Abstract
Early detection of faults in wind energy systems can reduce downtime, operating, and maintenance costs while increasing productivity. This paper proposes a method based on the analysis of generator stator current signals to detect faults in a wind turbine gearbox equipped with a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). A localized parameter model was established to simulate the vibratory response of a two-stage gear system under healthy and faulty conditions. The simulation was performed in the MATLAB/Simulink environment. The results include a detailed analysis of the mechanical part of the gearbox, highlighting mesh stiffness, output speed, and accelerations. Additionally, the electrical part was evaluated based on the current supplied by the doubly fed induction generator. The results were presented in the case of healthy gears and in the presence of faults such as a broken or cracked tooth. Fast Fourier transform (FFT) analysis was employed to detect gear defects in the stator current signal. The presence of a crack or broken tooth in the gearbox induces modulation of the DFIG stator current signals according to the shaft frequencies corresponding to the faulty gear. These findings provide a preliminary basis for the detection and diagnosis of this type of failure.
1. Introduction
An intricate electromechanical device called a wind turbine (WT) system transforms wind energy into electrical energy [1]. Figure 1 is an illustration of the most common setup. The three-bladed main rotor is supported by the main bearing, which also supplies the planetary gear with torque. The primary rotor is attached to a plate that serves as the planetary gear’s input. Three planets make up the planetary gear, and the shafts connecting them to the plate. The planets exert torque on the sun by rolling across the stationary ring. The planetary gear’s output is the sun shaft. Moreover, the two-stage parallel gear is dived by the sun. The parallel gear contains three shafts: the fast shaft, which drives the generator, the intermediate shaft, which is connected to the solar shaft, and the slow shaft, which drives the solar shaft. The parallel gear has a countershaft installed inside of it [2].
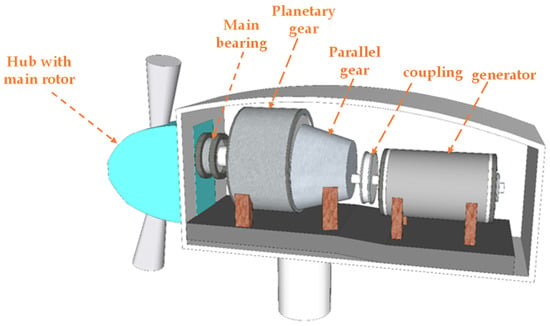
Figure 1.
Horizontal axis wind turbine with gearbox [2].
By the end of 2019, more than 650 gigawatts of wind capacity were installed worldwide [3,4]. However, the rate at which turbine failures occur makes it difficult to increase investment in wind energy [5].
In 2011, a study was carried out to identify the most critical component of WT [6]. This study pointed out the gearbox as one of the critical components. This component is known to have high downtimes and maintenance costs due to its repair and maintenance procedures [7]. Although, the failure rate of WT gearboxes is relatively low (8.9%). Its downtime is as long as 25.4 days in one year [8]. As a result, a large percentage of the energy is lost due to a malfunction of the latter [9]. Gearboxes come in second place in the failure downtime due to their size and robust linkage with other components, making them more difficult to access, repair, or even replace [10]. The majority of gearbox failures are caused by gear and bearing failures. According to [11], gear failures made up around 59% of wind turbine failure modes. The common gear faults are caused by anomalies in the gear tooth, such as a chipped tooth, broken tooth, root crack, spalling, wear, pitting, and surface damage [12].
The list of faults described above can be detected by analyzing vibration signals. Vibration analysis is the most widely used approach for fault detection in rotating machinery, particularly in WTs [13,14]. However, the application of vibration analysis requires additional vibration sensors and data acquisition devices. These sensors and devices are inevitably subject to failure, which could cause additional problems to system reliability and additional operating and maintenance costs. All these reasons led operators and researchers to look for other methods that would be less expensive to install [15]. It is noticed that a WT is an electromechanical system where the coupling between the generator and the damaged component in the gearbox generates vibrations induced by a gearbox fault which modulates the electrical signals measured from the generator terminals. As a result, gearbox faults can be diagnosed using generator current signals analysis (GCSA) [16].
This paper proposes a new approach for diagnosing gear tooth faults based on generator stator current analysis. Several research papers have discussed this technique [17,18,19,20,21,22,23], but they have overlooked one important aspect: the gearbox’s dynamic modeling. In this work, a mathematical model is developed for a system consisting of a two-stage gearbox and a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) to simulate the system under healthy and faulty conditions. The fast Fourier transform (FFT) analysis method detects faults in the stator current signal.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses the modeling of the studied system including the modeling of two stages gearbox, mesh stiffness calculation for (healthy, crack and a broken tooth) faults and modeling of the doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). The simulation results and discussion are in Section 3. Concluding remarks are presented in Section 4.
