Abstract
A single production of nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets was developed in this present work from a spent Zn-C primary battery. The electrochemically exfoliated nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets (EC-N-GNS) was applied in supercapacitor symmetric devices. As-prepared EC-N-GNS was utilized for a symmetric supercapacitor with natural seawater multivalent ion electrolyte. The recycling of graphite into nitrogen-doped graphene was characterized by X-ray diffraction and RAMAN spectroscopy. The few-layered morphological structures of EC-N-GNS were analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscope and field emission transmission electron microscope. The electrochemical analysis of the cyclic voltammetry curves observed an electrochemical double-layer capacitor (EDLC) behavior with a potential window of −0.8 V to +0.5 V. The electrochemical galvanostatic charge—discharge study was obtained to be maximum specific capacitance (Csp)—67.69 F/g and 43.07 F/g at a current density of 1 A/g. We promising the facile single-step electrochemically exfoliated EC-N-GNS was obtained from a waste zinc-carbon primary battery to recycle the graphite electrodes. The superior electrochemical performance comparatively bulk graphite and EC-N-GNS for potential energy storage supercapacitor applications.
1. Introduction
In recent years, billions of batteries are consumed and expended worldwide. However, the primary batteries can only be used once, and re-utilizing the spent batteries will be a perceptibly attractive and economically viable solution for energy storage devices [1]. In recent decades, non-rechargeable single-use batteries such as Zn-MnO2 alkaline and zinc-carbon (Zn-C) primary batteries are thrown away improperly due to their low cost and short cycle life. An primary Zn-Carbon battery system is separated into two parts, an anode and a cathode. The anode part is mainly a mixture of zinc powder combined with a potassium hydroxide (KOH) gel electrolyte. The cathode counterpart consists of a carbon rod as a carbon current collector surrounded by a mixture of manganese dioxide (MnO2), ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and Zinc chloride. The zinc-carbon (Zn-C) primary battery consists of a mixture of chemical compounds with MnO2, NH4Cl and ZnCl2 gel paste and carbon rod as a current collector [2]. Generally, graphene is a single atom thick, and its allotropes in the carbon family are two-dimensional (2D) structures with a sp2 carbon network hexagonal structure. For the first time, a developed thick atomic graphene was built using adhesive tape by mechanical cleavage from bulk graphite [3]. Typically, graphene preparation uses chemical oxidations agents and intercalation compounds such as concentrated H2SO4, KMNO4 and NaNO3. In chemical oxidation, modified hummers method is time-consuming, with multiple preparation steps with purifications [4]. The recently developed single-step facile synthesis of high-purity graphite rod uses discarded batteries for inexpensive and high-yield production using an aqueous electrolytic ionic solution.
Graphene nanosheets had excellent electrochemical properties for future electrochemical energy storage and conversion devices [5,6,7]. Generally, the synthesis of few-layer and multilayer graphene methods that are reported are modified hummers [8], thermal chemical vapor deposition (T-CVD) [9] or microwave-assisted [10]. Graphene is the most promising electrode-active material for supercapacitor applications and good electrical energy storage material. The graphene-based supercapacitor’s qualities such as lightweight, miniaturized size, high stability, high specific capacitance, high power density and energy density are superior to those of Li-ion batteries [11,12].
The recent development of hetero-atoms such as nitrogen (N)-doped carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene for electrochemical energy storage applications have been promising [13,14]. However, the N-atom doping in carbon networks could be favorable for increasing the electrochemical properties of supercapacitors [15,16]. In addition, nitrogen-doped single- and few-layer graphene production has different methods approach in chemical vapor deposition (CVD) [17], hydrothermal method [18], solvothermal method [19], and nitrogen plasma treatment [20]. Among these methods, the electrochemically exfoliation technique is a single-step and high-yield production of few-layer graphene nanosheets from directly bulk graphite rods.
Heteroatom-doped carbon-based nanostructured materials present electrical energy storage and energy conversion devices such as supercapacitors [21,22,23], lithium-ion batteries [24], fuel cells [25] and solar cells [26] device applications. Generally, Nitrogen atoms at different atomic sites such as the heterocyclic compound C-N bonded into graphene as a new form are pyrollic-N, pyroltic-N and graphitic-N. Particularly, nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets for electrochemical energy conversion fuel cell applications [27,28]. The N-doped graphene nanosheet different techniques were approached previously reported [29,30,31]. Recently, few-layer pure graphene nanosheet functionalization was reported in liquid-phase synthesis from bulk graphite [32,33,34,35]. In addition, micro and nano phase materials were recently reported using electrochemical techniques for SCs and NH3 ionic storage devices using MnO2 electrodes by electrochemical deposition for future energy storage [36,37].
The next-generation electrochemical supercapacitor was established for aqueous (aq.) electrolyte solutions such as acidic/alkali electrolytes corresponding to the aq. H2SO4 and aq. KOH, respectively [38]. Still, the development of aqueous electrolytes and eco-friendly natural seawater electrolytes energy storage devices is in its infancy [39,40,41]. An aqueous electrolyte based on sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl−) and magnesium (Mg+) multivalent ion salts provided greater ionic conductivity and quick ion transport between the electrodes, and natural seawater aqueous electrolytes safely convey and are economically viable for future energy storage devices. There have been a few recent reports on seawater-electrolyte for supercapacitors using MXene symmetric device [42] and carbon derived from natural cotton [43].
In this paper, we report on spent primary Zn-C battery utilized for cathodic current collector carbon rods with single-step exfoliation in the liquid phase. The electrochemical exfoliation of graphite cathode using a sulfuric acid (H2SO4) electrolyte containing urea (CH4N2O) as nitrogen (N) source. Although we prepared a few layers of N-doped graphene nanosheets through electrochemical exfoliation through a spent Zn-C primary battery with a thick carbon rod, the EC-N-GNS was easy to implement via electrochemical symmetric supercapacitor fabrication with the fresh seawater electrolyte solution, which was abundant and cheap. The bulk graphite and as-prepared electrochemical EDLC supercapacitor measurements were cyclic voltammetry, impedance and galvanostatic charge–discharge studies.
