Abstract
Mobile machines using a hydrostatic transmission is highly efficient under lower working-speed condition but less capable at higher transport velocities. To enhance overall efficiency, we have improved the powertrain design by combining a hydrostatic transmission with a dual-clutch transmission (DCT). Compared with other mechanical gearboxes, the DCT avoids the interruption of torque transmission in the process of shifting without sacrificing more transmission efficiency. However, there are some problems of unstable torque transmission during the shifting process, and an excessive torque drop occurring at the end of the gear shift, which result in a poor drive comfort. To enhance the performance of the novel structural possibility of powertrain design, we designed a novel control strategy, which maintains the sliding in the torque phase and reduces the difference before and after the engagement, for the motor torque and the clutch torques during the shifting process, and then validated the control effect with model-based simulation. As a result, the control strategy employing clutch and motor torque control achieve a smooth shifting process since the drive torque is well tracked, and highly dynamical actuators are not required. As another benefit, only two calibration parameters are designed and actually needed to adjust the control performance systematically, even for any different sizes machines. Our research indicates the possibility to adopt dual-clutch in the field of construction machines.
1. Introduction
The combination of a hydrostatic transmission and a mechanical gearbox can improve not only the system efficiency but also the usability of mobile machines. The reason is the shiftable mechanical gearbox can produce better working conditions for hydraulic components. Currently, a commonly used structure is the combination of a hydrostatic transmission (HST) with a summation gearbox, which has at least two hydraulic motors to propel the construction machinery. However, the additional cost of the second motor limits the scope of using of this structure in the market of medium-sized mobile machines. By contrast, we propose a novel structure that combines the HST with a dual-clutch transmission, see Figure 1. With this novel combination, we only need one hydraulic motor and thus reduce the total transmission costs compared with the one with a summation gearbox. However, such a drivetrain solution did not have a considerable market share in a long time. One of the reasons is the fluctuation of output torque during the shifting process. Based on the primary torque control concept from Bosch Rexroth [1,2,3], we developed a controller to optimize the shifting process of a dual-clutch transmission, resulting in a fast and smooth shifting process. As a basic idea of this algorithm, the hydraulic motor and the clutches should cooperate with each other to accurately track the desired drive torque.

Figure 1.
HST+DCT drivetrain.
In this paper, we will first reveal the mechanism of the problem mentioned above and then introduce the algorithm which can optimize the performance of the HST+DCT drivetrain. In addition, the algorithm has an easy calibration process since only two calibration parameters are needed.
Energy-saving is important in the field of mobile machines since current systems are far from satisfactory [4,5]. Except for the well-known energy-saving methods mentioned in the review paper [5,6,7,8,9], such as hybrid system and machine learning, combining a mechanical gearbox with a hydraulic drive and the corresponding optimization has raised more and more attention. Apparently, a hydrostatic drivetrain can decouple the vehicle speed and the engine speed so that it can achieve better engine efficiency. However, it does not always indicate better overall efficiency since the hydraulic pump or motor may work in a worse condition to guarantee the required transmission ratio. Thus, the introduction of a mechanical gearbox after the hydraulic drive system to avoid the unsuitable operating conditions has become a consensus [3]. Although the combination of HST and a mechanical gearbox is widely used in industry, it is rarely mentioned in research papers. We conjecture that this concept might not be published in the scientific papers in the databases “Sciencedirect” and “Scopus”. A comprehensive description and the advantages of HST plus a mechanical gearbox can be found in [1]. Although the hydrodynamic solution is also used in mobile machines, the hydrostatic solution has more potential in terms of efficiency. Thus, we focus on the previous works about the introduction of HST plus a dual-clutch gearbox, as shown in Figure 1.