2. Modeling of the Studied System
Diagnosing gearbox failures is a way to improve wind turbine reliability, prevent catastrophic failures, and reduce downtime and maintenance costs [24]. Several methods can be used to detect faults in gearboxes such as lubrication analysis, acoustic emission analysis and vibration analysis. However, the challenge lies in the application of electrical analysis [15].
Our system is made up of a two-stage gearbox (multiplier), a four gear ( = 100 teeth, = 29, = 90 and = 36) with a multiplication ratio of 8.62 ( = 8.62). The input shaft of this gearbox is connected to a turbine, while the output shaft is connected to a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG).
The primary aim of this study is to estimate the stator currents from the output of the doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) to diagnose faults in the wind turbine gearbox. To achieve this objective, a detailed modeling of the system’s homelands (see Figure 2) must be provided. This modeling includes an in-depth analysis of the system’s components and their interactions, which allows us to simulate the system’s behavior under different operating conditions. By accurately modeling the system, we can identify any deviations from normal operation and diagnose any potential faults in the gearbox.
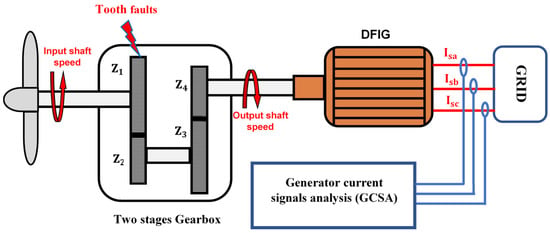
Figure 2.
Configuration of the two stages gearbox connected with a DFIG.
2.1. Modeling of Two Stages Gearbox
A nonlinear dynamic model of 10 degrees of freedom (DOF) was established using the concentrated mass method and ignoring the axial constraints, as shown in Figure 3. Some phenomena, such as friction between gear tooth, gearbox housing, and backlash, are ignored by this model. The following notation was used in this study [25,26]:
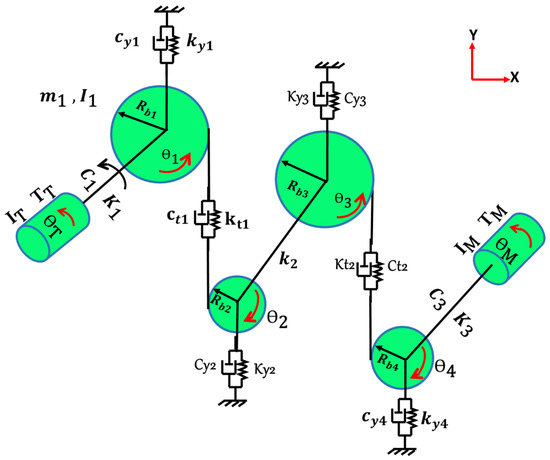
Figure 3.
Model of a two-stage spur gear system.
- mass of the gears 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- mass moment of inertia of gears 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- : turbine torque, machine torque;
- : base circle radius of gears 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- ,: turbine/machine angular displacement;
- ,: angular displacement of gears 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- , : mass moment of inertia of turbine/machine;
- : time-varying damping coefficient of first and second stage;
- : the radial damping coefficient along the direction of the y-axis of each bearing 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- : the damping coefficient of input, intermediate and output shafts, respectively;
- : time-varying meshing stiffness of first and second stages;
- : torsional stiffness of input, intermediate and output shafts, respectively.
We focused on the model response in the y direction, representing the effect of time-varying mesh stiffness, as the model response in the x direction is transient. According to Newton’s second law and considering the previous assumptions, the torsional vibration dynamics equations of the two-stage spur gear are as follows:
The equations of motion in the y direction of gear and pinion of the first stage are:
The equations of motion in the y direction of gear and pinion of the second stage are:
The rotary motion equations of the turbine and machine are:
The rotary motion equations of gear and pinion of the first stage are:
The rotary motion equations of gear and pinion of the second stage are:
The mesh damping is assumed proportional to the mesh stiffness in this study, and their ratio is calculated using the formula below [27]:
where: is the mean value of the mesh stiffness.
In this study, the damping ratio, denoted by , is taken to be 0.10 [27]. The mesh damping coefficient is calculated last, using the formula below:
The values of torsional stiffnesses used in [25] are adopted in this study: the torsional stiffnesses of the input shaft = 1381.6 Nm/ rad, of the intermediate shaft = 3555.446 Nm/rad and of the output shaft = 4824.705 Nm/ rad.
Mesh Stiffness Formulation
The gear mesh stiffness is a time-varying parameter that reflects the gear mesh conditions as the number of teeth in contact and the line of contact of the engaged gear teeth vary. It depends on the tooth geometry, position of the contact point, gear tooth deflections, gear tooth profile errors, gear hub torsional deformation, and local tooth faults [28].
- (A)
- Calculation of the mesh stiffness of a healthy gear
The potential energy technique presented by [29] was used as the basis for the gear stiffness model used in this study. This approach treats the gear tooth as a non-uniform cantilever beam that is subjected to a force. The various energies that can be stored in the gear tooth structure are calculated using beam theory. These energies are then converted to appropriate stiffnesses [30].
