Thermal Characterization, Kinetic Analysis and Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge Coupled with High Ash Ekibastuz Coal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Thermochemical Properties of the SS and Coal
2.3. Experimental Apparatus and Test Conditions for Combustion
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis of the SS and the Blends with Coal
3.2. Kinetic Analysis of SS Samples
3.3. Exit Gas Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kongar-Syuryun, C.B.; Aleksakhin, A.V.; Eliseeva, E.N.; Zhaglovskaya, A.V.; Klyuev, R.V.; Petrusevich, D.A. Modern Technologies Providing a Full Cycle of Geo-Resources Development. Resources 2023, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchurov, N.I.; Dedov, S.I.; Malozyomov, B.V.; Shtang, A.A.; Martyushev, N.V.; Klyuev, R.V.; Andriashin, S.N. Degradation of Lithium-Ion Batteries in an Electric Transport Complex. Energies 2021, 14, 8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malozyomov, B.V.; Martyushev, N.V.; Voitovich, E.V.; Kononenko, R.V.; Konyukhov, V.Y.; Tynchenko, V.; Kukartsev, V.A.; Tynchenko, Y.A. Designing the Optimal Configuration of a Small Power System for Autonomous Power Supply of Weather Station Equipment. Energies 2023, 16, 5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, G.; Romano, P. Evolution and Prospects in Managing Sewage Sludge Resulting from Municipal Wastewater Purification. Energies 2022, 15, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, D. Immobilization of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge during Land Application Process in China: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.M.; Kamyab, H.; Yuzir, A.; Ashokkumar, V.; Hosseini, S.E.; Balasubramanian, B.; Kirpichnikova, I. Review of the application of gasification and combustion technology and waste-to-energy technologies in sewage sludge treatment. Fuel 2022, 316, 123199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Ålmas, A.; Singh, B.R. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFPA, We, Kazakhstan. Population Situation Analysis of the Republic of Kazakhstan. 2019, Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan Committee on Statistics. p. 65. Available online: https://kazakhstan.unfpa.org/sites/default/files/pub-pdf/07_FEB_UNFPA_Report_20pager_ENG_PREVIEW%20%281%29_0.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- KAZENERGY, The National Energy Report 2019. Available online: https://www.kazenergy.com/upload/document/energy-report/NationalReport19_en.