Review of Hydro-Pneumatic Accumulator Models for the Study of the Energy Efficiency of Hydraulic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hydraulic Accumulators in Hydraulic Systems
- Energy storage and auxiliary power supply.HA is used as a secondary energy source during high fluid flow demand requirements.
- Power source in dual pressure circuits.HA can provide a higher flow rate for a high-hydraulic circuit.
- Emergency power source.HA can perform the necessary functions of the hydraulic system in the event of a loss of pump power and electric motor.
- Equalisation of fluid flow.HA can equalise the difference in fluid volume in a closed hydraulic system.
- Leak compensation.HA can replenish fluid in the hydraulic circuit when there is a leak.
- Thermal expansion compensation.HA can protect the hydraulic system from pressure changes resulting from fluid expansion under high heat conditions.
- Pulsation damping and hydraulic cushioning.HA can dampen pressure pulsations resulting from the effects of pump ripple and water hammer in hydraulic lines.
- Pressure holding.HA holds pressure in a hydraulic circuit at the same level for a long time when all valves are closed.
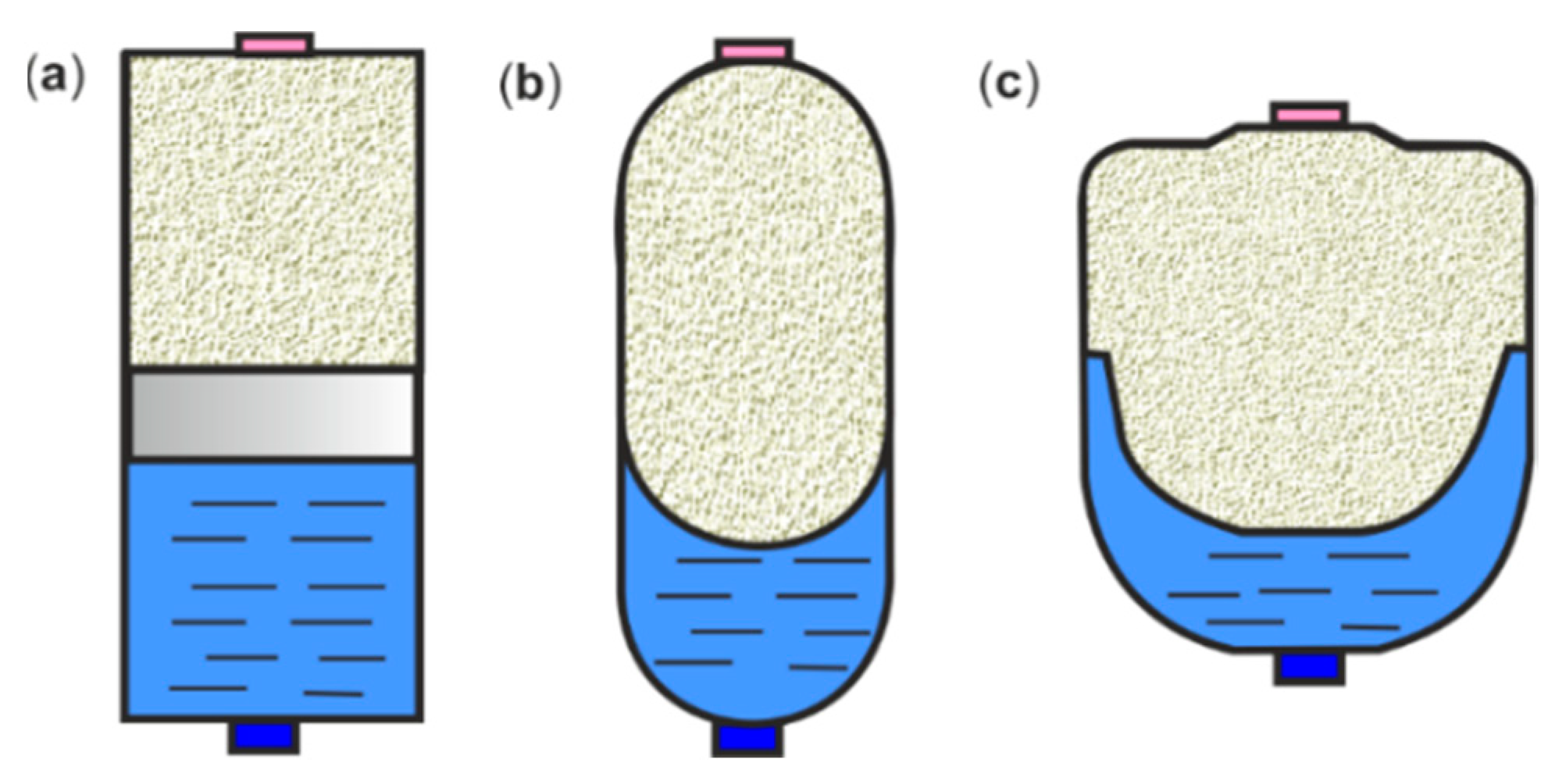
2.1. Gas-Charged Accumulators
- ―
- Hydraulic supply systems—hydraulic supply with energy storage capacity, pulsation damping, and smoothing of a pulsating flow.
- ―
- Hydraulic transmission system—recovery and regeneration (recuperation) energy, regenerative suspensions, wave energy converters.
- ―
- Suspension systems—hydro-pneumatic chassis systems for energy storage, pulsation suppression, and anti-roll stabilisation.
- ―
- Automotive—hydraulic hybrid drivetrain.
- ―
- Energy—hydraulic braking systems in wind turbines and energy reduction in photovoltaic installations.
- ―
- Oil and gas—hydraulic emergency safety features used on drilling rigs.
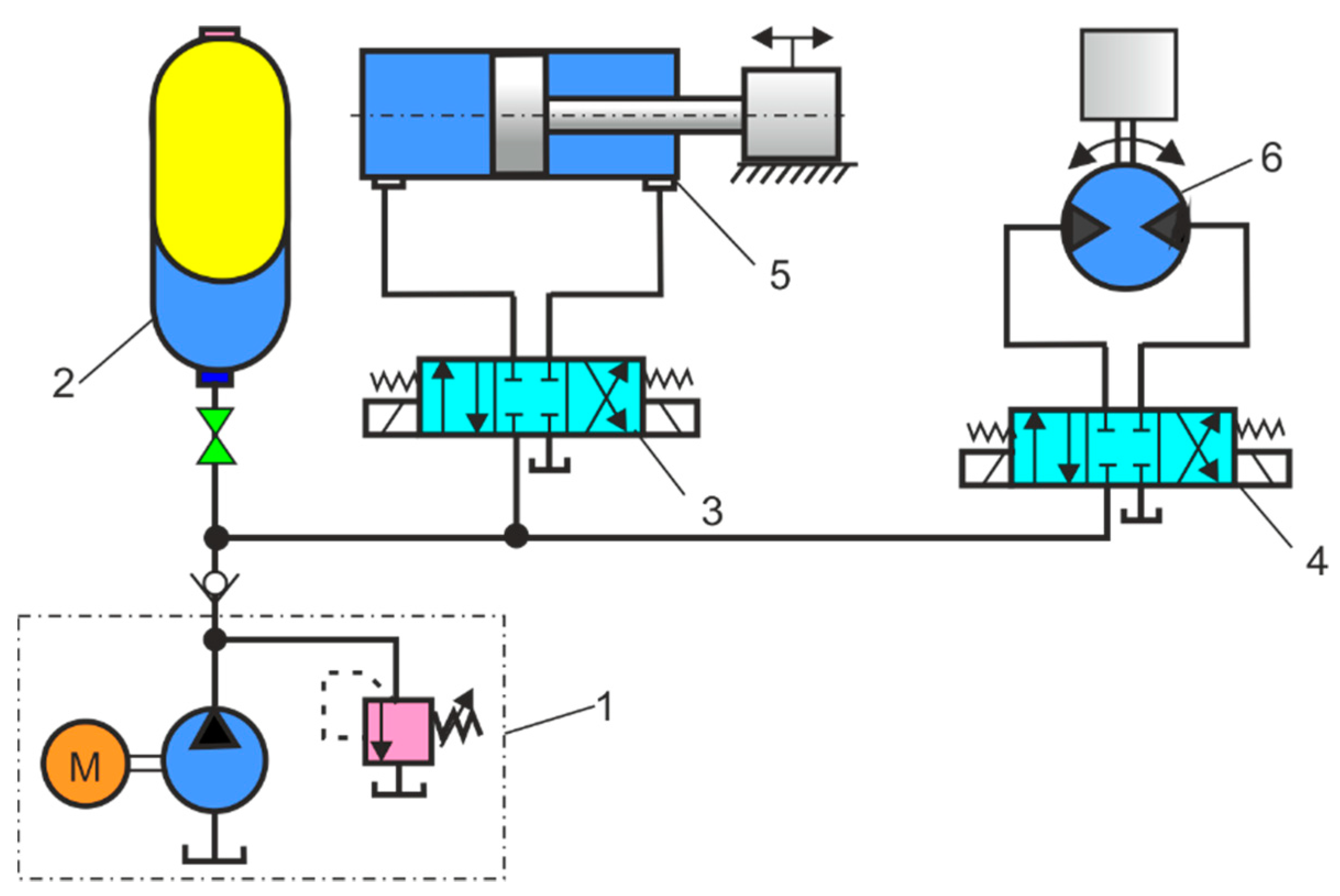
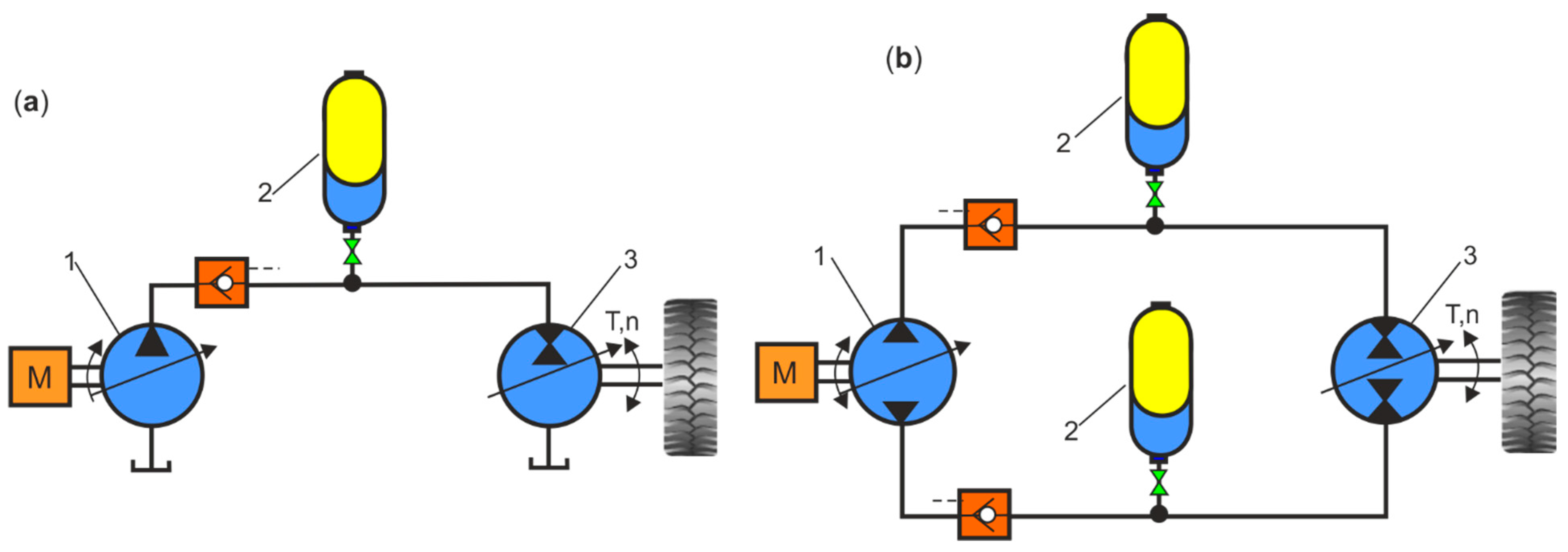
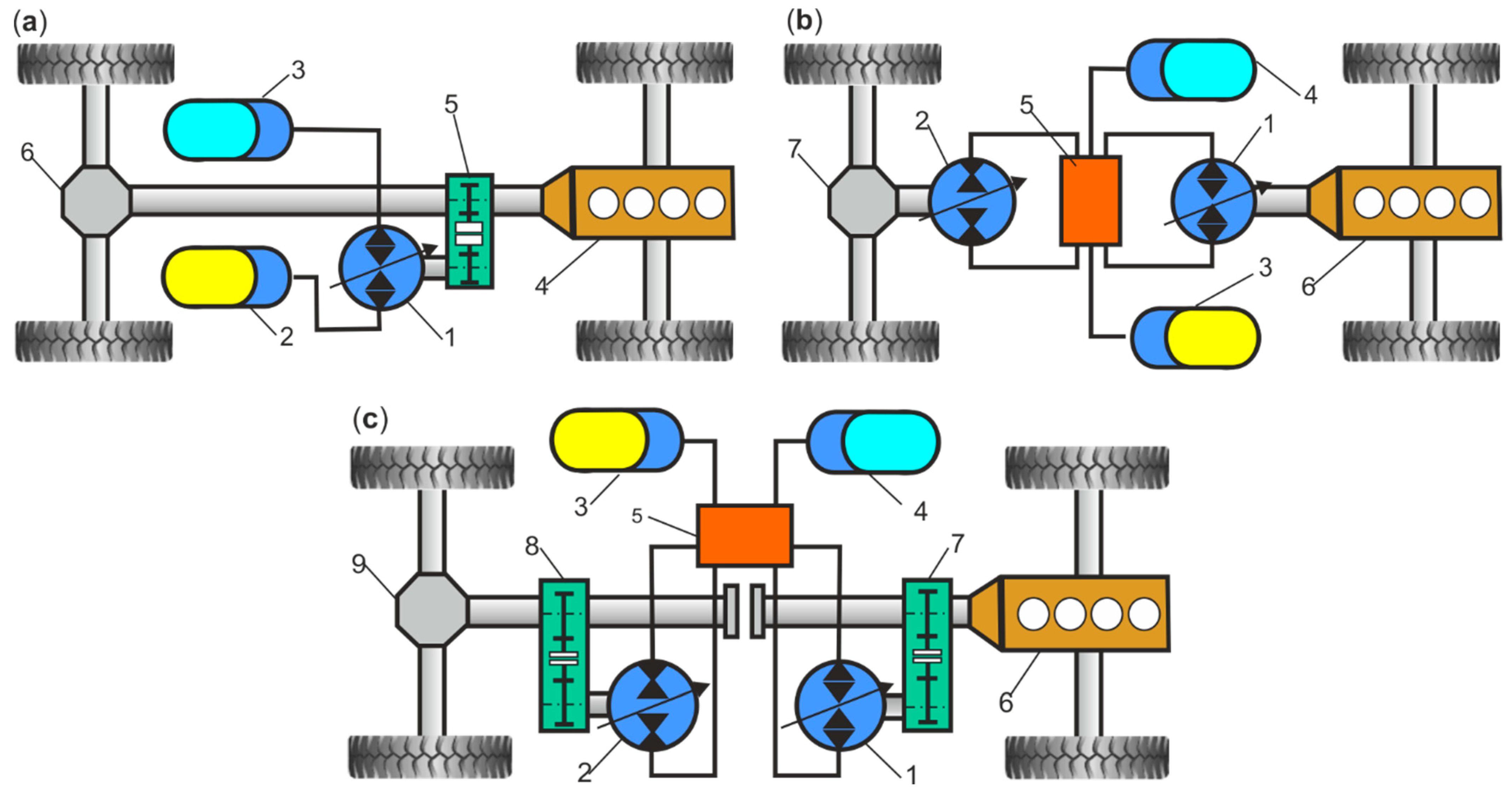
2.2. Basic Hydraulic Circuits with HPA
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
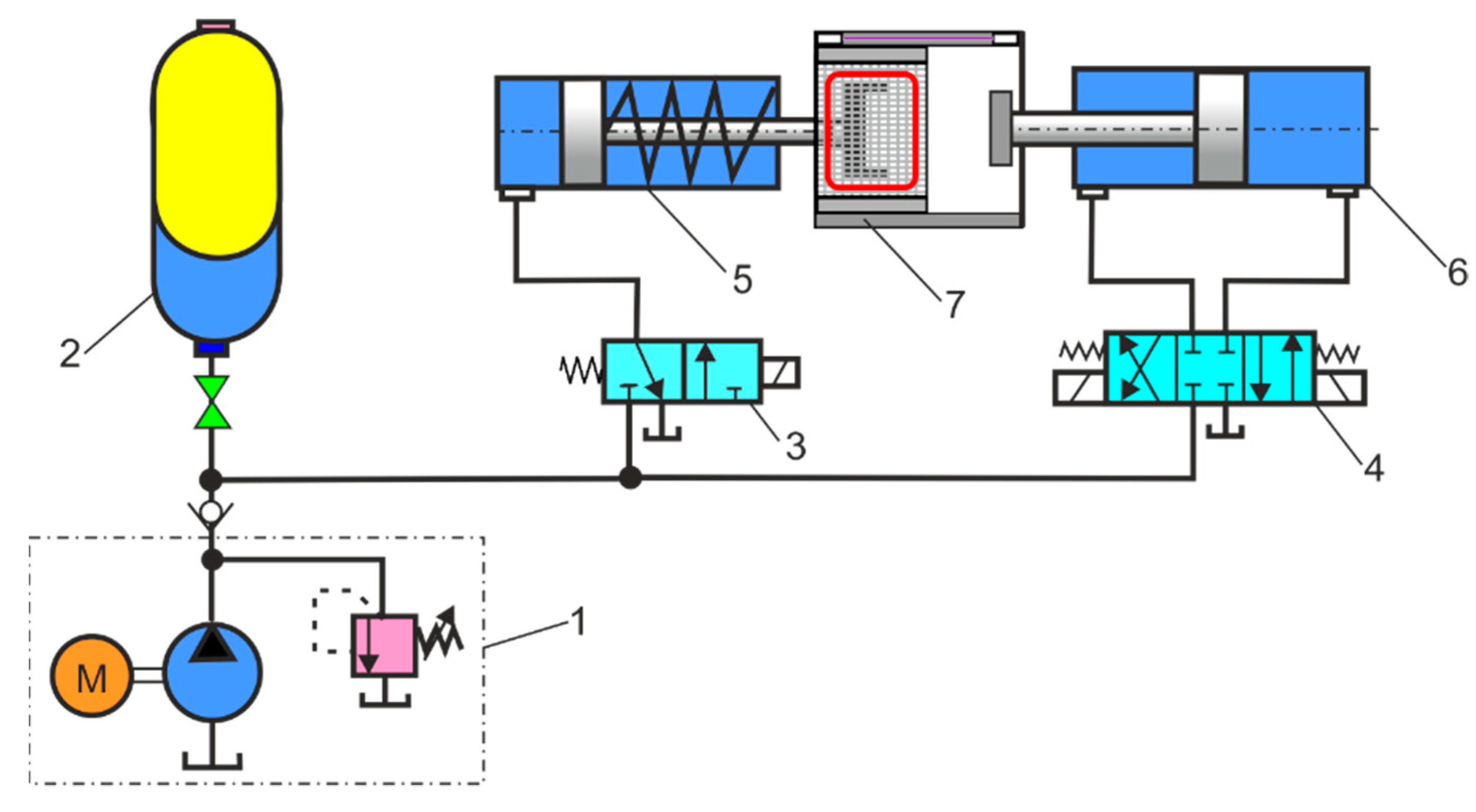
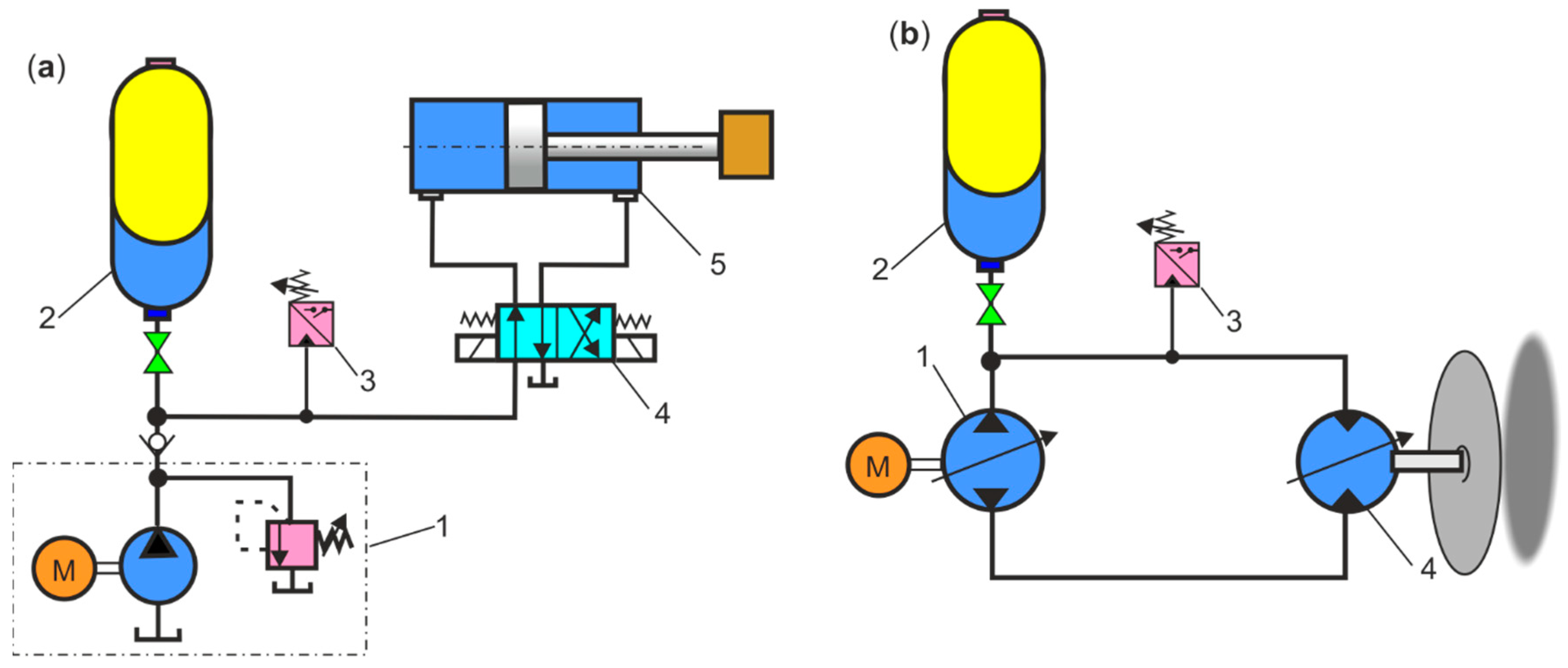
2.3. Hydraulic System with Energy Regeneration
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
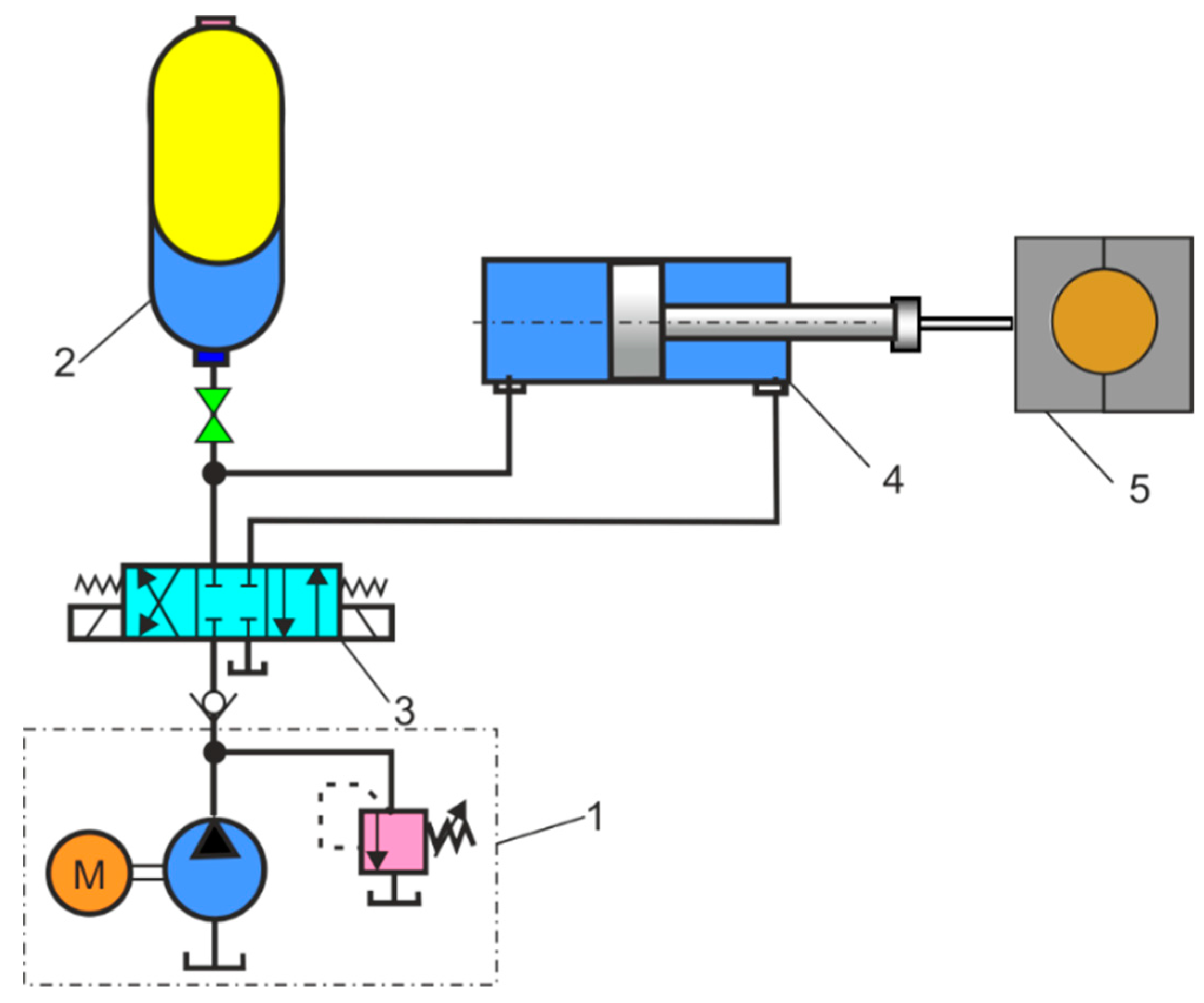