The analytical expressions of the Hertzian contact stiffness , the bending stiffness , shear stiffness and axial compressive stiffness are given as follows [31,32]:
where is the Young modulus, is the Poisson’s ratio, and is the tooth face width; the other variables are shown in Figure 4.
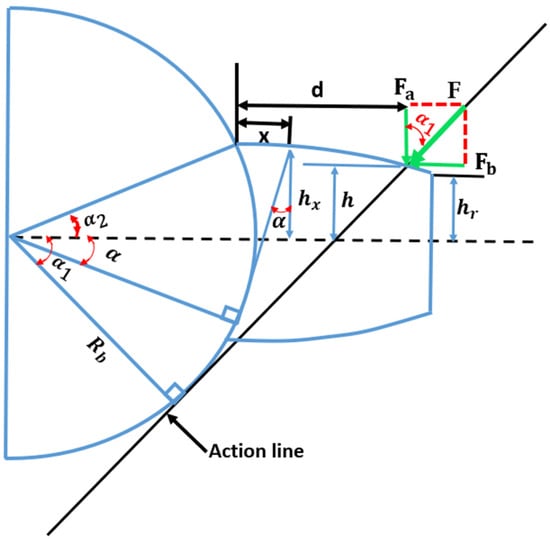
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of spur gear tooth model [33]. Where: : base circle radius of the gear; d: the distance from the point of contact and the root of the tooth; : pressure angle; : the distance between the point of contact and the center line of the tooth;: half the angle of the base of the tooth; : the distance between the involute point corresponding to the section which is at a distance X from the root of the tooth and the centerline of this last; : half the root width of the tooth; and F is the action force of the teeth in contact, which must always be aligned along the line of action. Consequently, F can be broken down into two perpendicular forces, and ; : the force that provides a bending effect while causes both an axial compression effect and a bending effect.
Hence, the total effective for the single tooth pair meshing duration can be represented as follows [29,33]:
The driving and driven gears are denoted, respectively, by subscripts 1 and 2.
For the double-tooth-pair meshing duration, the total effective mesh stiffness is the sum of the two pair’s stiffness, which can be expressed as [29,33]:
where i represents the i th pair of the meshing tooth.
- (B)
- Mesh stiffness calculation of gear with a cracked tooth
When a crack has been initiated at the base of one of the pinion gears, the bending and shear stiffness will change. This phenomenon will occur because when the crack is present, the effective moment of inertia of the surface and the cross-sectional area will change. So, for the single tooth mesh period, the total effective mesh stiffness is given by Equation (19), while Figure 5 shows a schematic of a pinion gear with a cracked tooth [34]. In this figure, represents the length of the crack, is the distance between the root of the crack and the tooth centerline, corresponding to point 𝑮 on the tooth profile and the angle , M represents the torque causing the bending effect of Fa, and v is the crack intersection angle.
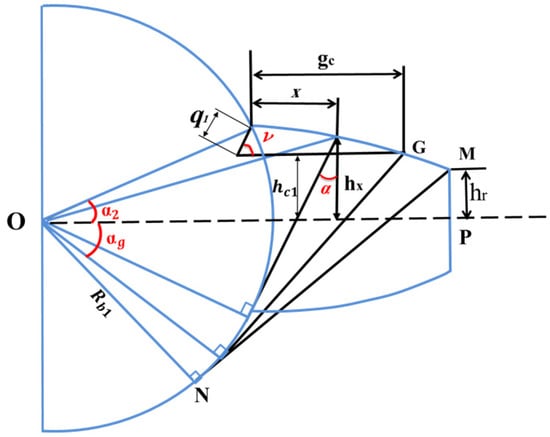
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of cracked tooth [34].
and are the cracked tooth’s bending and shear mesh stiffness, respectively. They are calculated as follows [34]:
- (C)
- Mesh stiffness calculation of gear with a broken tooth
Since the tooth will lose contact where the missing tooth was, only one pair of teeth will mesh during the first period of the double pair of teeth, contrary to the ideal scenario. As a result, the overall effective stiffness of the mesh will only be equal to the stiffness of a single pair of teeth. It will become:
2.2. Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) Modeling
The use of DFIG in wind energy systems offers several advantages. With the ability to control active and reactive power independently, wind turbines equipped with these generators can optimize their power output and improve efficiency. Additionally, the generators can operate at variable speeds, making them easier to integrate with the grid and providing reactive power support to maintain grid stability. Compared to other types of generators, asynchronous double-fed generators are cost-effective and have a higher power output, making them a popular and effective option for wind turbine manufacturers.
A DFIG is constructed similarly to a wound rotor induction generator and has a three-phase stator winding and a three-phase rotor winding. Slip rings are used to feed the latter. If neglecting the effects of the slotting, we assumed that the permeability of the iron parts is infinite and the flux density is radial in the air gap. The simplified and idealized DFIG model can be shown in Figure 6 [35,36].
