Impacts of Yield and Seasonal Prices on the Operation of Lancang Cascaded Reservoirs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
- (1)
- The water balancewhere the is the set of reservoirs immediately upstream of reservoir i and the is the time length in time-step t.
- (2)
- The lower and upper bounds on the storage
- (3)
- The release being nonnegative
- (4)
- The power yield Y at a certain reliabilitywhere the hydropower output of i in time-step t is determined withwith the final storage being determined via the water balance (4), the being the coefficient of generation efficiency, and the being the capacity of turbine discharge of hydropower reservoir i.
- (1)
- SDP-1: to maximize the energy production without power yield;
- (2)
- SDP-2: to maximize the revenue at seasonal prices without power yield, where is the seasonal price of electricity in time-step t;
- (3)
- SDP-3: to maximize the energy production with power yield (7).
3. Solution Procedures
3.1. The Typical Inflows and Their Transition Probabilities
- (1)
- Suppose the number of typical inflows in time-step t is K, and there are Y years of historical inflows observed, which ensure n (=Y/K) historical inflows be represented by one typical inflow, determined as the average over these n historical inflows.
- (2)
- Arrange the historical inflows for t = 1,2, …, T and y = 1,2, …, Y in order from the smallest to the largest: ; the typical inflow for any interval k (k = 1,2, …, K) in time-step t is determined as the average over n historical inflows, expressed as
- (3)
- Apparently, each historical inflow in any time-step t can be represented by one of the k typical inflows in this time-step, and the transition probability from the k-th in time-step t to the l-th in time-step t + 1 can be estimated as follows:where among n historical inflows represented by the k-th typical inflow in time-step t, there are of their successive inflows that are represented by the l-th typical inflow in time-step t + 1.
3.2. The Representative Storages
3.3. The Power Yield at Certain Reliability
3.4. Recursive Evolution
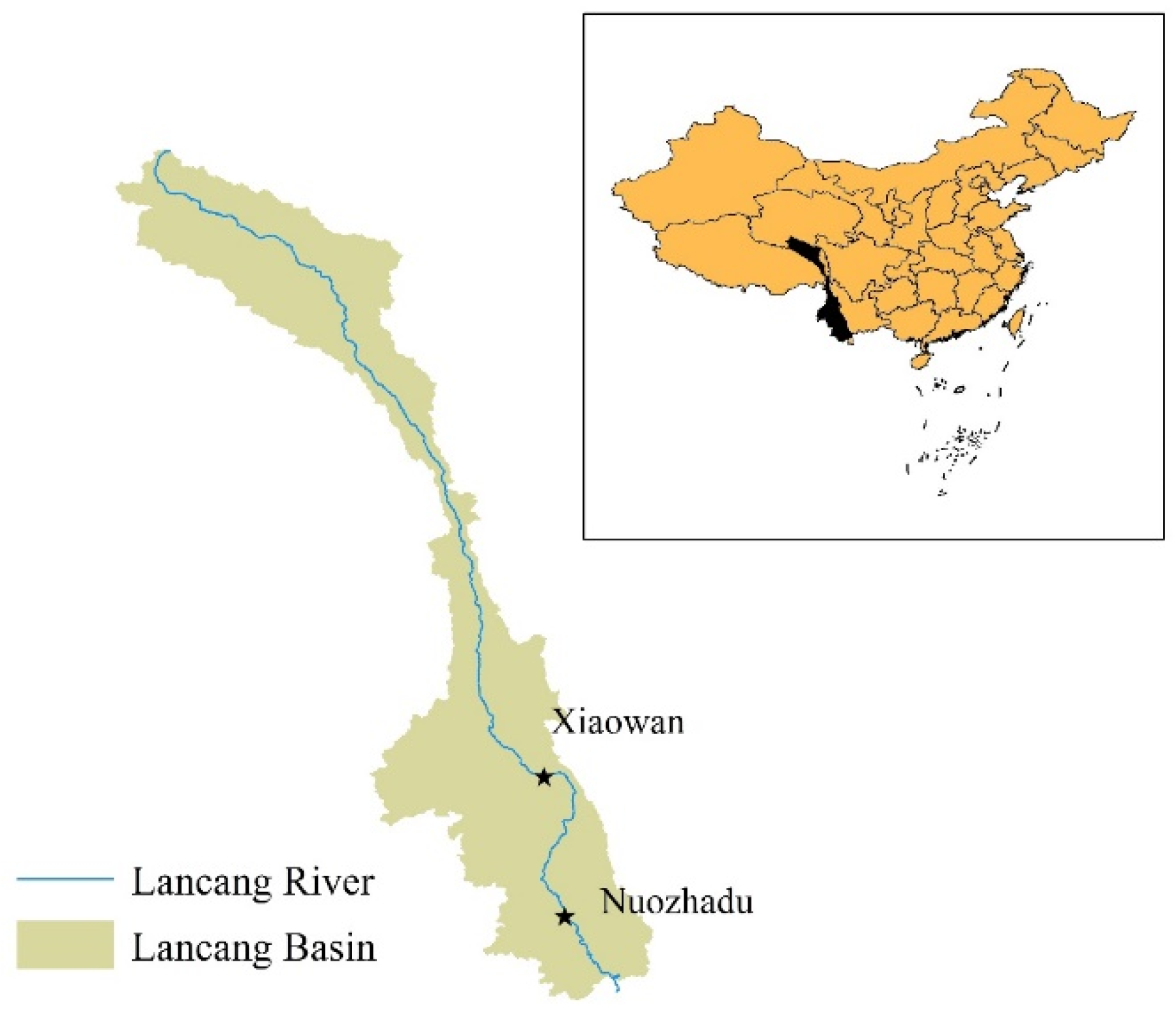
4. Engineering Applications
4.1. Engineering Background
4.2. Data Preparation and Setting
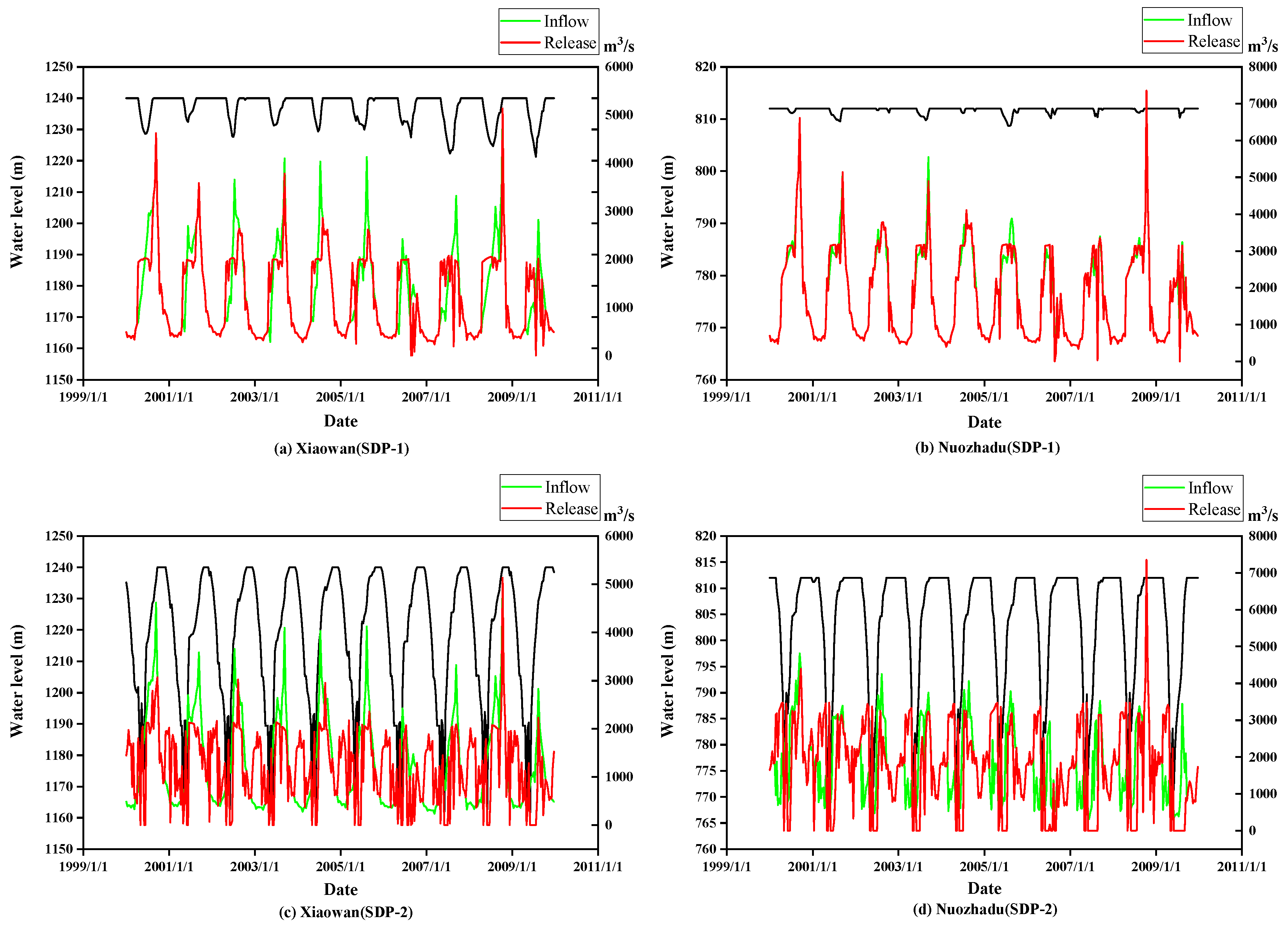