2.4. Hydraulic Hybrid System
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
3. HPA Calculation Parameters and Computational Models
3.1. HPA Calculation Parameters
- −
- useful (effective) volume of HPA
- −
- the volume required for the polytropic process
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
3.2. Energy Stored in the HPA
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
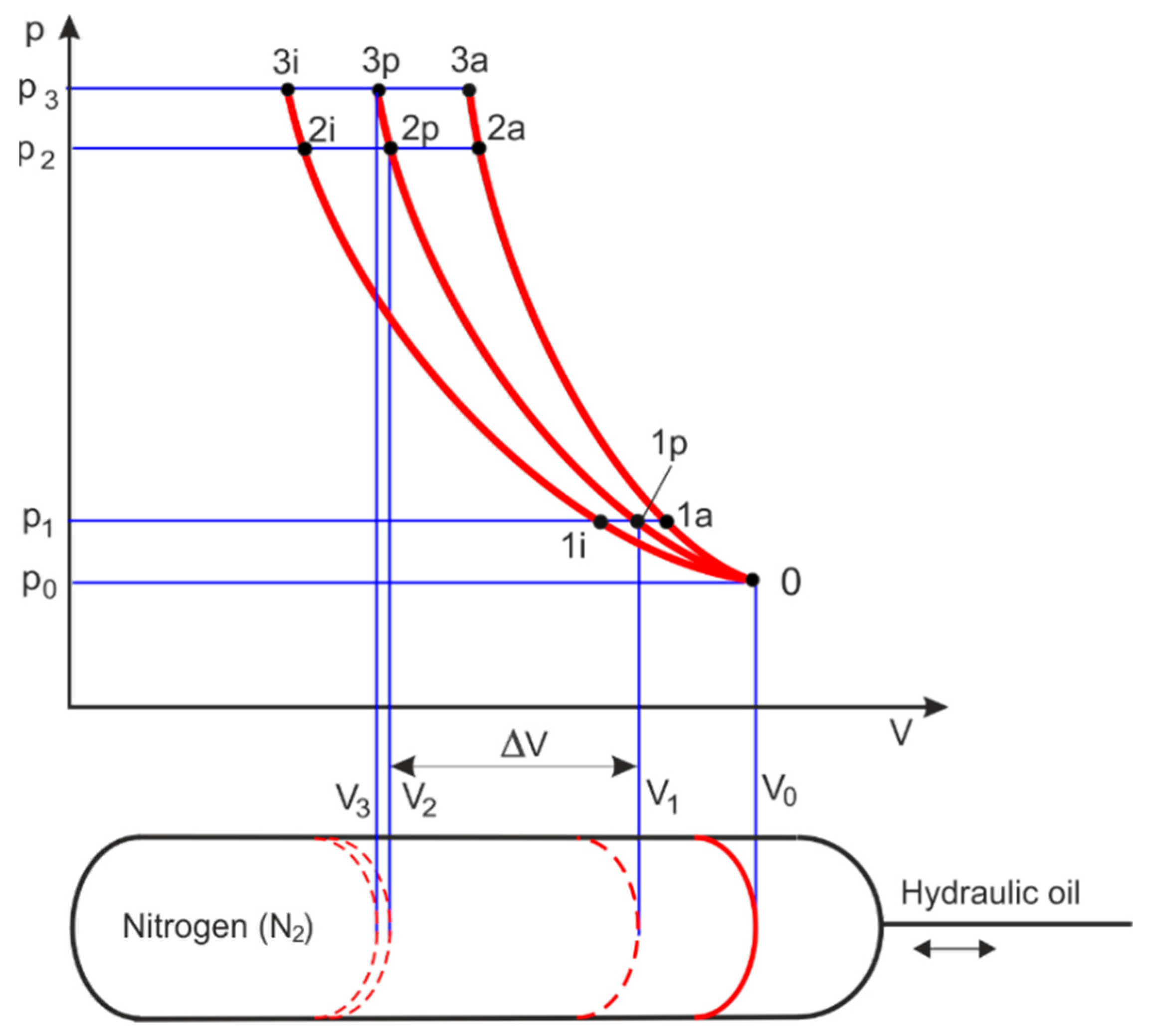
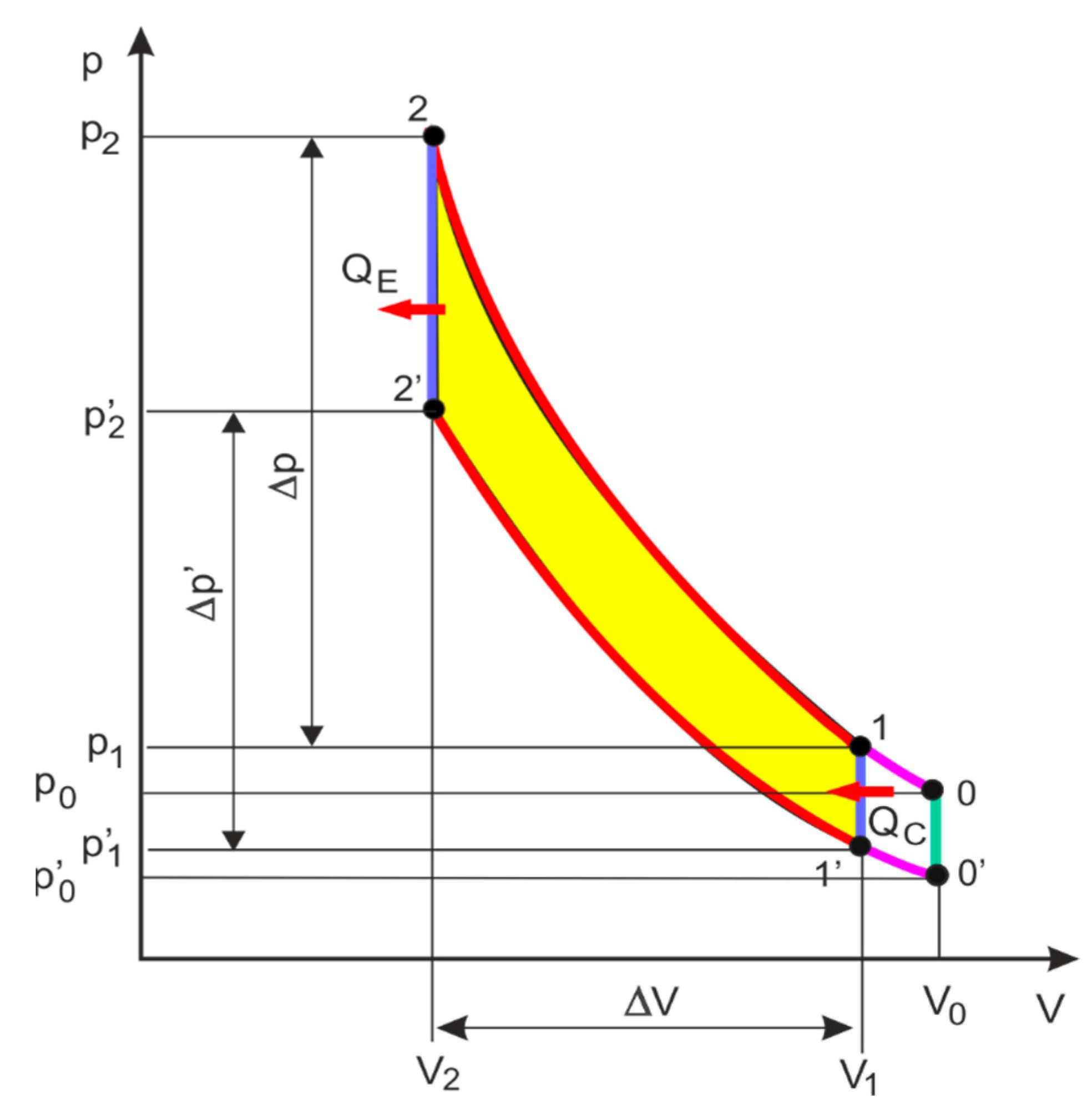
3.3. Thermodynamic Cycle of HPA
- −
- for isothermal processes
- −
- for polytropic processes
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
4. Dynamic Models of HPA
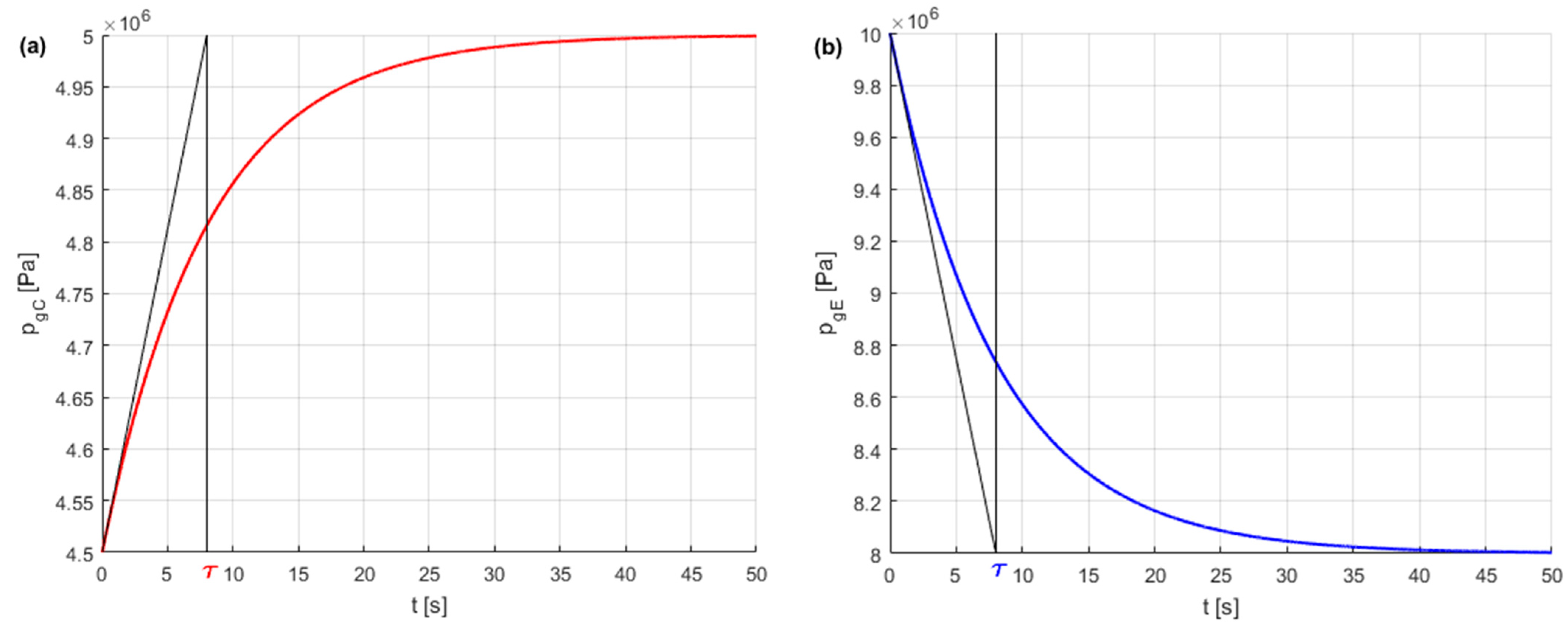
4.1. Thermodynamic Model of HPA
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
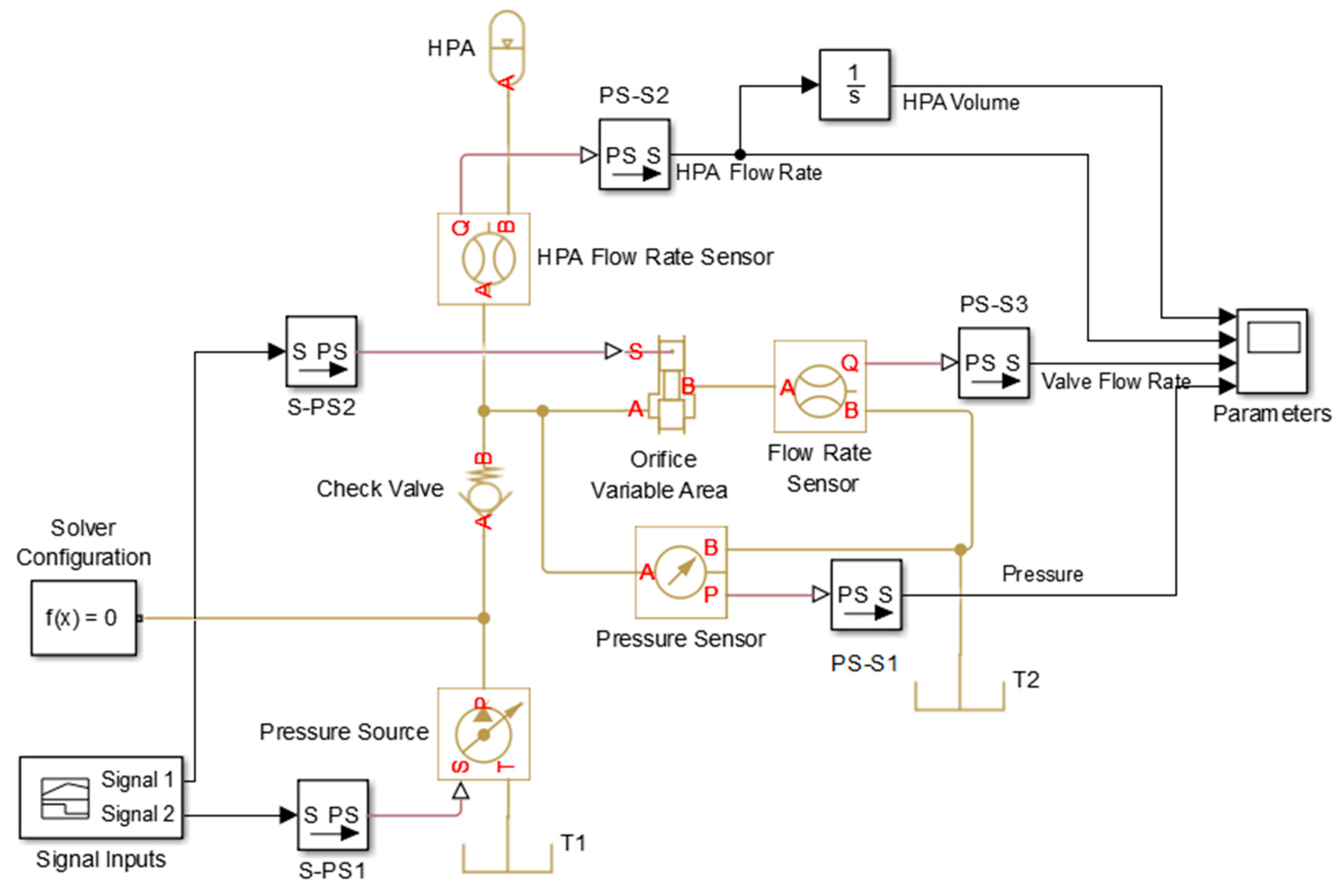
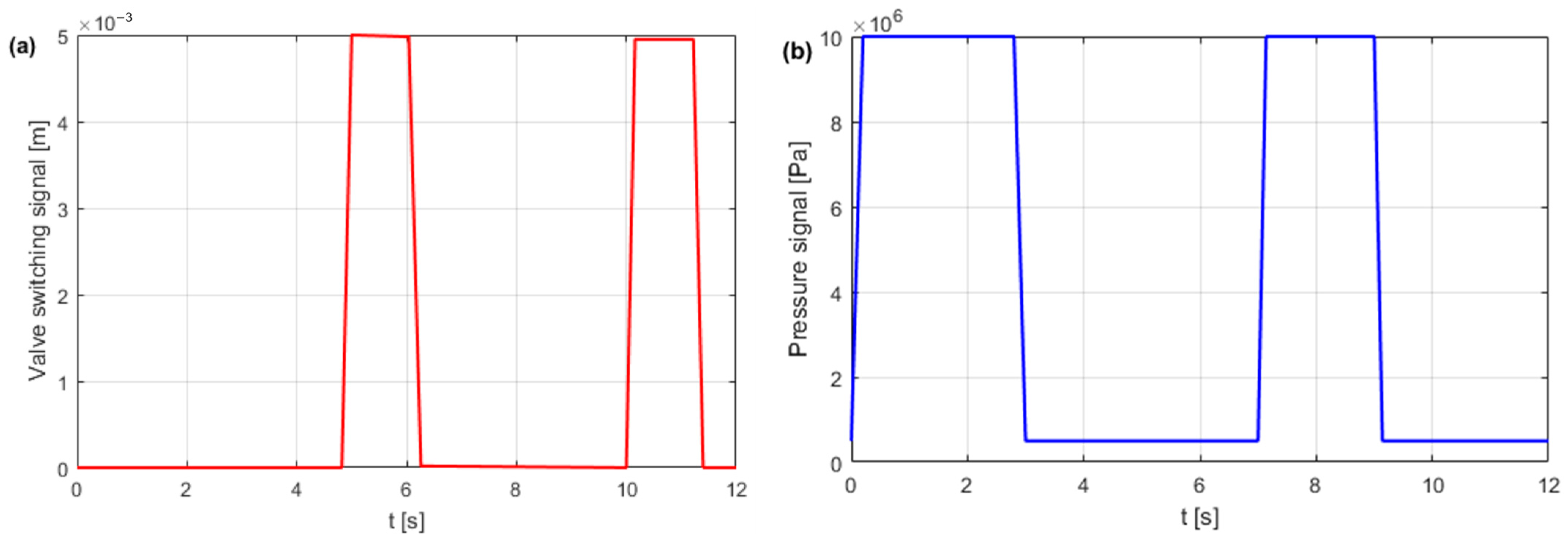
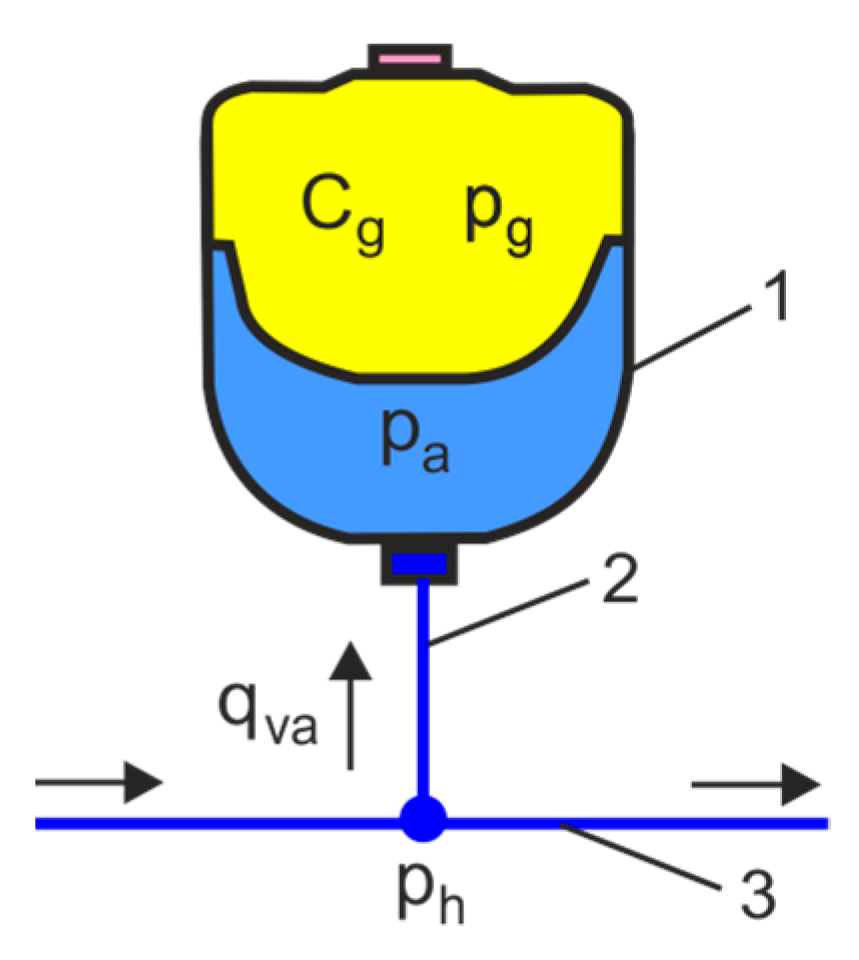
4.2. HPA Simulation Model
- The active state of HPA, where gas compression is taken into account on the basis of ideal gas thermodynamics for p > pg,
- The inactive state of HPA, where gas expansion is taken into account for p ≤ pg.