2. Experimental
In this work, collections of raw material carbon/graphite rod from spent only one zinc-carbon (Zn-C) primary battery were carefully disassembled using a steel cutter tool. After the Zn-C battery cells were dismantled, the center part of the graphite rod were washed with deionized water (DI) water. The electrochemical exfoliation part chemicals are sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and urea (CH4N2O) as “N”—doping agents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA. The single step was involved in the DC potential applied through carbon rod erosion slowly and good yield productions of EC-N-GNS active materials for energy storage devices from spent Zn-C primary battery.
2.1. Electrochemical Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Nanosheets
In a typical experimental set-up, nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets were synthesized by a single-step electrochemical method. In the experimental detail (Figure 1), the preparation system consisting of a carbon rod was carefully removed from one spent Zn-C primary battery that was disassembled. The graphite rod was used as an anode (4.2 cm length—0.8 cm dia), and a Pt wire electrode serves as a cathode. The electrolyte contained aqueous sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and urea (CH4N2O). The electrolyte was prepared by adding 10 mL of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) with 100 mL of deionized (DI) water and 0.5 g of urea (Sigma Aldrich grade) as a nitrogen precursor. Subsequently, the above mixture solutions were constantly stirred for 30 min at room temperature. Aqueous electrolyte solutions containing (H2SO4) and (CH4N2O) were taken in the 200 mL beaker and the above mixture was vigorously stirred for 10 min.
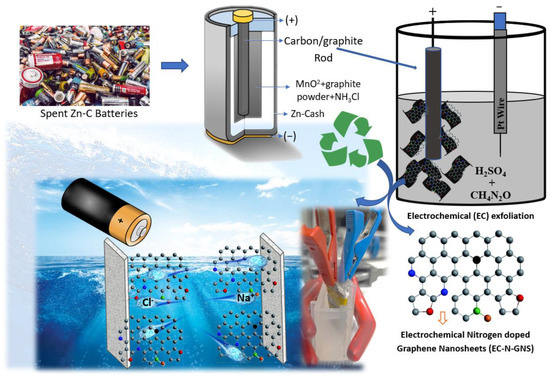
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the preparation graphic explains N-doped graphene nanosheets via electrochemical exfoliation from the spent Zn-C primary battery from the isolated N-graphene nanosheets.
The experimental setup was vertical and parallel to each other; the Zn-C carbon rod and Pt electrodes were partially immersed in the ionic aqueous electrolyte solutions separated by 5 cm distance to avoid shorting the circuit. The constant DC bias digital potential meter was used with a constant bias voltage of 5 V. When applied to DC constant potential, the electrochemical exfoliation began to gradually appear as dark black flakes in the electrolyte solutions. The graphite rod was slowly exfoliated and expanded after a few minutes. The exfoliation time of 30 mint continued, and the bulk graphite rod was completely eroded, with black suspension appearing in the electrolytes. As synthesized nitrogen (N) doped in the few-layer graphene sheets occurs an acidic nature, due to the aqueous acidic H2SO4 electrolyte. Hence, after synthesis, the solution was washed multiple times with deionized (DI) water with ethanol. The suspension solution was separated by decantation and centrifugation to remove large graphite flakes. Then, the fine, solid, black powders were dried in an oven at 100 °C for 4 hrs. Finally, we obtained good yield in a facile single-step process of the electrochemical synthesis of nitrogen (N)-doped graphene nanosheets (EC-N-GNS) as a final product for material characterizations and electrochemical SC applications.
2.2. Materials Characterization
Next was characterizing the as-prepared electrochemically exfoliated nitrogen-doped graphene (EC-N-GNS) and bulk carbon rod, respectively. The field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) images of EC-N-GNS and graphite microscale surface morphology were obtained on (FE-SEM S-4800 coupled with EDS, Tokyo, Japan) equipped under an accelerating voltage of 15 kV. Field emission electron transmission microscopy (FE-TEM) was used for nanoscale images where depth morphological images. The few layers of graphene were recorded with an FEI-Tecnai TF-20 through an operating accelerating voltage of 200 kV and also (HR-TEM, EDX line mapping) was used to EDX spectra evaluate the chemical composition with diffraction (SAED) pattern. The elemental nitrogen (N) doping was identified by FE-TEM attached with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) element analysis. The crystal structures and planes were examined using “X’Pert PRO PAN-Analytical” operating at 40 kV and 30 mA with Cu-Kα as an X-ray source (λ = 1.5406 Å), diffraction angle 10° to 80° with accelerating voltage of 30 kV, a beam current of 30 mA. The micro-laser Raman scattering spectra were recorded by XPLORA Plus (HORIBA Scientific, Horiba Jobin Yvon, France) at room temperature excited with a YAG (Nd) laser at 532 nm, the spectrum gaining time was 100 s and operating power at 10 mW. The functional groups were identified using a Perkin Elmer (Model no. Spectrum-100, Thermo Scientific; Waltham, MA, USA), and the spectra were recorded in transmittance (T%) mode in the wavenumber range from 400 to 4000 cm−1. All the characterization analyses were done by “the Center for Research Facilities” from Yeungnam University (South Korea).
2.3. Electrode Preparations of Slurry and Coating Process
The EC-N-GNS and graphite rod powders were the active material precursors for supercapacitor application, prepared by (i) active materials, (ii) activated carbon conductive black, (iii) poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) binder in a weight percentage of 80%, 10%, 10%. The above mixture was ground in a mortar and pestle in constant hand grinding to make the uniform ink-like slurry paste used in the N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) solvent. Then, the active material catalyst slurry ink manual coated on nickel foam (Ni) subtracts. The brush coating was even on the Ni-foam-like mesh size at 2 × 2 cm−2 (99%, MTI South Korea). Further, all the electrodes were heated at 90 °C overnight to remove the excess solvent. Electrochemical supercapacitor characterization was carried out by the 2-electrode device set-up with the electrode active materials slurry-coated on Ni foam. And EC-N-GNS electrode materials both anode and cathode materials act the cell device performance carried out natural seawater as the electrolyte (sea water collections from north Gyeongsang near Yeongildae Beach, Pohang, South Korea). The electrochemical measurement was carried out in cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) measurements were carried out in a multichannel Bio-Logic potentiostat VMP3 model. The active materials specific mass coated was found to be 2–3 mg.
