Autonomous Wireless Power Transfer System with Constant Output Voltage in a Wide Load Range
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- No additional DC/DC converter is necessary at the transmitter and receiver.
- (2)
- No bilateral communication is needed between the transmitter and receiver.
- (3)
- Constant voltage can be achieved in a wide load range.
2. System Circuit Structure and Output Voltage Characteristics
2.1. System Circuit Structure
2.2. Output Voltage Characteristic
3. Proposed Control Strategy for the Autonomous System
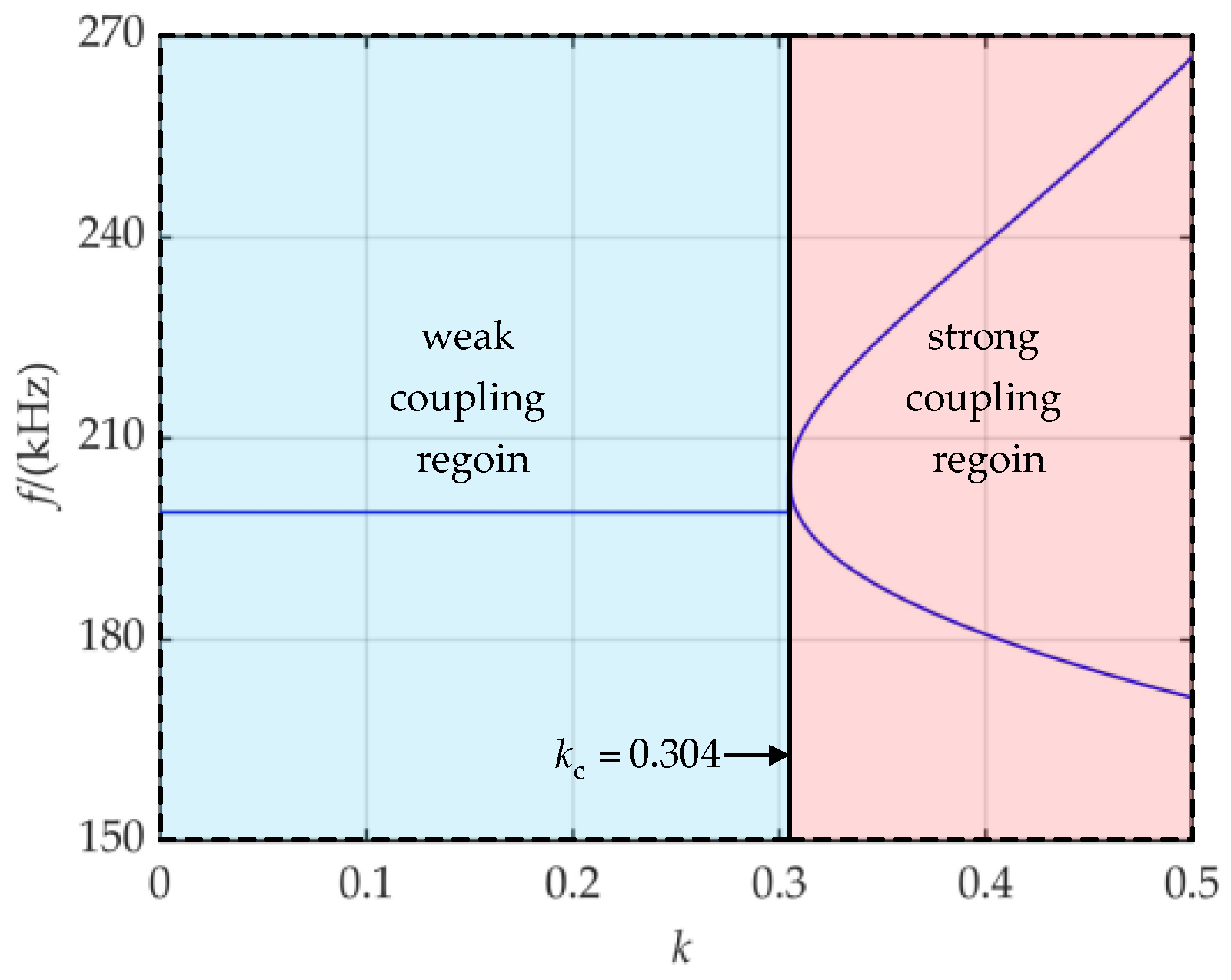
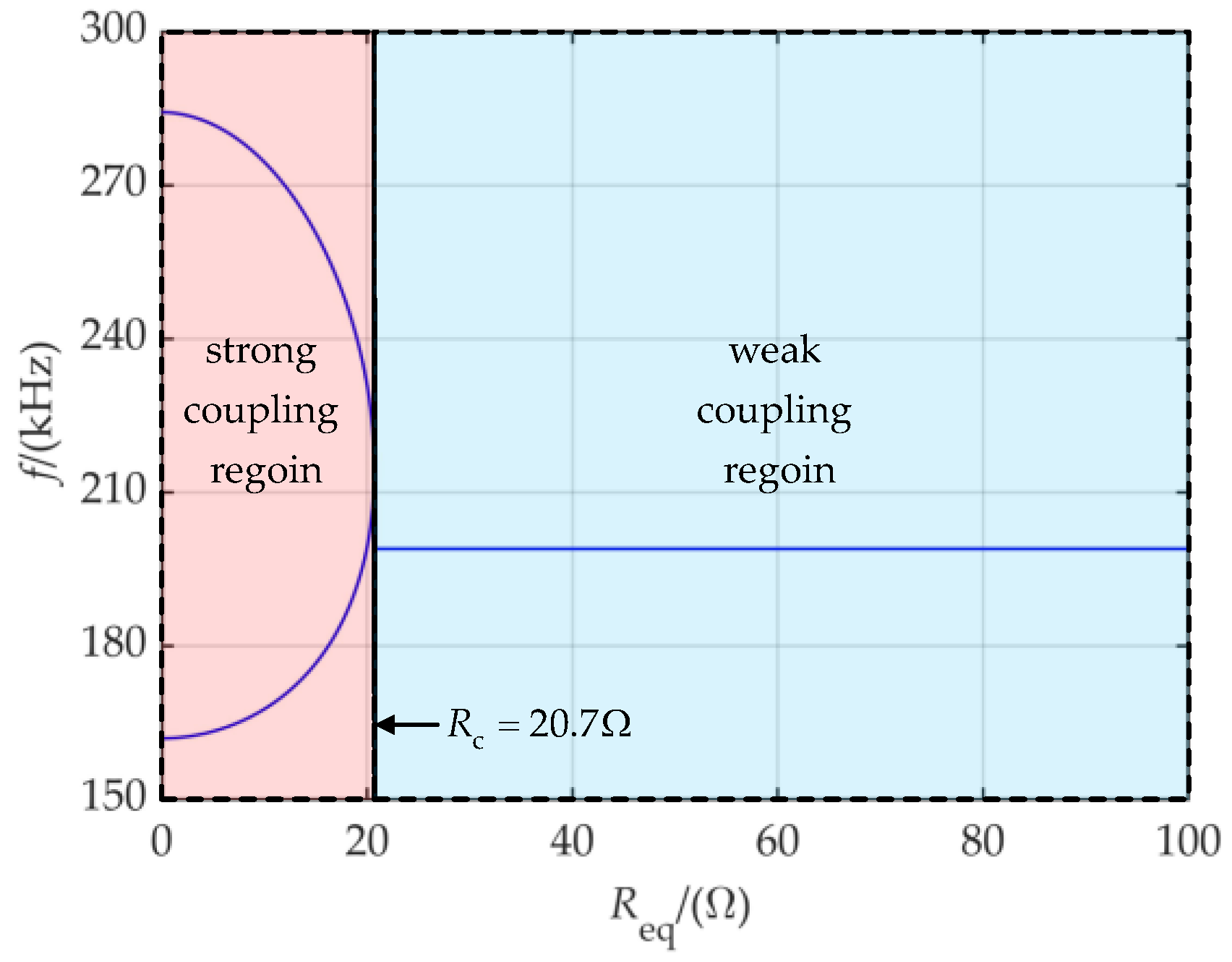
3.1. Coupling Region Estimation
3.2. Output Voltage Estimation in the Weak Coupling Region
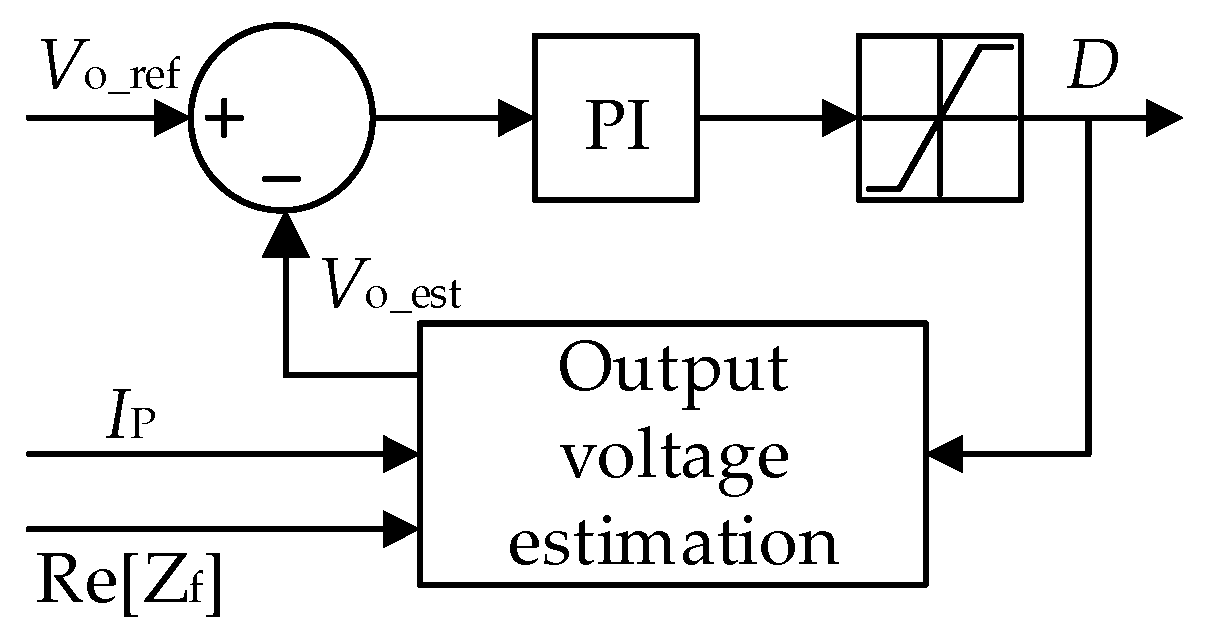
3.3. Control Strategy
4. Experiment Verification
4.1. Steady-State Performance
4.2. Dynamic Performance
4.3. Output Voltage and Overall Efficiency in a Wide Load Range
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mou, X.; Gladwin, D.; Jiang, J.; Li, K.; Yang, Z. Near-Field Wireless Power Transfer Technology for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: A Systematical Review. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2023, 4, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Tang, Y. Design of high-power static wireless power transfer via magnetic induction: An overview. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2023, 6, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Review of research progress and application of magnetic resonant WPT technology. In Proceedings of the CSAA/IET International Conference on Aircraft Utility Systems (AUS 2022), Nanchang, China, 11 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Hao, S.; Cheng, D.; Liao, C. Safety Enhancement by Optimizing Frequency of Implantable Cardiac Pacemaker Wireless Charging System. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuit Syst. 2022, 16, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, Z.; Kiani, M. A Study on Ultrasonic Wireless Power Transfer With Phased Array for Biomedical Implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuit Syst. 2023, 17, 713–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Su, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, F.; Deng, P. A Double-Receiver Compact SCC-WPT System with CV/CC Output for Mobile Devices Charging/Supply. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 9230–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, N.; Ahn, S.; Lee, W. Three-Dimensional Wireless Power Transfer System Using Multiple Orthogonal Resonators for Spatial Freedom. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 4036–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, A.P. A Robust Wireless Power Transfer System with Self-Alignment Capability and Controllable Output Current for Automatic-Guided Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 11898–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Guo, Q.; Yang, Z.; Lin, F.; Wang, Y. Design and Optimization of Real-Time Strong Coupling Coil of Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer for Electrical Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 11495–11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Tian, J.; Hu, J.; Mai, R.; He, Z. High-Efficiency WPT System for CC/CV Charging Based on Double-Half-Bridge Inverter Topology with Variable Inductors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, G. Variable Inductor Control for Misalignment Tolerance and Constant Current/Voltage Charging in Inductive Power Transfer System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 4563–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qu, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, P. Hybrid Inductive-Power-Transfer Battery Chargers for Electric Vehicle Onboard Charging with Configurable Charging Profile. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J. A Hybrid LCC-SP Compensation Network with Adjustable Impedance Angle Used for Single-Stage Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 3452–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, D. A Single-Stage Wireless Power Transfer Converter with Hybrid Compensation Topology in AC Input. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 8266–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J.; Song, K.; Wei, G. A 3-kW Wireless Power Transfer System for Sightseeing Car Supercapacitor Charge. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3301–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Joo, D.M.; Lee, B.K. Design and Control of Inductive Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicles Considering Wide Variation of Output Voltage and Coupling Coefficient. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, J.; Li, R.; Han, R.; Wang, Y. A High-Efficiency ZVS Wireless Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicle Charging WithVariable Angle Phase Shift Control. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 2356–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iam, I.W.; Hoi, I.U.; Huang, Z.; Gong, C.; Lam, C.S.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P.D.S. Constant-Frequency and Noncommunication-Based Inductive Power Transfer Converter for Battery Charging. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 2147–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.B.; Tran, D.H.; Choi, W. Implementation of the Constant Current and Constant Voltage Charge of Inductive Power Transfer Systems with the Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology for Electric Vehicle Battery Charge Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, M.; Geng, Z. Analysis and Design of an S/S/P-Compensated Three-Coil Structure WPT System with Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 2487–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, C. Constant Current/Voltage Charging Operation for Series–Series and Series–Parallel Compensated Wireless Power Transfer Systems Employing Primary-Side Controller. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8065–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. Primary-Side Linear Control for Constant Current/Voltage Charging of the Wireless Power Transfer System Based on the LCC-N Compensation Topology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 8895–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assawaworrarit, S.; Yu, X.; Fan, S. Robust wireless power transfer using a nonlinear parity–time-symmetric circuit. Nature 2017, 546, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, W.; Qiu, D.; Chen, Y. Nonlinear Parity-Time-Symmetric Model for Constant Efficiency Wireless Power Transfer: Application to a Drone-in-Flight