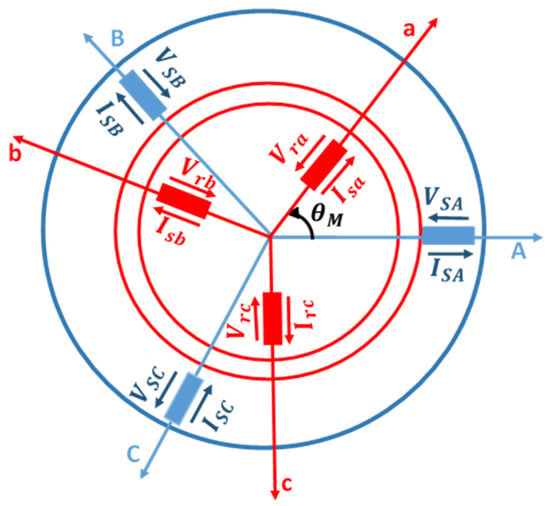
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the DFIG.
The stator and rotor voltage are represented as follows [35,36]:
where the voltages applied to the stator are , and . The stator currents in phases A, B and C are , and ; the rotor currents in phases a, b and c are , and ; the rotor voltages are , and ; and the stator and rotor fluxes are (,), (, and ).
The stator and rotor resistances of the DFIG are and , respectively.
Applying the park transformation to the three phases of DFIG gives the general model of DFIG as follows [37,38,39,40]:
where represent, respectively, the components along the d and q axes of the stator and rotor voltages, currents and flux.
and are the stator and rotor angular frequencies in and the relationship between them is:
where is the electrical angular frequency of the machine. In this case, the rotational speed of the gearbox output gear is defined by the following equation:
Similarly, is the mechanical angular speed, linked to the electrical frequency by a pair of poles, p:
The currents and fluxes for DFIG are related by the following equations:
and are the stator and rotor leakage inductances, respectively, with M serving as the mutual inductance.
We find Equation (30) by putting Equation (29) in (25) [41]:
Equation (30) is written in the matrix form as follows:
Starting from (31), we get the following equation:
After simplifying the previous equation, we get the following equation:
where:
is the leakage factor equal to .
Finally, the state model describes the doubly fed induction machine given as follows:
where:
The electromagnetic torque generated by the DFIG is represented by the following equation [42]:
3. Results and Discussion
To obtain digital solutions, we used Matlab/Simulink. Figure 7 shows the studied system’s Simulink model, and Table 1 and Table 2 list the system’s parameters.
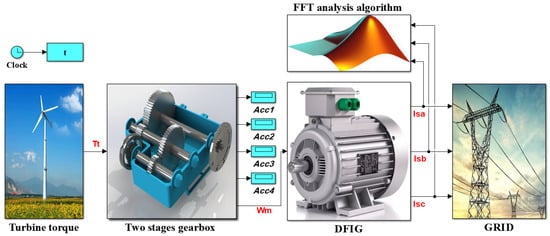
Figure 7.
Simulink model of the studied system.

Table 1.
Two-stage gear drive system parameters (delivered by the manufacturer).

Table 2.
DFIG parameters [43].
The two-stage gearbox was implemented using Equations (1)–(10). This gearbox is driven by a constant turbine torque with a value of 61.21 Nm.
On the other hand, the doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) was implemented using Equations (25)–(40). The DFIG trained at a fixed speed of 310 radians/s, powered directly by two perfect three-phase voltag sources. One is located at the stator with a frequency of 50 Hz and an amplitude of V, and the other is located at the rotor with an amplitude of 10 V and a frequency equal to the rotor frequency ( = s·.
A broken tooth fault is created at the level of the first gear in the first stage. The following Figure 8 and Figure 9 show the changes in the variation of meshing stiffness in the first and second stages, respectively, during the rotation of the gears. From these figures, we can see that the meshing stiffness of the gear system is approximately parabolic.
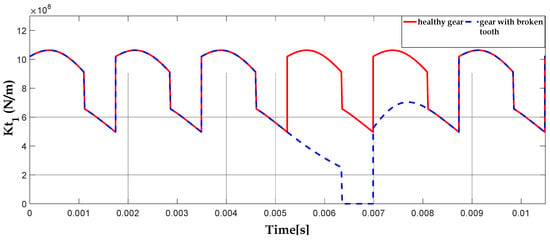
Figure 8.
Variation of meshing stiffness in N/m when a tooth of the first stage gear is broken.
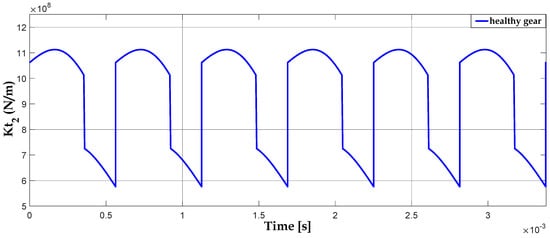
Figure 9.
