Three-Port Bi-Directional DC–DC Converter with Solar PV System Fed BLDC Motor Drive Using FPGA
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The proposed converter is utilized for simultaneous power management of a PV system with a battery;
- The charge and discharge controller provides control to the integrated battery to either absorb the additional power supplied during daytime or supply the power during absence of sun;
- The proposed system can be highly employed to low-power household applications, such as air conditioners.
2. Mathematical Modeling of the Proposed System
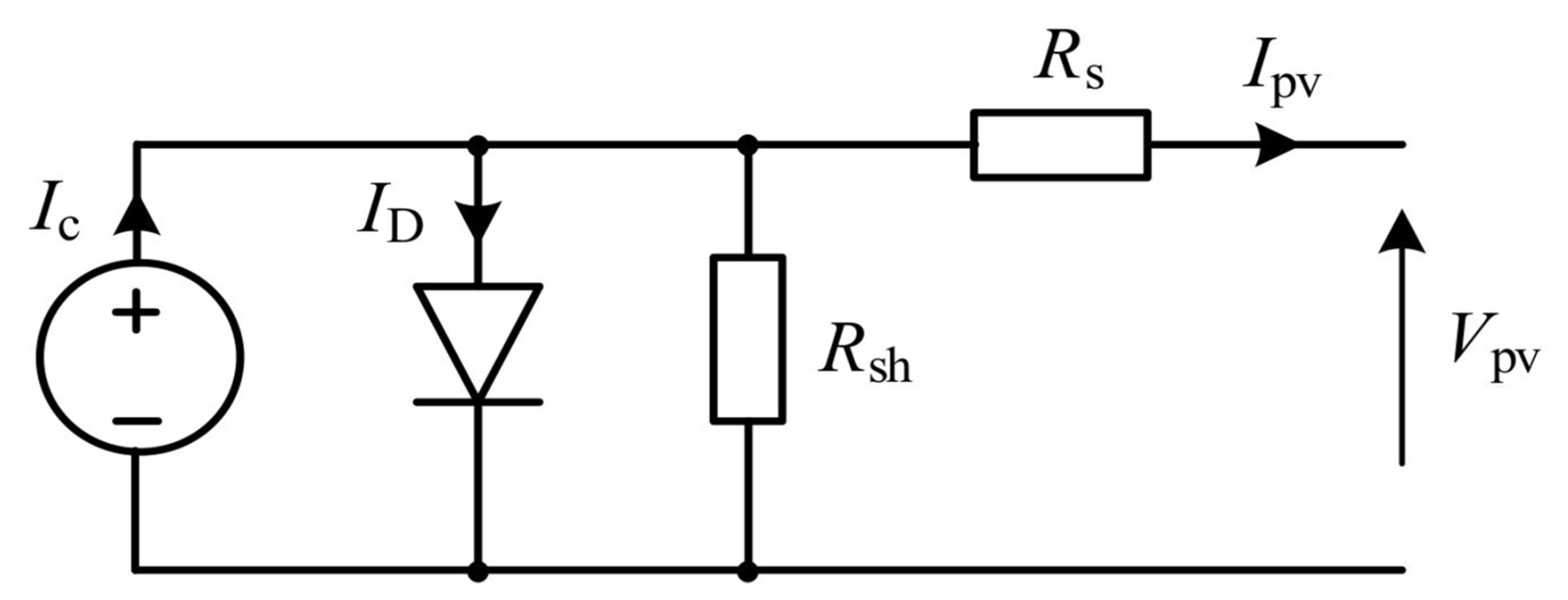
2.1. PV Modeling
2.2. Modeling of BLDC Motor Drive
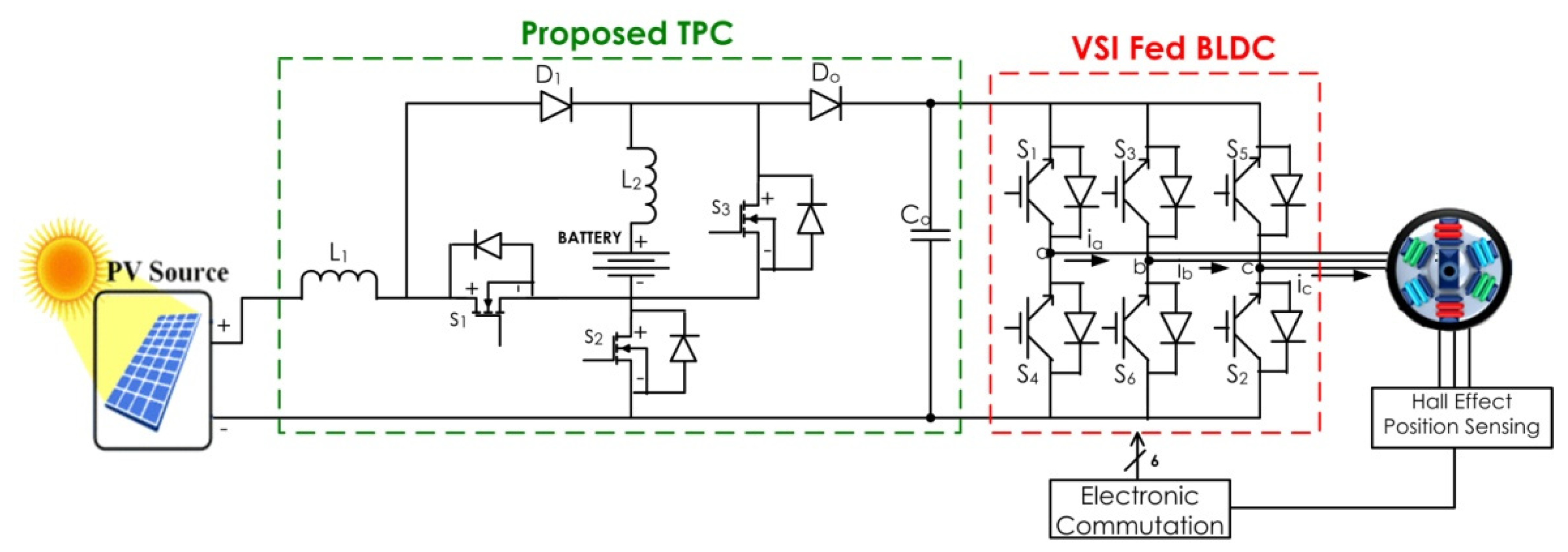
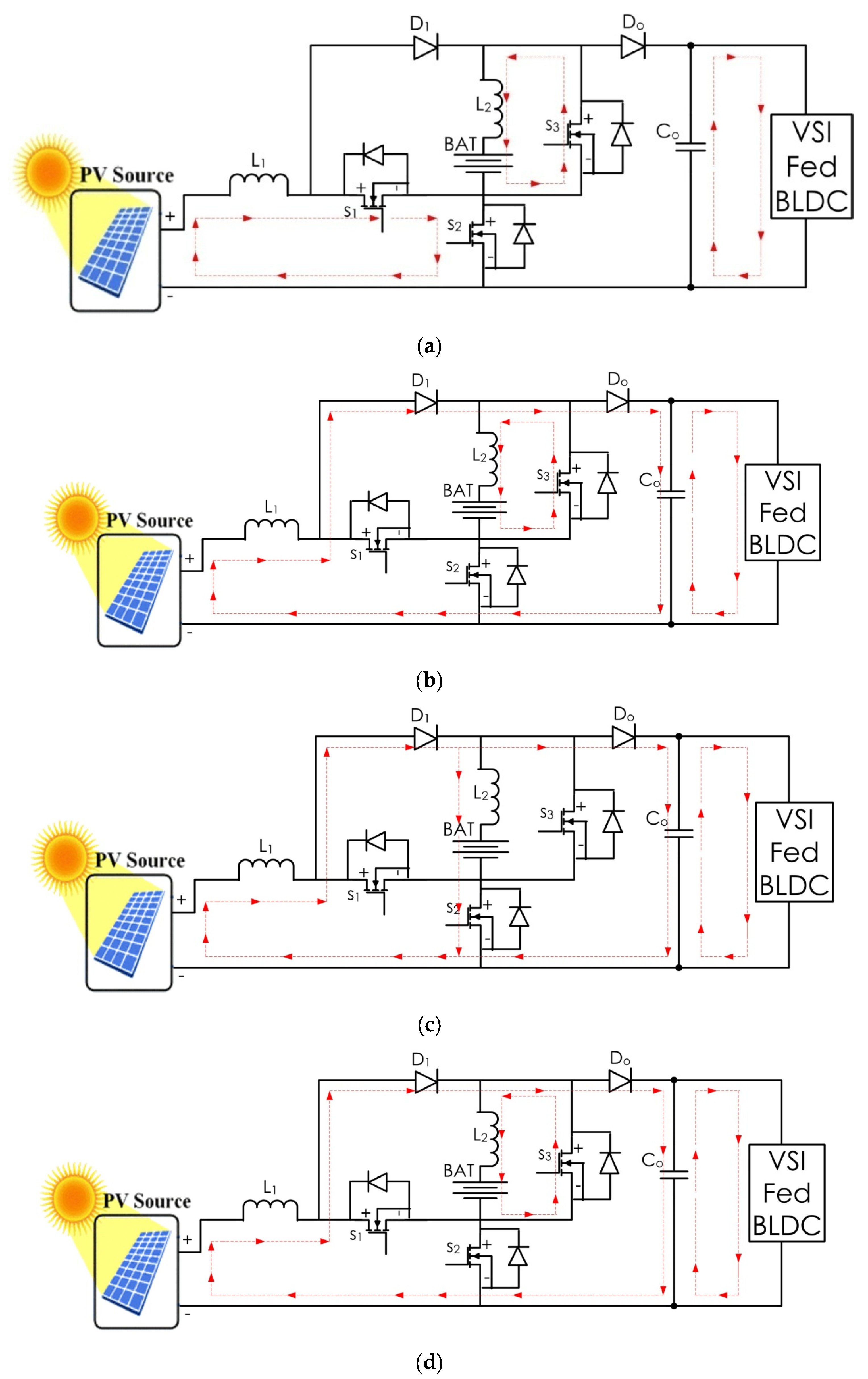
3. Design of Converter and Operating Principles
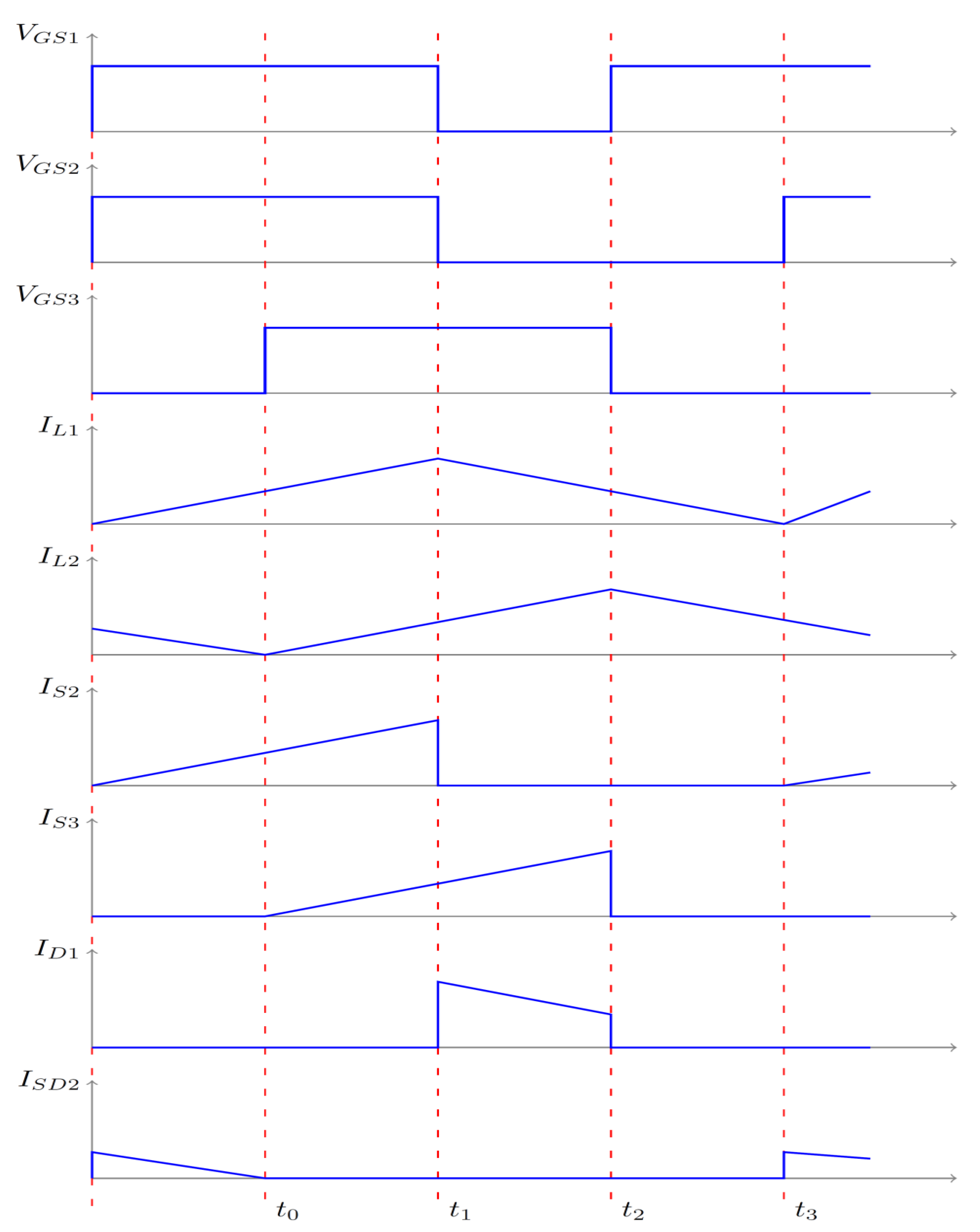
3.1. ESS Discharging Domain
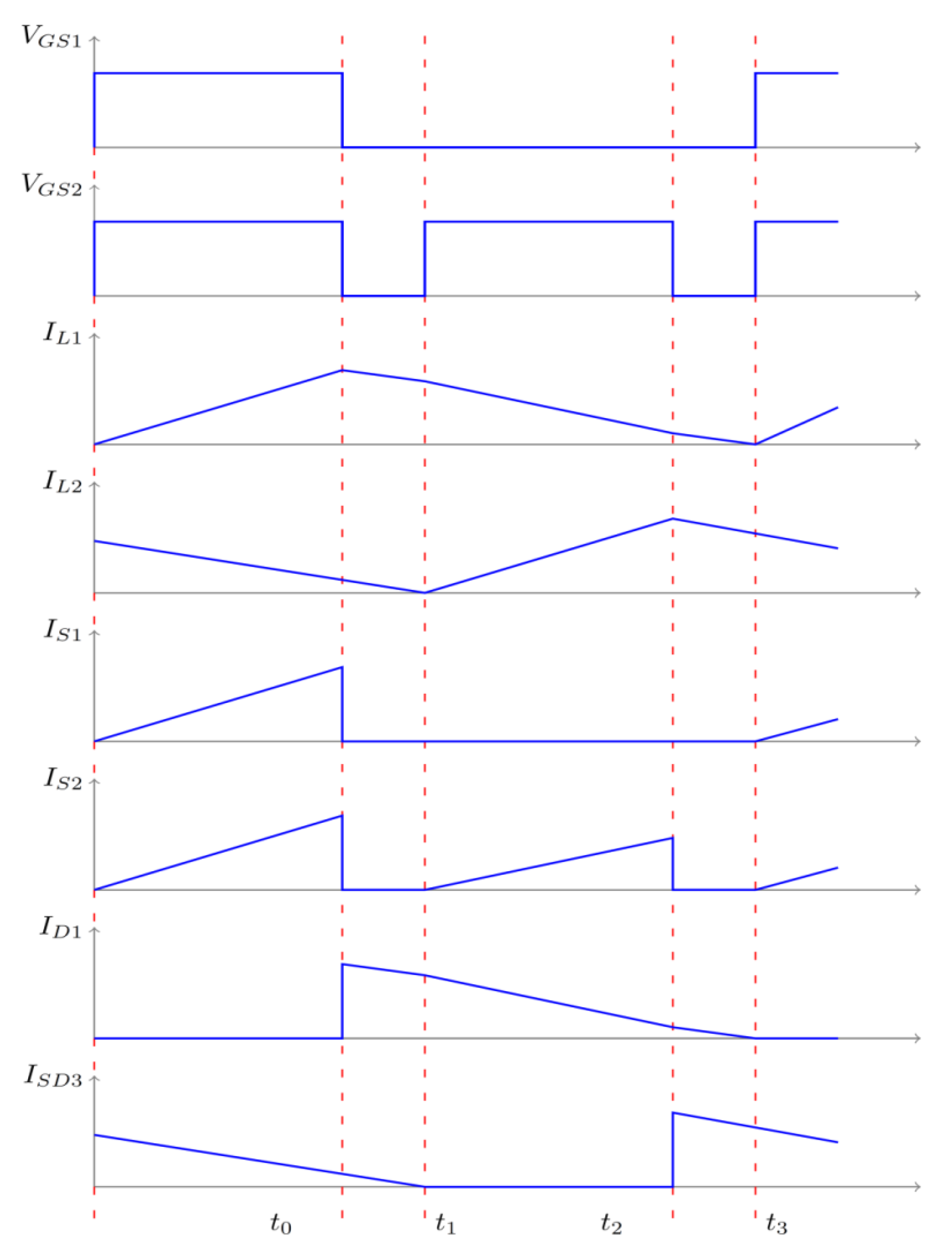
3.2. ESS Charging Domain
3.3. Design of Proposed Bi-Directional DC–DC Converter
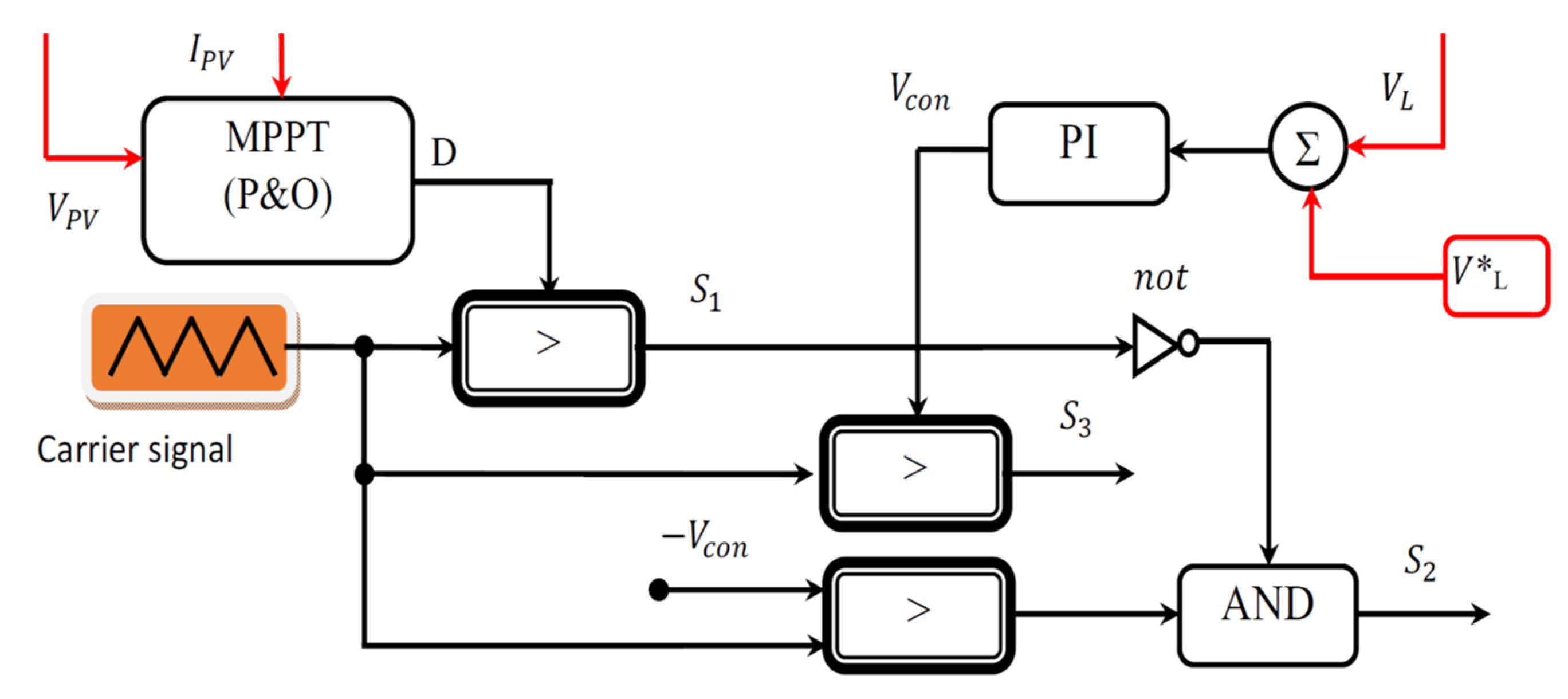
4. Proposed TPC Control
Control of Brushless DC Motor Drive
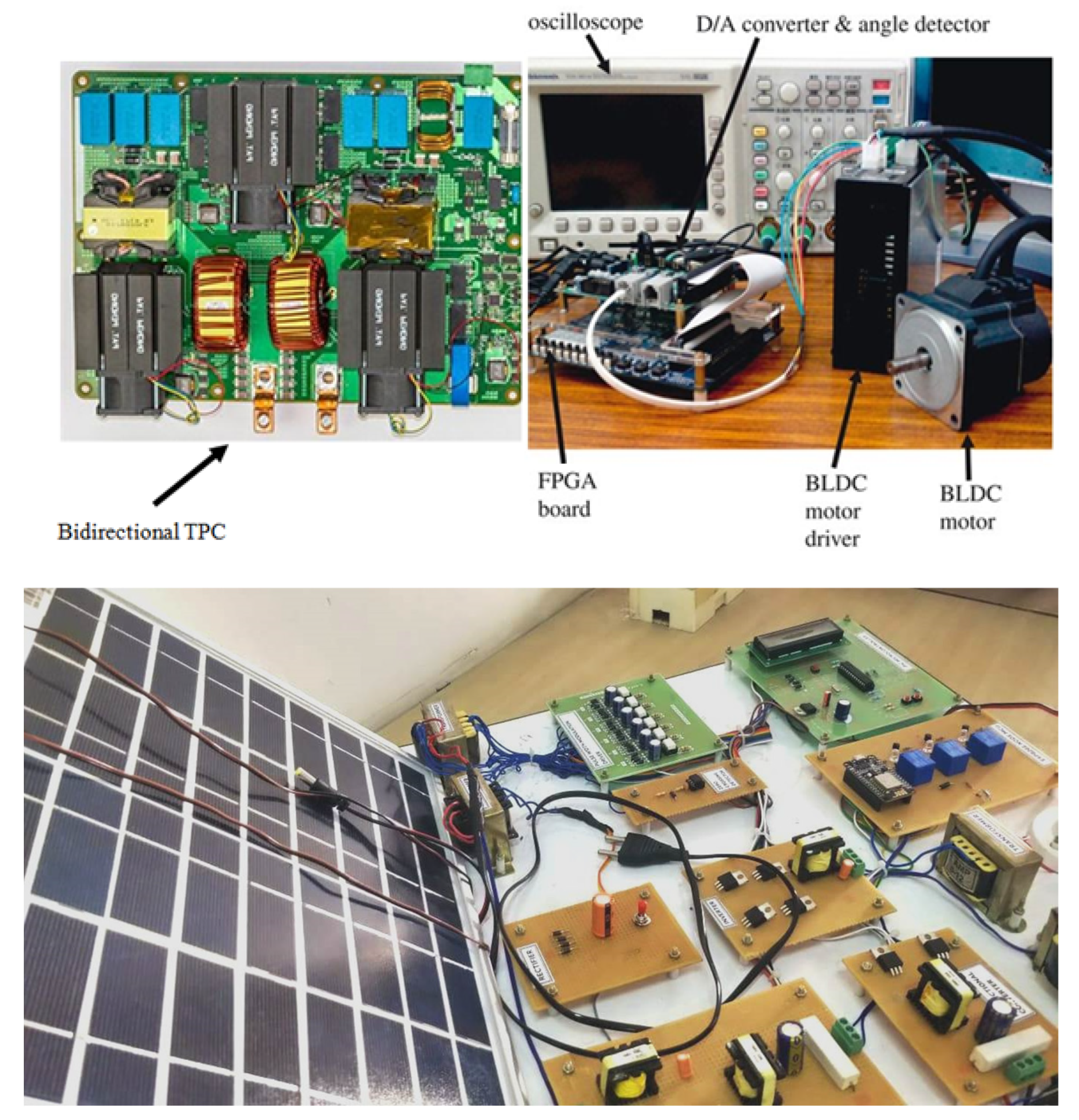
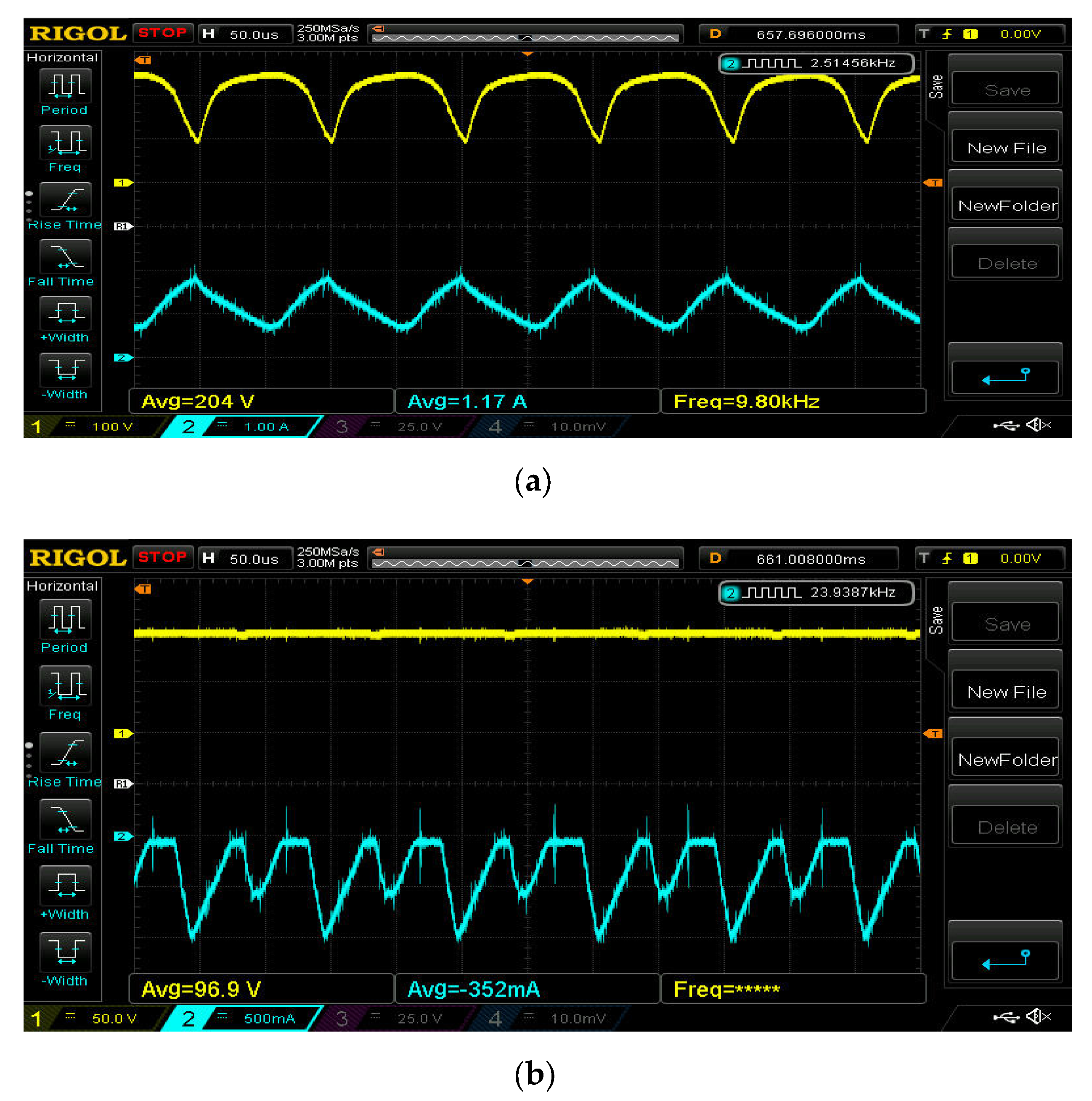
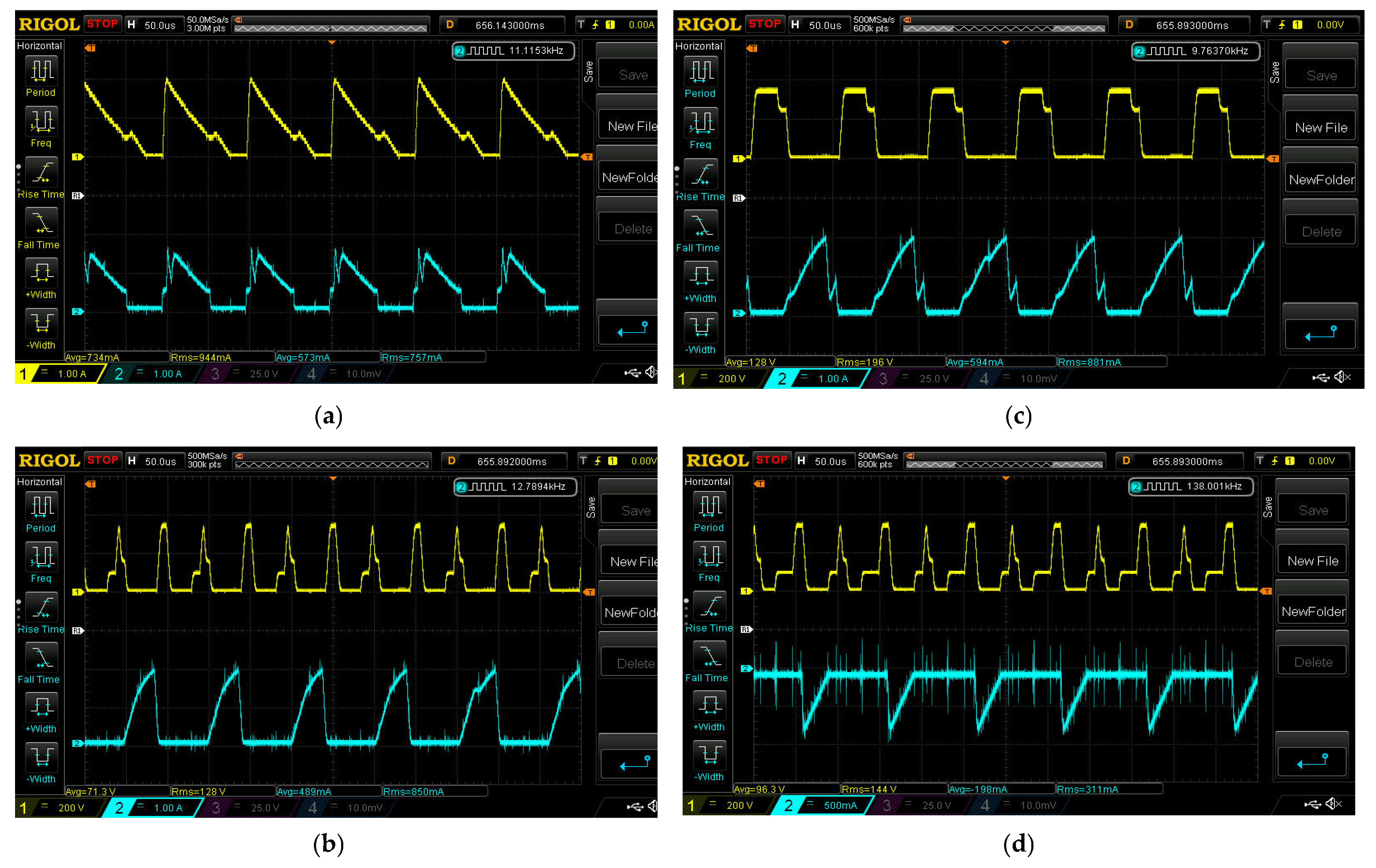
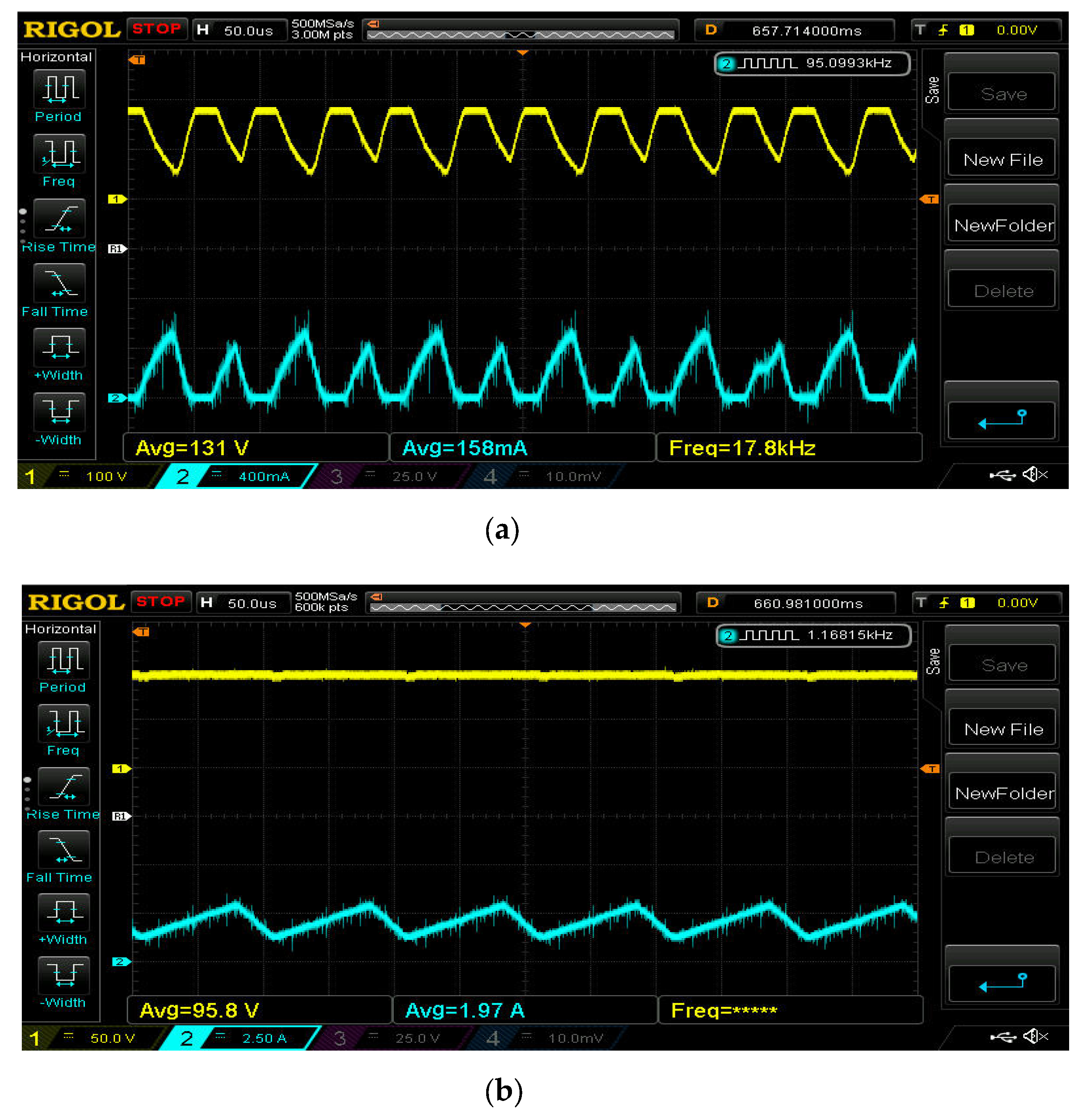
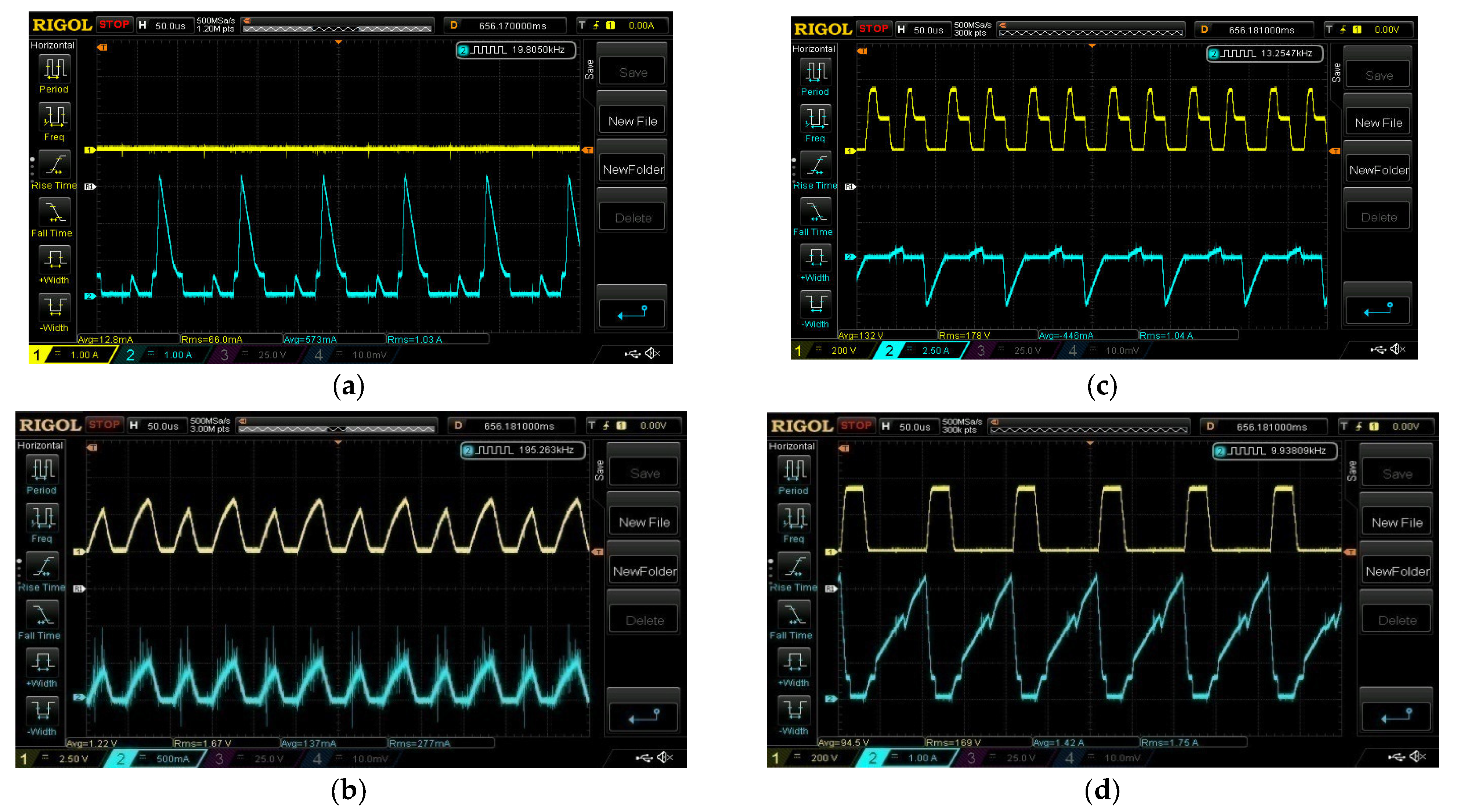
5. Experimental Results and Discussions
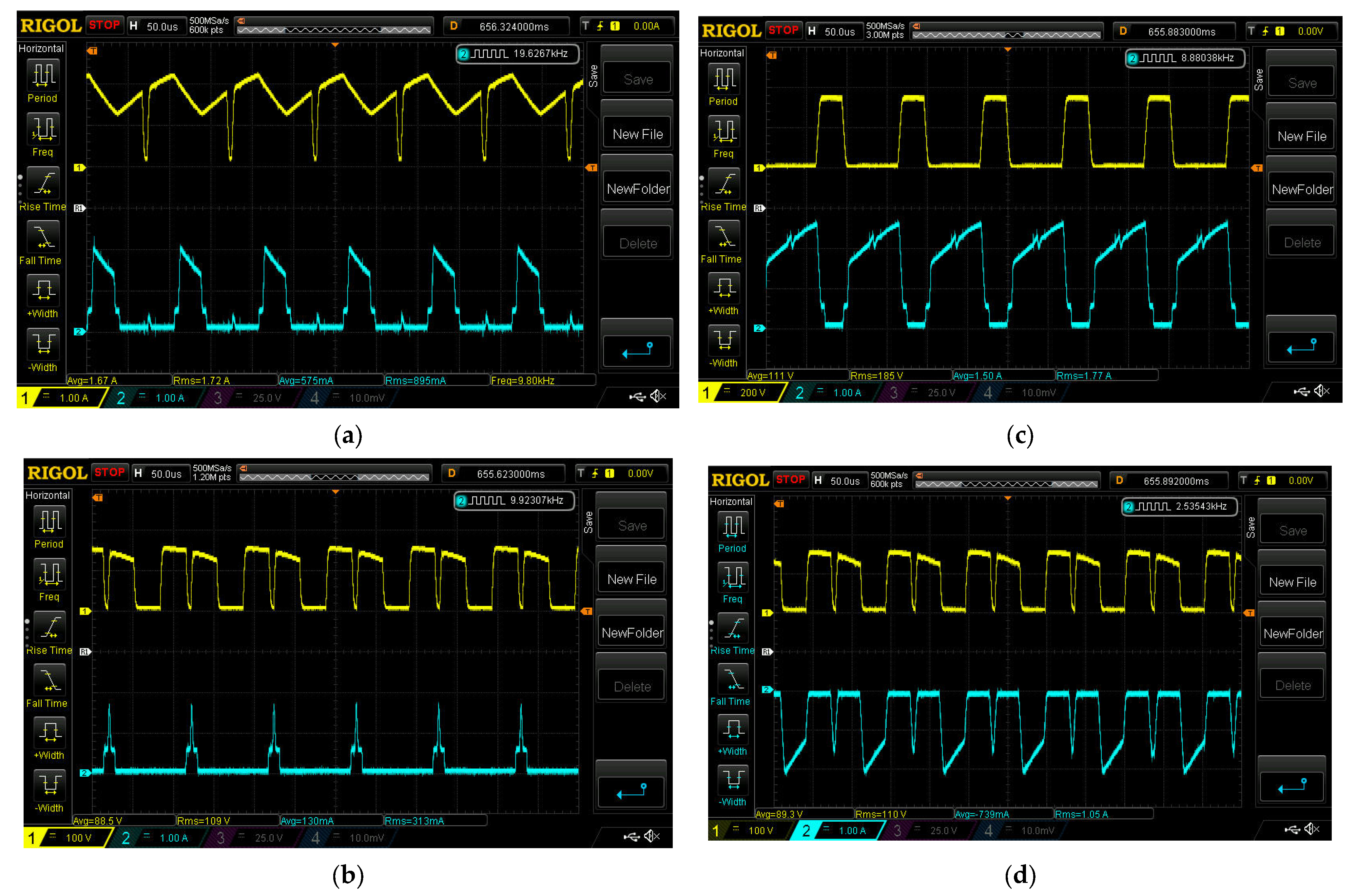
5.1. ESS Charging Domain
5.2. ESS Least Domain
5.3. ESS Discharging Domain
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Lu, X. A hardware decoupling method for series-resonance-based isolated three-port DC/DC converters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), SanAntonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Harb, S.; Fang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.J.; Batarseh, I. A three-port flyback for PV microinverter applications with power pulsation decoupling capability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3953–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Asymmetrical duty cycle control and decoupled power flow design of a three-port bidirectional DC-DC converter for fuel cell vehicle application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 27, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H. An integrated three-port bidirectional DC–DC converter for PV application on a DC distribution system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 4612–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Xing, Y.; Hu, H.; Ge, H. A family of three-port half-bridge converters for a stand-alone renewable power system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sun, K.; Chen, R.; Hu, H.; Xing, Y. Full-bridge three-port converters with wide input voltage range for renewable power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3965–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sun, K.; Zhu, L.; Xing, Y. An interleaved half-bridge three-port converter with enhanced power transfer capability using three-leg rectifier for renewable energy applications. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 4, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Mu, T.; Xing, Y. Secondary-side-regulated soft-switching full-bridge three-port converter based on bridgeless boost rectifier and bidirectional converter for multiple energy interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 4847–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Qin, X.; Xing, Y. PWM plus secondary-side phase-shift controlled soft-switching full-bridge three-port converter for renewable power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7061–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Athab, H.S.; Wu, B.; Gu, Y. PV isolated three-port converter and energy-balancing control method for PV-battery power supply applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, G.; Peng, L.; Kang, Y.; Chen, J. A family of cost-efficient non-isaolated single-inductor three-port converters for low power stand-alone renewable power applications. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Xu, D.; Lu, X. A series-resonance-based three-port converter with unified autonomous control method in DC microgrids. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), SanAntonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Y. A Family of Cost-efficient Integrated Single-switch Three-port Converters. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conferenceand Exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sun, K.; Ding, S.; Xing, Y. Topology derivation of nonisolated three-port DC–DC converters from DIC and DOC. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 3297–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Z. A nonisolated three-port DC–DC converter and three-domain control method for PV-battery power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4937–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Three-port dc/dc converter with all ports current ripple cancellation using integrated magnetic technique. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 2174–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.J.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, J.F.; Hsieh, Y.P. Novel three-port converter with high-voltage gain. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4693–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Huang, A.Q.; Yu, X. A high step-up three-port DC-DC converter for stand-alone PV/battery power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5049–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, M.I.; Alajmi, B.N.; Abdelsalam, I.; Ahmed, N.A. An integrated topology of three-port dc-dc converter for PV-battery power systems. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2022, 3, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino-Manzanares, F.; Garrigos, A. Bidirectional, interleaved, multiphase, multidevice, soft-switching, FPGA-controlled, buck–boost converter with PWM real-time reconfiguration. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9710–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvamuthukumaran, R.; Gupta, R. Rapid prototyping of power electronics converters for photovoltaic system application using Xilinx System Generator. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Batarseh, I. An Integrated Four-Port DC/DC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, D. Frequency Division Based Coordinated Control of Three-Port Converter Interfaced Hybrid Energy Storage Systems in Autonomous DC Microgrids. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25389–25398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.L.; Hendrix, M.; Simões, M.G. Three-port bidirectional converter for hybrid fuel cell systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Kotsopoulos, A.; Duarte, J.L.; Hendrix, M.A. Transformer-coupled multiport ZVS bidirectional dc–dc converter with wide input range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Duarte, J.L.; Hendrix, M.A. Three-port triple-half-bridge bidirectional converter with zero-voltage switching. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswami, H.; Mohan, N. Three-port series-resonant dc–dc converter to interface renewable energy sources with bidirectional load and energy storage ports. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Atrash, H.; Tian, F.; Batarseh, I. Tri-modal half-bridge converter topology for three-port interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hong, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D. A novel two-phase interleaved parallel bi-directional DC/DC converter. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2021, 70, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalbrzykowski, S.; Citko, T. A bidirectional DC-DC converter for renewable energy systems. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2009, 57, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirim, Y.; Sadikoglu, H.; Melikoglu, M. Technical and economic analysis of biogas and solar photovoltaic (PV) hybrid renewable energy system for dairy cattle barns. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Saha, S.; Islam, S.N.; Arif, M.T.; Mosadeghy, M.; Haque, M.E.; Oo, A.M. Analysis of power grid voltage stability with high penetration of solar PV systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 57, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Marthi, P.R.; Xia, Q.; Pan, J.; Saeedifard, M.; Vipin, V.N.; Chakraborty, S.; Arifujjaman, M. Renewable Integration in Hybrid AC/DC Systems Using a Multi-Port Autonomous Reconfigurable Solar Power Plant (MARS). IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 36, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghenai, C.; Bettayeb, M. Design and optimization of grid-tied and off-grid solar PV systems for super-efficient electrical appliances. Energy Efficiency. Energy Effic. 