Comparison of the Efficiency of Cross-Flow Plate Heat Exchangers Made of Varied Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
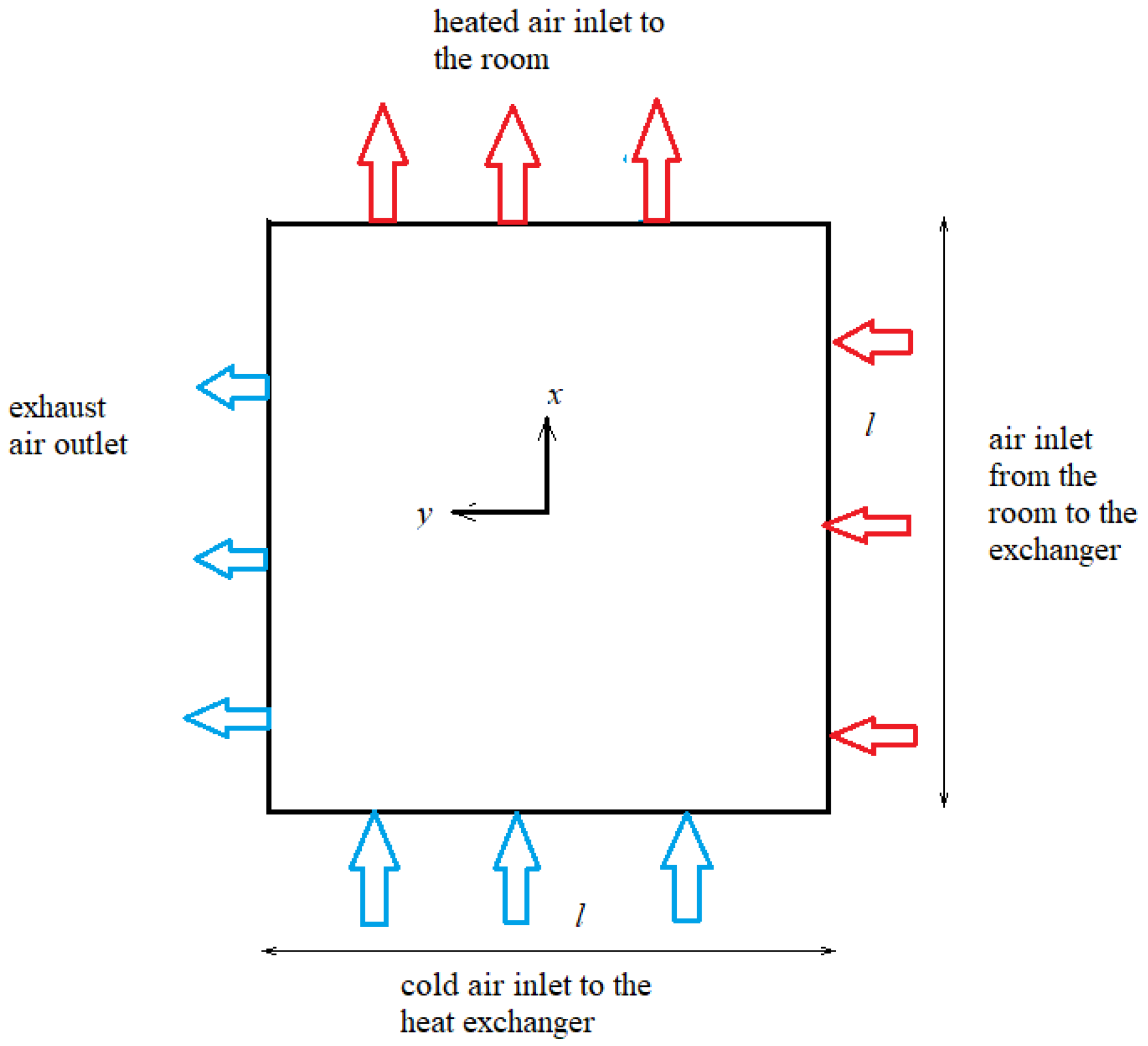
2. Formulation of Equations and Conditions for Both Tested Heat Exchangers
3. Solution Method
3.1. Trefftz Functions
