Experimental Study on Wind Turbine Airfoil Trailing Edge Noise Reduction Using Wavy Leading Edges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Set-Up and Procedures
2.1. Design of Wavy Leading Edges
2.2. Test Facility and Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussions
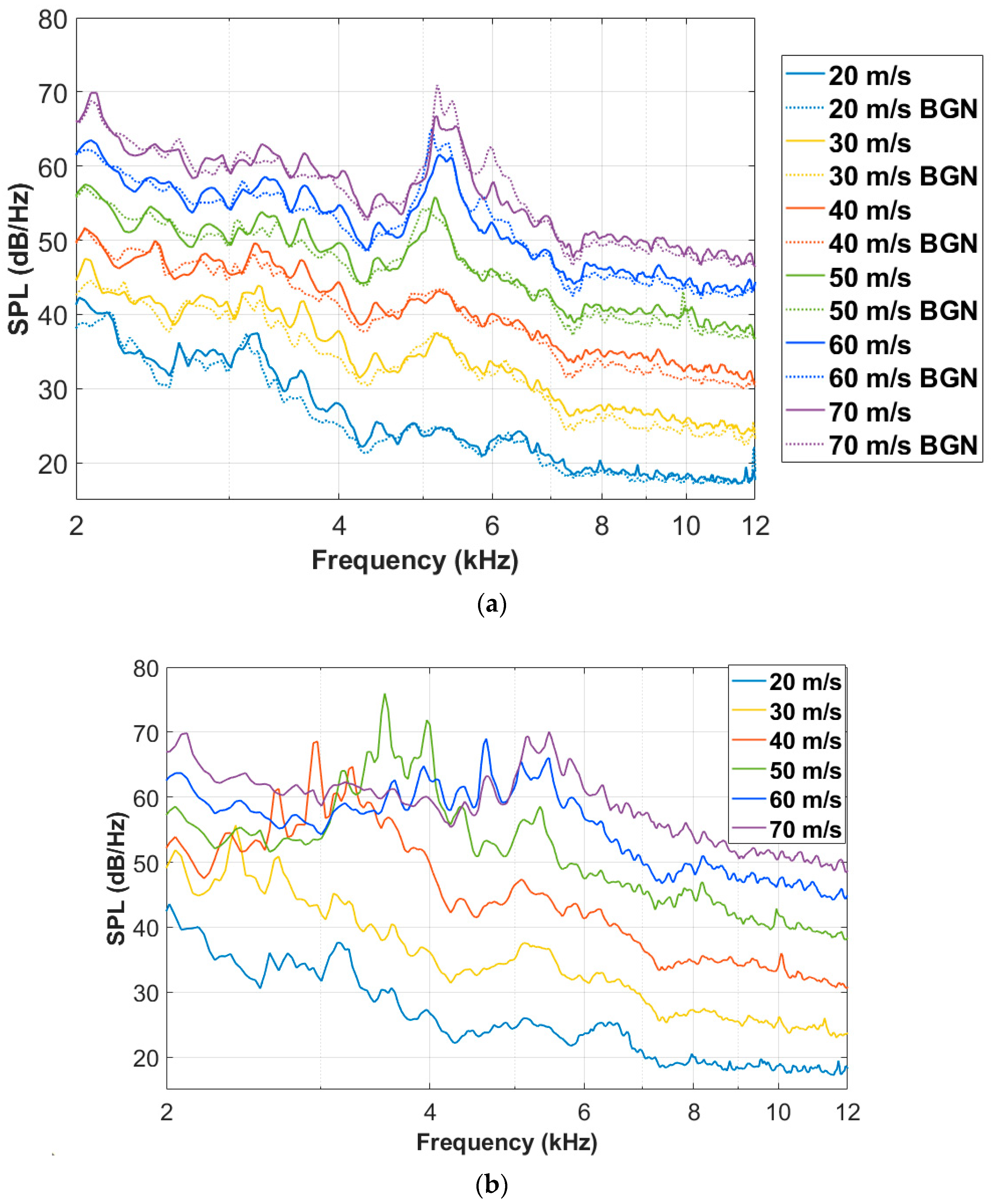
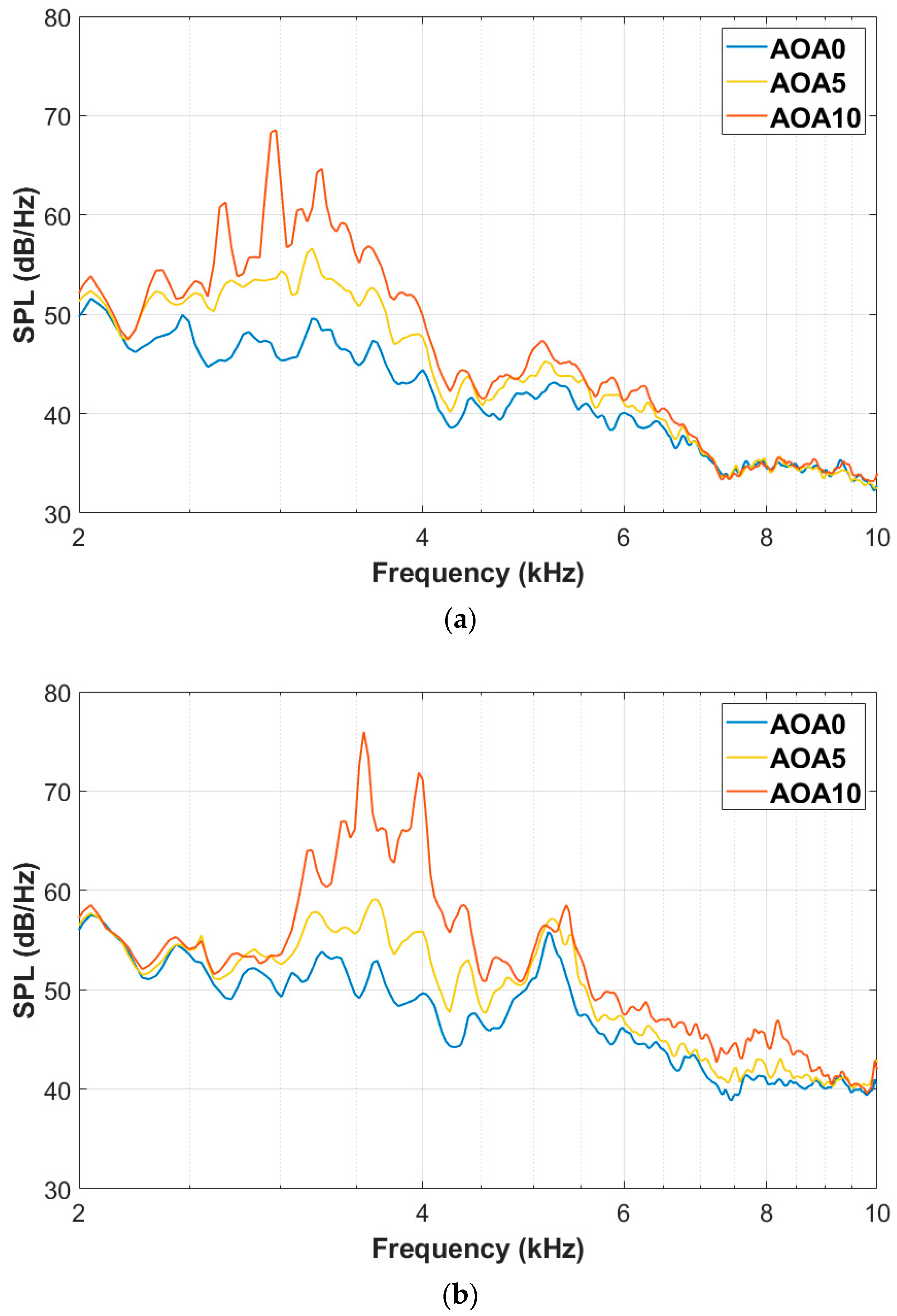
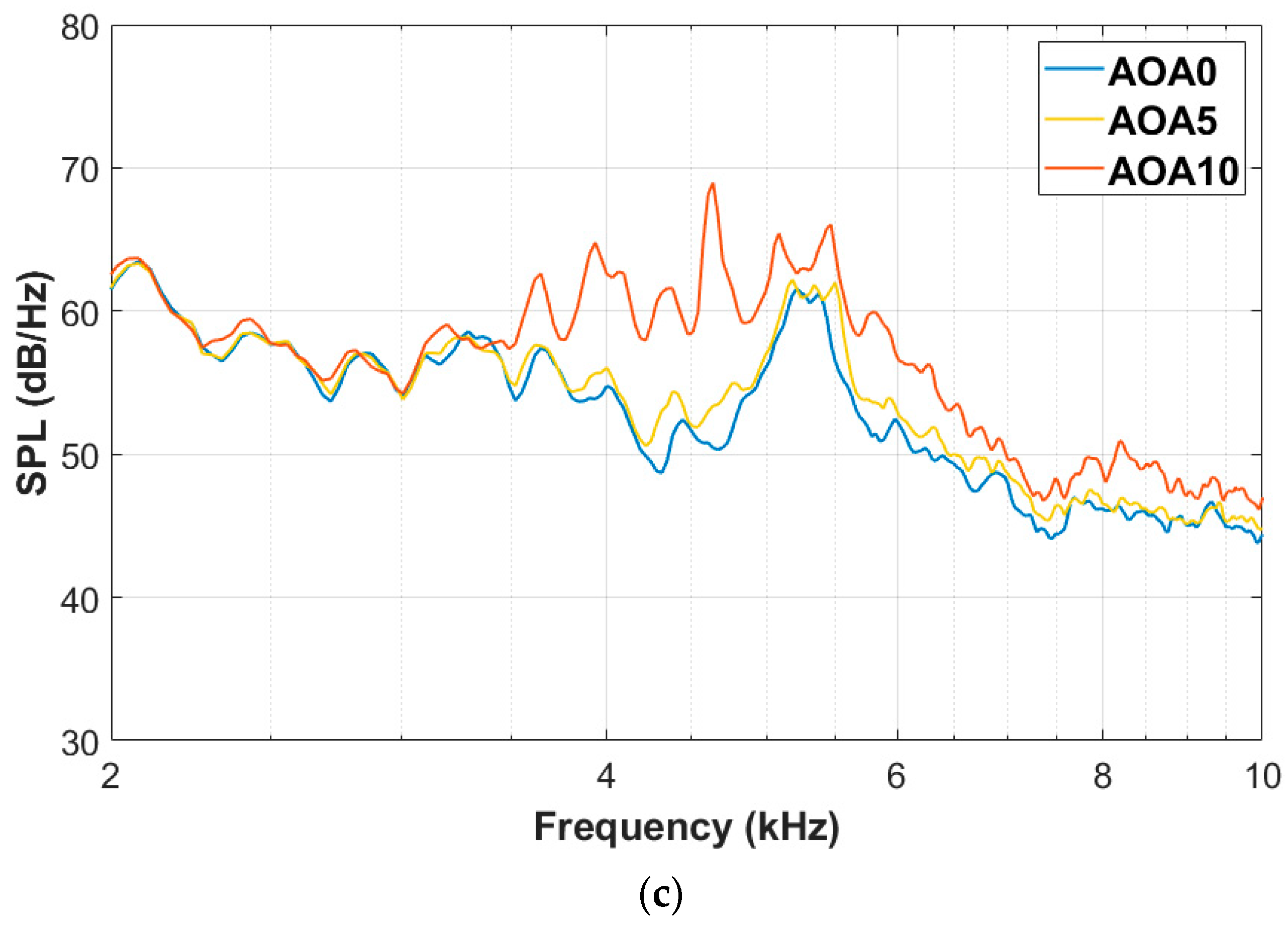
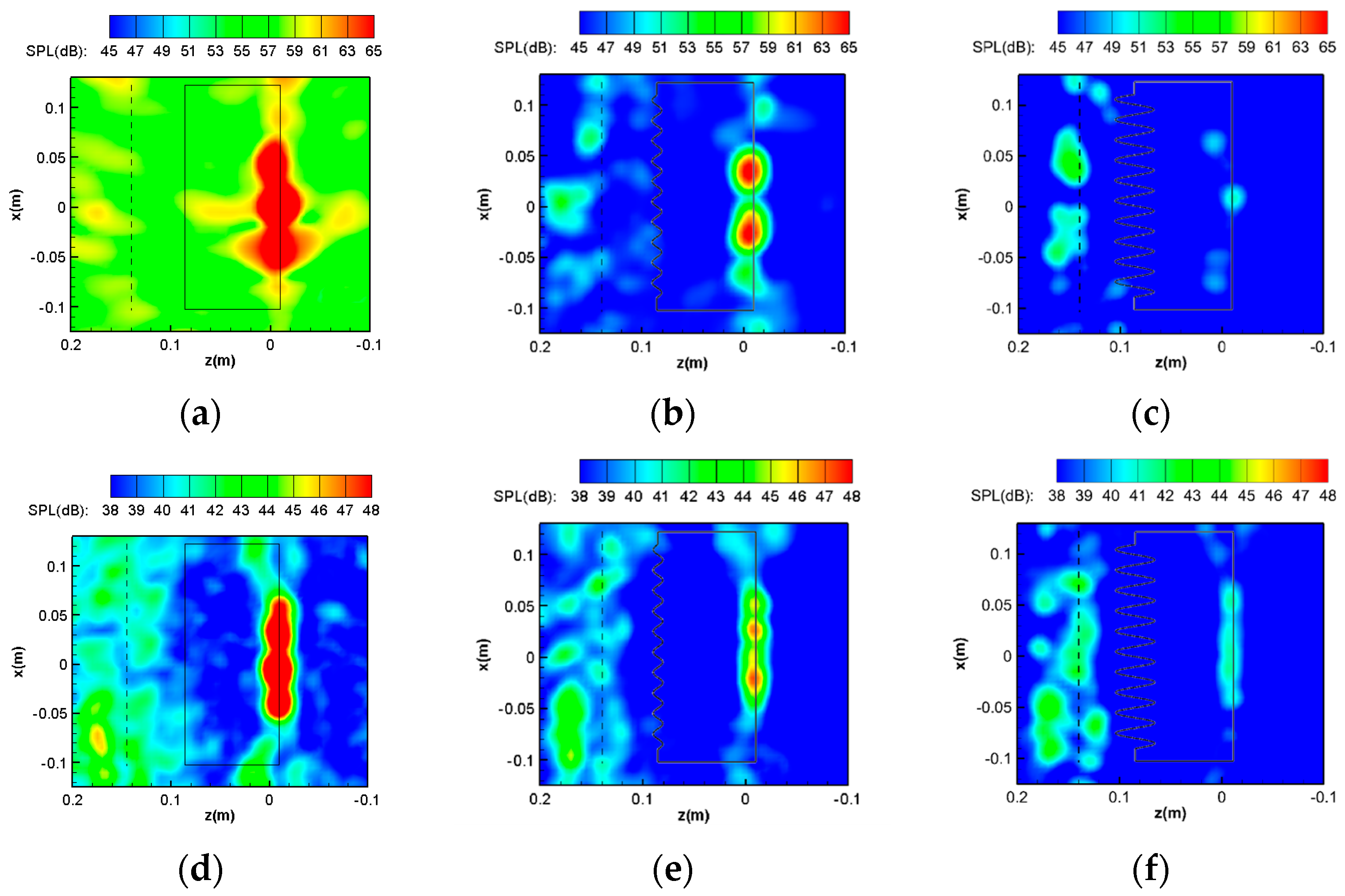
3.1. Noise Radiations of the Baseline Airfoil
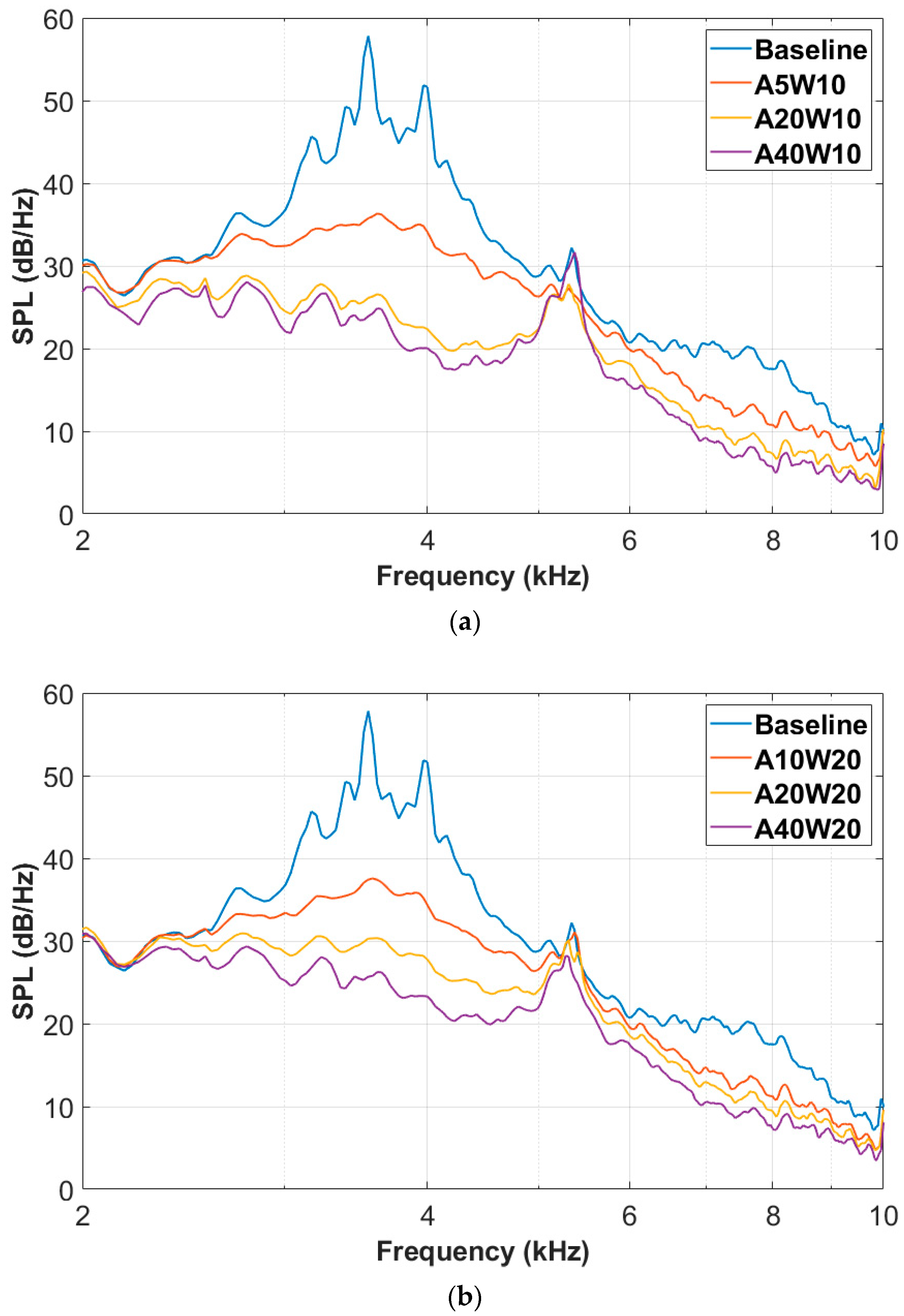
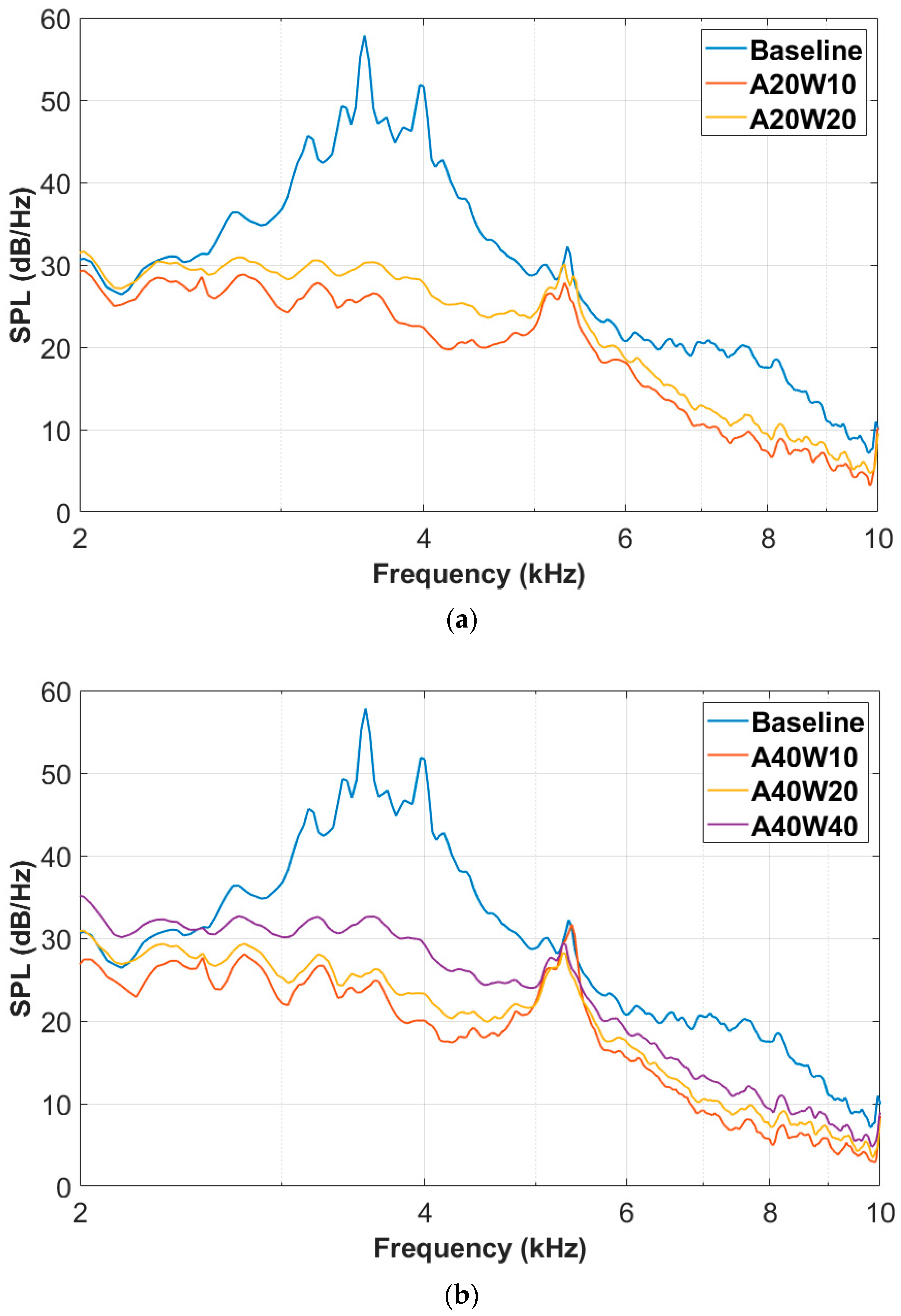
3.2. Noise Reduction Effect of the Wavy Airfoil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lund, H. Renewable energy strategies for sustainable development. Energy 2007, 32, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Global Wind Energy Council. Global Wind Report 2023. Available online: https://gwec.net/globalwindreport2023/ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Saidur, R.; Rahim, N.A.; Islam, M.R.; Solangi, K.H. Environmental impact of wind energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, C.; Lefèvre, M.; Champelovier, P.; Lambert, J.; Laumon, B.; Evrard, A.