2020, 13, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Veda, S.; Singh, S.P.; Jain, R.; Baggu, M. Event-Driven Predictive Approach for Real-Time Volt/VAR Control With CVR in Solar PV Rich Active Distribution Network. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 3849–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, R.I.; Rifa’i, M.; Adhisuwiginjo, S. Design of Buck Converter For Photovoltaic System Applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 Applied Electromagnetic Technology AEMT, Lombok, Indonesia, 11–15 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aragon-Aviles, S.; Kadam, A.H.; Sidhu, T.; Williamson, S.S. Modeling, Analysis, Design, and Simulation of a Bidirectional DC-DC Converter with Integrated Snow Removal Functionality for Solar PV Electric Vehicle Charger Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahani, R.; Jamil, M.; Iqbal, M.T. Direct Model Reference Adaptive Control of a Boost Converter for Voltage Regulation in Microgrids. Energies 2022, 15, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, Y.B.; Aslan, Y.; Yonetken, A.; Oguz, Y. Boost Converter Design and Analysis for Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Technology and Applied Sciences (ICETAS), Kiev, Ukraine, 24–28 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bhukya, L.; Kedika, N.R.; Salkuti, S.R. Enhanced Maximum Power Point Techniques for Solar Photovoltaic System under Uniform Insolation and Partial Shading Conditions: A Review. Algorithms 2022, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudhol, A.; Pius, A.J.P. Design and implementation of boost converter for photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Innov. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Control. Eng. 2016, 4, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, M.Z.; Azri, M.; Alias, A.; Talib, N.; Lazi, J.M. Simple control scheme buck-boost DC-DC converter for stand alone PV application system. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2019, 10, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danyali, S.; Aghaei, O.; Shirkhani, M.; Aazami, R.; Tavoosi, J.