There are a series of research papers that deal with the control of dual clutches gearbox in the automobile industry. Fischer demonstrates the typical problem by using a dual-clutch gearbox [10]. While upshifting, the torque goes down first and then goes up. At the end of the shifting process, there is a sudden torque drop, resulting in a vehicle jerk [10]. To deal with this problem, an easy but effective fashion is to increase the gear sets of the mechanical gearbox since the transmission ratio difference before and after the shifting process is reduced, and thus we alleviate the shifting process. As is evident, the automatic hydrodynamic gearboxes from ZF Friedrichshafen AG usually have more than 8 gear sets. Additionally, other international well-known automotive suppliers, such as Audi and BMW, adopt their automatic transmission with more than 7 gear sets. In addition to the hardware solution, many researchers propose their methods to improve the shift quality, i.e., short shift duration and smooth shift process [11,12,13,14,15,16]. Van Berkel introduces the concept of clutch-engagement phases so that a smooth clutch engagement to track the demanded torque without a noticeable torque dip precisely is accomplished [13]. Moreover, Kim develops an effective upper-level controller based on the optimal control allocation to produce the most suitable torque trajectories of the engine and clutches [16]. Both of them have a similar basic idea: the whole process should be divided into a series of subprocesses since they have different characteristics. Additionally, Oh proposes an original approach for the driveline modeling so that a complex clutch friction model can be avoided [17]. The purpose of his work centers on accurately estimating the torque transmitted through each clutch of the dual-clutch transmission. Based on his research, the comprehensive or very detailed modeling of a drivetrain is not always necessary to achieve accurate control. Additionally, as the review paper from Gatta [18] points out, simpler models could sometimes be preferable to more complex ones, to provide real-time torque estimation. Although optimal control techniques obtain good shifting quality and reject disturbances, the computational cost can be quite large for the onboard system and thus limits its usage. According to the literature review, kiss-point detection [19], temperature influence [20], clutch actuators [21], transmitted torque estimation [22,23], and engagement controls [24] are the main topics in the dual-clutch control strategy.
In the fields of mobile machines, the drivetrains using clutches to output continuous drive torque are called power shift transmission since they might have more than two clutches [25]. Unlike the automotive industry, precisely controlling the hydrostatic drivetrain torque was a challenging thing before about 2017 [2,26]; therefore, many mobile-machines researchers still use different concepts to design their drivetrain control strategy due to the absence of torque control. Bugusch shows that a powershift-hydrostatical drivetrain with three gears, developed by Göllner [27], can improve the vehicle efficiency by selecting the gear appropriately [28]. In his research, the control strategy of the shifting process is not shown. In another research paper, Mörsch has pointed out, in a patent, the need to improve the drive comfort during the shifting process: at least one variable should be used [29] without pointing out which variable in detail. As a backbone of our algorithm, the concept of torque control in construction machines should be explained clearly. The torque control can be divided into primary torque control [2] and secondary torque control [26,30,31,32]. Although both control the output torque on the hydraulic motor, the basic ideas behind them are quite different. Compared to the secondary torque control, which controls the torque by a variable displacement motor under constant pressure, the primary torque concept adapts the pressure inside the circuit to achieve the desired output torque. Obviously, the primary torque concept has a much quicker response, especially by a large difference between the desired and actual torque, thus being selected as our algorithm’s cornerstone.
2. Problem Statement
Most researchers try to increase the number of gears so that they can decrease the transmission ratio difference between each gear, which undoubtedly relieves the difficulties of the control algorithm. Secondly, for the cost reason, precise measurement of the signal is still challenging, and thus the actuator dynamics should be taken into account while designing the controller. Last but not least, although many companies in the field of mobile machines show great interest in using power shift transmission, they did not propose a concrete algorithm to achieve good shift quality. Consequently, the drive comfort during the shifting process of the HST+DCT drivetrain was never satisfying; no wonder it has only a small market share. We conjecture it might be that it is impossible to adopt the easiest method that increases the number of mechanical gears on a hydrostatic mobile machine.
3. Goal of This Research
The goal of our study is to find out a suitable control concept that guarantees a fast and smooth shift process of HST+DCT drivetrain for the whole shifting process. Concretely, we control the actual tractive effort so that it is almost the same as the desired tractive effort during the shifting process, as in Equation (1):
where and denote the shifting start and end time, is the actual Torque at the time t, and is apparently the desired torque.
4. System Modelling
4.1. Powertrain
In order to obtain more insight into the control algorithm, we greatly simplify the dual-clutches model according to [10]. The dual-clutch gearbox has primary parts (subsystem 1) and secondary parts (subsystem 2), corresponding to the part before the reduction gears and the part after the reduction gears, separately. Figure 2 illustrates the simplified powertrain model we use.

Figure 2.
Simplified powertrain model: is the rotation speed of primary part of the first gear, is the output torque of hydraulic motor, is the drive torque on the wheels, is the resistant force, and is the rotational inertia of the hydraulic motor.
The driving torque in the transmission chain is completely transmitted by the torques on both clutches and . Moreover, the transmission loss is given by the final drive, while the damping and stiffness of the drive shaft are not taken into account.