3. Result and Discussions
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
The field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) was achieved at different micro-scale magnifications. Figure 2a displays an FE-SEM image of the parental spent Zn-C graphite rod powder crushed into a fine powder, raw graphite powder images are highly stacked flat and thick layers with size ranges of over 2 µm, after electrochemical exfoliation techniques, virtually FE-SEM images of EC-N-GNS surface morphology has particle for thin graphene layers N- doped GNSs shown in Figure 2c–f.
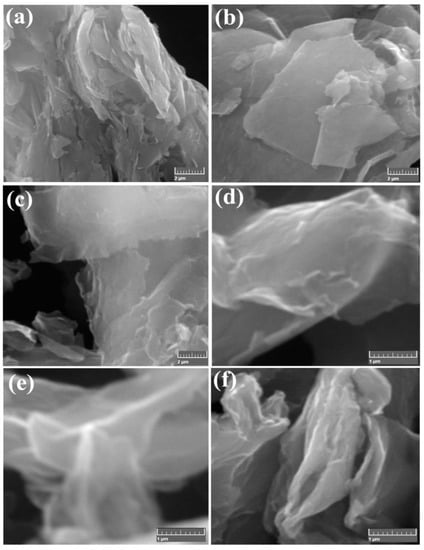

Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of (a,b) graphite. (c–f) The exfoliated N-doped few-layer sheets, the general curling and folded morphology.
To identify very fine morphology from the exfoliations of a graphite rod in well-layered sheets, the constant voltage (CV) and constant current source meter have to support layer-by-layer gradual erosion. Consequently, the prior methods of electrochemically prepared N-GNSs formations of H+ ions and SO42− were gradually intercalated into a host bulk carbon rod [38], the reaction mechanism of Equations (1)–(3). Figure 2e,f shows a nitrogen-doped graphene morphology notable aspect of electrochemically exfoliated sheets are relatively very fine surface morphological structures. This EC method to reveals the electrochemical exfoliation mass production compared to bulk graphite rod precursor materials. To conclude, the FE-SEM surface morphology and nanostructures images are an effective technique for producing pure and heteroatom-doped graphene nanosheets.
3.2. HR-TEM Analysis
As shown in Figure 3. the field emission transmission electron microscope (FE-TEM) morphological images of the EC-N-GNS were characterized by N-graphene nanosheets with different nanoscale magnifications images shown in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 3a,b were observed in the transparent few-layered graphene sheets, (Figure 3a) image edges of the graphene sheets due to bulk graphite exfoliated into few layers graphene was transparent and folded structure. The higher magnifications of a few layers contain in the graphene sheet have a 2D nanostructure morphology and highly wrinkled sheets and flats were also revealed at 50 nm scale bare. The FE-TEM image (Figure 3b) represents overlapped few graphene layers that are also observable in typical thin nanosheet layers one by one staked few-layer sheets.
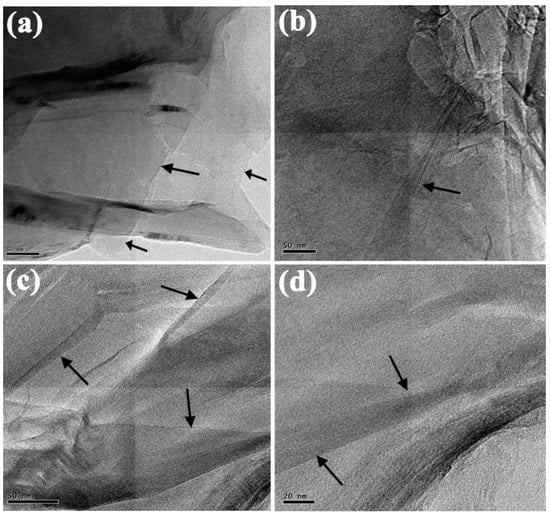
Figure 3.
(a–d), HR-TEM images of electrochemically exfoliated N-doped graphene sheets (c,d), HR-TEM image of the few-layered nanosheets (indicated by black arrows) facing out of the plane of folded few-layer view.
HR-TEM images revealed very thin sheet-like flat morphology, and after electrochemical exfoliation, the surface morphological N-doped graphene. Figure 3c,d reveal that the EC-N-GNS mainly exhibits a different focused point of view, few-layer graphene sheets were pointed out by the black colored arrow marks indication also can be observed N-doped few-layer additional confirmation. Its thin platelet sheet-like nature, which is composed of a few layers of graphene mostly shown in edges folded transparent layer, due to the constant potential was applied in bulk graphite rod. The EC-N-GNS material was observed that edges of the few layers graphene nanosheets. The high-resolution morphological images Figure 3c,d showing graphene exhibits layer by layer sheets partially overlapped and intersection such as termed few layer graphene nanosheets (black marks). The electrochemically N-doped graphene nanosheets were exfoliated using constant potential, exfoliation time and using an aqueous H2SO4 electrolyte [38] with urea source as nitrogen atom incorporated into graphene nanosheets. However, the few-layer exfoliations occurred in electrostatic intercalation with every few layers exfoliated due to the strong Van-der Waals forces among individual graphene nanosheets. From the morphological images, it is observed that almost all the few layers were uniformly distributed on the few nm sheets with the size of (50 nm to 20 nm). Hence, heteroatom doping and functionalization electrochemical exfoliation is a superior technique to produce the few-layer graphene as liquid exfoliation in the electrochemical reaction Equations (1)–(3) given below
H2SO4 → H+ + SO42
H2O + HSO4− + (C)graphite → (C)HSO4−·H2O + e−
CO(NH2)2 + HSO42−(aq) → CO + NH3 + 2e− SO3H
[NH2-CO-NH-SO3(−) NH4(+)] × (C)graphite in electrolyte
3.3. Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) Spectroscopy Analysis
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis was performed in the EC-N-GNS sample to confirm the addition of nitrogen content. Figure 4 EDX analysis to confirm the N atom doped graphene sample, to confirm the elemental composition presence of the nitrogen (N), carbon (C) and oxygen (O) and usually associated with the presence of copper (Cu) peaks, due to Cu—grid substrate. The EDX data also shows the qualitatively and there are found to be atomic percentages (at. %) level at N—1.84 at. %, C—94.06 at. %, O—4.08 at. %.