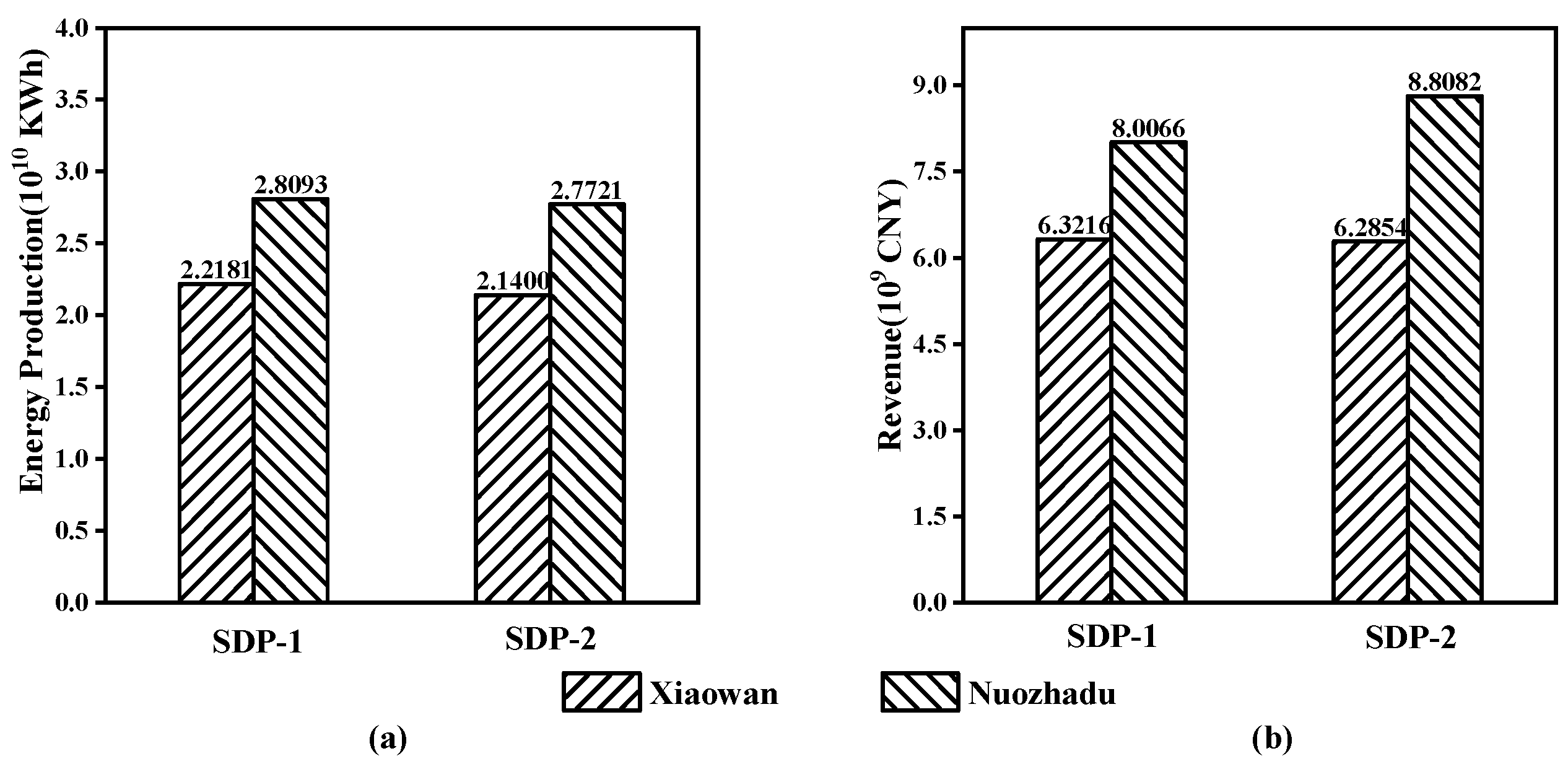
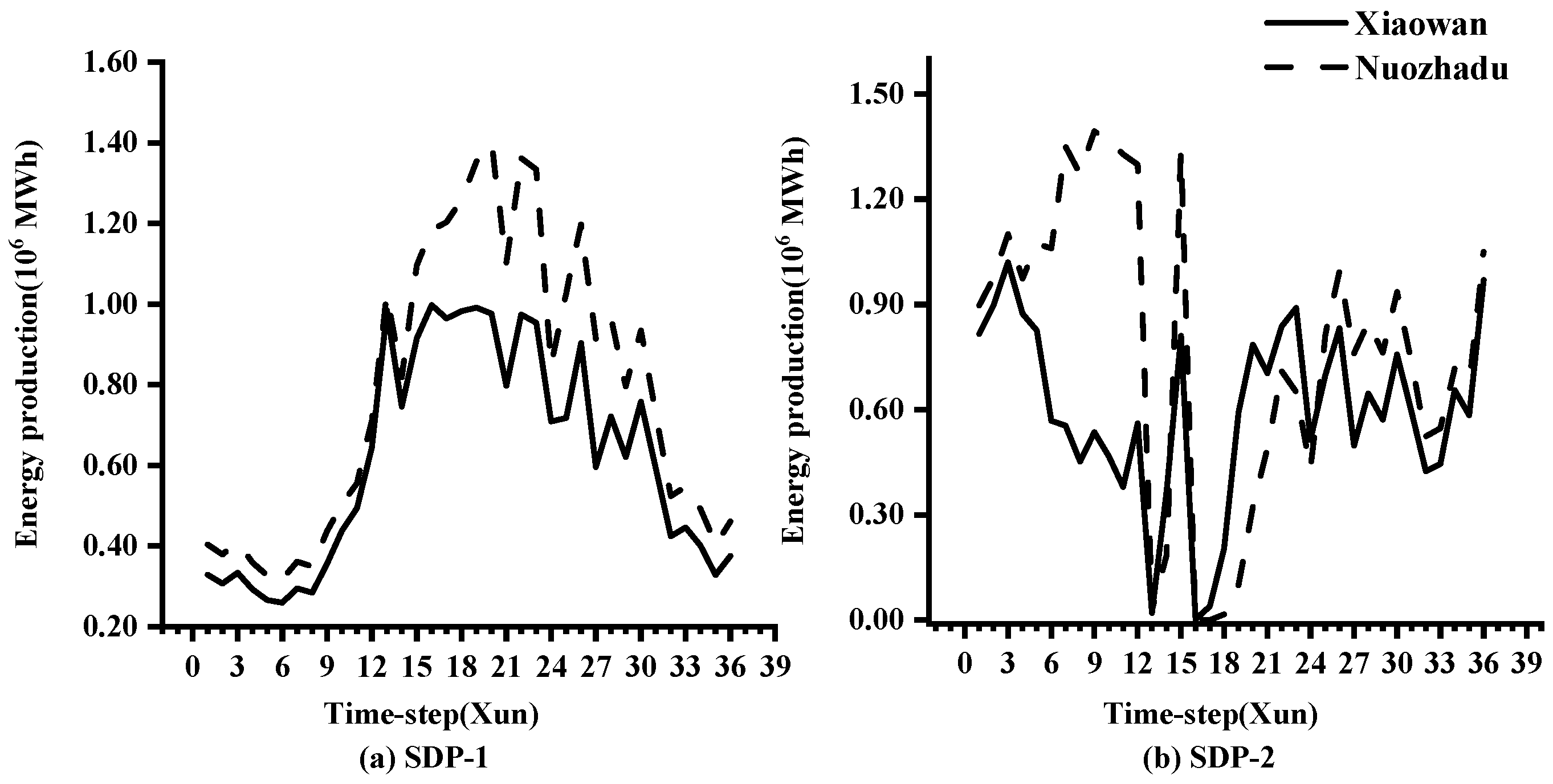
4.3. Comparison between the SDP-1 and SDP-2
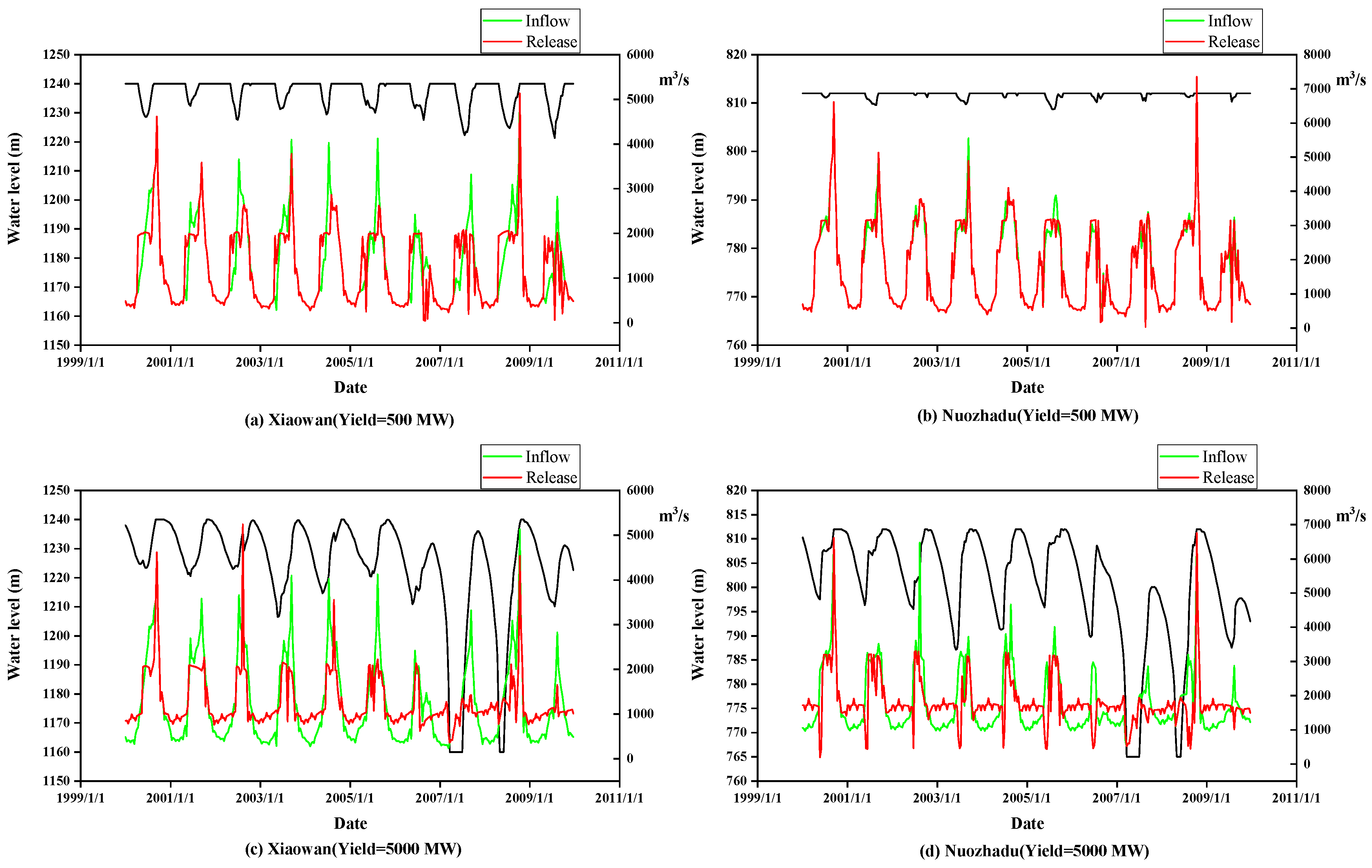
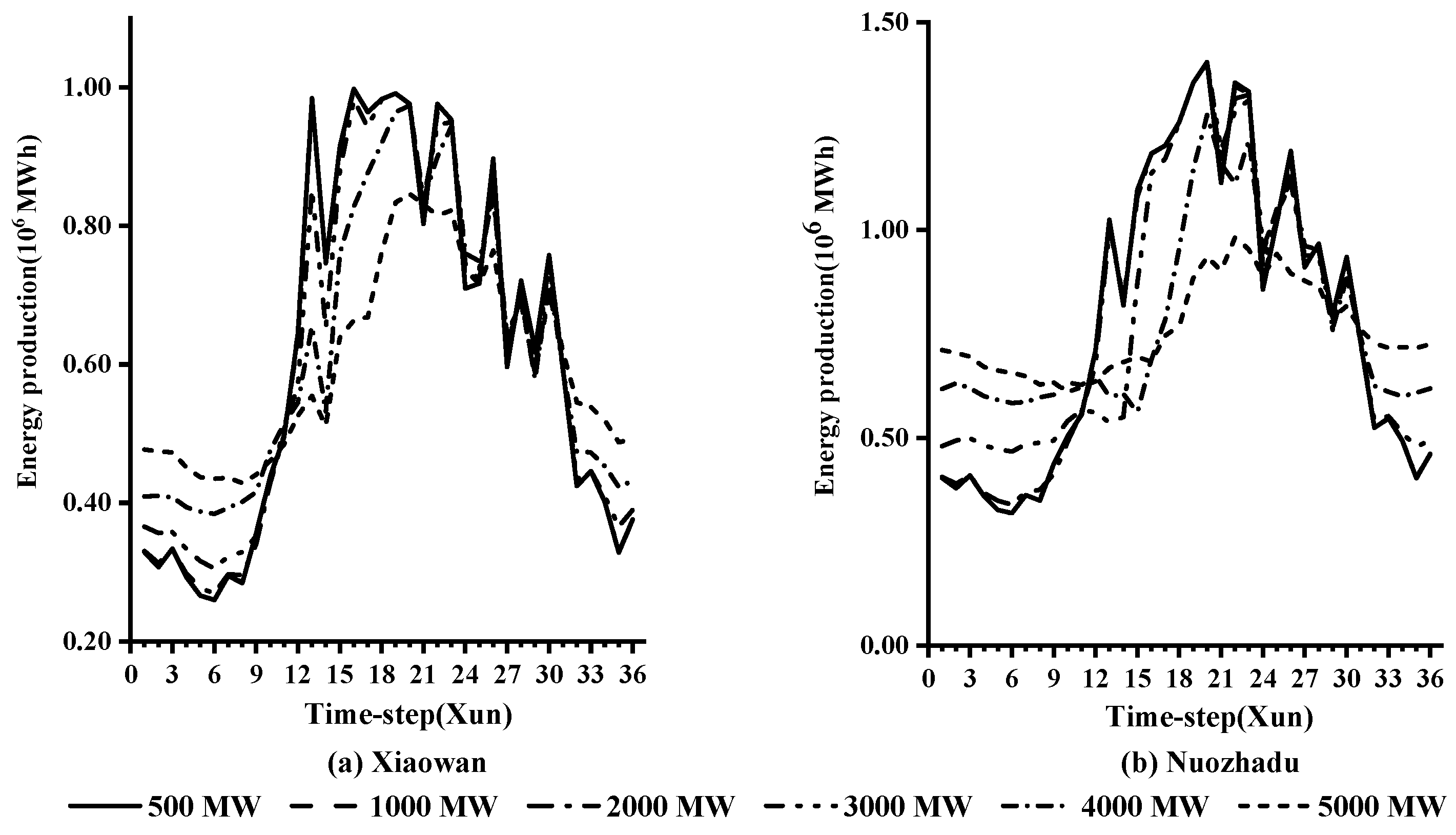
4.4. The Results by the SDP-3
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, C.X.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.W. An Efficient Linearization Method for Long-Term Operation of Cascaded Hydropower Reservoirs. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedinger, J.R.; Faber, B.A.; Lamontagne, J.R. Developments in Stochastic Dynamic Programming for Reservoir Operation Optimization. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2013: Showcasing the Future, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2013; pp. 1266–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Alaya, A.; Souissi, A.; Tarhouni, J.; Ncib, K. Optimization of Nebhana Reservoir Water Allocation by Stochastic Dynamic Programming. Water Resour. Manag. 2003, 17, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedinger, J.R.; Sule, B.F.; Loucks, D.P. Stochastic dynamic programming models for reservoir operation optimization. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, A. Stochastic optimization of multireservoir operation: The optimal reservoir trajectory approach. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarcelli, R.O.C.; Zambelli, M.S.; Soares, S.; Carneiro, A.A.F.M. Ensemble of Markovian stochastic dynamic programming models in different time scales for long term hydropower scheduling. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 150, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Guibert, J.A.; Johnson, S.A.; Stedinger, J.R. The Value of Hydrologic Information in Stochastic Dynamic Programming Models of a Multireservoir System. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.J.; Mahdizadeh, K.; Afshar, A. A stochastic dynamic programming model with fuzzy storage states for reservoir operations. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.K.; Niu, W.J.; Cheng, C.T.; Liao, S.L. Hydropower system operation optimization by discrete differential dynamic programming based on orthogonal experiment design. Energy 2017, 126, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.G.; Cai, X.M.; Lei, X.H.; Wang, H. Improved Dynamic Programming for Reservoir Operation Optimization with a Concave Objective Function. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. Asce 2012, 138, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Wang, S.; Chau, K.W.; Wu, X.Y. Parallel discrete differential dynamic programming for multireservoir operation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 57, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Q.; Cai, H.; Yan, M.; Zhang, M.; Wu, D.; Xie, M. Market reform of Yunnan electricity in southwestern China: Practice, challenges and implications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongling, L.; Chuanwen, J.; Yan, Z. A review on risk-constrained hydropower scheduling in deregulated power market. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, A. Reliability-constrained hydropower valuation. Energy Policy 2018, 118, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, M.; Asghari, K. Reliability Improved Stochastic Dynamic Programming for Reservoir Operation Optimization. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 1795–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, P.; Ming, B.; Huang, K.; Xu, W.; Wen, Y. Joint Optimization of Forward Contract and Operating Rules for Cascade Hydropower Reservoirs. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2022, 148, 04021099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kang, C.; Wang, J. Stochastic Linear Programming for Reservoir Operation with Constraints on Reliability and Vulnerability. Water 2018, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mujumdar, P.P.; Nirmala, B. A bayesian stochastic optimization model for a multi-reservoir hydropower system. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1465–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-O.; Palmer Richard, N. Value of Seasonal Flow Forecasts in Bayesian Stochastic Programming. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1997, 123, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haguma, D.; Leconte, R.; Côté, P. Evaluating Transition Probabilities for a Stochastic Dynamic Programming Model Used in Water System Optimization. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04017090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Houck, M.H. Annual and monthly reservoir operating rules generated by deterministic optimization. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Xiaowan | Nuozhadu |
|---|---|---|
| Dead storage capacity (bcm) | 4.662 | 10.414 |
| Normal storage capacity (bcm) | 14.557 | 21.749 |
| Minimum head (m) | 164 | 152 |
| Maximum head (m) | 251 | 215 |
| Generating discharge capacity (m3) | 2261 | 3429 |
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (CNY/KWh) | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.39 |
| Power Yield | 500 MW | 1000 MW | 2000 MW | 3000 MW | 4000 MW | 5000 MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reliability | 99.4% | 98.3% | 90.7% | 77.9% | 69.8% | 47.5% |
| 500 MW | 1000 MW | 2000 MW | 3000 MW | 4000 MW | 5000 MW | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (MWh) | Xiaowan | 22,180,172 | 22,179,661 | 22,179,003 | 22,176,101 | 22,160,479 | 21,512,030 |
| Nuozhadu | 28,093,066 | 28,093,517 | 28,092,104 | 28,071,902 | 27,933,721 | 27,214,184 | |
| Spillage (million m3) | Xiaowan | 1417.9 | 1416.8 | 1410.9 | 1367.1 | 1191.1 | 909.0 |
| Nuozhadu | 1282.5 | 1280.8 | 1278.3 | 1231.6 | 1072.5 | 594.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, M.; Feng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, C. Impacts of Yield and Seasonal Prices on the Operation of Lancang Cascaded Reservoirs. Energies 2022, 15, 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093247
Xie M, Feng S, Wang J, Zhang M, Chen C. Impacts of Yield and Seasonal Prices on the Operation of Lancang Cascaded Reservoirs. Energies. 2022; 15(9):3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093247
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Mengfei, Suzhen Feng, Jinwen Wang, Maolin Zhang, and Cheng Chen. 2022. "Impacts of Yield and Seasonal Prices on the Operation of Lancang Cascaded Reservoirs" Energies 15, no. 9: 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093247
APA StyleXie, M., Feng, S., Wang, J., Zhang, M., & Chen, C. (2022). Impacts of Yield and Seasonal Prices on the Operation of Lancang Cascaded Reservoirs. Energies, 15(9), 3247. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093247





