Control for Decentralized Inverter-dominated Power Systems: Analysis and Experiments. In Proceedings of the APEC 2019: Thirty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2019; pp. 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Nurdin, H.I.; Fletcher, J.E. Comparison of Virtual Oscillator and Droop Controlled Islanded Three-Phase Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.B.; Sinha, M.; Ainsworth, N.G.; Dorfler, F.; Dhople, S.V. Synthesizing Virtual Oscillators to Control Islanded Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6002–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisz, D.; Thai, T.T.; Monti, A. Power Control of Virtual Oscillator Controlled Inverters in Grid-Connected Mode. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 5916–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Awal, M.A.; Tu, H.; Husain, I.; Lukic, S. Comparative Transient Stability Assessment of Droop and Dispatchable Virtual Oscillator Controlled Grid-Connected Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 2119–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Dutta, S.; Purba, V.; Dhople, S.; Johnson, B. A Grid-compatible Virtual Oscillator Controller: Analysis and Design. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; pp. 2643–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Ndreko, M.; Rüberg, S.; Winter, W. Grid forming control scheme for power systems with up to 100% power electronic interfaced generation: A case study on Great Britain test system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xin, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, K.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Lu, C. A Virtual Synchronous Control for Voltage-Source Converters Utilizing Dynamics of DC-Link Capacitor to Realize Self-Synchronization. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouini, T.; Arghir, C.; Dörfler, F. Grid-Friendly Matching of Synchronous Machines by Tapping into the DC Storage. IFAC-Pap. 2016, 49, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, I.; Boroyevich, D.; Burgos, R.; Li, C.; Mattavelli, P. Modeling and control of grid-connected voltage-source converters emulating isotropic and anisotropic synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 16th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–15 July 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Milano, F.; Dorfler, F.; Hug, G.; Hill, D.J.; Verbic, G. Foundations and Challenges of Low-Inertia Systems (Invited Paper). In Proceedings of the PSCC: 2018 Power Systems Computation Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 11–15 June 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Qoria, T.; Gruson, F.; Colas, F.; Guillaud, X.; Debry, M.-S.; Prevost, T. Tuning of Cascaded Controllers for Robust Grid-Forming Voltage Source Converter. In Proceedings of the 2018 Power Systems Computation Conference (PSCC), Dublin, Ireland, 11–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X. Small-Signal Modeling and Controller Parameters Tuning of Grid-Forming VSCs With Adaptive Virtual Impedance-Based Current Limitation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 7185–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghir, C.; Jouini, T.; Dörfler, F. Grid-forming control for power converters based on matching of synchronous machines. Automatica 2018, 95, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Gross, D.; Anta, A.; Kupzog, F.; Dorfler, F. Frequency Stability of Synchronous Machines and Grid-Forming Power Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidse, L. SM3300_DTS_V202306. Available online: https://www.delta-elektronika.nl/sites/default/files/2023-06/SM3300_DTS_V202306.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Imperix, PEB8038—Half-Bridge SiC Power Module. Available online: https://cdn.imperix.com/wp-content/uploads/document/PEB8038.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Höcherl & Hackl, ACLS8450—Elektronische AC Last—Höcherl & Hackl. Available online: https://www.hoecherl-hackl.de/produktangebot/acls8450/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- DIN-50A. Available online: https://cdn.imperix.com/wp-content/uploads/document/DIN-50A.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- DIN-800V. Available online: https://cdn.imperix.com/wp-content/uploads/document/DIN-800V.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Imperix Ltd. B-Box RCP Datasheet. Available online: https://cdn.imperix.com/wp-content/uploads/document/B-Box_Datasheet.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).


