CFD-Based Erosion and Corrosion Modeling of a Pipeline with CO2-Containing Gas–Water Two-Phase Flow
Abstract
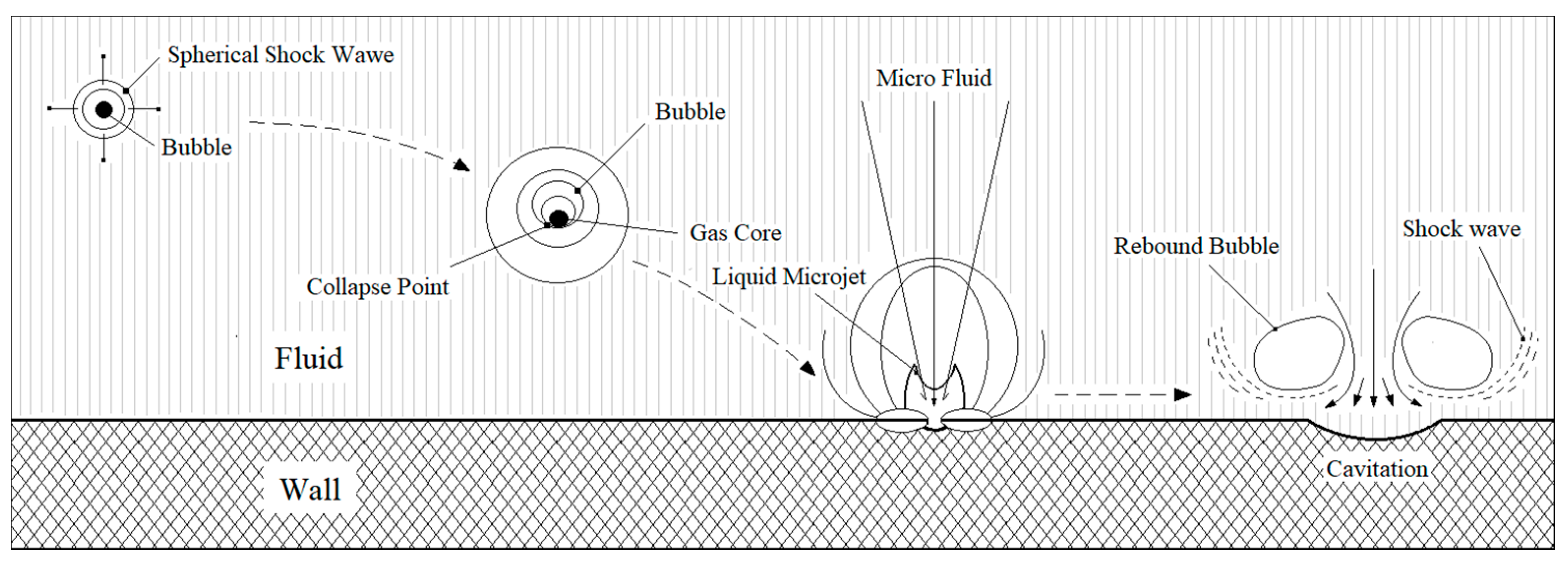
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
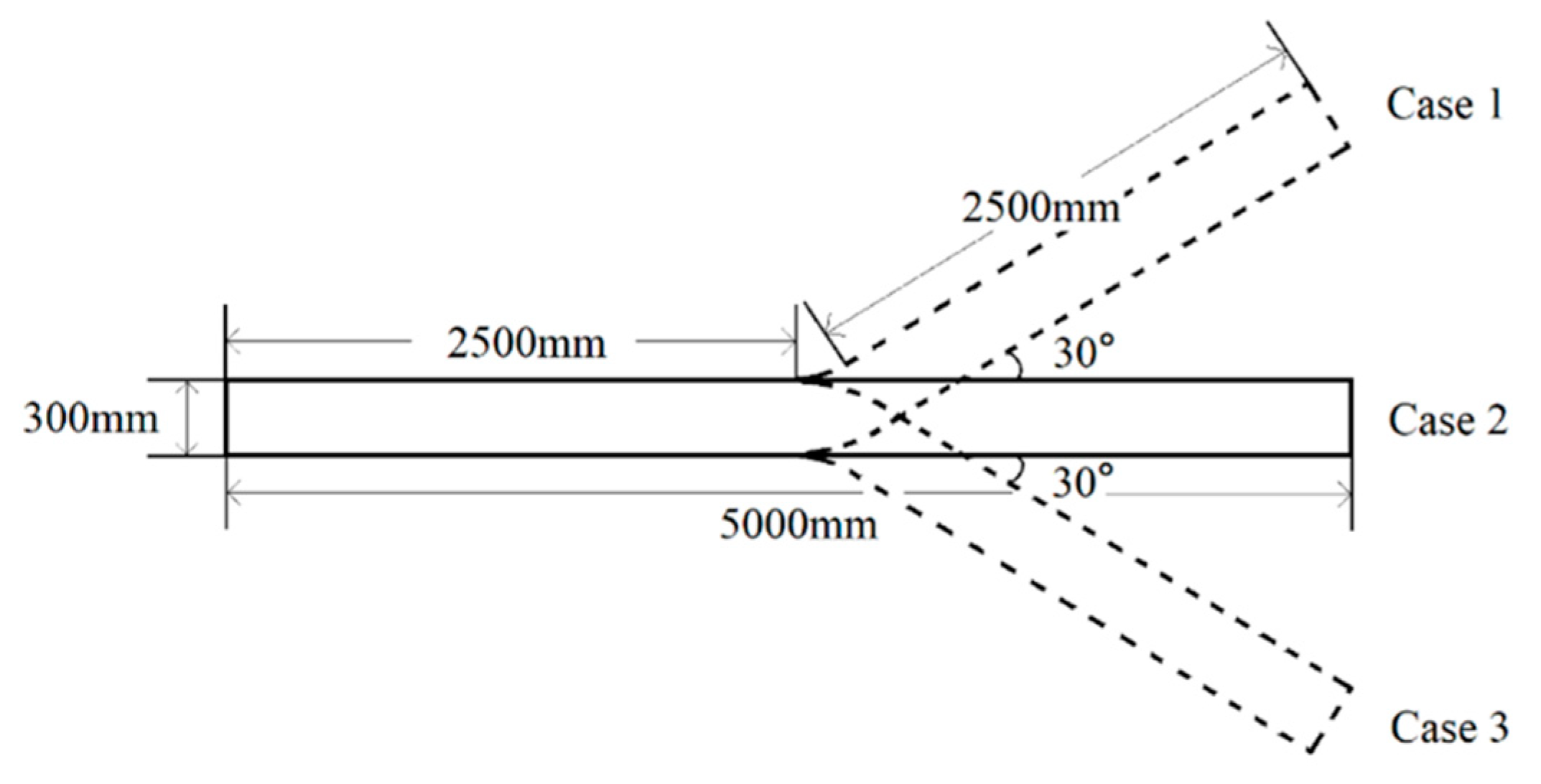
2.1. Operating Parameters
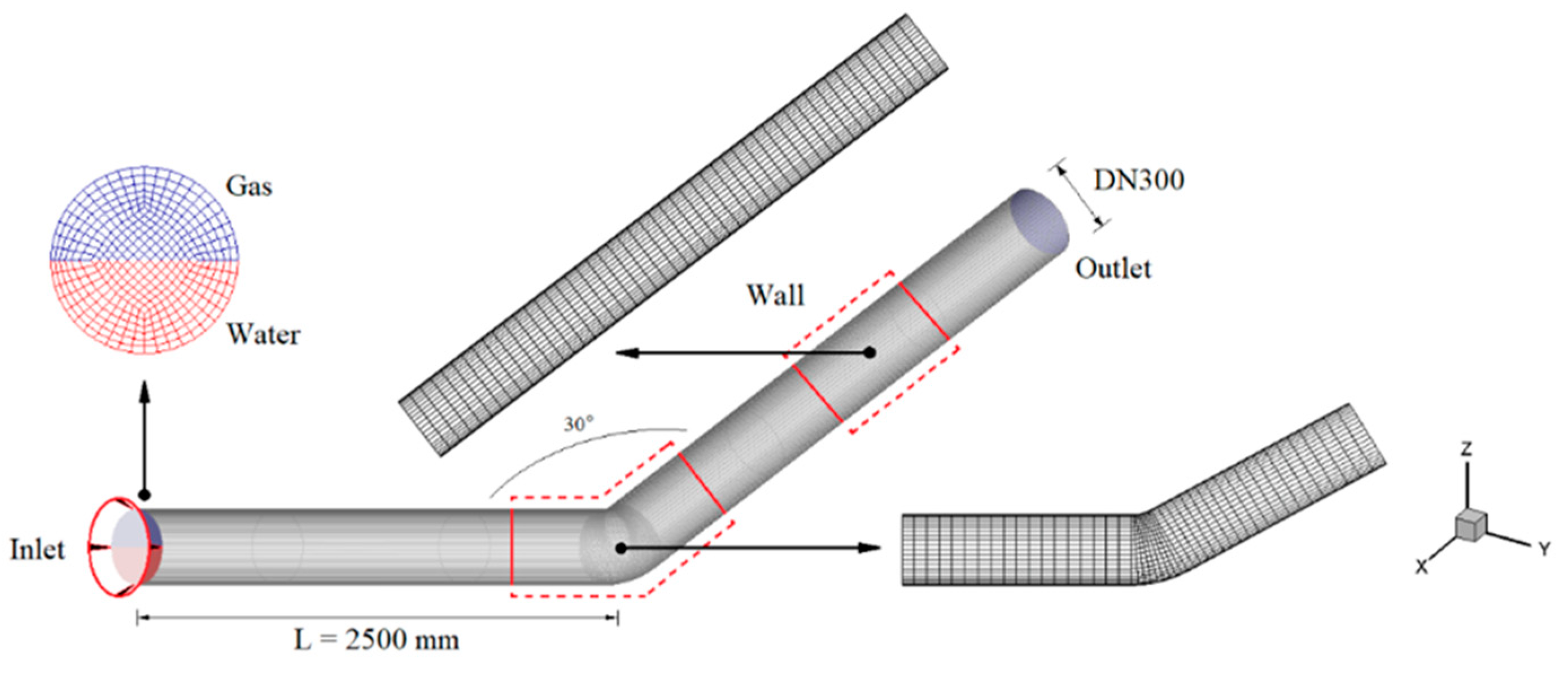
2.2. Meshing and Modeling
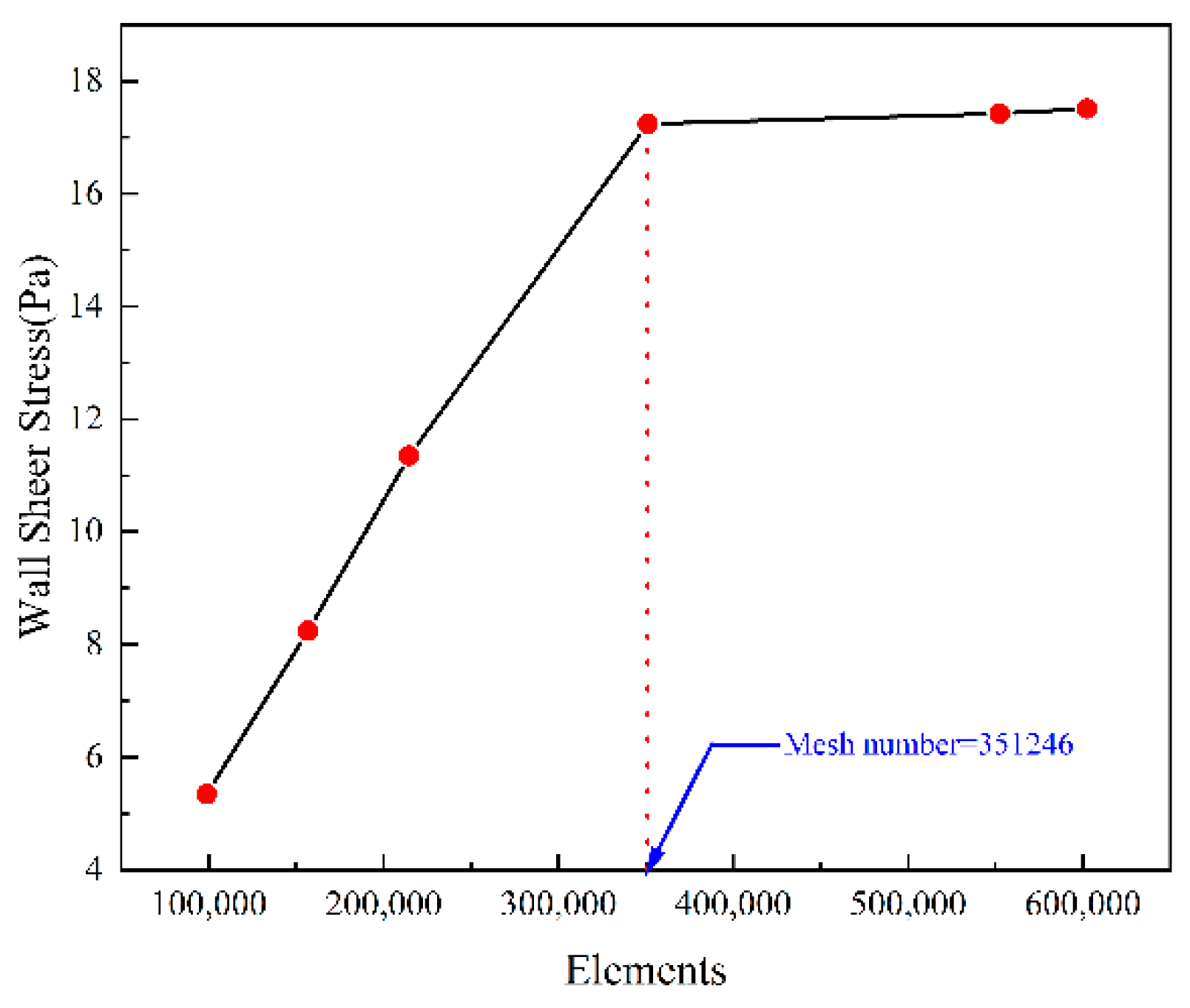
2.3. Mesh Independence Test
2.4. Assumptions and Initial Conditions
3. Results
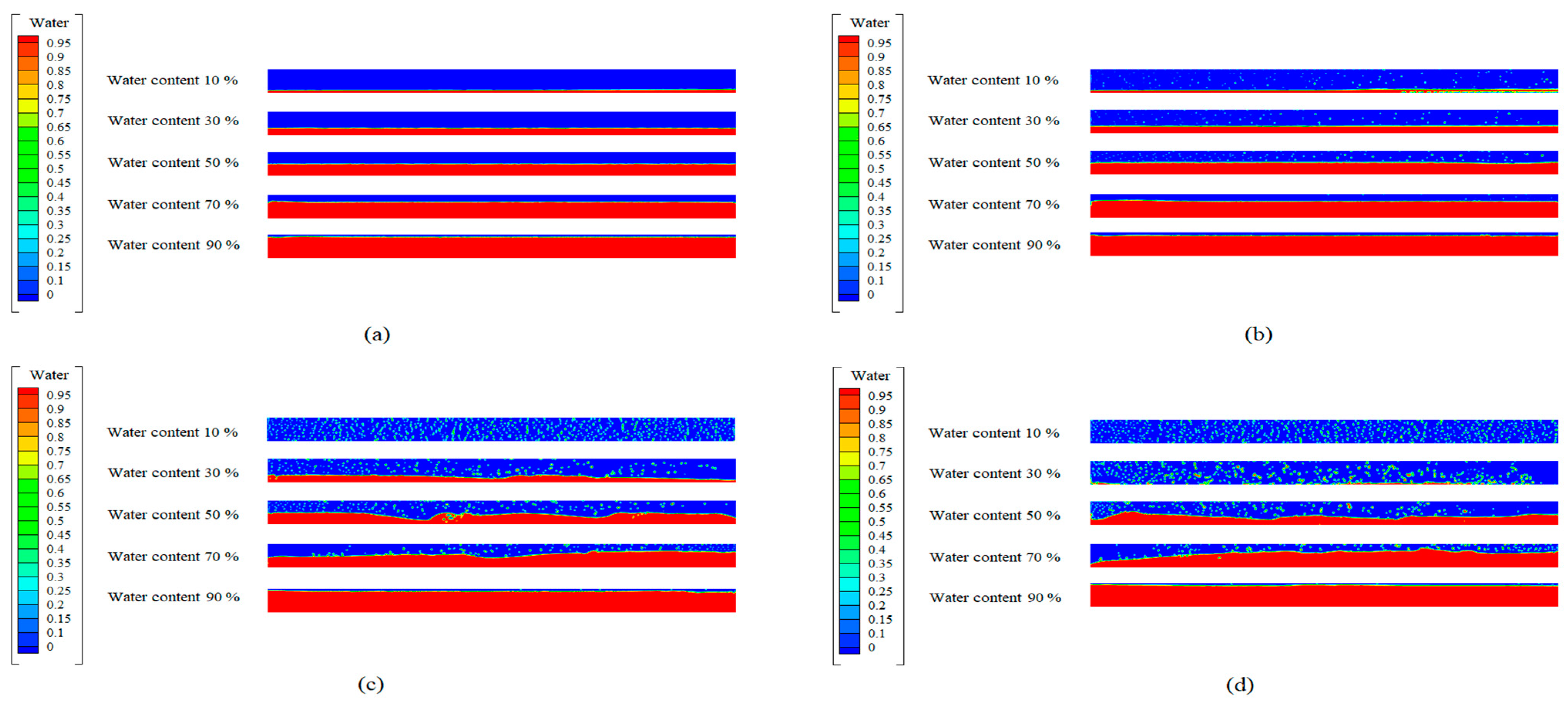
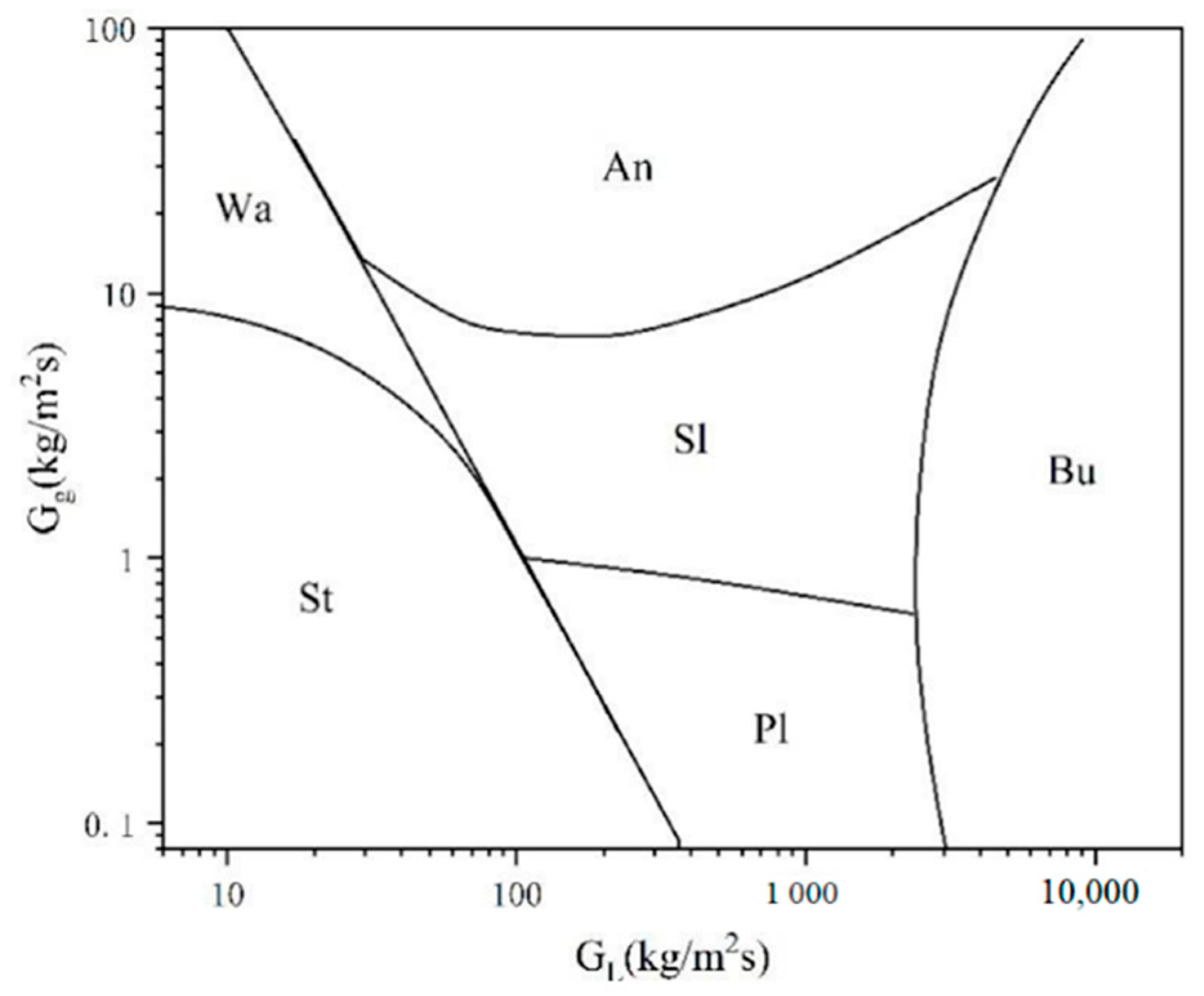
3.1. Flow Pattern for Straight Pipes
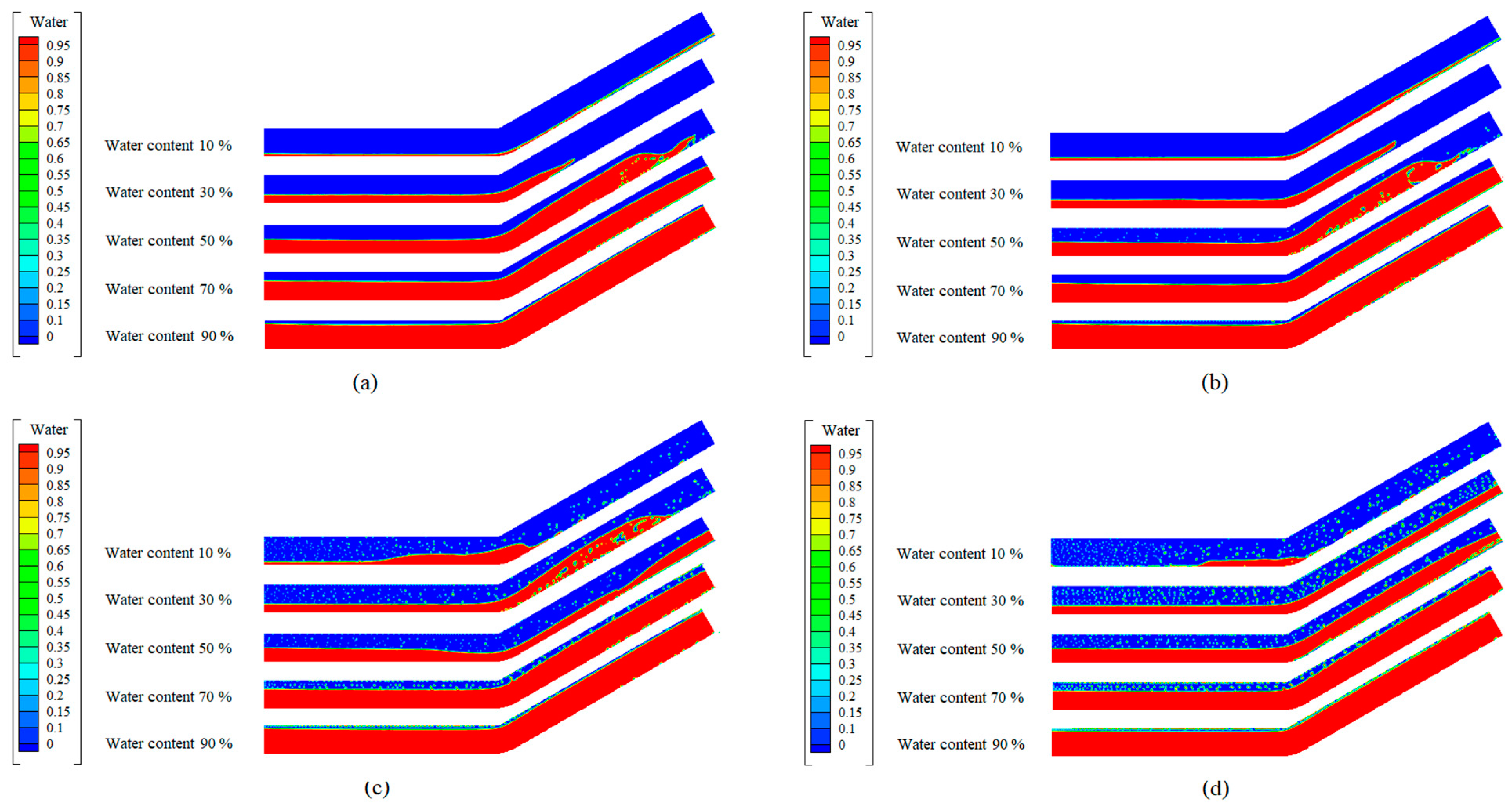
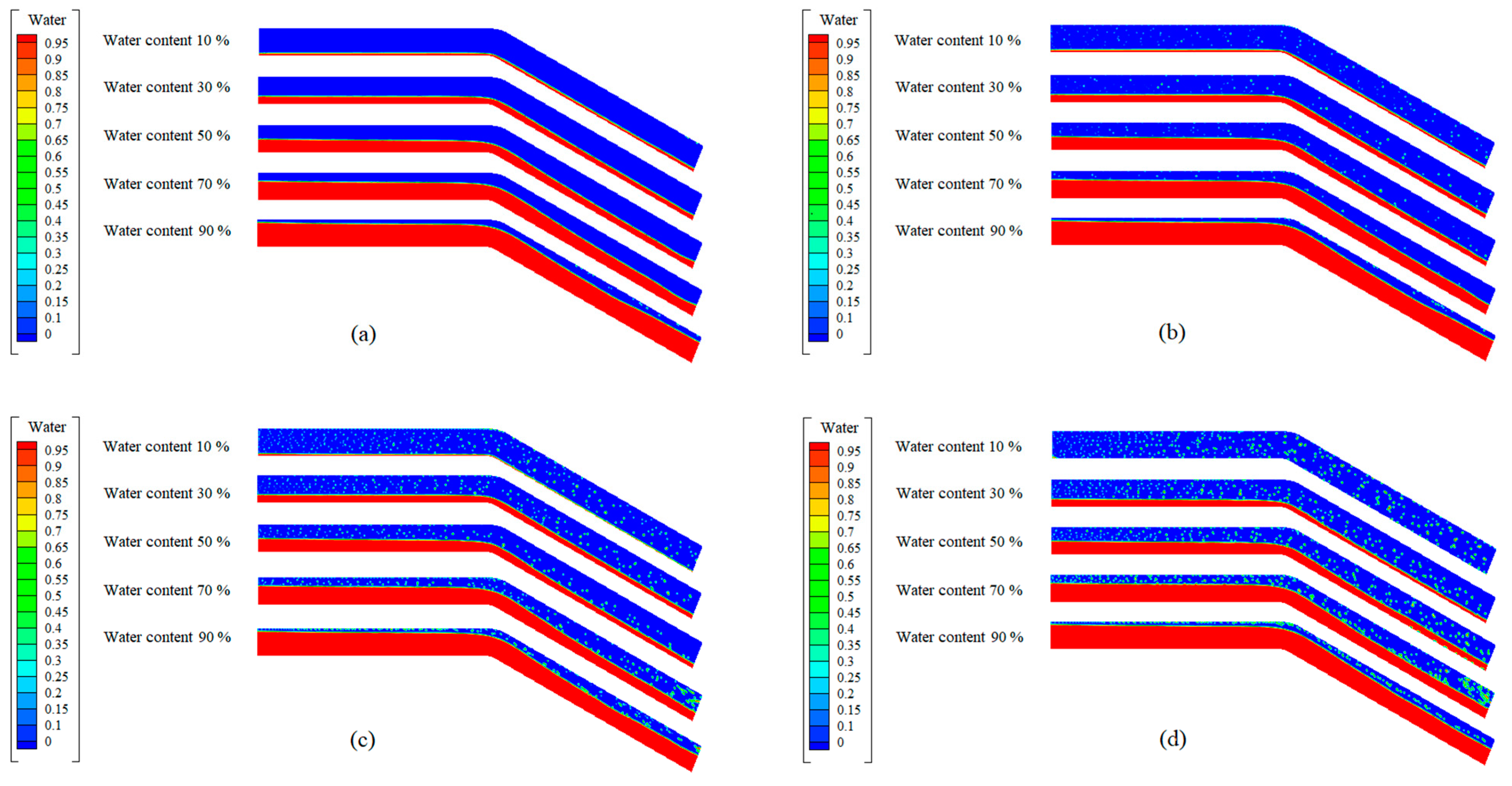
3.2. Flow Pattern for Inclined Pipe
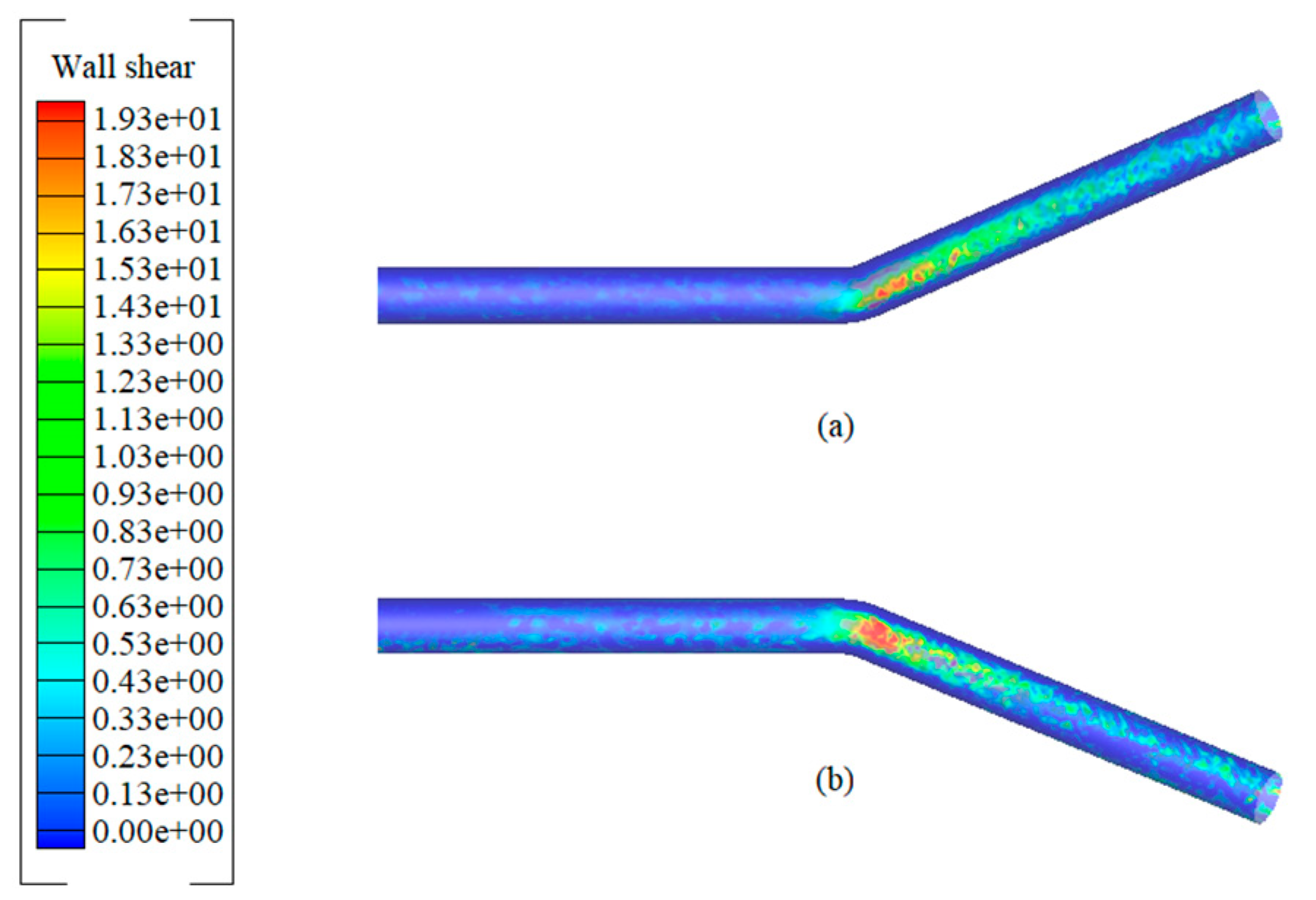
3.2.1. Upward-Inclined Pipe
3.2.2. Downward-Inclined Pipe
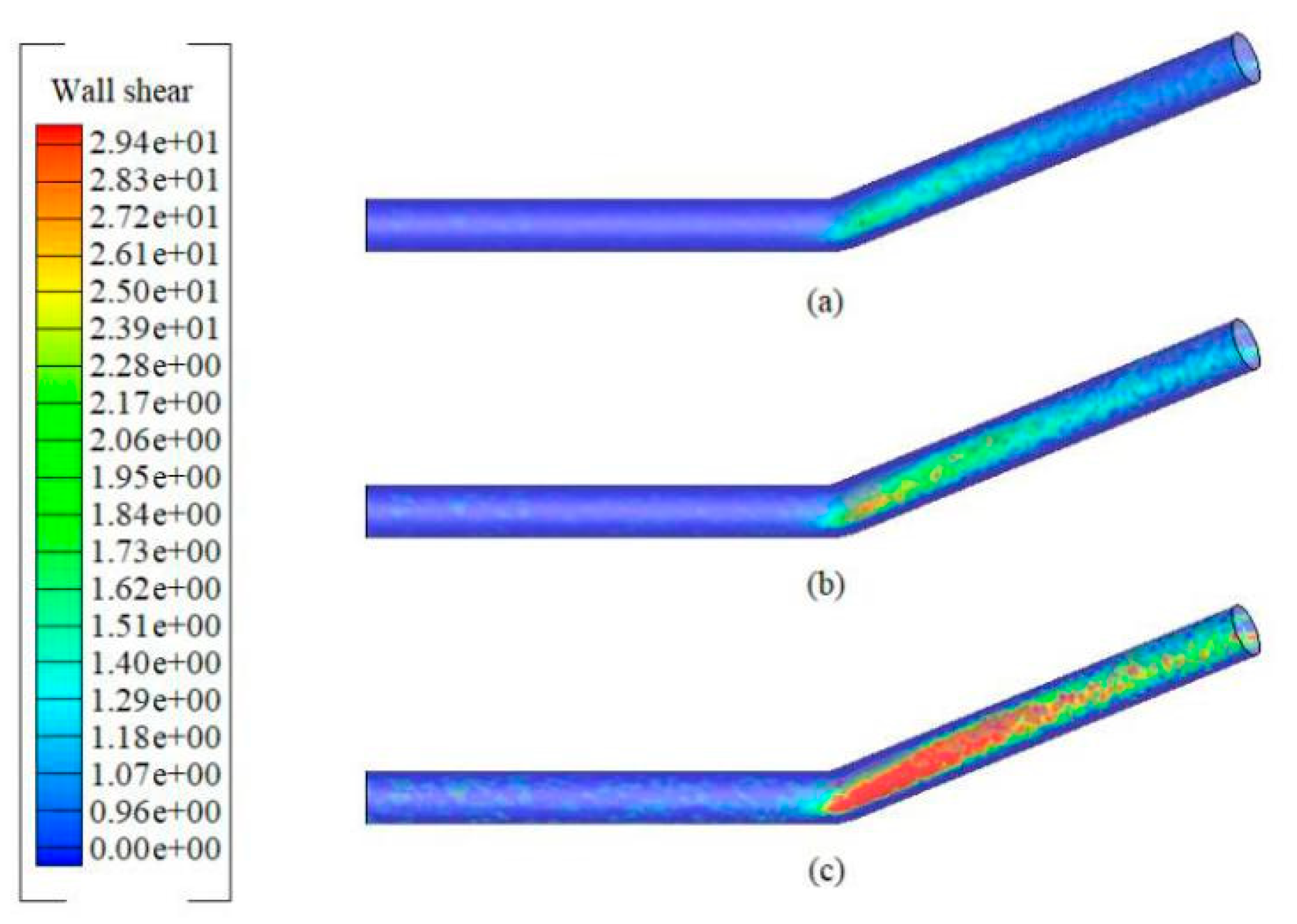
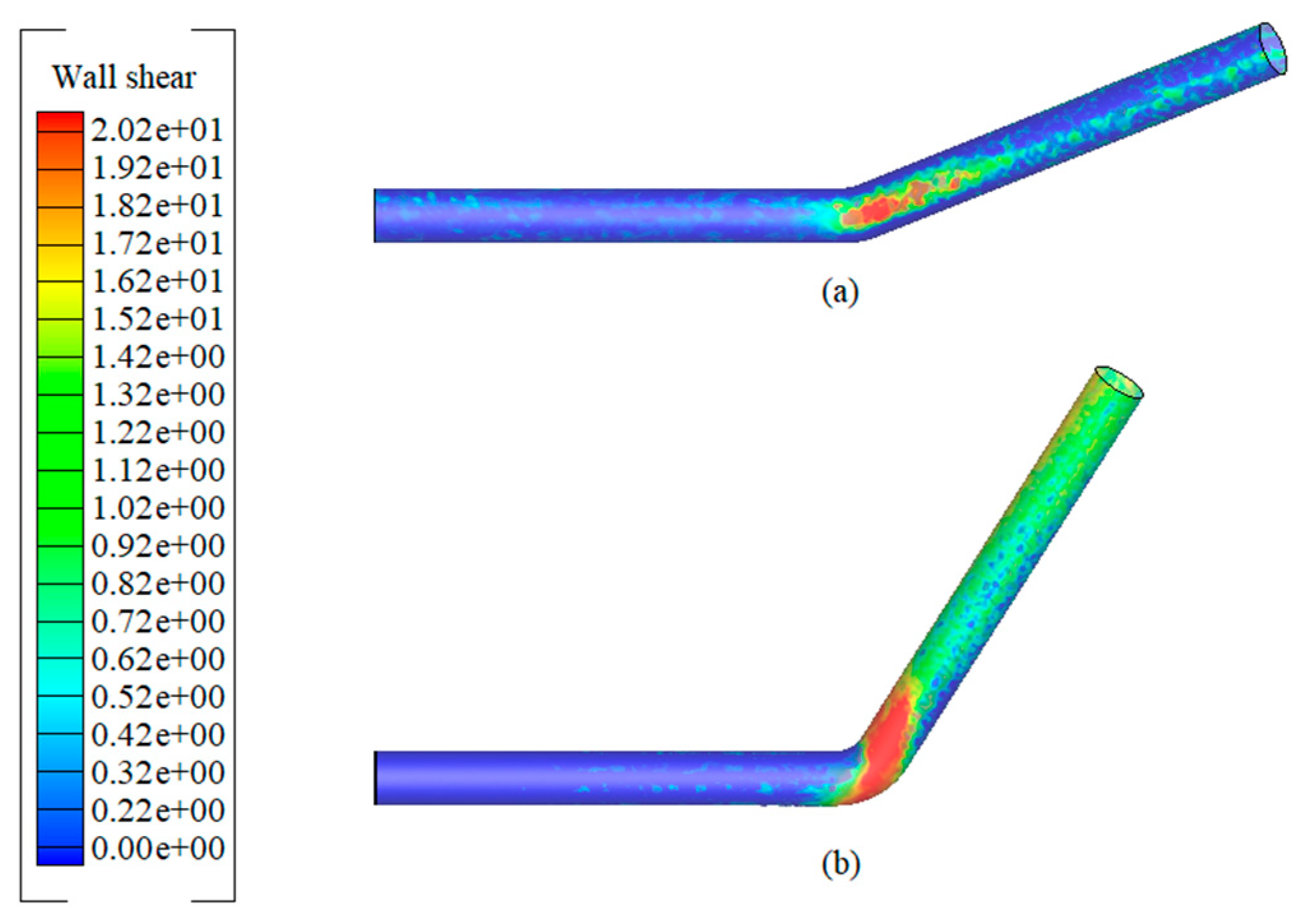
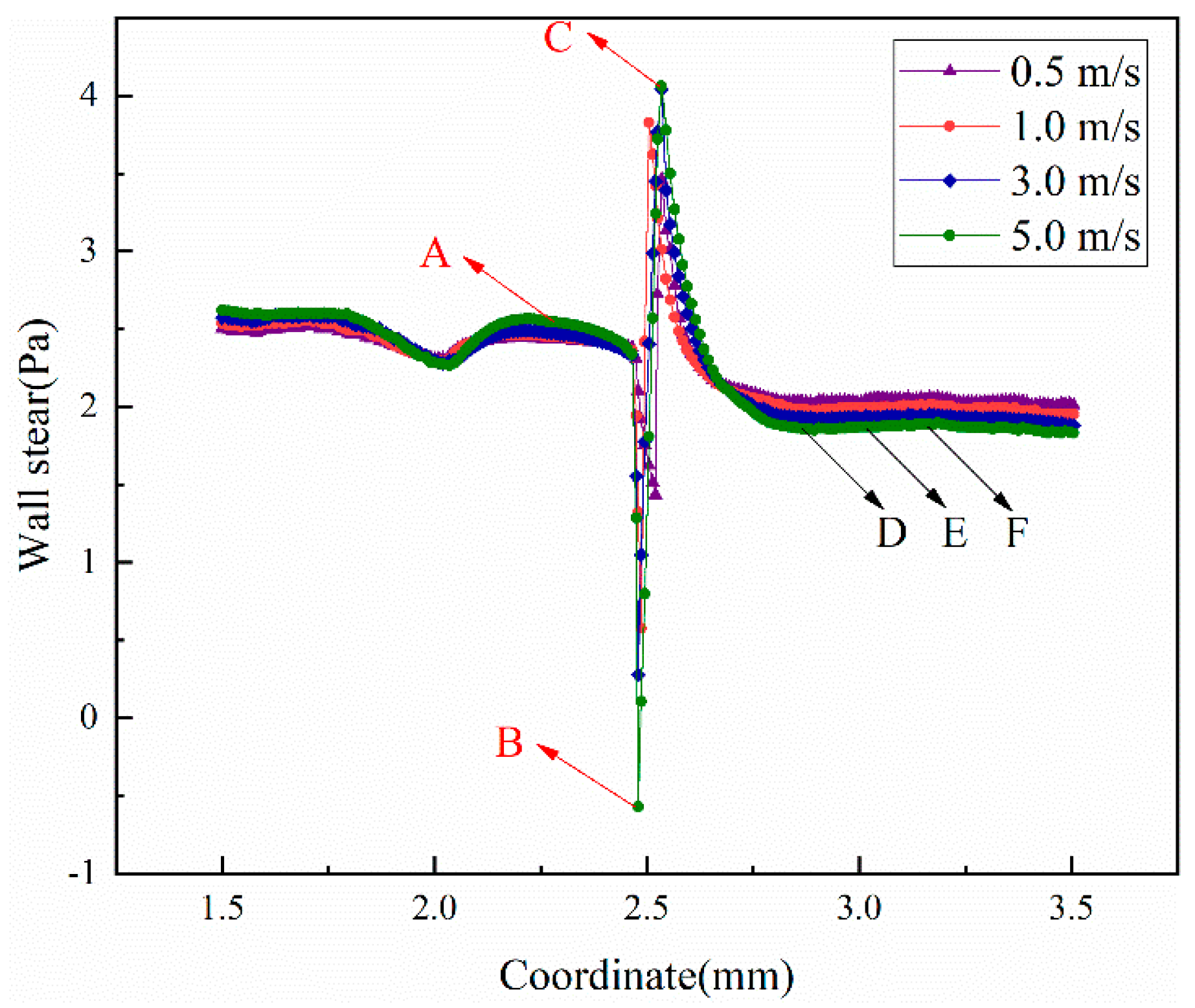
3.3. Wall Shear Stress in Inclined Pipes
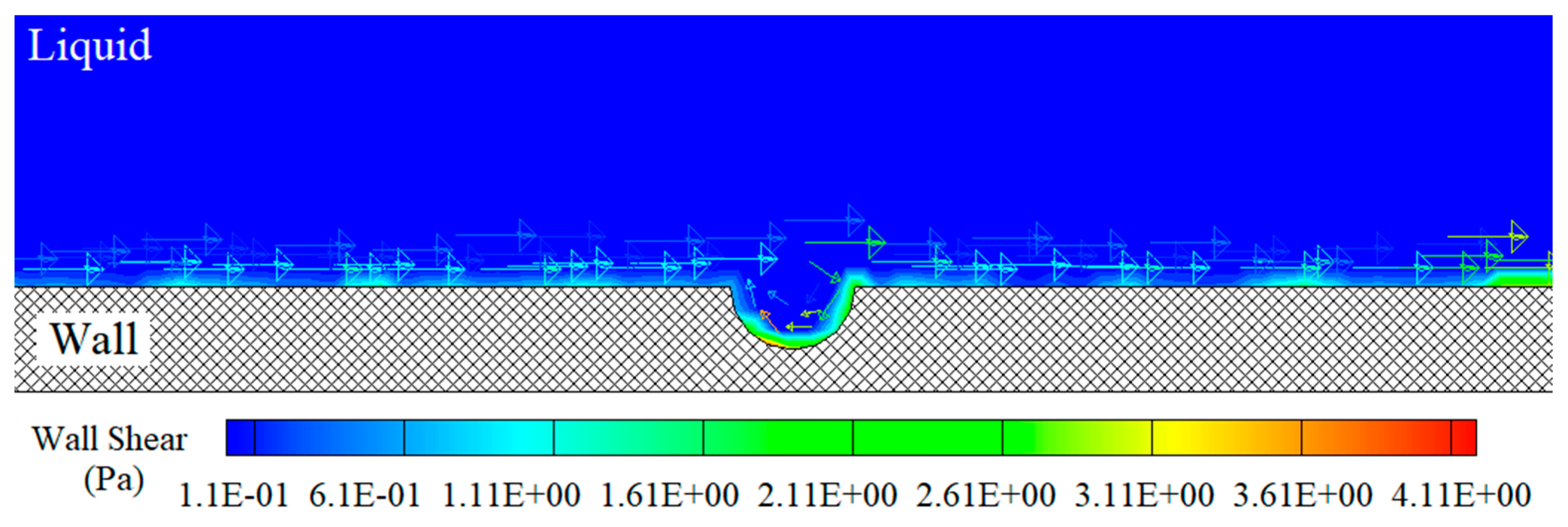
3.4. Localized Corrosion at Defect Sites
4. Discussion
4.1. CO2 Corrosion Mechanism
4.2. Localized Corrosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| VOF | Volume of fluid |
| FAC | Flow-assisted corrosion |
| ST | Stratified flow |
| Wa | Wavy flow |
| An | Annular flow |