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
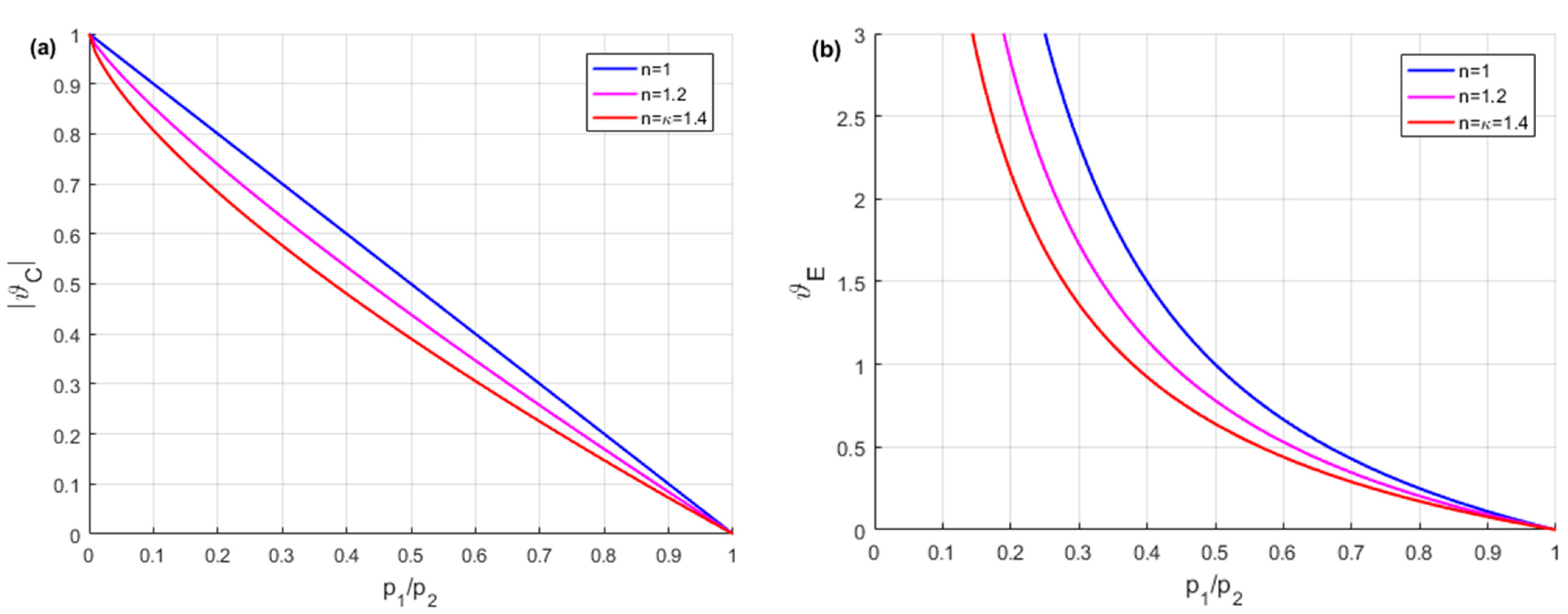
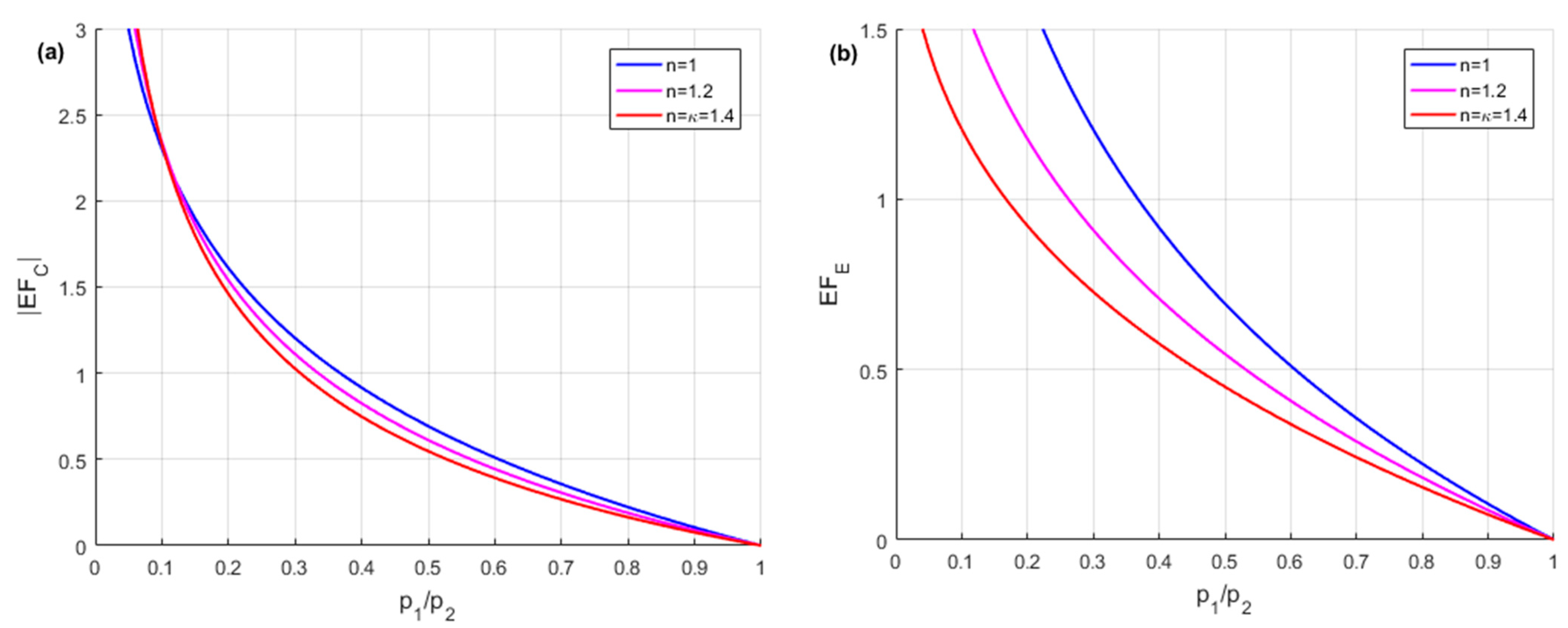
4.3. Dynamic Model of HPA
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
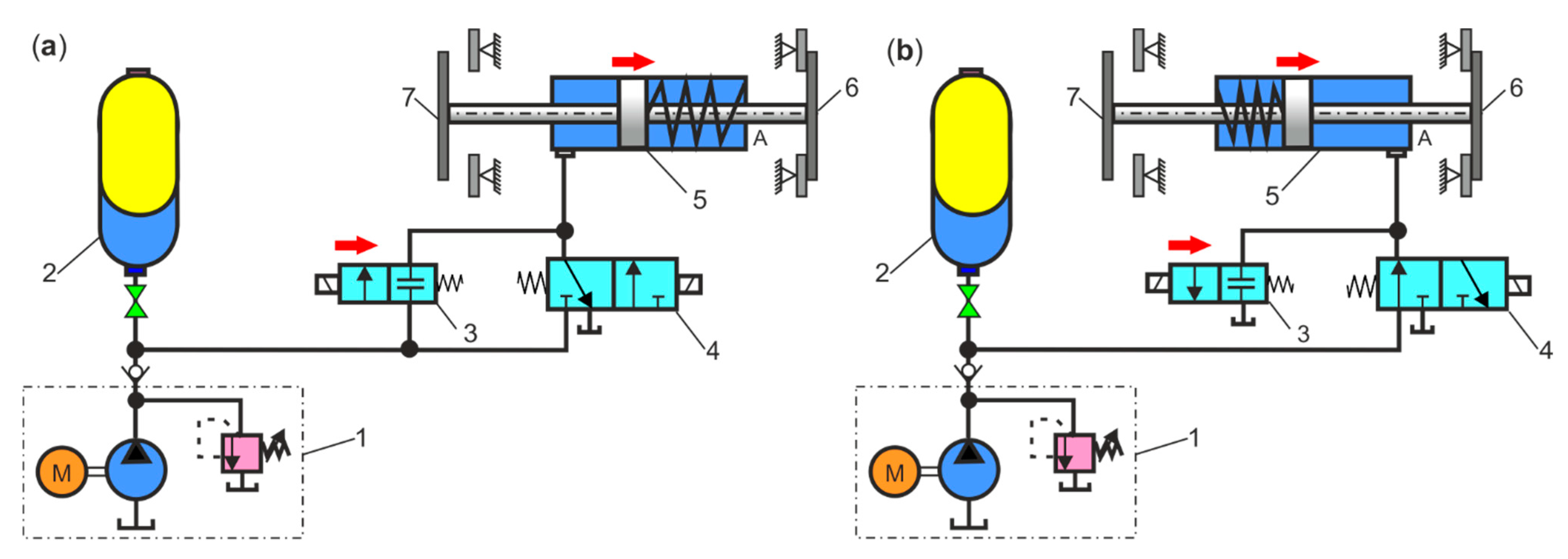
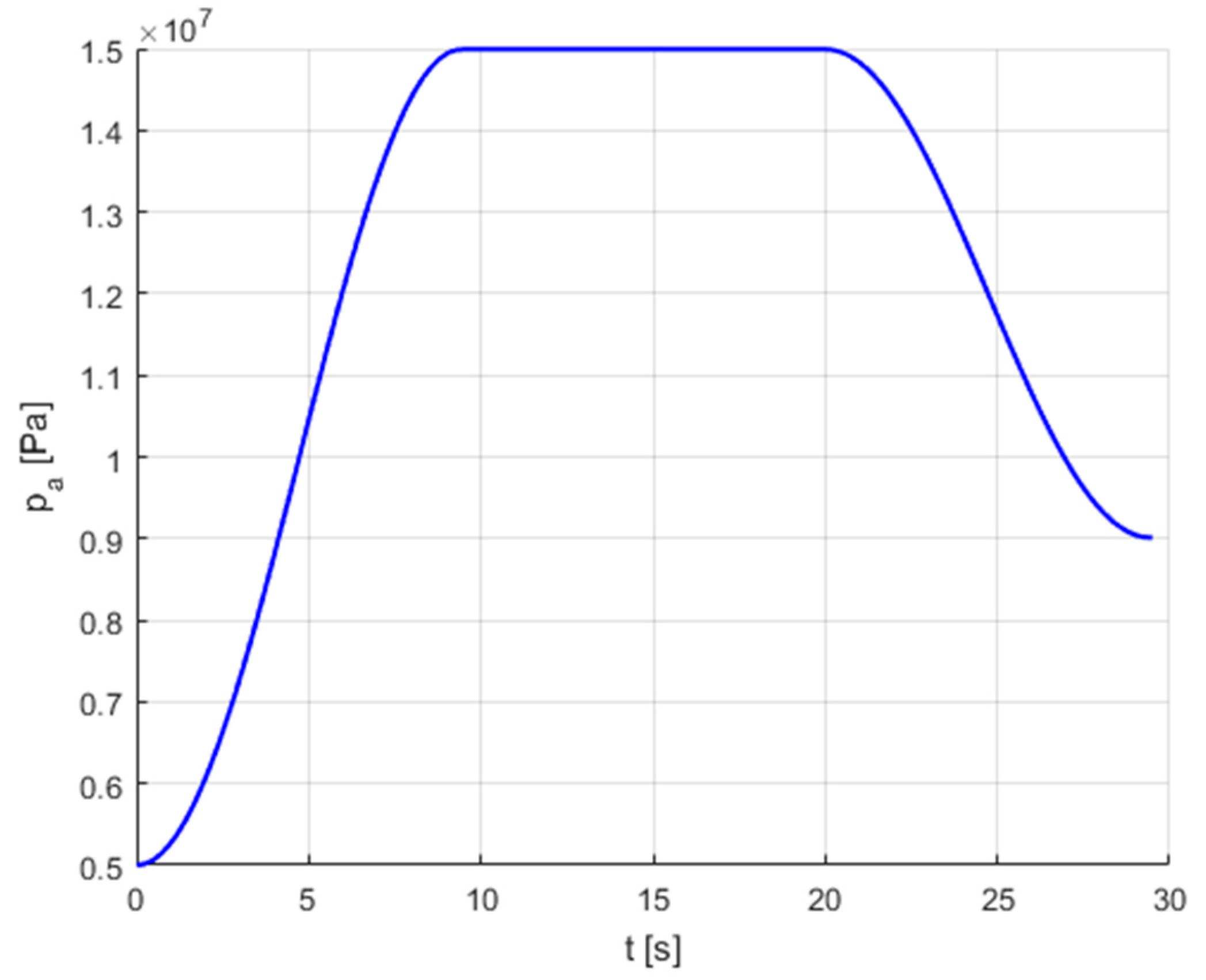
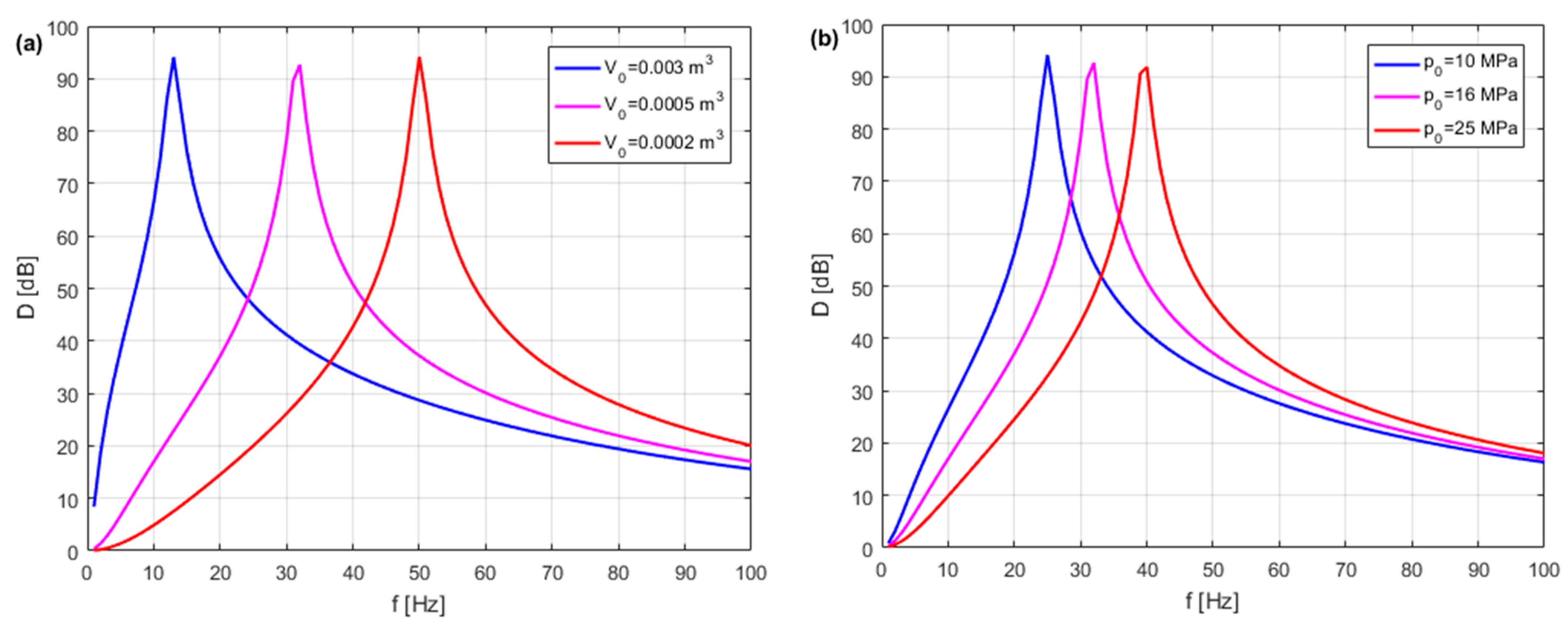
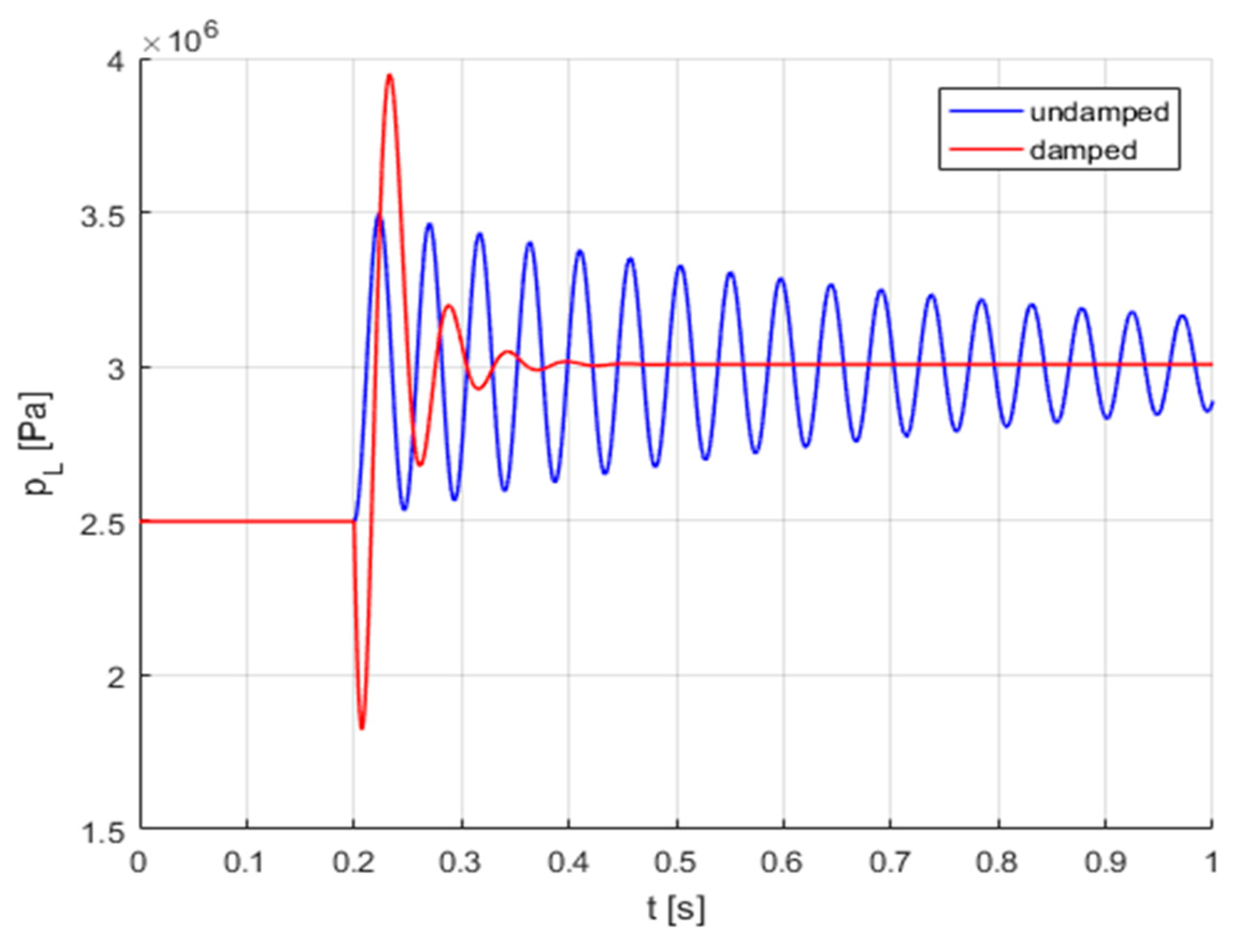
4.4. Dynamic Model of HPA as a Pulsation Damper
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