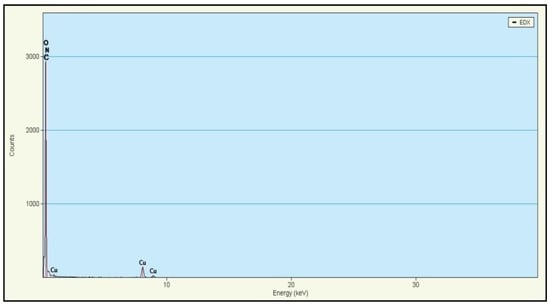
Figure 4.
Energy-Dispersive X-ray (EDX) Spectrum analysis of EC-N-GNS.
The EDX indicated that nitrogen atom-doped or nitro functional groups were still present in the graphene (carbon) structure. Hence, in the effective atomic doped graphene, the total percentage of nitrogen (N) observed in the carbon matrix was 1.84 at. %. This strongly reveals that the electrochemical exfoliation was a high-yield technique for preparing atomic-doped graphene.
3.4. XRD Analysis
The phase and crystal structure of the prepared samples were analyzed with XRD. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern peaks in Figure 5a,b show the before and after electrochemical exfoliations of nitrogen-doped graphene (EC-N-GNS) and bulk graphite powder with 2θ angle ranges of 10°–80°. The diffracted sharp peak was observed for bulk precursor graphite powder at 2θ at 26.47 corresponding to (002) planes. While comparative (Figure 5a) XRD plots reveal that EC-N-GNS was less intensity, Hence to clear observation enlarged (inset Figure 5b) EC-N-GNS for insert XRD plot was observed at 2θ = 25.03°, which corresponds to a plane (002) belongs to EC-N-GNS and it shows the good crystalline peaks 2θ at 25.03° (002) and 43.26° (100) planes, respectively. The d-spacing values of the bulk graphite and after exfoliated (EC-N-GNS) N-graphene layer inter atomic interlayer distance (d-spacing) value of 3.331 Å and 3.372 Å distance (d-spacing values) was slightly high compare to graphitic d-spacing values [44]. Owing to the N-atom/functionalities present inner carbon structures, which reveals that the electrochemically expanded with layer-by-layer graphene nanosheets are nitrogen atomic doping [45].
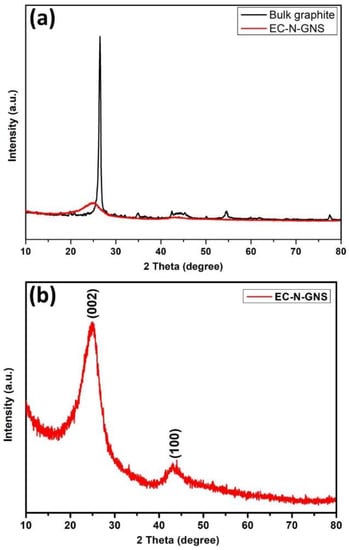
Figure 5.
(a) powder X-ray diffraction pattern of spent bulk graphite and EC-N-GNS and (b) magnified view XRD pattern of EC-N-GNS.
3.5. Raman Analysis
The Raman spectroscopy analysis is a sensitive technique for quality effects of doping, disorder and functional groups belongs to the sp2/sp3-bonded carbon allotropes. The Raman spectroscopy was active and provide the graphitic disorder ‘D’ and graphitic order ‘G’ bands. Figure 6, bulk graphite material showing the Raman shift peaks appear at 1344.13 cm−1 and 1593.22 cm−1 corresponding to D and G bands, respectively. As the quantity of disorder (D) in bulk graphite slightly increases, the Raman intensity increases compared to EC-N-GNS disorder peaks; due to the spent Zn-C primary battery inside cell few element compositions. Further investigations of the after-exfoliations of EC-N-GNS show the D and G-bands correspond to the Raman shift positions 1350.97 cm−1 and 1587.21 cm−1, respectively. In comparison, D band is less disorder Raman intensity D-band appears for nitrogen atoms present in carbon lattice. This D band gives the out-of-plane breathing mode of the sp3 atom due to defects and E2g phonons at the center of the Brillion zone. Then, the graphitic Raman intensity disorder ratio between the D & G band ratio relationship of the ID/IG ratio of 1.16 and 0.87, respectively, which is a lesser-intensity disorder ratio with “N” functionalities groups the sp2 (C=C) bonds [46]. Nevertheless, the minor peaks observed the D + D1 disorder in the sp3 electronic structure of the π and π* bands that carbon and oxygen bonding creates the resonant value of the phonon energy [47].
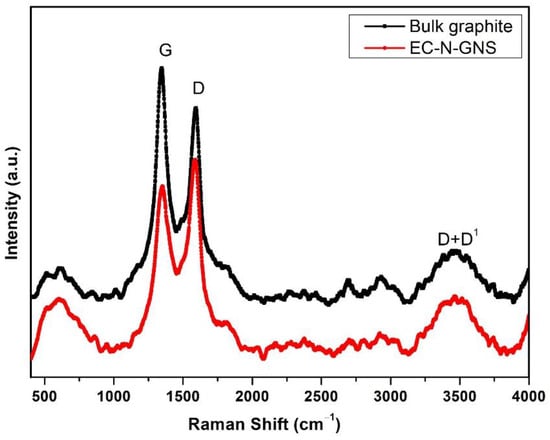
Figure 6.
Raman spectra of the bulk graphite powder and EC-N-GNS, the spectra consist of D, G, 2D and D + D1 bands.