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Sarbassov, Y.; Kerimbay, A.; Tokmurzin, D.; Tosato, G.; De Miglio, R. Electricity and heating system in Kazakhstan: Exploring energy efficiency improvement paths. Energy Policy 2013, 60, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosikov, I.I.; Martyushev, N.V.; Klyuev, R.V.; Savchenko, I.A.; Kukartsev, V.V.; Kukartsev, V.V.; Tynchenko, Y.A. Modeling and Complex Analysis of the Topology Parameters of Ventilation Networks When Ensuring Fire Safety While Developing Coal and Gas Deposits. Fire 2023, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malozyomov, B.V.; Golik, V.I.; Brigida, V.; Kukartsev, V.V.; Tynchenko, Y.A.; Boyko, A.A.; Tynchenko, S.V. Substantiation of Drilling Parameters for Undermined Drainage Boreholes for Increasing Methane Production from Unconventional Coal-Gas Collectors. Energies 2023, 16, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC, Fourth Biennial Report of the Republic of Kazakhstan to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. 2019. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/BR4_en.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Partnership for Action on Green Economy, Kazakhstan Finalizes the Carbon Neutrality Strategy until 2060, UN PAGE—Partnership for Action on Green Economy. 2022. Available online: https://www.un-page.org/news/kazakhstan-finalizes-the-carbon-neutrality-strategy-until-2060/ (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Druz, N. First Step: Opportunities to Reduce Methane Emissions in the Wastewater Treatment Sector in Kazakhstan [Russian]. 2018. Available online: https://nur.nu.edu.kz/bitstream/handle/123456789/6123/Book%20%28ru%29.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Zhumabayev, D.; Bakdolotov, A.; De Miglio, R.; Litvak, V.; Baibakisheva, A.; Sarbassov, Y.; Baigarin, K. Kazakhstan’s Road to Net Zero GHG Emissions, ed. G. Tosato. 2022. Available online: https://nur.nu.edu.kz/bitstream/handle/123456789/6123/Book%20%28eng%29.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Ospanov, K.; Myrzahmetov, M.; Zapparov, M. Study of the Products of Pyrolysis Recycling. Sewage Sludge in the Aeration Station Almaty, Kazakhstan. Procedia Eng. 2015, 117, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat, Sewage Sludge Production and Disposal from Urbanwastewater (in Dry Substance (d.s)). 