| Sl | Slug flow |
| Pl | Plug flow |
| Bu | Bubbly flow |
| Fe | Iron atom |
| Fe2+ | Iron ion |
| H | Hydrogen atom |
| H+ | Hydrogen ion |
| H2 | Hydrogen |
| H2CO3 | Carbonic acid |
| CO3− | Carbonate ion |
| e− | Free electron |
| u | Gas superficial velocity, m/s |
| Greek symbols | |
| τ | Shear stress, Pa |
| μ | Fluid viscosity, mPa·s |
References
- Sun, D.; Wu, M.; Xie, F. Effect of sulfate-reducing bacteria and cathodic potential on stress corrosion cracking of X70 steel in sea-mud simulated solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 721, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Wu, M.; Liu, G. Stress corrosion cracking behavior of rusted X100 steel under the combined action of Cl− and HSO3− in a wet-dry cycle environment. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahyarian, A.; Singer, M.; Nesic, S. Modeling of uniform CO2 corrosion of mild steel in gas transportation systems: A review. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 29, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Cheng, Y.F. Modeling by computational fluid dynamics simulation of pipeline corrosion in CO2-containing oil-water two phase flow. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouraria, H.; Seo, J.K.; Paik, J.K. A numerical study on water wetting associated with the internal corrosion of oil pipelines. Ocean Eng. 2016, 122, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesic, S.; Sun, W. Corrosion in Acid Gas Solutions. Shreir’s Corros. 2010, 2, 1270–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Kahyarian, A.; Nesic, S. A new narrative for CO2 corrosion of mild steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, C3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Liu, A.Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, G.L. Fluid structure governing the corrosion behavior of mild steel in oil–water mixtures. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. The corrosion behavior of X65 steel in CO2/oil/water environment of gathering pipeline. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2019, 66, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Mochida, A.; Ooka, R.; Kato, S.; Iizuka, S. Numerical prediction of flow around a building with various turbulence models: Comparison of k-ε EVM, ASM, DSM, and LES with wind tunnel tests. ASHRAE Trans. 1996, 102, 741–753. [Google Scholar]