The power train dynamic is described as follows: if both of the two clutches are not in an engagement state, the transmission chain is a 2DOF system. Regardless of upshifting or downshifting, we produce a positive drive torque on the wheels. Thus, the 2DOF system can be drawn as
where the value of driving torque depends on the values of the two clutch torques and the transmission parameters:
where the additional parameters and denote the normal force applying on the first and the second clutch, separately.
When the vehicle runs stably in gear 1, i.e., the clutch 1 is in engagement, the degree of freedom of the system is reduced by 1 because the rotational speed of motor shaft, the secondary side of the first clutch, and final-drive shaft must satisfy the following kinematics constraints. Considering the shifting process is either from the higher gear to the lower gear or in reverse, we define subscript L as the lower side and h as the higher side. For instance, is the rotation speed of the lower side because the system we use in this paper has only two gears; the lower gear is always the first gear.
Although the final-drive shaft rotates at an unidentical speed, the ratio is fixed. In order to simplify the expression, the other clutch is set to be entirely disengaged without sliding, ; thus, system equation is rewritten to
and the torque on the first clutch is calculated as follows:
If the first clutch is in the engagement state, its torque is no longer controlled only by the pressure acting on it. The result obtained by Equation (8) is the clutch torque required to meet the dynamics and kinematic constraints. The pressure on the clutch friction plate represents the maximum torque that the clutch can transmit.
Only when the following conditions are met, i.e., the maximal transmittable torque is larger than the desired transmit torque, the clutch maintains the engagement state; otherwise, it will start to slide.
Normally, the driving resistance of the vehicle is more difficult to measure or estimate. From another perspective, the desired clutch torque can be calculated from the torque balance on the motor side.
It can be seen from Equation (12), in the case where the motor output torque and the rotational acceleration of the drive shaft are known, that the value of the clutch torque required to maintain the stable running of the vehicle in gear one can be calculated, wherein the first derivative of vehicle speed can determine the rotational acceleration of the drive shaft.
It can be concluded that because the moment of inertia of the motor torque exists, the torque acting on the clutch is unidentical to the torque output by the motor, i.e., the driving torque acting on the transmission shaft cannot be directly converted from the motor output torque. It is also necessary to consider the torque required to accelerate the motor’s moment of inertia.
Similarly, when the vehicle is running stably at gear 2, the equation of 1 DOF system is given without derivation as the 1 DOF system equation for gear 2:
The torque is required to ensure that the clutch 2 does not slip.
4.2. Actuator
The input signal of the actuator is the output of the controller. Although the controller’s instructions are correct, the system may not perform well due to the slow response of the actuators. Thus, the controller must output the command in which the dynamics behavior of actuators is already considered. The dynamic response of the actuator is modeled as 1st order differential Equation [13],
and are the actuators’ time constant. The variables with an apostrophe are control signals, while the variables without a dot or apostrophe, e.g., , are the expected torque considering the dynamic response.
5. Power Shift Controller
The power shift controller consists of two parts, the Phase Selector and the Torque Generator. According to different shifting requirements (upshift or downshift), the phase selector selects the corresponding control mode. Additionally, the shifting process is further subdivided into different stages. The generator outputs a specific control signal according to the phase signal given by the phase selector.
5.1. Control Schema
The control framework based on the torque based control consists of a target torque generator, a powershift controller, an actuator dynamic module, and a power train model. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Power shift controller framework.
The controller outputs to the vehicle model three torque variables that affect the shifting process: motor torque, higher gear clutch torque, and lower gear clutch torque. The controller determines, according to the target, the driving condition, the driver’s wish, the state variable of the vehicle as a boundary condition, and whether the vehicle can complete the given shift command in the current driving situation; if so, it outputs the corresponding control variable, and if not, it outputs the control variable of the closest target requirement.
For the torque control of the shifting process, it is necessary to consider the blockage of the actuator when calculating the control variable to eliminate the influence of the dynamic response of the actuator on the control performance in the actual process.
5.2. Phase Selector
Figure 4 shows the schematic diagram of phase selector. The shifting process is divided into several sub-stages to distinguish different requirements of the power shift controller. Drive mode represents the drive chain, which is in the process of upshifting, downshifting, or maintaining the current gear. In the specific algorithm implementation, the upshift is divided into torque phase and inertia phase. Moreover, the inertia phase is subdivided into fast reduction of slip speed, controlled reduction of slip speed, and forcibly engaged phase.