2020. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/tgm/refreshTableAction.do?tab=table&plugin=1&pcode=ten00030&language=en (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- lincoln.ne.gov, Solid Waste Plan 2040. 2012. Available online: https://www.lincoln.ne.gov/City/Departments/LTU/Utilities/Solid-Waste-Management/SWMP (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Magdziarz, A.; Kosowska-Golachowska, M.; Kijo-Kleczkowska, A.; Środa, K.; Wolski, K.; Richter, D.; Musiał, T. Analysis of sewage sludge ashes from air and oxy-fuel combustion in a circulating fluidized-bed. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on the Sustainable Energy and Environment Development (SEED 2016), Kraków, Poland, 17–19 May 2016; Kosowska-Golachowska, M., Ed.; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Calvo, L.F.; Gil, M.V.; García, A.I.; Morán, A. Co-combustion of different sewage sludge and coal: A non-isothermal thermogravimetric kinetic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6311–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadziakiewicz, J.; Kozioł, M. Co-combustion of sludge with coal. Appl. Energy 2003, 75, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonts, I.; Azuara, M.; Gea, G.; Murillo, M.B. Study of the pyrolysis liquids obtained from different sewage sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žnidarčič, A.; Katrašnik, T.; Zsély, I.G.; Nagy, T.; Seljak, T. Sewage sludge combustion model with reduced chemical kinetics mechanisms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moško, J.; Pohořelý, M.; Zach, B.; Svoboda, K.; Durda, T.; Jeremiáš, M.; Šyc, M.; Václavková, S.; Skoblia, S.; Beňo, Z.; et al. Fluidized Bed Incineration of Sewage Sludge in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 Atmospheres. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Gai, C.; Liu, Z. Combination of hydrothermal carbonization and oxy-fuel combustion process for sewage sludge treatment: Combustion characteristics and kinetics analysis. Fuel 2019, 242, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Tariq, R.; Hameed, Z.; Ali, I.; Taqvim, S.A.; Naqvi, M.