3.2. Objective Functionals
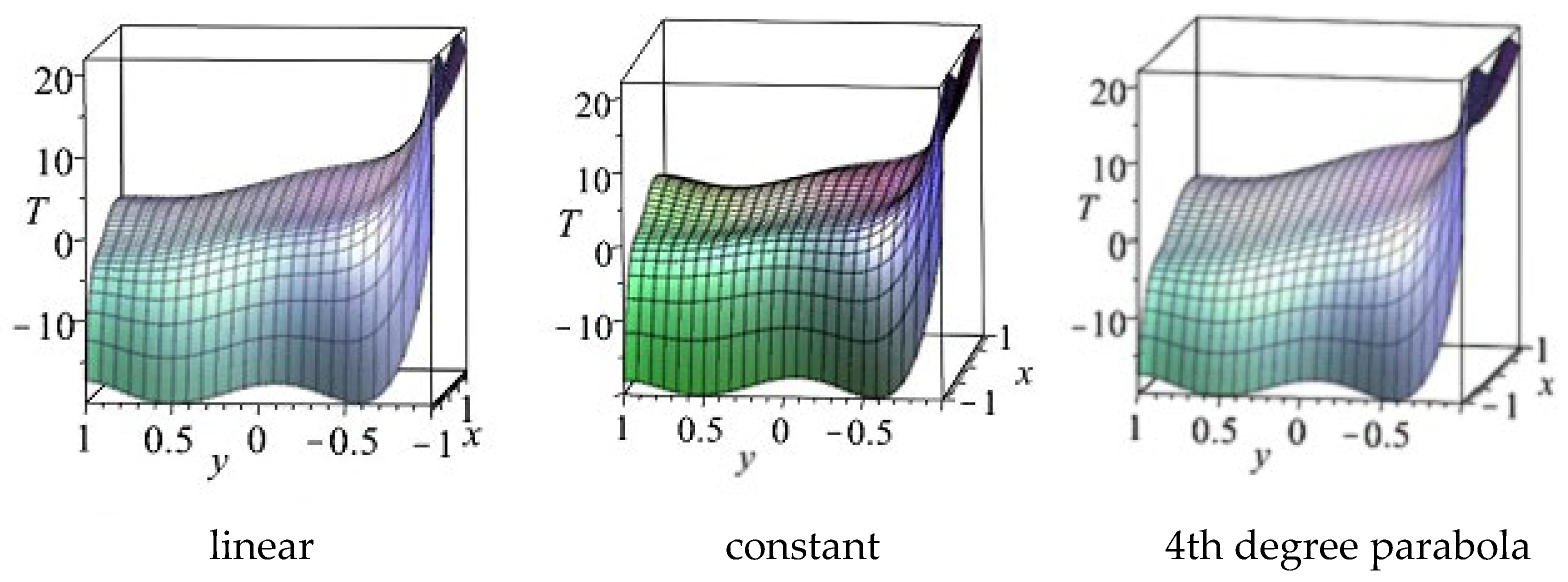
4. Computation Results
- °C (room or inside temperature),
- °C, 1 °C, or 31 °C (outside temperature),
- 1.2 m (plate section length),
- 0.0006 m (plate section half height),
- 0.5 m/s and 4.5 m/s,
- ,
- (257 T-functions).