- Pantokratoras, I.; Arapatsakos, C. Turbulence models comparison for the numerical study of the air flow, an internal combustion engine. In Engineering Mechanics and Material; Wseas LLC: Santorini, Greece, 2014; pp. 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Charriere, B.; Decaix, J.; Goncalves, E. A comparative study of cavitation models in a Venturi flow. Eur. J. Mech.-B Fluids 2015, 49, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolev, N.I.; Kolev, N.I. Multiphase Flow Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Balachandar, S.; Eaton, J.K. Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ren, H.; Li, H.; Tao, K. Quantitative analysis of hydroelastic characters for one segment of hull structure entering into water. Ocean Eng. 2019, 173, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.; Ramsey, C.; Barker, R.; Neville, A. Erosion-corrosion interactions of X65 carbon steel in aqueous CO2 environments. Wear 2018, 414, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malka, R.; Nešić, S.; Gulino, D.A. Erosion–corrosion and synergistic effects in disturbed liquid-particle flow. Wear 2007, 262, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.A.; Farhat, Z.N. The synergistic effect between erosion and corrosion of API pipeline in CO2 and saline medium. Tribol. Int. 2013, 68, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; H Ya, H.; Pao, W. An experimental study on the erosion-corrosion performance of AISI 1018 carbon steel and AISI 304L stainless steel 90-degree elbow pipe. Metals 2019, 9, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouraria, H.; Seo, J.K.; Paik, J.K. Numerical study of erosion in critical components of subsea pipeline: Tees vs. bends. Ships Offshore Struct. 2017, 12, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.A.; Guo, X.P. Erosion–corrosion at different locations of X65 carbon steel elbow. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; He, R. Numerical investigation of the erosion behavior in elbows of petroleum pipelines. Powder Technol. 2017, 314, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Song, L.; Du, C.; He, R. The Effect of Flowing Velocity and Impact Angle on the Fluid-Accelerated Corrosion of X65 Pipeline Steel in a Wet Gas Environment Containing CO2. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 6636–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Lian, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T. Study on Dynamic Erosion Behavior of 20# Steel of Natural Gas Gathering Pipeline. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yi, H.; Huang, Z.; Du, J. Erosion mechanism and sensitivity parameter analysis of natural gas curved pipeline. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2019, 141, 034502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S. The Influence of O2 on the Corrosion Behavior of the X80 Steel in CO2 Environment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, H.; Durst, F. Computations of Erosion–Corrosion Processes in Separated Two-Phase Flows; NACE Corrosion: Houston, TX, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, O. Design of pipelines for the simultaneous flow of oil and gas. In Fall Meeting of the Petroleum Branch of AIME; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Dalla, TX, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Desamala, A.B.; Dasamahapatra, A.K.; Mandal, T.K. Oil-water two-phase flow characteristics in horizontal pipeline—A comprehensive CFD study. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Nucl. Mater. Metall. Eng. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 8, 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, M.J.; Bush, J.W. Fluid pipes. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 466, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesic, S. Key issues related to modelling of internal corrosion of oil and gas pipelines—A review. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 4308–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pots, B.F.M.; Zhong, X.; Nesic, S. Inhibition of CO2 corrosion of mild steel—Study of mechanical effects of highly turbulent disturbed flow. Corros. Sci. 2017, 126, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesic, S.; Lee, K.L. A mechanistic model for carbon dioxide corrosion of mild steel in the presence of protective iron carbonate films—Part 3: Film growth model. Corrosion 2003, 59, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordsveen, M.; Nešic, S.; Nyborg, R.; Stangeland, A. A mechanistic model for carbon dioxide corrosion of mild steel in the presence of protective iron carbonate films—Part 1: Theory and verification. Corrosion 2003, 59, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Y. Development mechanism of internal local corrosion of X80 pipeline steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 49, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Y. Development mechanism of local corrosion pit in X80 pipeline steel under flow conditions. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model | Characteristic | Applicable |
|---|---|---|
| Standard k-ε | Moderate calculation and high precision | Fully turbulent |
| RNG k-ε | Transient or streamline bending flows | |
| Realizable k-ε | Rotary or separation flows | |
| k-ω | Moderate calculation and precision | Wall bound or free shear flows |
| Large eddy Simulation (LES) | Large calculation and high precision | Vortex flow |
| Reynolds stress model (RSM) | High precision | Strong vortex or hurricane flows |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Dong, M.; Chen, Y. CFD-Based Erosion and Corrosion Modeling of a Pipeline with CO2-Containing Gas–Water Two-Phase Flow. Energies 2022, 15, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051694
Wang W, Sun Y, Wang B, Dong M, Chen Y. CFD-Based Erosion and Corrosion Modeling of a Pipeline with CO2-Containing Gas–Water Two-Phase Flow. Energies. 2022; 15(5):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051694
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weiqiang, Yihe Sun, Bo Wang, Mei Dong, and Yiming Chen. 2022. "CFD-Based Erosion and Corrosion Modeling of a Pipeline with CO2-Containing Gas–Water Two-Phase Flow" Energies 15, no. 5: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051694
APA StyleWang, W., Sun, Y., Wang, B., Dong, M., & Chen, Y. (2022). CFD-Based Erosion and Corrosion Modeling of a Pipeline with CO2-Containing Gas–Water Two-Phase Flow. Energies, 15(5), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051694