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Mosavi, A. A New Model Predictive Control Method for Buck-Boost Inverter-Based Photovoltaic Systems. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, A.S.; Mahamad, A.K.; Saon, S.; Tuwoso, T.; Elmunsyah, H.; Mudjanarko, S.W. Maximum power point tracking using perturb and observe, fuzzy logic and ANFIS. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.G.; Ganesh, A.; Sireesha, N.V.; Kshatri, S.S.; Mishra, S.; Sharma, N.K.; Bajaj, M.; Kotb, H.; Milyani, A.H.; Azhari, A.A. Performance Analysis of an Optimized Asymmetric Multilevel Inverter on Grid Connected SPV System. Energies 2022, 15, 7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengqing, L.; Fujun, L.; Jian, Z.; Wen, C.; Donghui, Z. An improved MPPT control strategy based on incremental conductance method. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 6039–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.F.M.; Ishak, D.; Salem, M. An Improved Control Strategy for Single-Phase Single-Stage Grid-Tied PV System Based on Incremental Conductance MPPT, Modified PQ Theory, and Hysteresis Current Control. Eng. Proc. 2021, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jately, V.; Azzopardi, B.; Joshi, J.; Sharma, A.; Arora, S. Experimental analysis of hill-climbing MPPT algorithms under low irradiance levels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Mudassar, M.; Fazal, M.R.; Asghar, M.U.; Bilal, M.; Asghar, R. Implementation of improved Perturb & Observe MPPT technique with confined search space for standalone photovoltaic system. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 32, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahhir, S.; El Ghzizal, A.; Sebti, S.; Derouich, A. Modeling of photovoltaic system with modified incremental conductance algorithm for fast changes of irradiance. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 3286479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Shang, L.; Li, P.; Guo, H. Modified hill climbing MPPT algorithm with reduced steady-state oscillation and improved tracking efficiency. J. Eng. 2018, 17, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, B.; Muselli, M.; Poggi, P.; Dias, J.B. Historical trends in global energy policy and renewable power system issues in Sub-Saharan Africa: The case of solar PV. Energy Policy 2019, 127, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Meraj, S.T.; Singh, B.; Kannan, R.; Ibrahim, O. Review on non-isolated DC-DC converters and their control techniques for renewable energy applications. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 3747–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijarajreh, H.; Lu, D.D.-C.; Siwakoti, Y.P.; Tse, C.K. A Nonisolated Three-Port DC–DC Converter with Two Bidirectional Ports and Fewer Components. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 8207–8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Barbosa, P.M.; Ruiz, J.M.; Minli, J.; Hao, S. Isolated Three-Port Bidirectional DC-DC Converter for Electric Vehicle Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conferenceand Exposition (APEC), Houston, TX, USA, 20–24 March 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-E. Novel High-Step-Up/Step-Down Three-Port Bidirectional DC/DC Converter for Photovoltaic Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Lu, D.D.-C.; Qin, L. Non-Isolated Single-Inductor DC/DC Converter With Fully Reconfigurable Structure for Renewable Energy Applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs Copy 2018, 65, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.L.; Shen, Y.S.; Chiu, P.C.; Liang, T.C. Isolated bidirectional converter with minimum active switches for highvoltage ratio achievement and micro-grid applications. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Degree (°) | Switching States of PWM Inverter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | |
| 0–60 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 60–120 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 120–180 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 180–240 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 240–300 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 300–360 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Solar PV panel Specifications at Standard Test Conditions (STC) | |