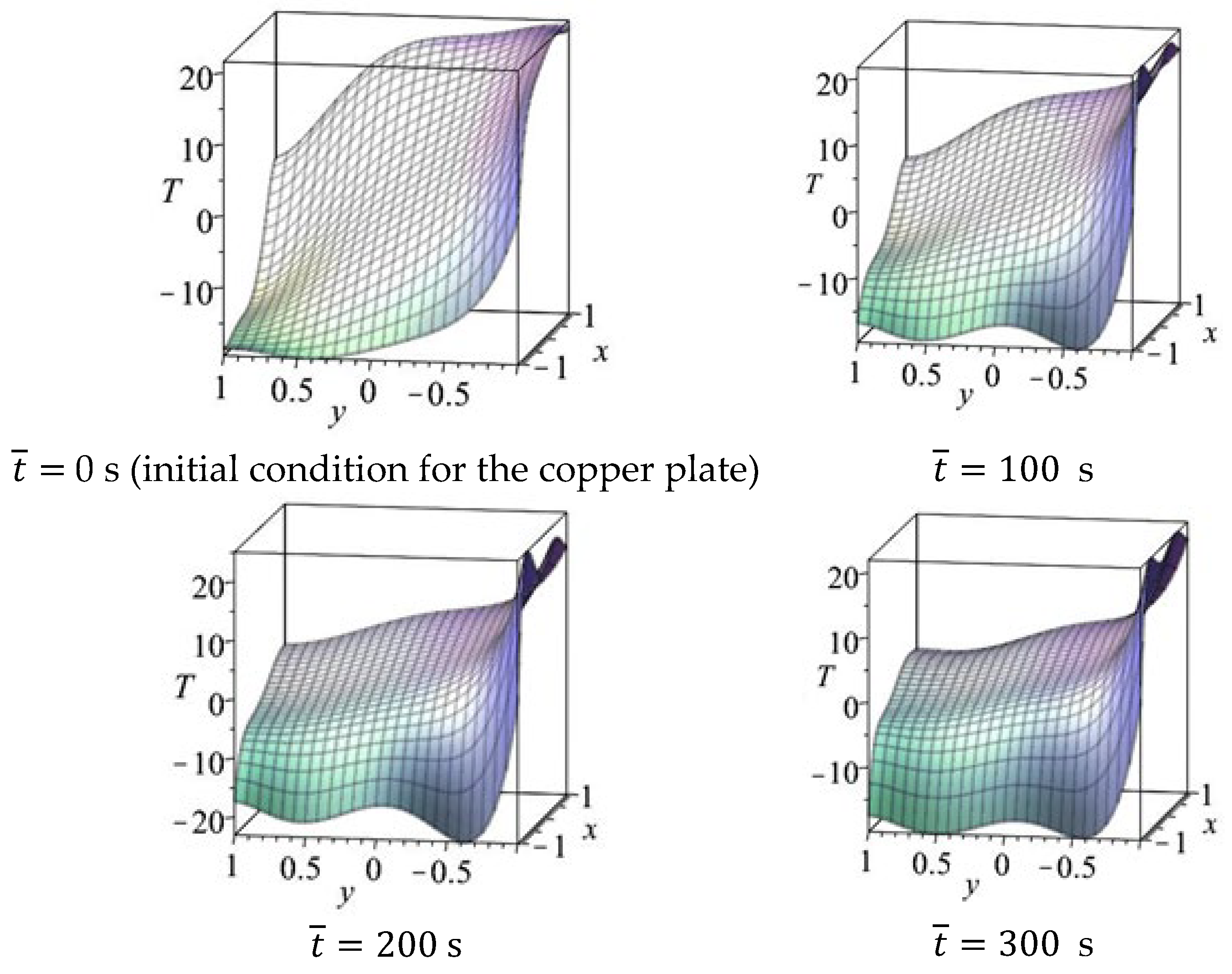
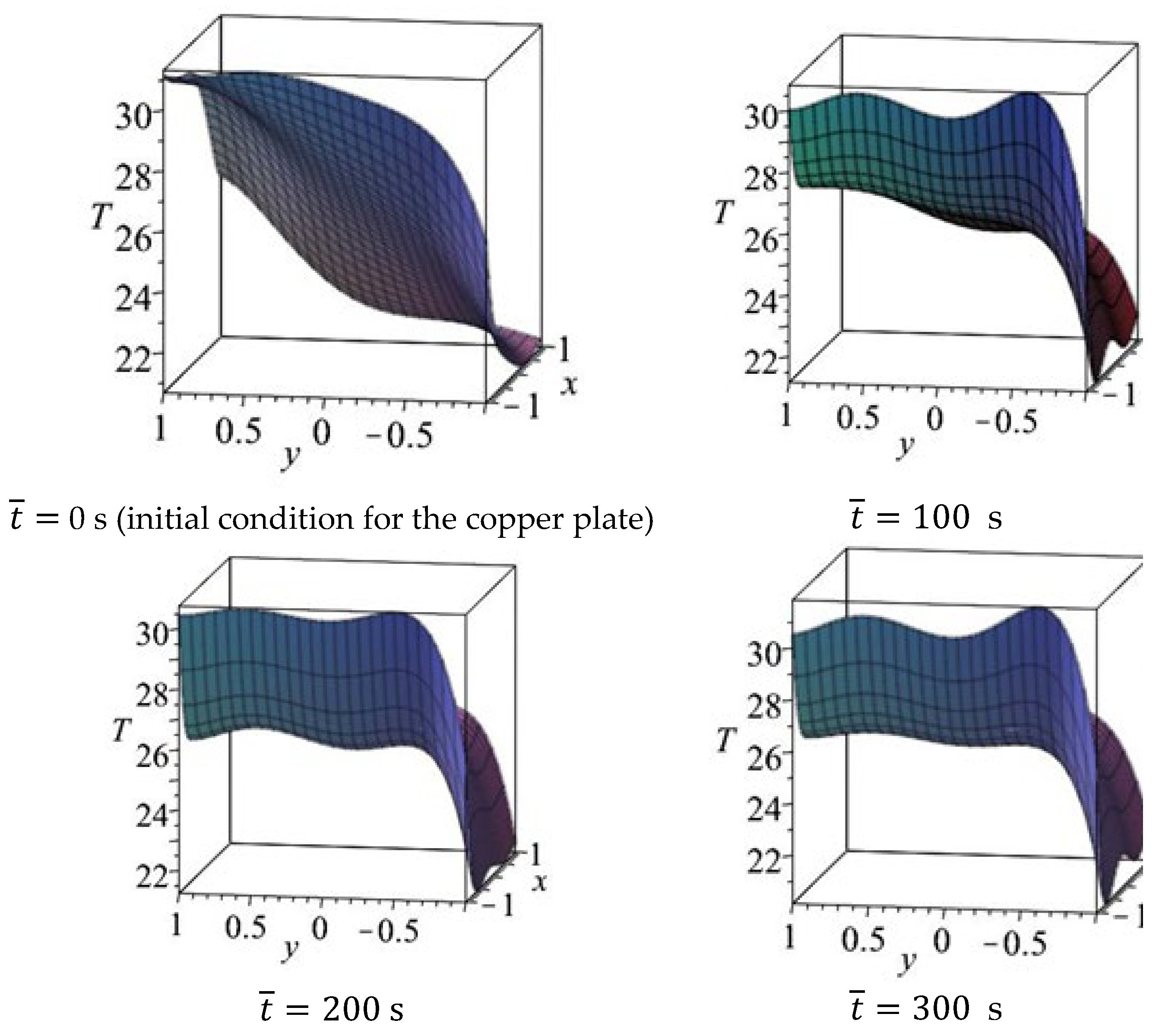
4.1. Results for Copper Plate
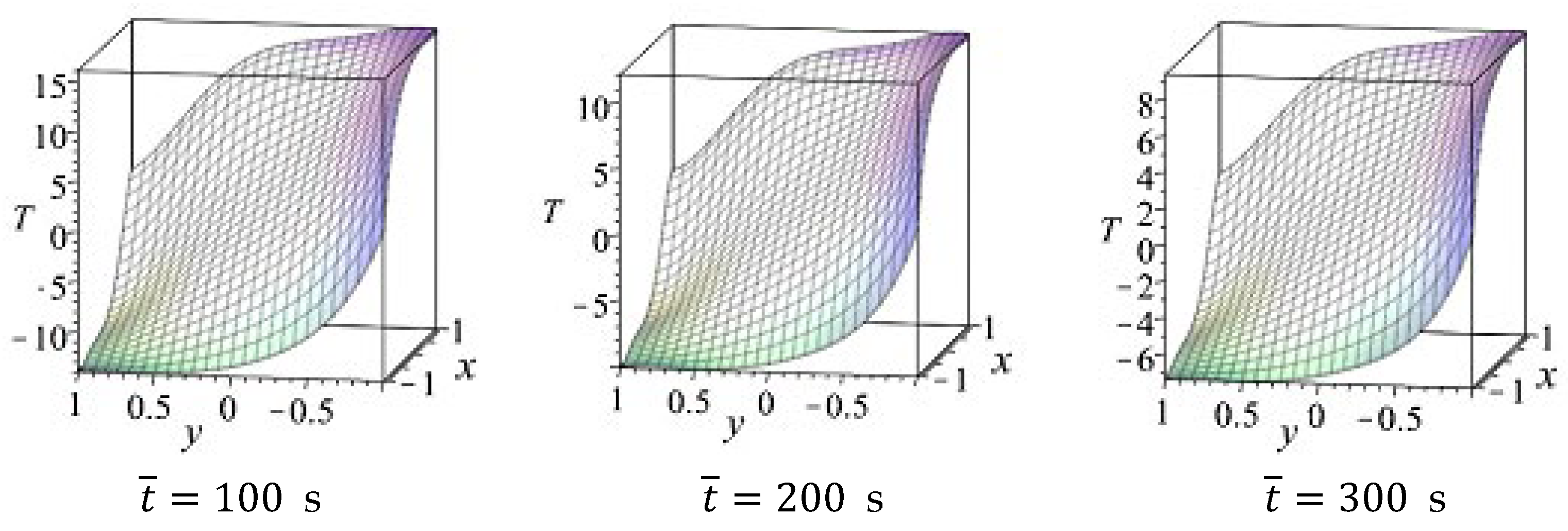
4.2. Results for a Copper, Aluminium, and Steel Plate—Comparison
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Latin Symbols | |
| Bi | Biot number, compare (2) |
| c | for specific heat, [J/(kg K)] |
| Fo | Fourier number (dimensionless time), comp (2) |
| h | air duct height, [m] |
| thermal conductivity coefficient, [W/(mK)] | |
| plate section length, [m] | |
| Reynolds number | |
| temperature, [K], | |
| approximation of temperature | |
| time, [s] | |
| dimensionless time | |
| velocity of air moving between plates, [m/s] | |
| , , | spatial coordinates, [m] |
| dimensionless spatial coordinates | |
| Greek Symbols | |
| heat transfer coefficients, [W/(m2K)] | |
| efficiency of the heat exchanger | |
| ρ | density, [kg/m3] |
| kinematic viscosity, [] | |
| nabla operator, | |
| Laplace operator | |
References
- Shah, R.K.; Sekulic, D.P. Chapter 1, Classification of Heat Exchangers. In Fundamentals of Heat Exchanger Design; John WIley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Sundén, B.; Manglik, R.M. Plate Heat Exchangers, Design, Applications and Performance; WIT Press Southampton: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.rekuperatory.pl/rekuperator#co-to-jest-rekuperator (accessed on 31 June 2021).
- Xu, K. Design and Optimization of Plate Heat Exchanger Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Manchester, Faculty of Science and Engineering, Manchester, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grysa, K.; Maciąg, A.; Ściana, A. Comparison of the Efficiency of Two Types of Heat Exchangers with Parallel Plates Made of Varied Materials. Energies 2021, 14, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://wentylacja.com.pl/news/plytowe-wymienniki-krzyzowe-do-odzysku-ciepla-63582.html (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Gao, T.; Sammakia, B.G.; Geer, J.F.; Ortega, A.; Schmidt, R. Dynamic Analysis of Cross Flow Heat Exchangers in Data Centers Using Transient Effectiveness Method. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 4, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, A.; Simonson, C.J.; Besant, R.W.; Mahmood, G. Numerical model and effectiveness correlations for a run-around heat recovery system with combined counter and cross flow exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 5827–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, A.; Ge, G.