| DC Bus Control | |||||
| DC bus voltage | 700 V | DC bus capacitance | 1 mF | ||
| Source voltage | 300 V | Voltage control P/I | 0.1/0.05 | ||
| Source filter | 2.2 mH | Current control P/I | 12.5/110 | ||
| Switching frequency | 20 kHz | DC current limit | 25 A | ||
| Inverter Control | |||||
| Grid inductance | 2.2 mH | Voltage magnitude control P/I | 0.1/5 | ||
| Grid capacitance | 100 mF | d-current control P/I | 6.25/55 | ||
| Load range | 1–7 kW | q-current control P/I | 12.5/110 | ||
| AC current limit | 30 A | d-voltage control P/I | 0.25/1 | ||
| AC voltage reference | 230 V | q-voltage control P/I | 0.23/1 | ||
| Angle sensitivity | 0.1257 | Reference angle frequency | 314 rad/s | ||
| Initial Load | Final Load |
|---|---|
| 236 Ω (0.9 kW) | 40 Ω (4 kW) |
| 40 Ω (4.0 kW) | 23 Ω (7 kW) |
| 40 Ω (4.0 kW) | 29 Ω (6 kW) |
| 29 Ω (6.0 kW) | 23 Ω (7 kW) |
| 236 Ω (0.9 kW) | 23 Ω (7 kW) |
| Test Nr. | p | i | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Iteration | |||||
| 1 | 0.075 | 0.0375 | 707.97 | 675.45 | 75.69 |
| 2 | 0.075 | 0.0500 | 711.00 | 678.11 | 75.14 |
| 3 | 0.075 | 0.0675 | 714.85 | 680.65 | 74.45 |
| 4 | 0.100 | 0.0375 | 703.60 | 678.67 | 61.26 |
| 5 | 0.100 | 0.0500 | 704.75 | 680.48 | 61.49 |
| 6 | 0.100 | 0.0675 | 706.65 | 681.89 | 61.00 |
| 7 | 0.125 | 0.0375 | 701.85 | 681.45 | 54.77 |
| 8 | 0.125 | 0.0500 | 702.73 | 682.67 | 54.69 |
| 9 | 0.125 | 0.0675 | 703.95 | 684.08 | 54.68 |
| 2nd Iteration | |||||
| 10 | 0.1562 | 0.0844 | 702.50 | 686.86 | 51.25 |
| 11 | 0.1953 | 0.1055 | 701.85 | 689.26 | 49.89 |
| 12 | 0.2441 | 0.1319 | 701.28 | 691.01 | 49.89 |
| 13 | 0.3051 | 0.1649 | 700.93 | 692.56 | 49.89 |
| 14 | 0.3814 | 0.2061 | 700.70 | 693.79 | 49.91 |
| Test Nr. | Test Nr. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.2500/1.00 | 0.2300/1.00 | 8 (repetition) | 0.1875/1.25 | 0.2875/1.25 |
| 1 | 0.1875/0.75 | 0.1725/0.75 | 9 | 0.3125/0.75 | 0.1725/0.75 |
| 2 | 0.1875/0.75 | 0.1725/1.25 | 10 | 0.3125/0.75 | 0.1725/1.25 |
| 3 | 0.1875/0.75 | 0.2875/0.75 | 11 | 0.3125/0.75 | 0.2875/0.75 |
| 4 | 0.1875/0.75 | 0.2875/1.25 | 12 | 0.3125/0.75 | 0.2875/1.25 |
| 5 | 0.1875/1.25 | 0.1725/0.75 | 13 | 0.3125/1.25 | 0.1725/0.75 |
| 6 | 0.1875/1.25 | 0.1725/1.25 | 14 | 0.3125/1.25 | 0.1725/1.25 |
| 7 | 0.1875/1.25 | 0.2875/0.75 | 15 | 0.3125/1.25 | 0.2875/0.75 |
| 8 | 0.1875/1.25 | 0.2875/1.25 | 16 | 0.3125/1.25 | 0.2875/1.25 |
| Test Nr. | THD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd Set | |||||
| 17 | 0.140 | 0.562 | 0.129 | 1.562 | 0.420 |
| 18 | 0.105 | 0.421 | 0.097 | 1.953 | 0.500 |
| 3rd Set | |||||
| 19 | 0.250 | 10 | 0.230 | 10 | 0.340 |
| 20 | 0.225 | 10 | 0.207 | 10 | 0.345 |
| 21 | 0.225 | 20 | 0.207 | 20 | 0.345 |
| 22 | 0.187 | 20 | 0.172 | 20 | 0.365 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez Anccas, E.D.; Pourhossein, K.; Becker, D.; Schulz, D. Detailed Controller Synthesis and Laboratory Verification of a Matching-Controlled Grid-Forming Inverter for Microgrid Applications. Energies 2023, 16, 8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248079
Gomez Anccas ED, Pourhossein K, Becker D, Schulz D. Detailed Controller Synthesis and Laboratory Verification of a Matching-Controlled Grid-Forming Inverter for Microgrid Applications. Energies. 2023; 16(24):8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248079
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez Anccas, Edgar Diego, Kazem Pourhossein, Daniel Becker, and Detlef Schulz. 2023. "Detailed Controller Synthesis and Laboratory Verification of a Matching-Controlled Grid-Forming Inverter for Microgrid Applications" Energies 16, no. 24: 8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248079
APA StyleGomez Anccas, E. D., Pourhossein, K., Becker, D., & Schulz, D. (2023). Detailed Controller Synthesis and Laboratory Verification of a Matching-Controlled Grid-Forming Inverter for Microgrid Applications. Energies, 16(24), 8079. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248079