-S. Aircraft Noise and Psychological Ill-Health: The Results of a Cross-Sectional Study in France. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ageborg, M.J.; Smith, M.G.; Ogren, M.; Thorsson, P.; Pedersen, E.; Forssen, J.; Persson, W.K. Wind turbine noise and sleep: Pilot studies on the influence of noise characteristics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaßner, L.; Blumendeller, E.; Müller, F.J.; Wigger, M.; Rettenmeier, A.; Cheng, P.W.; Hübner, G.; Ritter, J.; Pohl, J. Joint analysis of resident complaints, meteorological, acoustic, and ground motion data to establish a robust annoyance evaluation of wind turbine emissions. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 1072–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, C.E.; Bomberger Brown, M.; McGee, J.; Powell, L.A.; Walsh, E.J. Effects of wind turbine noise on the surrounding soundscape in the context of greater-prairie chicken courtship vocalizations. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 153, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Hansen, K. Recent Advances in Wind Turbine Noise Research. Acoustics 2020, 2, 171–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornung, C.; Lutz, T.; Krämer, E. Development of design guidelines for low noise but high yield wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Wind Turbine Noise, Lisbon, Portugal, 12–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oerlemans, S.; Sijtsma, P.; López, B.M. Location and quantification of noise sources on a wind turbine. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 299, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.F.; Pope, D.S.; Marcolini, M.A. Airfoil Self-Noise and Prediction (NASA Reference Publication); Technical Report 1218; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Lutz, T.; Herrig, A.; Würz, W.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Krämer, E. Design and wind-tunnel verification of low-noise airfoils for wind turbines. AIAA J. 2007, 45, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghyeon, K.; Cheolung, C. Development of low-noise drag-type vertical wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2015, 79, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Avallone, F.; Van Der Velden, W.C.P.; Ragni, D.; Casalino, D. Noise reduction mechanisms of sawtooth and combed-sawtooth trailing-edge serrations. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 848, 560–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Cao, H.; Zhang, M.; Liao, C.; Zhou, T. Optimal design of aeroacoustic airfoils with owl-inspired trailing-edge serrations. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 16, 056004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showkat, A.S.A.; Azarpeyvand, M.; Ilário, D.S.C.R. Trailing-edge flow and noise control using porous treatments. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 850, 83–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fish, F.E.; Battle, J.M. Hydrodynamic design of the Humpback Whale Flipper. J. Morphol. 1995, 225, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.L.; Kelso, R.M.; Doolan, C.J. Reduction of flow induced tonal noise through leading edge tubercle modifications. In Proceedings of the 16th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Stockholm, Sweeden, 7–9 June 2010; p. 3700. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, M.; Joseph, P.F.; Polacsek, C.; Chong, T.P. Noise reduction using combined trailing edge and leading edge serrations in a tandem airfoil experiment. In Proceedings of the 18th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference (33rd AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2012; p. 2134. [Google Scholar]
- Feinerman, J.A.; Koushik, S.; Schmitz, F.H. Effect of leading-edge serrations on helicopter blade-vortex interaction noise. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2017, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Qiao, W.Y.; Tong, F. Experimental investigation of wavy leading edges on rod-aerofoil interaction noise. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 422, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Manegar, F.; Carouls, T.; Binois, R. Experimental investigation of self-aligning trailing edge serrations for airfoil noise reduction. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Wind Turbine Noise, Lisbon, Portugal, 12–14 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitanya, P.; Joseph, P.; Narayanan, S. Performance and mechanism of sinusoidal leading edge serrations for the reduction of turbulenc-aerofoil interaction noise. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 818, 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, F.G.; Gill, J.; Angland, D. Wavy leading edge airfoils interacting with anisotropic turbulence. In Proceedings of the 23rd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 5–9 June 2017; p. 3370. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.J.; Qiao, W.Y.; Tong, F.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, X.N. Numerical investigation of wavy leading edges on rod-airfoil interaction noise. AIAA J. 2018, 56, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qiao, W.; Duan, W.; Wei, Z. Experimental study of airfoil instability noise with wavy leading edges. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 172, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, G.; Chaitanya, P.; Kim, J.H.; Berk, T.; Joseph, P.; Choi, K.S.; Ganapathisubramani, B.; Hasheminejad, S.M.; Chong, T.P.; Stalnov, O.; et al. Leading edge serrations for the reduction of aerofoil self-noise at low angle of attack, pre-stall and post-stall conditions. Int. J. Aeroacoust. 2021, 20, 130–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, K.S.; Lacagnina, G.; Chaitanya, P.; Joseph, P.; Hasheminejad, S.M.; Pei Chong, T.; Shahab, M.F.; Omidyeganeh, M.; Pinelli, A. Aerodynamic and aeroacoustic optimization of leading-edge undulation of a naca 65 (12)-10 airfoil. AIAA J. 2022, 60, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.F.; Marcolini, M.A.; Pope, D.S. Airfoil Trailing-Edge Flow Measurements. AIAA J. 1986, 24, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijtsma, P. CLEAN based on spatial source coherence. Int. J. Aeroacoust. 2007, 6, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, T.M.; Czeckay, P.; Geyer, T.F.; Kameier, F.; Paschereit, C.O. Effect of inflow conditions on the noise reduction through leading edge serrations. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 4104–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, P.D. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
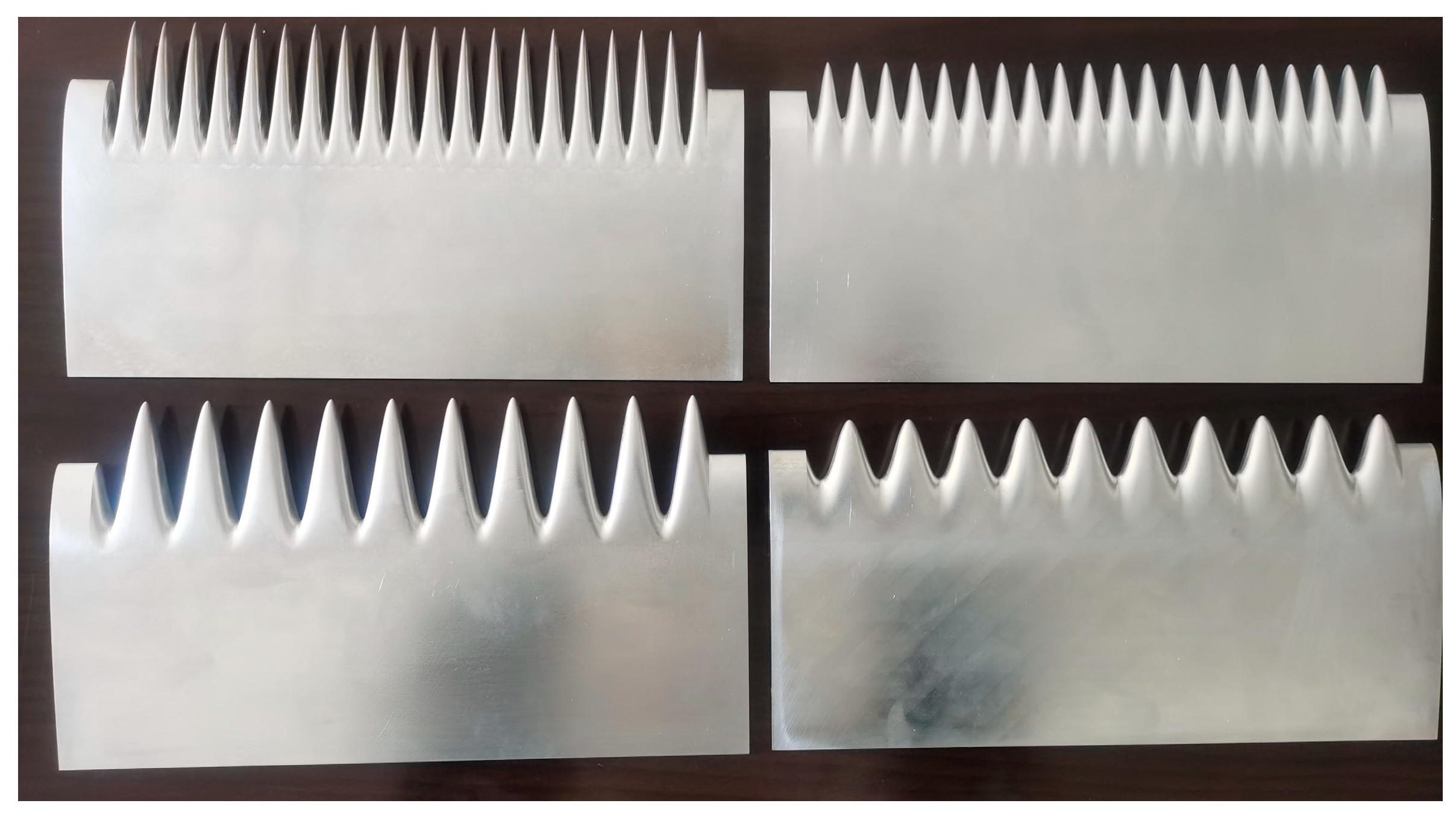
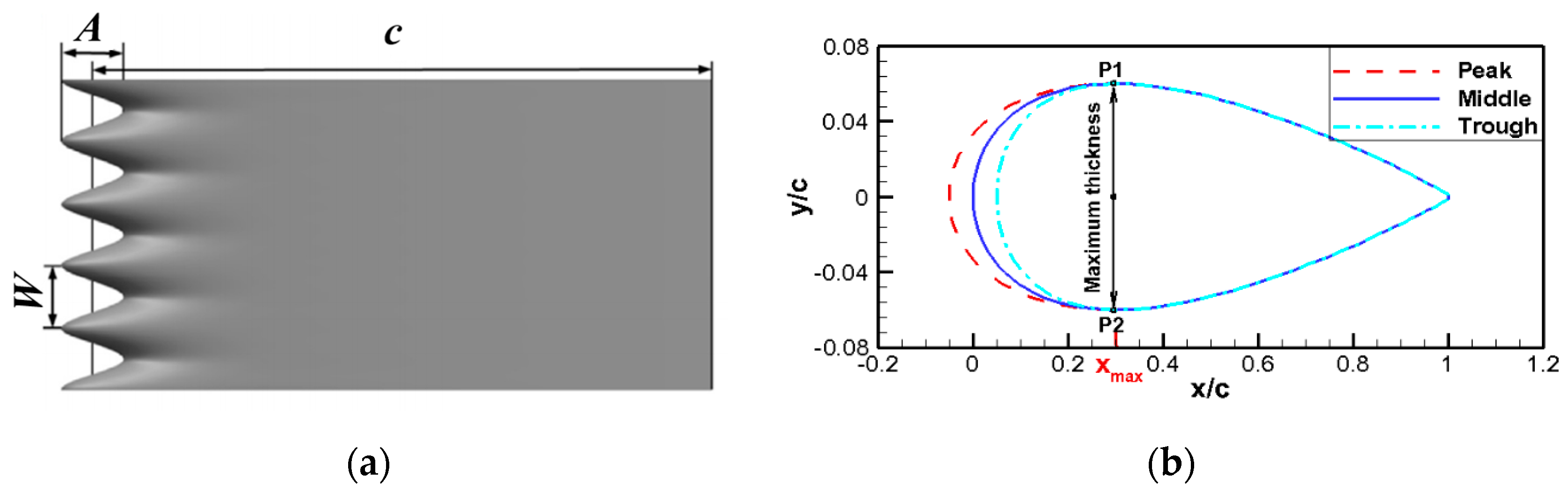

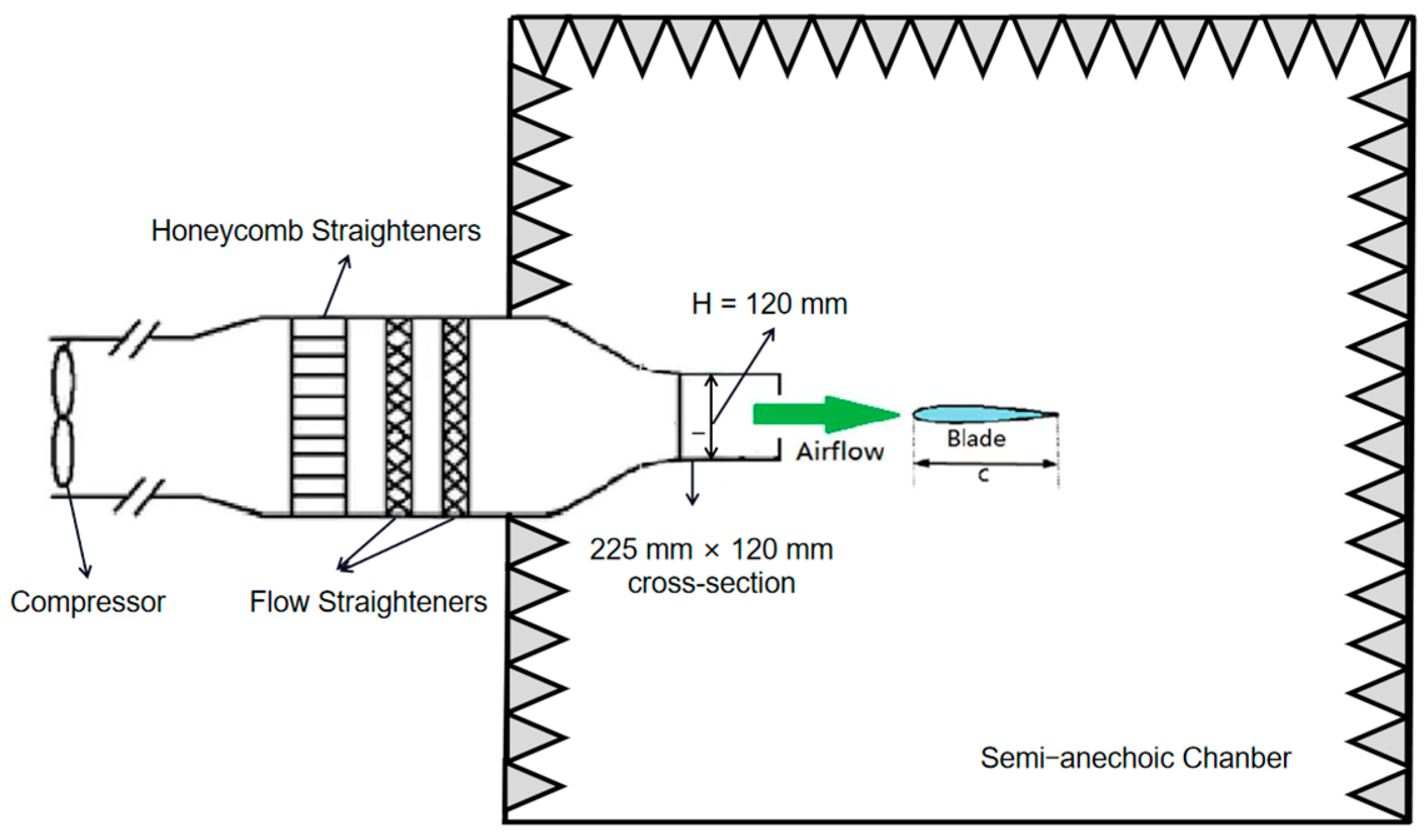

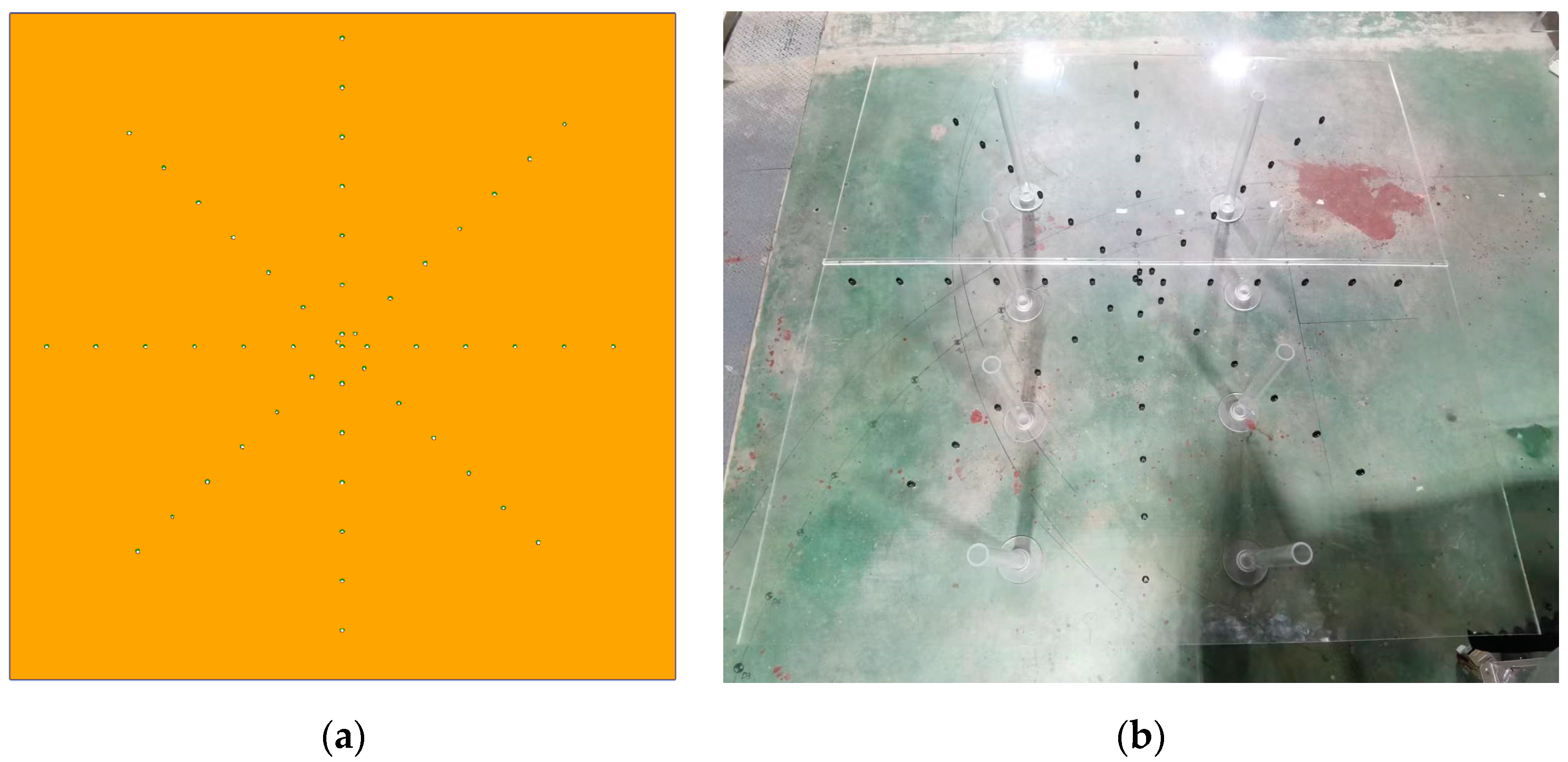


| Name | A (mm) | W (mm) | A/c (%) | W/c (%) | A/W | Wave Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| A5W10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 0.5 | 20 |
| A20W10 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 2 | 20 |
| A40W10 | 40 | 10 | 40 | 10 | 4 | 20 |
| A10W20 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 0.5 | 10 |
| A20W20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 10 |
| A40W20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 2 | 10 |
| A40W40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 1 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Tong, F.; Qiao, W. Experimental Study on Wind Turbine Airfoil Trailing Edge Noise Reduction Using Wavy Leading Edges. Energies 2023, 16, 5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165865
Xing Y, Wang X, Chen W, Tong F, Qiao W. Experimental Study on Wind Turbine Airfoil Trailing Edge Noise Reduction Using Wavy Leading Edges. Energies. 2023; 16(16):5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165865
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Yudi, Xingyu Wang, Weijie Chen, Fan Tong, and Weiyang Qiao. 2023. "Experimental Study on Wind Turbine Airfoil Trailing Edge Noise Reduction Using Wavy Leading Edges" Energies 16, no. 16: 5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165865
APA StyleXing, Y., Wang, X., Chen, W., Tong, F., & Qiao, W. (2023). Experimental Study on Wind Turbine Airfoil Trailing Edge Noise Reduction Using Wavy Leading Edges. Energies, 16(16), 5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165865