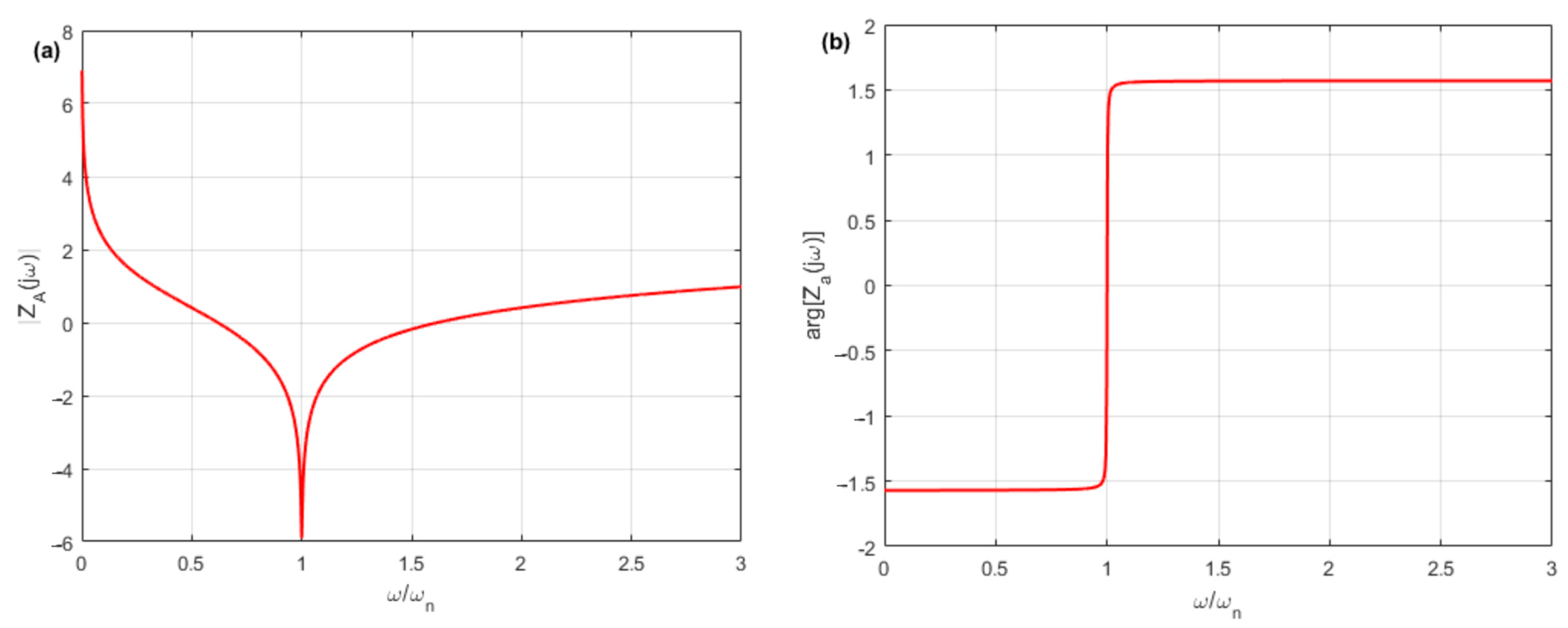
4.5. Dynamic Model of HPA as a Hydraulic Shock Absorber
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
5. HPA in Industrial Hydraulic Systems
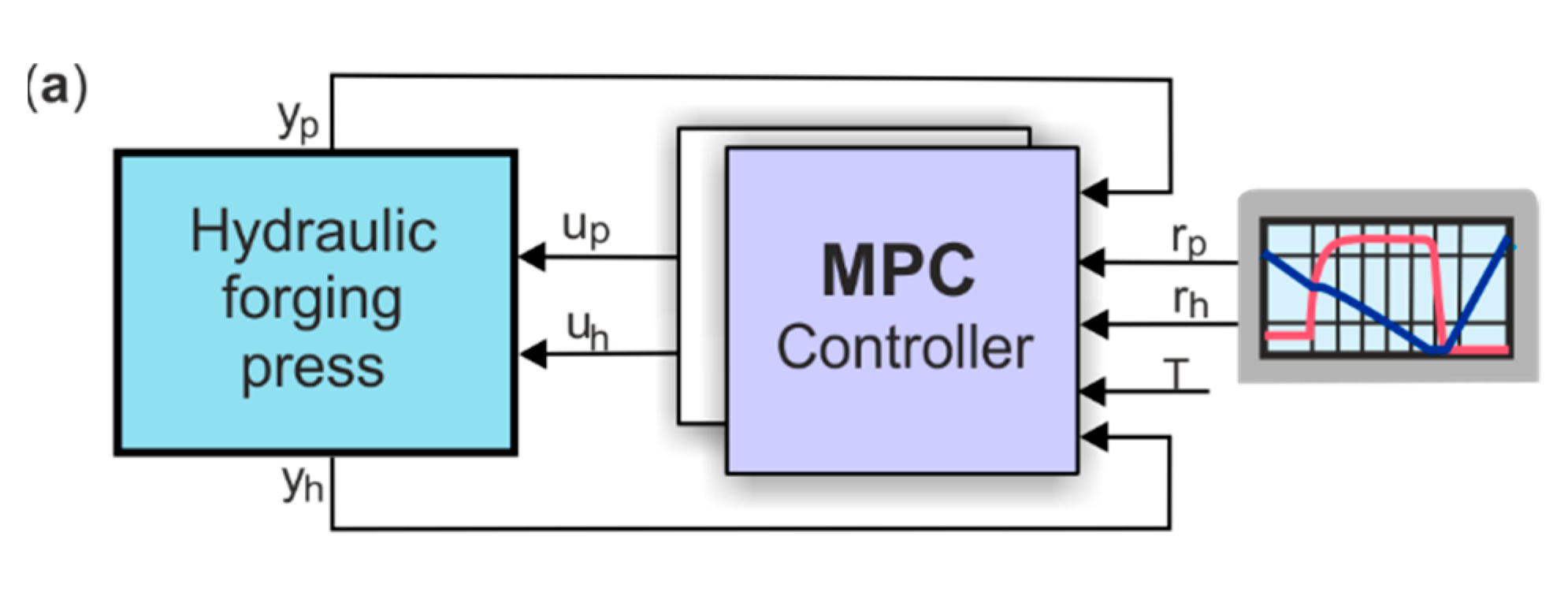
5.1. Energy-Saving Hydraulic Power Supply with HPA of Industrial HFP
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
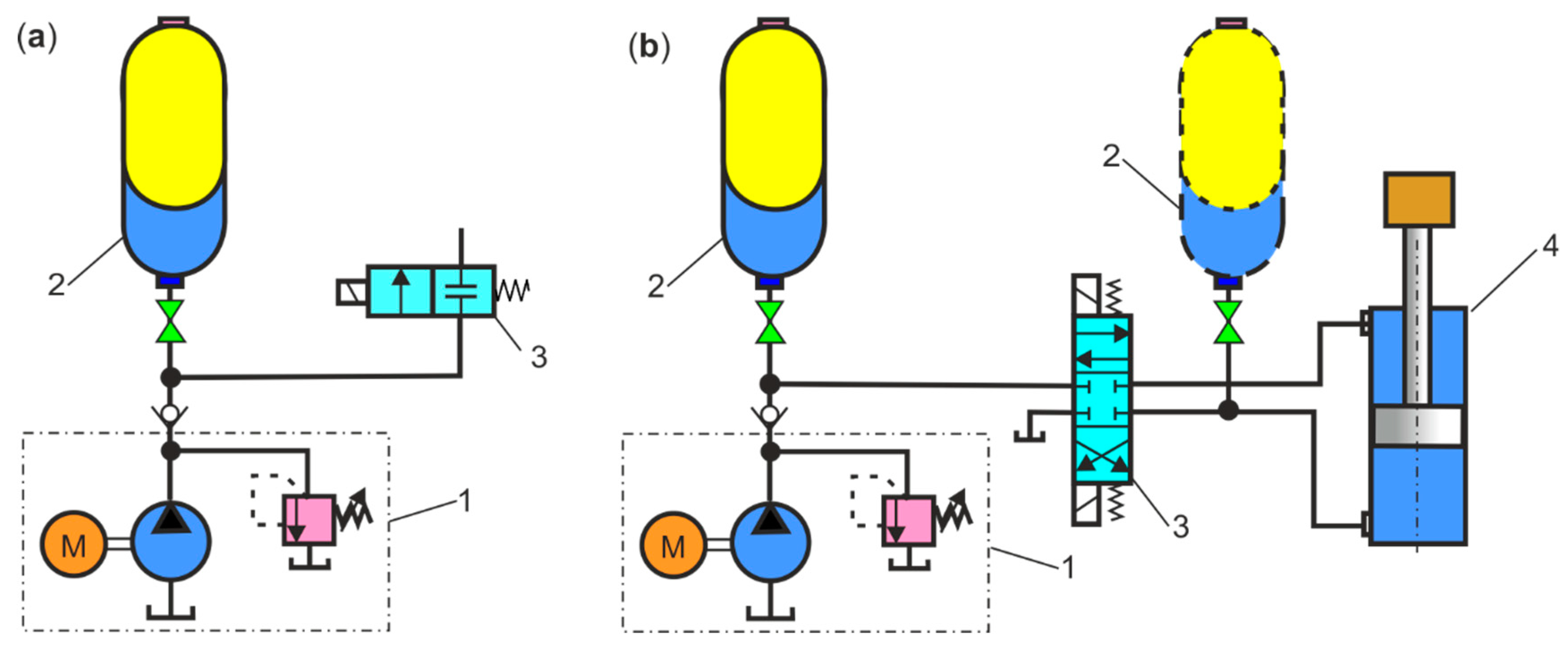
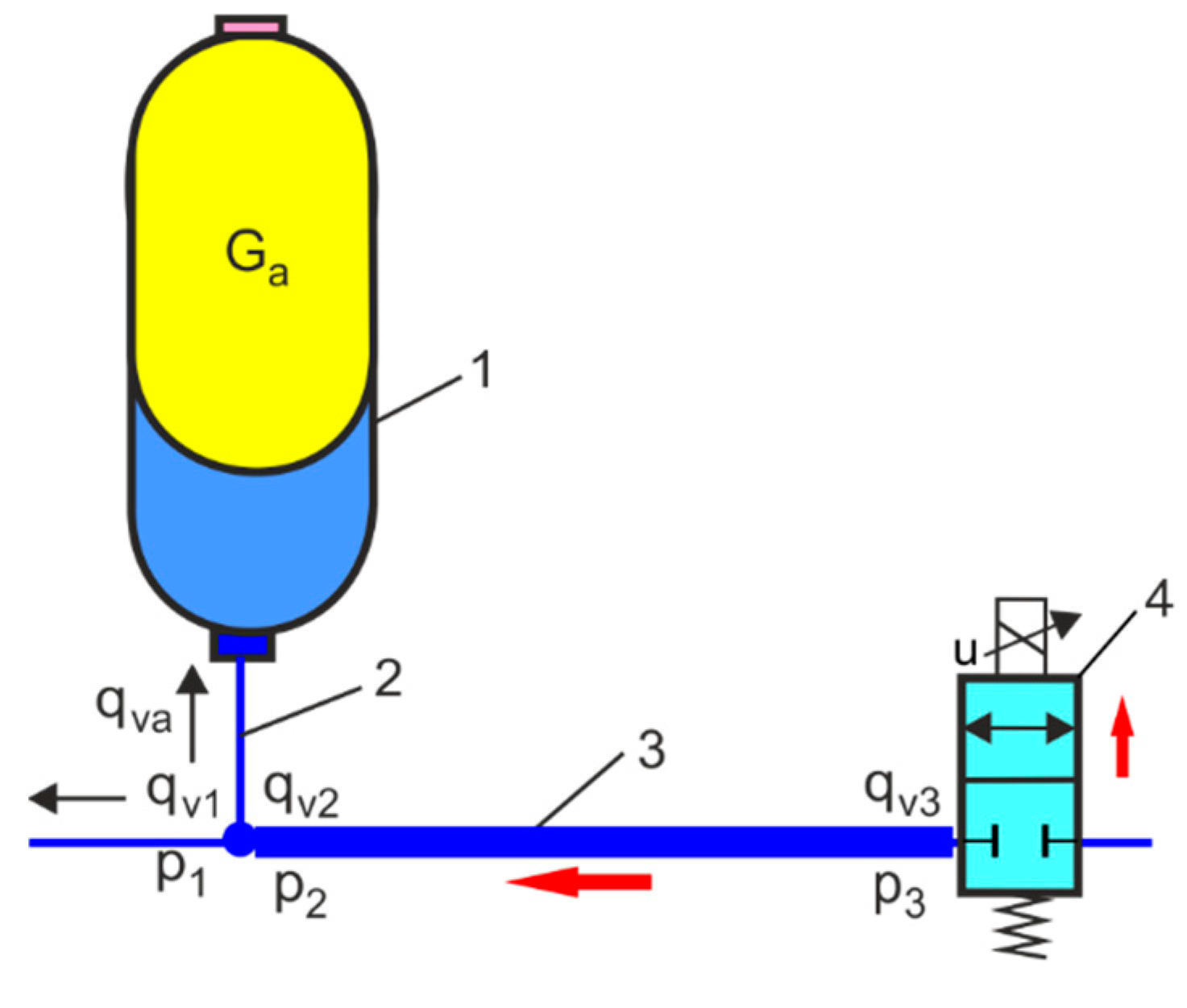
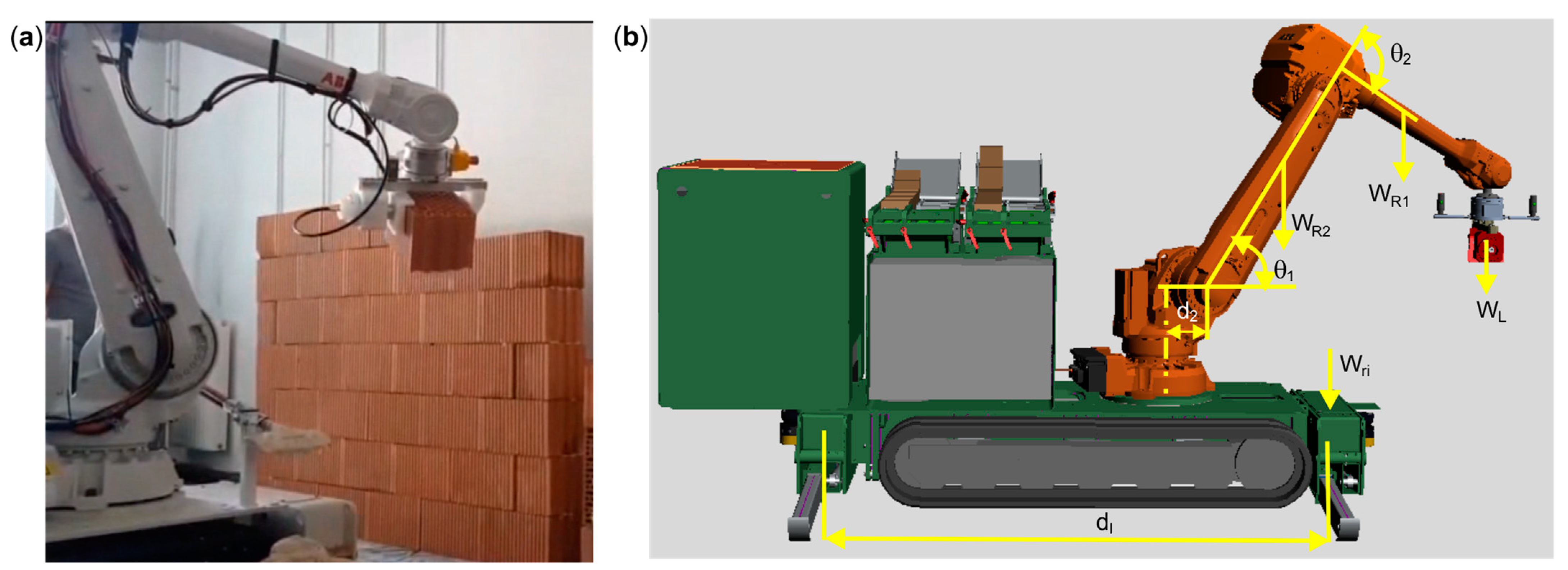
