Physical and Numerical Simulation of Tight Gas Flow at the Microscale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods
2.1. Basic Methods and Principles of the LBM
2.1.1. Basic Theory of the LBM
2.1.2. Boundary Conditions
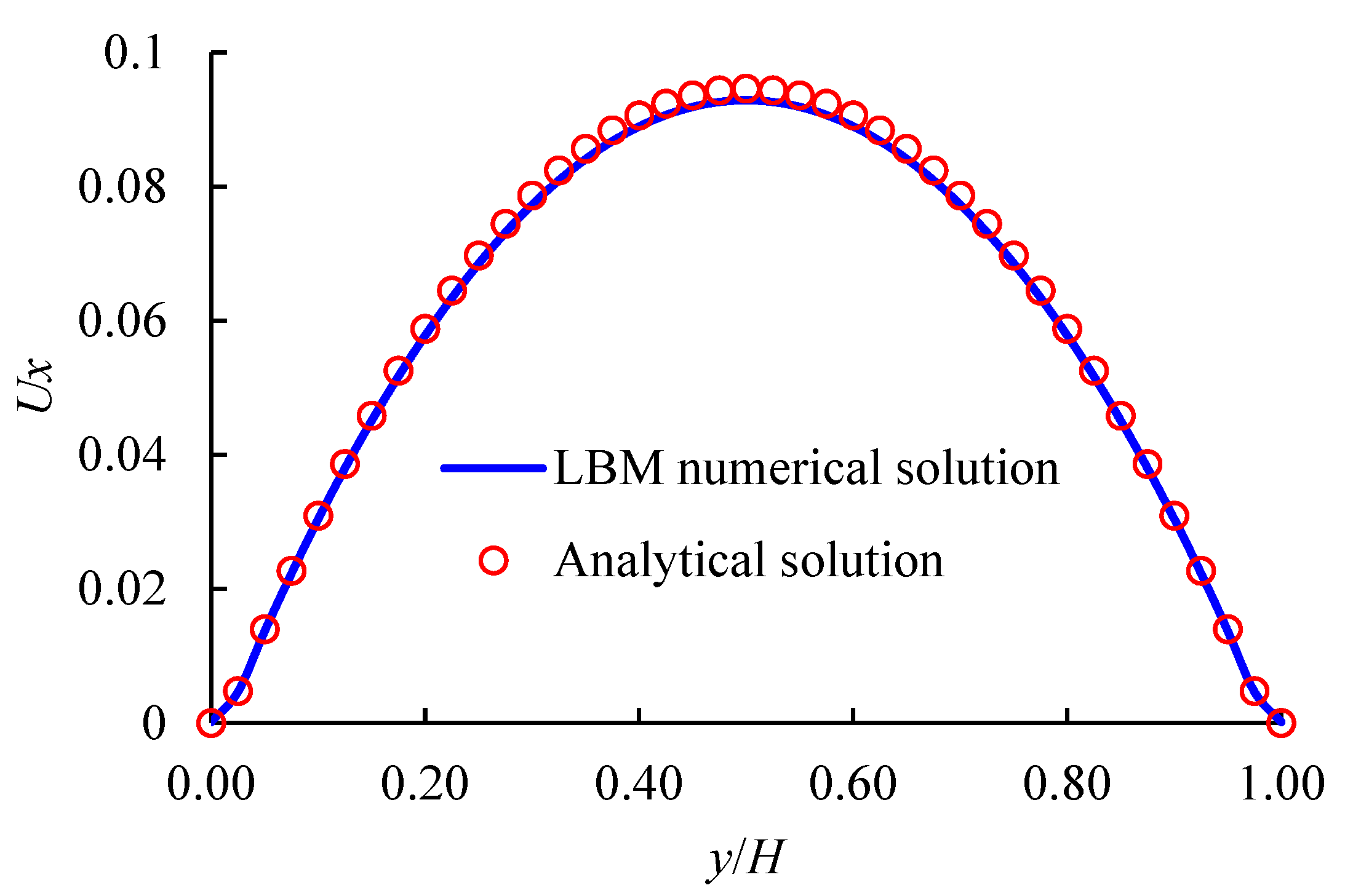
2.1.3. Model Validation
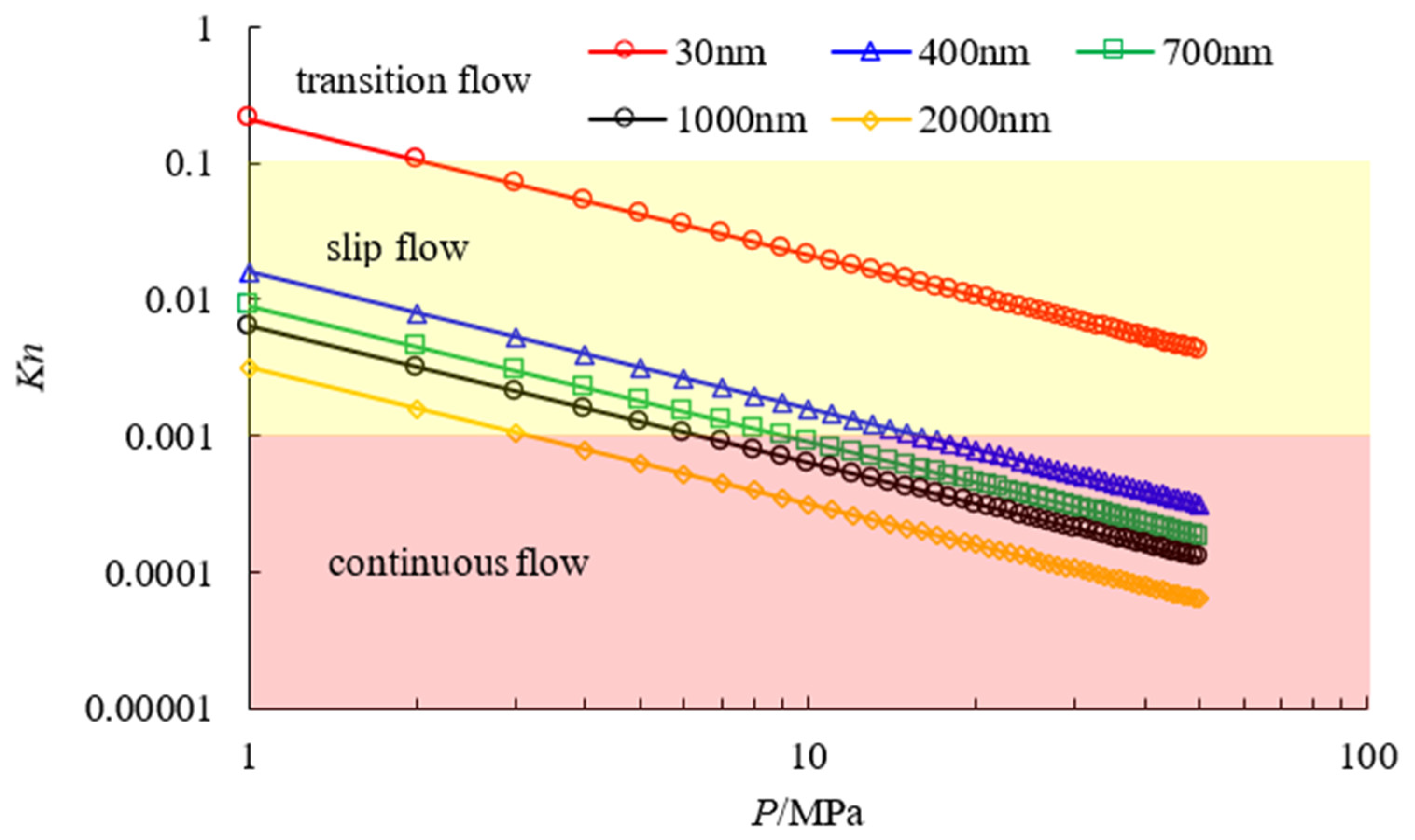
2.1.4. Applicability of the LBM Model
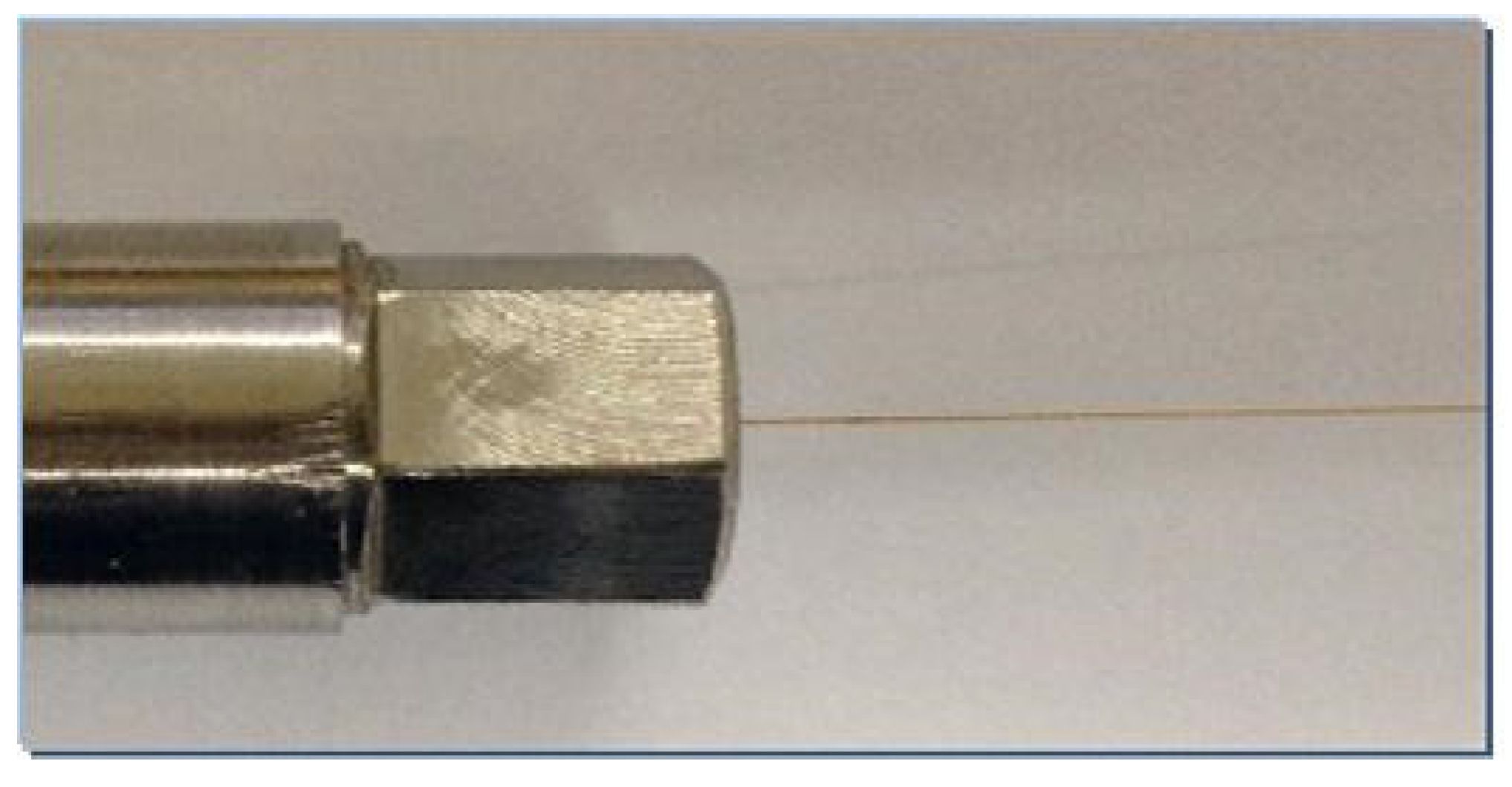
2.2. Microscale Gas Seepage Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.2. LBM Simulation of Gas Seepage in Parallel Micron Tubes
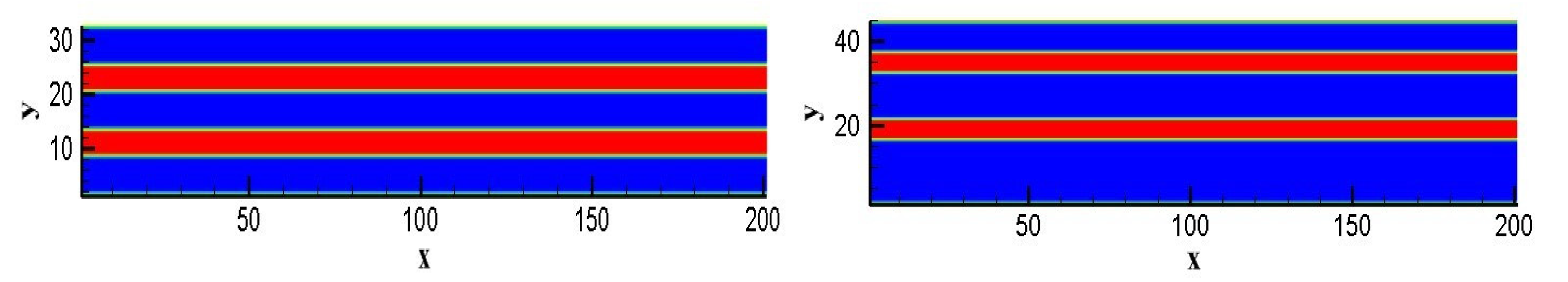
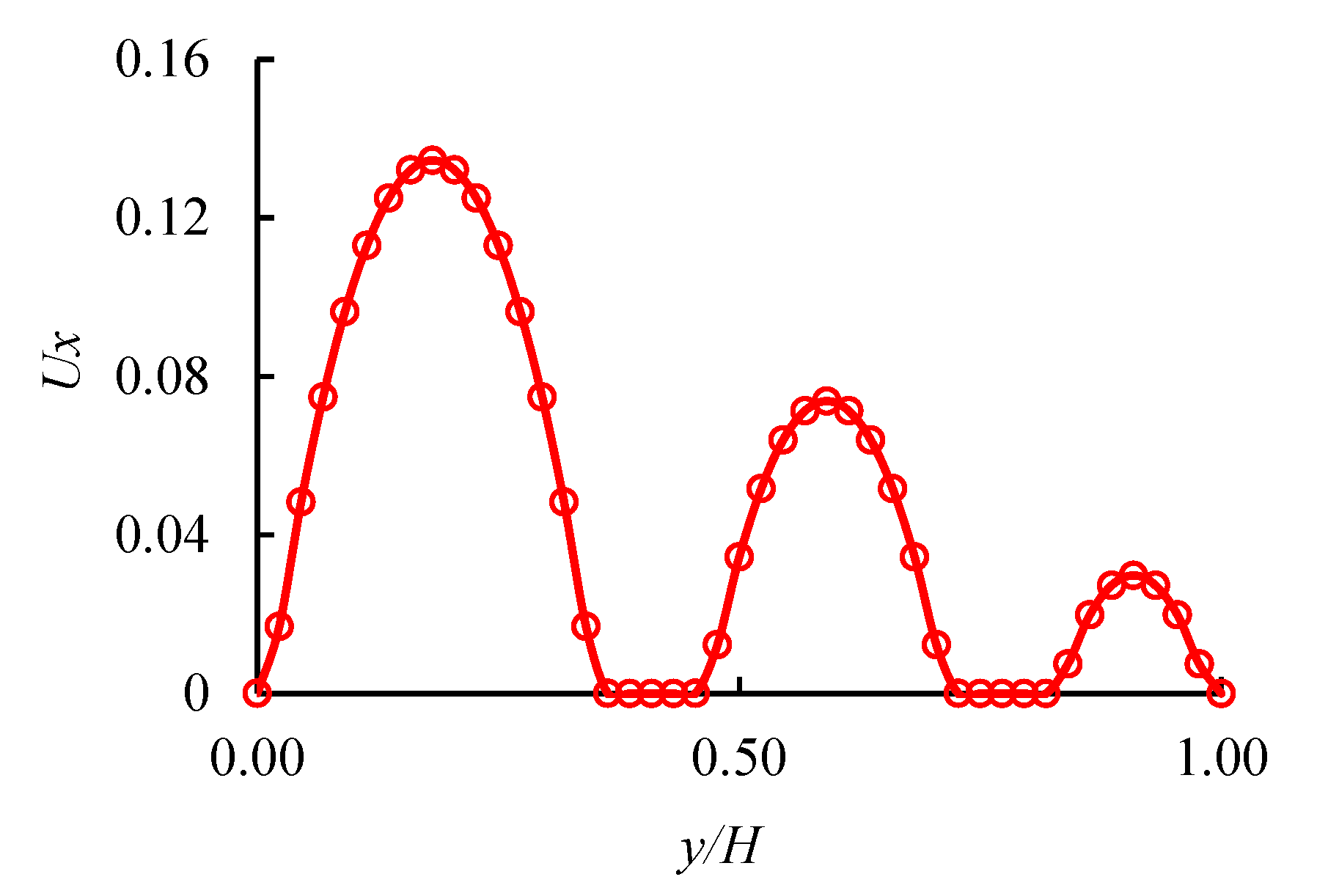
3.2.1. Disconnected Micron Tubes
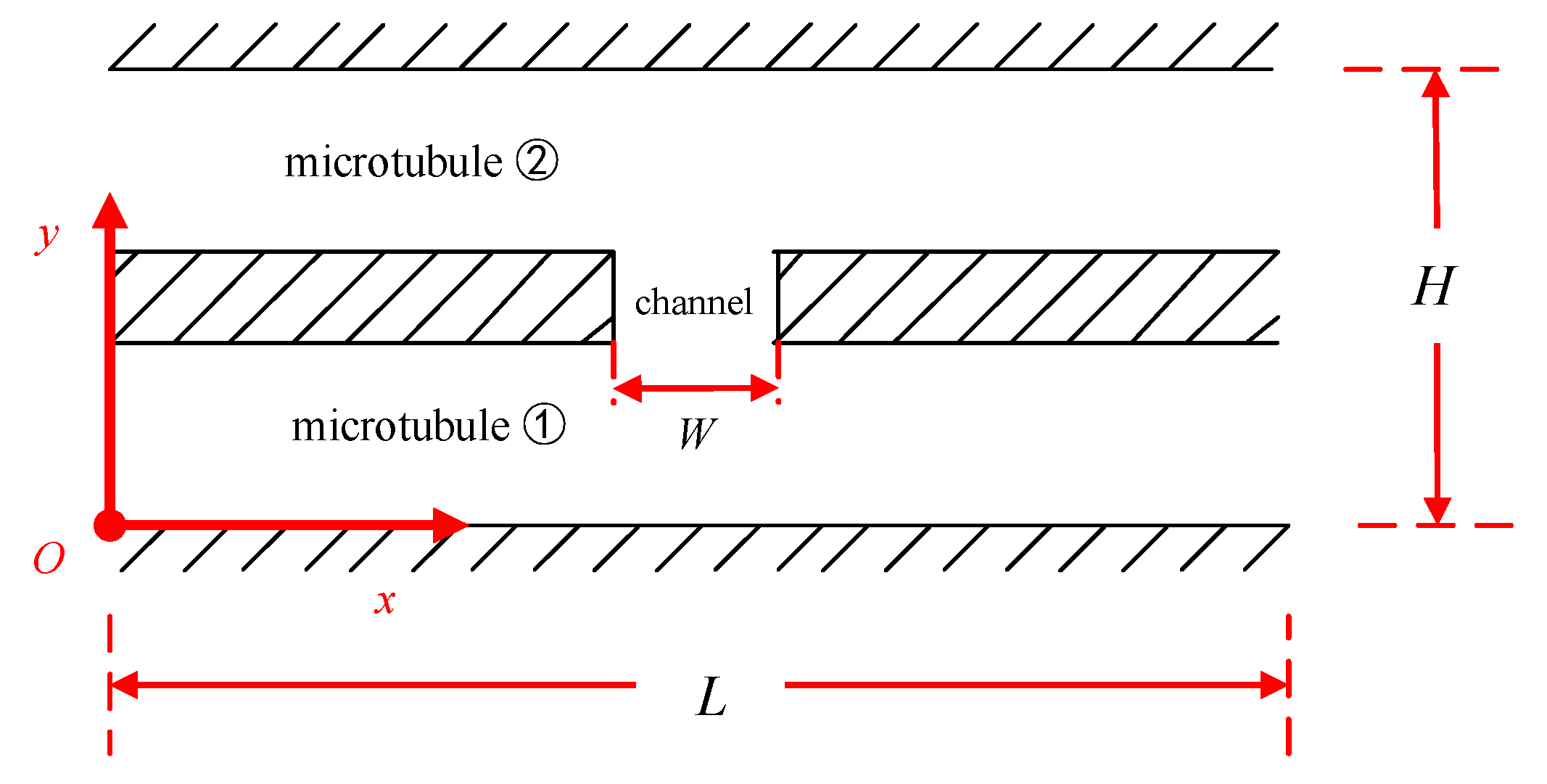
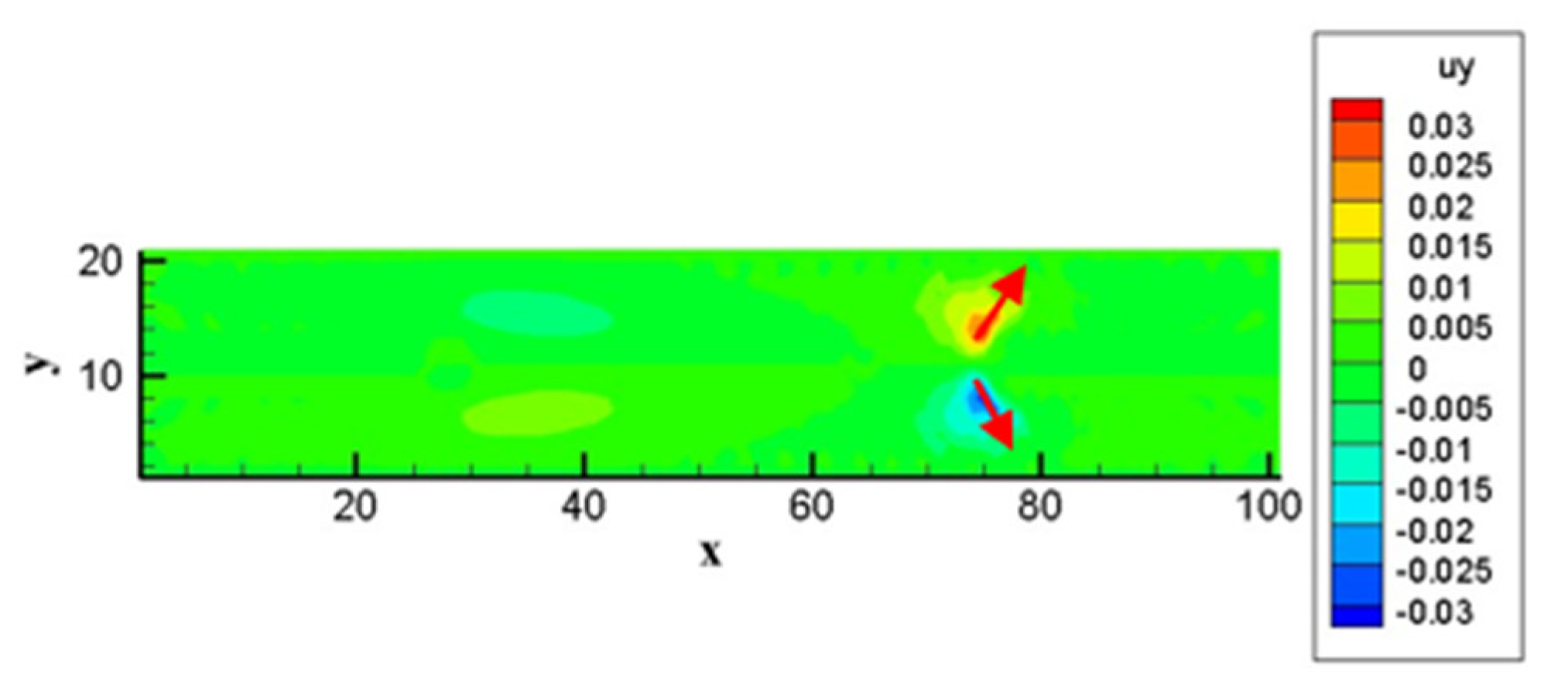
3.2.2. Interconnecting Parallel Micron Tubes
Influence of Channel Width on Seepage
Influence of Pore Size Ratio on Seepage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfahler, J.N.; Harley, J.; Bau, H.; Zemel, J. Gas and Liquid Flow in Small Channels. ASMEDSC 1991, 32, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.B.; Barrori, R.F.; Warrington, R.O. Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Micron tubes. ASMEDSC 1991, 32, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.H.; Yao, J.C.; Sun, D.J.; Cai, Y. Experimental Measurement of Gas Flow in a Microscale Circular Tube. Exp. Mech. 2001, 16, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.X. Effects of Compressibility and Roughness on Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics in Micron Tubes; Tsinghua University: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Thorne, D.T.; Schaap, M.G.; Sukop, M.C. Proposed Approximation for Contact Angles in Shan-and-Chen-type Multicomponent Multiphase Lattice Boltzmann Models. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 066701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kang, Q.; Leonardi, C.R.; Schmieschek, S.; Narváez, A.; Jones, B.D.; Williams, J.R.; Valocchi, A.J.; Harting, J. Multiphase Lattice Boltzmann Simulations for Porous Media Applications. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 20, 777–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Boek, E.S. A Comparsion Study of Multi-component Lattice Boltzmann Models for Flow in Porous Media Applications. Comput. Math. Appl. 2015, 65, 882–890. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.B.; Wang, L.; Lu, X.Y. Evaluation of Three Lattice Boltzmann Models for Multiphase Flows in Porous Media. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 61, 3606–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.M.; Hosseini, A.; Pop, I.; Kumar, S.; Freidoonimehr, N. Comparative Numerical Study of Single and two-phase Models of Nanofluid Heat Transfer in Wavy Channel. Appl. Math. Mech. 2014, 35, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A.; Wajid, H.A.; Rashidi, M.M. Numerical Modeling of Capillary-gravity Waves Using the Phase Field Method. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2014, 21, 1450036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boek, E.S.; Venturoli, M. Lattice Boltzmann Studies of Fluid Flow in Porous Media with Realistic Rock Geometries. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 59, 2305–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H. An integrated model with stable numerical methods for fractured underground gas storage. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 393, 136268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, Q.; Sohail, G.M.; Liu, K.Y.; Du, Q.Z.; Boateng, C.D. Study on brittleness templates for shale gas reservoirs—A case study of Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin, southern China. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1370–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Yang, E.Q.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.R. Pore and fracture characteristics of Cretaceous tight reservoir and its control effect on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Liuhe Basin. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.S.; Fan, X.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Q.; Lu, C.; Zhou, Z.L.; Jiang, D.W.; Zhan, J. Modeling transient flow behavior with the high velocity non-Darcy effect in composite naturally fractured-homogeneous gas reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 96, 104269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; Dong, P.C.; Yuan, Z.C.; Zhang, X.J.; Cao, N.; Yang, S. Study on Microscale Effect of Tight Gas Reservoir Based on Lattice Boltzmann Method. Fault Block Oil Field 2016, 23, 793–796. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, B. Influence of Pore Throat Structure on Microscale Seepage Characteristics of Tight Gas. Nat. Gas Ind. 2019, 39, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, E.; Tinni, A.; Akkutlu, I.Y. Correction to Klinkenberg Slip Theory for Gas Flow in Nano-capillaries. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoul, N.M.; Mahmoud, J. Study of Slip Flow in Shale and Tight Gas Reservoir Rocks Using Lattice Boltzmann Method. In Proceedings of the 79th EAGE Conference and Exhibition, Paris, France, 12–15 June 2017. Paper SPE-185807. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.H.; d’Humieres, D.; Lallemand, P. Lattice BGK models for Navier-Stokes equation. Eurphys. Lett. 1992, 17, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.L.; Zhen, C.G. The Principle and Application of Lattice Boltzmann Method; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Q.S.; He, X.Y. On Pressure and Velocity Boundary Conditions for The Lattice Boltzmann BGK Model. Phys. Fluid 1997, 9, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.H. Study on Microscale Gas Flow Characteristics; University of Science and Technology of China: Hefei, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.H. Pore-throat Sizes in Sandstones, Tight Sandstones, and Shales. AAPG Bull. 2009, 93, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhu, R.K.; Wu, S.T.; Yang, Z.; Tao, S.; Yuan, X.; Hou, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, D.; et