-M.; Besant, R.W.; Simonson, C.J. Numerical modeling of fluid flow and coupled heat and mass transfer in a counter-cross-flow parallel-plate liquid-to-air membrane Energy exchanger. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 1258–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.S.; Jain, S. Performance characteristics of cross-flow membrane contactors for liquid desiccant systems. Appl. Energy 2015, 141, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Zhang, Z.-D.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Yang, Y.-W. Investigation of effect on cross-flow heat exchanger with air flow non-uniformity under low Reynolds number. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017708088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.-Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.-W.; Chu, J.-Z. Parametric analysis of a cross-flow membrane-based parallel-plate liquid desiccant dehumidification system: Numerical and experimental data. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, V.; Vít, T. Numerical investigation of counter flow plate heat exchanger. Energy Procedia 2015, 83, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids; Oxford University: Oxford, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, A.F. Basic Heat and Mass Transfer; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, A.F.; Coimbra, C.F.M. Basic Heat and Mass Transfer; Temporal Publishing, LLC: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://thermopedia.com/content/1187/ (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Available online: https://www.engineersedge.com/thermodynamics/overall_heat_transfer-table.htm (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Inhelder, J. Verbrauchs und Schadstoffoptimiertes Ottomotor-Aufladekonzept, ETH No. 11948. Ph.D. Thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zürich, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, L.; Nielsen, L. Modeling and Control of Engines and Drivelines; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 530. [Google Scholar]
- Sforza, P. Commercial Airplane Design Principles; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-419953-8. [Google Scholar]
- White, F. Fluid Mechanics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-07-228192-8. [Google Scholar]
- Incropera, F.P.; DeWitt, D.P. Fundamentals of Heat Transfer; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981; ISBN 978-0-471-42711-7. [Google Scholar]