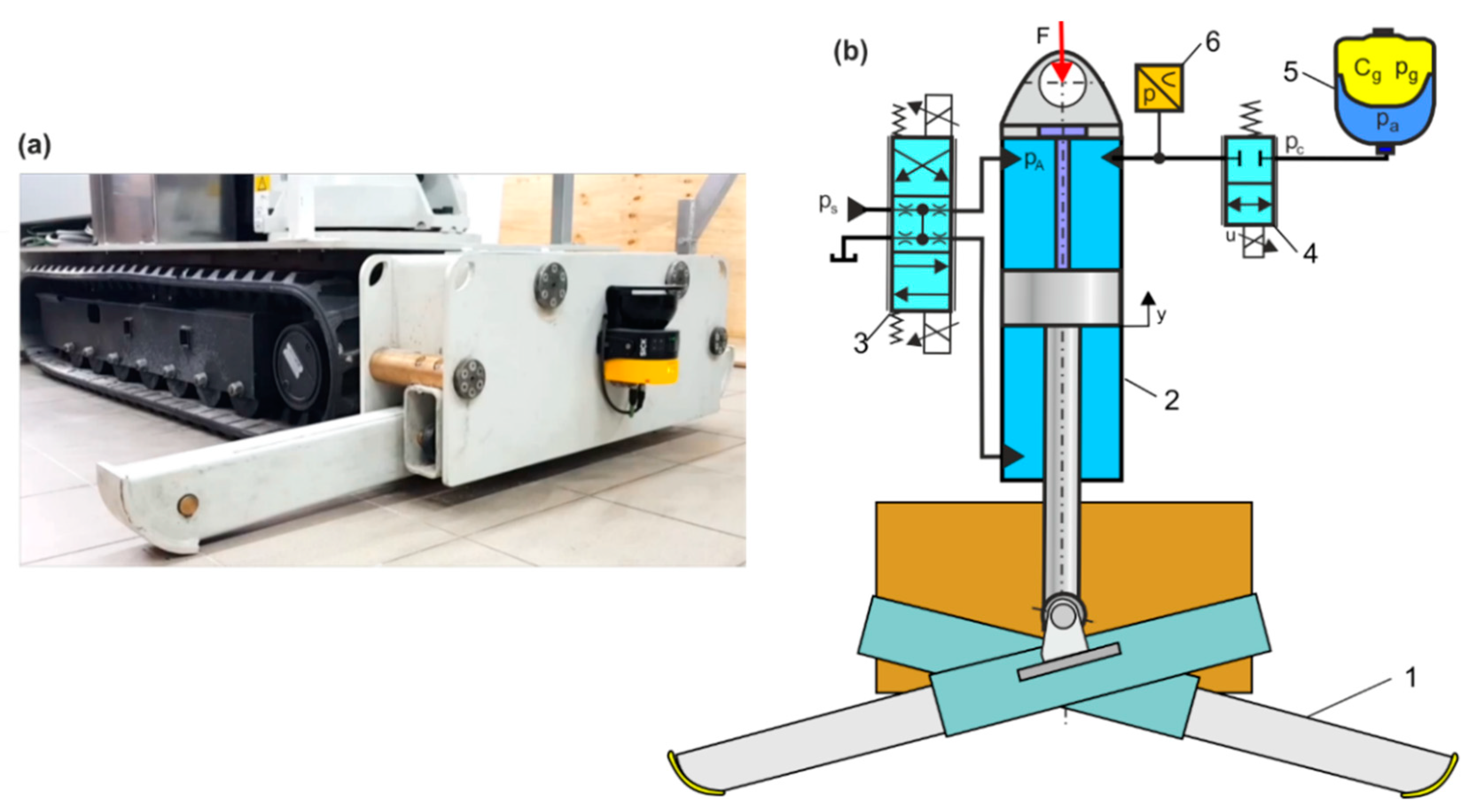
5.2. RBS Lifting and Levelling Module with HPA as a Shock Pulse Absorber
- Notes on future and frontier research methods
6. Future Directions of Development and Challenges
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EN 52021PC0558; Proposition for a Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on Energy Efficiency. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52021PC0558) (accessed on 14 July 2021).