Wireless Charging Platform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4097–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J. Efficiency Improvement of the Parity-Time-Symmetric Wireless Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12497–12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y. Position-Independent Constant Current or Constant Voltage Wireless Electric Vehicles Charging System without Dual-Side Communication and DC–DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 7930–07939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gu, W.; Shu, X. Wireless Power Transfer System with High-Order Compensation Network Based on Parity-Time-Symmetric Principle and Relay Coil. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| LP | Coil self-inductance of the transmitter | 31.9 μH |
| LS | Coil self-inductance of the receiver | 31.6 μH |
| RP | Coil internal resistance of the transmitter | 0.19 Ω |
| RS | Coil internal resistance of the receiver | 0.19 Ω |
| CP | Resonant capacitance of LP | 20.05 nF |
| CS | Resonant capacitance of LS | 20.24 nF |
| f0 | Natural resonant frequency | 199 kHz |
| Vin | DC input voltage | 24 V |
| k | Coupling coefficient | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, D.; Shu, X.; Zhou, Y. Autonomous Wireless Power Transfer System with Constant Output Voltage in a Wide Load Range. Energies 2023, 16, 8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248026
Jiang Y, Zhao X, Chen D, Shu X, Zhou Y. Autonomous Wireless Power Transfer System with Constant Output Voltage in a Wide Load Range. Energies. 2023; 16(24):8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248026
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yanwei, Xiaoguang Zhao, Dongliang Chen, Xujian Shu, and Yang Zhou. 2023. "Autonomous Wireless Power Transfer System with Constant Output Voltage in a Wide Load Range" Energies 16, no. 24: 8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248026
APA StyleJiang, Y., Zhao, X., Chen, D., Shu, X., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Autonomous Wireless Power Transfer System with Constant Output Voltage in a Wide Load Range. Energies, 16(24), 8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248026