- Trefftz, E. Ein Gegenstueck zum Ritz’schen Verfahren. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress of Applied Mechanics, Zurich, Switzerland, 12–17 September 1926; pp. 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Grysa, K.; Maciejewska, B. Trefftz functions for non-stationary problems. J. Theoret. Appl. Mech. 2013, 50, 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Frąckowiak, A.; Wróblewska, A.; Ciałkowski, M. Trefftz numerical functions for solving inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 177, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, A.; Ciałkowski, M.; Wróblewska, A. Iterative algorithms for solving inverse problems of heat conduction in multiply connected domains. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciałkowski, M.J.; Frackowiak, A. Thermal and related functions used in solving certain problems of mechanics, Part, I. Solving some differential equations with the use of inverse operator. In Modern Problems of Technics; University of Zielona Góra Publishers: Zielona Góra, Poland, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 7–70. [Google Scholar]
- Maciąg, A.; Grysa, K. Trefftz Method of Solving a 1D Coupled Thermoelasticity Problem for One- and Two-Layered Media. Energies 2021, 14, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudlik, W. Exchange and Heat Exchangers; Gdańsk University of Technology: Gdańsk, Poland, 2012; p. 320. Available online: https://pbc.gda.pl/Content/4404/wymiana-i-wymienniki-final.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2022). (In Polish)
- Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/heat-recovery-efficiency-d_201.html (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Available online: https://agmetalminer.com/metal-prices/ (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Available online: https://www.moneymetals.com/copper-prices (accessed on 8 July 2022).
| Material | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | −19 | −10.88 | −5.39 | −5.21 | −5.93 | −5.99 | −5.93 |
| 1 | 5.06 | 7.80 | 7.89 | 7.54 | 7.50 | 7.53 | |
| 31 | 28.97 | 27.60 | 27.55 | 27.73 | 27.75 | 27.73 |
| ρ [kg/m3] | c [J/(kg K)] | k [W/(mK)] | a 106 [m2/s] | α (W/(m2K)) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 8933 | 385 | 386 | 112.2 | |
| Aluminium | 2702 | 903 | 204 | 83.6 | |
| Stainless steel | 7970 | 561 | 19.5 | 4.36 |
| l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | |
| °C | 1.0 | 1.0 | −17.5 | −17.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 19.5 | 19.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | |
| °C | 11.0 | 11.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 20.3 | 20.3 | 12.8 | 12.8 |
| l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | |
| °C | 26.0 | 26.0 | 30.6 | 30.6 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 21.4 | 21.4 | 25.1 | 25.1 |