Figure 4.
Phase selector.
In the downshift process, there is no apparent torque phase. The cross-shift occurs during the second inertia phase. Concretely, it begins at the time when the first reaches the .
The phase transition is determined according to the vehicle state. For example, in the torque phase, when the phase selector judges whether the cross shift has ended, it is necessary to pass the clutch torque feedback to indicate whether the clutch has been disengaged. In the inertia phase, it determines whether the controller flows into the next stage base on the slip speed and slip acceleration.
5.3. Torque Generator
The concept is shown in Figure 5, where the torque generator is the core module of the torque controller. The controller’s input signals are , drive mode, phase signal, and vehicle state. The tracking of target driving torque is the main task of the power shift controller, drive mode and phase can be seen as boundary conditions, and vehicle state is the feedback from power train dynamics.
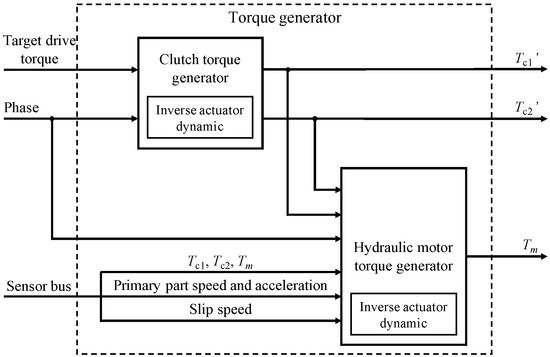
Figure 5.
Torque generator.
The clutch torque generator needs to give the clutch torque and its rate of change required to track the target driving torque according to the boundary conditions. Furthermore, the motor torque generator needs to calculate the motor torque according to the vehicle state feedback to meet the controllable condition of the clutch torque.
If the torque balance is destroyed during the shifting process, a completely different control performance will be produced; thus, a precise torque control is required. It is necessary to pre-consider the effect of the actuator delay, i.e., the inversed actuator dynamics will be taken into account when designing the control signal. In this way, after the actuator delay the control signal can still complete the control tasks.
6. Control Algorithm
6.1. Torque Phase
In the upshifting process, the first torque drop happens in the torque phase [33] when the cross shift occurs. The core idea of the solution is to let the hydraulic motor rotate faster than the primary part of dual-clutch transmission so that the system is decoupled and can be controlled separately. In the case of upshifting, at the initial point of the torque phase, there is no slip, i.e., . The concrete control idea can be illustrated with the following equations.
Equation (20) shows the necessary condition to achieve the control algorithm. Otherwise, the Equations (18) and (19) will have a different sign, which makes the control dramatically difficult. According to Equation (18), the transmitted torque of the second clutch can be calculated based on and . Since goes to zero while upshifting with a specific slope given by the designer, we can acquire . After we obtain , the desired hydraulic motor torque can be acquired. For the purpose of the robustness of the controller, the should be selected carefully to guarantee the slip is always positive. However, it might lead to an unnecessary additional friction loss of the clutches. Therefore, this safety value should be as small as possible from the respective of energy loss. Taking the actuator dynamics into account, we describe the control signal of hydrostatic motor torque as Equation (21),
6.2. Inertia Phase
In the inertia phase of the upshifting process, the hydraulic motor rotation speed must slow down to the corresponding upcoming gear. In this case, the slip between hydraulic motor and primary part of the dual-clutch absolutely exists. Thus, the output torque on vehicle wheels is further controlled by clutches. However, the challenge of implementing a control algorithm on a vehicle is dealing with the transmit torque when the clutch has just been engaged. At this time, the system will lose one degree of freedom, i.e., from 2 DoF to 1 DoF system, resulting in the last torque dip. Thus, the driving force might change immediately. The following equations illustrate the solution to this problem.
