Numerical Simulation on Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Oscillated by Speed Ripple of AC Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
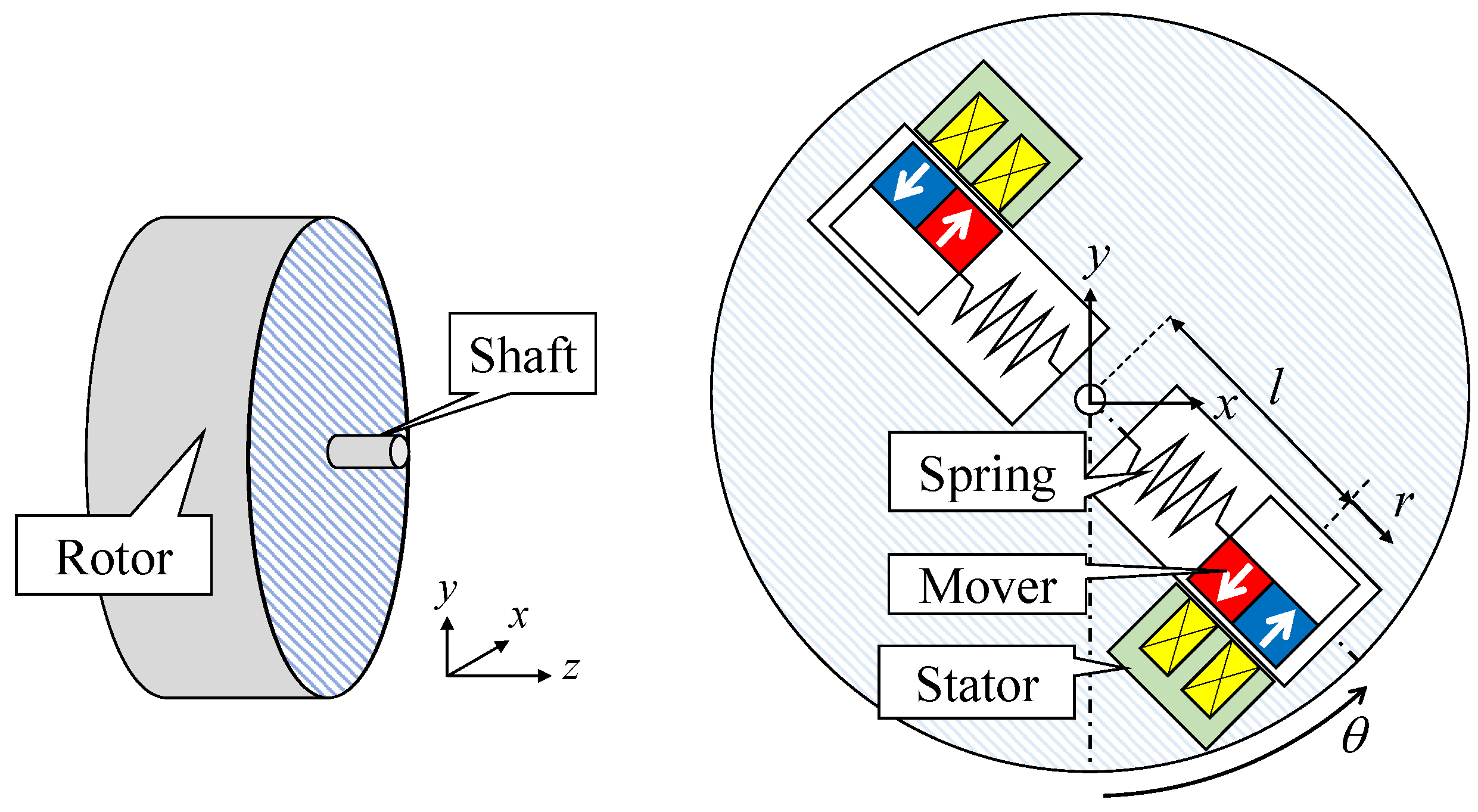
2. Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Oscillated by Speed Ripple of Motors
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.2. Operational Principle of Power Generation
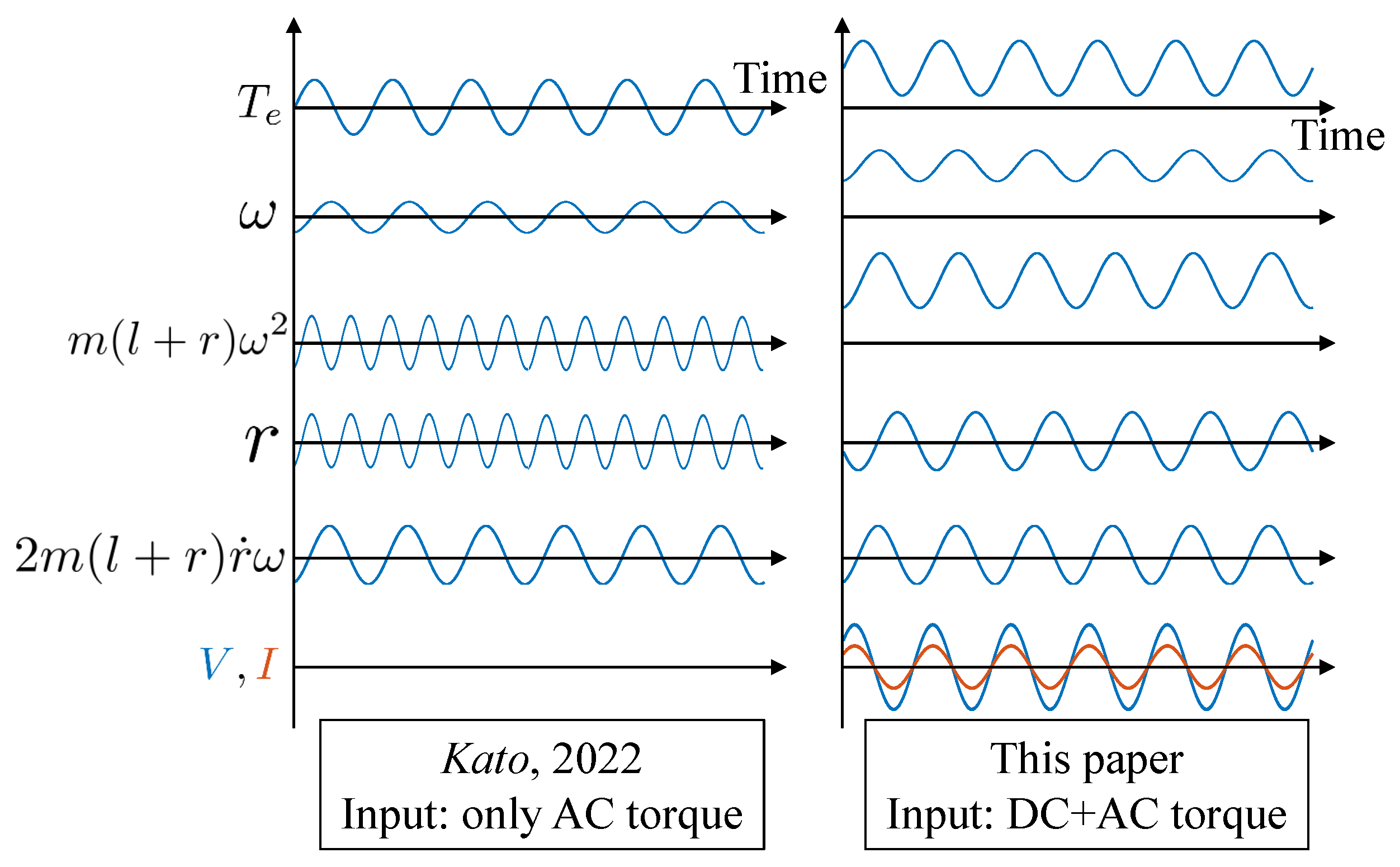
3. Numerical Simulation Results
3.1. MATLAB/Simulink Model and Condition
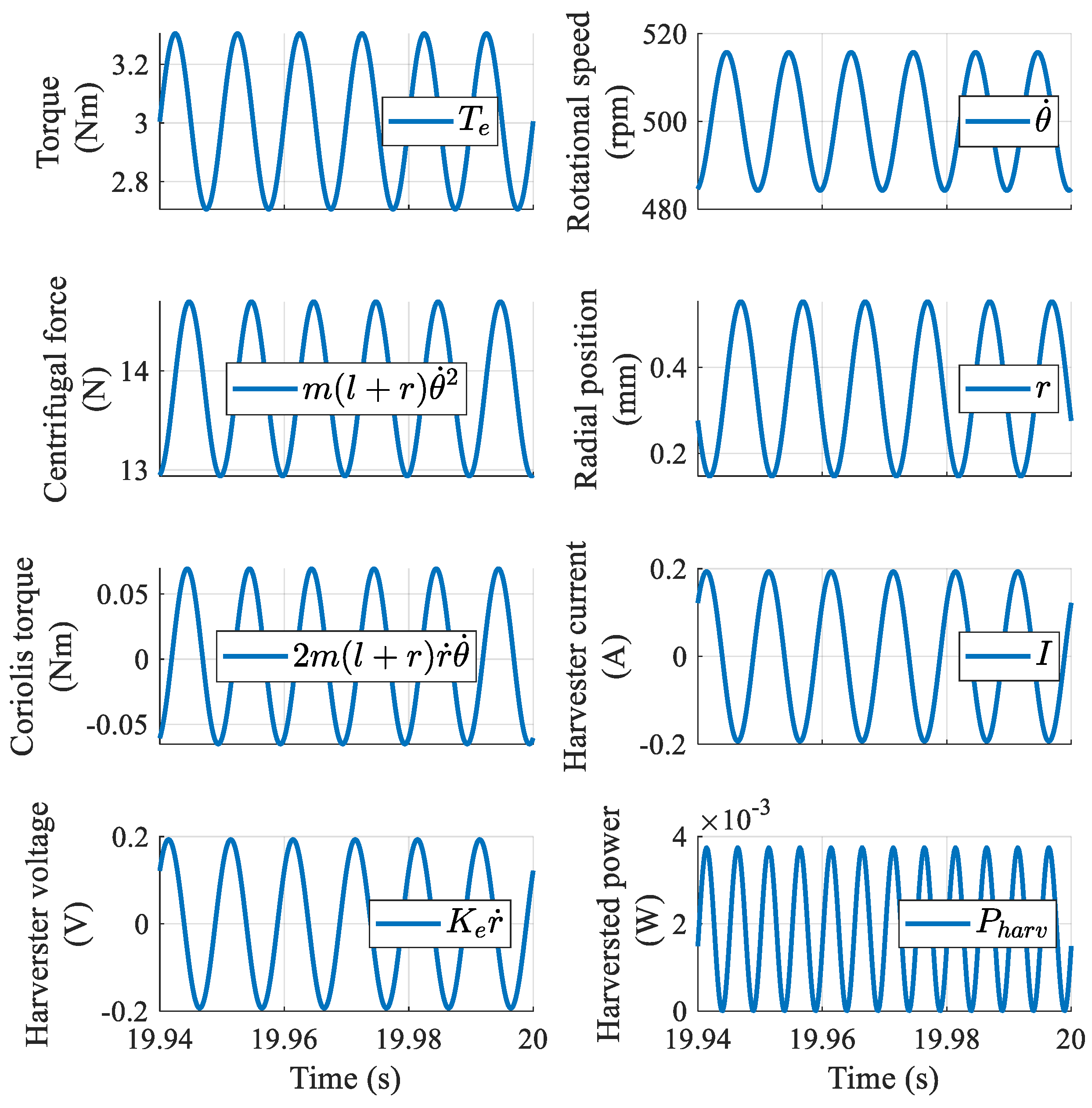
3.2. Verification of the Operational Principle
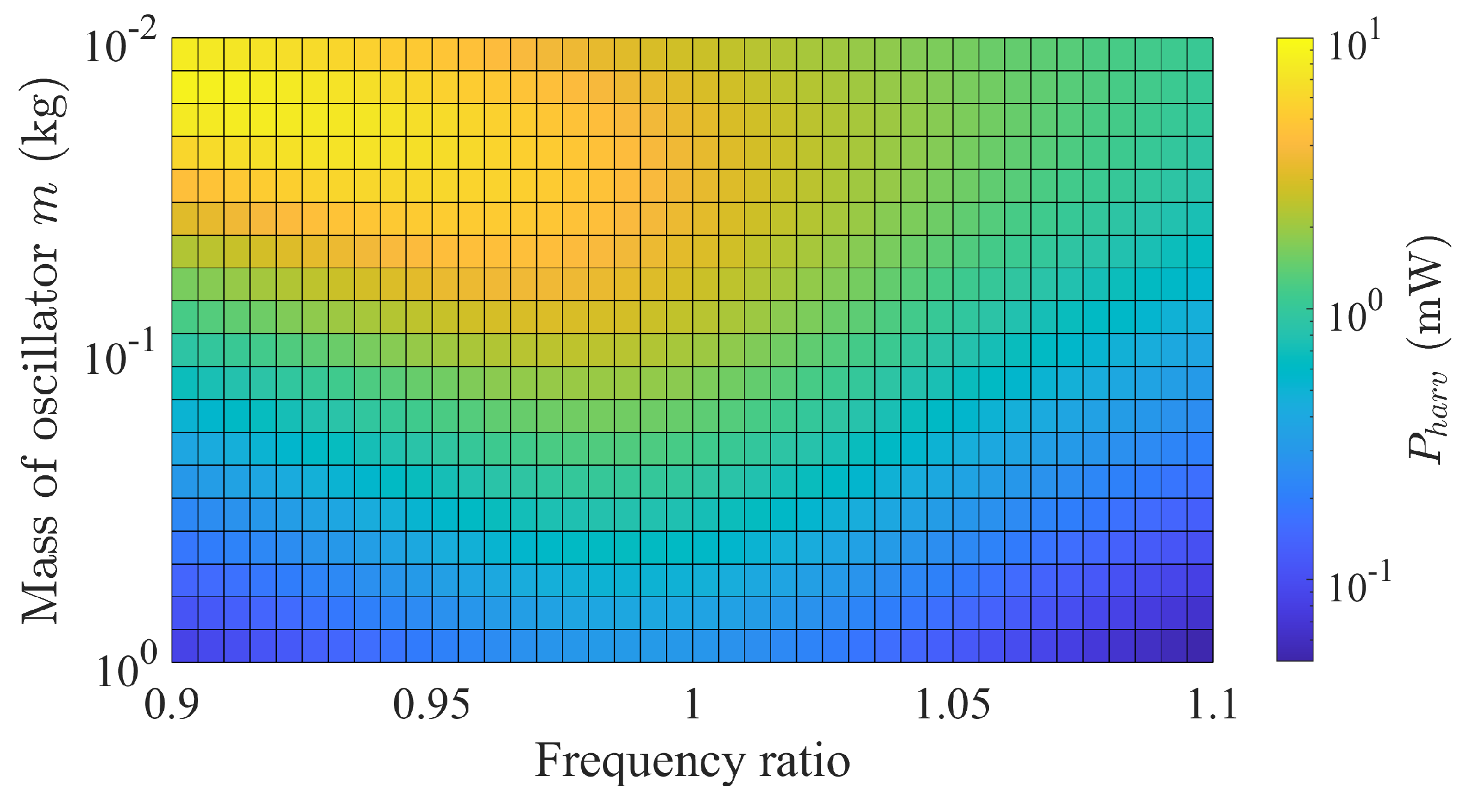
3.3. Parametric Study of the Power Generation
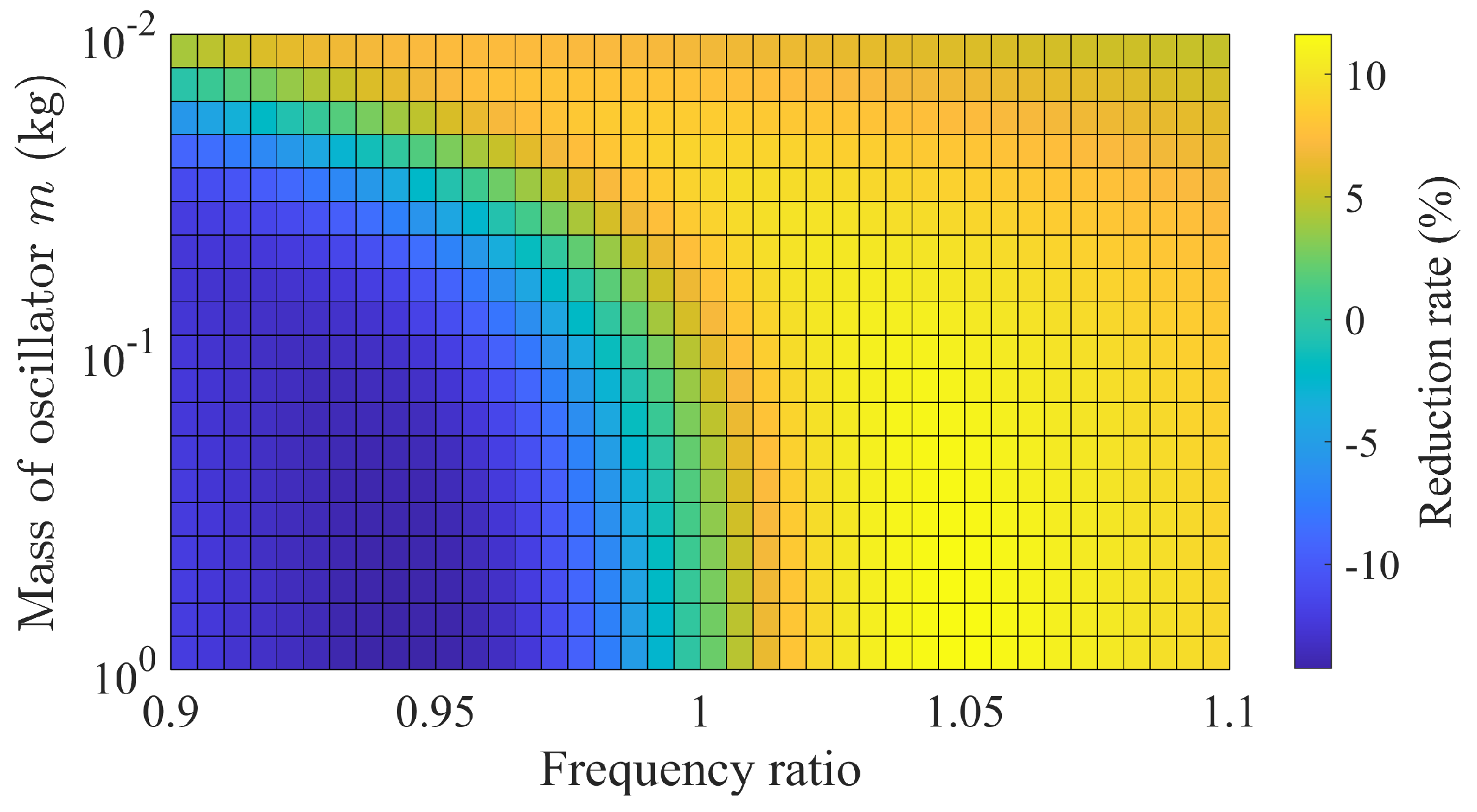
3.3.1. Oscillator Mass and Frequency Ratio
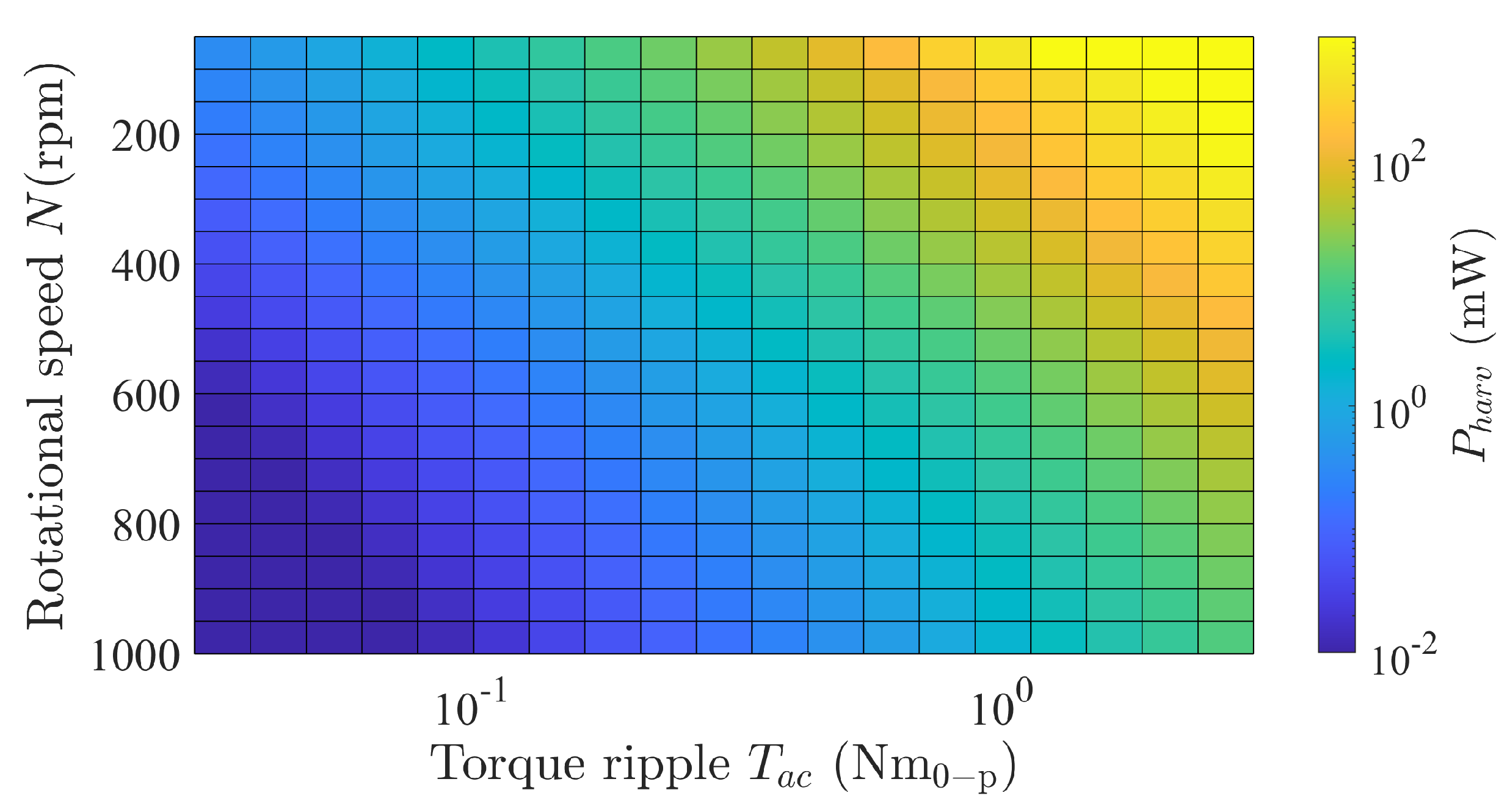
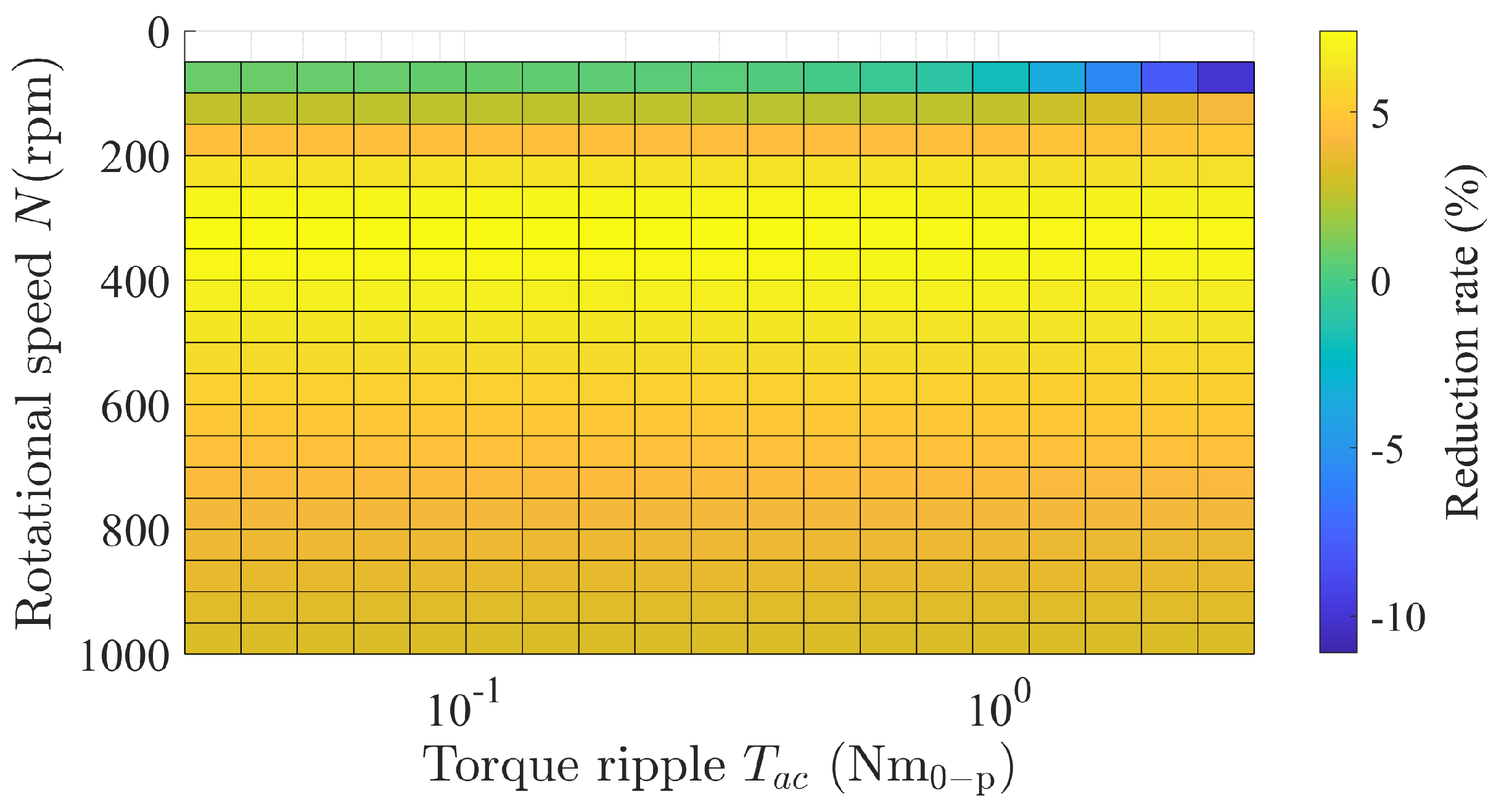
3.3.2. Rotational Speed and Torque Ripple