Variation of the meshing stiffness in N/m of the second stage.
To explain and extract the characteristics of the first stage stiffness signal shown in Figure 8, a spectral analysis (FFT) has been presented in Figure 10 and Figure 11 for healthy and faulty gear.
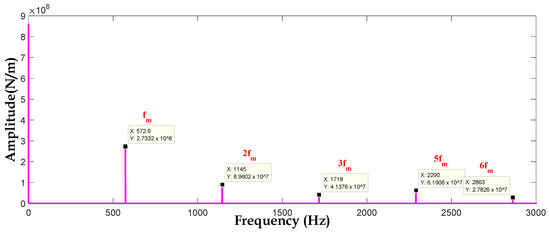
Figure 10.
Spectrum of first stage meshing stiffness for healthy gear.
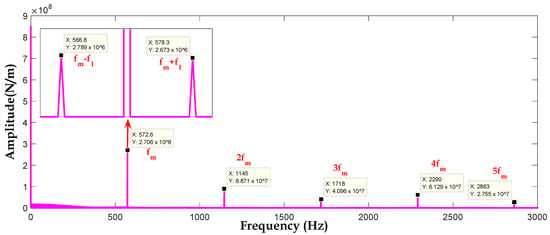
Figure 11.
Spectrum of first stage meshing stiffness with a broken tooth in first gear.
The spectrum of meshing stiffness of the first stage () is represented in Figure 10; this spectrum shows a multitude of peaks whose amplitude decreases very quickly. The largest amplitude line is observed at the fundamental meshing frequency = 572.6 Hz (=· = 572.6 Hz), then the next in decreasing order of amplitude at 1145 Hz, then at 1718 Hz, then at 2290 Hz, etc. For the healthy gear, the signal spectrum makes it possible to read the meshing frequency and its harmonics (2 … n.).
Figure 11 represents the spectrum of meshing stiffness for the first stage in the presence of broken tooth faults of a Gear one notices on the spectrum of the meshing stiffness of the lateral bands on either side of the meshing frequency ( = = 572.6 Hz) and its harmonics, the distances between the peaks is equal to 5.7 Hz. This frequency corresponds to the frequency of rotation of the Gear it is the frequency of repetition of the broken tooth.
Figure 12 represents the accelerations of , , and , respectively. We notice multitudes of peaks separated by a distance of 0.1747 s between two adjacent peaks. It represents the period of rotation of the first shaft (=). It can be seen that with a broken tooth fault, the whole system will be influenced by this defect. Although the fault is on the first floor, it can be observed in the vibration responses of the entire system.
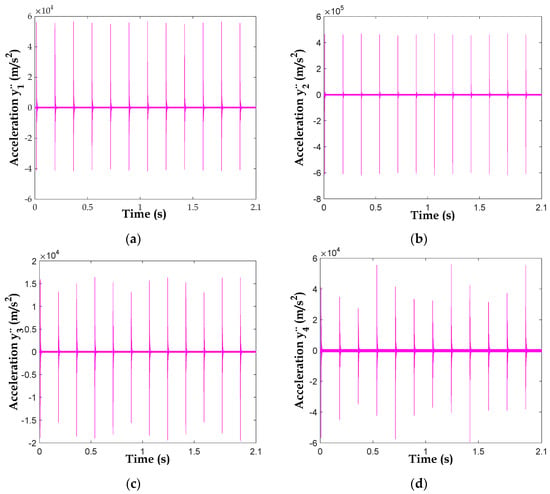
Figure 12.
Acceleration responses with broken tooth: (a) , (b) , (c) and (d).
In Figure 13, the rotational speed of the gearbox output gear is presented. The speed remains steady at a value of 310 radians/s, which is consistent with the normal operating range of the system. However, the appearance of sharp peaks at specific times indicates the presence of faults in the system.
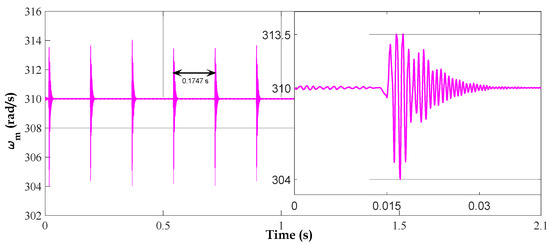
Figure 13.
The rotational speed of the gearbox output gear with a broken tooth.
These peaks appear every 0.1747 s, corresponding to the period of repetition of the broken tooth.
Researchers using vibration analysis to detect gearbox problems will find these results a valuable resource. They offer interesting data and references that advance diagnostic and fault prevention techniques.
To clarify the effect of crack fault on the mesh stiffness, we presented the gear mesh stiffness for different crack lengths with the same crack angle v = 22.5° in Figure 14; we note a degradation of the value of total stiffness proportionally with the crack size due to the change of the bending stiffness.
