Analysis and Cogging Torque Minimization of a Novel Flux Reversal Claw Pole Machine with Soft Magnetic Composite Cores
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Topology of FRCPM
3. Design Optimization
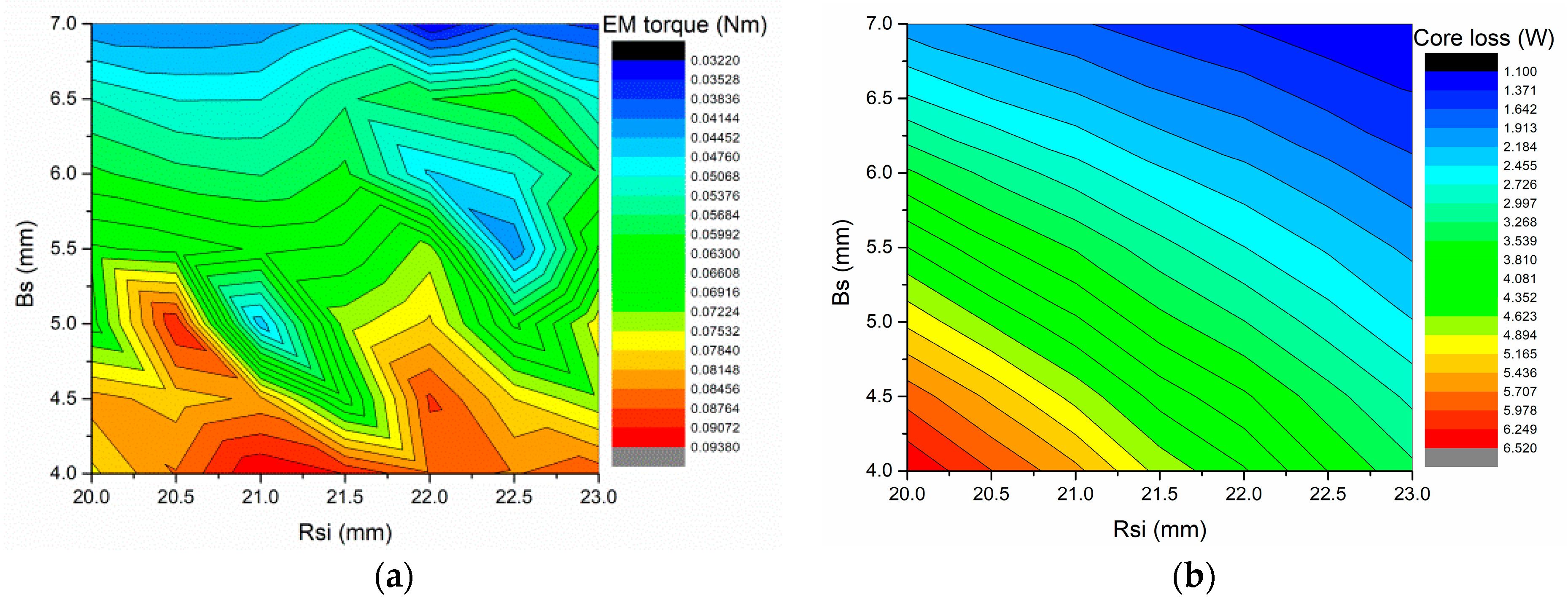
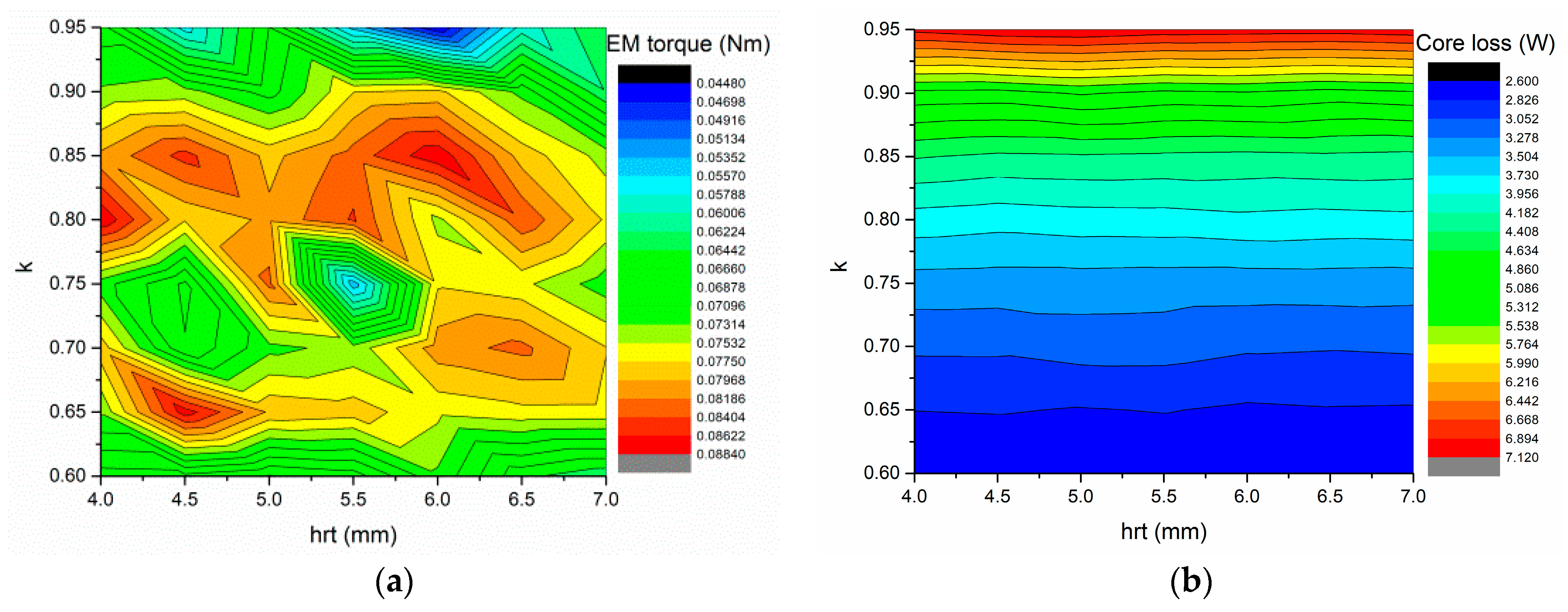
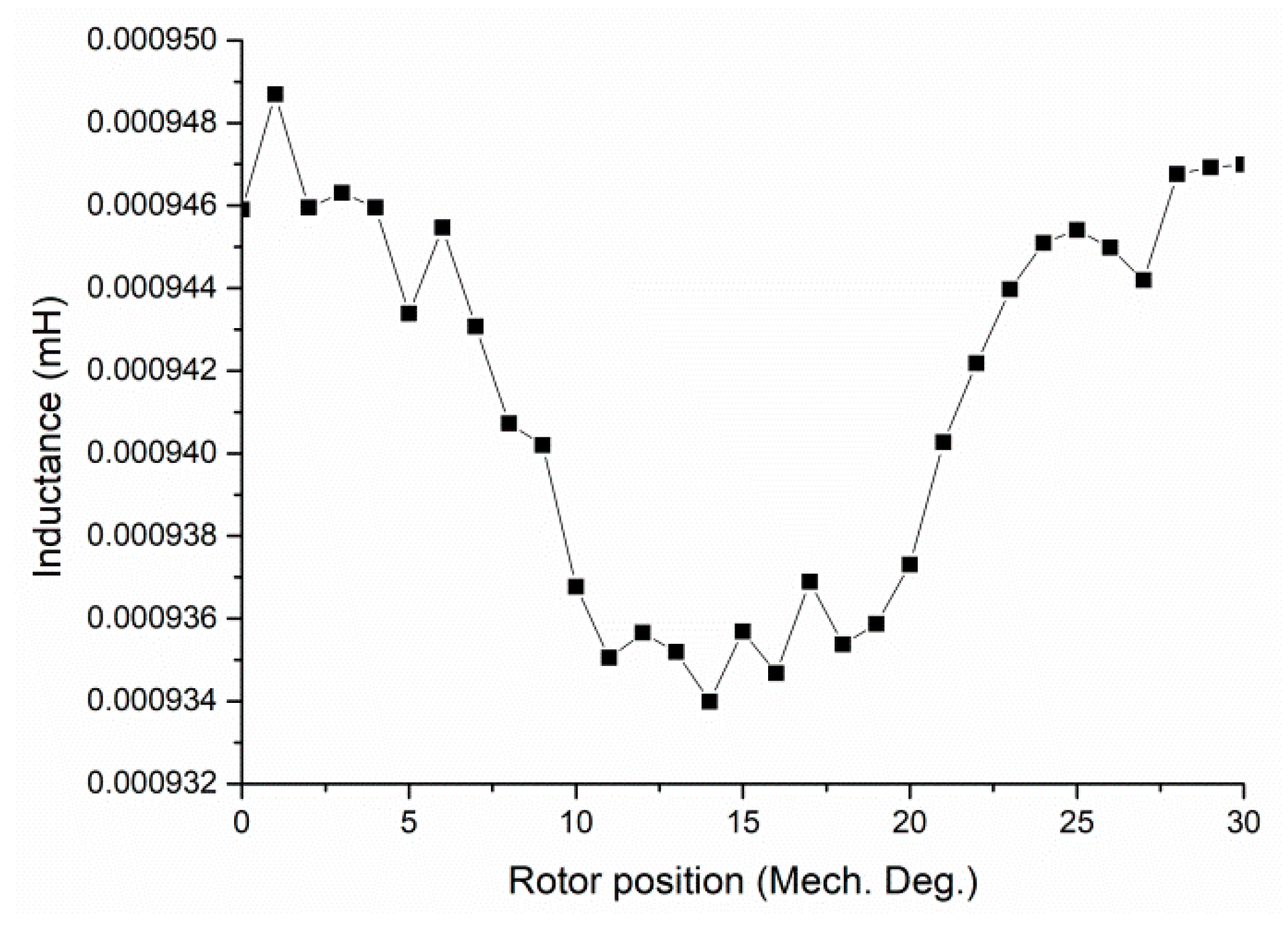
4. Parameters Analysis
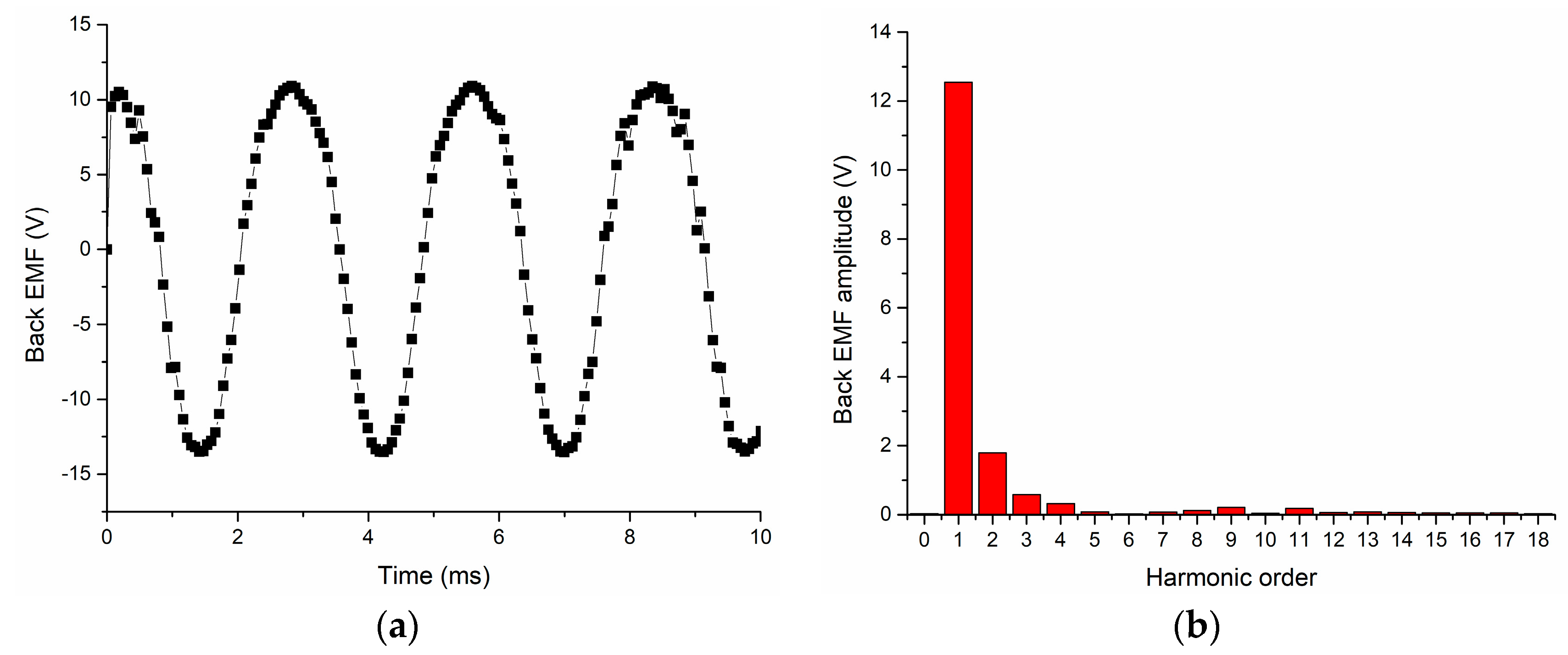
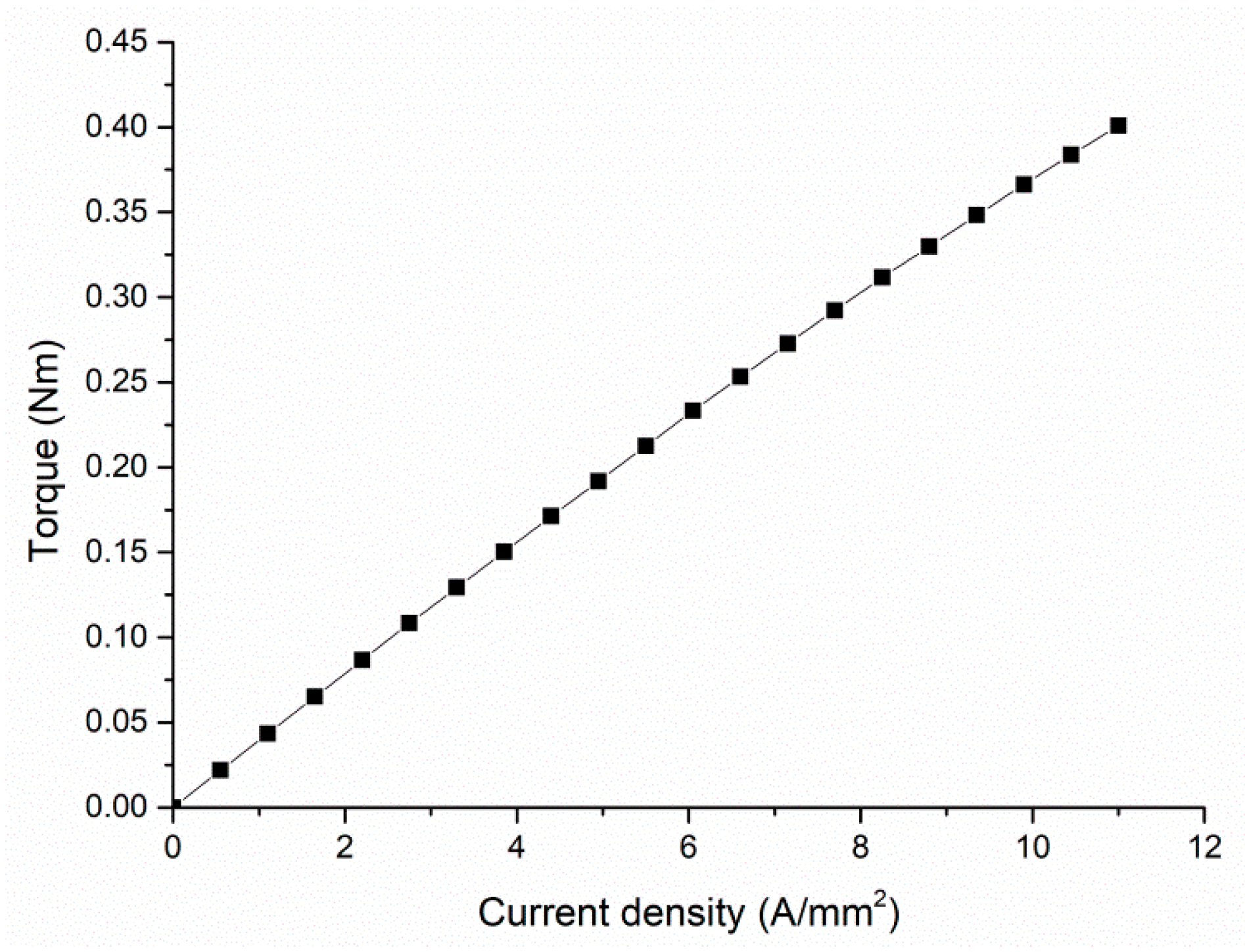
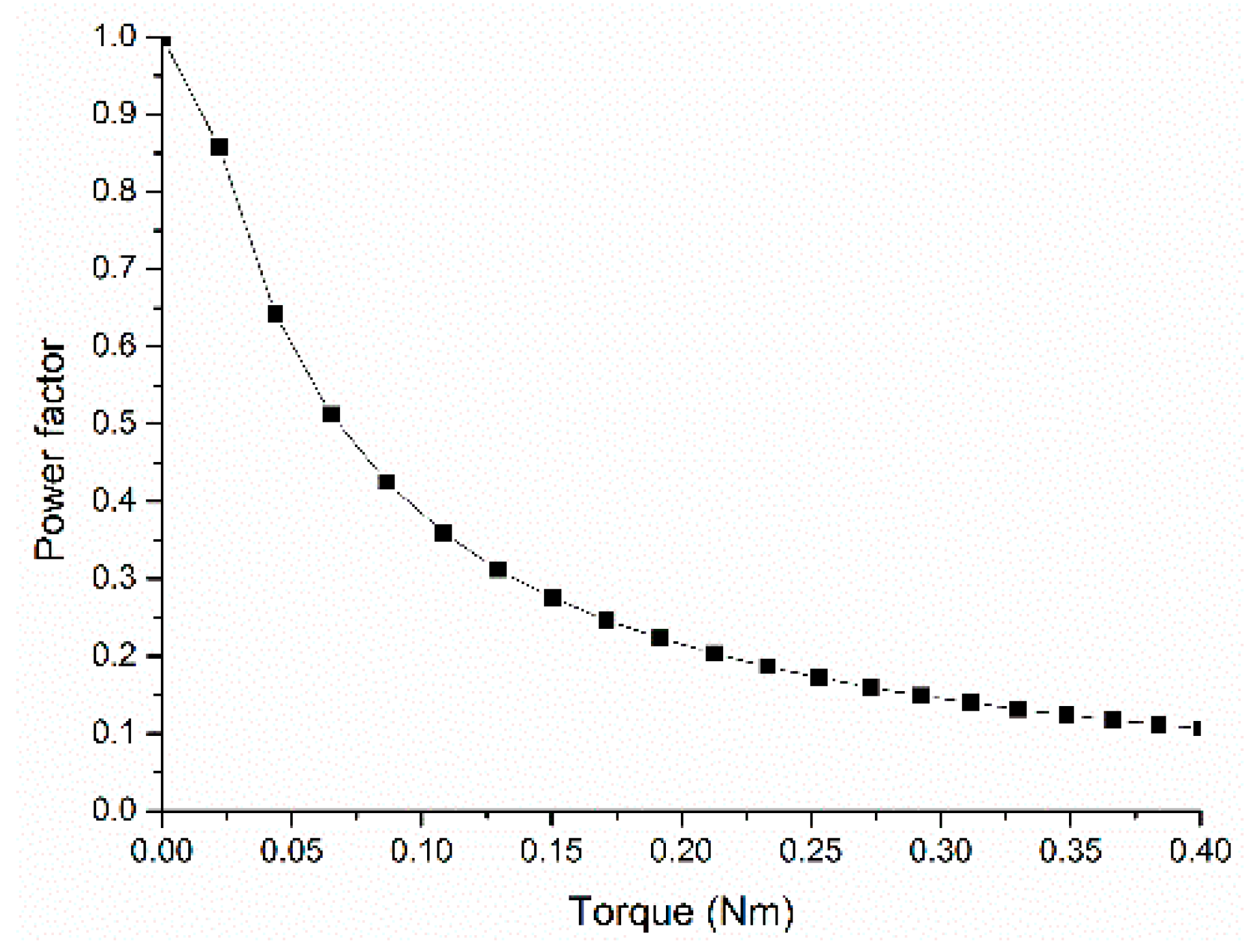
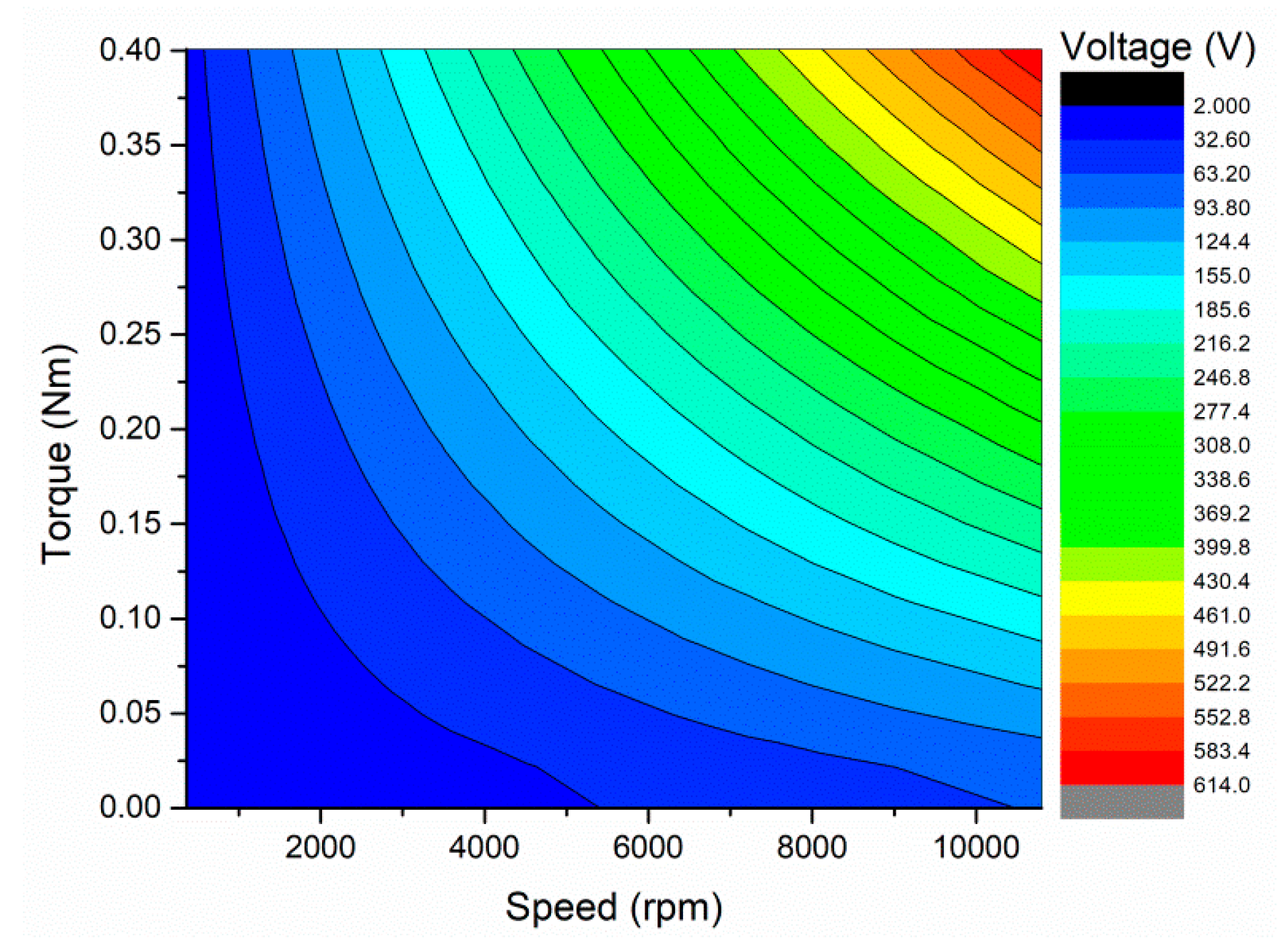
5. Performance Analysis
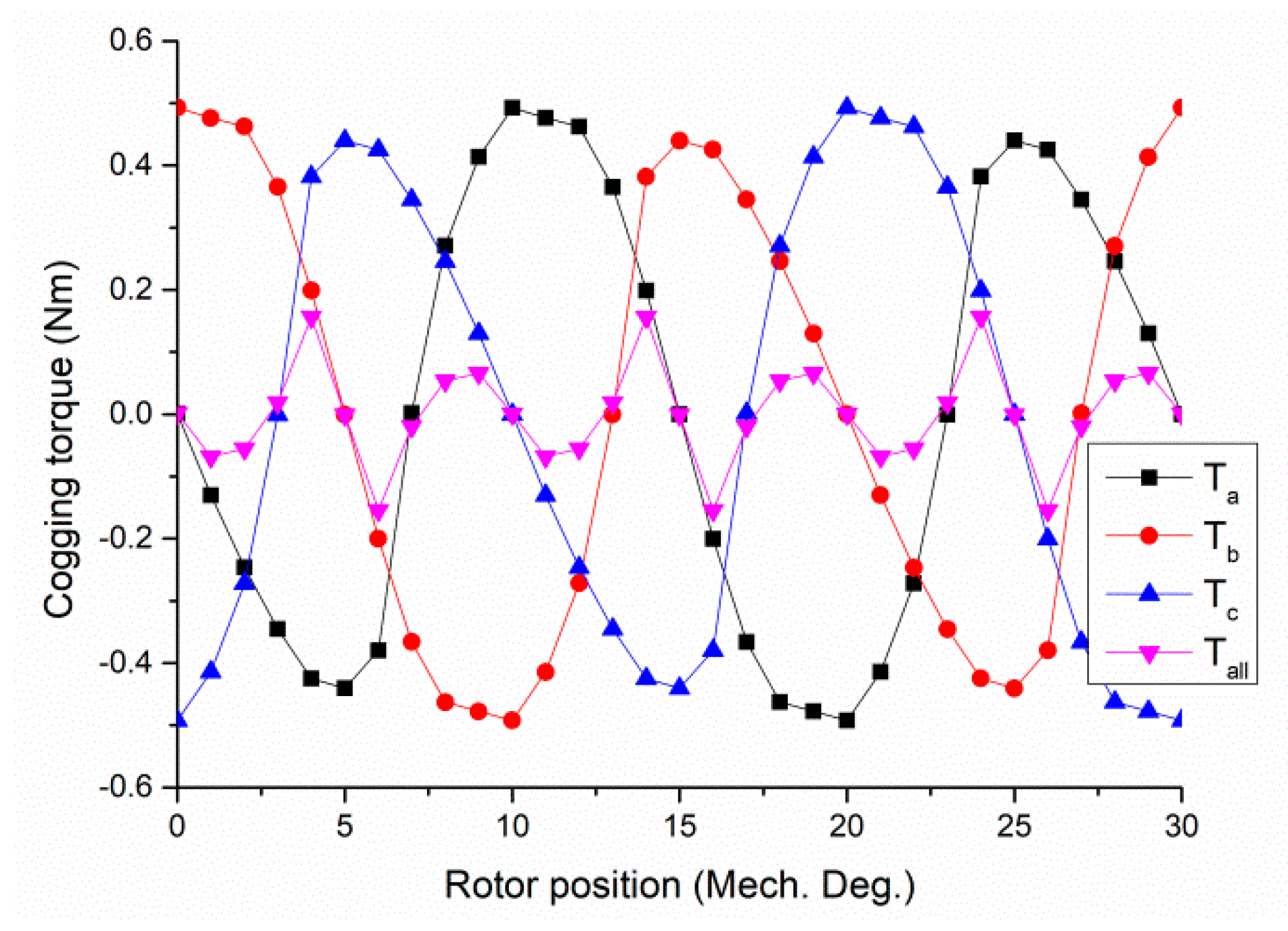
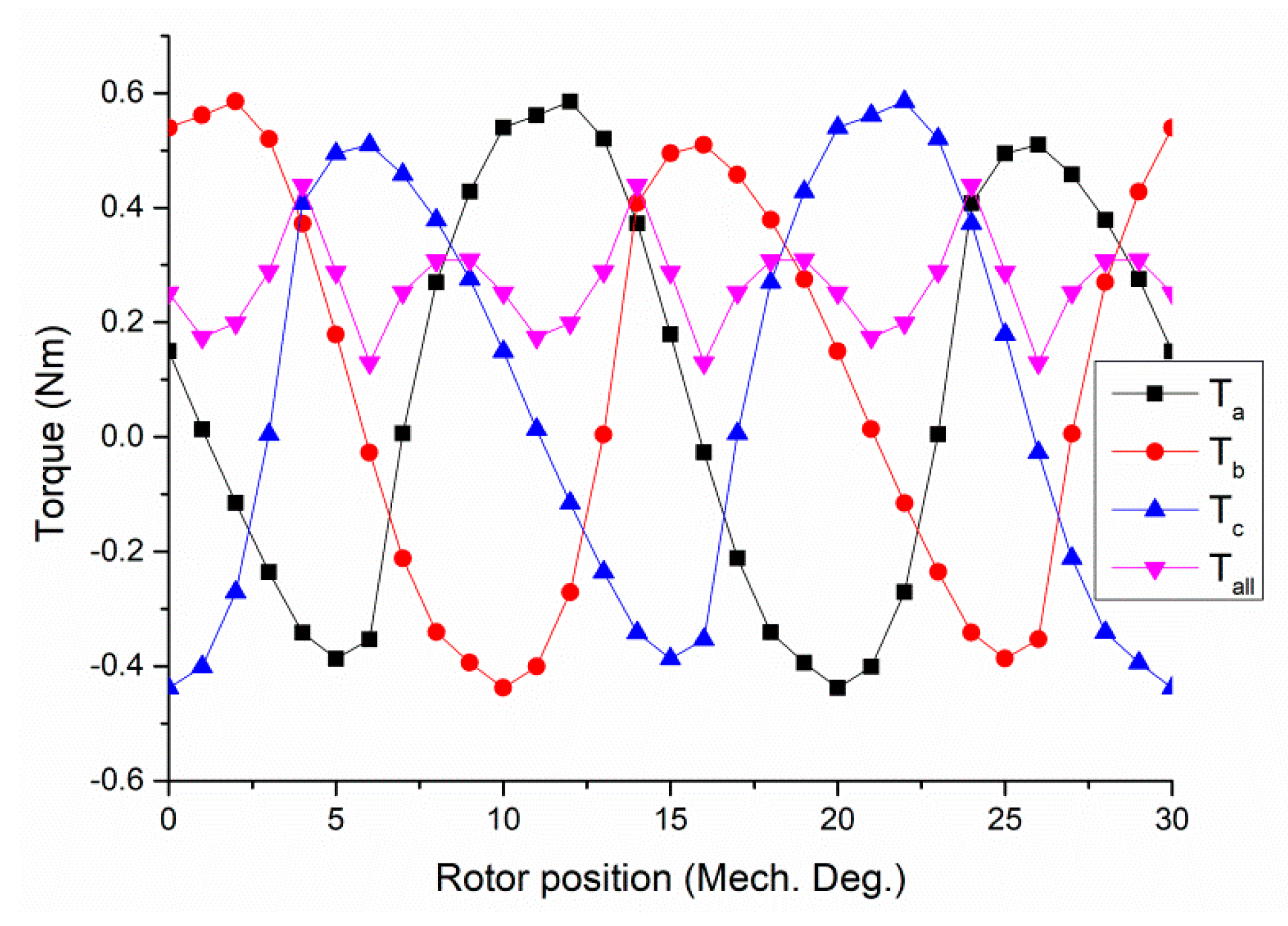
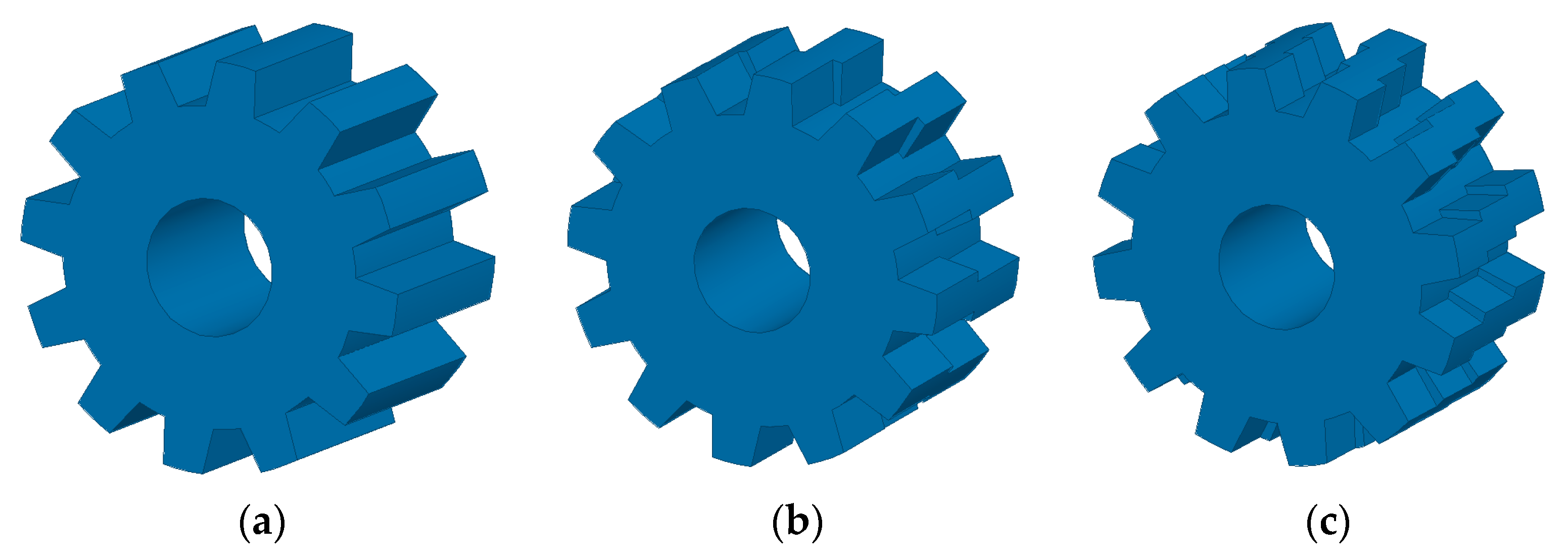
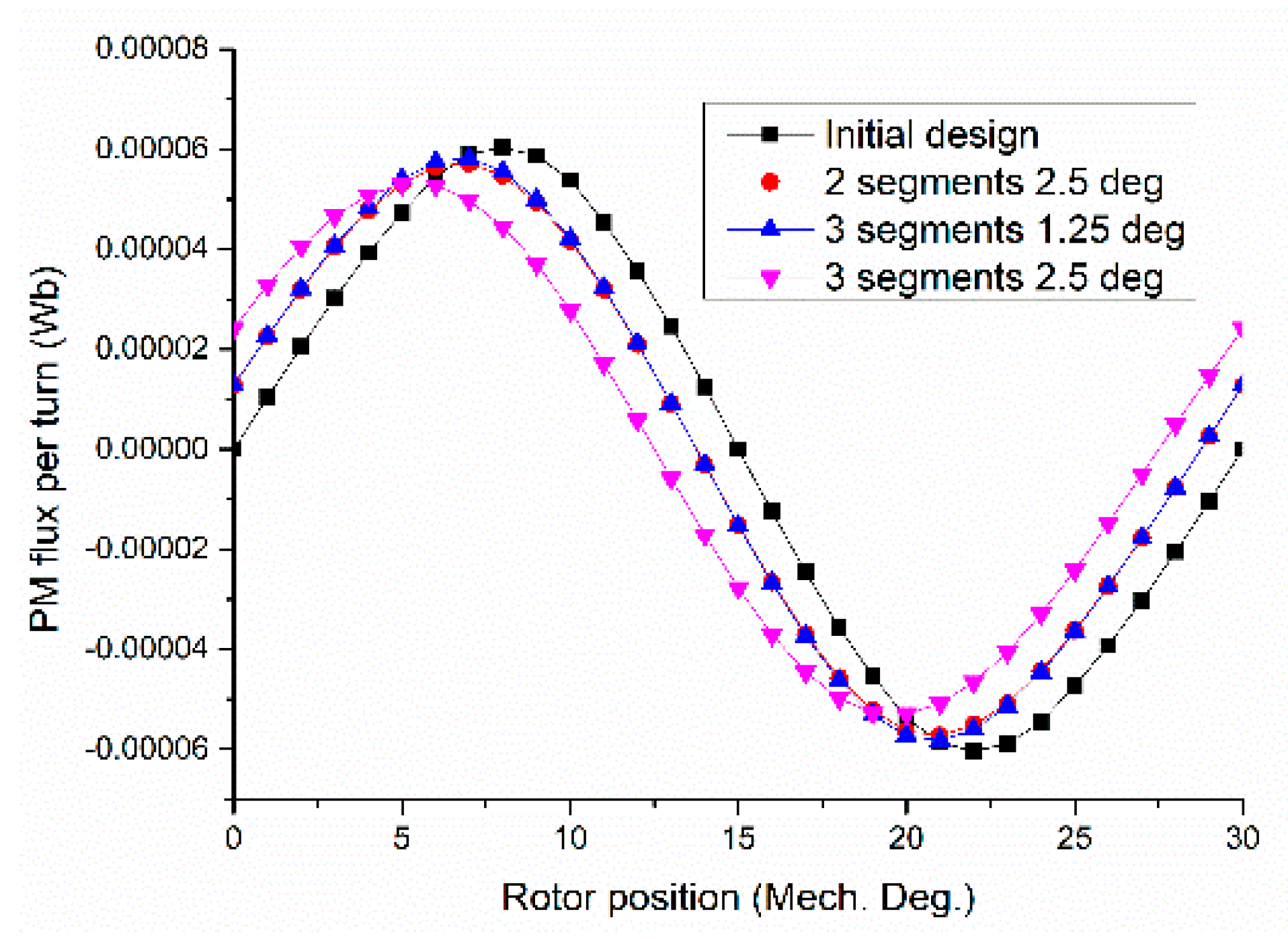
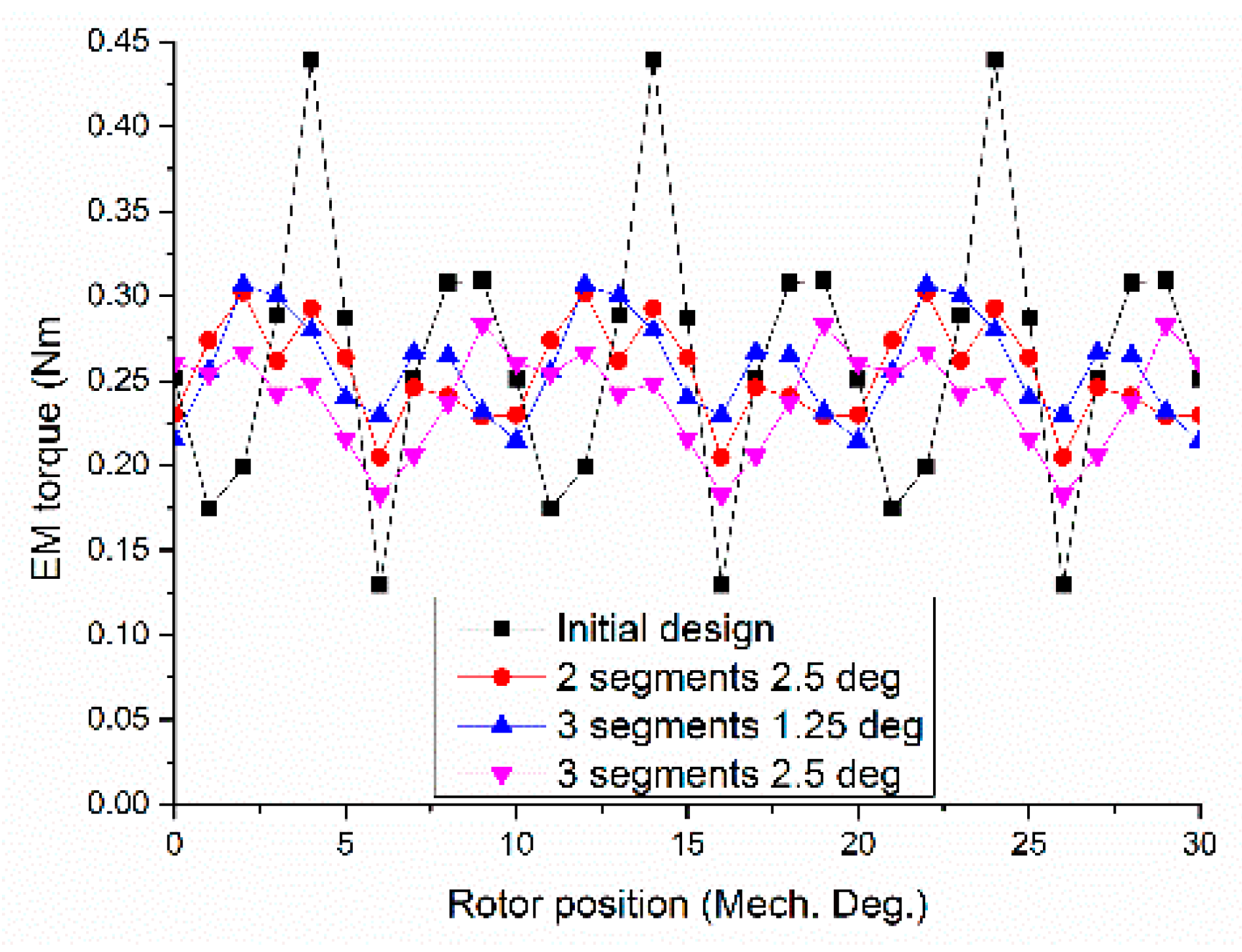
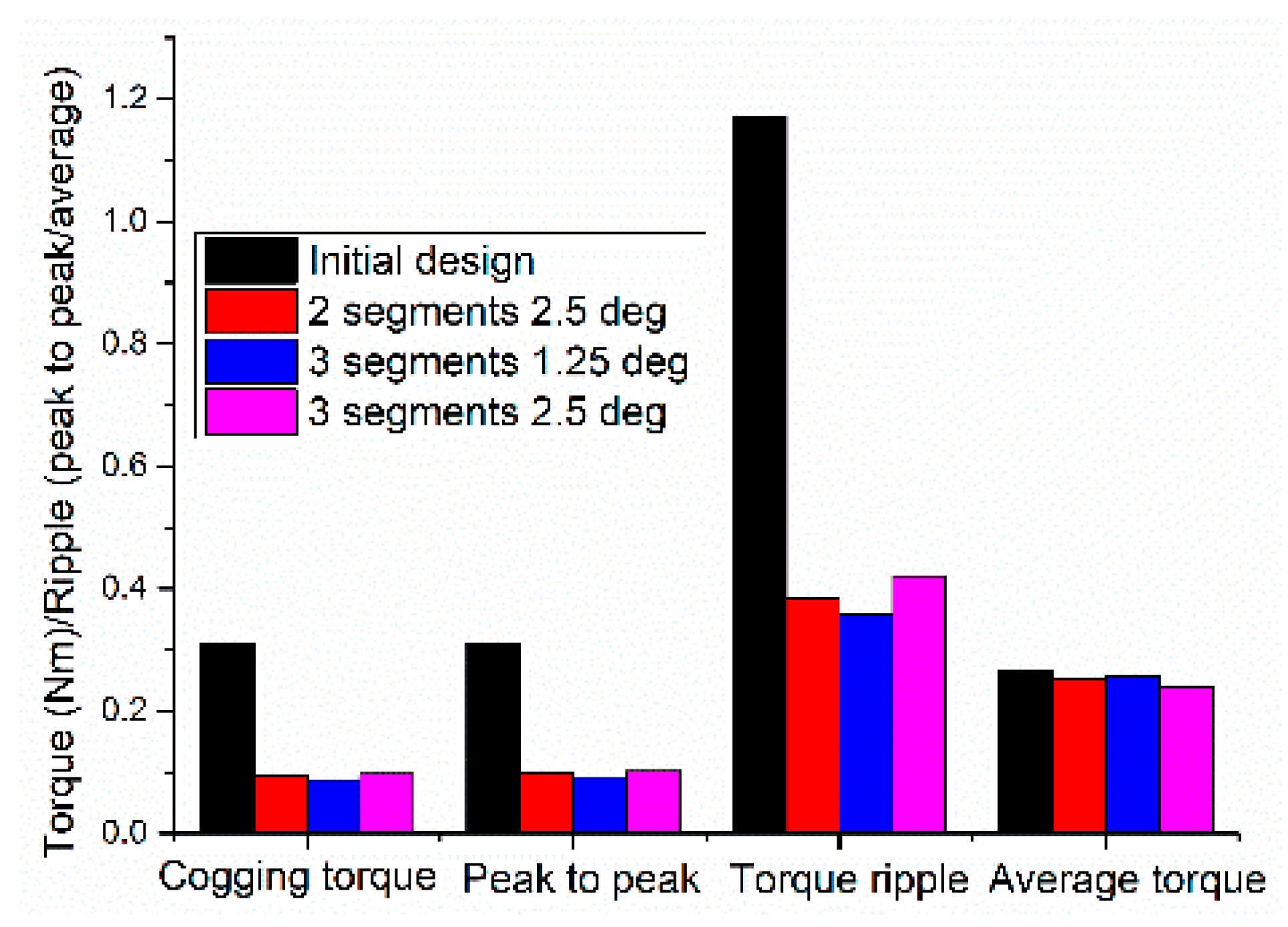
6. Cogging Torque Minimization