| Input power (180 W solar PV panel–10 Nos. connected in series) | 1800 W |
| Voc(Open circuit voltage in volts) | 42.48 V |
| Isc(Short Circuit current in Ampere) | 4.8 A |
| Vmp(Voltage at MPP condition) | 36 V |
| Imp (Current at MPP condition) | 5 A |
| Cell Temperature at STC | 25 °C |
| Irradiance at STC | 1000 W/m2 |
| Load–BLDC Motor Drive | |
| Power Rating | 250 W |
| Voltage Rating | 110 V |
| Speed | 1500 RPM |
| Torque | 12 N-m |
| Storage Battery Specifications | |
| Voltage Rating | 24 V |
| Battery Capacity | 135 Ah |
| DC–DC Converter Specifications | |
| Inductor L1, L2 | 320 μH |
| Capacitor C0 | 1000 μF |
| Description | Switching Loss (W) | Other Losses (W) | Total Power Loss (W) | Loss Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESS charging domain | 7.20 | 4.67 | 11.87 | 7.43 |
| ESS least Domain | 3.20 | 0.83 | 4.03 | 3.56 |
| ESS Discharging domain | 6.53 | 2.45 | 8.87 | 4.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Udayakumar, A.K.; Raghavan, R.R.V.; Houran, M.A.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Kalavathy, A.N.; Hossain, E. Three-Port Bi-Directional DC–DC Converter with Solar PV System Fed BLDC Motor Drive Using FPGA. Energies 2023, 16, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020624
Udayakumar AK, Raghavan RRV, Houran MA, Elavarasan RM, Kalavathy AN, Hossain E. Three-Port Bi-Directional DC–DC Converter with Solar PV System Fed BLDC Motor Drive Using FPGA. Energies. 2023; 16(2):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020624
Chicago/Turabian StyleUdayakumar, Arun Kumar, Raghavendra Rajan Vijaya Raghavan, Mohamad Abou Houran, Rajvikram Madurai Elavarasan, Anushkannan Nedumaran Kalavathy, and Eklas Hossain. 2023. "Three-Port Bi-Directional DC–DC Converter with Solar PV System Fed BLDC Motor Drive Using FPGA" Energies 16, no. 2: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020624
APA StyleUdayakumar, A. K., Raghavan, R. R. V., Houran, M. A., Elavarasan, R. M., Kalavathy, A. N., & Hossain, E. (2023). Three-Port Bi-Directional DC–DC Converter with Solar PV System Fed BLDC Motor Drive Using FPGA. Energies, 16(2), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020624