- Sikora, A. European Green Deal–legal and financial challenges of climate change. ERA Forum 2021, 21, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU 2019/1781; UE Commission of 1 October 2019 Laying Down Ecodesign Requirements for Electric Motors and Variable-Speed Drives. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2019/1781/oj (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Pantano, S. Super-efficient equipment and appliances deployment (SEAD) initiative. In Proceedings of the IEEJS&L Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 10 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Globe Newswire. Hydraulic Power Unit Global Market Report 2023. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/08/04/2719228/0/en/Hydraulic-Power-Unit-Global-Market-Report-2023.html (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- International Energy Agency. Tracking Clean Energy Progress 2023. Available online: https://translate.google.pl/?hl=pl&sl=en&tl=pl&text=Tracking%20Clean%20Energy%20Progress%202023%0A.&op=translate (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Demonstrating Lower Emissions and Higher Efficiency through Innovative Hydraulic Systems in Demolition Machinery; LIFE20 ENV/SK/000392; Idraulica Sighinolfi Albano: Nonantola MO, Italy, 2021; Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/life/publicWebsite/project/details/5612 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Gerke, B.F.; McNeil, M.A.; Tu, T. The International Database of Efficient Appliances (IDEA): A new tool to support appliance energy-efficiency deployment. App. Energy 2017, 205, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydberg, K.-E. Energy efficient hydraulics–System solutions for loss minimization. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Fluid Power, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 16–17 March 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mahato, A.C.; Ghoshal, S.K. Energy-saving strategies on power hydraulic system: An overview. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2021, 235, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghestan, K.; Rezaei, S.M.; Talebi, H.A.; Zareinejad, M. An energy-saving nonlinear position control strategy for electro-hydraulic servo systems. ISA Trans. 2015, 59, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.H.; Le, T.D. Development and evaluation of energy-saving electro-hydraulic actuator. Actuators 2021, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.; Hansen, K.V. Electro-hydraulic variable-speed drive networks—Ideas, perspectives, and energy saving potentials. Energies 2022, 15, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratumsuwan, P.; Hutamarn, S.; Watcharin, P.-N. Energy saving in electro-hydraulic system using a MIMO fuzzy controller. Energy Res. Power Eng. 2014, 622–623, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Padovani, D.; Fresia, P.; Rundo, M.; Altare, G. Downsizing the electric machines of energy-efficient electro-hydraulic drives for mobile hydraulics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2385, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrat, G.; Bhola, M.; Ranjan, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Das, J. Energy saving and Fuzzy-PID position control of electro-hydraulic system by leakage compensation through proportional flow control valve. ISA Trans. 2020, 101, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzia, K.A. Method of determining optimal parameters for the secondary energy source of a multisource hydrostatic drive system in machines working in closed spaces. Energies 2022, 15, 5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. A novel energy recovery system integrating flywheel and flow regeneration for a hydraulic excavator boom system. Energies 2020, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, D.; Rundo, M.; Altare, G. The working hydraulics of valve-controlled mobile machines: Classification and review. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2020, 142, 070801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, A. Improvement of Hydraulic Energy Efficiency Be Means of Energy Recuperations; Monograph 403; Cracow University of Technology: Cracow, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Casoli, P.; Riccò, L.; Campanini, F.; Bedotti, A. Hydraulic hybrid excavator—Mathematical model validation and energy analysis. Energies 2016, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Noskievič, P. Position tracking control with load-sensing for energy-saving valve-controlled cylinder system. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Ge, L.; Weil, Z.; Li, Y.W.; Quan, L. A survey of powertrain technologies for energy-efficient heavy-duty machinery. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casoli, P.; Scolari, F.; Vescovini, C.M.; Rundo, M. Energy comparison between a load sensing system and electro-hydraulic solutions applied to a 9-ton excavator. Energies 2022, 15, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Gong, W. Development of hybrid powered hydraulic construction machinery. Autom. Constr. 2010, 19, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedotti, A.; Pastori, M.; Casoli, P. Modelling and energy comparison of system layouts for a hydraulic excavator. Energy Procedia 2018, 148, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Hu, B. A review of developments in energy storage systems for hybrid excavators. Autom. Constr. 2017, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, W.; Xu, B. New investigation in energy regeneration of hydraulic elevators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4126-1:2013; Safety Devices for Protection against Excessive Pressure—Part 1: Safety Valves. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:4126:-1:ed-3:v1:en (accessed on 16 July 2013).
- Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU; European Parliament and of the Council: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; Available online: http://publications.europa.eu/resource/cellar/1ddec7ca-0e96-11e4-a7d0-01aa75ed71a1.0006.03/DOC_1 (accessed on 15 May 2014).
- HYDAC. Safety and Shut-Off Block; Hydac International: Sulzbach/Saar, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ORELL. Hydraulic Accumulators Application; ORELL Tec AG: Düdingen, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- HYDRO LEDUC. Hydraulic Accumulators; HYDRO LEDUC: Azerailles, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- HANSA. Hydraulic Accumulators; HANSA TMP: Modena, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- HANSA-FLEX. Hydraulic Accumulators; HANS-FLEX AG: Bremen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FOX. Hydraulic Accumulators; FOX s.r.l.: Milano, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FPE. Hydraulic Accumulators; EPE Italiana s.r.l.: Cologno Monzese, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- HYDAC. Hydraulic Accumulators; Hydac International: Sulzbach/Saar, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ripke, R. Hydraulic Accumulators: Learn How Hydraulic Accumulators Work: Hydraulic Accumulators How They Work; Amazon Digital Services LLC.: Seattle, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ibbetson, W. Accumulator Charging-Maintenance and Repair; Read Books Ltd.: Redditch, England, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nisters, C.; Bauer, F.; Brocker, M. Condition Monitoring Systems for Hydraulic Accumulators–Improvements in Efficiency, Productivity and Quality; Technische Universität Dresden: Dresden, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dindorf, R.; Wos, P. Development of Hydraulic Power Systems; Monograph M72; Kielce University of Technology: Kielce, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Xiaoa, G.; Hua, B.; Tana, L.; Tanga, H.; Hea, S.; Hea, Z. The applications of energy regeneration and conversion technologies based on hydraulic transmission systems: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydberg, K.-E. Energy efficient hydraulic hybrid drives. In Proceedings of the 11th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, SICFP’09, Linköping, Sweden, 2–4 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Man, Z.; Ding, F.; Ding, C.; Liu, S. Study of an energy regeneration system with accumulator for hydraulic impulse testing equipment. Stroj. Vestn.–J. Mech. Eng. 2015, 61, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Denis Ashok, S.; Nagaraj, S.; Adithyakumar, C.R.; Lohith, M.; Reddy, K.; Naulakha, K.N. Design of an energy efficient hydraulic regenerative circuit. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 310, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Chen, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Miao, C.; Fu, S.; Chen, Q. Energy Regeneration Hydraulic System via a Relief Valve with Energy Regeneration Unit. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapka, M.; Nevrly, J.; Panacek, T. Experimental rig for simulation of hydromechanical system with energy regeneration. Eng. Mech. 2014, 21, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.H.; Ahn, K.K. Modeling and simulation of hydrostatic transmission system with energy regeneration using hydraulic accumulator. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minav, T.; Henri Hänninen, H.; Sinkkonen, A.; Laurila, L.; Pyrhonen, J. Electric or hydraulic energy recovery systems in a reach truck—A comparison. Stroj. Vestn. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 60, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Quiroga, J.; Newell, B.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Gonzalez-Mancera, A.; Garcia-Bravo, J. Energy efficiency comparison of hydraulic accumulators and ultracapacitors. Energies 2020, 13, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M. HRB–Hydrostatic Regenerative Braking System. The Hydraulic Hybrid Drive from Bosch Rexroth; Bosch Rexroth AG: Elchingen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baseley, S.; Ehret, C.; Greif, E.; Kliffken, M. Hydraulic Hybrid Systems for Commercial Vehicles; SAE 2007 Commercial Vehicle Engineering Congress & Exhibition; Technical Paper 2007-01-4150; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, C. High-pressure hybrids: Fuel-efficient hydraulic vehicles come of age. Sci. Am. 2010, 303, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- PSA Peugeot Citroen. Hybrid Air, An Innovative Petrol Full Hybrid Solution for the Car of the Future. Available online: https://www.groupe-psa.com/en/newsroom/automotive-innovation/hybrid-air (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Feng, B.; Xu, H.; Wang, A.; Gao, L.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, X. A comprehensive review of energy regeneration and conversion technologies based on mechanical–electric–hydraulic hybrid energy storage systems in vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L. Design and validation of a novel hydraulic hybrid vehicle with wheel motors. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103, 0036850419878024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masser, R.; Hoffmann, K.H. Endoreversible modeling of a hydraulic recuperation system. Entropy 2020, 22, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; He, X.; Shen, X. Improving energy recovery rate of the regenerative braking system by optimization of influencing factors. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Gao, H.; Liu, Z.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X. Potential energy recovery and direct reuse system of hydraulic hybrid excavators based on the digital pump. Energies 2023, 16, 5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-S. Energy efficiency comparison between hydraulic hybrid and hybrid electric vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 4697–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASPlight. Tools for Optimal Calculation of the Hydraulic Accumulator. Available online: https://www.hydac.com/en/online-tools/asplight (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- HYDAC. Sizing Accumulators; Hydac International: Sulzbach/Saar, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Li, M.; Iqbal, M.Y.; Xu, G. Investigation of accumulator main parameters of hydraulic excitation system. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 93, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, A.; Glück, T.; Kemmetmüller, W.; Kugi, A. Mathematical modelling of a hydraulic accumulator for hydraulic hybrid drives. Math. Comp. Model. Dyn. Syst. 2016, 22, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamcic, S.; Bogdevicius, M. Simulation of dynamic processes in hydraulic accumulators. Transport 2010, 25, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Das, J.; Dasgupta, K.; Barnwal, M.-K. Effect of hydraulic accumulator on pressure surge of a hydrostatic transmission system. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. 2018, 99, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petric, J. Modeling of hydro-pneumatic energy storage system. In Proceedings of the 8th EUROSIM Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Cardiff, UK, 10–13 September 2013; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, T.; Xin, Y. Modeling and simulation of a hydro-pneumatic accumulator system for hybrid air development. Appl. Mech. Mat. 2014, 733, 763–767. [Google Scholar]
- Rotthäuser, S. Verfahren zur Berechnung and Untersuchung Hydropneumatischer Speicher. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hochschule Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita, S.; Zhang, S.; Kazushi Sanada, K. A study on a mathematical model of gas in accumulator using van der Waals equation. In Proceedings of the 15th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, SICFP’17, Linköping, Sweden, 7–9 June 2017; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Wang, D.; Jin, C.; Yi, T. Modelling and performance analysis of cyclic hydro-pneumatic energy storage system considering the thermodynamic characteristics. Energies 2022, 15, 6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmussen, M.F.; Liniger, J.; Sepehri, N.; Pedersen, H.C. Pre-charge pressure estimation of a hydraulic accumulator using surface temperature measurements. Wind 2022, 2, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, F. Hydrospeicher als Energiespeicher; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Pourmovahed, A.; Otis, D.R. An experimental thermal time-constant correlation for hydraulic accumulators. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1990, 112, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, K.-R. Hydrospeicher. Experimentelle und Analytische Untersuchungen zur Energiespeicherung. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hochschule Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Akers, A.; Gassman, M.; Smith, R. Hydraulic Power System Analysis; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Figiel, A.; Kudzma, Z.; Stosiak, M. Low-frequency pressure fluctuation damper based on hydro-pneumatic spring with constant stiffness. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2019, 56, 841–855. [Google Scholar]
- Krus, P. Transmission Line Modelling for System Simulation; Linköping University: Linköping, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Watton, J.; Tadmori, M.J. A comparison of techniques for the analysis of transmission line dynamics in electrohydraulic control systems. Appl. Math. Model. 1988, 12, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindorf, R.; Woś, P. A case study of a hydraulic servo drive flexibly connected to a boom manipulator excited by the cyclic impact force generated by a hydraulic rock breaker. IEEE-Access 2022, 10, 7734–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J.; Woś, P. Research Report. Demonstration of the Open-Die Forging Process for Large-Size Hardly Deformable Forgings with the Use of an Innovative Energy-Saving Power Supply System and Intelligent Control of Hydraulic Presses in Real-Time; Kielce University of Technology: Kielce, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dindorf, R.; Wos, P. Energy-saving hot open-die forging process of heavy steel forgings on an industrial hydraulic forging press. Energies 2020, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindorf, R. Energy saving and intelligent control of the forging process. Forg. Today 2020, 10, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J.; Woś, P. Parameters prediction of the hot open die elongation forging process on an 80 MN hydraulic forging press. Open Eng. 2021, 11, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J.; Wos, P. Innovative power supply and intelligent control of an industrial hydraulic forging press. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 13, pp. 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J.; Wos, P. Research Reports. Robotic Bricklaying System; Kielce University of Technology: Kielce, Poland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dindorf, R.; Woś, P. Innovative solution of mobile robotic unit for bricklaying automation. J. Civil Eng. Transp. 2022, 4, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wos, P.; Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J. The electro-hydraulic lifting and leveling system for the bricklaying robot. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 13, pp. 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wos, P.; Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J. Bricklaying robot lifting and leveling system. Commun.-Sci. Lett. Univ. Žilina 2021, 23, B257–B264. [Google Scholar]
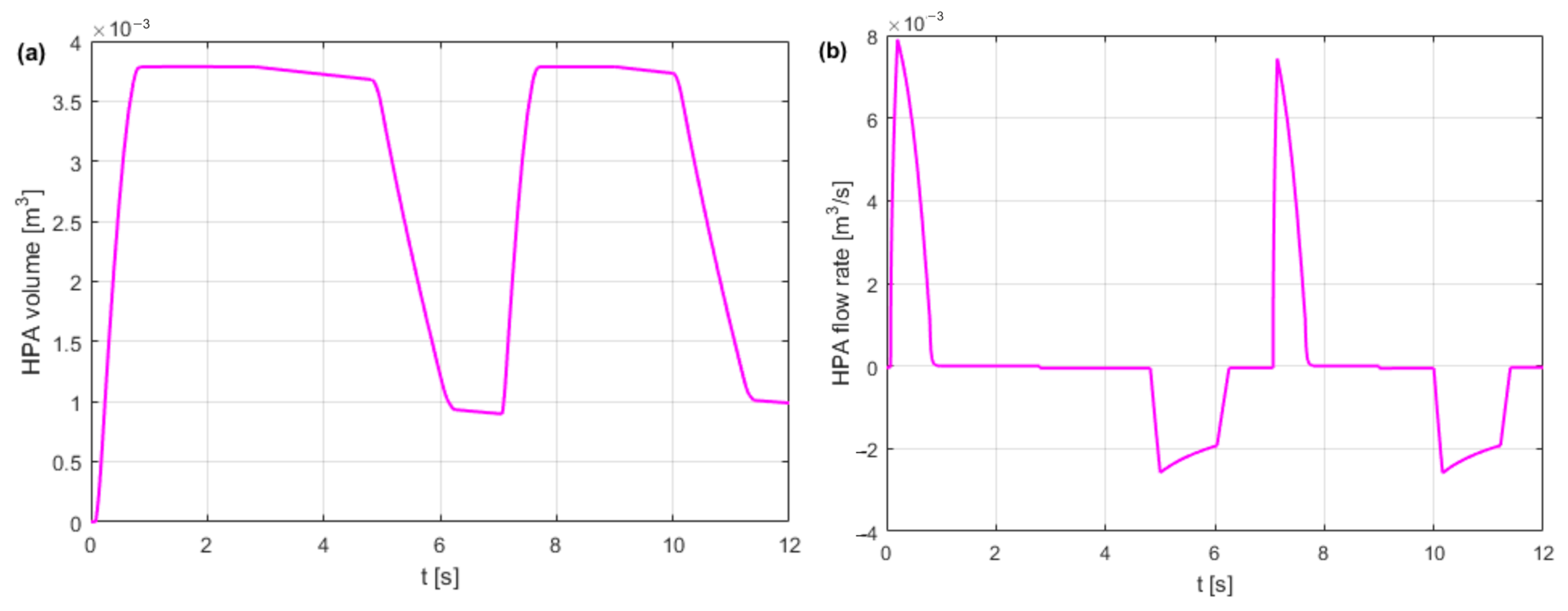
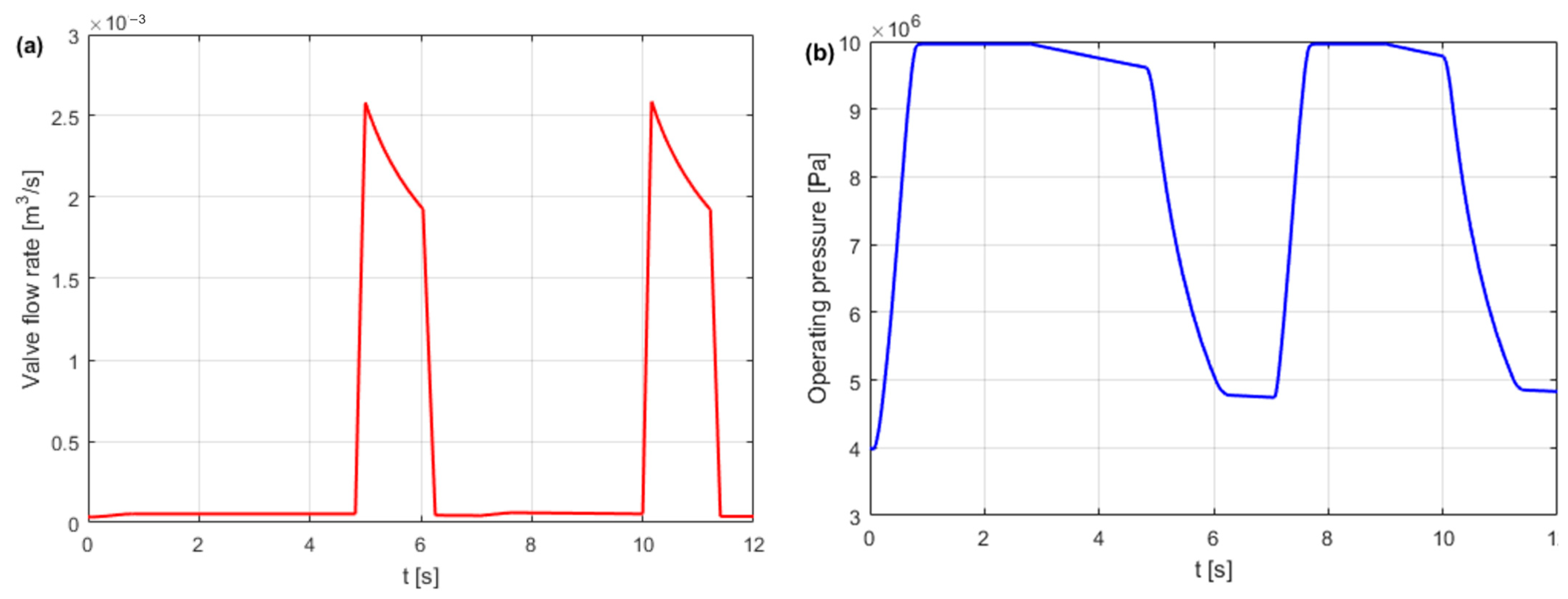
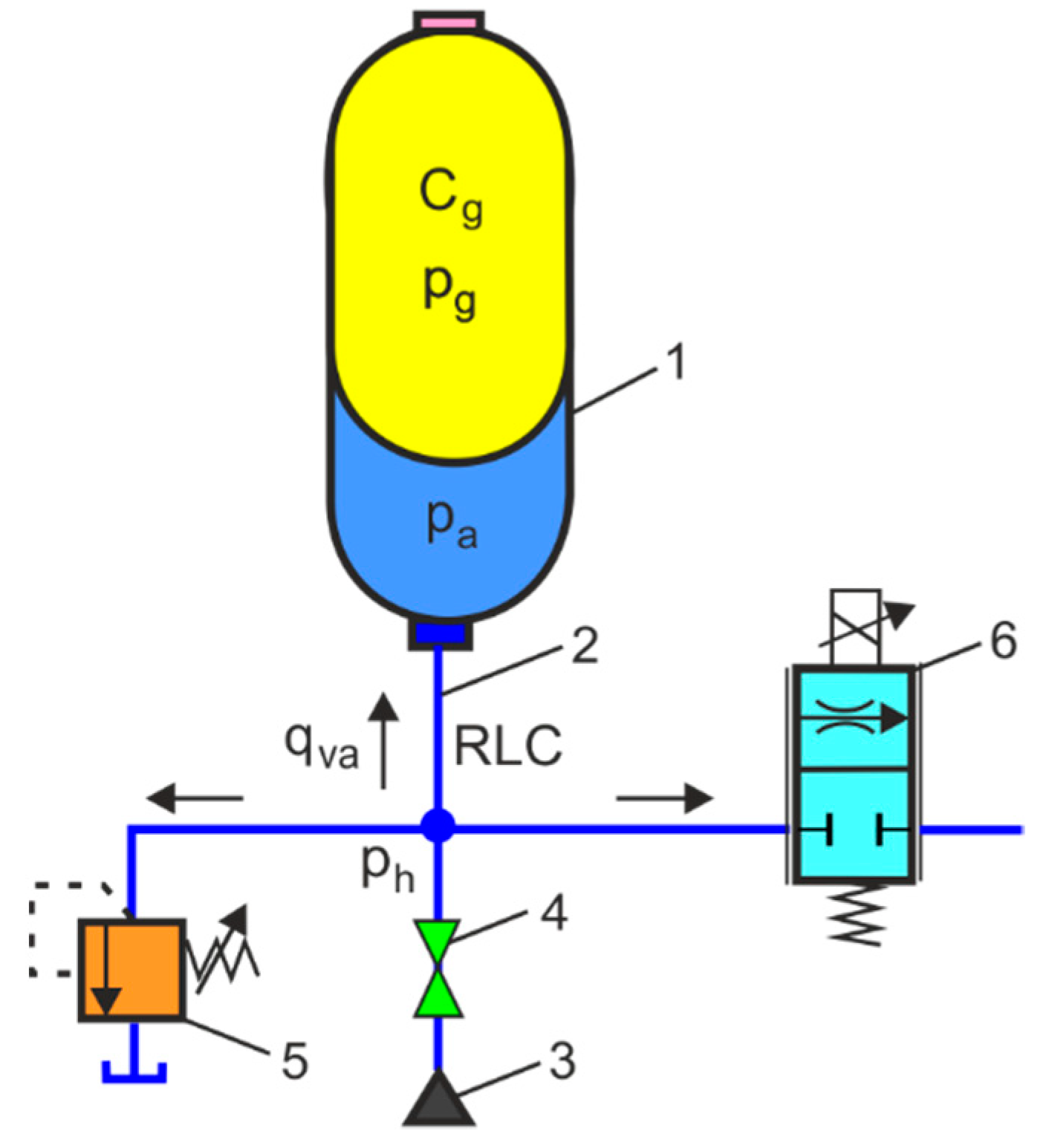
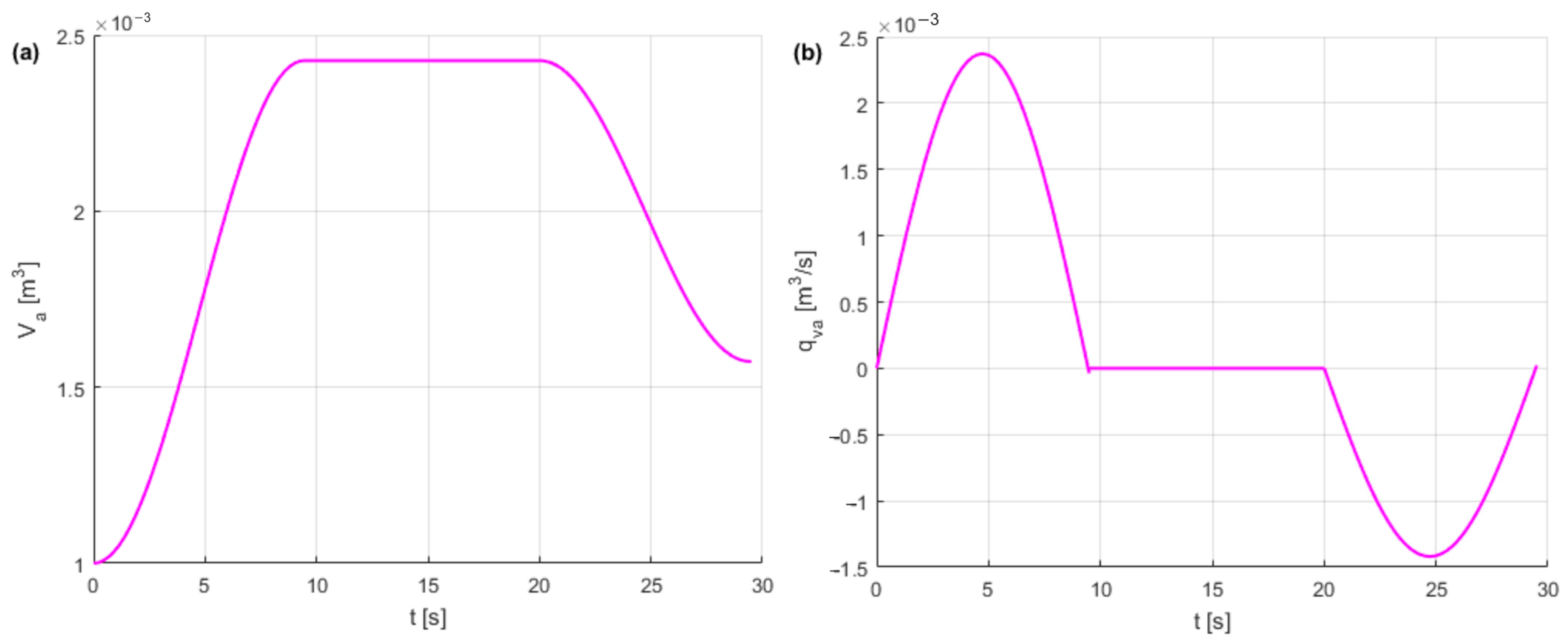
- Dindorf, R.; Wos, P. Energy efficiency of pressure shock damper in the hydraulic lifting and levelling module. Energies 2022, 15, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hua, L.; Zhao, X. Analysis of energy characteristic and working performance of a novel controllable hydraulic accumulator with simulation and experimental methods. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Ven, J.D. Constant pressure hydraulic energy storage through a variable area piston hydraulic accumulator. Appl. Energy 2013, 105, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ge, W.; Mo, X.; Liu, B.; Dong, D. Design of a new hydraulic accumulator for transient large flow compensation. Energies 2019, 12, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, J. Hydrospeicher mit Adsorbentien. Ph.D. Thesis, Technischen Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chioreanu, N.; Mitran, T.; Rus, A.; Beles, H. Numerical simulation of thermal-hydraulic generators running in a single regime. Cent. Eur. J. Eng. 2014, 4, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Gong, H.; Wang, L.; Yun, F. Frequency response function and design parameter effects of hydro-pneumatic tensioner for top-tensioned riser. Processes 2021, 9, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendra, P.; Gangbing, S. Shape memory alloy actuated accumulator for ultra-deepwater oil and gas exploration. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 045012. [Google Scholar]
- GlobalData Report; Leading Innovators in Hydraulic Accumulators Dredging for the Construction Industry: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.worldconstructionnetwork.com/data-insights/innovators-hydraulic-accumulators-dredging-construction/?cf-view (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Freudenberg Sealing Technologies. Innovative Lightweight Piston Accumulator for Hydraulic Systems in Hybrid Powertrains; Freudenberg Sealing Technologies GmbH & Co. KG: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; Available online: https://www.fst.com/-/media/files/pr/2017/2017-07/freudenberg-lightweightpistonaccumulator_press.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2017).
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P.; Ma, W.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X. Study on optimization of thermal spinning process of accumulator shell. Mech. Ind. 2020, 21, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Battery | Ultracapacitor | HPA |
|---|---|---|
| Mass 9.8 kg | Mass 12.2 g | Mass 4.53 kg |
| Energy capacity 1127 Wh | Energy capacity 1.82 Wh | Energy capacity 1.77 Wh |
| Voltage 48 V | Voltage 2.7 V | Volume capacity 950 cm3 |
| Current 60 A | Current 6.1 A | Pressure 207 bar |
| Energy Storage | Energy/Volume Wh/m3 | Energy/Mass Wh/kg | Cost/Energy EUR/Wh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | 195,144 | 115.2 | 0.42 |
| Ultracapacitor | 2539.70 | 2.72 | 129 |
| HPA | 1227 | 0.29 | 376 |
| Energy Storage | Power/Volume kW/m3 | Power/Mass kW/kg | Cost/Power EUR/kW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | 325.24 | 0.192 | 252 |
| Ultracapacitor | 2588 | 2.21 | 202 |
| HPA | 7548 | 2.69 | 70 |
| Vehicle Configuration | Improvement Economic Savings | Energy Consumption kW/km | Energy Cost EUR/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICE | Base data | 2568 | 0.075 |
| SHEV | 15.4% | 2174 | 0.064 |
| SHHV | 33.8% | 1700 | 0.045 |
| PHEV | 38.2% | 1586 | 0.046 |
| PHHV | 35.9% | 1646 | 0.044 |
| EV | 72.6% | 513 | 0.020 |
| HEHV | 75.7% | 455 | 0.018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dindorf, R.; Takosoglu, J.; Wos, P. Review of Hydro-Pneumatic Accumulator Models for the Study of the Energy Efficiency of Hydraulic Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186472
Dindorf R, Takosoglu J, Wos P. Review of Hydro-Pneumatic Accumulator Models for the Study of the Energy Efficiency of Hydraulic Systems. Energies. 2023; 16(18):6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186472
Chicago/Turabian StyleDindorf, Ryszard, Jakub Takosoglu, and Piotr Wos. 2023. "Review of Hydro-Pneumatic Accumulator Models for the Study of the Energy Efficiency of Hydraulic Systems" Energies 16, no. 18: 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186472
APA StyleDindorf, R., Takosoglu, J., & Wos, P. (2023). Review of Hydro-Pneumatic Accumulator Models for the Study of the Energy Efficiency of Hydraulic Systems. Energies, 16(18), 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186472