al. Types, Characteristics, Genesis and Prospects of Conventional and Unconventional Hydrocarbon Accumulations: Taking Tight Oil and Tight Gas in China as An Instance. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zou, C.N.; Wu, S.T.; Tao, S.Z.; Hou, L.H.; Zhu, R.K.; Yuan, X.J. Characteristics of Nano-Sized Pore-throat in Unconventional Tight Reservoir Rocks and Its Scientific Value. J. Shenzhen Univ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 32, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.M.; Yue, X.G.; Wang, F.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Y. Flow Characteristics of High Pressure Gas in Microcircular Tube. J. China Univ. Pet. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2012, 36, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.Z. Rarefaction Effect and Compressibility Effect of Gas Flow in Micro Circular Tube. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2001, 29, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.B.; Xu, B.; Xue, H.; Wu, J. Analysis of Rarefied Gas Flow Characteristics and Research Status. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2005, 26, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.C.; Fei, L.S. Small Flow Gas Flow Measurement Method and Application. Rocket. Propuls. 2009, 35, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, G. Preparation and Properties of Flexible Silica Aerogel; Beijing University of Chemical Technology: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.M.; Gao, S.S.; Xue, H.; Ye, L.Y.; Liu, H.X.; Shen, R.; Zhu, W.Q. Micron Tube Gripper. Beijing CN104533398B, 7 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Song, F.Q.; Hu, X. Characteristics of Fluid Flow in Nanotubes. In Abstract Collection of the 10th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics; Chinese Society of Mechanics: Hangzhou, China, 2018; pp. 218–219. [Google Scholar]










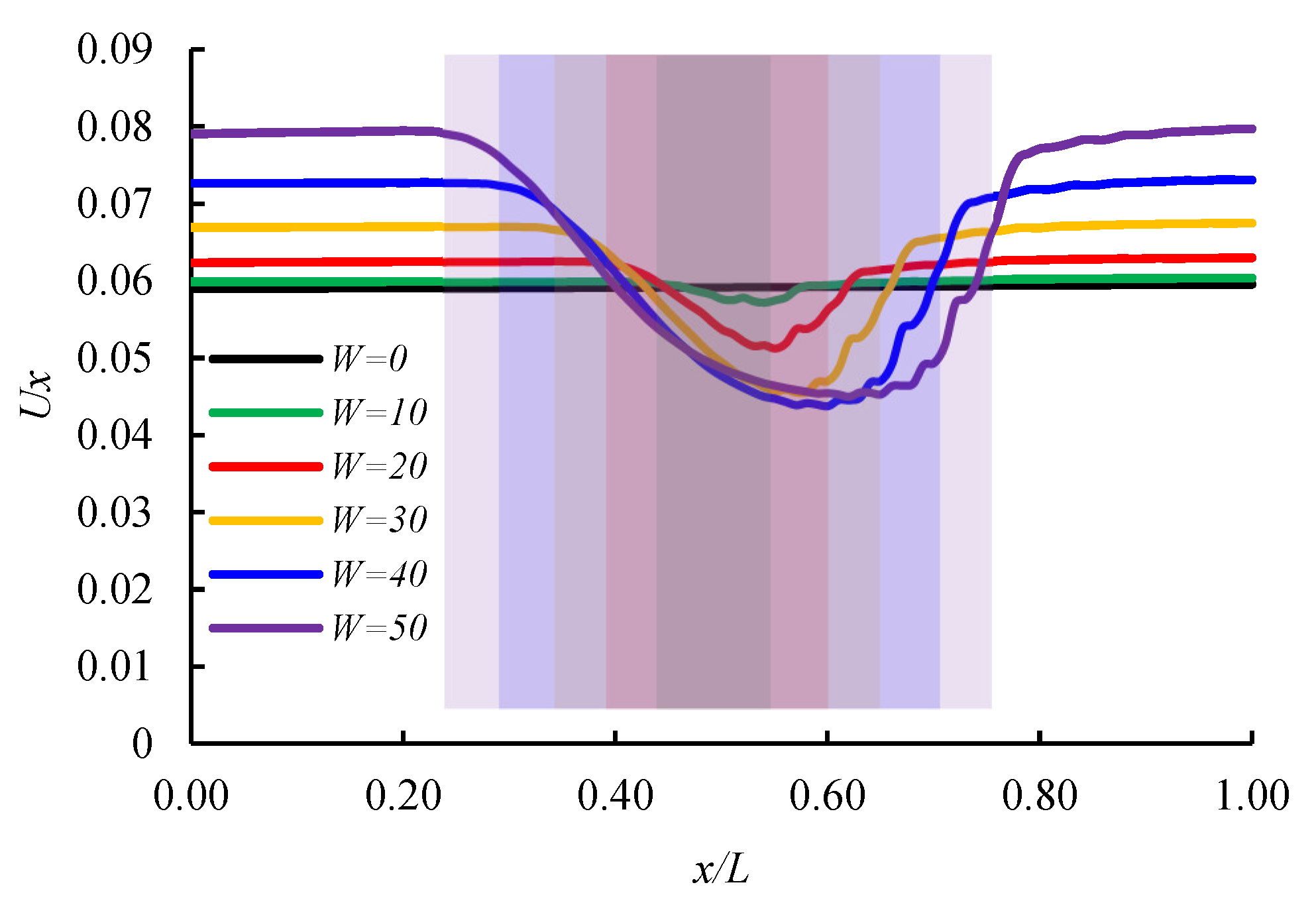




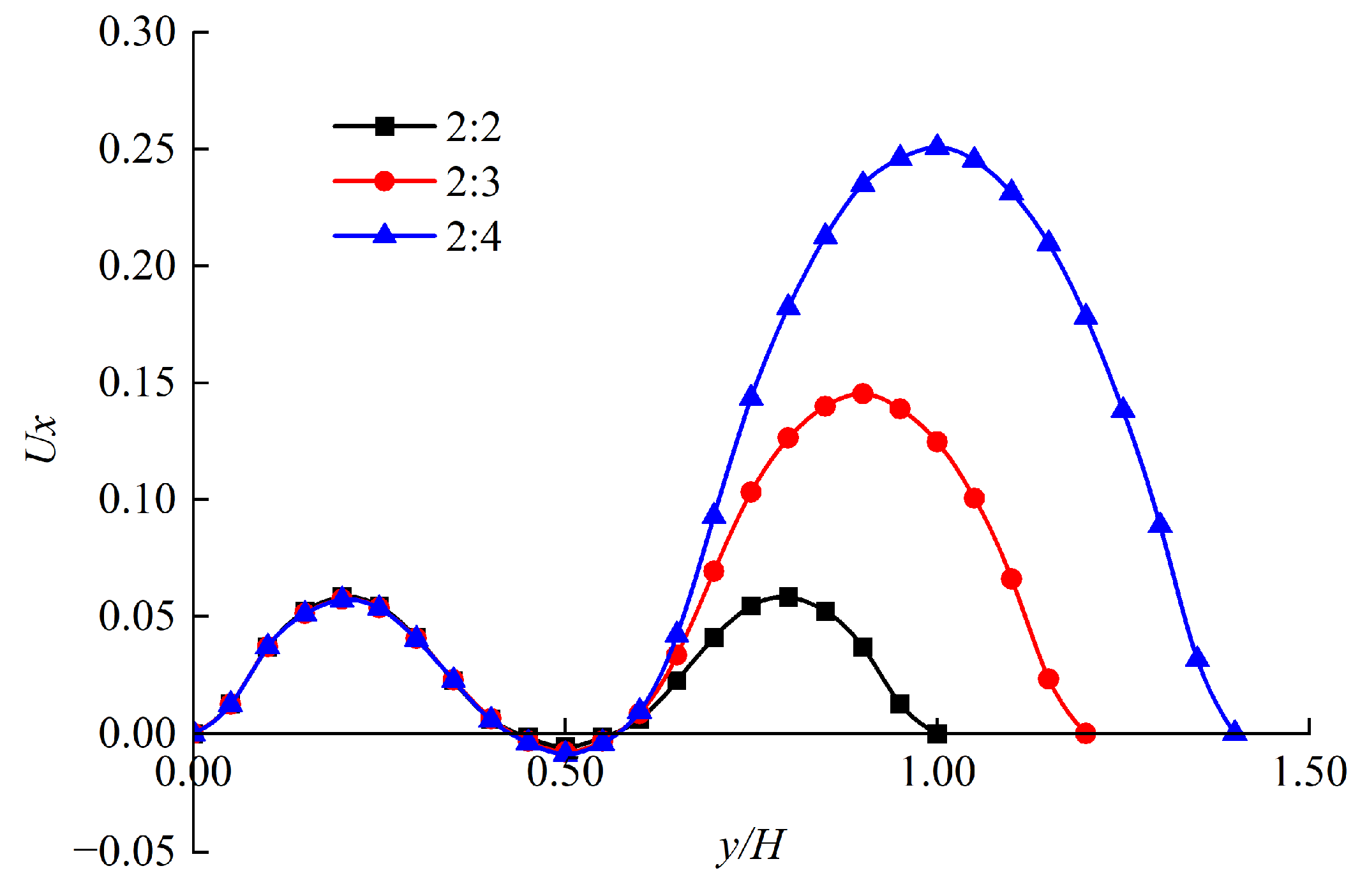
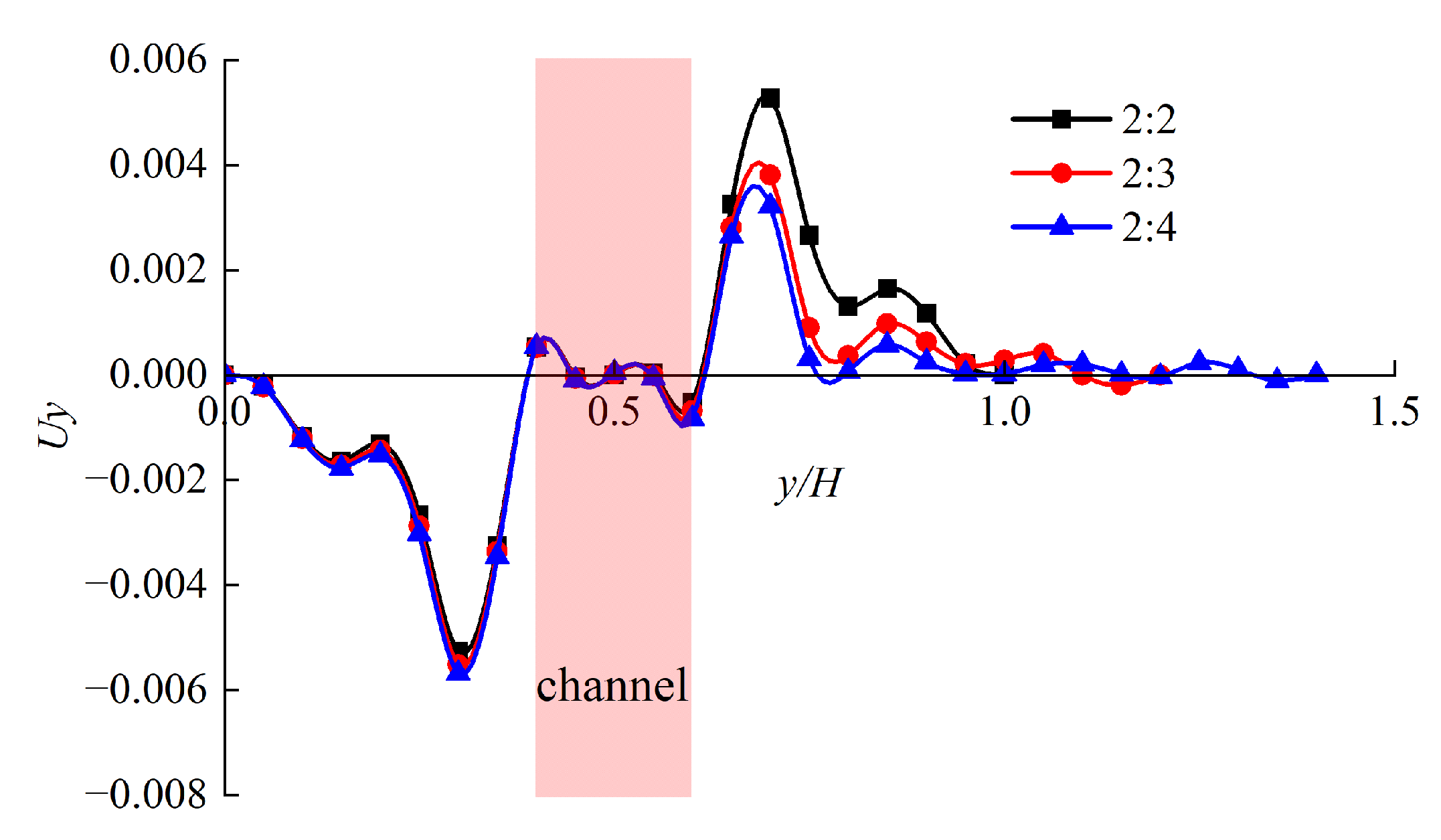
| Width of Channel W | Velocity Ux at the Outlet | Percentage Velocity Drop at the Center/% | Flow Rate | Percentage Change of Flow Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0595 | 0 | 2.4225 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.0604 | 5.12 | 2.5075 | 3.51 |