The drive torque before engagement is demonstrated as Equation (22),
In contrast, the drive torque after engagement is demonstrated as
Equation (22),
Since the motor torque and the driving resistance is continuous,
The drive torque, i.e., the difference between the drive chain output before and after the engagement are the object of the controller to minimize:
After is substituted into the Equation (26), the torque drop is interpreted as:
As shown in Equation (27), is the only controllable variable since the other parameters are fixed after the vehicle is designed. Formally, if is 0 when the clutch is just engaged, theoretically, there should not be a torque drop. However, to control the is a difficult task in practice. First and foremost, is challenging to measure because there is usually no acceleration sensor on the shaft to measure the rotation acceleration. Besides, to measure the slip acceleration, at least two acceleration sensors must be used. Moreover, the dynamics of actuators might be quite different, thus making the calibration process considerably difficult. Last but not least, the acceleration sensors have higher noise in general and surely have a negative influence on control performance. Alternatively, we use an algorithm based on the concept from van Berkel [13], which only uses as the measured term. Figure 6 illustrates the control algorithm in the inertia process for a downshift process since downshift is the more complicated process. In order to achieve the fast and smooth engagement, the inertia phase is further divided into five sub-phases: the first fast phase (P0), the first smooth phase (P1), the second fast phase (P2), the second smooth phase (P3), and the forcibly engaged phase (P4).

Figure 6.
Algorithm explanation during the downshifting inertia phase: and are the triggers for the first and second smooth phase separately.
By deriving the differential equation containing the controlled object , the design method of the control variable could be obtained.
When the form of Equation (28) can be converted into
under the condition of , this equation can be described as a critical damping system. The dynamics of slip speed should be critically dampened since the response will be fastest without overshooting, which fits the requirement of faster shifting process.
Here, we introduce a constant offset , and the modified slip speed is . The value of is peripheral since it will be eliminated in the transformation of equations. The equation after linearisation is
7. Simulation Results
In this section, the performance of the control algorithm would be validated. The drivetrain parameters used in simulations are based on a real wheel loader and shown in Table A1.
Notice that, for validation the algorithm, we consciously let the drivetrain track a constant drive force demand since it must be the most challenging use case.
As shown in Figure 7, transmittable clutch torque controls the torque on the wheels during the whole downshifting process, while the hydraulic motor takes the responsibility to minimize the friction loss, positive power flow, and the fast and smooth engagement process. The next figure, Figure 8, shows how the variables vary during the shifting process, where denotes the slip speed between the hydraulic motor and primary first gear part of dual-clutch transmission and indicates the second gear. The torque drop due to engagement is controllable and defined by since the at the moment of the engagement.

Figure 7.
Simulation results illustrating the control strategy and the performance during the downshifting process.

Figure 8.
Control variables during the downshifting process.
As aforementioned, while the mechanism of the inertia phase before the final engagement is the same between upshifting and downshifting, the torque phase is the unique phase during the upshifting process. As shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10, after the driver gives the upshift command, the motor shaft speed is slightly increased under motor torque control. It can also be observed in the figures, so that by increasing the slip acceleration, the slip speed is controlled to be a small positive value. By ensuring that the clutch one is sliding, the condition that the clutch torque is controllable in the torque phase is satisfied.

Figure 9.
Simulation results illustrating the control strategy and the performance during the upshifting process.

Figure 10.
Control variables during the upshifting process.
As the simulation results show, the slip is the prerequisite of this algorithm and the correct control of is the core to achieve a fast and smooth shifting process. Additionally, there is no sudden change of control signal, which demonstrates that high dynamic actuators are not in need.
8. Shift Management
Although the powershift with acceptable comfort is viable, the friction in the clutches is unavoidable. In order to extend the service time of the transmission, the powershift shall only occur when the vehicle is uphill and at a low velocity, to avoid the roll down situation. In other scenarios, the interruption of tractive effort is not a problem, so we recommend engaging the upcoming gear after the ongoing gear is totally disengaged.
9. Conclusions and Outlook
This article proposes a control strategy for the shifting process of construction machines equipped with a dual-clutch transmission. We firstly conclude with the main problems that occurred during the shifting process. First of all, although the initial intention of using the dual-clutch is to avoid the torque interruption during the shifting process, the torque output from the powertrain still has large fluctuations. Moreover, there is a dilemma between the rapidity and the smoothness of the shifting.
To solve the above problems, we divide the shifting process into different stages to break down the complex control task into sub-tasks and define a clear boundary line for each sub-phases to realize the modular control of the sub-process. By summarizing the characteristics of the sub-stages that appear in the downshift, we sum up the mathematical problems with unity from these sub-stages. The shift duration and the torque drop at the end of the shift are all affected by the slip acceleration. The first-order derivative of the slip acceleration is related to the changing rate of the motor and clutch torques. Therefore, the control of the shifting process is a control of the changing rate of the torque according to the demand.