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Noor, T.; Farooq, W. Pyrolysis of high-ash sewage sludge: Thermo-kinetic study using TGA and artificial neural networks. Fuel 2018, 233, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Bi, H.; Jiang, C.; Sun, H.; Zhou, W.; Tian, J.; Lin, Q. Investigation of co-combustion of sewage sludge and coffee industry residue by TG-FTIR and machine learning methods. Fuel 2022, 309, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunphorka, S.; Chalermsinsuwan, B.; Piumsomboon, P. Artificial neural network model for the prediction of kinetic parameters of biomass pyrolysis from its constituents. Fuel 2017, 193, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgueras, M.; Díaz, R.; Xiberta, J.; Prieto, I. Thermogravimetric analysis of the co-combustion of coal and sewage sludge. Fuel 2003, 82, 2051–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Toyono, M.; Ohsawa, H. Emissions of NOx and N2O during co-combustion of dried sewage sludge with coal in a bubbling fluidized bed combustor. Fuel 2007, 86, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarska, B.; Baron, J.; Kandefer, S.; Zukowski, W. Incineration of Municipal Sewage Sludge in a Fluidized Bed Reactor. Engineering 2013, 5, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Niu, M.; Jiang, X.; Liu, J. Combustion Characteristics of Sewage Sludge in a Fluidized Bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10565–10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckner, B.; Åmand, L.; Lücke, K.; Werther, J. Gaseous emissions from co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal/wood in a fluidized bed. Fuel 2004, 83, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åmand, L.; Leckner, B. Metal emissions from co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal/wood in fluidized bed. Fuel 2004, 83, 1803–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Verdugo, A.; Kauppinen, J.; Soini, T.; García-Gutiérrez, L.M.; Pikkarainen, T. Pollutant emissions released during sewage sludge combustion in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor. J. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Kamran, K.; Quan, C.; Williams, P.T. Thermochemical conversion of sewage sludge: A critical review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 79, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimenova, B.; Aimbetov, B.; Shah, D.; Anthony, E.J.; Sarbassov, Y. Attrition of high ash Ekibastuz coal in a bench scale fluidized bed rig under O2/N2 and O2/CO2 environments. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 216, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.; Dubinin, Y.V.; Yeletsky, P.; Fedorov, I.A.; Shelest, S.N.; Yakovlev, V. Combustion of sewage sludge in a fluidized bed of catalyst: ASPEN PLUS model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 18134-3:2023; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Moisture Content—Part 3: Moisture in General Analysis Sample. 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/83193.html (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- ISO 18122:2022; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Content. 2022. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/83190.html (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- ISO 18123:2023; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Volatile Matter. 2023. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/83192.html (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Saparov, A.; Kulmukanova, L.; Mostafavi, E.; Sarbassov, Y.; Inglezakis, V.; Anthony, E.J.; Shah, D. Development and validation of a novel process model for fluidized bed combustion: Application for efficient combustion of low-grade coal. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 99, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Song, X.; Zhao, L. Study on the combined sewage sludge pyrolysis and gasification process: Mass and energy balance. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipkhunthod, P.; Meeyoo, V.; Rangsunvigit, P.; Kitiyanan, B.; Siemanond, K.; Rirksomboon, T. Predicting the heating value of sewage sludges in Thailand from proximate and ultimate analyses. Fuel 2005, 84, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z. Evolution of trace elements and polluting gases toward clean co-combustion of coal and sewage sludge. Fuel 2020, 280, 118685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvuka, D.; Salpigidou, N.; Kastanaki, E.; Sfakiotakis, S. Possibility of using paper sludge in co-firing applications. Fuel 2009, 88, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Kanhar, A.H. Sludge Acts as a Catalyst for Coal during the Co-Combustion Process Investigated by Thermogravimetric Analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdziarz, A.; Wilk, M. Thermogravimetric study of biomass, sewage sludge and coal combustion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 75, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahira, T.; Sunuse, T.T. Joint Convention of Four Electrical Institutes; Chiba Institute of Technology: Chiba, Japan, 1971; pp. 22–31. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284662595_Joint_convention_of_four_electrical_institutes (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Ozawa, T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, C.D. Series approximations to the equation of thermogravimetric data. Nature 1965, 207, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.X.; Shen, D.; Li, Y.X.; Yu, C.J.; Luo, Z.Y.; Cen, K.F. Kinetic study on pyrolysis and combustion of wood under different oxygen concentrations by using TG-FTIR analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2006, 77, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: Fundamentals, challenges and considerations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 888–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiao, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Consequences of sludge composition on combustion performance derived from thermogravimetry analysis. J. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

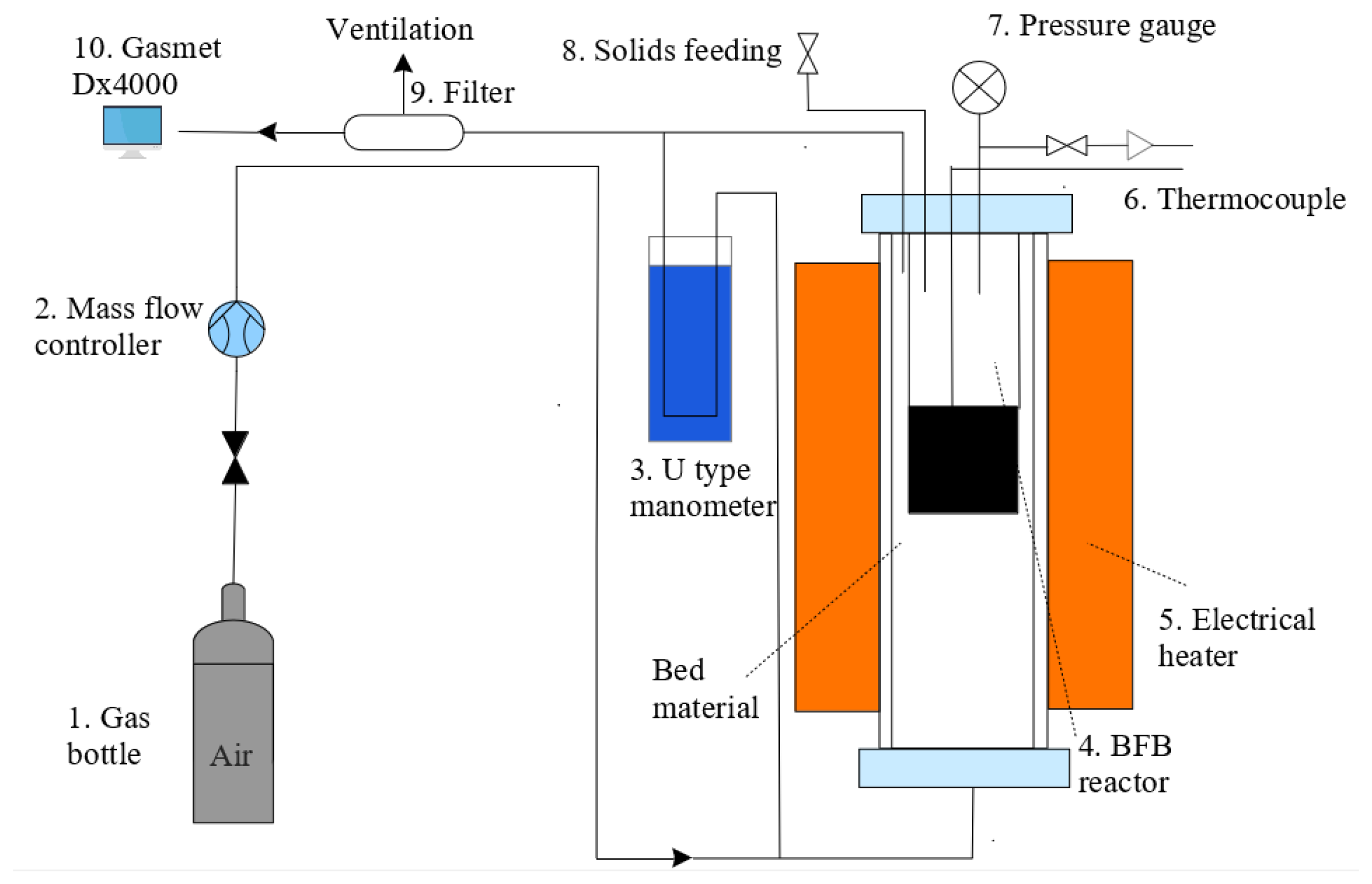

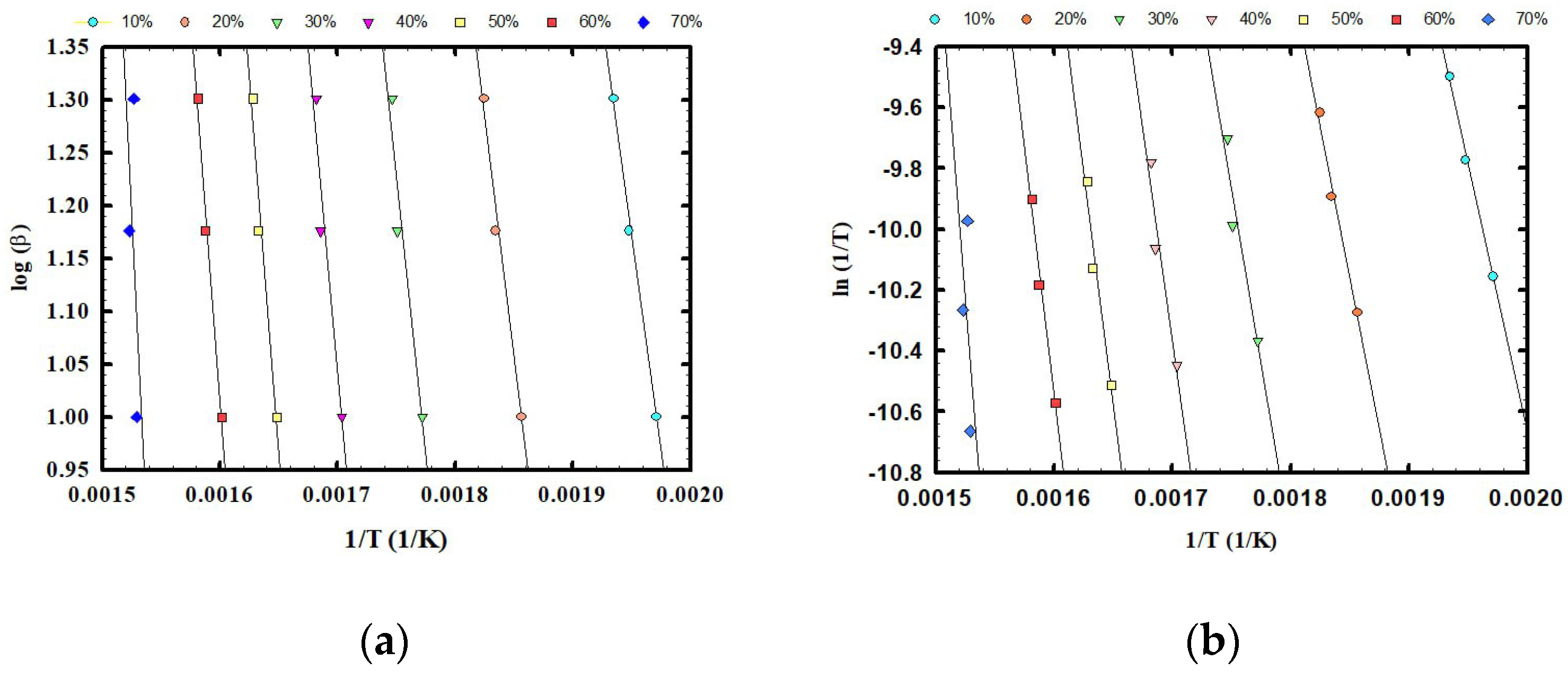
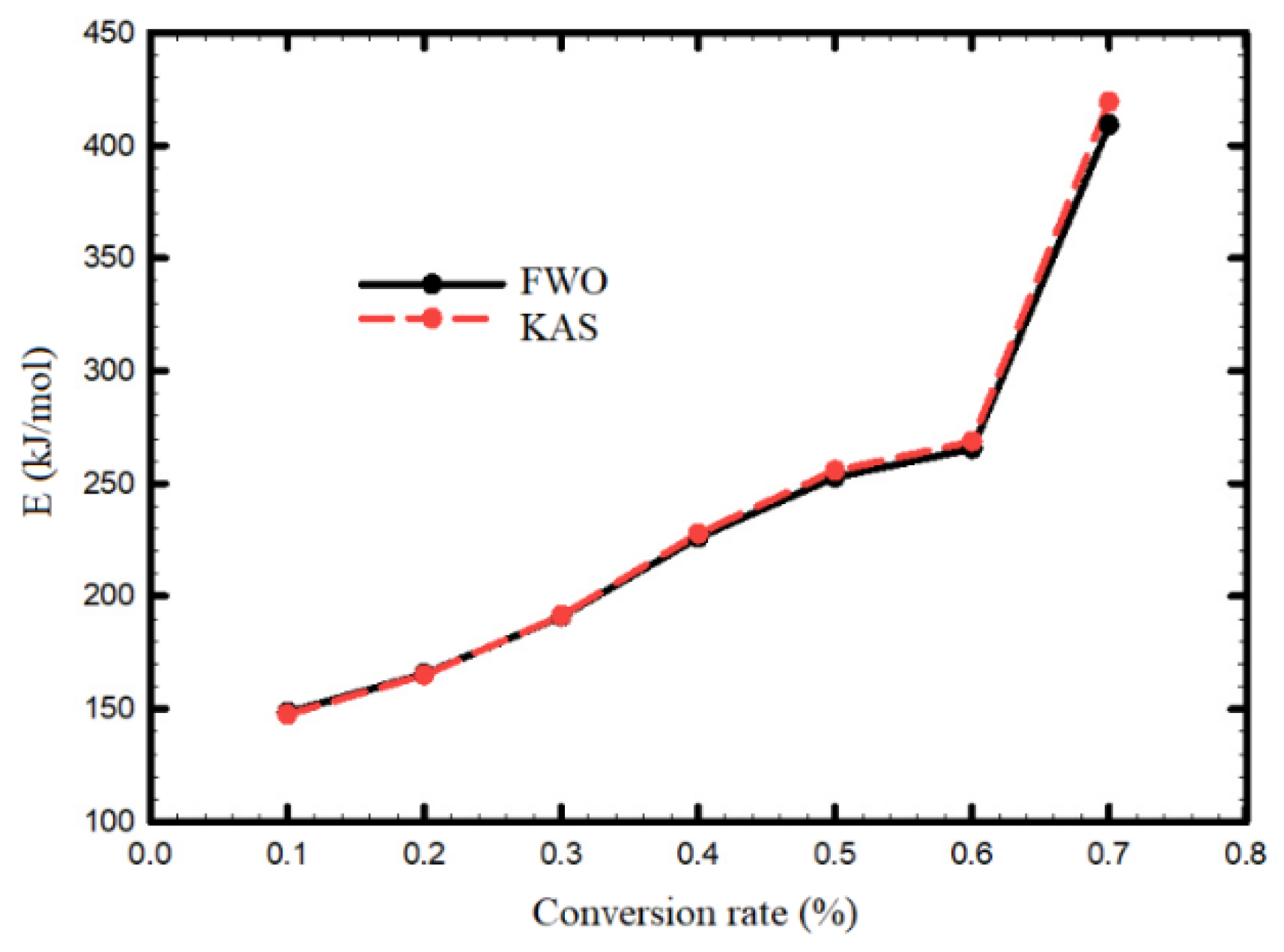
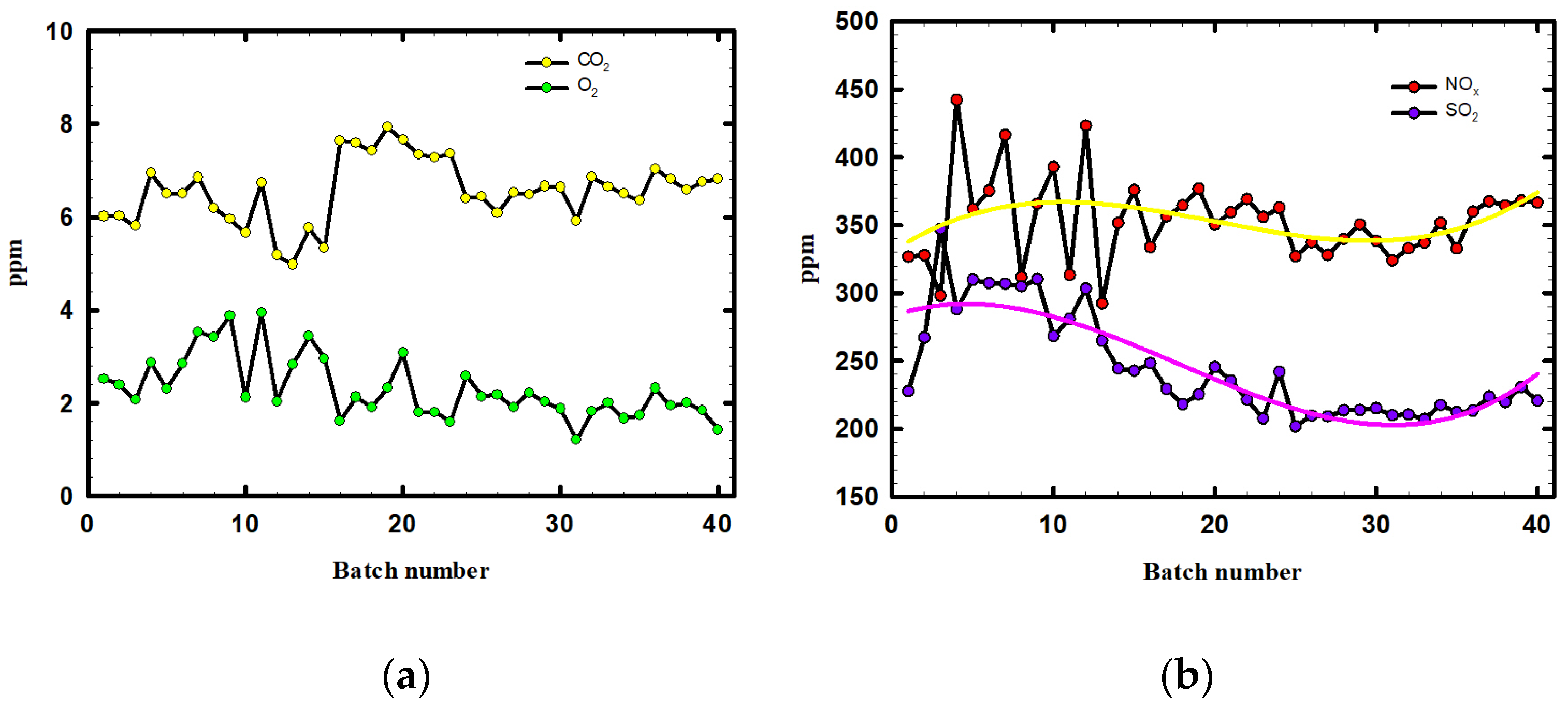

| Type of Reactor | Blend Solid Fuel | Temperature | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| TGA [30] | 10% SS/coal, 50% SS/coal | 800 °C | 50 wt% blends had two regions of reactivity. At T < 350 °C reactivity were similar to sludge, while for T > 350 °C had reactivity close to coal |
| Bubbling fluidized bed [31] | SS with High, medium, and low volatile bituminous coal | 850 °C | NOx increased during SS feeding, while only slight change was noted N2O emissions |
| Fluidized bed combustor [25] | 100% SS | 720–930 °C | NOx and SO2 increased with an increase in bed temperature; N2O slightly reduced. |
| Fluidized bed reactor [32] | 100% SS, 30% SS/62% coal/8% CaCO3 | 800 °C | Decline of SO2 emissions during the co-combustion of SS and coal with CaCO3 |
| Fluidized bed reactor [33] | 100% SS | 700 °C | Moisture content of the sludge affects the conversion of SO2 to H2SO3, but has no effect on NOx emissions |
| Fluidized bed [34] | 100% coal, blends with 70%, 55%, 30%, and pure SS | 800–900 °C | Emissions from combustion and optimal blends based on emissions were investigated |
| Fluidized bed [35] | 100% coal 13% coal/87% SS 46% coal/54% SS | 840 °C | Heavy metals content during co-combustion were analyzed |