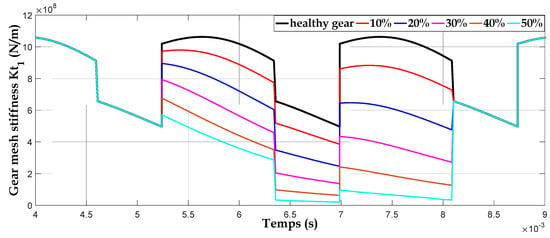
Figure 14.
Gear mesh stiffness for different crack lengths.
In this party, we consider a crack fault at the gable root with a depth of = 7.5 mm (50% tooth width) and an angle of v = 22.5° on the gear at stage 1. The accelerations , , and are depicted in Figure 15. Once again, we observe numerous peaks that are smaller compared to the case of a broken tooth. These peaks are separated by a distance of 0.1747 s, representing the period of rotation of the first shaft (period of repetition of the cracked tooth).
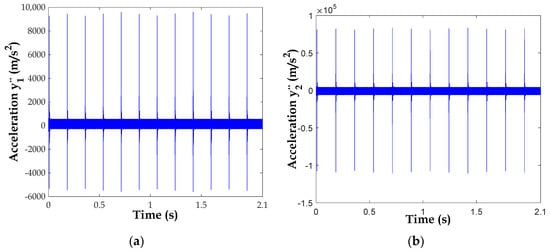
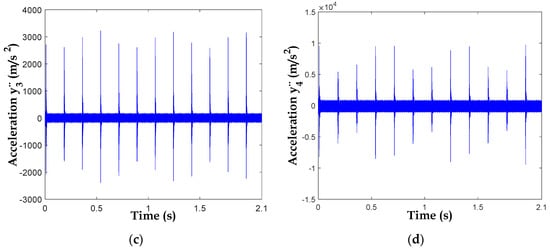
Figure 15.
Acceleration responses with cracked tooth: (a) , (b), (c) and (d) .
Figure 16 shows the angular rotation speed of the output shaft of the gearbox. A constant speed of 310 radians/s is observed. However, periodic peaks appear every 0.1747 s. These peaks are related to the rotation of the first wheel with a cracked tooth. In comparison to the peaks observed in the case of a broken tooth, these spikes are less pronounced.
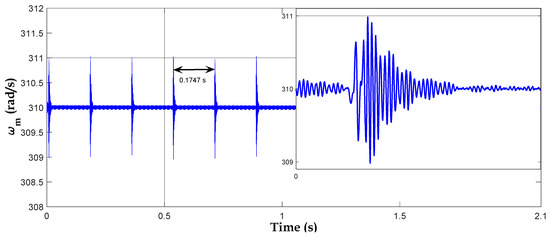
Figure 16.
The rotational speed of the gearbox output gear with a cracked tooth.
Figure 17 represents the stator current of the DFIG. We can see that it has a sinusoidal format after a transient state.
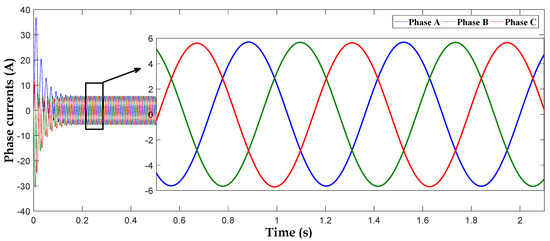
Figure 17.
Stator current Is (ABC).
To detect broken and cracked tooth faults in the gear system, a spectral analysis of phases currents A, B, and C are presented in Figure 18, Figure 19 and Figure 20, respectively. From these Figures, we can notice that the current spectra in healthy gear are composed of a fundamental (network frequency) and for the case, broken, and cracked teeth are composed of a fundamental and a series of harmonics with frequencies () and (), where is the rotation frequency of the first shaft corresponding to the defective wheel and K is the integer number.
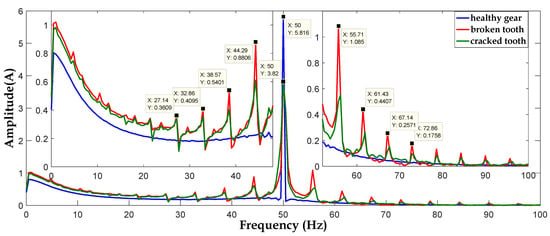
Figure 18.
The spectrum of phase (A) current signals.
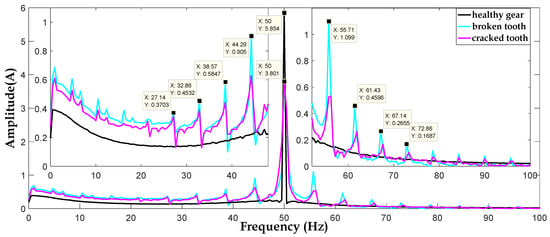
Figure 19.