As shown in the simulation results, the control strategy by means of clutch and motor torque control to achieve a smooth shifting process is feasible since the desired drive torque is well tracked. In addition, the highly dynamical actuator is not required to achieve the control performance, which shows the practical meaning of this control algorithm. When tracking the target drive torque during the shifting process, the controller firstly calculates the changing rate of the clutch torques; to meet the controllability condition of the clutch torque, the controller calculates the corresponding motor torque simultaneously. By applying this control algorithm, the systematically adjustable control performance is possible. To adjust the contradiction between rapidity and smoothness during the inertia phase, the controller uses two calibration parameters: and .
Outlook
The limitation of the research is that the powertrain model used in this paper does not consider the stiffness and damping of the transmission shaft. If the neglected damping and stiffness are found to have a strong influence on the control effect in actual situations, the changing rate of the control signal needs to be constrained. The target is prevent the excitation signal and the characteristic frequency of the system from coinciding, which may lead to a sympathetic vibration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Y.X.; methodology: Y.X.; software: Y.X. and R.L.; validation: R.L.; formal analysis: Y.X. and R.L.; investigation: Y.X. and R.L.; resources: Y.X. and R.L.; data curation: Y.X. and R.L.; writing—original draft preparation: Y.X. and R.L.; writing—review and editing: Y.X. and M.G.; visualization: R.L. and X.L.; supervision: M.G.; project administration: C.B.; funding acquisition: C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. The study is not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge: Steffen Mutschler; Robert Bosch GmbH, for his enthusiastic encouragement and insightful discussions on dual-clutch transmission; and Hengping Zhao, Beijing Institute of Technology, for proof reading.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
We give the parameters of the vehicle to help the readers to reproduce the results of our algorithm. They are based on the real parameters of the machine with acceptable measurement error. Based on our study, the algorithm is robust and still works in case the settings change. Note that, for commercial use, you should ask for our permission since we have applied for the patent.

Table A1.
Vehicle model parameters.
Table A1.
Vehicle model parameters.
| Symbol | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | kg m2 | Motor inertia | |
| 9450 | kg | Vehicle mass | |
| 615 | mm | Wheel radius | |
| 3574.2 | kg m2 | Vehicle equivalent inertia | |
| 0.8 | − | Drag coefficient | |
| 0.8 | m2 | Reference area | |
| 1.293 | kg/m3 | Density of air | |
| 3.74 | − | Gear one ratio | |
| 1.5 | − | Gear two ratio | |
| 15.429 | − | Final drive ratio | |
| 1.5 | kg m2 | Motor inertia | |
| 0.9 | − | Final drive efficiency | |
| 0.08 | s | Motor time constant | |
| 0.04 | s | Clutch time constant |
References
- Xiang, Y.; Geimer, M. Optimization of operarion strategy for primary torque based hydrostatic drivetrain using artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 12th International Fluid Power Conference, Dresden, Germany, 12–14 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mutschler, S.; Brix, N.; Xiang, Y. Torque control for mobile machines. In Proceedings of the 11th International Fluid Power Conference, Aachen, Germany, 19–21 March 2018; Murrenhoff, H., Ed.; RWTH Publications: Aachen, Germany, 2018; pp. 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Mutschler, S.; Brix, N.; Brach, C.; Geimer, M. Optimization of hydrostatic-mechanical transmission control startegy by means of torque control. In Proceedings of the 12th International Fluid Power Conference, Dresden, Germany, 12–14 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Quan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Yang, J. Efficiency improvement and evaluation of electric hydraulic excavator with speed and displacement variable pump. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, M.; Bogdevičius, M. Review of Energy-saving Technologies in Modern Hydraulic Drives. Moksl. Liet. Ateitis 2017, 9, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Jeong, E.; Ahn, K. Review of Energy Saving Technology of Hybrid Construction Machine. J. Drive Control. 2018, 15, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Su, T.; Brach, C.; Liu, X.; Geimer, M. Realtime estimation of IEEE 802.11 p for mobile working machines communication respecting delay and packet loss. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19 October–13 November 2020; pp. 1516–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Z.; Ge, L.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.W.; Quan, L. A Survey of Powertrain Technologies for Energy-Efficient Heavy-Duty Machinery. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Tang, T.; Su, T.; Brach, C.; Liu, L.; Mao, S.S.; Geimer, M. Fast crdnn: Towards on site training of mobile construction machines. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 124253–124267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Küçükay, F.; Jürgens, G.; Najork, R.; Pollak, B. The Automotive Transmission Book; Powertrain; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, P.D.; Zhang, N.; Tamba, R. Control of gear shifts in dual clutch transmission powertrains. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 1923–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Liu, J.; Smedley, D. Simulation Study of Dual Clutch Transmission for Medium Duty Truck Applications. SAE Trans. 2005, 114, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel, K.; Hofman, T.; Serrarens, A.; Steinbuch, M. Fast and smooth clutch engagement control for dual-clutch transmissions. Control. Eng. Pract. 2014, 22, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.; Shim, T.; Zhang, Y. Shift dynamics and control of dual-clutch transmissions. Mech. Mach. Theory 2007, 42, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y. Shift control strategy and experimental validation for dry dual clutch transmissions. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 75, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Oh, J.; Choi, S. Gear shift control of a dual-clutch transmission using optimal control allocation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 113, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.J.; Choi, S.B.; Kim, J. Driveline modeling and estimation of individual clutch torque during gear shifts for dual clutch transmission. Mechatronics 2014, 24, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Gatta, A.; Iannelli, L.; Pisaturo, M.; Senatore, A.; Vasca, F. A survey on modeling and engagement control for automotive dry clutch. Mechatronics 2018, 55, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, V.; Cappetti, N.; Pisaturo, M.; Senatore, A. Improving the engagement smoothness through multi-variable frictional map in automated dry clutch control. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Houston, TX, USA, 9–15 November 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 45271, pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pisaturo, M.; D’Auria, C.; Senatore, A. Friction coefficient influence on the engagement uncertainty in dry-clutch AMT. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 7561–7566. [Google Scholar]
- Lucente, G.; Montanari, M.; Rossi, C. Modelling of an automated manual transmission system. Mechatronics 2007, 17, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcini, P.J.; Canudas-de Wit, C.; Béchart, H. Dry Clutch Control for Automotive Applications; Springer Science Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pica, G.; Cervone, C.; Senatore, A.; Lupo, M.; Vasca, F. Dry dual clutch torque model with temperature and slip speed effects. Intell. Ind. Syst. 2016, 2, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garofalo, F.; Glielmo, L.; Iannelli, L.; Vasca, F. Smooth engagement for automotive dry clutch. In Proceedings of the 40th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (Cat. No. 01CH37228), Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 December 2001; Volume 1, pp. 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- Geimer, M.; Pohlandt, C. Grundlagen Mobiler Arbeitsmaschinen. Karlsruher Schriftenreihe Fahrzeugsystemtechnik; KIT Scientific Publishing: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2014; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel, M.; Bleazard, T.; Haria, H.; Ivantysynova, M. Implementation of a Novel Hydraulic Hybrid Powertrain in a Sports Utility Vehicle. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 15, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollner, W. Hydrostatic Mechanical Gearbox. U.S. Patent 2007281815, 6 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bagusch, J.; Rahmfeld, R.; Göllner, W. Neue Antriebsstrategien für Radlader mit hydrostatischem Getriebe. In Hybride und Energieeffiziente Antriebe für Mobile Arbeitsmaschinen; Danfoss Power Solutions GmbH: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Moersch, C.; Birkmann, C. Landwirtschaftliche Arbeitsmaschine Und Verfahren Zum Betrieb Einer Landwirtschaftlichen Arbeitsmaschine. European Patent EP 3457000 A1, 20 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vukovic, M.; Sgro, S.; Murrenhoff, H. STEAM—A mobile hydraulic system with engine integration. In Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 2013 Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control, Sarasota, FL, USA, 6–9 October 2013; p. V001T01A005–V001T01A005. [Google Scholar]
- Vukovic, M.; Leifeld, R.; Murrenhoff, H. STEAM—A hydraulic hybrid architecture for excavators. In Proceedings of the 10th International Fluid Power Conference, Dresden, Germany, 8–10 March 2016; Technische Universität Dresden: Dresden, Germany, 2016; pp. 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel, M.W. Influence of Architecture Design on the Performance and Fuel Efficiency of Hydraulic Hybrid Transmissions. Dissertations, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, M.; Levesley, M.C.; Crolla, D.A. Emissions: Advanced catalyst and substrates, measurement and testing, and diesel gaseous emissions. In Proceedings of the Powertrain and Fluid Systems Conference and Exhibition, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 27–30 October 2003; Westin Convention Center Hotel: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).