| l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | |
| °C | 26.0 | 26.0 | 30.4 | 30.4 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 21.6 | 21.6 | 26.0 | 26.0 |
| l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | |
| °C | 11.0 | 11.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 11.1 | 11.1 |
| l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | −l/2 | 0 | 0 | |
| −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | −h/2 | h/2 | |
| °C | 1.0 | 1.0 | −16.8 | −16.8 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 18.8 | 18.8 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Copper | Aluminium | Steel | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l/2 | l/2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| −l/2 | l/2 | −17.50 | −16.80 | −17.10 | −13.00 | −7.40 | −0.80 |
| −l/2 | −l/2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| l/2 | −l/2 | 19.50 | 18.80 | 19.10 | 15.00 | 9.39 | 2.80 |
| l/2 | 0 | 4.50 | 1.20 | 3.30 | 0.90 | 8.00 | 2.40 |
| Copper | Aluminium | Steel | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l/2 | l/2 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 |
| −l/2 | l/2 | 1.70 | 2.10 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 6.81 | 10.10 |
| −l/2 | −l/2 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 |
| l/2 | −l/2 | 20.30 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 18.00 | 15.19 | 11.90 |
| l/2 | 0 | 12.80 | 11.10 | 12.10 | 11.00 | 14.50 | 11.70 |
| Copper | Aluminium | Steel | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| l/2 | l/2 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 |
| −l/2 | l/2 | 30.60 | 30.40 | 30.50 | 30.00 | 28.10 | 26.40 |
| −l/2 | −l/2 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 |
| l/2 | −l/2 | 21.40 | 21.60 | 21.50 | 22.50 | 23.90 | 25.50 |
| l/2 | 0 | 25.10 | 26.00 | 25.40 | 26.00 | 24.30 | 25.60 |
| T(lin) | T(const) | T(parab) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| l/2 | l/2 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| −l/2 | l/2 | −17.50 | −18.30 | −17.50 |
| −l/2 | −l/2 | 0.53 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| l/2 | −l/2 | 20.10 | 20.30 | 19.50 |
| l/2 | 0 | 3.80 | 1.83 | 4.50 |
| T [°C] | −19 | −19 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 31 | −19 | −19 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 31 | |
| [m/s] | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 |
| −l/2 | l/2 | −15.8 | −8.9 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 30.2 | 28.5 | −17.1 | −13.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 30.5 | 30.0 |