| 20 | 0.0630 | 18.49 | 2.6460 | 9.23 |
| 30 | 0.0675 | 32.39 | 2.8467 | 17.51 |
| 40 | 0.0732 | 39.95 | 3.0918 | 27.63 |
| 50 | 0.0797 | 43.45 | 3.3812 | 39.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Xiong, W.; Ye, L.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Mu, Y.; Niu, W. Physical and Numerical Simulation of Tight Gas Flow at the Microscale. Energies 2023, 16, 5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165937
Zhang J, Gao S, Xiong W, Ye L, Liu H, Zhu W, Mu Y, Niu W. Physical and Numerical Simulation of Tight Gas Flow at the Microscale. Energies. 2023; 16(16):5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165937
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianzhong, Shusheng Gao, Wei Xiong, Liyou Ye, Huaxun Liu, Wenqing Zhu, Ying Mu, and Wente Niu. 2023. "Physical and Numerical Simulation of Tight Gas Flow at the Microscale" Energies 16, no. 16: 5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165937
APA StyleZhang, J., Gao, S., Xiong, W., Ye, L., Liu, H., Zhu, W., Mu, Y., & Niu, W. (2023). Physical and Numerical Simulation of Tight Gas Flow at the Microscale. Energies, 16(16), 5937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165937