| Proximate (wt% as Received) | Ultimate Analysis (wt%, Dry Ash Free) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sewage sludge | Bituminous coal | Sewage sludge | Bituminous coal | ||
| FC | 2.69 | 38.90 | C | 48.21 | 83.45 |
| VM | 62.82 | 21.55 | H | 5.69 | 5.35 |
| Ash | 32.22 | 38.24 | N | 5.49 | 1.40 |
| Moisture | 2.27 | 1.31 | S | 1.62 | 0.60 |
| HHV (MJ/kg) | 18.87 | 19.40 | O * | 38.99 | 9.2 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Bed temperature, °C | 850 * |
| Operating pressure, kPa | 101.3 |
| Weight of bed material, g | 390 |
| Superficial gas velocity, m/s | 0.112 |
| Pressure drop, kPa | 2.05 |
| Primary air flow rate, lpm | 3.0 |
| Secondary air flow rate, lpm | 0 ** |
| Average pellet surface area, mm2 | 226 |
| Pellet weight (one batch), g | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
| Parameter | Mean | |
|---|---|---|
| Pure SS | Blend (75% SS/25% Coal) | |
| Pellet mass (g) | 0.55 ± 0.5 | |
| O2 min (vol%) | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.5 |
| max CO2 (vol%) | 6.81 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 0.34 |
| max NOx (ppm) | 356 ± 26 | 204 ± 47 |
| max SO2 (ppm) | 247 ± 39 | 249 ± 71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aidabulov, M.; Zhakupov, D.; Zhunussova, K.; Temireyeva, A.; Shah, D.; Sarbassov, Y. Thermal Characterization, Kinetic Analysis and Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge Coupled with High Ash Ekibastuz Coal. Energies 2023, 16, 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186634
Aidabulov M, Zhakupov D, Zhunussova K, Temireyeva A, Shah D, Sarbassov Y. Thermal Characterization, Kinetic Analysis and Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge Coupled with High Ash Ekibastuz Coal. Energies. 2023; 16(18):6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186634
Chicago/Turabian StyleAidabulov, Madiyar, Daulet Zhakupov, Khabiba Zhunussova, Aknur Temireyeva, Dhawal Shah, and Yerbol Sarbassov. 2023. "Thermal Characterization, Kinetic Analysis and Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge Coupled with High Ash Ekibastuz Coal" Energies 16, no. 18: 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186634
APA StyleAidabulov, M., Zhakupov, D., Zhunussova, K., Temireyeva, A., Shah, D., & Sarbassov, Y. (2023). Thermal Characterization, Kinetic Analysis and Co-Combustion of Sewage Sludge Coupled with High Ash Ekibastuz Coal. Energies, 16(18), 6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186634