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deodhar, R.; Andersson, S.; Boldea, I.; Miller, T. The flux-reversal machine: A new brushless doubly-salient permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, D.S.; Kalluru, H.; Fernandes, B.G. Outer rotor flux reversal machine for rooftop wind generator. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 5–9 October 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.X.; Boldea, I.; Nasar, S.A. Characterization of three phase flux reversal machine as an automotive generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2001, 16, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Li, H. Analysis of Novel Consequent Pole Flux Reversal Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, D.; Fernandes, B. Analysis of flux-reversal machine based on fictitious electrical gear. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldea, I.; Zhang, L.; Nasar, S.A. Theoretical characterization of flux reversal machine in low-speed servo drives—The pole-PM configuration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Wu, L. Design of three-phase flux reversal machines with fractional-slot windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, D.; Fernandes, B. Power density improvement of three phase flux reversal machine with distributed winding. IET J. Elect. Power Appl. 2010, 4, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Won, S.; Bong, K.; Lee, J. Reduction in cogging torque in flux reversal machine by rotor teeth pairing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 3964–3966. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Li, J. Torque performance analysis of three phase flux reversal machines for electric vehicle propulsion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2110–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hua, W.; Wu, Z. Cogging torque suppression in flux reversal permanent magnet machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 12, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lei, G.