The spectrum of phase (B) current signals.
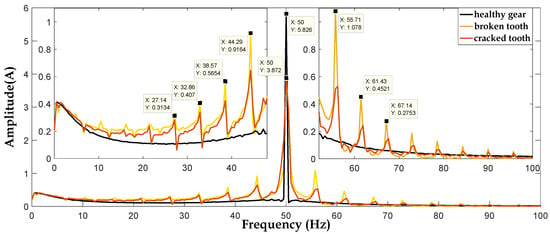
Figure 20.
The spectrum of phase (C) current signals.
A small difference, of 0.016 Hz, between the calculated theoretical frequency ( = 5.726 Hz) and that of the spectrum ( = 5.71 Hz) is quite normal.
As a comparison, we can notice that the spectrum of stator current in the case of a cracked tooth has the same characteristic as the spectrum of the case of a broken tooth with smaller amplitudes.
4. Conclusions
A method based on the analysis of stator current signals has been presented for fault detection of wind gearbox equipped with a DFIG system. This one was modeled to simulate the behavior in a healthy, cracked, and broken tooth fault of the first gear of the gearbox. The results showed that the proposed stator current signal analysis approach effectively detects and diagnoses various gear failures. The presence of a crack or broken fault in the gear tooth of the gearbox induces a modulation of the DFIG stator current signals by the frequencies of the shaft corresponding to the defect gear. These results can provide a preliminary basis for detecting and diagnosing this type of failure.
Looking forward, the authors plan to further test the proposed method in a practical setting using a dedicated test bed. By doing so, they hope to validate the effectiveness of the approach in a real-world scenario and optimize the method for industrial application. This study serves as a promising starting point for future research aimed at improving wind turbine gearbox reliability and reducing the overall cost of wind energy production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.I., K.E.H. and A.S.; methodology, I.I., K.E.H. and A.S.; software I.I., K.E.H. and A.S.; validation I.I., K.E.H. and A.S.; formal analysis, I.I.; investigation, I.I.; resources, I.I.; data curation, I.I.; writing—original draft preparation, I.I.; writing—review and editing, I.I., K.E.H. and A.S; visualization, I.I.; supervision, I.I. and K.E.H.; project administration, I.I. and K.E.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gao, Z.; Liu, X. An Overview on Fault Diagnosis, Prognosis and Resilient Control for Wind Turbine Systems. Processes 2021, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barszcz, T. Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring of Wind Turbines; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 3-030-05971-5. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, A. Vibration Fault Diagnosis in Wind Turbines Based on Automated Feature Learning. Energies 2022, 15, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Ding, X.; Tang, S.; Xu, J.; Shi, B.; Liu, Y. Vibration Analysis for Fault Detection of Wind Turbine Drivetrains—A Comprehensive Investigation. Sensors 2021, 21, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, C.; Kazemtabrizi, B.; Crabtree, C. Wind Turbine Reliability Data Review and Impacts on Levelised Cost of Energy. Wind Energy 2019, 22, 1848–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Faulstich, S.; Hahn, B.; Tavner, P.J. Wind Turbine Downtime and Its Importance for Offshore Deployment. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Sánchez, R.-V. Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on the Optimized LSTM Neural Network with Cosine Loss. Sensors 2020, 20, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, B.; Deng, L.; Tan, Q.; Yu, H. A Fault Diagnosis Method for Wind Turbines Gearbox Based on Adaptive Loss Weighted Meta-ResNet under Noisy Labels. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 161, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakoua, P.; Wamkeue, R.; Ouhrouche, M.; Slaoui-Hasnaoui, F.; Tameghe, T.A.; Ekemb, G. Wind Turbine Condition Monitoring: State-of-the-Art Review, New Trends, and Future Challenges. Energies 2014, 7, 2595–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinato, F.; Tavner, P.J.; Van Bussel, G.J.; Koutoulakos, E. Reliability of Wind Turbine Subassemblies. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2009, 3, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, H.; LaCava, W.; van Dam, J.; McNiff, B.; Sheng, S.; Wallen, R.; McDade, M.; Lambert, S.; Butterfield, S.; Oyague, F. Gearbox Reliability Collaborative Project Report: Findings from Phase 1 and Phase 2 Testing; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kia, S.H.; Henao, H.; Capolino, G.-A. Gear Tooth Surface Damage Fault Detection Using Induction Machine Stator Current Space Vector Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tang, B.; Han, J.; Lu, X.; Hu, N.; He, Z. The Structure Healthy Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis Methods in Wind Turbines: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Z.; Hong, Y.; Cho, Y.; Ahn, S.; Song, C. Condition Monitoring and Fault Detection of Wind Turbines and Related Algorithms: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, J.P.; Cauet, S.; Etien, E.; Sakout, A.; Rambault, L. Gearbox Condition Monitoring in Wind Turbines: A Review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 111, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Peng, Y.; Qu, L.; Qiao, W. Current-Based Fault Detection and Identification for Wind Turbine Drivetrain Gearboxes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 53, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Qiao, W.; Gong, X. Current-Based Gear Fault Detection for Wind Turbine Gearboxes. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.R.; Kar, C. Fault Detection in a Multistage Gearbox by Demodulation of Motor Current Waveform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, H.D.; Liu, Z.; Lee, J.; Bravo-Imaz, I.; Arnaiz, A. Motor Current Signature Analysis for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis in Transient Speed Regimes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Prognostics and Health Management (PHM), Austin, TX, USA, 22–25 June 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Wei, C.; Qu, L.; Qiao, W. Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Gearbox Using DFIG Stator Current Analysis. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 10, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Gong, X.; Qiao, W. Current-Based Diagnosis for Gear Tooth Breaks in Wind Turbine Gearboxes. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Raleigh, NC, USA, 15–20 September 2012; pp. 3780–3786. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo-Imaz, I.; Ardakani, H.D.; Liu, Z.; García-Arribas, A.; Arnaiz, A.; Lee, J. Motor Current Signature Analysis for Gearbox Condition Monitoring under Transient Speeds Using Wavelet Analysis and Dual-Level Time Synchronous Averaging. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 94, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touti, W.; Salah, M.; Bacha, K.; Chaari, A. Condition Monitoring of a Wind Turbine Drivetrain Based on Generator Stator Current Processing. ISA Trans. 2022, 128, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Cheng, F.; Peng, Y.; Qiao, W.; Qu, L. Drivetrain Gearbox Fault Diagnosis: Vibration-and Current-Based Approaches. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2018, 24, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Cui, L. Nonlinear Dynamic Response Analysis of Two-Stage Spur Gear Space Driving Mechanism with Large Inertia Load. J. Vibroeng. 2018, 20, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyousfi, B.; Soualhi, A.; Medjaher, K.; Guillet, F. A Model-Based Analysis of Crack Fault in a Two-Stage Spur Gear System. In Proceedings of the 2020 Prognostics and Health Management Conference (PHM-Besançon), Besancon, France, 4–7 May 2020; pp. 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.H.; Liou, C.-H. A Parametric Study of Spur Gear Dynamics; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chaari, F.; Fakhfakh, T.; Haddar, M. Analytical Modelling of Spur Gear Tooth Crack and Influence on Gearmesh Stiffness. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2009, 28, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lin, J. Hertzian Damping, Tooth Friction and Bending Elasticity in Gear Impact Dynamics. J. Mech. Trans. Automation. 1987, 109, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yousfi, B.; Soualhi, A.; Medjaher, K.; Guillet, F. A New Analytical Method for Modeling the Effect of Assembly Errors on a Motor-Gearbox System. Energies 2021, 14, 4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zuo, M.J.; Patel, T.H. Evaluating the Time-Varying Mesh Stiffness of a Planetary Gear Set Using the Potential Energy Method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2014, 228, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Shao, Y.; Rao, M.; Yu, W. Effects of the Gear Eccentricities on the Dynamic Performance of a Planetary Gear Set. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 91, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zuo, M.J.; Fyfe, K.R. Analysis of the Vibration Response of a Gearbox with Gear Tooth Faults. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 13–19 November 2004; Volume 47063, pp. 785–793. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zuo, M.J.; Parey, A. Simulation of Spur Gear Dynamics and Estimation of Fault Growth. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 317, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Deicke, M.; De Doncker, R.W. Doubly Fed Induction Generator Systems for Wind Turbines. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2002, 8, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, G.; Lopez, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Marroyo, L.; Iwanski, G. Doubly Fed Induction Machine: Modeling and Control for Wind Energy Generation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 1-118-10495-1. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y. Dynamic Modeling and Control of DFIG-Based Wind Turbines under Unbalanced Network Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicatos, M.; Tegopoulos, J. Transient State Analysis of a Doubly-Fed Induction Generator under Three Phase Short Circuit. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1991, 6, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitiers, F.; Bouaouiche, T.; Machmoum, M. Advanced Control of a Doubly-Fed Induction Generator for Wind Energy Conversion. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortmann, J. Modeling of Wind Turbines with Doubly Fed Generator System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 3-658-06882-5. [Google Scholar]
- Keltoum, L.; Leila, B.; Abderrahmen, B. Speed Control of a Doubly-Fed Induction Motor (DFIM) Based on Fuzzy Sliding Mode Controller. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2017, 10, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrane, F.; Francois, B.; Chaiba, A. Experimental Investigation of Efficient and Simple Wind-Turbine Based on DFIG-Direct Power Control Using LCL-Filter for Stand-Alone Mode. ISA Trans. 2022, 125, 631–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensou, S.; Essadki, A.; Nasser, T.; Idrissi, B.B.; Ben Tarla, L. Dspace DS1104 Implementation of a Robust Nonlinear Controller Applied for DFIG Driven by Wind Turbine. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).