3.6. FT-IR Analysis
The FT-IR spectrum of bulk graphite and EC-N-GNS spectrum were used to analyze by major functional groups Figure 7. The bulk graphite powders reveal that the few functional groups, low transmittance peak at O-H (3449 cm−1) stretching compare to after EC method. The carbon atom bonded to oxygen such as hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups, which mainly consist of C=C (1633 cm−1) bond in aromatic rings. The EC-N-GNS major functional groups appeared at 3035 cm−1, 1730 cm−1, 1639 cm−1 and 1383 cm−1 corresponding to carbon functionalities O-H, C=O, C=C and C-N stretching, respectively. In FT-IR spectra, the sharp major peak at 1383 cm−1 is attributed to the presence of aromatic amine nitro groups to be found at the N atoms bonded into the carbon network [48]. The IR spectra indicate the stronger carbon-nitrogen C-N bond stretching; therefore, nitrogen functional groups are present in the N-graphene. The broad peak appears at 3442 cm−1 corresponding to the presence of O-H stretching of oxygen-containing functional groups confirming that the graphite rod was exfoliated with a carboxyl functional group from the H2SO4 electrolyte. In order to, the EC-N-GNS material found in functional groups in FT-IR spectra strongly believes that ‘N’ atom doping into graphene sheets. It can be taking place and a C–N bond identical to the sp3 bonded carbon aromatic heterocyclic compounds [49]. It’s similar to matching repents the above discussed in EC-N-GNS material for Raman spectra also D-band presents the sp2 carbon networks into N-atom functionalities are the sp3 carbon network. The IR spectra were indicating the successful doping in facile single-step doping of nitrogen (N) functional groups in graphene nanosheets.
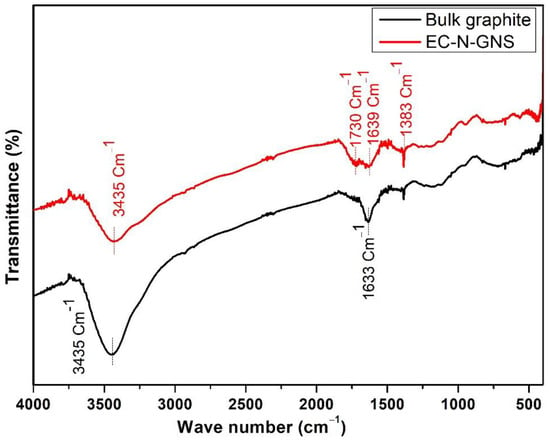
Figure 7.
The FT-IR spectrum of a bulk graphite powder and EC-N-GNS materials.
4. Electrochemical Performance—Sea Water Symmetric Supercapacitor
The electrochemical symmetric supercapacitor device study was tested by cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) with the electrochemical analysis under room conditions. The CV and GCD analysis potential range from −0.8 to +0.5 V. The assembling of a symmetric supercapacitor device demonstrated as mechanically hand-pressed Ni-foam-like mesh into the smooth surface with active materials coated, act as both anode and cathode nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets (N-GNS). This work demonstrated without any modification natural seawater is used as an aqueous electrolyte. The natural seawater was filtered by Whatman filter paper to remove some small sea sand and other dust particles. The concentration of NaCl in the aqueous electrolyte to the pH of seawater is around 7.41–8.34. In the sea-water electrolyte, multiple major ions that occur in the water content in the solution are sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−), including magnesium (Mg2+), sulfate (SO24−), calcium (Ca2+) and potassium (K+) [41,42,43]. These major ions make up for energy storage of SCs with sodium chloride (NaCl) electrolyte solutions presence of about 60–70% [44,45]. Further evaluating the electrochemical properties CV and GCD, under a stable potential window of −0.8 V to +0.5 V with the scan rates at 10–100 mV/s and applied current densities 1–5 A/g, respectively. Moreover, the specific capacitance (Csp) of the EC-N-GNS electrode can be calculated from the galvanostatic charge and discharge via the GCD curves by the Equation (4)
where the applied charge-discharge current is I (A), the discharge time is ∆t (s), the specific mass of the active material (80%) is ‘m’ (milligrams) and the active potential window is ∆V (V). The gravimetric specific capacitance (F/g) was calculated based on active mass for N-GNS//N-GNS and graphite//graphite devices.
The energy density (ED), Wh/kg and power density (PD), W/kg for NGNS and graphite devices can be observed by the GCD measurements. The ED and PD relation equations are as follows Equations (5) and (6):
where, C is the specific capacitance (Csp-F/g), ΔV-potential difference (V) and ∆t (s) is the discharge time for the gravimetric energy and power density.
4.1. Cyclic Voltammetry—CV and EIS Analysis
The cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves of the N-GNS//N-GNS and graphite//graphite symmetric supercapacitor at different scan rates were optimized with active potential window range −0.8 to +0.5 V. As shown in Figure 8a, exhibit a typical good rectangular the CV curve profiles, signifying higher reversibility of the multiple ions transport between electrochemically exfoliated N-GNS active electrode material at various scan rates of 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 and 100 mV/s. As-prepared N-GNS//N-GNS device was demonstrated similarly to a carbon-carbon symmetric two-electrode supercapacitor an excellent electrochemical active window CV curves as shown in Figure 8a. Its demonstrations evenly increased the current rates with increasing scan rates potential (mV/s), the clear mechanisms of during forward and reverse bias scanning voltage 10–100 mV/s. The N-GNS//N-GNS device confirmation to given electric double layer capacitor (EDLC) nature with fast-moving seawater electrolytes ion’s without any disturbance during CV curves.