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Comparative study of small electrical machines with soft magnetic composite cores. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y. Design considerations of PM transverse flux machine with SMC cores. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5203505. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.C.; Wang, D.Y.; Wang, S.P.; Wang, Y.H. A Novel Flux Reversal Claw Pole Machine with Soft Magnetic Composite Cores. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2020, 30, 5202905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Watterson, P.; Wu, W. Development of a PM transverse flux motor with soft magnetic composite core. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, A.G.; Mecrow, B.C.; Maddison, C.P.; Wahab, N.A. Claw pole armature permanent magnet machines exploiting soft iron powder metallurgy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference Record, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–21 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.G.; Zhu, J.G.; Dorrell, D.G. Design and analysis of a claw pole permanent magnet motor with molded soft magnetic composite core. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 4582–4585. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, G.; Wang, T.S.; Guo, Y.G.; Zhu, J.G.; Wang, S.H. System level design optimization methods for electrical drive systems: Deterministic approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6591–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Wang, T.S.; Zhu, J.G.; Guo, Y.G.; Wang, S.H. System level design optimization methods for electrical drive systems: Robust approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4702–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Hahn, I. Axially Stacked Multiphase Flux Reversal Machine. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Niu, F.; Wang, Y.; Lei, G.; Zhu, J. Design and Analysis of a New Permanent Magnet Claw Pole Machine with S-Shape Winding. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 8103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Li, J.; Liang, D. Vibration Suppression for Flux-Switching PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Wang, Y. Comparison of the Stator Step Skewed Structures for Cogging Force Reduction of Linear Flux Switching Permanent Magnet Machines. Energies 2018, 11, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, L.; Lin, M.; Xu, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, W. Analysis of Cogging Torque Reduction Techniques in Axial-Field Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5200605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
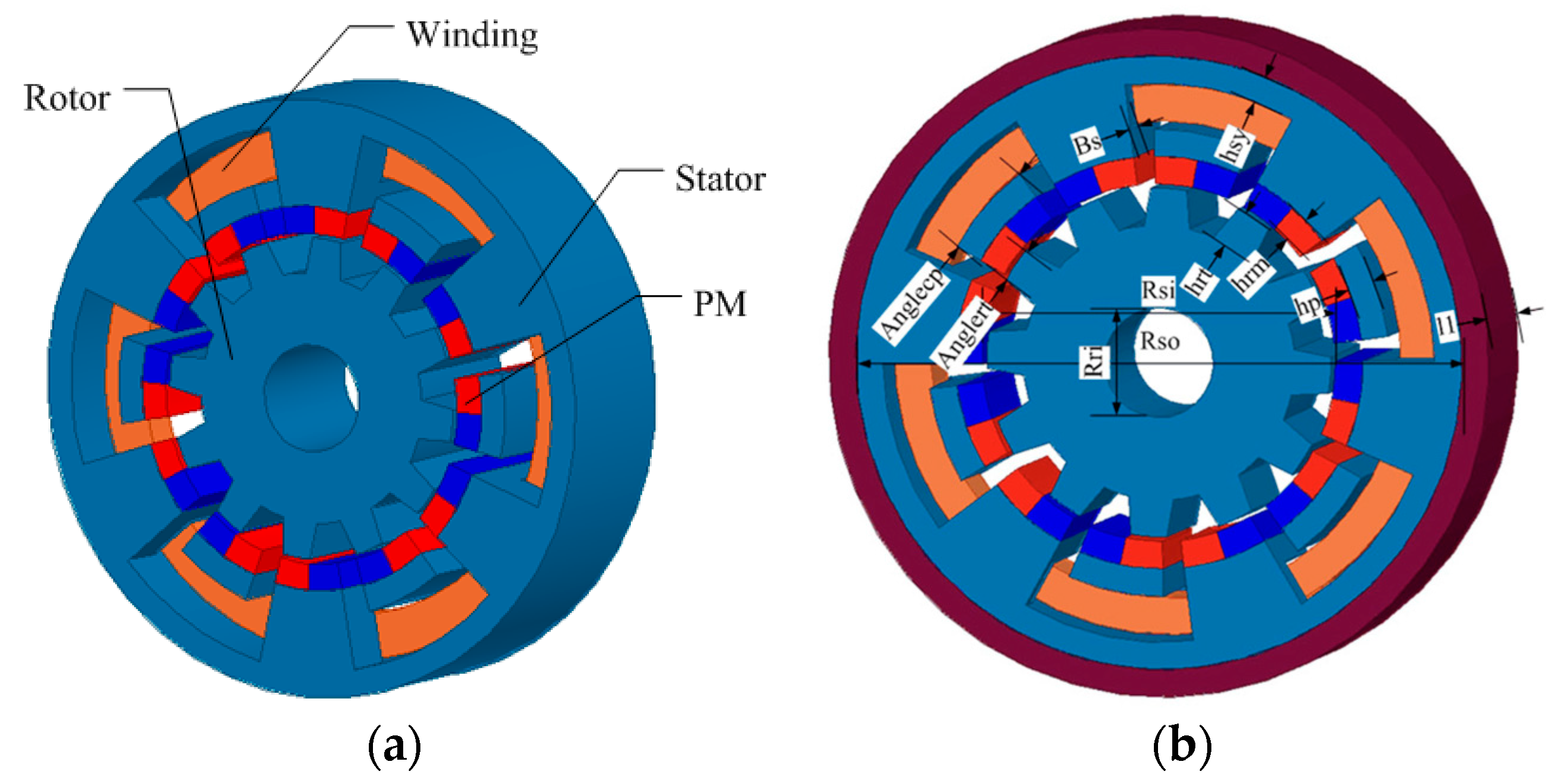




| Type | FRPMM | CPM | FRCPM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stucture |  | 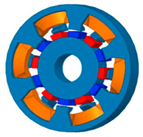 |  |