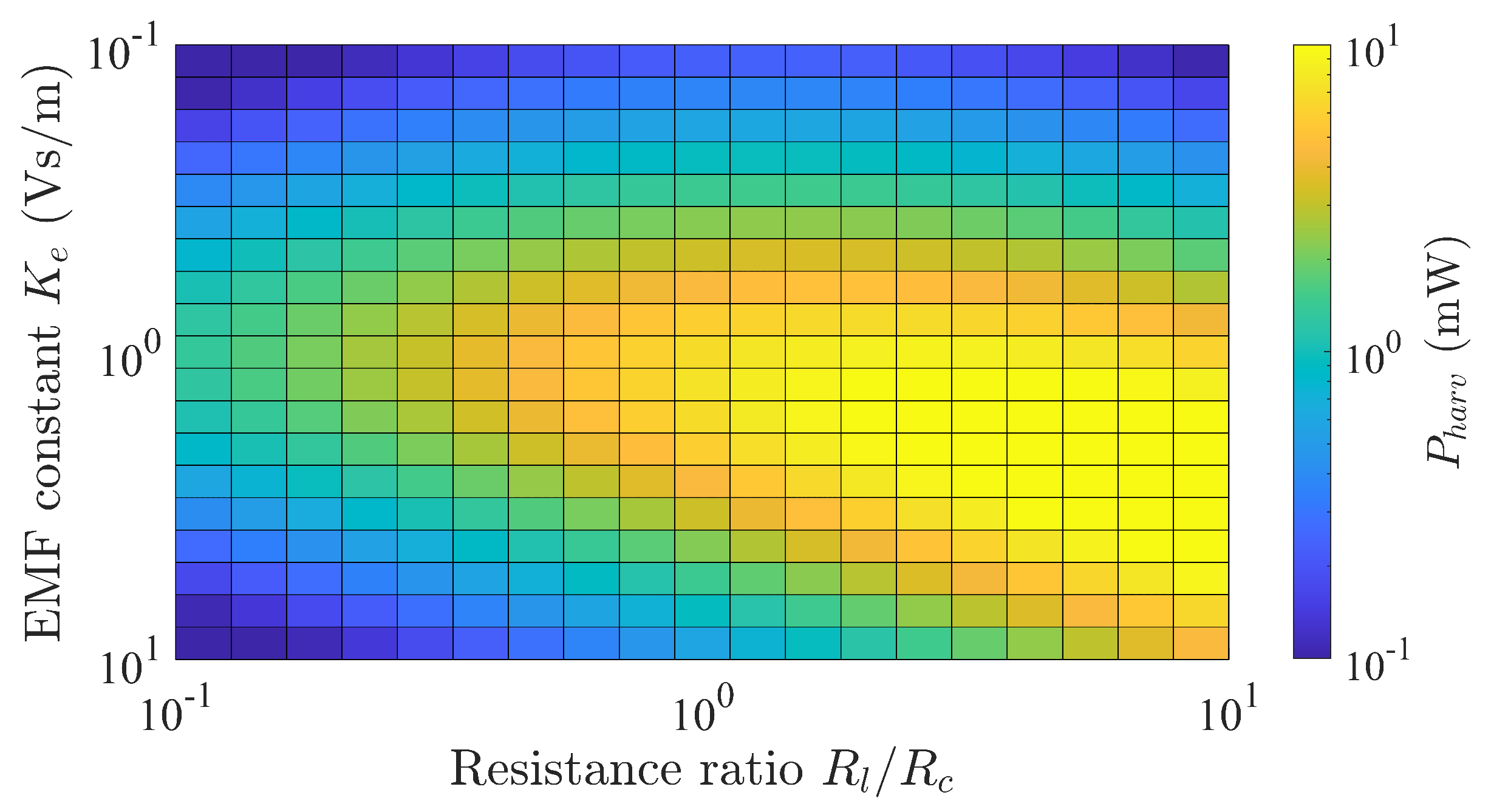
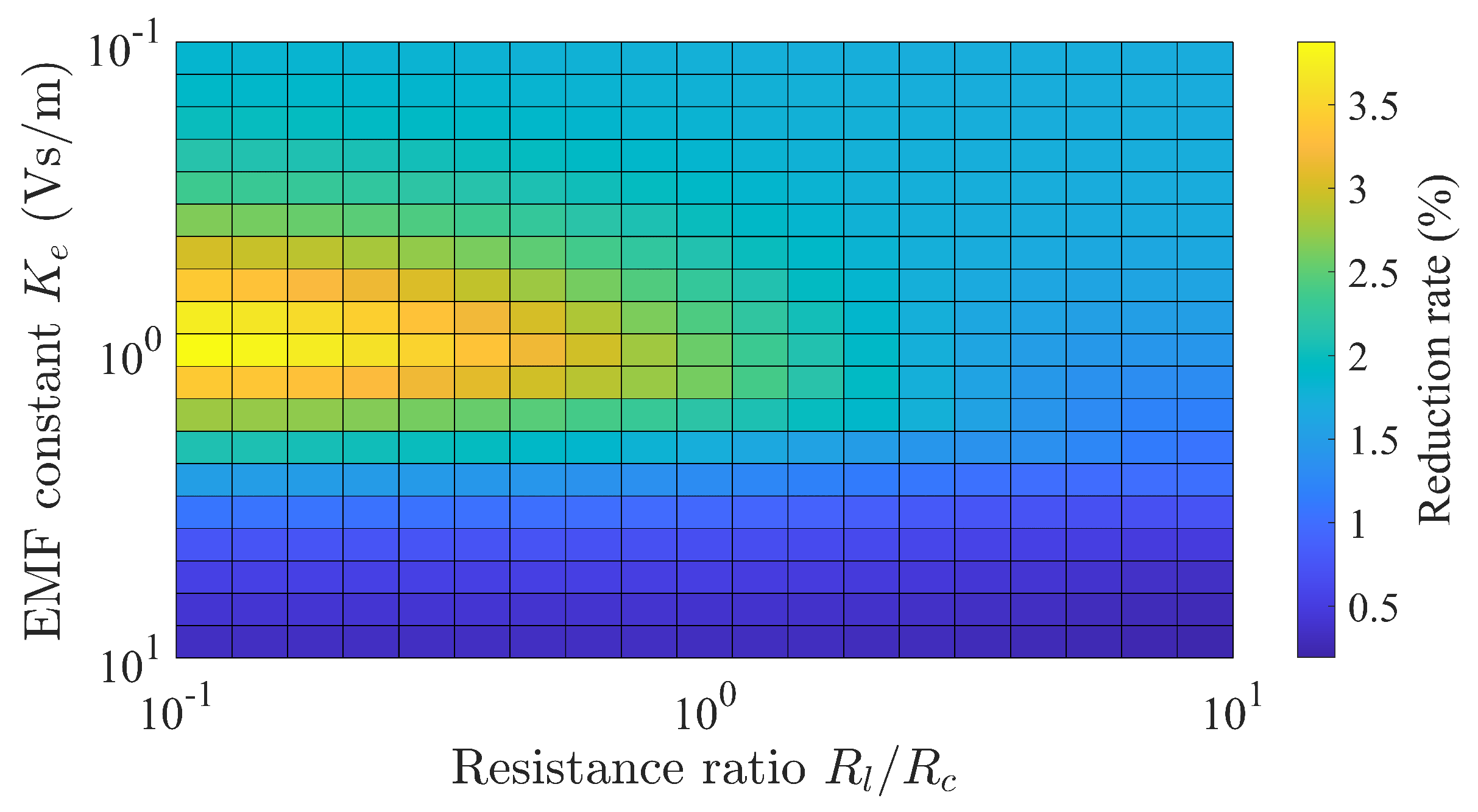
3.3.3. EMF Constant and Impedance Matching
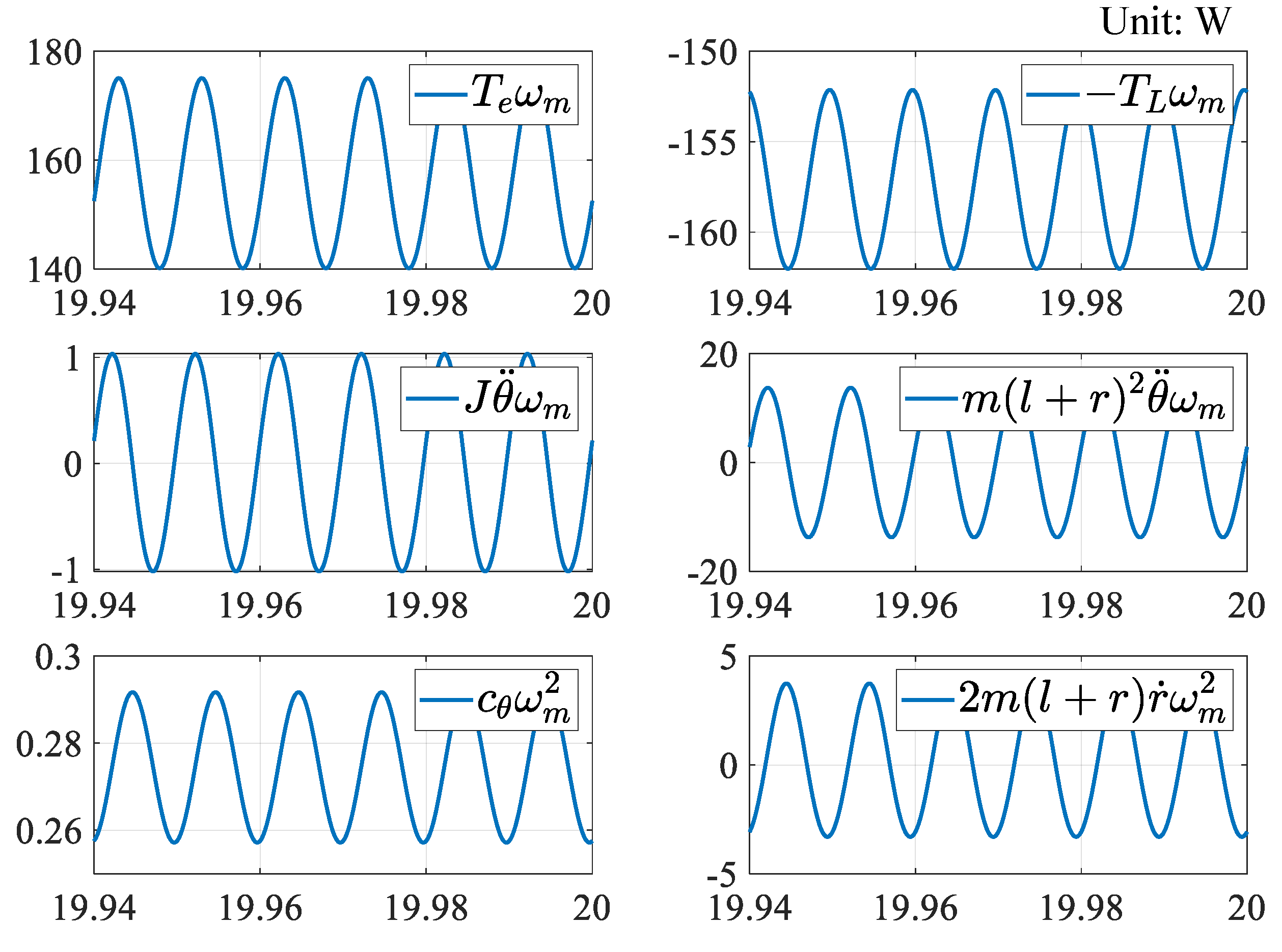
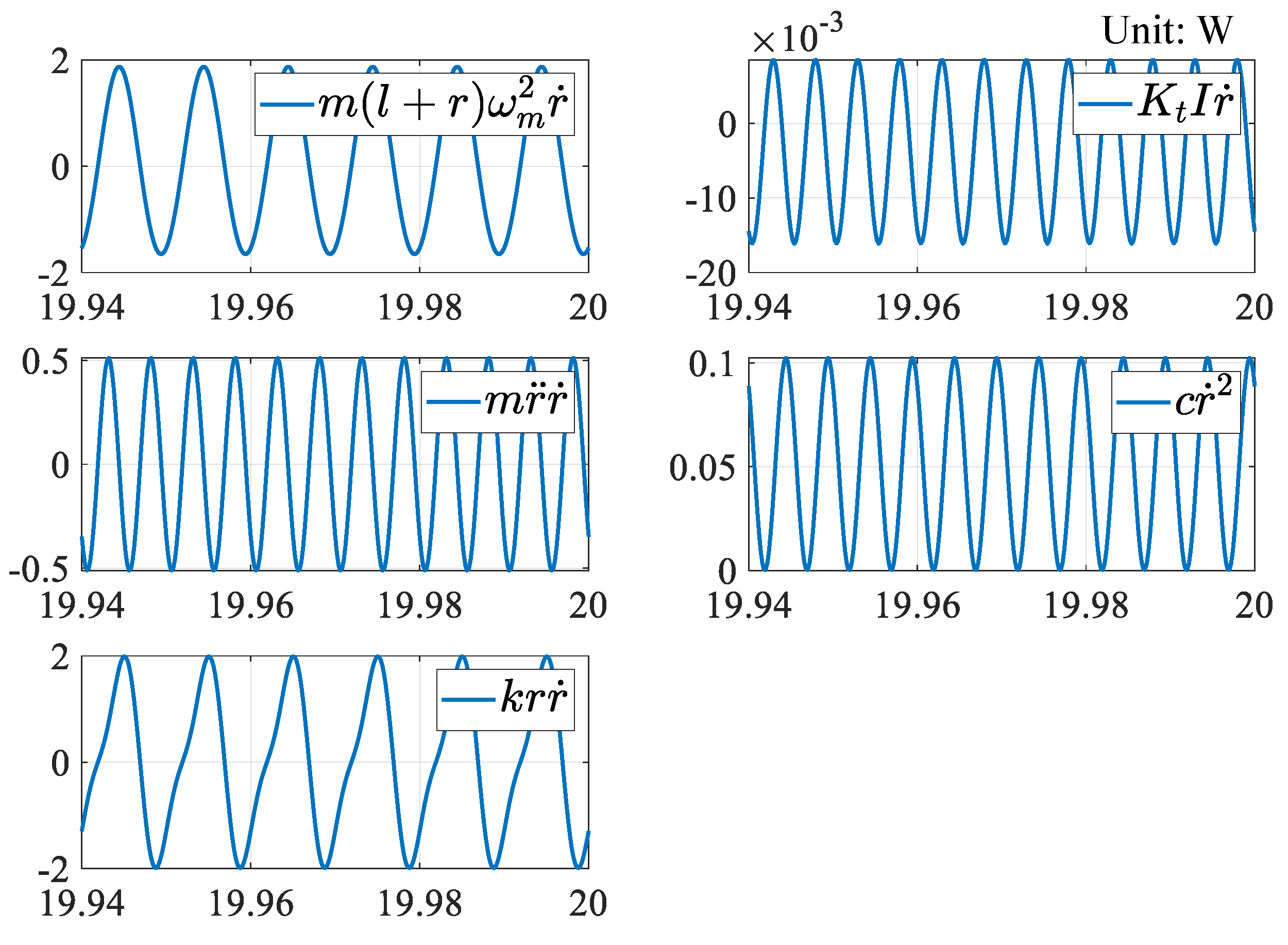
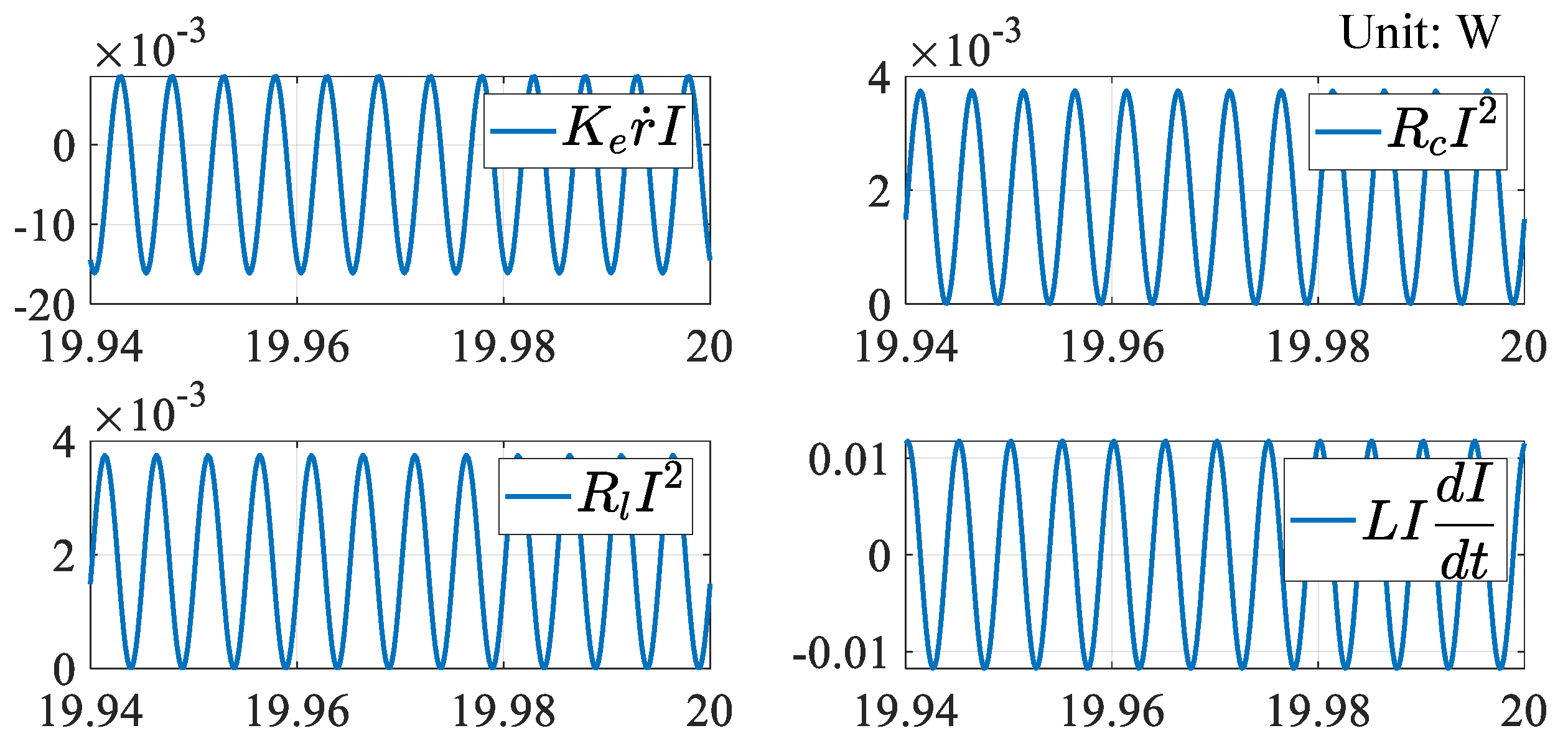
4. Discussion on Energy Flow
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sul, S.K.; Kim, S. Sensorless Control of IPMSM: Past, Present, and Future. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2012, 1, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, T.M.; Soong, W.L. Pulsating Torque Minimization Techniques for Permanent Magnet AC Motor Drives-A Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totoki, E.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Ito, K.; Daikoku, A.; Morimoto, S. Torque Ripple Reduction for Permanent Magnet Motor using New Configuration for Concentrated Windings. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2022, 11, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, K.; Takeda, Y.; Sanada, M.; Morimoto, S. Torque Ripple Reduction of Reluctance Torque Assisted Motors Using Asymmetric Flux Barriers. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2004, 124, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M.; Inoue, Y. Reduction of Torque Ripple in Synchronous Reluctance Motor by Combining Different Flux Barrier Structures. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2019, 8, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Fujimoto, H.; Fujitsuna, M. Torque Ripple Suppression Control for PM Motor Considering the Bandwidth of Torque Meter. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2010, 130, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, N.; Akatsu, K. Torque Ripple Control Based on Instantaneous Torque Estimation in PMSMs. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2011, 131, 1120–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Jatskevich, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S. Torque Ripple Reduction Method for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives With Novel Harmonic Current Control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2502–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Naito, S.; Kitayama, F. Basic Study on Reduction of Rotational Vibration Using Linear Oscillatory Actuator. J. Jpn. Soc. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2021, 29, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Kitayama, F. Reduction of Rotational Vibration Using Coriolis Force Generated by Electromagnetic Oscillatory Actuator Moving in Radial Direction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8200205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Ratha, S.; Rout, C.S.; Nayak, S.K. Self-charging supercapacitors for smart electronic devices: A concise review on the recent trends and future sustainability. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 4399–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Optimization of Galloping Piezoelectric Energy Harvester with V-Shaped Groove in Low Wind Speed. Energies 2019, 12, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharne, B.; Gupta, B.; Litak, G. Simulation of Synchronized-Switching Method Energy Harvester Including Accurate Piezoceramic Nonlinear Behavior. Energies 2019, 12, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, G.; Han, C. A Free-Standing Electromagnetic Energy Harvester for Condition Monitoring in Smart Grid. Wirel. Power Transf. 2021, 2021, 6685308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, P.; Arafa, M.; Anis, Y. An Electromagnetic Vibration Energy Harvester with a Tunable Mass Moment of Inertia. Sensors 2021, 21, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foisal, A.-R.-M.; Hong, C.; Chung, G.-S. Multi-frequency electromagnetic energy harvester using a magnetic spring cantilever. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 182, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, L.D.; Anh, N.D.; Matsuhisa, H. The effective damping approach to design a dynamic vibration absorber using Coriolis force. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Hattori, S.; Ishida, M.; Hori, T. Suppression Control Method for Torque Vibration of AC Motor Utilizing Repetitive Controller with Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 39, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar]
- [RTML-001] PMSM/IPM Constant Rating 1000(W) 3-Phase. Available online: https://www.jmag-international.com/modellibrary/001/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Thompson, S.P. Dynamo-Electric