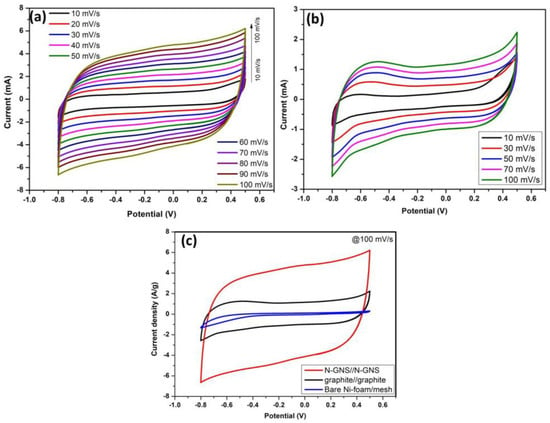
Figure 8.
CV curves at the different scan rates of 10–100 mV/s, (a) After exfoliated EC-N-GNS device, (b) bulk graphite and (c) comparative CV curves with Ni-substrate bare electrodes, graphite N-GNS, devices at 100 mV/s.
On another hand comparing the electrochemical behaviors of bulk graphite shows the EDLC nature with few oxygen and hydrogen evaluations end of the forward and reversible potential (−0.8 V to +0.5 V) and various scan rates 10, 30, 50, 70, 100 mV/s shown in Figure 8b. The graphite//graphite device exposed a reduced amount of electrochemical CV active area compared to N-GNS symmetric device. Figure 8c overall comparison of CV curves reveals that the nickel mesh/foam bare electrodes, the spent Zn-C graphite electrode and N-GNS symmetric devices. Bare Ni substrates/electrode was very less active and partially active graphite consisted of the stacked carbon layers, which is the larger sea-water electrolytic ions that hinder inserting ions otherwise absorptions/insertions from bulk graphite electrodes. After exfoliated nitrogen heteroatom doped graphene nanosheets were more wide CV curves of electrochemical active areas.
The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy characteristics of the as-prepared material Nyquist plot diagram of the NGS and bulk graphite materials from 100 KHz to 10 mHz with potential 10 mV/s amplitude. Figure 9a,b shows comparative materials N-GNS and graphite materials, EIS plots were considerable information from high and low-frequency regions. Furthermore, Figure 9b EIS high-frequency region reveals that the magnified view for key component materials was low semicircle with the real axis (x-axis→Z′) intercept representing solutions resistance (R1-Rs), charge transfer resistance (R2-Rct) and the ionic resistance between the ‘active material electrode @ electrolyte’ interface. As well, the capacitive imaginary part (y-axis→Z′) in the low-frequency region comprises the Warburg (W1–WΩ) impedance electrolytic ions diffusion rates.
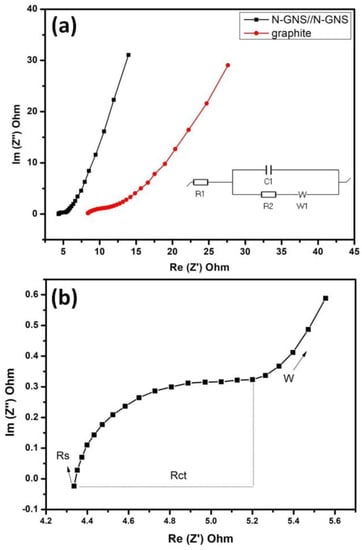
Figure 9.
(a,b) The EIS Nyquist plots of the N-GNS and graphite symmetric devices with inst Randals circuits; (b) shows the magnified high-frequency region of the Nyquist plots.
Figure 9a Nyquist plot defined from Randal’s equivalent circuit (R1 + C1/(R2 + W1)) inset from Figure 9a low-frequency region nearly linear line represents the Warburg angle around the 45–50° sloop, it shows a good ideal electric double layer capacitance (C1–Cdl) with overall From the EIS Nyquist plot obtained the charge transfer resistance (Rct) values 5.3 Ω and 10.7 Ω correspond to the N-GNS and graphite devices. So, the N-GNS device was lesser charge transfer resistive behaviors compare to bulk graphite after the EC method exfoliated the expanded graphitic layer for higher transport ions through active materials-sea water electrolytic multivalent ion’s transfer, which led to superior electrochemical capacitance N-GNS device [50].
4.2. Charge/Discharge Studies for Sea Water-Supercapacitor Devices
Figure 10a,b shows the galvanostatic charge/discharge (GCD) curves of the N-GNS//N-GNS and graphite//graphite symmetric EDLC devices at potential ranges (−0.8 to +0.5 V). The GCD curves (Figure 10a) The N-GNS device charge-discharge studies with different applied current densities at 1–5 A/g. The galvanostatic charge/discharge (GCD) curves show a nearly symmetrical triangular shape, that CGD curves, demonstrating a non-faradaic mechanism in the charge-discharge process. Furthermore, the seawater ions are fast transport efficiency with the opposite directions positive and negative pole attraction Na+, Cl− attractive during the charge-discharge process. Based on the GCD curves, EDLC capacitive properties were calculated from Equation (4). The measurements from the GCD curves aim to specific capacitance values from Figure 10a Csp-67.69, 33.07, 20, 13 and 11.69 F/g corresponds to current densities 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 A/g, respectively. Correspondingly, graphite//graphite symmetric capacitance of calculated from GCD curves was presented in Figure 10b. The bulk graphite device, the specific capacitance Csp-43.07, 26, 13.84, 7.69 and 4 F/g matches current densities 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 A/g.
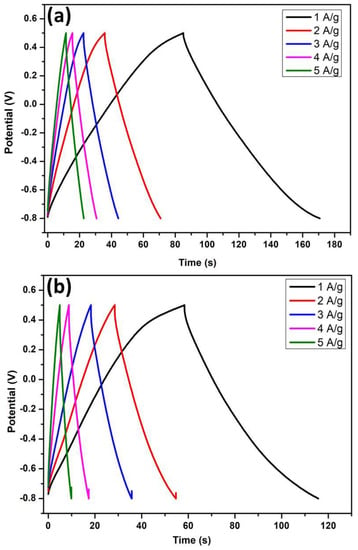
Figure 10.
Galvanostatic charge/discharge curves of the (a) N-GNS//N-GNS devices and (b) bulk graphite electrode with current densities ranges at (1–5 A/g).