| Character | High fault tolerance and mechanical robustness. | High torque and power factor. | High torque and speed operation. |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator outer radius | Rso | 33.5 | mm |
| Stator inner radius | Rsi | 22.5 | mm |
| Axial length per stack | L1 | 18.2 | mm |
| Thickness of stator wall | Bs | 4 | mm |
| Thickness of stator claw pole | Hp | 3 | mm |
| Thickness of stator yoke | Hsy | 3 | mm |
| Angle of stator claw pole | Anglecp | 24 | deg |
| Thickness of PM | hrm | 3 | mm |
| Air gap length | g1 | 0.5 | mm |
| Rotor outer radius | Rro | 19 | mm |
| Angle of rotor teeth | Anglert | 12 | deg |
| Length of rotor teeth | hrt | 4 | mm |
| Rotor inner radius | Rri | 6 | mm |
| Number of winding turns | Ncoil | 100 | |
| Stator core material | SMOLAY 500 TM | ||
| PM material | Br = 1.15 T, ur = 1.05 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z. Analysis and Cogging Torque Minimization of a Novel Flux Reversal Claw Pole Machine with Soft Magnetic Composite Cores. Energies 2022, 15, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041285
Li B, Li X, Wang S, Liu R, Wang Y, Lin Z. Analysis and Cogging Torque Minimization of a Novel Flux Reversal Claw Pole Machine with Soft Magnetic Composite Cores. Energies. 2022; 15(4):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041285
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Xue Li, Shaopeng Wang, Rongmei Liu, Youhua Wang, and Zhiwei Lin. 2022. "Analysis and Cogging Torque Minimization of a Novel Flux Reversal Claw Pole Machine with Soft Magnetic Composite Cores" Energies 15, no. 4: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041285
APA StyleLi, B., Li, X., Wang, S., Liu, R., Wang, Y., & Lin, Z. (2022). Analysis and Cogging Torque Minimization of a Novel Flux Reversal Claw Pole Machine with Soft Magnetic Composite Cores. Energies, 15(4), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041285