| −l/2 | −l/2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 |
| l/2 | −l/2 | 17.8 | 10.9 | 19.4 | 16.0 | 21.8 | 23.5 | 19.1 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 18.0 | 21.5 | 22.5 |
| l/2 | 0 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 11.2 | 11.2 | 25.9 | 25.9 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 12.1 | 11.0 | 25.4 | 26.0 |
| T [°C] | −19 | −19 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 31 | −19 | −19 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 31 | |
| [m/s] | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | |
| l/2 | l/2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 |
| −l/2 | l/2 | −3.10 | 0.10 | 8.90 | 10.60 | 27.00 | 26.20 | −7.40 | −0.80 | 6.81 | 10.10 | 28.10 | 26.40 |
| −l/2 | −l/2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 11.00 | 11.00 | 26.00 | 26.00 |
| l/2 | −l/2 | 5.10 | 1.90 | 13.10 | 11.40 | 25.00 | 25.80 | 9.39 | 2.80 | 15.19 | 11.90 | 23.90 | 25.50 |
| l/2 | 0 | 4.10 | 1.80 | 12.60 | 11.40 | 25.00 | 25.80 | 8.00 | 2.40 | 14.50 | 11.70 | 24.30 | 25.60 |
| T [°C] | −19 | −19 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 31 | −19 | −19 | 1 | 1 | 31 | 31 |
| [m/s] | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| Plate made of | ||||||||||||
| Cu | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 13.01 | 11.29 | 17.01 | 16.15 | 23.00 | 23.43 |
| Al | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 12.30 | 10.93 | 16.65 | 15.96 | 23.18 | 23.52 |
| Steel | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 13.93 | 11.61 | 17.46 | 16.31 | 22.77 | 23.35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grysa, K.; Maciąg, A.; Ściana, A. Comparison of the Efficiency of Cross-Flow Plate Heat Exchangers Made of Varied Materials. Energies 2022, 15, 8425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228425
Grysa K, Maciąg A, Ściana A. Comparison of the Efficiency of Cross-Flow Plate Heat Exchangers Made of Varied Materials. Energies. 2022; 15(22):8425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228425
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrysa, Krzysztof, Artur Maciąg, and Artur Ściana. 2022. "Comparison of the Efficiency of Cross-Flow Plate Heat Exchangers Made of Varied Materials" Energies 15, no. 22: 8425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228425
APA StyleGrysa, K., Maciąg, A., & Ściana, A. (2022). Comparison of the Efficiency of Cross-Flow Plate Heat Exchangers Made of Varied Materials. Energies, 15(22), 8425. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228425