The comparative plots of N-GNS and graphite devices were maximum specific capacitance Csp, 67.69 F/g and 44.07 F/g at 1 A/g, respectively. To conclude that both symmetric devices CVs and GCD resultant delivered an electrical double layer capacitive (EDLC) nature using the natural seawater-based electrolyte. The aqueous sea water without redox reactions ions and fast surface adsorbing fast charged ions from the seawater for the superior electrochemical performance of the nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets.
The GCD long cycling stability of both active materials devices carried out the fixed current density of 3 A/g (Figure 11). To confirm both device stability number of charge-discharge cycles and good cyclability performance up to 2000 cycles. After long cyclic stability for discharge capacitance retention (CR-%) belongs to N-GNS and graphite symmetric devices plot of the CR at 98.28% and 72.28% and excellent coulombic efficiency of almost 99%.
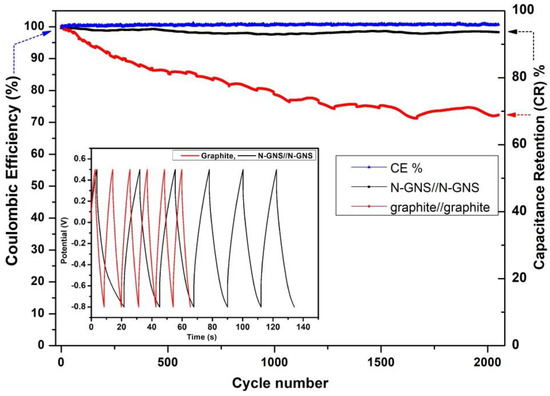
Figure 11.
Cycling stability performance of N-GNS//N-GNS and bulk graphite//graphite electrode devices; inset is the charge/discharge initial cycles.
Figure 10 the comparative plots were discharging capacitance retention (CR-%) and excellent coulombic efficiency (CE-%) demonstrated for 2000 (GCD) cycles that the capacitance values remained constant. The Equations (5) and (6) belong to the maximum energy density (ED) at 15.44 Wh/kg and power density (PD) at 631.63 W/kg for NGNS and graphite devices, respectively. To, increase recycling waste batteries and graphitic carbon materials are reproduced into valuable products of future electrochemical energy storage devices sea water electrolyte-based symmetric supercapacitor devices are interesting to demonstrate.
5. Conclusions
The successfully demonstrated facile single-step efficient way nitrogen-doped few-layer graphene nanosheets from spent Zn-C primary battery recycling of graphite rod by liquid phase electrochemical exfoliation technique. The materials conformations of FE-SEM and FE-TEM, XRD, laser micro RAMAN, FT-IR. The exfoliated N-graphene nanosheet to conformations from FE-TEM with lateral size 50–20 nm. The atomic doping ‘N’ atom confirmed from FE-TEM, EDX analysis of 1.84 at. %. To demonstrate the electrochemical energy storage performance used as bulk graphite powder materials and as-prepared EC-N-GNS (N-GNS) active materials for symmetric supercapacitor applications using natural seawater electrolyte. To successfully fabricate supercapacitor devices N-GNS//N-GNS and graphite//graphite for cyclic voltammetry (CV), EIS analysis and GCD measurements are well performed. The maximum considerable for N-GNS and graphite symmetric devices were specific capacitance value Csp, 67.69 F/g and 43.07 F/g current density at 1 A/g. in addition to the maximum specific energy density—ED at 15.44 Wh/kg (N-GNS) and 9.82 Wh/kg (graphite). To conclude the comparison of stability ~98.28% for 2000 cycles plots for N-GNS//N-GNS device with seawater electrolyte delivered the stable capacitive performance. The electrochemical method was the mass production of graphene as well as electrochemical energy storage supercapacitor device application. The recycling of the spent primary battery part of the graphitic rod has been utilized reusable for N-doped few layers graphene electrode exhibits comparable electrochemical performances and high stability in the seawater electrolyte. This work demonstrated with hazards of waste battery recycling to utilize low coast and natural resources sea-water electrolyte-based future energy storage supercapacitor.
Author Contributions
Investigation, V.T.; Resources, T.V.M.S.; Writing—review & editing, V.T.; Supervision, K.Y.; Project administration, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No: 2022R1A2C1005357).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferella, F.; Michelis, I.D.; Veglio, F. Process for the recycling of alkaline and zinc–carbon spent batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, S.; Tejangkura, W.; Sawangphruk, M. Graphite/Graphene Composites from the Recovered Spent Zn/Carbon Primary Cell for the High-Performance Anode of Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Omega 2020, 25, 15240–15246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimiev, A.M.; Tour, J.M. Mechanism of Graphene Oxide Formation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shi, G. Graphene based new energy materials. Energy Envion. Sci. 2011, 4, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; You, H.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Wan, L.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Tian, R.; Yu, Z.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of few-layered graphene using CVD. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2009, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Stoller, M.D.; Velamakanni, A.; Piner, R.D.; Ruoff, R.S. Microwave assisted exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide for ultracapacitors. Carbon 2010, 48, 2118–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Yanwu, Z.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-Based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.S.; Pei, S.; Ren, W.; Tang, D.; Gao, L.; Liu, B.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.M. Field emission of single-layer graphene films prepared by electrophoretic deposition. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumal, V.; Pandurangan, A.; Jayavel, R.; Krishnamoorthi, S.R.; Ilangovan, R. Synthesis of nitrogen doped coiled double walled carbon nanotubes by chemical vapor deposition method for supercapacitor applications. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang., X.; Yang, S. High performance supercapacitors based on highly conductive nitrogen-doped graphene sheets. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 12554–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrones, H.; Lv, R.; Terrones, M.; Dresselhaus, M.S. The role of defects and doping in 2D graphene sheets and 1D nanoribbons. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 062501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, X. Chemically Functionalized Graphene and Their Applications in Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage. In Advances in Graphene Science; Aliofkhazraei, M., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; Chapter-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Yu, G. Synthesis of N-Doped Graphene by Chemical Vapor Deposition and Its Electrical Properties. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yang, J.J.; Li, S.S.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, T.Y.; Qian, Y.H.; Yu, S.H. Hydrothermal synthesis of macroscopic nitrogen-doped graphene hydrogels for ultrafast supercapacitor. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Pan, X.; Yu, L.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, W.X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, X.; Xue, Q.; et al. Toward N-Doped Graphene via Solvothermal Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.M.; Lee, J.W.; Shin, W.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, H.J.; Kang, J.K. Nitrogen-doped graphene for high-performance, ultracapacitors and the importance of nitrogen-doped sites at basal planes. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, C.P.; Glerup, M. Nitrogen Doping in Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 1345–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Engelhard, M.H.; Li, G.; Shao, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Nitrogen-doped graphene and its electrochemical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7491–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, X.; Mao, S.; Bo, Z.; Kim, H.; Cui, S.; Lu, G.; Feng, X.; Chen, J. Crumbeld Nitrogen doped graphene Nanosheets with ultra high pore volume for high performance supercapacitor. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5610–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.L.M.; Srivastava, A.; Gowda, S.R.; Gullapalli, H.; Dubey, M.; Ajayan, P.M. Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Films for Lithium Battery Application. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6337–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, J.; Jie, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, F.; Yin, Y.; Gu, J.; Zou, Z. Preparation and electrochemical characterisation of nitrogen doped graphene by microwave as supporting materials for fuel cell catalysts. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 60, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Lv, R.; Huang, Z.H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; Kang, F.; Wang, K.; Wu, D. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon thin films and their applications in solar cells. Carbon 2011, 49, 5022–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Song, M.K.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wong, C.P. Facile preparation of nitrogen-doped graphene as a metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Ding, F.; Tao, X.; Chen, W. Manageable N-doped graphene for high performance oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Yoon, Y.; Weber, P.K.; Wang, H.L.; Guo, J.; Dai, H. N-doping of graphene through electrothermal reactions with ammonia. J. Sci. 2009, 324, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Li, W.; Ling, L.; Miyawaki, J.; Mochida, I.; Yoon, S.H. Preparation of nitrogen-doped graphene sheets by a combined chemical and hydrothermal reduction of graphene oxide. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiu, P.W. Controllable graphene N-doping with ammonia plasma. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 133110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, Y.; Nicolosi, V.; Lotya, M.; Blighe, F.M.; Sun, Z.; De, S.; McGovern, I.T.; Holland, B.; Byrne, M.; Gun’Ko, Y.K.; et al. High-yield production of graphene by liquid phase exfoliation of graphite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.X.; Wang, B.; Park, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Yao, J. Highly efficient and large scale synthesis of graphene by electrolytic exfoliation. Carbon 2009, 47, 3242–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Grande, L.; Chundi, V.; White, R.; Bower, C.; Andrew, P.; Ryhanena, T. Graphene from electrochemical exfoliation and its direct applications in enhanced energy storage devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, K.; Li, R.; Puniredd, S.R.; Hernandez, Y.; Hinkel, F.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Mullen, K. Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene as Solution Proces sable, Highly Conductive Electrodes for Organic Electronics. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3598–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Pan, Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.X.; Liu, T. A Review on Nano-/Microstructured Materials Constructed by Electrochemical Technologies for Supercapacitors. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Pan, Q.; Lv, H.; Yang, D.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, M.Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.X. Ammonium-Ion Storage Using Electrodeposited Manganese Oxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5718–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zheng, W. A review for aqueous electrochemical supercapacitors. Front. Energy Res. 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J. Sea Water as an Electrolyte. In Chemistry of Marine Water and Sediments; Gianguzza, A., Pelizzetti, E., Sammartano, S., Eds.; Environmental Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Mueller, F.; Kim, H.; Bresser, D.; Park, J.S.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, G.T.; Passerini, S.; Kim, Y. Rechargeable-hybrid-seawater fuel cell. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Hu, W.; Komarneni, S. Electrochemical behavior of representative electrode materials in artificial seawater for fabricating supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 318, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.X.; Shinde, N.M.; Zhang, T.; Yun, J.M.; Zhou, A.; Mathur, S.; Mane, R.S.; Kim, K.H. Seawater Electrolyte-Mediated High Volumetric MXene-based Electrochemical Symmetric Supercapacitors. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8676–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challagulla, N.V.; Vijayakumar, M.; Rohita, D.S.; Elsa, G.; Sankar, A.B.; Rao, T.N.; Karthik, M. Hierarchical Activated Carbon Fibers as a Sustainable Electrode and Natural Seawater as a Sustainable Electrolyte for High-Performance Supercapacitor. Energy Technol. 2020, 8, 2000417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Chen., Y. Enhancing Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction on Nitrogen-Doped Graphene by Active Sites Implantation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhoua, M.; Tang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, G.; Cui, P.; Qin, L.C. Few-layer graphene obtained by electrochemical exfoliation of graphite cathode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 572, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, S.M.; Ritikos, R.; Whitcher, T.J.; Razib, N.M.; Bien, D.C.S.; Chanlek, N.; Nakajima, H.; Saisopa, T.; Songsiriritthigul, P.; Huang, N.M.; et al. A practical carbon dioxide gas sensor using room-temperature hydrogen plasma reduced graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betriu, X.D.; Garcia, S.A.; Botas, C.; Alvarez, P.; Marcos, J.S.; Prieto, C.; Menéndez, R.; Andres, A.D. Raman spectroscopy for the study of reduction mechanisms and optimization of conductivity in graphene oxide thin films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 6905–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Z.; Han, G.Y.; Yuan, J.P.; Fu, D.Y.; Liu, F.F.; Li, S.D. Using hydroxylamine asa reducer to prepare N-doped graphene hydrogels used in high-performance energy storage. J. Power Sources 2013, 238, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Tyagi, P.K.; Singh, M.K.; Misra, D.S. FTIR studies of nitrogen doped carbon nanotubes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.J.; Tian, C.G.; Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.; Nong, X.; Qiao, Y.; Fu, H. Highly concentrated, stable nitrogen-doped graphene for supercapacitors: Simultaneous doping and reduction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3438–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).