Machinery; A Manual for Students of Electrotechnics; Bibliolife: Charleston, SC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Power (W) | 1000 |
| Number of poles | 4 |
| Number of slots | 24 |
| Diameter of stator (mm) | 54 |
| Diameter of rotor (mm) | 27.5 |
| Stack length (mm) | 51 |
| Winding type | Distributed winding |
| Number of turns | 46 |
| Inertia J () | 1.8 × 10 |
| Torque constant (Nm/A) | 0.126 |
| Parameter (Unit) | Value |
|---|---|
| Rotational speed (rpm) | 500 |
| DC component of motor torque (Nm) | 3 |
| AC component of motor torque () | 0.3 |
| Frequency of torque ripple (Hz) | 100 |
| Load torque (Nm) | 3 |
| Mass of mover m (kg) | 0.1 |
| Spring constant (N/mm) | 39.5 |
| Viscous damping coefficient (Ns/m) | 6.3 |
| Thrust constant (= ) (N/A) | 1 |
| Arm length l (mm) | 50 |
| Coil resistance () | 0.1 |
| Load resistance () | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kato, M. Numerical Simulation on Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Oscillated by Speed Ripple of AC Motors. Energies 2023, 16, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020940
Kato M. Numerical Simulation on Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Oscillated by Speed Ripple of AC Motors. Energies. 2023; 16(2):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020940
Chicago/Turabian StyleKato, Masayuki. 2023. "Numerical Simulation on Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Oscillated by Speed Ripple of AC Motors" Energies 16, no. 2: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020940
APA StyleKato, M. (2023). Numerical Simulation on Electromagnetic Energy Harvester Oscillated by Speed Ripple of AC Motors. Energies, 16(2), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020940










